Professional Documents
Culture Documents
What Does An Atom Look Like (Draw The Atomic Structure and Label) ?
Uploaded by
Sheda RumOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
What Does An Atom Look Like (Draw The Atomic Structure and Label) ?
Uploaded by
Sheda RumCopyright:
Available Formats
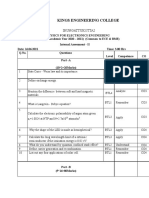
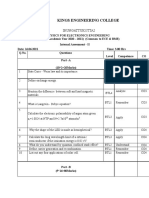
SEP 2018 / DME214
QUESTION 1
a) What are atoms? (3 marks)
[PO1, CO2]
b) What does an atom look like (draw the atomic structure and label)? (7 marks)
[PO1, CO1]
c) Determine the ground state electron configurations (Aufbau Principle) (10 marks)
and the orbital notations for the following elements? [PO1, CO1]
i. He
ii. Al
iii. S
iv. Li
v. P
QUESTION 2
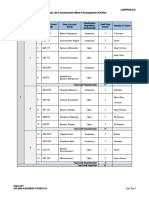
a) Complete Table 2.1 of crystalline structure below (12 marks)
[PO1, CO2]
Body Centered Face Centered
Simple Cubic
Types Cubic Cubic
(SC)
(BCC) (FCC)
The Crystal Structure (sketch)
Atomic Packing Factor
(Show formula and calculation)
No. of atom/unit cell
Table 2.1
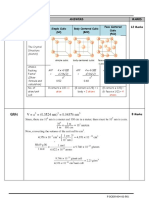
b) Calculate the density for nickel (simple cubic structure). Note that the (8 marks)
unit cell edge length ‘a’ for nickel is 0.3524 nm. [PO1, CO2]
QUESTION 3
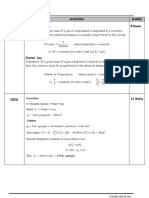
Figure 3.1 illustrate a system with two-components (Cu, Ni) and two phases
(liquid, solid solution).
©KOLEJ WIT 2 of 4 CONFIDENTIAL
SEP 2018 / DME214
Figure 3.1
a) At point B (35 wt% Ni, 1250ºC) on figure 3.1, what are the mass fraction (5 Marks)
[PO1, CO1]
liquid and the mass fraction solid?
a) Calculate the amount of each phase present in 1 kg of a 50 wt.% Ni- 50 wt.% (15 Marks)
[PO1, CO3]
Cu alloy at:
i. 1400°C
ii. 1300°C
iii. 1200°C.
QUESTION 4
a) Explain corrosion and what are the measures that may be taken to (8 marks)
prevent, or at least to reduce the corrosion [PO1, CO3]
b) There are eight common types of corrosion. List four and give (12 marks)
explanation for each type of corrosion listed. [PO1, CO3]
©KOLEJ WIT 3 of 4 CONFIDENTIAL
SEP 2018 / DME214
QUESTION 5
a) Determine three categories of electrical materials (6 marks)
[PO1, CO5]
b) Compute the electrical conductivity of a 5.1 mm (0.2 in.) diameter (14 marks)
cylindrical silicon specimen 51 mm (2 in.) long in which a current of [PO1, CO5]
0.1A passes in axial direction. A voltage of 12.5V is measured across two
probes that are separated by 38 mm (1.5 in.)
QUESTION 6
a) What is the main difference between heat-treatable and non-heat-treatable (4 marks)
alloys? [PO1, CO3]
b) Give the distinctive features, limitations, and applications of the following (16 marks)
alloy groups: titanium alloys, refractory metals, superalloys, and noble [PO1, CO3]
metals.
