Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Cells Reviewer
Uploaded by
Ivy Lumapac0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
66 views3 pagesOriginal Title
CELLS REVIEWER
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
66 views3 pagesCells Reviewer
Uploaded by
Ivy LumapacCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
ANATOMY – CELLS REVIEWER 40.
generally composed of one or more substances, called
solutes, dissolved in the predominant liquid or gas, which
1. basic living unit of all organisms is called the solvent
2. Within cells, specialized structures that perform specific 41. Solutes, such as ions or molecules, tend to move from an
functions area of higher concentration of a solute to an area of
3. an organelle containing the cell’s genetic material lower concentration of that same solute in solution.
4. living material surrounding the nucleus 42. The difference in the concentration of a solute in a
5. The cytoplasm is enclosed by the solvent between two points divided by the distance
6. Contains genetic material of cell (DNA) and nucleoli; between the two points.
site of RNA synthesis and ribosomal subunit assembly 43. An important means of transporting substances through
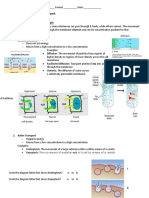
7. Site of protein synthesis the extracellular and intracellular fluids in the body
8. Has many ribosomes attached; site of protein synthesis 44. acts as a barrier to most water-soluble substances
9. Site of lipid synthesis; participates in detoxification 45. consist of large protein molecules that extend from one
10. Modifies protein structure and packages proteins in surface of cell membranes to the other
secretory vesicles 46. channels that constantly allow ions to pass through
11. Contains materials produced in the cell; formed by the 47. channels limit the movement of ions across the
Golgi apparatus; secreted by exocytosis membrane by opening and closing
12. Contains enzymes that digest material taken into the cell 48. A measure of the tendency of water to move by osmosis
13. Site of aerobic respiration and the major site of ATP across a selectively permeable membrane.
synthesis 49. the diffusion of water (a solvent) across a selectively
14. Supports cytoplasm; assists in cell division and forms permeable membrane, such as the cell membrane, from a
components of cilia and flagella region of higher water concentration to one of lower
15. Facilitate the movement of chromosomes during cell water concentration
division 50. the force required to prevent the movement of water
16. Move substances over surfaces of certain cells across a selectively permeable membrane
17. Propel sperm cells 51. Lower concentration of solutes and a higher
18. Increase surface area of certain cells concentration of water relative to the cytoplasm of the
19. Functions of the Cell cell.
52. Hypo means
53. The concentrations of various solutes and water are the
same on both sides of the cell membrane. The cell
therefore neither shrinks nor swells.
20. Cells synthesize various types of molecules, including 54. Iso means
proteins, nucleic acids, and lipids. 55. Hyper means
21. The chemical reactions that occur within cells are 56. The solution usually has a higher concentration of
collectively called cell metabolism. Energy released solutes and a lower concentration of water relative to the
during metabolism is used for cell activities. cytoplasm of the cell.
22. Cells produce and receive chemical and electrical signals 57. cell shrinkage is also called
that allow them to communicate with one another. 58. proteins within the cell membrane
23. Encloses the cytoplasm and forms the boundary between 59. It moves large, water-soluble molecules or electrically
material inside the cell and material outside it. charged ions across the cell membrane
24. Each cell contains a copy of the genetic information of 60. Carrier-mediated transport mechanisms exhibit
the individual. _____________; that is, only specific molecules are
25. The outermost component of a cell. transported by the carriers.
26. Substances outside the cell 61. three kinds of carrier mediated transport:
27. Substances inside the cell
28. Supports the cell contents, acts as a selective barrier that
determines what moves into and out of the cell, and plays
a role in communication between cells. 62. a carrier-mediated transport process that moves
29. The major molecules that make up the cell membrane substances across the cell membrane from an area of
30. model of cell structure is called the higher concentration to an area of lower concentration of
