Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Simple past vs past continuous
Uploaded by
kelvinOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Simple past vs past continuous
Uploaded by
kelvinCopyright:
Available Formats
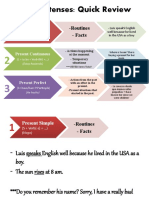
Simple past VS Past continuous
Past simple
The past simple shows us that an action was in the past, not in the present. Regular past simple
verbs have -ed at the end (e.g. called, played, arrived). Irregular verbs have a different form,
usually with a different vowel sound (e.g. wake → woke, break → broke, feel → felt).
kalimat positif (+) The teacher came
S + Verb-2 (past tense)
S + be (was/were) I was a stamp collector
kalimat negatif (-) The teacher didn’t come
S + did + not + bare infinitive
S + be (was/were) + not I wasn’t a stamp collector
kalimat interogatif (?) Did the teacher come
did + S + bare infinitive
be (was/were) + S Was I a stamp collector
Past continuous
The past continuous shows us that the action was already in progress at a certain time in the
past. We can use the following time expressions with the past perfect simple: already, just,
recently, before, after, earlier, and by the time to show the order in which the two past events
happened.
(+) S+ be (was/were) + verb (-ing)
She was waiting for you yesterday.
They were discussing my birthday party.
(-) S +be (was/were) + not + verb (-ing)
She was not waiting for you yesterday
They were not discussing my birthday party
(?) Be (was/were) + S + verb (-ing)?
Was she waiting for you yesterday?
Were they discussing my birthday party?
The difference
Past Simple Past continuous
Short action Long action
Finished action Unfinished action
Ex:
Yesterday I _____ (Drive) home and I _____ (kill) a cat.
So we say, yesterday I was driving home. It’s not finnish, it’s a longer action than the other
action. So how long does it take to kill a cat? It doesn’t take long. It’s a short action and it’s
finnish. The moment was driving the cat is killed.
You might also like
- Simple Present Countinuous TenseDocument15 pagesSimple Present Countinuous TenseNazarudinNo ratings yet
- How to Use the Word “Come” In English: A Comprehensive Guide to the Word “Come”From EverandHow to Use the Word “Come” In English: A Comprehensive Guide to the Word “Come”No ratings yet
- English Task 2 M Ilham Febrian PDFDocument4 pagesEnglish Task 2 M Ilham Febrian PDFaisyah hartonoNo ratings yet
- Past TenseDocument9 pagesPast Tensesecret147No ratings yet
- Learn about simple past and past continuous tensesDocument7 pagesLearn about simple past and past continuous tensesAjeng kenvanysahNo ratings yet
- K 2Document20 pagesK 2Nadea OctaryanaNo ratings yet
- What Is The Past Simple Tense?: Last Saturday) or Discussing A Specific Point in Time (E.g. I Studied Today)Document2 pagesWhat Is The Past Simple Tense?: Last Saturday) or Discussing A Specific Point in Time (E.g. I Studied Today)yepurilaNo ratings yet
- Simple Past Tense: I Often Watched Documenter MoviesDocument3 pagesSimple Past Tense: I Often Watched Documenter MoviesPanjul IdNo ratings yet
- Tugas B InggrisDocument4 pagesTugas B InggrisWulan SariNo ratings yet
- Middle Test of English Tenses SummaryDocument4 pagesMiddle Test of English Tenses SummaryIphone XrNo ratings yet
- Tenses 1Document23 pagesTenses 1Puspita IsnainiNo ratings yet
- Past Tense Simple: S V S V Did S VDocument2 pagesPast Tense Simple: S V S V Did S VAndrei MarinNo ratings yet