END OF QUESTION PAPER
©KOLEJ WIT 4 of 4 CONFIDENTIAL
You might also like
- Bahasa Inggeris Kertas 1Document13 pagesBahasa Inggeris Kertas 1Sheda Rum100% (5)
- Chem Prev QuesDocument43 pagesChem Prev QuesMelwin JosephNo ratings yet
- Structure of Atom Imp Questions PaperDocument1 pageStructure of Atom Imp Questions PaperSonali SinghNo ratings yet
- Inorg RevDocument4 pagesInorg RevMarvin JeaNo ratings yet
- Cat Questions For 3RD Term - Chemistry - Senior SchoolDocument1 pageCat Questions For 3RD Term - Chemistry - Senior SchoolEliezer EzeugahNo ratings yet
- QB Me With BT 1Document4 pagesQB Me With BT 1FUNTUBENo ratings yet
- Xii Chemistry Previous Questions by Anil Kumar K.L (Hsslive - In)Document3 pagesXii Chemistry Previous Questions by Anil Kumar K.L (Hsslive - In)snehasis banerjeeNo ratings yet
- IAT - II - 16.06.2021 - ECE & BME-newDocument3 pagesIAT - II - 16.06.2021 - ECE & BME-newRoyalNo ratings yet
- IAT - II - 16.06.2021 - ECE & BME-newDocument3 pagesIAT - II - 16.06.2021 - ECE & BME-newRoyalNo ratings yet
- The Solid State-Anilkumar-hssliveDocument3 pagesThe Solid State-Anilkumar-hssliveMathew YoyakkyNo ratings yet
- Apc - Pi 16Document2 pagesApc - Pi 16Pralay MaitiNo ratings yet
- 9-Model Question Paper I-Sem-2023Document2 pages9-Model Question Paper I-Sem-2023Sathish Kumar KurapatiNo ratings yet
- Apc - Pi 18Document2 pagesApc - Pi 18Pralay MaitiNo ratings yet
- CCB 231 Supp ExamDocument6 pagesCCB 231 Supp ExamTumisang100% (1)
- PG, 1 Sem, Apc, CC-1, Question Paper - Jan 23Document3 pagesPG, 1 Sem, Apc, CC-1, Question Paper - Jan 23Pralay MaitiNo ratings yet
- Chem 1216Document6 pagesChem 1216Mathieu CarringtonNo ratings yet
- SL Periodicity Revision: (33 Marks)Document6 pagesSL Periodicity Revision: (33 Marks)Marcelo Andrade SantiagoNo ratings yet
- Bindura University of Science Education Chemistry DepartmentDocument3 pagesBindura University of Science Education Chemistry DepartmentdestinyyNo ratings yet
- Part 2 Microscopic World (I) LQDocument14 pagesPart 2 Microscopic World (I) LQWing LamNo ratings yet
- Che s4 Exam Term 1 - QP - 074533Document4 pagesChe s4 Exam Term 1 - QP - 074533nshimiyimanasamuel1983No ratings yet
- WWW - Manaresults.Co - In: Engineering ChemistryDocument5 pagesWWW - Manaresults.Co - In: Engineering ChemistryaravindNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 2021 PAPERDocument8 pagesChemistry 2021 PAPERcabek22797No ratings yet
- MayJune - 2019Document2 pagesMayJune - 2019Akshay ChowdaryNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 Coordination SolutionDocument12 pagesUnit 5 Coordination Solutionsuryansh.yt9641No ratings yet
- 2 In-Sem Exam - BEE034A - SET-1 DR Avireni SrinivasuluDocument2 pages2 In-Sem Exam - BEE034A - SET-1 DR Avireni SrinivasuluHimanshuNo ratings yet
- 2 In-Sem Exam - BEE034A - SET-1 DR Avireni Srinivasulu PDFDocument2 pages2 In-Sem Exam - BEE034A - SET-1 DR Avireni Srinivasulu PDFHimanshuNo ratings yet
- BLE1Document2 pagesBLE1Neethu BhaskaranNo ratings yet
- Ramaiah: MSEE02Document2 pagesRamaiah: MSEE02hari krishnaNo ratings yet
- OPR752 Processing of PolymerDocument2 pagesOPR752 Processing of PolymerVivekananda SubramaniNo ratings yet
- The Solid State Previous Qns. and AnswersDocument7 pagesThe Solid State Previous Qns. and AnswersSooraj SubhashNo ratings yet
- SCH 2109 Chemistry I - RoseDocument2 pagesSCH 2109 Chemistry I - RosekiokocurtisNo ratings yet
- CE101 July 2003Document4 pagesCE101 July 2003ffgfgfgffgNo ratings yet
- Apc (P-I) 19Document2 pagesApc (P-I) 19Pralay MaitiNo ratings yet
- Iat I Set IiDocument2 pagesIat I Set IiarulsivagiriNo ratings yet
