Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Vicia Faba Dracocephalum Moldavica
Uploaded by
International Network For Natural SciencesOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Vicia Faba Dracocephalum Moldavica
Uploaded by
International Network For Natural SciencesCopyright:
Available Formats
J. Bio. & Env. Sci.
2017
Journal of Biodiversity and Environmental Sciences (JBES)
ISSN: 2220-6663 (Print) 2222-3045 (Online)
Vol. 10, No. 6, p. 186-192, 2017
http://www.innspub.net
RESEARCH PAPER OPEN ACCESS
Growth characteristics and grain yield of faba bean (Vicia faba L.)
as influenced by intercropping with Moldavian balm
(Dracocephalum moldavica) and fertilizers application
Leyli Vafadar-Yengeje*, Rouhollah Amini, Adel Dabbagh Mohammadi-Nasab
Department of Plant Ecophysiology, Faculty of Agriculture, University of Tabriz, Tabriz, Iran
Article published on June 24, 2017
Key words: Faba bean, Grain yield, Intercropping, Organic fertilizer, Vermicompost
Abstract
In order to evaluate the effect of different fertilizer treatments and intercropping patterns on growth characteristics
and grain yield of faba bean (Vicia faba L.), a field experiment was conducted as factorial on the bases of
randomized complete block design with three replications in 2015. The first factor was four cropping systems
including monoculture of faba bean; row intercropping of faba bean with Moldavian balm (Dracocephalum
moldavica) at three patterns (1 row faba bean-1 row Moldavian balm; 2 rows faba bean-2 row Moldavian balm; 4
rows faba bean-2 row Moldavian balm and the second factor was three levels of fertilizers including 100% chemical
fertilizer, 50% chemical fertilizer + biofertilizers (Azoto barvar + Barvar 2) and vermicompost. The results showed
that the maximum chlorophyll content index and leaf number per plant was obtained in chemical fertilizer
treatment. The highest plant height (62.14cm) was observed in 1:1 intercropping system. The effect of fertilizer
treatment was not significant on plant height. The highest amount of number of pods per plant (3.52) was obtained
from 2:2 intercropping system and chemical fertilizer application. The maximum grain yield per occupied unit area
was observed in sole cropping (279.41g/m2) and among fertilizer treatments was belonged to 100% chemical
fertilizer (222.08g/m2). In comparison of intercropping patterns the 2-4 faba bean- Moldavian balm pattern could
be recommended to farmers for higher faba bean growth and production.
*Corresponding Author: Leyli Vafadar-Yengeje vafadar.leyla@gmail.com
186 | Yengeje et al.
J. Bio. & Env. Sci. 2017
Introduction The continued use of chemical fertilizers causes health
In recent years, a trend in agricultural production and environmental hazards such as ground and surface
systems has changed towards achieving high water pollution by nitrate leaching. Intensive use of
productivity and promotes sustainability over time. chemical fertilizers and other chemicals has produced
Farmers are developing different crop production environmental problems and increased production
systems to increase productivity and sustainability costs. There centesimo crisis and environmental
since ancient times. This includes crop rotation, relay problems has raised interest in environmental friendly
cropping and intercropping of major crops with other sustainable agricultural practices, which can reduce
crops. Intercropping, the agricultural practice of input costs (Salantur et al., 2005).
cultivating two or more crops in the same space at the
Biofertilizers are becoming increasingly popular in
same time is an old and commonly used cropping
many countries and for many crops. They are defined
practice which aims to match efficiently crop demands
as products containing active or latent strains of soil
to the available growth resources and labor. The most
microorganisms, either bacteria alone or in
common advantage of intercropping is the production
combination with algae or fungi that increase the plant
of greater yield on a given piece of land by making
availability and uptake of mineral nutrients (Vessey,
more efficient use of the available growth resources
2003). There is a wide range of reports on the effect of
using a mixture of crops of different rooting ability,
biofertilizer application in crops. Razie and Anas
canopy structure, height, and nutrient requirements
(2008) claimed that the inoculation of rice seedlings
based on the complementary utilization of growth
with Azotobacter spp. and Azospirillum spp. was able
resources by the crops (Silwana and Lucas, 2002).
to substitute for the application of inorganic N
Grain legumes (pulses) such as faba bean (Viciafaba fertilizer, and that this technology enabled rice yields of
3.9 to 6.4 ton/ha (yield increases in comparison with
L.) are rich in protein and suited for animal feed as
the control were about 2–3 ton/ha).
well as for human diet. Other positive effects of faba
bean is the symbiotic nitrogen (N2) fixation (SNF)
Vermiform posting is a low-cost method of treating
ability supplying N for agriculture, recycling of N-rich
organic wastes exploiting the ability of some earthworms
crop residues and the break-crop effect in cereal-rich
to fragment the waste residuals in their grinding gizzards
rotations (Jensen, 1997).
(Atiyeh et al., 2002).
The Moldavian balm (Dracocephalum moldavica L.)
The digestion process fragments the waste substrate,
is an annual, herbaceous, essential oil-producing,
accelerates rates of decomposition and increases its
spicy aromatic medicinal plant of the deadnettle
plant available nutrient content. Vermicomposts can
family (Lamiaceae), which reaches 25-75cm in height.
contain biologically active substances such as plant
D. moldavica contains 0.06–0.92% essential oil, with
growth regulators and have frequently been shown to
the maximal level during flowering. Its lemon-like increase plant growth rates in glasshouse and field trials,
scented essential oil consists mainly of oxygenated whether used as a soil additive or as a substitution to
acyclic monoterpenes, e.g. geraniol, geranyl acetate, soilless growth media. Most studies have reported
geranial, neral and nerylacetate. It has been reported beneficial effects of vermicompost on germination, plant
that the plant possesses antibacterial, antioxidant and growth and yield with substitutions of 20-40% of
cardio protective effects (Dastmalchi et al., 2007). vermicompost into a commercial growth medium
(Chaoui et al., 2003; Arancon et al., 2004).
