Professional Documents
Culture Documents
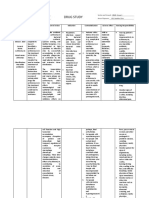
Drug Classification/Indicati ON Mechanis MOF Action Contraindication Adverse Reaction Dose, Route, Frequenc Y Nursing Responsibiliti ES
Uploaded by
Nicole cuencos0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
23 views5 pagesOriginal Title
DRUG-pneumonia2018
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
23 views5 pagesDrug Classification/Indicati ON Mechanis MOF Action Contraindication Adverse Reaction Dose, Route, Frequenc Y Nursing Responsibiliti ES
Uploaded by
Nicole cuencosCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 5
DRUG CLASSIFICATION/INDICATI MECHANIS CONTRAINDICATION ADVERSE DOSE, NURSING
ON M OF REACTION ROUTE, RESPONSIBILITI
ACTION FREQUENC ES
Y
Generic Acute bacterial worsening Binds to the Contraindicated in CNS: fatigue, -500 mg P.O. -Monitor patient
name: of COPD caused by 50S subunit patients headache, for superinfection.
AZITROMYCI Haemophilis influenza, bacteria hypersensitive to somnolence, Drug may cause
N Moraxella catarrhalis, or ribosomes, azithromycin, dizziness. overgrowth of non-
Streptocccus pnemoniae; blocking erythromycin, or CV: chest pain susceptible bacteria
Brand name: uncomplicated skin and protein other macrolide or palpitations or fungi.
AzaSite, skin-structure infections synthesis; ketolide antibiotics EENT: eye irritation -Monitor patient
Zithromax, caused by Staphylococcus bacteriostatic and in those with (ophthalmic) for CDAD, which
Zmax aureus, Sterptococcus or history of GI: abdominal pain, may range in
pyogens second-lined bactericidal, cholestatic jaundice anorexia, diarrhea, severity from mild
therapy for phyryngitis or depending on or hepatic nausea, vomiting, diarrhea to fatal
tonsillitis caused by concentration dysfunction from pseudomembranous colitis
S.pyogens prior use of colitis, dyspepsia, -Consider full risk
Community-acquired azithromycin flatulence, melena profile when
pneumonia caused by C. Don’t use oral drug Hepatic: cholestatic choosing
pneumoniae, H influenza, in patients with jaundice appropriate
M. pneumoniae, or S. pneumonia or in Skin: antibiotic therapy.
pneumoniae those with photosensitivity Alternative
Acute bacterial sinusitis moderate to severe reactions, rash pain macrolide or
caused by H. infdluenzae, illness or risk at injection site fluoroquinolone
M catarrhalis or S. factors (such as pruritus. class drugs also
pneumoniae cystic fibrosis, Other: angioedema have potential to
To prevent disseminated nosocomially cause QT-interval
Mycobacterium avium acquired infections, prolongation and
complex in patients with known or other significant
advanced HIV infection suspected adverse effects.
Bacterial conjunctivitis bacteremia; -Warn patient to
caused by coryneform hospitalized, seek immediate
group G, H. influenza elderly, or medical care for
Staphylococcus aureus, debilitated irregular heartbeat,
Streptococcus mitis group. patients; or shortness of
patients with breath, dizziness or
immunodeficiency fainting.
or functional
asplenia.
Elderly patients
may be at
increased risk for
drug associated QT-
interval effects.
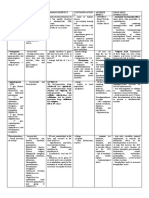
DRUG CLASSIFIACATION/INDICATI MECHANISM CONTRAINDICATION ADVERSE REACTION DOSE, NURSING
ON OF ACTION ROUTE, RESPONSIBILI
FREQUENC TIES
Y
Bespri Initial treatment of CV disorders eg, Thought to -Avoid use in patients with -GI disturbances eg, 75-100 mg Give the
n angina pectoris & MI. Prevention of produce severe hepatic impairment nausea, dyspepsia & medication on a
cerebrovascular disorders eg, analgesia and or history of active peptic vomiting. Urticaria & schedule rather
stroke. exert its anti- ulcer disease. other skin eruptions, than as needed.
