Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Organization of MAS Practice
Uploaded by
Brix Arriola0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views2 pagesOriginal Title
332563209-Organization-of-MAS-Practice-doc.docx
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views2 pagesOrganization of MAS Practice
Uploaded by
Brix ArriolaCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
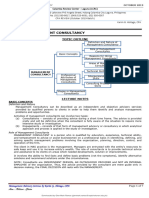
Organizational Structure of the MAS Practice or Division
I. STAFF PYRAMID AND BILLING RATES
LEVE POSITIONS DESCRIPTION ACTIVITIES BILLING
L RATES
1 Partners, The Top of the pyramid Performing P10, 000 to
Principals, Typically the most practice planning, P20,000 per
Directors experienced highly paid Administering hour
Senior professionals and developing
Managers, Normally responsible for practice,
Managers, the: Consulting with
Supervisors - Successful completion of top-client
Senior engagements managers,
Consultants, - Dealing directly with Approving
Seniors clients engagement
Associate - For selling work reports, and
Consultants, Managing client
Staff crises
2 Senior The next tier of the pyramid Planning P 8,000 to P
Managers, is made up of them engagements 10, 000 per
Managers, They perform week-to-week Evaluating hour
Supervisors management of consultants
engagements and are Supervising
responsible for: consultants
- Identifying new client Writing proposals
prospects Reviewing
- Assisting in the sales working papers
process and reports
Consulting with
client managers
Serves as expert
in one or more
applied
knowledge areas
3 Senior The third tier of the pyramid P5,000 to P
Consultants, includes these individuals 8,000 per
Seniors They typically have 2 or 3 hour
years of consulting
experience
They are capable of
supervising the daily work
of the younger staff.
They possess the right
combination of experience
and dedication to complete
different projects with
limited supervision
Normally, seniors are short
in supply in most firms
4 Associate The final layer of the P2,000 to P
Consultants, pyramid consists of the 5,000 per
Staff young or new staff hour
Depending upon the firm,
these individuals usually
have less than 2 years of
consulting experience and
may have been hired
directly out of graduate or
undergraduate school
Some firms require prior
business experience, while
others prefer to train their
own personnel and hire
some undergraduate
students
II. PROBLEM AREAS IN RENDERING MAS BY AN INDEPENDENT ACCOUNTING FIRM
1. Questions as to the effect of the practice of MAS on the firm’s independence.
2. Development and maintenance of a high level of competence in MAS.
3. Questions of what fee to charge.
4. Question of AUDIT-MAS cooperation in obtaining engagements.
5. Question of regular communication between the MAS function and the rest of the firm.
III. FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT OF A MAS PRACTICE
A consulting practice is a business and, like all businesses, must have financing.
Financing can be provided by capital invested by you or the initial group of consultants or by funds
borrowed from banks and others
This will be used to pay and fund for:
- Monthly operating expenses
- Accounts receivable that represent time billings to client.
It is prudent to have working capital for at least three to four months’ expenses
- Care should be exercised to avoid a FINANCIAL TRAP where funds are received and spent
before the work is actually performed.