Plant nutrition is one of the most important factors
that increase plant production. The use of chemical Intercropping of faba bean and Moldavian balm
fertilizers has been increased worldwide for plant would increase the productivity of these crops in this
production due to availability of inexpensive region also the effect of different fertilizer treatments
fertilizers (Abril et al., 2007). could be evaluated.
187 | Yengeje et al.
J. Bio. & Env. Sci. 2017
So the aims of this study were investigating the effect The triple super phosphate was used at planting time.
of different intercropping patterns of faba bean and The first irrigation was done after planting and the
Moldavian balm on some growth parameters and next irrigations were performed once a week by
grain yield of faba bean. furrow irrigation method.
Material and methods Measurement of traits
Site description and experimental design To specify plant height and pod number per plant, ten
The field experiment was conducted in 2015 at the plants were selected from the middle of the plots and
Research Farm of the University of Tabriz, Iran then, they were measured. Also at maturity, to
(latitude 38°05_N, longitude 46°17_E, altitude 1360 determine of grain yield an area equal to 1m2 was
m above sea level). The climate of research area is harvested from middle part of each plot considering
characterized by mean annual precipitation of 285 border effect. Harvested plants were dried in 25°C
mm, mean annual temperature of 10°C, mean annual and under shadow and air flow, and then grains were
maximum temperature of 16.6°C and mean annual separated from the remains by threshing. At
minimum temperature of 4.2°C. flowering stage, three plants were randomly selected
and chlorophyll content index (CCI) of upper, middle
The experiment was arranged as factorial based on and lower leaves was measured by a chlorophyll
randomized complete block design with 12 treatments meter (CCM-200, Opti-Science, USA).
and three replications. The first factor was four
cropping systems including monocropping of faba Statistical analysis
bean; row intercropping of faba bean with Moldavian Statistical analysis of the data was performed with
balm at three patterns (1 row faba bean-1 row MSTAT-C software. Duncan multiple range test was
Moldavian balm; 2 rows faba bean-2 row Moldavian applied to compare means of each trait at 5%
balm; 4 rows faba bean-2 row Moldavian balm and probability.
the second factor was three levels of fertilizers as
100% chemical fertilizer, 50% chemical fertilizer + Results and discussion
biofertilizer (Azoto barvar + Barvar 2) and Chlorophyll content index, significantly affected by
vermicompost. The 100% chemical fertilizer was urea fertilizer treatment, but cropping pattern and their
at a rate of 50kg/ha and 80kg/ha triple super interaction had no effect on this trait (Table 1).
phosphate. The biofertilizer was Azoto barvar + Minimum Chlorophyll content index (33.39) was
Barvar 2 as inoculation with the seed at planting time obtained under vermicompost treatment (Fig. 1).
and the vermicompost was used in rate of 5 ton /ha. Highest Chlorophyll content index (39.22) was
The faba bean was planted at density of 40 achieved at 100% chemical fertilizers treatment (Fig.
plants/m2. The plot size (rows number) was different 1). Chlorophyll content is of particular significance to
for treatments with 5m long and 25cm row distance. precision in agriculture as an indicator of
At intercropping patterns the Moldavian balm was photosynthetic activity. A positive correlation
planted at the same rows with replacement patterns. between N fertilization and the chlorophyll content is
The bio-fertilizers were inoculated with faba bean and well documented for a number of plant species and
Moldavian balm seeds at planting time. has been investigated for rapid Ndetermination for
most major crops including corn, rice, wheat (Sabo et
The vermicompost was used before planting and al., 2002; Bojovic and Stojanovic, 2005; Houles et al.,
mixed with the soil. The urea fertilizer was used at 2007). The results obtained in this study are
three stages including planting time, three-leaf stage confirmed with those obtained by Kate et al., (2005)
and early flowering. on potato and Golkz et al., (2006) on Sweet basil.
188 | Yengeje et al.
J. Bio. & Env. Sci. 2017
Plant height of faba bean significantly affected by
cropping pattern. Effect of fertilizer treatment and
interaction effect of cropping pattern × fertilizer was not
significant on plant height (Table 1). The greatest faba
bean height was observed in 1-1 intercropping and this
was significantly different from the other cropping
systems (Fig. 2). The canopy characteristics of crops are
not constant, but may change due to the presence of
other crops species (Caldwell, 1987). This result is
similar with finding of Silwana and Lucas (2002) who
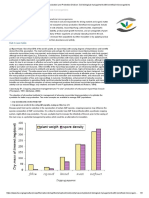
Fig. 1. Effect of different fertilizer treatments (F1, F2 reported that intercropping of maize with bean
and F3: chemical 100%, vermicompost and 50% enhanced the plant height of maize. In other results,
chemical + biofertilizer) on chlorophyll content index Thwala and Ossom (2004) did not find any significant
of faba bean (Different letters indicate significant difference in plant height between mono cropping and
differences at p≤ 0.05). intercropping of maize with sugar bean and ground nuts.
Table 1. Analysis of variance of faba bean traits affected by fertilizer and intercropping patterns.
Mean
Square
S.O.V df Pod
Chlorophyll Plant Leaf
number yield
content index height number
per plant
Block 2 3.402 1.381 0.91 0.204** 6706.078**
Cropping pattern (C) 3 0.014 35.69* 4.31 0.205** 26186.978**
Fertilizer(F) 2 107.383* 0.003 23.163* 0.739** 4574.774**
F×C 6 0.062 0.015 0.499 0.042** 37.782*
Error 22 19.283 8.914 4.426 0.004 10.532
*and ** = Significant at 5% and 1% probability level, respectively.