inflammatory -use cautiously in patients angioedema, rhinitis &
effected by with GI lesions impaired severe/fatal paroxysmal -Monitor elderly
inhibiting renal function, bronchospasm & dyspnea. patients closely
prostaglandin hypoprothrombinemia, Increased bleeding time, because they may
and other vitamin K deficiency, decreased platelet be more
substances that thrombotic adhesiveness & susceptible to
sensitize pain thrombocytopenic purpura. hypoprothrombinemia aspirins toxic
receptors. Drug (large dose). May exhibit effects.
may relieve cross-sensitivity to other
fever through NSAIDs. Symptoms of -Monitor patient
central action in salicylism eg, dizziness, for
the tinnitus, deafness, hypersensitivity
hypothalamic sweating, nausea & reactions such as
heat-regulating vomiting, headache & anaphylaxis and
center. In low mental confusion; trauma.
doses, drug also
appears to
interfere with
clothing by
keeping a
platelet-
aggregating
substance from
forming.
DRUG CLASSIFIACATION/INDICATI MECHANISM CONTRAINDICATIO ADVERSE DOSE, NURSING
ON OF ACTION N REACTION ROUTE, RESPONSIBILITIES
FREQUENC
Y
Provasc - Chronic stable angina, Inhibits calcium -contraindicated in CNS: Oral ; Monitor patient carefully.
vasospatic angina; to reduce ion influx patients hypersensitive headache, 500mg /tab Some patients, especially
Generic risk of hospitalization across cardiac to drug. fatigue, those with severe
name – because of angina; to reduce and smooth- -use cautiously in dizziness obstructive CAD, have
amlodipine risk of coronary muscle cells, patients receiving other CV: edema, developed increased
revascularization procedure dilates coronary peripheral vasodilators, flushing, frequency, duration or
in patients with recently arteries and especially those with palpitations severity of angina or acute
documented CAD by arterioles and GI: nausea, MI after inhibition of
severe aortic stenosis or
angiography and without HF decrease BP abdominal calcium channel blocker
hypertrophic
or with LVEF less than 40% and myocardial pain therapy or at time of
- Hypertension oxygen cardiomyopathy with Respiratory: dosage increase.
demand. outflow tract pulmonary
obstruction, and in edema,
patients with HF with dyspnea
reduced LVEF. Because Skin: prutish,
drug is metabolized by rash.
the liver, use cautiously
and reduce dosage in
patients with severe
hepatic diseases.
You might also like
- Azithromycin Drug StudyDocument2 pagesAzithromycin Drug StudyMelissa Marie Custodio100% (1)
- Drug Study of CiprofloxacinDocument3 pagesDrug Study of CiprofloxacinZyra MendozaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study GuideDocument2 pagesDrug Study GuideAubrey SungaNo ratings yet
- Drug Name Therapeutic Actions Indications Adverse Effect Indication Contraindication Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument5 pagesDrug Name Therapeutic Actions Indications Adverse Effect Indication Contraindication Nursing ResponsibilitiesJoshua Davantes100% (1)
- Azithromycin Drug StudyDocument1 pageAzithromycin Drug StudyChristine IbiasNo ratings yet
- Drug Study of Generation Antibiotics Mohamedzein, Nura Mohamedzein, SalwaDocument8 pagesDrug Study of Generation Antibiotics Mohamedzein, Nura Mohamedzein, SalwaNone BbNo ratings yet
- Drug Study (Clindamycin)Document1 pageDrug Study (Clindamycin)roseonabreeze100% (7)
- Drug StudyDocument2 pagesDrug StudyMonica Gagarin CortezNo ratings yet
