Professional Documents
Culture Documents
EV305-311 Test 2 Water N Wastewater Engineering
Uploaded by
Sam KhorOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
EV305-311 Test 2 Water N Wastewater Engineering
Uploaded by
Sam KhorCopyright:
Available Formats
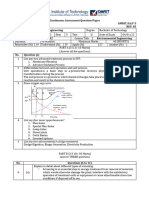
EV305/311 WATER AND WASTEWATER ENGINEERING
TEST 2 (JAN-APRIL 2019)
Student ID :
:
Student Name
Date: 25 March 2020 (5.00 pm)
Instruction
Part 1:
Answer ALL questions.
Part 1 consists of 3 pages excluding cover page. Answers are to be written in the answer
sheets provided. You need to answer the questions during the online class. The answer must
be submitted by the end of the class (25/3/2020 at 6.30pm)
Part 2:
Take Home Test
Please answer the questions and submit online by 27/3/2020
Warning: Failure to submit by the stated time will result in deduction of marks.
Test 2 – EV305/311 Water and Wastewater Engineering
Part 1: to be submitted by end of the online class today (25/3/2020 - 6.30pm)
Q1 (a) Explain the main similarities and differences between:
(i) Primary clarifier and secondary clarifier
Primary Secondary
Similarities
Differences
(ii) Suspended growth system and attached growth system
Primary Secondary
Similarities
Differences
(8 marks)
Test 2 – EV305/311 Water and Wastewater Engineering
Q2. A new sewage treatment plant will be constructed in the upland of Taman Flora. Data
on the existing building and infrastructure at Taman Flora are provided below.
Premise Unit/Area Others
Residential House 750 -
Flora Primary School 1 unit (10000 m2) 700 students
Flora Secondary School 1 unit (13500 m2) 650 students
Mosque 1 unit 50% of residential population
Restaurant 1 unit (500 m2) 10 staff
Flora Polyclinic 1 unit (500 m2) 25 beds
(6 marks)
Test 2 – EV305/311 Water and Wastewater Engineering
Q3 Differentiate between Aerobic and Anaerobic process in terms of:
• Oxygen
• Air circulation
• Biogas
• Energy efficiency
(4 marks)
Test 2 – EV305/311 Water and Wastewater Engineering
Part 2:
Take Home Test – to be submitted by Friday (27/3/2020)
Q1. A completely mixed activated sludge is designed to treat sewage from a community
of 37500 PE. The influent BOD is 230 mg/L. The design effluent BOD is 20 mg/L.
Recommended design parameters are a sludge age of 10 days, MLSS of 3300 mg/L
and an underflow concentration of 10,000 mg/L. The kinetic constants from a bench-
scale treatability study are Y = 0.6 kg/kg and k d = 0.06 per day. Based on the above
information, determine:
(i) Volume of the reactor
(ii) The dimensions of the aeration tank. Use width-to-length ratio of 1:2 and
water depth of 3.6 m.
(iii) Food to microorganism ratio
(iv) The flow rate of sludge wastage
(v) Recycle ratio (show mass balance around final clarifier)
(12 marks)
Q2. Draw and label a flow diagram of sludge treatment system. Explain the function of
each process.
(4 marks)
Q3 (i) Installation of manhole is essential in sewer system. Elucidate the purpose of
manhole. (2 marks)
(ii) Give THREE (3) locations where manhole should be installed in a sewer
system. (3 marks)
Q4 Grit chamber is installed after screening to remove grit particles. The depth of
chamber is 1.2 m, and assuming settling velocity, vs is 1.25 x 10-5 m/s, density, s is
2.6 g/cm3 and dynamic viscosity, is 10-3 kg/m.s, calculate:
i. The size of particle that could be entirely removed. (3 marks)
ii. Detention time, td. (2 marks)
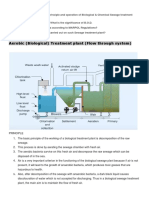
Q5 Sketch, label and explain the process of:
i. Activated sludge system
ii. Trickling filter system
iii. Rotating biological contactor (RBC)
(9 marks)
Test 2 – EV305/311 Water and Wastewater Engineering
Q6 Two sedimentation tanks operate in parallel. The combined flow to the two tanks is
360 m3/hr. Given that,
i. The volume of each tank is 750 m3. What is the detention time of each
tank? (3 marks)
ii. The depth of each tank is 2.2 m and each has a detention time of 4 hours.