You might also like
- Organizational Structure of The MAS Practice or Division I. Staff Pyramid and Billing Rates Leve L Positions Description Activities Billing RatesDocument2 pagesOrganizational Structure of The MAS Practice or Division I. Staff Pyramid and Billing Rates Leve L Positions Description Activities Billing RatesBrix ArriolaNo ratings yet
- Organization and Management of MAS PracticeDocument14 pagesOrganization and Management of MAS PracticeJohn AlbateraNo ratings yet
- Management skills vital for business successDocument19 pagesManagement skills vital for business successŽahra Ňah IdNo ratings yet
- Associate Consultant, Financial Due DiligenceDocument1 pageAssociate Consultant, Financial Due Diligencevinay narneNo ratings yet
- Embedding Sustainabilty: The Evolution of RaiseDocument24 pagesEmbedding Sustainabilty: The Evolution of RaiseAstha AggarwalNo ratings yet
- Communication Plan and KPIs for Organizational ChangeDocument3 pagesCommunication Plan and KPIs for Organizational Changenav randhawaNo ratings yet
- Organization and Management of Mas PracticeDocument12 pagesOrganization and Management of Mas PracticeKimberly Ann Lumanog AmarNo ratings yet
- Praxis Global Alliance - JDDocument3 pagesPraxis Global Alliance - JDShubhamNo ratings yet
- Organizational and Management Plan: Form of Business: (Say Something More About Your Business Structure)Document4 pagesOrganizational and Management Plan: Form of Business: (Say Something More About Your Business Structure)Chara etangNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6-8 Chapter 6 - Organization and Management of Mas Practice Developing MAS PracticeDocument18 pagesChapter 6-8 Chapter 6 - Organization and Management of Mas Practice Developing MAS PracticeKimberly MaragañasNo ratings yet
- A Pragmatic Introduction to Middle Manager Fundamentals: Part 2 - Managing at a DistanceFrom EverandA Pragmatic Introduction to Middle Manager Fundamentals: Part 2 - Managing at a DistanceNo ratings yet
- BF Program DescriptionDocument13 pagesBF Program DescriptionVarudhini PatkiNo ratings yet
- Client Relationship Management Skills: Euromoney TrainingDocument4 pagesClient Relationship Management Skills: Euromoney Trainingrajjusingh68No ratings yet
- Most Common Interview Questions:: - Answering IncomingDocument3 pagesMost Common Interview Questions:: - Answering IncomingMuaz MuzNo ratings yet
- CMGR Brochure AU Kathy PagesDocument2 pagesCMGR Brochure AU Kathy PagesgeorgvinodNo ratings yet
- Finance for Non-Finance Executives SeminarDocument4 pagesFinance for Non-Finance Executives Seminarabhimani5472No ratings yet
- LT Corp Pres Broch 10 27 20Document14 pagesLT Corp Pres Broch 10 27 20Maynord ArgüelloNo ratings yet
- Level 3 Business Administrator ApprenticeshipDocument1 pageLevel 3 Business Administrator ApprenticeshipcococatelulNo ratings yet
- IIM Calcutta EPBM B27 BrochurDocument18 pagesIIM Calcutta EPBM B27 BrochurVishal ParikhNo ratings yet
- NSWDocument6 pagesNSWRam PNo ratings yet
- Lecture Chapter 4Document8 pagesLecture Chapter 4Billy Joe VinluanNo ratings yet
- Whitepaper Future of Project ManagementDocument4 pagesWhitepaper Future of Project Managementluis lopezNo ratings yet
- HR Manager Job ProfileDocument6 pagesHR Manager Job ProfileRehan TyagiNo ratings yet
- Developing Leadership Style - Case StudyDocument2 pagesDeveloping Leadership Style - Case StudyTuấn PhápNo ratings yet
- Financial Acumen MasteryDocument3 pagesFinancial Acumen Masteryabc ptcNo ratings yet
- 1aa - Outsourcing Proposal Online VersionDocument35 pages1aa - Outsourcing Proposal Online VersionTawo MogbojuriNo ratings yet