The lowest leaf number (14.2) was recorded under
vermicompost treatment (Fig. 3). Gulser (2005) also
reported that increments in the nitrogen rate of the
fertilizers increased the number of leaves in spinach.
Shahbazi (2005) showed that there was a significant
differences in the number of leaves among nitrogen
levels (0, 50, 100, 150 and 200kgN/ha), and that the
highest leaf number was obtained with 200kgN/ha.
Fig. 2. Effect of different cropping pattern on plant Our results showed that cropping pattern, fertilizer
height of faba bean (Different letters indicate treatment and interaction of cropping pattern and
significant differences at p≤ 0.05). fertilizer treatments had significant effect on pod
number per plant (Table 1). The maximum pod
There was no significant difference in leaf number of number per plant (3.52) was obtained from 2-2
faba bean among the cropping systems as shown in intercropping pattern and 100% chemical fertilizer
Table 1, but this trait significantly affected by fertilizer treatment (Fig.4). The minimum pod number per
treatments. The highest leaf number (16.6) of faba plant (2.65) obtained from 2-4 intercropping pattern
bean was obtained in 100% chemical fertilizer under vermicompost treatment (Fig. 4). Similarly,
treatment. Amir Mardfar et al., (2013) observed that at
189 | Yengeje et al.
J. Bio. & Env. Sci. 2017
intercropping of wheat and oilseed rape, strip In agreement to this research, the general trend in most
intercropping with 12 rows of wheat and 4 rows of intercropping experiments is that the grain yield of a
oilseed rape and application of 100% chemical given crop in a mixture are less than the yield of the
fertilizers had the highest spike per plant, grain yield same crop grown alone, but in total productivity per unit
and highest land equivalent ratio (LER), that of land is usually greater than for sole crop (Natarajan
indicates these cropping patterns could be and willy1981). Competition for soil moisture and
recommended to growers. nutrients could have been high and might have caused
the yields of faba bean to drop significantly. N fertilizer
in this study had a significant effect on faba bean grain
yield. Study on the effect of N fertilization on growth and
yield components showed increase in canola grain yield
(Ahmadi and Bahrani, 2009). Evaluating the
intercropping of corn, sunflower and soybean indicated
that the most grain yield of corn was obtained at
intercropping patterns of corn-soybean and corn-
soybean-sunflower-soybean (Amini et al., 2013).
Fig. 3. Effect of different fertilizer treatments (F1, F2 and Dabbagh Mohammad Nassab et al., (2015) found that
F3: chemical 100%, vermicompost and 50% chemical + application of bio-fertilizers had no significant effect on
biofertilizer) on leaf number of faba bean (Different grain yield of corn at intercropping with red kidney bean
letters indicate significant differences at p≤ 0.05). (Phaseolus vulgaris L.).
Fig. 4. The interaction effect of cropping pattern and Fig. 5. Effect of different fertilizer treatments (F1, F2 and
fertilizers (F1, F2 and F3: chemical 100%, F3: chemical 100%, vermicompost and 50% chemical +
vermicompost and 50% chemical + biofertilizer) on biofertilizer) on grain yield of faba bean (Different letters
pod number per plant of faba bean (Different letters indicate significant differences at p≤ 0.05).
indicate significant differences at p≤ 0.05).
Grain yield significantly affected by cropping pattern
and fertilizer treatments, whereas interaction of
cropping pattern and fertilizer treatments had no
significant effect on the grain yield (Table 1). The
highest grain yield (222.08g/m2) was observed in
100% chemical fertilizer and the lowest was observed
at vermicompost treatment (Fig. 5). The monoculture
cropping patterns had the highest faba bean grain Fig. 6. Effect of different cropping pattern on grain
yield (279.41g/m2) and the lowest grain yield was yield of faba bean (Different letters indicate
observed in 1-1 intercropping pattern (Fig. 6). significant differences at p≤ 0.05).
190 | Yengeje et al.
J. Bio. & Env. Sci. 2017
Conclusion Bojovic B, Stojanovic J. 2005. Chlorophyll and
In the present investigation, grain yield of faba bean carotenoid content in wheat cultivars as a function of
in sole system was generally greater than those of mineral nutrition. Archives of Biological Sciences 57,
intercropping system. It can be concluded that 283-290.
chemical fertilizers increased grain yield of faba bean
in sole and intercropping system. In comparison of Caldweel MM. 1987. Plant architecture and
intercropping patterns, the 2-4 faba bean-Moldavian resource competition. Ecological Studies 61, 164-179.
balm patterns could be recommended to growers for
higher faba bean growth and production. Chaoui HI, Zibilske LM, Ohno T. 2003. Effects of
earthworm casts and compost on soil microbial
References activity and plant nutrient availability. Soil Biology
Abril A, Baleani D, Casado-Murillo N, Noe L.
and Biochemistry 35, 295-302.
2007. Effect of wheat crop fertilization on nitrogen
dynamics and balance. Agriculture Ecosystems and Dabbagh-Mohammadi-Nassab A, Amini R,
Environment 119, 171- 176. Tamari E. 2015. Evaluation of maize (Zea mays L.)
and three cultivars of common bean (Phaseolus
Ahmadi M, Bahrani MJ. 2009. Yield and yield
vulgaris L.) intercropping with application of
components of rapeseed as influenced by water stress
biofertilizers and chemical fertilizers. Journal of
at different growth stages and nitrogen levels.
American-Eurasian Journal of Agriculture and Sustainable Agriculture and Production 25, 99-113.
Environmental Science 5, 755-761.
Dastmalchi K, Damien-Dorman HJ, Laakso I,
Allahdadi M, Shakiba MR, Dabbagh- Hiltunen R. 2007. Chemical composition and ant
Mohammadi-Nasab A, Amini R. 2013. Evaluation oxidative activity of Moldavian balm (Dracocephalum
of yield and advantages of soybean (Glycine max L.) and moldavica L.) extracts. Food Science and Technology
Calendula (Calendula officinalis L.) intercropping 40,1655-1663.
systems. Journal of Sustainable Agriculture and
Production 23, 47-58. Golcz A, Politycka B, Seidler-Lozykowska K.