- Coordination Chemistry PDFDocument4 pagesCoordination Chemistry PDFBudhaditya BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- Modul 3Document9 pagesModul 3asmidahNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Technology 2 Int 1 Question PaperDocument1 pageManufacturing Technology 2 Int 1 Question PaperRamNo ratings yet
- C-Chemical Bonding and Mol - StructurexiDocument2 pagesC-Chemical Bonding and Mol - Structurexivsg12umtNo ratings yet
- Ea7145df 2Document5 pagesEa7145df 2KevinNo ratings yet
- Rr411801 Electrometallurgy and CorrosionDocument7 pagesRr411801 Electrometallurgy and CorrosionSrinivasa Rao GNo ratings yet
- XII Chemistry QuestionBank Hathim HssliveDocument9 pagesXII Chemistry QuestionBank Hathim HsslivekeerthyNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 20CYC01Document2 pagesChemistry 20CYC01BonVoyaegeNo ratings yet
- Subject: Foundation Chemistry Code: 2811: Maximum MarkDocument10 pagesSubject: Foundation Chemistry Code: 2811: Maximum MarkJFGHANSAHNo ratings yet
- Engg. Metallurgy M Iat - 1 Question Paper - Set-3Document2 pagesEngg. Metallurgy M Iat - 1 Question Paper - Set-3SCT HOD - MechanicalNo ratings yet
- Material Science & Metallurgy: Third Semester B.E. Degree (CBCS) Examination, Dec.2016/Jan.2017Document2 pagesMaterial Science & Metallurgy: Third Semester B.E. Degree (CBCS) Examination, Dec.2016/Jan.2017Shaikh MuzaffarNo ratings yet
- Engineering Chemistry II - QP ADocument3 pagesEngineering Chemistry II - QP ABOScoNo ratings yet
- Past Paper - Microscopic WorldDocument7 pagesPast Paper - Microscopic Worldapi-3739994100% (1)
- Previous Hse Questions From The Chapter "Co-Ordination Compounds"Document3 pagesPrevious Hse Questions From The Chapter "Co-Ordination Compounds"SOny binuNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure & The Periodic Table 3 QPDocument9 pagesAtomic Structure & The Periodic Table 3 QPMagd OsamaNo ratings yet
- ACFrOgDx1bVYvYs4ZSOHncy Lxwh252QwZ3fFL9jXIkG3a3C1VLDY Vr37kfXVajSVfx5aaqhaxlzrLaHGCZJqMVo6sl xJ6PpIbb 9PdW2nmPH61nrs58pY8k6KWgfbxmkEfVWkqRByaPp7m4RDocument9 pagesACFrOgDx1bVYvYs4ZSOHncy Lxwh252QwZ3fFL9jXIkG3a3C1VLDY Vr37kfXVajSVfx5aaqhaxlzrLaHGCZJqMVo6sl xJ6PpIbb 9PdW2nmPH61nrs58pY8k6KWgfbxmkEfVWkqRByaPp7m4RDr. Fatima IhsanNo ratings yet
- Final SSC-I Chemistry Model PaperDocument8 pagesFinal SSC-I Chemistry Model Papershamsuddin816191No ratings yet
- Chemistry 1 1Document7 pagesChemistry 1 1nassorussi9No ratings yet
- THE Solid State: Chapter - 1Document7 pagesTHE Solid State: Chapter - 1Mohamed YaseenNo ratings yet
- AL Chemistry 1996 Paper 1+2Document12 pagesAL Chemistry 1996 Paper 1+2api-3734333No ratings yet
- Past Papers and MCQs Class 9 - RemovedDocument22 pagesPast Papers and MCQs Class 9 - RemovedboundaryblastsNo ratings yet
- Structure of The Atom and Periodic TablesDocument135 pagesStructure of The Atom and Periodic TablesCarol SoiNo ratings yet
- CHE 1010 Tutorial Sheet 3Document5 pagesCHE 1010 Tutorial Sheet 3Chimuka Onson MapikiNo ratings yet
- Goldengate Int'L College: First Terminal Examination-2080Document2 pagesGoldengate Int'L College: First Terminal Examination-2080sachin shahNo ratings yet
- F40809 Chem (1) FeDocument16 pagesF40809 Chem (1) FeVincent haNo ratings yet
- Chemistry-TermII-Set2 21649Document4 pagesChemistry-TermII-Set2 21649Mridula MishraNo ratings yet
- What Does An Atom Look Like (Draw The Atomic Structure and Label) ?Document3 pagesWhat Does An Atom Look Like (Draw The Atomic Structure and Label) ?Sheda RumNo ratings yet
