Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Hyperbola
Uploaded by
Leo HiddenValley0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
28 views1 pageCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
28 views1 pageHyperbola
Uploaded by
Leo HiddenValleyCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
Hyperbola
- In mathematics, a hyperbola is a type of smooth curve, lying in a plane, defined by its geometric
properties or by equations for which it is the solution set. A hyperbola has two pieces, called connected
components or branches, that are mirror images of each other and resemble two infinite bows. The
hyperbola is one of the four kinds of conic section, formed by the intersection of a plane and a
double cone. (The other conic sections are the parabola, the ellipse, and the circle; the circle is a special
case of the ellipse). If the plane intersects both halves of the double cone but does not pass through the
apex of the cones then the conic is a hyperbola.
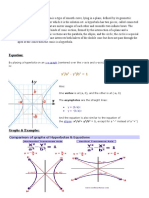
Equation:
By placing a hyperbola on an x-y graph (centered over the x-axis and y-axis), the equation of the curve
is:
x2/a2 - y2/b2 = 1
Also:
One vertex is at (a, 0), and the other is at (-a, 0)
The asymptotes are the straight lines:
y = (b/a)x
y = -(b/a)x
And the equation is also similar to the equation of
the ellipse: x2/a2+ y2/b2 = 1, except for a "-" instead of a "+")
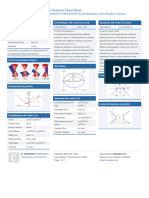
Graphs & Examples:
Comparison of graphs of Hyperbolas & Equations
You might also like
- Learning Module Week 6 in Math 411 PDFDocument11 pagesLearning Module Week 6 in Math 411 PDFAllyzzaNo ratings yet
- Simple CurveDocument2 pagesSimple CurvefillosheenaNo ratings yet
- Graphing Hyperbolas in Standard FormDocument12 pagesGraphing Hyperbolas in Standard FormJackylyn FalejoNo ratings yet
- Matutum View Academy: (The School of Faith)Document14 pagesMatutum View Academy: (The School of Faith)Neil Trezley Sunico BalajadiaNo ratings yet
- Hyperbola CharacteristicsDocument8 pagesHyperbola Characteristicsmeda kumarNo ratings yet
- Paul's Notes HyperbolasDocument5 pagesPaul's Notes HyperbolasaaNo ratings yet
- Hyperbola EquationDocument4 pagesHyperbola Equationapi-174638550No ratings yet
- Pre-Calculus Project (Hyperbola) : This Study Resource WasDocument8 pagesPre-Calculus Project (Hyperbola) : This Study Resource WasBay-as OlagetNo ratings yet
- Linear EquationDocument8 pagesLinear EquationkleyrgNo ratings yet
- Guide to quadratic surfacesDocument11 pagesGuide to quadratic surfacesdatta agniNo ratings yet
- Group 2 Hyperbola - ReportDocument10 pagesGroup 2 Hyperbola - ReportMicko RenomeronNo ratings yet
- G9 Math Q1 - Week 6 - Quadratic Functions and Its GraphDocument27 pagesG9 Math Q1 - Week 6 - Quadratic Functions and Its GraphMechael ManzanoNo ratings yet
- Linear SystemsDocument17 pagesLinear Systemsvuphuonganh2211No ratings yet
- Slope-Intercept Form: (A and B Cannot Both Be 0)Document3 pagesSlope-Intercept Form: (A and B Cannot Both Be 0)Femie SurNo ratings yet
- Linear Equation: Submitted By: Angelene L. CalingasanDocument7 pagesLinear Equation: Submitted By: Angelene L. CalingasanJillianne PadilloNo ratings yet
- Mat061 Calculus 2 Parametric Curves and Polar CoordinatesDocument14 pagesMat061 Calculus 2 Parametric Curves and Polar CoordinatesBenhar Masahod BLM-VLOGNo ratings yet
- Conic Section DefinitionDocument5 pagesConic Section DefinitionElyssamae PonceNo ratings yet
- HYPERBOLAAAAAAADocument10 pagesHYPERBOLAAAAAAAjhayserie wangNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Linear Equations, Functions and Their ApplicationsDocument18 pagesChapter 1 Linear Equations, Functions and Their Applicationsyonas100% (1)