2006. The effect of nitrogen fertilization and stage of
Amini R, An M, Pratley J, Azimi S. 2009. plant development on the mass and quality of sweet
Allelopathic assessment of annual ryegrass (Lolium basil leaves (Ocimum basilicumL.). Herba Polonica
rigidum): Bioassays. Allelopathy Journal 24, 67-76.
52, 22-30.
Amir-Mardfar R, Raei Y, Dabbagh-Mohammadi-
Gulser F. 2005. Effect of ammonium sulphate and
Nassab A, Khaghaninia S, Amini R. 2013. Yield
urea on accumulation nutrient contents in spinach.
and yield components of wheat as influenced by
Scientia Horticulturae 106, 330-340.
intercropping of oilseed rape and fertilizers. Journal of
Biodiversity and Environmental Sciences 3, 38-46. Houles V, Guerfi M, Mary B. 2007. Elaboration of
a nitrogen nutrition indicator for winter wheat based
Arancon NQ, Edwards CA, Bierman P, Welch C,
on leaf area index and chlorophyll content for making
Metzge JD. 2004. Influences of vermicompost on field
nitrogen recommendations. European Journal of
strawberries. Bioresearch Technology 93, 145-153.
Agronomy 27, 1-11.
Atiyeh RM, Arancon NQ, Edwards CA,
Metzger JD. 2002. The influence of earthworm- Jensen ES. 1996. Grain yield, symbiotic N2 fixation
processed pig manure on the growth and productivity and interspecific competition for inorganic N in pea–
of marigolds. Bioresearch Technology 81, 103-108. barley intercrops. Plant and Soil 182, 25-38.
191 | Yengeje et al.
J. Bio. & Env. Sci. 2017
Kate DM, Solanke AV, Tiwari TK, Nemade SM. Shahbazi M. 2005. Effects of different nitrogen
2005. Growth and yield of potato cultivars as affected by levels on the yield and nitrate in lettuce cultivars. MSc
integrated nutrient management system. Journal of Thesis, Islamic Azad University, Tehran Iran.
Maharashtra Agricultural Universities 30, 236-237.
Silwana TT, Lucas WO. 2002. The effect of planting
Natarajan M, Willey RW. 1981. Sorghum-pigeon
combinations and weeding and yield of components
pea intercropping and the effects of plant population
density. Journal of Agricultural Sciences 95, 51-58. crops of maize, bean and maize, pumpkin intercrops.
Journal of Agricultural Sciences 138, 193-200.
Razie F, Anas I. 2008. Effect of Azotobacter and
Azospirillum on growth and yield of rice grown on Thwala MG, Ossom EM. 2004. Legume-maize
tidal swamp rice fields in south Kalimantan. Jurnal
association influences crop characteristics and yields.
Tanah dan Lingkungan 10, 41-45.
4th international crop science congress. 26 Sep-01 Oct,
Sabo M, Teklic T, Vidovic I. 2002. Photosynthetic 2004. Brisbane, Australia.
productivity of two winter wheat varieties (Triticum
aestivum L.). Rostlinna Vybroba 48, 80-86. Vessey JK. 2003. Plant growth promoting
rhizobacteria as biofertilizers. Plant and Soil 255,
Salantur A, Ozturk A, Akten S, Sahin F,
571-586.
Donmez F. 2005. Effect of inoculation with non-
indigenous and indigenous rhizobacteria of Erzurum
(Turkey) origin on growth and yield of spring barley.
Plant and Soil 275, 147-156.
192 | Yengeje et al.
You might also like
- Functional Diversity of Mycorrhiza and Sustainable Agriculture: Management to Overcome Biotic and Abiotic StressesFrom EverandFunctional Diversity of Mycorrhiza and Sustainable Agriculture: Management to Overcome Biotic and Abiotic StressesNo ratings yet
- Effects of Azospirillum Bacteria and Gibberellin HormoneDocument8 pagesEffects of Azospirillum Bacteria and Gibberellin HormoneOliver TalipNo ratings yet
- Influence of Vermicomposted Soil Amendments On Plant Growth and Dry Matter Partitioning in Seedling ProductionDocument10 pagesInfluence of Vermicomposted Soil Amendments On Plant Growth and Dry Matter Partitioning in Seedling ProductionPremier PublishersNo ratings yet
- Effect of Different Intercropping Patterns and Fertilizers On Some Growth Characteristics of Faba Bean (Vicia Faba L.)Document7 pagesEffect of Different Intercropping Patterns and Fertilizers On Some Growth Characteristics of Faba Bean (Vicia Faba L.)Md Ashikur RahmanNo ratings yet
- Effect of The Combination Rhizophagus Intraradices and 50% of NPK On Maize (Zea Mays L.) Growth and Yield in Central Benin - IJAAR-Vol-16-No-1-p-1-15Document15 pagesEffect of The Combination Rhizophagus Intraradices and 50% of NPK On Maize (Zea Mays L.) Growth and Yield in Central Benin - IJAAR-Vol-16-No-1-p-1-15International Network For Natural SciencesNo ratings yet
- Assessing Growth and Yield of Two Maize Cultivars Under Different Levels of Vermicompost ApplicationDocument8 pagesAssessing Growth and Yield of Two Maize Cultivars Under Different Levels of Vermicompost ApplicationSaboor OfficialNo ratings yet
- Plant Production and Protection Division - Soil Biological Management With Beneficial MicroorganismsDocument3 pagesPlant Production and Protection Division - Soil Biological Management With Beneficial MicroorganismsCyberSquare IndiaNo ratings yet