- Wharton - AMP - India - Brochure - 20 - 02 - 2020 Executive EducationDocument18 pagesWharton - AMP - India - Brochure - 20 - 02 - 2020 Executive Educationsantosh kumarNo ratings yet
- MS01Document4 pagesMS01Leodeza MactalNo ratings yet
- Interim Executives Achieve Goals 20 Times Faster: Cutting Perks?Document4 pagesInterim Executives Achieve Goals 20 Times Faster: Cutting Perks?Tim DixonNo ratings yet
- Expectation Management - Session 3Document1 pageExpectation Management - Session 3Hiren TrivediNo ratings yet
- CBHRM NamrataDocument4 pagesCBHRM NamrataAmit RuikarNo ratings yet
- Back Office ManagementDocument6 pagesBack Office ManagementKeith Parker100% (2)
- Analyzing Key Job RolesDocument5 pagesAnalyzing Key Job RolesjustineNo ratings yet
- CertifiedCompensation&BenefitsProfessional 13th 16thMay2024KualaLumpurDocument6 pagesCertifiedCompensation&BenefitsProfessional 13th 16thMay2024KualaLumpurdesmondsam.officialNo ratings yet
- 2835717pembentukan Kerani Yang CemerlangDocument1 page2835717pembentukan Kerani Yang CemerlangMaxieNo ratings yet
- BF Program DescriptionDocument9 pagesBF Program DescriptionBharatNo ratings yet
- Ma BrochureDocument12 pagesMa BrochureCristiane GanduNo ratings yet
- JD and JS HRMDocument9 pagesJD and JS HRMKalpesh ChaudhariNo ratings yet
- Wa0012.Document4 pagesWa0012.dhruvpalan123No ratings yet
- Acs - HRDocument3 pagesAcs - HRAnkit Sharma 028No ratings yet
- Uob Mba Brochure 210104Document2 pagesUob Mba Brochure 210104draco hackeyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12-14 MASDocument3 pagesChapter 12-14 MAScrispyy turonNo ratings yet
- Prelims - MANREP PDFDocument24 pagesPrelims - MANREP PDFdakis cherishjoyfNo ratings yet
- Acca ExemptionsDocument6 pagesAcca ExemptionsDarylaNo ratings yet
- Man PrintDocument24 pagesMan PrintRoselene LansonNo ratings yet
- IIM Nagpur GMP - BrochureDocument17 pagesIIM Nagpur GMP - Brochuregprakash00820No ratings yet
- Supporting The Under-Performing ManagerDocument5 pagesSupporting The Under-Performing ManagervinayakaNo ratings yet
- Activity 1 - Chapter 6Document1 pageActivity 1 - Chapter 6CLEAR MELODY VILLARANNo ratings yet
- GROUP 8 TecSmart ElecronicsDocument3 pagesGROUP 8 TecSmart ElecronicsXyrus SalayonNo ratings yet
- Developing Professionals: The BCG WayDocument7 pagesDeveloping Professionals: The BCG WayNitish KishoreNo ratings yet
- MS Concepts, Practices, and StandardsDocument14 pagesMS Concepts, Practices, and StandardsRuiz, CherryjaneNo ratings yet
- General MBA BrochureDocument4 pagesGeneral MBA BrochureRawnee HoNo ratings yet
- People in Organizations (Unit 2)Document22 pagesPeople in Organizations (Unit 2)Marisa Olarte RosillasNo ratings yet
- The Consulting Industry and Its Transformations in WordDocument23 pagesThe Consulting Industry and Its Transformations in Wordlei ann magnayeNo ratings yet
- MBA BrochureDocument3 pagesMBA BrochureNasir ShabbirNo ratings yet
- Career Pathway: Business Change and ConsultingDocument2 pagesCareer Pathway: Business Change and ConsultingDom LeppardNo ratings yet
- Project Management Professional: Exam Preparation CourseDocument8 pagesProject Management Professional: Exam Preparation Coursemarks2muchNo ratings yet
- Manajemen Proyek 2015Document43 pagesManajemen Proyek 2015abuNo ratings yet
- Exciting Career - Business Development Administrator - AuditDocument1 pageExciting Career - Business Development Administrator - AuditWamweru LeahNo ratings yet
- FMI7e ch12Document41 pagesFMI7e ch12lehoangthuchienNo ratings yet