- 2018 COMPARATIVE MICRO MeningoencephalitisDocument6 pages2018 COMPARATIVE MICRO MeningoencephalitisMarianneTee-ruhNo ratings yet
- AzithromycinDocument1 pageAzithromycinGrape JuiceNo ratings yet
- Drug Study ICUDocument3 pagesDrug Study ICURolina ParagasNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument5 pagesDrug Studyapi-3717941100% (6)
- Drug Study-ClindamycinDocument3 pagesDrug Study-ClindamycinDUMANGENG ELLAINE D.100% (1)
- AzithromycinDocument3 pagesAzithromycinnekoleanNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument4 pagesDrug StudyJavie Bryant RedilNo ratings yet
- Bibliography: Life Span - Philadelphia, PA 19103: F.A. Davis CompanyDocument5 pagesBibliography: Life Span - Philadelphia, PA 19103: F.A. Davis CompanyCarlos LleverNo ratings yet
- Drug Classificati ON Indication Contraindica Tion Side Effects Nursing Responsibili TiesDocument2 pagesDrug Classificati ON Indication Contraindica Tion Side Effects Nursing Responsibili TiesMelduard Godwin R. PulidoNo ratings yet
- Name Mode of Action Indications Contraindications Adverse Effects Health Teaching Generic Name: Classifications: CNS: Chills, FatigueDocument2 pagesName Mode of Action Indications Contraindications Adverse Effects Health Teaching Generic Name: Classifications: CNS: Chills, FatigueAngelica OlivarNo ratings yet
- Macrolide Drug StudyDocument3 pagesMacrolide Drug StudyEmagra AzilNo ratings yet
- FNP-Board ReviewDocument94 pagesFNP-Board ReviewSoojung Nam95% (22)
- CEFUROXIMEDocument2 pagesCEFUROXIMEMelvz BallesterosNo ratings yet
- Drug Index Generic Name MOA Clinical Uses Side Effects/ Contraindications DosageDocument3 pagesDrug Index Generic Name MOA Clinical Uses Side Effects/ Contraindications Dosageyoke limuriaNo ratings yet
- Wesleyan: College of Nursing and Allied Medical SciencesDocument2 pagesWesleyan: College of Nursing and Allied Medical SciencesShane Aileen AngelesNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument2 pagesDrug StudyRoland YusteNo ratings yet
- CeftriaxoneDocument1 pageCeftriaxoneJayson Almario Aranas100% (2)
- Aminoglycosides - Synergistic Bactericidal EffectDocument12 pagesAminoglycosides - Synergistic Bactericidal EffectBern NerquitNo ratings yet
- BCG Vaccine Drug StudyDocument2 pagesBCG Vaccine Drug StudyLegendX83% (6)
- Case Study of Black Death: Our Lady of Fatima UniversityDocument7 pagesCase Study of Black Death: Our Lady of Fatima UniversityJanna PimentelNo ratings yet
- Drug Study in GentamicinDocument2 pagesDrug Study in Gentamicinanthony_alviar100% (1)
- AmpicillinDocument3 pagesAmpicillinIvy RuzolNo ratings yet
- AsncudDocument2 pagesAsncudJaylord VerazonNo ratings yet
- Isah Drug StudyDocument2 pagesIsah Drug StudyJames AbendanNo ratings yet
- CefuroximeDocument1 pageCefuroximeAbijah Leris SarmientoNo ratings yet
- Cefuroxime (Drug Study)Document2 pagesCefuroxime (Drug Study)Rosebel LaguraNo ratings yet
- Microbiology Assignment. ADocument26 pagesMicrobiology Assignment. ACynthia AbbangNo ratings yet
- Drugstudy 20Document9 pagesDrugstudy 20MahledJoy EnriquezNo ratings yet
- Case Pres Drug StudyDocument3 pagesCase Pres Drug StudyMark Teofilo Dela PeñaNo ratings yet
- Tetracycline Drug StudyDocument5 pagesTetracycline Drug StudyEmagra AzilNo ratings yet
- Diphteria, Pertussis and Staphylococcal Infections-1Document15 pagesDiphteria, Pertussis and Staphylococcal Infections-1Nwosu Ogbonna GabrielNo ratings yet