- Nodulation, Growth and Yield Response of Five Cowpea (VignaDocument12 pagesNodulation, Growth and Yield Response of Five Cowpea (VignaPremier PublishersNo ratings yet
- Growth Nodulation and Yield Response of Soybean ToDocument9 pagesGrowth Nodulation and Yield Response of Soybean TomuhammadrafiqyNo ratings yet
- Nitro Kara ZimbaveDocument12 pagesNitro Kara Zimbavesiamak77No ratings yet
- Full+Paper_Isaias+--+ALDocument7 pagesFull+Paper_Isaias+--+ALfundalaytNo ratings yet
- Vermiwash and Vermicompost Effect on Tomato GrowthDocument6 pagesVermiwash and Vermicompost Effect on Tomato GrowthUtkarsh GoyalNo ratings yet
- Effects of vermicompost and IMO on growth and yield of cucumberDocument23 pagesEffects of vermicompost and IMO on growth and yield of cucumberTishianie O. JunioNo ratings yet
- Full Length Article Article Open AccessDocument5 pagesFull Length Article Article Open AccessVikash KumarNo ratings yet
- Gupta Et Al 2016 EJSBDocument8 pagesGupta Et Al 2016 EJSBrg1326No ratings yet
- JPP - Volume 9 - Issue 5 - Pages 449-458Document10 pagesJPP - Volume 9 - Issue 5 - Pages 449-458iffa afiqa khairaniNo ratings yet
- MuscapaperDocument10 pagesMuscapaperwxcwpbmmhqNo ratings yet
- Shahabuddin Et Al. 2021 - Agrivita CompressDocument10 pagesShahabuddin Et Al. 2021 - Agrivita Compressshahab69No ratings yet
- Dmbal publicationDocument13 pagesDmbal publicationArarsa LetaNo ratings yet
- Article 1 Biofertilizers and Sustainable AgricultureDocument12 pagesArticle 1 Biofertilizers and Sustainable AgriculturePaolita CortesNo ratings yet
- Crop Protection: Virender Sardana, Gulshan Mahajan, Khawar Jabran, Bhagirath S. ChauhanDocument7 pagesCrop Protection: Virender Sardana, Gulshan Mahajan, Khawar Jabran, Bhagirath S. ChauhanEdilsonGiraldoNo ratings yet
- LiteratureReviewMatrix AlphinelynM SildaDocument31 pagesLiteratureReviewMatrix AlphinelynM SildaApril Rose Silda MangyanNo ratings yet
- Jayraj Synposis Okra 1Document24 pagesJayraj Synposis Okra 1MOHIT SomaniNo ratings yet
- Fruits 75 (6), 281-287 Effect of Fertilizer Treatments On Fruit Nutritional Quality of Plantain Cultivars and Derived HybridsDocument7 pagesFruits 75 (6), 281-287 Effect of Fertilizer Treatments On Fruit Nutritional Quality of Plantain Cultivars and Derived HybridsSol InvictusNo ratings yet
- Pengaruh Mikroba Tanah Terhadap Pertumbuhan Dan Hasil Panen Kedelai (Glycine Max L.)Document6 pagesPengaruh Mikroba Tanah Terhadap Pertumbuhan Dan Hasil Panen Kedelai (Glycine Max L.)Annas Emma ANo ratings yet
- MainDocument26 pagesMainEstefania GarciaNo ratings yet
- GJESM Volume 7 Issue 3 Pages 401-418Document18 pagesGJESM Volume 7 Issue 3 Pages 401-418GJESMNo ratings yet
- IntercroppingincitrusDocument11 pagesIntercroppingincitrusmanishdgNo ratings yet
- Advances in Environmental BiologyDocument8 pagesAdvances in Environmental Biologyمحمّدرضا زرگران خوزانیNo ratings yet
- dashadiASB5 8 2011Document13 pagesdashadiASB5 8 2011Mohammad Mosharraf HossainNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2-REVIEW OF RELATED LITERATUREDocument18 pagesChapter 2-REVIEW OF RELATED LITERATUREMaria Lovella Misolas Diaz100% (1)
- 1 s2.0 S0570178320300324 MainDocument9 pages1 s2.0 S0570178320300324 MainAsh RafiNo ratings yet
- Kumar Et Al 2013 Evaluating The Plant Growth Promoting AbilityDocument8 pagesKumar Et Al 2013 Evaluating The Plant Growth Promoting AbilitykumarmicroNo ratings yet
- 1.isca Rjafs 2017 001Document4 pages1.isca Rjafs 2017 001zubairshahid1061No ratings yet
- Land Equivalent Ratio, Growth, Yield and Yield Components Response of Mono-Cropped vs. Inter-Cropped Common Bean and Maize With and Without Compost ApplicationDocument10 pagesLand Equivalent Ratio, Growth, Yield and Yield Components Response of Mono-Cropped vs. Inter-Cropped Common Bean and Maize With and Without Compost ApplicationsardinetaNo ratings yet
- Jurnal InternationalDocument8 pagesJurnal InternationalѼ҆҆҅҄҃҆҆҅҄҃-ҳ-Ѽ҆҆҅҄҃҆҆҅҄҃҆҆҅҄҃ Нттр.Шшш. Ыобѕрот.мр.сомNo ratings yet
- Journal Homepage: - : IntroductionDocument11 pagesJournal Homepage: - : IntroductionIJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet
- Biofertilizers A Nexus Between Soil FertilityDocument14 pagesBiofertilizers A Nexus Between Soil FertilityMAURICIO ALFONSO AGUILERA OSORIONo ratings yet
- Effects of Algal Bio-Fertilizer On The Growth Of: Vigna RadiataDocument5 pagesEffects of Algal Bio-Fertilizer On The Growth Of: Vigna RadiataerpublicationNo ratings yet
- 2 - 1-S2.0-S0304423818304886-MainDocument7 pages2 - 1-S2.0-S0304423818304886-MainWaldyr italo Serafim AraujoNo ratings yet
- Research Pepar Biofertilizers, Impact On Soil Fertility and Crop Productivity Under Sustainable AgricultureDocument7 pagesResearch Pepar Biofertilizers, Impact On Soil Fertility and Crop Productivity Under Sustainable AgriculturePradip GhuleNo ratings yet
- Growth, Yield and Quality of Papaya Improved by Organic FertilizersDocument16 pagesGrowth, Yield and Quality of Papaya Improved by Organic Fertilizersmwah mwahNo ratings yet