- Program: Cme Course Title: Applied Mechanics Course Code: CGE 220 Groups: 2K14CME1, 2K14CME4 Lecturer(s) : Siti Syahidah Mohd RumDocument5 pagesProgram: Cme Course Title: Applied Mechanics Course Code: CGE 220 Groups: 2K14CME1, 2K14CME4 Lecturer(s) : Siti Syahidah Mohd RumSheda RumNo ratings yet
- DerivativesDocument13 pagesDerivativessanjeeviNo ratings yet
- LIMIT An IntroductionDocument20 pagesLIMIT An IntroductionSheda RumNo ratings yet
- Atoms Are Basic Building Blocks of Matter That Make Up Everyday Objects. A Desk The Air, Even Human Is Made Up of AtomsDocument1 pageAtoms Are Basic Building Blocks of Matter That Make Up Everyday Objects. A Desk The Air, Even Human Is Made Up of AtomsSheda RumNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Intro To DrawingDocument67 pagesLesson 1 Intro To DrawingGiang Hoai Vu100% (1)
- Atoms Are Basic Building Blocks of Matter That Make Up Everyday Objects. A Desk The Air, Even Human Is Made Up of AtomsDocument1 pageAtoms Are Basic Building Blocks of Matter That Make Up Everyday Objects. A Desk The Air, Even Human Is Made Up of AtomsSheda RumNo ratings yet
- Refrigeration Cycles Study Guide in Powerpoint: To AccompanyDocument20 pagesRefrigeration Cycles Study Guide in Powerpoint: To AccompanyDocumentos De Interés para IngenieríaNo ratings yet
- Answers Marks Q3 I) Calculate, Assuming Slow Cooling, The Volume Fraction and Composition of The Solid at 600ºC 6 MarksDocument2 pagesAnswers Marks Q3 I) Calculate, Assuming Slow Cooling, The Volume Fraction and Composition of The Solid at 600ºC 6 MarksSheda RumNo ratings yet
- Answers Marks Q2 (A) 4 Marks: Kolej Wit School of EngineeringDocument1 pageAnswers Marks Q2 (A) 4 Marks: Kolej Wit School of EngineeringSheda RumNo ratings yet
- Marking Scheme - DME 214 - SEP18 Q6Document1 pageMarking Scheme - DME 214 - SEP18 Q6Sheda RumNo ratings yet
- Wave MotionDocument41 pagesWave MotionyididiyayibNo ratings yet
- Material ScienceDocument1 pageMaterial ScienceSheda RumNo ratings yet
- Lance Taylor Jessi Hartman Adam Flournoy: ENGR 45, SRJC, Fall 2013Document35 pagesLance Taylor Jessi Hartman Adam Flournoy: ENGR 45, SRJC, Fall 2013Sheda RumNo ratings yet
- Lampiran B (I) Table 2 (A) : List of Course/module Offered in The Programme (Full Time)Document3 pagesLampiran B (I) Table 2 (A) : List of Course/module Offered in The Programme (Full Time)Sheda RumNo ratings yet
- Types Simple Cubic (SC) Body Centered Cubic (BCC) Face Centered Cubic (FCC)Document1 pageTypes Simple Cubic (SC) Body Centered Cubic (BCC) Face Centered Cubic (FCC)Sheda RumNo ratings yet
- Answers Marks Q4 (A) Corrosion 8 Marks: Kolej Wit School of EngineeringDocument2 pagesAnswers Marks Q4 (A) Corrosion 8 Marks: Kolej Wit School of EngineeringSheda RumNo ratings yet
- Answers Marks Q2 (A) 4 Marks: Kolej Wit School of EngineeringDocument1 pageAnswers Marks Q2 (A) 4 Marks: Kolej Wit School of EngineeringSheda RumNo ratings yet
- Answers Marks Q3 (A) Boyle's Law 8 Marks: Kolej Wit School of EngineeringDocument1 pageAnswers Marks Q3 (A) Boyle's Law 8 Marks: Kolej Wit School of EngineeringSheda RumNo ratings yet
- Answers Marks Q4 (A) 7 Marks: Kolej Wit School of EngineeringDocument1 pageAnswers Marks Q4 (A) 7 Marks: Kolej Wit School of EngineeringSheda RumNo ratings yet
- Syarahan English NurinDocument2 pagesSyarahan English NurinSheda RumNo ratings yet
- Chapter-8 Quality Control Quality AssuranceDocument35 pagesChapter-8 Quality Control Quality AssuranceMei YeeNo ratings yet
- Learn The Names of Simple MachinesDocument2 pagesLearn The Names of Simple MachinesSheda RumNo ratings yet