What is the surface area of each tank and what is the overflow rate of each
tank in m3/d.m2? (4 marks)
Test 2 – EV305/311 Water and Wastewater Engineering
You might also like
- The Openuniversity of Sri Lanka: Department of Civil Engineering Bachelor of Technology (Civil) - Level 6Document4 pagesThe Openuniversity of Sri Lanka: Department of Civil Engineering Bachelor of Technology (Civil) - Level 6kz_kamranNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 3 Eap315Document7 pagesTutorial 3 Eap315IsbelNo ratings yet
- Waste Water Management (CIE 2254) RCS (Makeup)Document2 pagesWaste Water Management (CIE 2254) RCS (Makeup)anshikaNo ratings yet
- Confidential UTHM Environmental Engineering Final ExamDocument4 pagesConfidential UTHM Environmental Engineering Final ExamAlisa NaziraNo ratings yet
- Bfc32403 Environmental EngineeringDocument4 pagesBfc32403 Environmental Engineeringznyaphotmail.comNo ratings yet
- Ece 2313 Public Health Engineering IiDocument3 pagesEce 2313 Public Health Engineering Iiaggrey noahNo ratings yet
- 3rd BTech 2021-22civil EE Ses-K2Document5 pages3rd BTech 2021-22civil EE Ses-K2Telugu films and technical INo ratings yet
- Final Assessment Test - November 2016: Course: - Class NBR(S) : Slot: Time: Three Hours Max. Marks: 100Document2 pagesFinal Assessment Test - November 2016: Course: - Class NBR(S) : Slot: Time: Three Hours Max. Marks: 100VarunNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 4Document2 pagesTutorial 4princekamutikanjoreNo ratings yet
- الامتحان الجزئي CE467-sp06Document2 pagesالامتحان الجزئي CE467-sp06farajelmabroukNo ratings yet
- Test 2Document2 pagesTest 2Nurul AlizaNo ratings yet
- CE 467-F-Final05Document3 pagesCE 467-F-Final05farajelmabroukNo ratings yet
- Gujarat Technological UniversityDocument2 pagesGujarat Technological UniversityChemical ljietNo ratings yet
- CVL212 Sedimentation HW QuestionsDocument3 pagesCVL212 Sedimentation HW QuestionsABHIJEET NONDANo ratings yet
- Model Question PaperDocument2 pagesModel Question Paper4si21cv008No ratings yet
- Question Paper Code:: Time: Three Hours Maximum: 100 Marks Answer ALL Questions Part - ADocument3 pagesQuestion Paper Code:: Time: Three Hours Maximum: 100 Marks Answer ALL Questions Part - ASrikrishnan DhanajiNo ratings yet
- UNIKZN Environmental Chemistry Exam QuestionsDocument11 pagesUNIKZN Environmental Chemistry Exam QuestionsmohammedNo ratings yet
- Sem 1 2012-2013 (January) Ska 2922 Set ADocument7 pagesSem 1 2012-2013 (January) Ska 2922 Set AAfendi AriffNo ratings yet
- Ee TutorialsDocument9 pagesEe TutorialsKush PatelNo ratings yet
- Environmental Engineering UTHM CQI Test 2Document2 pagesEnvironmental Engineering UTHM CQI Test 2InahMisumiNo ratings yet
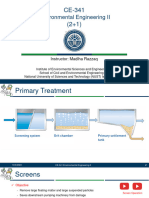
- CE-341 Lec 1Document40 pagesCE-341 Lec 1Hexxacord The BetterNo ratings yet
- BKC4543 - Environmental Engineering 21516 PDFDocument16 pagesBKC4543 - Environmental Engineering 21516 PDFmiza adlinNo ratings yet
- L0 Zero Lecture CIV424Document27 pagesL0 Zero Lecture CIV424Sumit Kumar SinhaNo ratings yet