- A Research Study On The Effects of CashlDocument93 pagesA Research Study On The Effects of CashlWynona PinlacNo ratings yet
- Stock Offerings and Investor Monitoring: Financial Markets and Institutions, 7e, Jeff MaduraDocument47 pagesStock Offerings and Investor Monitoring: Financial Markets and Institutions, 7e, Jeff MaduraTalib DoaNo ratings yet
- Stock Offerings and Investor Monitoring: Financial Markets and Institutions, 7e, Jeff MaduraDocument47 pagesStock Offerings and Investor Monitoring: Financial Markets and Institutions, 7e, Jeff MaduraTalib DoaNo ratings yet
- FMI7e ch12Document41 pagesFMI7e ch12lehoangthuchienNo ratings yet
- Stock Offerings and Investor Monitoring: Financial Markets and Institutions, 7e, Jeff MaduraDocument47 pagesStock Offerings and Investor Monitoring: Financial Markets and Institutions, 7e, Jeff MaduraTalib DoaNo ratings yet
- Stock Offerings and Investor Monitoring: Financial Markets and Institutions, 7e, Jeff MaduraDocument47 pagesStock Offerings and Investor Monitoring: Financial Markets and Institutions, 7e, Jeff MaduraTalib DoaNo ratings yet
- Stock Offerings and Investor Monitoring: Financial Markets and Institutions, 7e, Jeff MaduraDocument47 pagesStock Offerings and Investor Monitoring: Financial Markets and Institutions, 7e, Jeff MaduraTalib DoaNo ratings yet
- FMI7e ch12Document41 pagesFMI7e ch12lehoangthuchienNo ratings yet
- Charlie Vaughan: Objectives Career HistoryDocument2 pagesCharlie Vaughan: Objectives Career HistoryBrix ArriolaNo ratings yet
- Stock Offerings and Investor Monitoring: Financial Markets and Institutions, 7e, Jeff MaduraDocument47 pagesStock Offerings and Investor Monitoring: Financial Markets and Institutions, 7e, Jeff MaduraTalib DoaNo ratings yet
- FMI7e ch12Document41 pagesFMI7e ch12lehoangthuchienNo ratings yet
- Stock Offerings and Investor Monitoring: Financial Markets and Institutions, 7e, Jeff MaduraDocument47 pagesStock Offerings and Investor Monitoring: Financial Markets and Institutions, 7e, Jeff MaduraTalib DoaNo ratings yet
- Stock Offerings and Investor Monitoring: Financial Markets and Institutions, 7e, Jeff MaduraDocument47 pagesStock Offerings and Investor Monitoring: Financial Markets and Institutions, 7e, Jeff MaduraTalib DoaNo ratings yet
- Stock Offerings and Investor Monitoring: Financial Markets and Institutions, 7e, Jeff MaduraDocument47 pagesStock Offerings and Investor Monitoring: Financial Markets and Institutions, 7e, Jeff MaduraTalib DoaNo ratings yet
- CFF 302Document40 pagesCFF 302Les CanoNo ratings yet
- The Financial Environment: Markets, Institutions, and Interest RatesDocument31 pagesThe Financial Environment: Markets, Institutions, and Interest RatesLokkhi BowNo ratings yet
- CFF 308Document49 pagesCFF 308daidainaNo ratings yet
- Risk and Rates of Return: Stand-Alone Risk Portfolio Risk Risk & Return: CAPM/SMLDocument55 pagesRisk and Rates of Return: Stand-Alone Risk Portfolio Risk Risk & Return: CAPM/SMLBrix ArriolaNo ratings yet
- CFF 301Document17 pagesCFF 301Putera Petir GundalaNo ratings yet
- Time Value of Money: Future Value Present Value Rates of Return AmortizationDocument58 pagesTime Value of Money: Future Value Present Value Rates of Return AmortizationdaidainaNo ratings yet
- Financial Planing & ForecastingDocument31 pagesFinancial Planing & ForecastingRetno Yuniarsih Marekhan IINo ratings yet
- Bangalore University Bangalore 560 056, Karnataka StateDocument96 pagesBangalore University Bangalore 560 056, Karnataka StateGopinath Basavaiah SiddaiahNo ratings yet
- YIBS BrochureDocument12 pagesYIBS BrochurepwittipearlsNo ratings yet