- Effect of Farmyard Manure and Planting Densities OnDocument6 pagesEffect of Farmyard Manure and Planting Densities OnRomeo SyNo ratings yet
- Seed Treatment With Liquid Microbial Consortia For Germination and Vigour Improvement in Tomato (Solanum Lycopersicum L.)Document6 pagesSeed Treatment With Liquid Microbial Consortia For Germination and Vigour Improvement in Tomato (Solanum Lycopersicum L.)Shailendra RajanNo ratings yet
- Influenceof FertilizeronmaizeandsoilDocument15 pagesInfluenceof FertilizeronmaizeandsoilAbdulmalik AlayandeNo ratings yet
- Noraina Thesis ProposalDocument18 pagesNoraina Thesis ProposalMAE ANN TOLENTINONo ratings yet
- Litreture ReviewDocument4 pagesLitreture ReviewWalter HudsonNo ratings yet
- Bio efficacyofOrganicFormulationsonCropProduction AReviewDocument18 pagesBio efficacyofOrganicFormulationsonCropProduction AReviewArsh SidhuNo ratings yet
- Applsci 13 01127 v2Document17 pagesApplsci 13 01127 v2NaztovenNo ratings yet
- Effects of Pre and Post-Emergence Herbicides on Chickpea GrowthDocument7 pagesEffects of Pre and Post-Emergence Herbicides on Chickpea GrowthFajar Islam SitanggangNo ratings yet
- Response of Maize Productivity To Nitrogen Fertilizer and Spraying With Blue Green Algae Extract - IJAARDocument11 pagesResponse of Maize Productivity To Nitrogen Fertilizer and Spraying With Blue Green Algae Extract - IJAARInternational Network For Natural SciencesNo ratings yet
- R. Preetham, Et AlDocument8 pagesR. Preetham, Et AlRamprakash tataNo ratings yet
- Integrated Nutrient Management Boosts Cluster Bean Growth and YieldDocument21 pagesIntegrated Nutrient Management Boosts Cluster Bean Growth and YieldMOHIT SomaniNo ratings yet
- A Review On Role of Bio-Fertilizers in Fruit Crops: Plant ArchivesDocument5 pagesA Review On Role of Bio-Fertilizers in Fruit Crops: Plant ArchivesParth HatiskarNo ratings yet
- Modification of Media For Banana in Vitro Propagation With Foliar Fertilizer and Coconut Water in Cv. RajabuluDocument10 pagesModification of Media For Banana in Vitro Propagation With Foliar Fertilizer and Coconut Water in Cv. RajabuluAbrahamEko SetiaAnugrahNo ratings yet
- Rawal and Pawar, 2017. Delonix Regia Inhibited MungbeanDocument6 pagesRawal and Pawar, 2017. Delonix Regia Inhibited MungbeanmnmsidhuNo ratings yet
- Effect of Organic-Cum-Inorganic Sources of Nutrients On Growth, Yield and Economical Gain From GuavaDocument6 pagesEffect of Organic-Cum-Inorganic Sources of Nutrients On Growth, Yield and Economical Gain From GuavaTJPRC PublicationsNo ratings yet
- Influence of Biofertilizers On Growth and Yield of Winged Bean (Psophocarpus Tetragonolobus (L.) DC.)Document4 pagesInfluence of Biofertilizers On Growth and Yield of Winged Bean (Psophocarpus Tetragonolobus (L.) DC.)Rocky ThokchomNo ratings yet
- Biofertilzer Application)Document10 pagesBiofertilzer Application)ahmad baqir taqiyNo ratings yet
- Diagne 2013Document9 pagesDiagne 2013Wendy BautistaNo ratings yet
- Structure of Zooplanktonic Communities in Lakes Ossa and Mwembe at Dizangue (Cameroun, Central Africa) - JBES 2021Document15 pagesStructure of Zooplanktonic Communities in Lakes Ossa and Mwembe at Dizangue (Cameroun, Central Africa) - JBES 2021International Network For Natural SciencesNo ratings yet
- Growth and Yield Performance of Pechay (Brassica Napus L.) in Hydroponics System As Influenced by Magnetic Field - IJAAR 2021Document8 pagesGrowth and Yield Performance of Pechay (Brassica Napus L.) in Hydroponics System As Influenced by Magnetic Field - IJAAR 2021International Network For Natural SciencesNo ratings yet
- Musa X Paradisiaca Manihot Esculenta FoutouDocument9 pagesMusa X Paradisiaca Manihot Esculenta FoutouInternational Network For Natural SciencesNo ratings yet
- Assessment of Bud-Grafting and Side-Grafting Techniques To Support The Improvement of Productivity and Quality of Somatic Embryogenesis Cocoa (Theobroma Cacao L.) in South SulawesiDocument9 pagesAssessment of Bud-Grafting and Side-Grafting Techniques To Support The Improvement of Productivity and Quality of Somatic Embryogenesis Cocoa (Theobroma Cacao L.) in South SulawesiInternational Network For Natural SciencesNo ratings yet
- A Cross Sectional Study On Bacteriological Profile and Antibiogram of Cholecystitis and Cholelithiasis - IJMM 2021Document7 pagesA Cross Sectional Study On Bacteriological Profile and Antibiogram of Cholecystitis and Cholelithiasis - IJMM 2021International Network For Natural SciencesNo ratings yet
- Reuse of Wastewater For Irrigation Purposes - JBES 2021 by INNSPUBDocument12 pagesReuse of Wastewater For Irrigation Purposes - JBES 2021 by INNSPUBInternational Network For Natural SciencesNo ratings yet
- Archive - April Issue 2021 by IJB Journals - INNSPUBDocument4 pagesArchive - April Issue 2021 by IJB Journals - INNSPUBInternational Network For Natural SciencesNo ratings yet