- CE-341 Lec 2Document13 pagesCE-341 Lec 2Hexxacord The BetterNo ratings yet
- Thickening of Biological Sludge by Electro-Coagulation-Flotation ProcessDocument11 pagesThickening of Biological Sludge by Electro-Coagulation-Flotation ProcessFarah El ShahawyNo ratings yet
- DesalinationDocument6 pagesDesalinationNavneet SinghNo ratings yet
- GTU Wastewater Engineering Exam QuestionsDocument2 pagesGTU Wastewater Engineering Exam Questionsfeyayel988No ratings yet
- CS, CH, MF,: Section-2Document2 pagesCS, CH, MF,: Section-2anirudtNo ratings yet
- University of Zimbabwe B.Sc. (Engineering) Honours - Level IVDocument6 pagesUniversity of Zimbabwe B.Sc. (Engineering) Honours - Level IVkundayi shavaNo ratings yet
- Municipal and Industrial Wastewater TreatmentDocument4 pagesMunicipal and Industrial Wastewater TreatmentCheuk Yin NGNo ratings yet
- Environmental Engineering Unit Test 2 SolutionsDocument5 pagesEnvironmental Engineering Unit Test 2 SolutionsMyeisha WilliamsNo ratings yet
- Advanced Waste-Water Treatment: Indian Institute of Technology Jodhpur RajasthanDocument9 pagesAdvanced Waste-Water Treatment: Indian Institute of Technology Jodhpur RajasthanDeepak Manihar (M20CI002)No ratings yet
- Reg. No. 55248 Question Paper Code CE 2304 Environmental Engineering IDocument3 pagesReg. No. 55248 Question Paper Code CE 2304 Environmental Engineering ISudharsanamurthy PunniamurthyNo ratings yet
- Gujarat Technological UniversityDocument2 pagesGujarat Technological Universityfeyayel990No ratings yet
- Wastewater QuestionDocument18 pagesWastewater Questionth3mannnNo ratings yet
- Final Exam SEAA 2922 19 July 2021 New - With Answer SchemeDocument12 pagesFinal Exam SEAA 2922 19 July 2021 New - With Answer SchemeNurul AlizaNo ratings yet
- Questions STPDocument22 pagesQuestions STPRabindra SinghNo ratings yet
- Final Assessment (CCB31403)Document4 pagesFinal Assessment (CCB31403)Naz HelmiNo ratings yet
- Water Treatment and Management ExamsDocument2 pagesWater Treatment and Management ExamsSonchifua IsaacNo ratings yet
- CE 467-Final-01-2011Document3 pagesCE 467-Final-01-2011farajelmabroukNo ratings yet
- 07a60101 Geotechnical EngineeringDocument8 pages07a60101 Geotechnical EngineeringSatish KumarNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 - Sept 2021Document4 pagesAssignment 1 - Sept 2021Jack YongNo ratings yet
- Extended Assignment Sept 2020 SemesterDocument5 pagesExtended Assignment Sept 2020 SemesterAlya BatrisyiaNo ratings yet
- Ce71 Environmental Engineering - IIDocument2 pagesCe71 Environmental Engineering - IIDanish BhatNo ratings yet
- HS22 (4) EnvironmentDocument3 pagesHS22 (4) EnvironmentSachin MogerNo ratings yet
- Cive3223 5 2014 2Document4 pagesCive3223 5 2014 2Yannick HowNo ratings yet
- SCTEVT 6th Sem Civil SyllabusDocument27 pagesSCTEVT 6th Sem Civil SyllabusMUSTARD CATNo ratings yet
- Sctevt 6th Sem Electrical SyllabusDocument32 pagesSctevt 6th Sem Electrical SyllabusAsh67% (3)
- Universiti Malaysia Pahang Environmental Engineering ExamDocument8 pagesUniversiti Malaysia Pahang Environmental Engineering ExamMohd AizadNo ratings yet