- Graphing Circles, Conic Sections and ParabolasDocument4 pagesGraphing Circles, Conic Sections and ParabolassaaskaphoneNo ratings yet
- Linear Equations in Two Variables, Explain The Geometry of Lines or TheDocument10 pagesLinear Equations in Two Variables, Explain The Geometry of Lines or Thejasmin jeharaNo ratings yet
- Math 101a - Topic 5Document5 pagesMath 101a - Topic 5Takashi TiteNo ratings yet
- Math 101a - Topic 5Document5 pagesMath 101a - Topic 5Takashi TiteNo ratings yet
- Pre Cal ReviewerDocument16 pagesPre Cal ReviewerMaxine AlipioNo ratings yet
- Conic Section NcertDocument22 pagesConic Section NcertRaja KumarNo ratings yet
- Crossant - Conic-Sections FormulaDocument1 pageCrossant - Conic-Sections Formulaalireza katebiNo ratings yet
- Group 2 - HyperbolaDocument9 pagesGroup 2 - HyperbolaMicko RenomeronNo ratings yet
- HYPERBOLADocument2 pagesHYPERBOLAjhayserie wangNo ratings yet
- (LEC) 1.2 Conic SectionsDocument28 pages(LEC) 1.2 Conic Sectionserwin_garcia_7No ratings yet
- Ellipse: Intercepts. The Endpoints of The Minor Axis Are (0, B) and (0, - B) and Are Referred To AsDocument18 pagesEllipse: Intercepts. The Endpoints of The Minor Axis Are (0, B) and (0, - B) and Are Referred To AseL LeahNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Conic SectionsDocument20 pagesIntroduction To Conic Sectionssir jjNo ratings yet
- The Hyperbola: Standard Equation, Asymptotes, and ExamplesDocument10 pagesThe Hyperbola: Standard Equation, Asymptotes, and Examplesmudabbir muhammadNo ratings yet
- Hyperbola-01 - TheoryDocument15 pagesHyperbola-01 - TheoryRaju SinghNo ratings yet
- IIT - Notas de Hipérbole PDFDocument27 pagesIIT - Notas de Hipérbole PDFlucasNo ratings yet
- STM NotesDocument3 pagesSTM NotesDiako Unknown 12No ratings yet
- 4.B. Tangent and Normal Lines To ConicsDocument10 pages4.B. Tangent and Normal Lines To ConicsyrodroNo ratings yet
- Acute Angle DefinitionDocument5 pagesAcute Angle Definitionapi-126876773No ratings yet
- HyperbolaDocument32 pagesHyperbolaDiane Mendez100% (1)
- Precal Week 5-6Document4 pagesPrecal Week 5-6Ken FerrolinoNo ratings yet
- Conic Sections Engineering DrawingDocument34 pagesConic Sections Engineering DrawingIsSidNo ratings yet
- Conic Section PDFDocument22 pagesConic Section PDFishad satyen100% (2)
- Math - 7th Grade Teaching NotesDocument16 pagesMath - 7th Grade Teaching NotesPara ParadiseNo ratings yet
- Hyperbola: Equation of Vertical, Shifted and Rotated Hyperbolas and Parametric Coordinates of HyperbolaDocument13 pagesHyperbola: Equation of Vertical, Shifted and Rotated Hyperbolas and Parametric Coordinates of HyperbolaJatin SinglaNo ratings yet
- Introductory Mathematics, MAT100a, D, Fall 2020 October 1Document20 pagesIntroductory Mathematics, MAT100a, D, Fall 2020 October 1Nika FrolovaNo ratings yet
- Two or More Variables FunctionsDocument11 pagesTwo or More Variables FunctionsAndrés FelipeNo ratings yet
- Math ReviewerDocument1 pageMath ReviewerfloriemangupitNo ratings yet
- Group 4Document14 pagesGroup 4alethuaNo ratings yet
- HYPERBOLADocument10 pagesHYPERBOLAChazz RensNo ratings yet
- Conics: ParabolasDocument13 pagesConics: ParabolasJJ MosesNo ratings yet
- Algebraic Curves NotesDocument10 pagesAlgebraic Curves NotesManuel CebolloNo ratings yet
- Linear Functions: Characteristics, Forms, Graphing and ModelingDocument5 pagesLinear Functions: Characteristics, Forms, Graphing and ModelingSofía Peregrino ArgüelloNo ratings yet
- CIRCLE INSPIRATIONDocument74 pagesCIRCLE INSPIRATIONTimotei22 Abaya RoldanNo ratings yet
- Analytic GeometryDocument14 pagesAnalytic GeometrySherwinNo ratings yet
- 32 Linear EquationsDocument5 pages32 Linear Equationsapi-299265916No ratings yet