- Call For Paper 2022 - IJMM Journals by INNSpubDocument1 pageCall For Paper 2022 - IJMM Journals by INNSpubInternational Network For Natural SciencesNo ratings yet
- Reuse of Wastewater For Irrigation Purposes - JBES 2021 by INNSPUBDocument12 pagesReuse of Wastewater For Irrigation Purposes - JBES 2021 by INNSPUBInternational Network For Natural SciencesNo ratings yet
- The Effectiveness of Experience and Nature-Based Learning Activities in Enhancing Students Environmental Attitude - JBES @scribdDocument14 pagesThe Effectiveness of Experience and Nature-Based Learning Activities in Enhancing Students Environmental Attitude - JBES @scribdInternational Network For Natural SciencesNo ratings yet
- Study of Virulence Genes in Vancomycin Resistant Enterococci (Vre) From Animals and Human Clinical Isolates-IJB 2021Document15 pagesStudy of Virulence Genes in Vancomycin Resistant Enterococci (Vre) From Animals and Human Clinical Isolates-IJB 2021International Network For Natural SciencesNo ratings yet
- Ormosia Calavensis Litsea PhilippinensisDocument9 pagesOrmosia Calavensis Litsea PhilippinensisInternational Network For Natural SciencesNo ratings yet
- Medicinal Plants Used Against Epilepsy by The Local Communities of Sargodha Region, Pakistan-JBESDocument13 pagesMedicinal Plants Used Against Epilepsy by The Local Communities of Sargodha Region, Pakistan-JBESInternational Network For Natural SciencesNo ratings yet
- Call For Paper - IJAAR JournalsDocument1 pageCall For Paper - IJAAR JournalsInternational Network For Natural SciencesNo ratings yet
- Impact of Phragmanthera Capitata (Sprenge.) Balle On Pod and Beans Production of Two Cocoa Clones in Nkoemvone Seed Fields (South Cameroun) - JBES @scribdDocument9 pagesImpact of Phragmanthera Capitata (Sprenge.) Balle On Pod and Beans Production of Two Cocoa Clones in Nkoemvone Seed Fields (South Cameroun) - JBES @scribdInternational Network For Natural SciencesNo ratings yet
- Review On: Impact of Seed Rates and Method of Sowing On Yield and Yield Related Traits of Teff (Eragrostis Teff (Zucc.) Trotter) - IJAAR @scribdDocument8 pagesReview On: Impact of Seed Rates and Method of Sowing On Yield and Yield Related Traits of Teff (Eragrostis Teff (Zucc.) Trotter) - IJAAR @scribdInternational Network For Natural SciencesNo ratings yet
- Meat Tenderization Through Plant Proteases - A Mini Review-IjbDocument13 pagesMeat Tenderization Through Plant Proteases - A Mini Review-IjbInternational Network For Natural SciencesNo ratings yet
- The Effect of Seed Coat Removal On Seed Germination of Terminalia Superba Engl. & Diels-JBESDocument10 pagesThe Effect of Seed Coat Removal On Seed Germination of Terminalia Superba Engl. & Diels-JBESInternational Network For Natural Sciences100% (1)
- Research Paper: Journal NameDocument10 pagesResearch Paper: Journal NameInternational Network For Natural SciencesNo ratings yet
- Vegetative Propagation of Anonidium Mannii (Oliver) Engler & Diels (Annonaceae) by Leafy Stem Cuttings in Kisangani, DR Congo-IJAARDocument11 pagesVegetative Propagation of Anonidium Mannii (Oliver) Engler & Diels (Annonaceae) by Leafy Stem Cuttings in Kisangani, DR Congo-IJAARInternational Network For Natural SciencesNo ratings yet
- Occurrence Level of Urban and Peri-Urban Farming Activities Across Major Network Links of Nairobi County, Kenya - IJAAR @scribdDocument13 pagesOccurrence Level of Urban and Peri-Urban Farming Activities Across Major Network Links of Nairobi County, Kenya - IJAAR @scribdInternational Network For Natural SciencesNo ratings yet
- Effectiveness of Community Forest Association and Water Resource Users' Associations in Discharging Their Statutory Functions: A Case of Kilungu Catchment, Kenya - JBES - INNSPUBDocument16 pagesEffectiveness of Community Forest Association and Water Resource Users' Associations in Discharging Their Statutory Functions: A Case of Kilungu Catchment, Kenya - JBES - INNSPUBInternational Network For Natural SciencesNo ratings yet
- Carbonized Rice Hull (CRH) Silica Extract Efficiency For Yield and Nutrient Uptake of Cucumber - IJB JournalDocument7 pagesCarbonized Rice Hull (CRH) Silica Extract Efficiency For Yield and Nutrient Uptake of Cucumber - IJB JournalInternational Network For Natural SciencesNo ratings yet
- Impacts of Management and Modernization On Water Savings in Large Irrigation SystemsDocument11 pagesImpacts of Management and Modernization On Water Savings in Large Irrigation SystemsInternational Network For Natural SciencesNo ratings yet
- Findings From A Survey in Western Kenya To Determine The Soil Fertility Replenishment Technologies-IJAAR - INNSPUBDocument11 pagesFindings From A Survey in Western Kenya To Determine The Soil Fertility Replenishment Technologies-IJAAR - INNSPUBInternational Network For Natural SciencesNo ratings yet