31. The polar, phosphate-containing ends of the that substance; movement is with the concentration
phospholipids are gradient, metabolic energy in the form of ATP is not
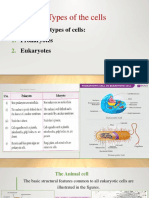
32. The nonpolar, fatty acid ends of the phospholipids are required.
33. ______________ within the phospholipid membrane 63. a carrier-mediated process that moves substances across
gives it added strength and flexibility the cell membrane from regions of lower concentration
34. ______________________ and carrier molecules are to those of higher concentration against a concentration
involved with the movement of substances through the gradient
cell membrane. 64. a genetic disorder that affects the active transport of Cl−
35. Are part of an intercellular communication system that into cells
enables cell recognition and coordination of the activities 65. moves Na+ out of cells and K+ into cells
of cells 66. Involves the active transport of one substance, such as
36. Cell membranes are ____________ ___________, Na+, across the cell membrane, establishing a
meaning that they allow some substances, but not others, concentration gradient.
to pass into or out of the cells 67. the diffusing substance moves in the same direction as
37. Movement through the cell membrane may be the transported substance
68. the diffusing substance moves in a direction opposite to
that of the transported substance
38. Does not require the cell to expend energy; mechanisms 69. Large water-soluble molecules, small pieces of matter,
include diffusion, osmosis, and facilitated diffusion. and even whole cells can be transported across cell
39. Does require the cell to expend energy, usually in the membranes in membrane-bound sacs called
form of ATP; mechanisms include active transport, _____________
secondary active transport, endocytosis, and exocytosis. 70. the uptake of material through the cell membrane by the
formation of a vesicle
71. This organelle invaginates (folds inward) to form a 106. small organelles with inner and outer membranes
vesicle containing the material to be taken into the cell. separated by a space
72. When a specific substance binds to the receptor 107. Folds that project like shelves into the interior of the
molecule, endocytosis is triggered, and the substance is mitochondria.
transported into the cell. This process is 108. major sites of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) production
called________________________ within cells
73. Examples of molecules that can be taken into a cell by 109. Mitochondria carry out what type of respiration?
receptor-mediated endocytosis. 110. A series of chemical reactions that require O2 to break
74. Used for endocytosis when solid particles are ingested. down food molecules to produce ATP
Cell-eating 111. consists of proteins that support the cell, hold organelles
75. An important means by which white blood cells take up in place, and enable the cell to change shape
and destroy harmful substances that have entered the 112. Protein structure of the cytoskeleton:
body.
76. Distinguished from phagocytosis in that much smaller
vesicles are formed, and they contain liquid rather than
particles. 113. Hollow structures formed from protein subunits that
77. Membrane-bound sacs that accumulate materials for perform a variety of roles, such as helping support the
release from the cell. cytoplasm of cells, assisting in cell division, and forming
78. The secretory vesicles move to the cell membrane, where essential components of certain organelles, such as cilia
the membrane of the vesicle fuses with the cell and flagella.
membrane, and the material in the vesicle is eliminated 114. Small fibrils formed from protein subunits that
from the cell. This process is called the structurally support the cytoplasm.
79. a little nut or the stone of a fruit 115. Fibrils formed from protein subunits that are smaller in
80. large organelle usually located near the center of the cell diameter than microtubules but larger in diameter than
81. The nucleus is bounded by this, which consists of outer microfilaments. They provide mechanical support to the
and inner membranes with a narrow space between them cell.
82. At many points on the surface of the nucleus, the inner 116. A specialized zone of cytoplasm close to the nucleus,
and outer membranes come together to form where microtubule formation occurs.
________________ , through which materials can pass 117. The centrosome contains ____________
into or out of the nucleus. 118. a small, cylindrical organelle composed of nine triplets;
83. The nuclei of human cells contain how many pairs of each triplet consists of three parallel microtubules joined
chromosomes together
84. the chromosomes are loosely coiled and collectively 119. It projects from the surface of cells; cylindrical
called _____________ structures that extend from the cell; composed of
85. a condensed region of the nucleus not bounded by a microtubules, organized in a pattern
membrane and consisting mostly of RNA and protein 120. Their coordinated movement transports mucus, in which
86. consists of inner and outer membranes, which become dust particles are embedded
fused at the nuclear pores 121. Flagellum means
87. diffuse bodies with no surrounding membrane that are 122. Have a structure similar to that of cilia but are much
found within the nucleus longer, and they usually occur only one per cell.