- Prerequisite CEU311 Environmental Engineering IDocument4 pagesPrerequisite CEU311 Environmental Engineering IEng.Gholamsakhi IbrahimzadahNo ratings yet
- Operation and Maintenance of Urban Sewage System in Puducherry (Cpet 711 Summer Training)Document24 pagesOperation and Maintenance of Urban Sewage System in Puducherry (Cpet 711 Summer Training)md adimNo ratings yet
- Enviromental and CPM Question PapersDocument3 pagesEnviromental and CPM Question PapersICE Group of Education BhopalNo ratings yet
- Mineral Processing Mid/Final Test 2021-2022Document3 pagesMineral Processing Mid/Final Test 2021-2022emir akbarNo ratings yet
- Bioseparation Pratice QuestionsDocument1 pageBioseparation Pratice QuestionsAnkit SinghNo ratings yet
- WasteWater Engineering 1516 Sem 1Document7 pagesWasteWater Engineering 1516 Sem 1Tidus FarronNo ratings yet
- Environmental Engineering QuestionsDocument10 pagesEnvironmental Engineering QuestionsSuresh Raju0% (1)
- E 6YI 7650-E: Thapar Institute of Engineering & Technology, PatialaDocument1 pageE 6YI 7650-E: Thapar Institute of Engineering & Technology, PatialaVaisnavi VNo ratings yet
- Geological Carbon Storage: Subsurface Seals and Caprock IntegrityFrom EverandGeological Carbon Storage: Subsurface Seals and Caprock IntegrityStéphanie VialleNo ratings yet
- On Solar Hydrogen and NanotechnologyFrom EverandOn Solar Hydrogen and NanotechnologyLionel VayssieresNo ratings yet
- Membrane Processes: Pervaporation, Vapor Permeation and Membrane Distillation for Industrial Scale SeparationsFrom EverandMembrane Processes: Pervaporation, Vapor Permeation and Membrane Distillation for Industrial Scale SeparationsNo ratings yet
- Test 2 - May 2019 Highway Engineering EV303 EV411Document2 pagesTest 2 - May 2019 Highway Engineering EV303 EV411Sam KhorNo ratings yet
- BEV2036 - EV414 Chpt. 2 Water PollutionDocument76 pagesBEV2036 - EV414 Chpt. 2 Water PollutionSam KhorNo ratings yet
- BEV2036 - EV414 Chpt. 2 Water PollutionDocument59 pagesBEV2036 - EV414 Chpt. 2 Water PollutionSam KhorNo ratings yet
- BEV2036 - EV414 Chpt. 3 Air Pollution PDFDocument67 pagesBEV2036 - EV414 Chpt. 3 Air Pollution PDFSam KhorNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Environmental EngineeringDocument51 pagesIntroduction to Environmental EngineeringSam KhorNo ratings yet
- Occupational Safety and Health Act 1994 (Act 514) Ve - OSHADocument31 pagesOccupational Safety and Health Act 1994 (Act 514) Ve - OSHAExsan OthmanNo ratings yet
- Online Test 1 (May - Aug 2020)Document3 pagesOnline Test 1 (May - Aug 2020)Sam KhorNo ratings yet
- BEV2036 EV414 Exercises On Energy and Materials BalanceDocument4 pagesBEV2036 EV414 Exercises On Energy and Materials BalanceSam KhorNo ratings yet
- Manual On Traffic Control Devices: Road Marking and DileanationDocument39 pagesManual On Traffic Control Devices: Road Marking and DileanationSam KhorNo ratings yet
- Answer For Alkalinity and Hardness ExercisesDocument4 pagesAnswer For Alkalinity and Hardness ExercisesSam KhorNo ratings yet