- Performance Assessment of Water Filtration Plants in Pakistan MDocument15 pagesPerformance Assessment of Water Filtration Plants in Pakistan MInternational Network For Natural SciencesNo ratings yet
- Identification and Pharmacological Properties of Coastal Plants From Barangay Diguisit, Baler, Aurora - JBES-Vol-18-No-6Document11 pagesIdentification and Pharmacological Properties of Coastal Plants From Barangay Diguisit, Baler, Aurora - JBES-Vol-18-No-6International Network For Natural SciencesNo ratings yet
- Productivity and Quality of Sugar Beet As Affecting by Sowing and Irrigation Methods and Hill Spacings-IJAARDocument11 pagesProductivity and Quality of Sugar Beet As Affecting by Sowing and Irrigation Methods and Hill Spacings-IJAARInternational Network For Natural SciencesNo ratings yet
- Study of Virulence Genes in Vancomycin Resistant Enterococci (Vre) From Animals and Human Clinical - IJBDocument16 pagesStudy of Virulence Genes in Vancomycin Resistant Enterococci (Vre) From Animals and Human Clinical - IJBInternational Network For Natural SciencesNo ratings yet
- Prediction and Evaluation of Deleterious Non-Synonymous SNPs (NSSNPS) in Human IL17A Gene - IJB-2021Document12 pagesPrediction and Evaluation of Deleterious Non-Synonymous SNPs (NSSNPS) in Human IL17A Gene - IJB-2021International Network For Natural SciencesNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 2 of Thesis On Stabilization RahulDocument5 pagesCHAPTER 2 of Thesis On Stabilization RahulSanjay TiwariNo ratings yet
- C4008 - Geotechnic 2 (Kertas Soalan Politeknik-Politeknik Malaysia Kejuruteraan Awam)Document7 pagesC4008 - Geotechnic 2 (Kertas Soalan Politeknik-Politeknik Malaysia Kejuruteraan Awam)Azil14100% (1)
- Production Technology of RosemaryDocument17 pagesProduction Technology of RosemaryDr. Uttam Tripura100% (2)
- BorLog - SPT - Student Center - PolinemaDocument3 pagesBorLog - SPT - Student Center - PolinemaDoiti ImathuladaNo ratings yet
- MSC Thesis Updated Today PDFDocument89 pagesMSC Thesis Updated Today PDFDaguale Melaku AyeleNo ratings yet
- The Garden Yard A Handbook of Intensive FarmingDocument352 pagesThe Garden Yard A Handbook of Intensive Farmingliketoread100% (3)
- Cropsci AlugbatiDocument2 pagesCropsci AlugbatiDianne Nicole TioNo ratings yet
- Profile of Dillenia SerrataDocument2 pagesProfile of Dillenia SerrataSitti Rafiah Aminullah100% (1)
- Fabaceae Legume Angiosperms Asteraceae Sunflower Orchid Poaceae Grass PlantDocument4 pagesFabaceae Legume Angiosperms Asteraceae Sunflower Orchid Poaceae Grass PlantBert DayritNo ratings yet
- Rockwool in Horticulture, and Its Importance and Sustainable Use in New ZealandDocument10 pagesRockwool in Horticulture, and Its Importance and Sustainable Use in New ZealandWalid T. AlkhaldiNo ratings yet
- QTY Description Rate Per Day # of Working Days Estimated CostDocument5 pagesQTY Description Rate Per Day # of Working Days Estimated Costrazor freaksNo ratings yet
- Drained Strength Characteristics of Sands - DiscussionsDocument11 pagesDrained Strength Characteristics of Sands - DiscussionsAntuan PamplonaNo ratings yet
- How to set up irrigation systems in your greenhouseDocument4 pagesHow to set up irrigation systems in your greenhouseKevinNo ratings yet
- The Structure of The Flower 1Document11 pagesThe Structure of The Flower 1Gerald BenjaminNo ratings yet
- LandscapeDocument13 pagesLandscapetaapsiiiNo ratings yet
- Lawn Care Month by Month For PADocument6 pagesLawn Care Month by Month For PAKirk's Lawn Care100% (1)
- Listado AciDocument10 pagesListado AciRicardo Celi Macias100% (1)
- Rice Husk Ash Soil StabilizationDocument2 pagesRice Husk Ash Soil StabilizationBgee Lee100% (1)
- Oil CropsDocument19 pagesOil CropsThea VitalNo ratings yet
- 2nd Summative Test in Agriculture 6Document2 pages2nd Summative Test in Agriculture 6Bea Claresse Tarape0% (1)
- Prepare The Land For PlantingDocument11 pagesPrepare The Land For Plantingjeshmarie gumabayNo ratings yet
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Reinforced Brick MasonryDocument1 pageAdvantages and Disadvantages of Reinforced Brick MasonryKamran FareedNo ratings yet
- Plant PartsDocument3 pagesPlant Partsmonkey luffyNo ratings yet
- Analysis of RateDocument6 pagesAnalysis of Ratehs_civilNo ratings yet
- (Tangerine, Clementine, Mandarin) : Citrus ReticulataDocument4 pages(Tangerine, Clementine, Mandarin) : Citrus ReticulataAngelica GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Learning Level-1,2: Use of MaterialsDocument34 pagesLearning Level-1,2: Use of MaterialsUmair AshrafNo ratings yet
- BIOFERTILIZERDocument39 pagesBIOFERTILIZERkiranNo ratings yet
- 20 Common Urban Plants in IrelandDocument5 pages20 Common Urban Plants in Irelandapi-370321792No ratings yet
- C 011151719Document3 pagesC 011151719ARAV PRAJAPATINo ratings yet
- Seepage Behind Retaining WallsDocument15 pagesSeepage Behind Retaining WallsSania MehraNo ratings yet