88. produced within the nucleolus, to form large and small 123. specialized extensions of the cell membrane that are
ribosomal subunits supported by microfilaments
89. organelles where proteins are produced, may be attached 124. mikros,_______________ + villus, ____________
to other organelles, such as the endoplasmic reticulum 125. do not actively move as cilia and flagella do; numerous
90. Ribosomes that are not attached to any other organelle on cells that have them and they increase the surface area
91. It means a network of those cell
92. a series of membranes forming sacs and tubules that 126. Composed of nine triplets of microtubules. Each triplet
extends from the outer nuclear membrane into the contains one complete microtubule fused to two
cytoplasm incomplete microtubules.
93. site for lipid synthesis and participates in detoxification 127. assembled to synthesize proteins, including the transport
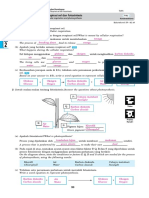
of chemicals within cells proteins of the cell membrane
94. ER with ribosomes attached to it 128. DNA contains the information that directs protein
95. ER without ribosomes is called synthesis.
96. consists of closely packed stacks of curved, membrane- 129. Protein synthesis is also called
bound sacs 130. Influences the structural and functional characteristics of
97. A small, membrane-bound sac that transports or stores the entire organism because it directs protein synthesis.
materials within cells. 131. consists of nucleotides joined together to form two
98. collects, modifies, packages, and distributes proteins and nucleotide strands
lipids manufactured by the ER 132. They function as chemical “letters” that form chemical
99. They pinch off from the margins of the Golgi apparatus “words.”
and move to the cell membrane 133. a sequence of nucleotides (making a word) that provides
100. Membrane-bound vesicles formed from the Golgi a chemical set of instructions for making a specific
apparatus. They contain a variety of enzymes that protein
function as intracellular digestive systems. 134. Gene expression involves two steps:
101. small, membrane-bound vesicles containing enzymes
that break down fatty acids, amino acids, and hydrogen
peroxide
102. Chemical formula for hydrogen peroxide 135. Through________________, the cell makes a copy of
103. A by-product of fatty acid and amino acid breakdown the gene necessary to make a particular protein
and can be toxic to a cell. 136. The copy, which is __________________, travels from
104. It is continuous with the nuclear envelope the nucleus to the ribosomes in the cytoplasm, where the
105. The main energy source for most chemical reactions information in the copy is used to construct a protein by
within the cell means of translation
137. Specialized molecules that carry the amino acids to the - each set of chromosomes has reached an opposite pole
ribosome of the cell, and the cytoplasm begins to divide.
138. converting that copied information into a protein 166. In this stage:
139. first step in gene expression, - chromosomes in each of the daughter cells become
140. Transcription takes places in? organized to form two separate nuclei.
141. serve as a template to determine the number and - The nuclear envelopes and the nucleoli form, and the
sequence of nucleotides in the mRNA cytoplasm continues to divide to form two cells.
142. DNA nucleotides pair only with specific RNA 167. Any swelling that occurs within the body, usually
nucleotides: involving cell proliferation.
168. Programmed cell death, is a normal process by which
143. The information in mRNA is carried in groups of three cell numbers within various tissues are adjusted and
nucleotides called ________, which specify a particular controlled.
amino acid. 169. The Cellular Aspects of Aging:
144. There are _____ possible mRNA codons, but only __
amino acids
145. acts as a signal to end the translation process
146. the synthesis of proteins based on the information in 170. One hypothesis of aging suggests the existence of a
mRNA cellular clock that, after a certain passage of time or a
147. Where does translation occur? certain number of cell divisions, results in the death of a
148. The process of translation requires two types of RNA in given cell line
addition to the mRNA: 171. Another hypothesis suggests that there are “death
genes,” which turn on late in life, or sometimes
prematurely, causing cells to deteriorate and die
149. a series of three nucleotides of tRNA that pairs with the 172. Through time, DNA is damaged, resulting in cell
codon of the mRNA degeneration and death.