- Test 1 - May 2019 Highway Engineering EV303 EV411Document6 pagesTest 1 - May 2019 Highway Engineering EV303 EV411Sam KhorNo ratings yet
- EV304 Test 2 ResultsDocument6 pagesEV304 Test 2 ResultsSam KhorNo ratings yet
- EV406 - Jan 2020 - Online Assessment QDocument4 pagesEV406 - Jan 2020 - Online Assessment QSam KhorNo ratings yet
- Online Assessment EV415 - EV301 Engineering HydrologyDocument4 pagesOnline Assessment EV415 - EV301 Engineering HydrologySam Khor100% (1)
- Online Assessment EV307 - BEV2043 HydraulicsDocument2 pagesOnline Assessment EV307 - BEV2043 HydraulicsSam KhorNo ratings yet
- Online Quiz (19th March 2020) PDFDocument1 pageOnline Quiz (19th March 2020) PDFSam KhorNo ratings yet
- Exercise STP Primary TankDocument3 pagesExercise STP Primary TankSam Khor100% (1)
- EM317 - Assignment 2 - Jan-Apr 2018Document3 pagesEM317 - Assignment 2 - Jan-Apr 2018Sam KhorNo ratings yet
- Concentration Day 1 Day 5: 10 1 BOD LDocument1 pageConcentration Day 1 Day 5: 10 1 BOD LSam KhorNo ratings yet
- EV314 RCC Design 2: Taha AlesawyDocument48 pagesEV314 RCC Design 2: Taha AlesawySam KhorNo ratings yet
- Road 1 - CS - Part 1 PDFDocument1 pageRoad 1 - CS - Part 1 PDFSam KhorNo ratings yet
- Highway Engineering EV303/EV411: Class BriefingDocument10 pagesHighway Engineering EV303/EV411: Class BriefingSam KhorNo ratings yet
- Numerical Analysis AssignmentDocument5 pagesNumerical Analysis AssignmentSam KhorNo ratings yet
- Numerical Analysis AssignmentDocument5 pagesNumerical Analysis AssignmentSam KhorNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5 - Section 12 - 2SPPDocument9 pagesLecture 5 - Section 12 - 2SPPSam KhorNo ratings yet
- 1.0 Introduction To Highway EngineeringDocument19 pages1.0 Introduction To Highway EngineeringSam Khor100% (1)
- Lost and Found FormDocument1 pageLost and Found FormSam KhorNo ratings yet
- Read MeDocument3 pagesRead MeKhamarul AriffinNo ratings yet
- Absolute Dependent Motion Analysis of Two Particles: Today's ObjectivesDocument22 pagesAbsolute Dependent Motion Analysis of Two Particles: Today's ObjectivesAtef NazNo ratings yet
- Winery Wastewater Treatment For Water Reuse Purpose - Conventional Activated Sludge Versus Membrane Bioreactor MBRDocument7 pagesWinery Wastewater Treatment For Water Reuse Purpose - Conventional Activated Sludge Versus Membrane Bioreactor MBRsulihah12No ratings yet
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) On Wastewater - Sewage Treatment Plants (STP)Document11 pagesFrequently Asked Questions (FAQ) On Wastewater - Sewage Treatment Plants (STP)Krishna SrikanthNo ratings yet
- Aeration Commisioning - STPDocument7 pagesAeration Commisioning - STPdexterNo ratings yet
- Water Resources EngineeringDocument2 pagesWater Resources EngineeringErald EnriquezNo ratings yet
- STP & Water Design Design SheetDocument5 pagesSTP & Water Design Design SheetVishnu PrajapatiNo ratings yet
- Artikel B.inggrisDocument11 pagesArtikel B.inggrisNur Indriati Harahap100% (1)