- 01 02 Functions Business SettingDocument35 pages01 02 Functions Business SettingFernando Lipardo Jr.No ratings yet
- PrecDocument5 pagesPrecAngel EspinoNo ratings yet
- Pre CalculusDocument8 pagesPre CalculusAngel EspinoNo ratings yet
- AMI, Award & Phoenix BIOS Beep Code Troubleshooting GuideDocument2 pagesAMI, Award & Phoenix BIOS Beep Code Troubleshooting GuideLeo HiddenValleyNo ratings yet
- Differences Between And: Groups TeamsDocument1 pageDifferences Between And: Groups TeamsLeo HiddenValleyNo ratings yet
- Leveling of ExpectationDocument1 pageLeveling of ExpectationLeo HiddenValleyNo ratings yet
- Unit Title Elements Performance Criteria Content Learning Activities Time DurationDocument3 pagesUnit Title Elements Performance Criteria Content Learning Activities Time DurationLeo HiddenValleyNo ratings yet
- Map LARGE FILE FOR PRINTING 8 FT X 12 FT PDFDocument1 pageMap LARGE FILE FOR PRINTING 8 FT X 12 FT PDFLeo HiddenValleyNo ratings yet
- Unit Title Elements Performance Criteria Content Learning Activities Time DurationDocument3 pagesUnit Title Elements Performance Criteria Content Learning Activities Time DurationLeo HiddenValleyNo ratings yet
- Facilities MaintenanceDocument18 pagesFacilities MaintenanceLeo HiddenValleyNo ratings yet
- E Emanual X550la LB LC Ver7926Document130 pagesE Emanual X550la LB LC Ver7926cyborg806No ratings yet
- HyperbolaDocument1 pageHyperbolaLeo HiddenValleyNo ratings yet
- Micro TeachingDocument14 pagesMicro TeachingLeo HiddenValleyNo ratings yet
- Ecc List of DocumentsDocument1 pageEcc List of DocumentsLeo HiddenValleyNo ratings yet
- HyperbolaDocument1 pageHyperbolaLeo HiddenValleyNo ratings yet
- Income Generating ProjectDocument2 pagesIncome Generating ProjectLeo HiddenValleyNo ratings yet
- Maxx CandyDocument2 pagesMaxx CandyLeo HiddenValleyNo ratings yet
- Digital Running Dice Hardware Design ProjectDocument2 pagesDigital Running Dice Hardware Design ProjectLeo HiddenValleyNo ratings yet
- Micro Teaching2Document13 pagesMicro Teaching2Leo HiddenValleyNo ratings yet
- ScanSoft PDF Converter 3.0DFGDFGHDSHDocument1 pageScanSoft PDF Converter 3.0DFGDFGHDSHramssreemantulaNo ratings yet
- Assembly: Automatic Switch Outdoor Building LightingsDocument2 pagesAssembly: Automatic Switch Outdoor Building LightingsLeo HiddenValleyNo ratings yet
- The Pink Panther Team: Eva C. Sison Rosario J. Gapasin Annaliza C. Victorio Abraham A. Balayo Leonides G. AgravanteDocument2 pagesThe Pink Panther Team: Eva C. Sison Rosario J. Gapasin Annaliza C. Victorio Abraham A. Balayo Leonides G. AgravanteLeo HiddenValleyNo ratings yet
- Maxx CandyDocument2 pagesMaxx CandyLeo HiddenValleyNo ratings yet
- Differences Between And: Groups TeamsDocument1 pageDifferences Between And: Groups TeamsLeo HiddenValleyNo ratings yet
- Math 4 Ellipse: Hans Christian M. Gregorio CHS - 2Document2 pagesMath 4 Ellipse: Hans Christian M. Gregorio CHS - 2Leo HiddenValleyNo ratings yet
- Micro Teaching2Document13 pagesMicro Teaching2Leo HiddenValleyNo ratings yet
- Rooster Biotech's Probiotic Supplement Achieves Zero Disease and MortalityDocument21 pagesRooster Biotech's Probiotic Supplement Achieves Zero Disease and MortalityLeo HiddenValleyNo ratings yet
- Traffic Rules and RegulationDocument62 pagesTraffic Rules and RegulationLeo HiddenValleyNo ratings yet
- Hardware SpecificationsDocument4 pagesHardware SpecificationsLeo HiddenValleyNo ratings yet
- Provide Team LeadershipDocument1 pageProvide Team LeadershipLeo HiddenValleyNo ratings yet
- Hardware SpecificationsDocument4 pagesHardware SpecificationsLeo HiddenValleyNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Basic Parts of ComputerDocument2 pagesIntroduction To Basic Parts of ComputerHannah ShiiNo ratings yet