- Was (I, He, She, It) Were (You, We, They) : Past Simple Verb (ED) Past TimeDocument1 pageWas (I, He, She, It) Were (You, We, They) : Past Simple Verb (ED) Past TimeangelNo ratings yet
- Learn English Tenses in 40 StepsDocument10 pagesLearn English Tenses in 40 StepsKamelitagaluh PratiwiNo ratings yet
- Power Point Bilingual Kelompok 5Document10 pagesPower Point Bilingual Kelompok 5Khoirani febryNo ratings yet
- (Don't You?) : Present Simple TenseDocument46 pages(Don't You?) : Present Simple TensedorinaNo ratings yet
- All Present-Past TensesDocument15 pagesAll Present-Past TensesLaura RamosNo ratings yet
- Tenses+Part+IIDocument21 pagesTenses+Part+IIKrisna Budi JuliantoroNo ratings yet
- Tugas Mandiri: Menentukan Tenses Dalam Sebuah Artikel Mata Kuliah: ToeflDocument5 pagesTugas Mandiri: Menentukan Tenses Dalam Sebuah Artikel Mata Kuliah: ToeflFauji BaexNo ratings yet
- PAST SENTENCESDocument15 pagesPAST SENTENCESRatna AuliaNo ratings yet
- Adjective clauses and past tenses explainedDocument16 pagesAdjective clauses and past tenses explainedJohanesKokoNo ratings yet
- Verb Tense: Tense / Form Use / Example NoteDocument4 pagesVerb Tense: Tense / Form Use / Example NoteVi NguyenNo ratings yet
- PresentDocument3 pagesPresentTrandafir VladutNo ratings yet
- Present Tenses Quick ReferenceDocument15 pagesPresent Tenses Quick ReferenceLaura RamosNo ratings yet
- B.inggris Simple Past TenseDocument12 pagesB.inggris Simple Past TenseSririzkii WahyuniNo ratings yet
- Group The Power Puff AND Two Prince: Benny J Cindy O Shilvi T Zulfan (PIC)Document15 pagesGroup The Power Puff AND Two Prince: Benny J Cindy O Shilvi T Zulfan (PIC)Cindy OktavianaNo ratings yet
- Pengertian, Rumus Dan Contoh Simple Past TenseDocument13 pagesPengertian, Rumus Dan Contoh Simple Past TenseFargani MutiyasNo ratings yet
- Understanding Passive Voice FormsDocument8 pagesUnderstanding Passive Voice FormsRahma DindaaNo ratings yet
- Modul Kls X Sem2 2019Document17 pagesModul Kls X Sem2 2019Yuni TrisniadartiNo ratings yet
- Simple Past: By: Rohmat Hidayat, S.S., M.PD KH. A. Wahab Hasbullah UniversityDocument9 pagesSimple Past: By: Rohmat Hidayat, S.S., M.PD KH. A. Wahab Hasbullah UniversityADH ChannelNo ratings yet
- Tenses in EnglishDocument4 pagesTenses in EnglishJhonytowengtoweng Indigo DudulNo ratings yet
- Makalah TensesDocument18 pagesMakalah TensesIka NirmalasariNo ratings yet
- Past TenseDocument4 pagesPast TensedepaNo ratings yet
- Past Tenses GuideDocument14 pagesPast Tenses GuideSartiNo ratings yet
- Makalah Kel THE CONCEPT OF SIMPLE TENSESDocument4 pagesMakalah Kel THE CONCEPT OF SIMPLE TENSESJosua SiahaanNo ratings yet
- Past Tense X-D (Fix)Document28 pagesPast Tense X-D (Fix)Michelle ReginaNo ratings yet
- Makalah Simple Past TenseDocument10 pagesMakalah Simple Past TenseKadir JavaNo ratings yet
- English verb tenses cheat sheetDocument1 pageEnglish verb tenses cheat sheetHijjul HakimNo ratings yet
- Nesti Puji Astuti - 5117011 - Perbaikan NilaiDocument24 pagesNesti Puji Astuti - 5117011 - Perbaikan NilaiNesti PujiaNo ratings yet
- Tema 2 B1 Past Simple - Continuous PDFDocument5 pagesTema 2 B1 Past Simple - Continuous PDFJuan AntonioNo ratings yet
- Tenses: Simple Present Tense, Simple Past Tense Simple Future TenseDocument39 pagesTenses: Simple Present Tense, Simple Past Tense Simple Future TensedeanisaNo ratings yet