- Social Innovation Project-Group 51Document53 pagesSocial Innovation Project-Group 51Janine CrisoloNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Pollution and Deforestation in VenezuelaDocument3 pagesUnit 2 Pollution and Deforestation in VenezuelaProvi SionalmenteNo ratings yet
- Module 2 BioGeoChemical CyclesDocument25 pagesModule 2 BioGeoChemical CyclesPonce GuerreroNo ratings yet
- WATER TREATMENT AND DISTRIBUTION SYSTEMSDocument15 pagesWATER TREATMENT AND DISTRIBUTION SYSTEMSElvira LawrenceNo ratings yet
- Fowzia Adiyahba PDFDocument86 pagesFowzia Adiyahba PDFGlomarie GonayonNo ratings yet
- Citarum River-3Document32 pagesCitarum River-3Reza FahreziNo ratings yet
- Lesson 14 - Environmental Education, Protection and ManagementDocument13 pagesLesson 14 - Environmental Education, Protection and ManagementMary Joy CuetoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3: Stewardship and Accountability for a Sustainable EnvironmentDocument23 pagesLesson 3: Stewardship and Accountability for a Sustainable EnvironmentJean Aireen Bonalos EspraNo ratings yet
- Community Catalyst - Building A Water Sanitation System For Social Inclusion in Winneba, GhanaDocument12 pagesCommunity Catalyst - Building A Water Sanitation System For Social Inclusion in Winneba, Ghanaqinhui ongNo ratings yet
- Codex GPFH CXC 1 1969 Rev 5 2020 Update Version 1686665627Document60 pagesCodex GPFH CXC 1 1969 Rev 5 2020 Update Version 1686665627Nurul FikriNo ratings yet
- Biological & Chemical Sewage Treatment Plant Principles, Operation, and MaintenanceDocument5 pagesBiological & Chemical Sewage Treatment Plant Principles, Operation, and MaintenanceAnakin SkywalkerNo ratings yet
- Kingdom of Cambodia Wastewater GuidelineDocument88 pagesKingdom of Cambodia Wastewater GuidelineRudy HerreraNo ratings yet
- Mesh To Micron Conversion Chart Ecologix SystemsDocument3 pagesMesh To Micron Conversion Chart Ecologix SystemsPitipong SunkhongNo ratings yet
- EVS Notes PDFDocument73 pagesEVS Notes PDFSenthil Ilangovan83% (6)
- FYP Proposal EFPDocument33 pagesFYP Proposal EFPSharifah Zulaikha BenYahyaNo ratings yet
- ĐỀ THAM KHẢO ÔN TUYỂN SINH VÀO 10 CÓ KEY giaoandethitienganh 4Document5 pagesĐỀ THAM KHẢO ÔN TUYỂN SINH VÀO 10 CÓ KEY giaoandethitienganh 424 11Y6C Phạm Lâm TùngNo ratings yet
- Rapid Mix Design Calculation 1Document4 pagesRapid Mix Design Calculation 1Yang Ching HianNo ratings yet
- Disposal of Trade WastewaterDocument3 pagesDisposal of Trade WastewaterCarloNo ratings yet
- Mepc 2 (Vi)Document9 pagesMepc 2 (Vi)Aleksey MoiseyenkoNo ratings yet
- Concept PaperDocument3 pagesConcept Papergladylou siocoNo ratings yet
- Projecting Land Demand For Sanitary LandfillsDocument2 pagesProjecting Land Demand For Sanitary LandfillsRhea CelzoNo ratings yet
- Isometric Plan: Catch Basin DetailDocument1 pageIsometric Plan: Catch Basin DetailFahmie PagayawanNo ratings yet
- EXP 6 - Fecal Coliform Test - StudentDocument8 pagesEXP 6 - Fecal Coliform Test - StudentAbo SmraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Quantity of Waste WaterDocument30 pagesChapter 2 Quantity of Waste Watershiksha gauliNo ratings yet