- Azi FinDocument1 pageAzi FinpeternohibiNo ratings yet
- Penicillin Drug StudyDocument2 pagesPenicillin Drug StudyEmagra AzilNo ratings yet
- DRUG-STUDY Piptaz ClindamycinDocument2 pagesDRUG-STUDY Piptaz ClindamycinJAYMIE ROSE M. MANUELNo ratings yet
- Clarithromycin Drug StudyDocument1 pageClarithromycin Drug StudyDivine LavaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Dose, Route and Frequency Mechanism of Action Indications Contra-Indications Side Effects Adverse Effects Nursing ConsiderationDocument8 pagesDrug Study Dose, Route and Frequency Mechanism of Action Indications Contra-Indications Side Effects Adverse Effects Nursing Considerationsneb1392No ratings yet
- ContraindicationDocument1 pageContraindicationichiro017No ratings yet
- NICU Drug StudyDocument2 pagesNICU Drug StudyMay Chelle ErazoNo ratings yet
- Clarithromycin (Biaxin)Document1 pageClarithromycin (Biaxin)Jocelyn Rivera100% (1)
- AlphaDocument11 pagesAlphaAlphagene FontanillaNo ratings yet
- Medication Management in OBDocument5 pagesMedication Management in OBLouwella RamosNo ratings yet
- Drug Study MMRDocument2 pagesDrug Study MMRErika Marie Calucab100% (2)
- Drug Study Ko BFF Pa-Print Pls Thanks Much Mwa!Document3 pagesDrug Study Ko BFF Pa-Print Pls Thanks Much Mwa!shasheeeeyNo ratings yet
- ... Drug Study...Document2 pages... Drug Study...Chona FontanillaNo ratings yet
- ClindamycinDocument2 pagesClindamycinassilamorNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY Bronchitis CorsigaDocument8 pagesDRUG STUDY Bronchitis CorsigaKasandra Dawn Moquia BerisoNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument3 pagesDrug StudyRainny CommsNo ratings yet
- Pregnancy Category BDocument6 pagesPregnancy Category BMBCNo ratings yet
- Patient 6 Drug Study Day 1 BCGDocument4 pagesPatient 6 Drug Study Day 1 BCGJackieMae100% (1)
- Step 2 UWORLD Sub DivisionDocument323 pagesStep 2 UWORLD Sub DivisionabimurgenNo ratings yet
- Infections in Cancer Chemotherapy: A Symposium Held at the Institute Jules Bordet, Brussels, BelgiumFrom EverandInfections in Cancer Chemotherapy: A Symposium Held at the Institute Jules Bordet, Brussels, BelgiumNo ratings yet
- Case Ana-Hypothyroidism 2020Document7 pagesCase Ana-Hypothyroidism 2020Nicole cuencosNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology CLEFT LIP AND CLEFT PALATEDocument2 pagesPathophysiology CLEFT LIP AND CLEFT PALATENicole cuencosNo ratings yet
- Fdar-Labor PainDocument5 pagesFdar-Labor PainNicole cuencos100% (1)
- Weigght Gain NCPDocument1 pageWeigght Gain NCPNicole cuencosNo ratings yet
- Drug Classification/Indicati ON Mechanis MOF Action Contraindication Adverse Reaction Dose, Route, Frequenc Y Nursing Responsibiliti ESDocument5 pagesDrug Classification/Indicati ON Mechanis MOF Action Contraindication Adverse Reaction Dose, Route, Frequenc Y Nursing Responsibiliti ESNicole cuencosNo ratings yet
- Labor Pain Case StudyDocument7 pagesLabor Pain Case StudyNicole cuencosNo ratings yet
- COLON CANCER NCP-impaired nutrITIONDocument3 pagesCOLON CANCER NCP-impaired nutrITIONNicole cuencosNo ratings yet
- Weigght Gain NCPDocument1 pageWeigght Gain NCPNicole cuencosNo ratings yet
- APPENDIC CASES Cuenco2020Document3 pagesAPPENDIC CASES Cuenco2020Nicole cuencosNo ratings yet
- Depression Case StudyDocument1 pageDepression Case StudyNicole cuencos100% (1)