- Regulator With NRVDocument2 pagesRegulator With NRVBiswanath LenkaNo ratings yet
- 6.0 Biology Lab ManualDocument49 pages6.0 Biology Lab ManualJacob SmithNo ratings yet
- Magneto Hydro Dynamic GeneratorDocument19 pagesMagneto Hydro Dynamic GeneratorKarthik ViratNo ratings yet
- Multiparticulate Delayed Release Drug Delivery SystemDocument24 pagesMultiparticulate Delayed Release Drug Delivery SystemAarti koramNo ratings yet
- 0423a ASKIN XFLAM Performance Panel Roofing-1Document11 pages0423a ASKIN XFLAM Performance Panel Roofing-1MacNo ratings yet
- Soda AshDocument10 pagesSoda Ashdr chatti hanumantha rao0% (1)
- Bet MethodDocument16 pagesBet MethodG Nivetha100% (1)
- Effect of Corrosion in StructuresDocument32 pagesEffect of Corrosion in StructuresasvihariNo ratings yet
- Application of ESP For Gas Cleaning in Cement Industry - With Reference To IndiaDocument24 pagesApplication of ESP For Gas Cleaning in Cement Industry - With Reference To IndiaSJ ChuaNo ratings yet
- Formulation Development and Evaluation of Unit Moulded Herbal Semisolid Jelly Useful in Treatment of Mouth UlcerDocument9 pagesFormulation Development and Evaluation of Unit Moulded Herbal Semisolid Jelly Useful in Treatment of Mouth UlcerLaeeq R MalikNo ratings yet
- Waste Management AustriaDocument34 pagesWaste Management AustriaregiapursofNo ratings yet
- Spesifikasi Material Finishing Unit ApartemenDocument34 pagesSpesifikasi Material Finishing Unit ApartemenArif GumelarNo ratings yet
- Carboxylic Acids and Derivatives (Formal Report)Document5 pagesCarboxylic Acids and Derivatives (Formal Report)Sar Caermare0% (4)
- Cbse Class 10 Science SyllabusDocument2 pagesCbse Class 10 Science Syllabusराहुल रविराजNo ratings yet
- The Municiplaity of Busia Solid Waste Management PlanDocument15 pagesThe Municiplaity of Busia Solid Waste Management PlanToi JanetNo ratings yet
- Chemical Compositions of Banana Peels (Musa Sapientum) Fruits Cultivated in Malaysia Using Proximate AnalysisDocument6 pagesChemical Compositions of Banana Peels (Musa Sapientum) Fruits Cultivated in Malaysia Using Proximate AnalysiszawNo ratings yet
- 161Document7 pages161KierCliffenvilleGanadosPacienteNo ratings yet
- Specifications: Customer Item Model Name Part No DateDocument11 pagesSpecifications: Customer Item Model Name Part No Datejoroma58No ratings yet
- Green Glue Material Safety DataDocument4 pagesGreen Glue Material Safety DatawilldoyeahNo ratings yet
- Model C-1 Electrostatic Airless Spray Gun: Customer Product Manual Part 104 326DDocument50 pagesModel C-1 Electrostatic Airless Spray Gun: Customer Product Manual Part 104 326DUlpianoxx19920% (1)
- Lecture 3 GlycosidesDocument18 pagesLecture 3 Glycosidessami ullahNo ratings yet
- (MySchoolChildren) SKEMA Biologi Percubaan SPM 2012 SBP QDocument27 pages(MySchoolChildren) SKEMA Biologi Percubaan SPM 2012 SBP QIsmaliza IshakNo ratings yet
- pg1 PDFDocument1 pagepg1 PDFSanjeev GuptaNo ratings yet
- A Brief Introduction To Pressure Vessels: (Clarification Needed)Document3 pagesA Brief Introduction To Pressure Vessels: (Clarification Needed)daniNo ratings yet
- High Voltage Cable JointingDocument7 pagesHigh Voltage Cable Jointingscrapmail9No ratings yet
- Cell Wall: Presented by M. Vijaya LakshmiDocument9 pagesCell Wall: Presented by M. Vijaya LakshmiATCHUNALA SAINo ratings yet
- Science MCQDocument241 pagesScience MCQBeeresha T NNo ratings yet
- Valves SpecificationDocument13 pagesValves Specificationkselvan_1No ratings yet
- Industrial Materials: Instructed By: Dr. Sajid ZaidiDocument13 pagesIndustrial Materials: Instructed By: Dr. Sajid ZaidiarulmuruguNo ratings yet