150. An enzyme associated with the ribosome causes the 173. DNA is also susceptible to direct damage, resulting in
formation of a ___________ between the amino acids mutations that may result in cellular dysfunction and,
bound to the tRNAs and As the process continues, a ultimately, cell death. One of the major sources of DNA
________________ is formed. damage is apparently this, which are atoms or molecules
151. The cell life cycle includes two major phases: with an unpaired electron
174. Mitochondrial DNA may be more sensitive to
free-radical damage than is nuclear DNA. May result in
152. A non-dividing phase; where cells spends most of its life loss of proteins critical to mitochondrial function.
cycle performing its normal functions.
153. During this, the DNA (located in chromosomes in the
cell’s nucleus) is replicated
154. At the end of interphase, a cell has
155. The DNA is dispersed throughout the nucleus as thin
threads called
156. The formation of daughter cells from a single parent
cell. The new cells necessary for growth and tissue repair
are formed through this
157. the sex cells necessary for reproduction are formed
through
158. Each cell of the human body, except for sex cells,
contains how many chromosomes?
159. The 23rd chromosome is called the
160. The remaining 22 pairs of chromosomes are called
161. A parent cell divides to form two daughter cells with the
same amount and type of DNA as the parent cell.
162. mitosis is divided into four stages:
163. In this stage:
- chromatin condenses to form visible chromosomes.
- each chromosome is made up of two genetically
identical strands of chromatin, called chromatids which
are linked at one point by a specialized region called the
centromere
- microtubules called spindle fibers extend from the
centrioles to the centromere
- centrioles divide and migrate to each pole of the cell.
- the nucleolus and nuclear envelope disappear
164. In this stage:
- chromosomes align near the center of the cell.
165. In this stage:
- The chromatids separate, and it’s now called
chromosomes
- Each of the two sets of 46 chromosomes is moved by
the spindle fibers toward the centriole at one of the poles
of the cell
You might also like
- Intro To CellsDocument7 pagesIntro To CellsKalina KichukovaNo ratings yet
- Biology Definitions Grade 11Document3 pagesBiology Definitions Grade 11lprinsloo75No ratings yet
- 3 ReviewDocument19 pages3 ReviewJohn CastillejaNo ratings yet
- 2f7a3f9c-cb36-469b-96f4-72c9e24a82c0Document12 pages2f7a3f9c-cb36-469b-96f4-72c9e24a82c0Kalina KichukovaNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure and Function 1Document4 pagesCell Structure and Function 1Dianne LarozaNo ratings yet
- Ark Elvin Academy Year 9 Science Study Pack Autumn AssessmentDocument25 pagesArk Elvin Academy Year 9 Science Study Pack Autumn AssessmentLabeenaNo ratings yet
- Cell Biology Activity GuideDocument4 pagesCell Biology Activity GuidePamaran, Kristel DenishNo ratings yet
- 复习笔记IBDP Biology SL complete notesDocument5 pages复习笔记IBDP Biology SL complete notescynwuyxNo ratings yet
- 4 Movement of Substances Across The Cell MembraneDocument5 pages4 Movement of Substances Across The Cell MembraneVenice LoNo ratings yet
- CELL STRUCTURES AND FUNCTIONSDocument27 pagesCELL STRUCTURES AND FUNCTIONSVince Martin ManaigNo ratings yet