- Simple Past Tense GuideDocument9 pagesSimple Past Tense GuideMarcell PardedeNo ratings yet
- Group 2 Written ReportDocument12 pagesGroup 2 Written ReportPRECIOUS KAYE MARIE BANTIGUENo ratings yet
- B. Inggris Zahira Meica SyahputriDocument6 pagesB. Inggris Zahira Meica Syahputriaisyahisut60No ratings yet
- 16 Tenses in English ALIAMSAH RITONGA DoDocument9 pages16 Tenses in English ALIAMSAH RITONGA Doindah pratiwiNo ratings yet
- Simple Past TenseDocument2 pagesSimple Past Tenseanis fuadhiNo ratings yet
- Simple Past & Past ContinuousDocument15 pagesSimple Past & Past ContinuousDevie Y. FiliyantiNo ratings yet
- Simple Past Tense: Presented by Indah Dwi Permanawati 1305020082Document7 pagesSimple Past Tense: Presented by Indah Dwi Permanawati 1305020082Indah Dwi PNo ratings yet
- Catatan TensesDocument3 pagesCatatan TensesdennisNo ratings yet
- Conjugar en AnglèsDocument5 pagesConjugar en AnglèsMarina Canaleta TarrésNo ratings yet
- Simple Past Tense - KP.3Document22 pagesSimple Past Tense - KP.3Saeful BahriNo ratings yet
- English TensesDocument5 pagesEnglish TensesislamiclearntvNo ratings yet
- SIMPLE PRESENT-1 SusiDocument3 pagesSIMPLE PRESENT-1 SusiUulAmrelNo ratings yet
- Past Simple and Continuous TensesDocument11 pagesPast Simple and Continuous TensesFernando HazzNo ratings yet
- Simple Past Tense & ContinuousDocument17 pagesSimple Past Tense & ContinuousshellagherinaNo ratings yet
- English Course Grade VII Writing Past ExperienceDocument1 pageEnglish Course Grade VII Writing Past ExperienceEty Dwi Jayanti100% (1)
- Time and Tense (Past Tense)Document25 pagesTime and Tense (Past Tense)Ruli OktariveriusNo ratings yet
- Simple Past TenseDocument10 pagesSimple Past TenseAristia AstutiNo ratings yet
- Outer Galaxies Astronomy Education Center by SlidesgoDocument10 pagesOuter Galaxies Astronomy Education Center by SlidesgoAmyyy FsNo ratings yet
- Neat Illustrated Gaming InfographicDocument1 pageNeat Illustrated Gaming InfographickelvinNo ratings yet
- Eula 2Document3 pagesEula 2norafiraNo ratings yet
- Logo Here: (Company Name) (Street Address, City, ST ZIP Code) (Phone) (Email) (Website)Document1 pageLogo Here: (Company Name) (Street Address, City, ST ZIP Code) (Phone) (Email) (Website)kelvinNo ratings yet
- Logo Here: (Company Name) (Street Address, City, ST ZIP Code) (Phone) (Email) (Website)Document2 pagesLogo Here: (Company Name) (Street Address, City, ST ZIP Code) (Phone) (Email) (Website)kelvinNo ratings yet
- Template WordDocument4 pagesTemplate WordMackara KurNo ratings yet
- Brosur WkakakahhsgggaaDocument4 pagesBrosur WkakakahhsgggaaDiko AprilioNo ratings yet
- Brosur WkakakahhsgggaaDocument4 pagesBrosur WkakakahhsgggaaDiko AprilioNo ratings yet
- Report Title 2018: November 4Document2 pagesReport Title 2018: November 4Kitty ThanaNo ratings yet
- DASDDocument1 pageDASDeka putraNo ratings yet
- (First Name) (Surname) : ExperienceDocument1 page(First Name) (Surname) : ExperienceSci CalNo ratings yet
- DASDDocument1 pageDASDeka putraNo ratings yet
- Brosur WkakakahhsgggaaDocument4 pagesBrosur WkakakahhsgggaaDiko AprilioNo ratings yet
- AffandiDocument2 pagesAffandikelvinNo ratings yet
- Brosur ContohDocument2 pagesBrosur ContohawangNo ratings yet
- November 2019 monthly calendarDocument1 pageNovember 2019 monthly calendarkelvinNo ratings yet
- Resume for Marketing CoordinatorDocument1 pageResume for Marketing CoordinatorArbi Yuda PamungkasNo ratings yet