- Alteration of The Starling Forces Which Control Transfer of Fluid From The Vascular Compartment To Surrounding Tissue SpacesDocument3 pagesAlteration of The Starling Forces Which Control Transfer of Fluid From The Vascular Compartment To Surrounding Tissue SpacesNicole cuencosNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan - Acute Pain Assessment Diagnosis Scientific Rationale Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan - Acute Pain Assessment Diagnosis Scientific Rationale Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationNicole cuencosNo ratings yet
- Appendicities Disease Process Nursing ProcessDocument2 pagesAppendicities Disease Process Nursing ProcessNicole cuencosNo ratings yet
- Schizophrenia NCPDocument2 pagesSchizophrenia NCPNicole cuencos100% (2)
- Deficient Fluid Volume Related To Polyuria and Dehydration AEB Dry Mucus MembraneDocument1 pageDeficient Fluid Volume Related To Polyuria and Dehydration AEB Dry Mucus MembraneNicole cuencosNo ratings yet
- NCP - Impaire Urinary EliminationDocument3 pagesNCP - Impaire Urinary EliminationNicole cuencosNo ratings yet
- Nursing Drug StudyDocument10 pagesNursing Drug StudyNicole cuencosNo ratings yet
- Deficient Fluid Volume Related To Polyuria and Dehydration AEB Dry Mucus MembraneDocument1 pageDeficient Fluid Volume Related To Polyuria and Dehydration AEB Dry Mucus MembraneNicole cuencosNo ratings yet
- Alteration of The Starling Forces Which Control Transfer of Fluid From The Vascular Compartment To Surrounding Tissue SpacesDocument3 pagesAlteration of The Starling Forces Which Control Transfer of Fluid From The Vascular Compartment To Surrounding Tissue SpacesNicole cuencosNo ratings yet
- Spinal Bifida Ncp-Impaired Physical MobilityDocument3 pagesSpinal Bifida Ncp-Impaired Physical MobilityNicole cuencos50% (2)
- Computation FormulasDocument1 pageComputation FormulasNicole cuencosNo ratings yet
- Duavent Drug StudyDocument2 pagesDuavent Drug StudyNicole cuencosNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Subjective CuesDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan: Subjective CuesNicole cuencosNo ratings yet
- Communicable Disease NursingDocument44 pagesCommunicable Disease NursingFreeNursingNotes100% (17)
- Top Communicable Diseases in The Philippines 2019Document4 pagesTop Communicable Diseases in The Philippines 2019Nicole cuencosNo ratings yet
- Significance of The Study & Scope, Limitations and Delimitations-HIV2019Document1 pageSignificance of The Study & Scope, Limitations and Delimitations-HIV2019Nicole cuencosNo ratings yet
- SgotsgptDocument23 pagesSgotsgptUmi MazidahNo ratings yet
- SBAR HandoutDocument3 pagesSBAR HandoutNikiNo ratings yet
- DR Paul Krawitz - Ultimate Insiders Guide To Eye HealthDocument60 pagesDR Paul Krawitz - Ultimate Insiders Guide To Eye HealthPro ANo ratings yet
- Altamash Shabbir Maniyar Resume 22-05-2023-04-03-54 230601 200613Document3 pagesAltamash Shabbir Maniyar Resume 22-05-2023-04-03-54 230601 200613Kanhaiya VermaNo ratings yet
- Koch PostulatesDocument1 pageKoch PostulatescdumenyoNo ratings yet
- Maternal Serum Alpha-Fetoprotein (MSAFP)Document2 pagesMaternal Serum Alpha-Fetoprotein (MSAFP)Shaells JoshiNo ratings yet
- Program and Proceedings - 11th International Regional "Stress and Behavior" Neuroscience and Biopsychiatry Conference (North America), June 22-24, 2017, Miami Beach, FL, USADocument49 pagesProgram and Proceedings - 11th International Regional "Stress and Behavior" Neuroscience and Biopsychiatry Conference (North America), June 22-24, 2017, Miami Beach, FL, USAISBS_SocietyNo ratings yet