- Cell Reviewer Seeley'sDocument2 pagesCell Reviewer Seeley'smarielle castroNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 Homeostasis and Transport Review PacketDocument9 pagesUnit 4 Homeostasis and Transport Review PacketShannon ErdmanNo ratings yet
- Containing The Cell: Cell Membrane: Part I: Locating Physiology On The Web of KnowledgeDocument5 pagesContaining The Cell: Cell Membrane: Part I: Locating Physiology On The Web of KnowledgeEly TrajicoNo ratings yet
- AP Bio Unit 2 Review Shee1Document8 pagesAP Bio Unit 2 Review Shee1ytran11No ratings yet
- Notes - Chapter 3 - Cellular Level of OrganizationDocument7 pagesNotes - Chapter 3 - Cellular Level of OrganizationRogie P. BacosaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy & Physiology Reviewer: CHAPTER 3: Cell Structure and Their Functions 3.1 Cell StructureDocument4 pagesAnatomy & Physiology Reviewer: CHAPTER 3: Cell Structure and Their Functions 3.1 Cell StructureChris Deinielle Marcoleta SumaoangNo ratings yet
- Cell Reviewer Seeley'sDocument3 pagesCell Reviewer Seeley'smarielle castroNo ratings yet
- CellsDocument69 pagesCellsP1No ratings yet
- Cell Physiology EssentialsDocument3 pagesCell Physiology EssentialsDel Enriquez RiboNo ratings yet
- Cell Biology HandoutsDocument37 pagesCell Biology HandoutsIanDiel ParagosoNo ratings yet
- AP Biology Review Sheet Prokaryotic Bacteria Eukaryotic (Other Living Things)Document4 pagesAP Biology Review Sheet Prokaryotic Bacteria Eukaryotic (Other Living Things)api-286357921No ratings yet
- Cell Structure and FunctionsDocument45 pagesCell Structure and FunctionsVince Martin ManaigNo ratings yet
- Cell Cheat SheetDocument5 pagesCell Cheat SheetAJ Coots100% (2)
- Biology Short NoteDocument10 pagesBiology Short NotePatrix ParkerNo ratings yet
- The Cellular Level of Organization PDFDocument7 pagesThe Cellular Level of Organization PDFGol D. AceNo ratings yet
- Endocytosis vs exocytosis: how cells transport moleculesDocument11 pagesEndocytosis vs exocytosis: how cells transport moleculesJGHUNGERNo ratings yet
- Plasma Membrane Structure and FunctionDocument50 pagesPlasma Membrane Structure and Functiondhea wirantiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Student Copy ZoologyDocument5 pagesChapter 2 Student Copy Zoologyapi-530699294No ratings yet
- General Biology 1: Quarter 1 - Cell: The Basic Unit of LifeDocument10 pagesGeneral Biology 1: Quarter 1 - Cell: The Basic Unit of LifeMega CyclopsNo ratings yet
- Cell BiologyDocument14 pagesCell BiologyKhadija AhmedNo ratings yet
- Envelope: The Cell Structure That Is Composed of rRNA and Protein and Is The Site of Protein Synthesis Is The RibosomesDocument3 pagesEnvelope: The Cell Structure That Is Composed of rRNA and Protein and Is The Site of Protein Synthesis Is The RibosomesTyranica CaseyNo ratings yet
- The Working Cell: Chapter ObjectivesDocument12 pagesThe Working Cell: Chapter Objectivesirene9tan9ailianNo ratings yet
- CellsDocument5 pagesCellsCaroleNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 CytologyDocument26 pagesLecture 2 CytologyMohamed AshrafNo ratings yet
- Cells: Transport of Materials Across The Cell MembraneDocument6 pagesCells: Transport of Materials Across The Cell MembraneSara SalmanNo ratings yet
- PRINTED Cell HandoutsDocument8 pagesPRINTED Cell HandoutsKate GutierrezNo ratings yet
- ANPH-M1-CU2. The Cell & Cellular Metabolism and Reproduction (Mitosis and Meiosis)Document25 pagesANPH-M1-CU2. The Cell & Cellular Metabolism and Reproduction (Mitosis and Meiosis)Angelo SoteroNo ratings yet