- Gael Sfeir - CVDocument1 pageGael Sfeir - CVGaelNo ratings yet
- IEPM 2020 Part 1 V4 PDFDocument49 pagesIEPM 2020 Part 1 V4 PDFRestu Dinda PagamundiNo ratings yet
- Uber CEO's Challenge to Transform Corporate CultureDocument13 pagesUber CEO's Challenge to Transform Corporate CultureIsabella SydneyNo ratings yet
- Appendices Appendix I: Survey QuestionnareDocument6 pagesAppendices Appendix I: Survey Questionnarehabtamu fentaNo ratings yet
- Learning Activity 1 TECH 101Document2 pagesLearning Activity 1 TECH 101Carmel An100% (1)
- The Communication Gurukul - Corporate SpeakDocument36 pagesThe Communication Gurukul - Corporate SpeakSiddharth MetitoNo ratings yet
- Strategic Management Creating Competitive Advantages 7th Edition Dess Solutions ManualDocument26 pagesStrategic Management Creating Competitive Advantages 7th Edition Dess Solutions ManualNataliePowelljdmb100% (32)
- Join DECA 2023Document2 pagesJoin DECA 2023Mono PNo ratings yet
- Todd Combs Transcript Art of Investing 10 Oct 2023Document22 pagesTodd Combs Transcript Art of Investing 10 Oct 2023ACasey101No ratings yet
- Business Hive Solutions Company ProfileDocument11 pagesBusiness Hive Solutions Company ProfileMwila KasondeNo ratings yet
- Customer Experience Expert - CV PDFDocument1 pageCustomer Experience Expert - CV PDFJamesNo ratings yet
- CSEC Principles of Accounts Syllabus 2019Document130 pagesCSEC Principles of Accounts Syllabus 2019John Coxx100% (2)
- Chapter 6Document31 pagesChapter 6h.a.m OmanNo ratings yet
- Employee Performance Evaluation FormDocument2 pagesEmployee Performance Evaluation FormZafeer HasnainNo ratings yet
- Global Marketing Module Handbook 2020-21Document19 pagesGlobal Marketing Module Handbook 2020-21Badshah Bolna BadshahNo ratings yet
- TLE6 - q1 - Melc28 - How To Be A Successful Entrepreneur in AnimalFish Raising - v1Document19 pagesTLE6 - q1 - Melc28 - How To Be A Successful Entrepreneur in AnimalFish Raising - v1Lea Mae T. NavarroNo ratings yet
- Full Download Ebook PDF International Marketing 18th Edition by Philip Cateora PDFDocument41 pagesFull Download Ebook PDF International Marketing 18th Edition by Philip Cateora PDFjoel.lasala545100% (28)
- Inventory Management JapanDocument4 pagesInventory Management JapanSURUCHI KUMARINo ratings yet
- B.ethics Q3-W1-2Document14 pagesB.ethics Q3-W1-2Luis Dominic A. CrisostomoNo ratings yet
- NITI Policy-Paper BMID 2023-MayDocument20 pagesNITI Policy-Paper BMID 2023-MayAmardeep RavalNo ratings yet
- 300 Vidushi UpadhyayDocument47 pages300 Vidushi UpadhyayPraveen KumarNo ratings yet
- A Study On Women Entrepreneurship in India: June 2020Document12 pagesA Study On Women Entrepreneurship in India: June 2020Ankapali MukherjeeNo ratings yet
- Eritrea - AR - Support To Technical Vocational Education and Training ProjectDocument31 pagesEritrea - AR - Support To Technical Vocational Education and Training ProjectMearg NgusseNo ratings yet
- Beginners Guide To Day Trading Responsibly 1Document21 pagesBeginners Guide To Day Trading Responsibly 1Julian CristianNo ratings yet
- Chief Product Officer Program BrochureDocument4 pagesChief Product Officer Program BrochureanikbiswasNo ratings yet
- Strategic Service ManagementDocument312 pagesStrategic Service ManagementMarwaneEl-lamraniNo ratings yet
- Provisional Academic Transcript: S.No. Course Credit GradeDocument4 pagesProvisional Academic Transcript: S.No. Course Credit GradeNishant PrasadNo ratings yet
- Hero Cycles - Operating Break-EvensDocument26 pagesHero Cycles - Operating Break-EvensParth SinglaNo ratings yet