- Anti Dumping DietDocument3 pagesAnti Dumping DietFelixDrummaruNo ratings yet
- Discharge Planning ProjectDocument5 pagesDischarge Planning Projectapi-325271731No ratings yet
- Physical FormDocument4 pagesPhysical Formapi-352931934No ratings yet
- Adoptive Immunotherapy - Methods and Protocols - B. Ludewig, M. Hoffmann (Humana, 2005) WW PDFDocument517 pagesAdoptive Immunotherapy - Methods and Protocols - B. Ludewig, M. Hoffmann (Humana, 2005) WW PDFSilviuNo ratings yet
- The Smart Chiropractor A Guide To Marketing Your PracticeDocument43 pagesThe Smart Chiropractor A Guide To Marketing Your PracticeAaron DriverNo ratings yet
- Biblical Support To The Use of Plants For Medicinal Purposes: in African Perspective 2020Document24 pagesBiblical Support To The Use of Plants For Medicinal Purposes: in African Perspective 2020Nwaozuru JOHNMAJOR ChinecheremNo ratings yet
- Health Income and Poverty - Where We Are and What Could HelpDocument1 pageHealth Income and Poverty - Where We Are and What Could Helpapi-466415791No ratings yet
- Secrets of Korean MedicineDocument70 pagesSecrets of Korean Medicineemedronho4550100% (3)
- Investigations For Diseases of The Tongue A Review PDFDocument6 pagesInvestigations For Diseases of The Tongue A Review PDFShantanu DixitNo ratings yet
- Pod Uveitis Book RevDocument252 pagesPod Uveitis Book Revelika dwi100% (1)
- Sales and Distribution Management PDFDocument30 pagesSales and Distribution Management PDFNalin SenthilNo ratings yet
- Referat Distosia Bahu ElfaDocument16 pagesReferat Distosia Bahu ElfaElfa RiniNo ratings yet
- Telepharmacy ResearchDocument8 pagesTelepharmacy Researchugwuja marcyNo ratings yet
- Passenger/Traveler Details: Undertaking and Acknowledgement Form Related To COVID-19 Health MeasuresDocument1 pagePassenger/Traveler Details: Undertaking and Acknowledgement Form Related To COVID-19 Health MeasuresLabli BicNo ratings yet
- Automated DatabasesDocument14 pagesAutomated DatabasesAnilkumar Sagi100% (4)
- Ventilator Draeger Evita V300 - Spesifikasi Teknis PDFDocument4 pagesVentilator Draeger Evita V300 - Spesifikasi Teknis PDFArifyadin SudonoNo ratings yet
- Audits & Inspections CRO Perspective: DR - Prashant BodheDocument74 pagesAudits & Inspections CRO Perspective: DR - Prashant BodheJayanta DasguptaNo ratings yet
- Malnutrition in Older AdultsDocument44 pagesMalnutrition in Older Adultsjohnjoe subaynoNo ratings yet
- Tutorial PathologyDocument4 pagesTutorial PathologyNURIN INSYIRAH MOHD ZAMRINo ratings yet
- Overt Diabetes in PregnancyDocument12 pagesOvert Diabetes in PregnancyGestne AureNo ratings yet
- Hypertension and Cardiac Arrhythmias A Consensus Document From The Ehra and Esc Council On Hypertension Endorsed by Hrs Aphrs and SoleaceDocument21 pagesHypertension and Cardiac Arrhythmias A Consensus Document From The Ehra and Esc Council On Hypertension Endorsed by Hrs Aphrs and SoleaceDaimon MichikoNo ratings yet
- Protocolo Cochrane REHABILITACIÓN COGNITIVA en Demencia (2019)Document17 pagesProtocolo Cochrane REHABILITACIÓN COGNITIVA en Demencia (2019)Sara Daoudi FuentesNo ratings yet
- Name of Pharmacy: ................................. CityDocument1 pageName of Pharmacy: ................................. Cityravi sheladiyaNo ratings yet