- Cell Membrane and Transport in Under 40Document6 pagesCell Membrane and Transport in Under 40ASHLEY MONICA PLATANo ratings yet
- Cell Parts and Membrane TransportDocument4 pagesCell Parts and Membrane TransportSylvanus Rein LangreoNo ratings yet
- Cell Theory: Overview of The Cellular Basis of LifeDocument6 pagesCell Theory: Overview of The Cellular Basis of LifeRiy KimNo ratings yet
- Cell Membrane and Cell TransportDocument4 pagesCell Membrane and Cell TransportAtasha MojecaNo ratings yet
- Cell MembraneDocument17 pagesCell MembraneEloisa MadrilenoNo ratings yet
- Full Download Zoology 9th Edition Miller Solutions ManualDocument35 pagesFull Download Zoology 9th Edition Miller Solutions Manualcaveneywilliams100% (14)
- Reviewer (Cells)Document6 pagesReviewer (Cells)Sophia Mae ClavecillaNo ratings yet
- Session 1,2 - Human Organism Cell Structures and Their FunctionsDocument92 pagesSession 1,2 - Human Organism Cell Structures and Their FunctionsalamisjealdenNo ratings yet
- Cell BiologyDocument3 pagesCell BiologyjamjamjamNo ratings yet
- The Plasma Membrane: Membranes Cover The Surface of Every Cell, and Also Surround Most OrganellesDocument11 pagesThe Plasma Membrane: Membranes Cover The Surface of Every Cell, and Also Surround Most OrganellesSyeda Kaneez Mohammadi MohammadiNo ratings yet
- Cell Structures and Their FunctionsDocument2 pagesCell Structures and Their FunctionsSheikha KamidNo ratings yet
- (L9) Transport Across MembranesDocument22 pages(L9) Transport Across MembranesJhon TorresNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class IX Biology Fundament Unit of Life Chapter NotesDocument7 pagesCBSE Class IX Biology Fundament Unit of Life Chapter NotesDremaraanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7Document4 pagesChapter 7Astrii LyNo ratings yet
- Govt. Girls High School Pura Heeran, SialkotDocument7 pagesGovt. Girls High School Pura Heeran, SialkotFizza cooks foodNo ratings yet
- AnaPhy - Reviewer (Final)Document7 pagesAnaPhy - Reviewer (Final)HyvieNo ratings yet
- The Cell and Cellular Metabolism ReproductionDocument4 pagesThe Cell and Cellular Metabolism ReproductionApple AbriamNo ratings yet
- Comparing Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsDocument118 pagesComparing Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsATIKAH NUR HAFIZHAHNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 & 3 - ZoologyDocument4 pagesChapter 2 & 3 - ZoologyAngel MerilloNo ratings yet
- Biology Notebook: 02.03 Early Cells: Key Questions and Terms NotesDocument4 pagesBiology Notebook: 02.03 Early Cells: Key Questions and Terms NotesAloni CampbellNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Student Copy ZoologyDocument5 pagesChapter 2 Student Copy Zoologyapi-523871804No ratings yet
- Cell, Cell Membrane, To Transport, Substances, Structure of The MembraneDocument4 pagesCell, Cell Membrane, To Transport, Substances, Structure of The MembraneИрина КривошеяNo ratings yet
- Staphylococcus Aureus (14.3%), Erwinia Spp. (14.3%) and Pseudomonas Spp. (14.3%) While Salmonella SPPDocument11 pagesStaphylococcus Aureus (14.3%), Erwinia Spp. (14.3%) and Pseudomonas Spp. (14.3%) While Salmonella SPPDrizzy MarkNo ratings yet
- Excretion in Annelida:: (A) NephridiaDocument3 pagesExcretion in Annelida:: (A) NephridiaSubhashree satapathyNo ratings yet
- FREE TOEFL TEST II PENJELASAN GUIDEDocument19 pagesFREE TOEFL TEST II PENJELASAN GUIDEbudiyono9No ratings yet
- Lab 5 Spotters 7Document7 pagesLab 5 Spotters 7madura cNo ratings yet
- Third Assignment (Forensic)Document2 pagesThird Assignment (Forensic)Dean Mark AnacioNo ratings yet
- Full Download Test Bank Pathophysiology The Biologic Basis For Disease 8th Edition PDF Full ChapterDocument36 pagesFull Download Test Bank Pathophysiology The Biologic Basis For Disease 8th Edition PDF Full Chapterwomanlylegionry9hsn1f100% (17)
- Cellular Cancer TherapyDocument208 pagesCellular Cancer TherapyneuralterapianetNo ratings yet
- Disinfectant Antiseptic2019Document52 pagesDisinfectant Antiseptic2019milka bellaNo ratings yet
- Non-Mendelian GeneticsDocument3 pagesNon-Mendelian GeneticsMarlon EllamilNo ratings yet
- The Microbial WorldDocument2 pagesThe Microbial WorldBaymax McCauliffNo ratings yet
- Gamete Formation and Meiosis ExplainedDocument26 pagesGamete Formation and Meiosis ExplainedIslahNo ratings yet
- CMB Chapter 15Document32 pagesCMB Chapter 15cyorogNo ratings yet
- Micropropagation of Banana ThesisDocument7 pagesMicropropagation of Banana ThesisWhereCanIFindSomeoneToWriteMyPaperCanada100% (2)
- Dissertation LeucodermaDocument90 pagesDissertation LeucodermaRashmi Mishra100% (1)
- Online Cee Model ExaminationDocument72 pagesOnline Cee Model ExaminationPrepladder ChayNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of quality assessment molecular amplification methodsDocument15 pagesFundamentals of quality assessment molecular amplification methodsMaya RustamNo ratings yet
- Entropy: Autocatalytic Sets and The Origin of LifeDocument10 pagesEntropy: Autocatalytic Sets and The Origin of LifeKamagara Roland AndrewNo ratings yet
- Induction Presentation Biology A Level and Gcse.204719226Document25 pagesInduction Presentation Biology A Level and Gcse.204719226Cut TirayaNo ratings yet
- Biology As Level (Form Five) - Gaseous Exchange and Respiration - (PDF) EcoleDocument31 pagesBiology As Level (Form Five) - Gaseous Exchange and Respiration - (PDF) EcoleJohannes MuthombeniNo ratings yet
- DLP in DnaDocument3 pagesDLP in DnaBenjamen Lapag Banaag Jr.100% (1)
- Answer Page 30 - 33Document4 pagesAnswer Page 30 - 33Shavonne LaiNo ratings yet
- Analogous Structures: Structures With Similar Functions But Different OriginsDocument13 pagesAnalogous Structures: Structures With Similar Functions But Different OriginsDaphne GuraNo ratings yet
- Topic 6 Gene Control: Suggested ActivitiesDocument2 pagesTopic 6 Gene Control: Suggested ActivitiesSemwezi EnockNo ratings yet
- Biodesulfurizare 1Document30 pagesBiodesulfurizare 1Stan Dragos-MihaiNo ratings yet
- Veterinary Immunology Tanuvas Notes VMC - 221 PDFDocument124 pagesVeterinary Immunology Tanuvas Notes VMC - 221 PDFSantosh BhandariNo ratings yet
- 5e Heredity Genetics Unit Portfolio CrespoDocument6 pages5e Heredity Genetics Unit Portfolio Crespoapi-247308630No ratings yet
- Lecture Title: Gross Human Structural BiologyDocument2 pagesLecture Title: Gross Human Structural BiologyLaish Christle CapiendoNo ratings yet
- Genetic EngineeringDocument23 pagesGenetic EngineeringAlexander Salas EspaderaNo ratings yet
- Hill Side School Biology WorksheetDocument2 pagesHill Side School Biology WorksheetHe NiNo ratings yet
- E. Coli Final ProposalDocument4 pagesE. Coli Final ProposalNicholas KingNo ratings yet