Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Hydrometeorological Hazards: Geological Hazards Occur Because
Uploaded by
hazelOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Hydrometeorological Hazards: Geological Hazards Occur Because
Uploaded by
hazelCopyright:
Available Formats
Hydrometeorological hazards Keep an eye on lighted candles or gas lamps.
Geological hazards occur because Do not wade through floodwaters to avoid
of geological processes such as movement in the being electrocuted and contracting diseases.
tectonic plates and volcanic activity. ...
If there is a need to move to an evacuation
Meteorological hazards include extreme temperatures,
center, follow these reminders.
hurricanes, tornadoes, droughts, and severe
storms. Hydrological hazards are hazards involving Evacuate calmly.
water processes.
Close the windows and turn off the main power
switch.
What to do before, during, and after a
Put important appliances and belongings in a
Typhoon. high ground.
Before the Typhoon:
Avoid the way leading to the river.
Store an adequate supply of food and clean
water
Prepare foods that need not be cooked. After the Typhoon:
Keep flashlights, candles and battery-powered If your house was destroyed, make sure that it
radios within easy reach. is already safe and stable when you enter.
Examine your house and repair its unstable Beware of dangerous animals such as snakes
parts. that may have entered your house
Always keep yourself updated with the latest Watch out for live wires or outlet immersed in
weather report. water.
Harvest crops that can be yielded already. Report damaged electrical cables and fallen
electric posts to the authorities.
Secure domesticated animals in a safe place.
Do not let water accumulate in tires, cans or
For fisher folks, place boats in a safe area.
pots to avoid creating a favorable condition for
Should you need to evacuate, bring clothes, first mosquito breeding.
aid kit, candles/flashlight, battery-powered
radio, food, etc.
Genetics
the study of heredity and variation of living organisms
and how genetic information is passed from one
During the Typhoon: generation to the next
Stay inside the house.
Always keep yourself updated with the latest
Gene
weather report. a part of a chromosome that governs the expression of
a trait and is passed on to offspring; it has a specific
If safe drinking water is not available, boil water DNA sequence
for at least 20 minutes. Place it in a container
with cover.
Asexual reproduction Evolution
reproduction that requires only one parent and
produces genetically identical offspring
Change in a kind of organism over time; process by
which modern organisms have descended from ancient
Sexual reproduction organisms
reproduction that requires two parents and
produces genetically distinct offspring Genetic variation
A variation of genes among a group of population
Gamete caused by mutation which permanently changes the
structure one's gene.
a male or female reproductive cell
Zygote
a cell formed by the fusion of two gametes
Fertilization
in humans, the joining of male and female haploid
gametes
In vitro fertilization
the technique used to fertilize egg cells outside the
female's body
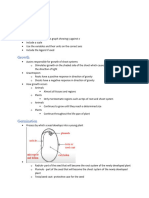
The functions of plant organs
Stem cell In plants, each organ has several jobs, or functions.
an undifferentiated cell that can develop and become
Roots keep a plant in the ground. They also take
specialized into different cell types of the body
in water and nutrients from the soil.
Leaves absorb sunlight, and make food for the
DNA
plant by photosynthesis. The waste product of
Deoxyribonucleic acid; present in nearly all living cells,
photosynthesis, oxygen, escapes through tiny
main constituent of chromosomes, the carrier of
holes in the leaves.
genetic information
The stem supports the leaves and flowers. It
also transports water and nutrients between
Mutation the roots and the leaves.
When a DNA sequence for a gene is changed. Mutations
can be hereditary or somatic (happens during Reproductive organs allow a plant to produce
someone's life). Causes and scale of mutation varies. new plants.
Together, the organs of a plant allow it to carry out the
Natural Selection seven processes of life.
Two major mechanisms that drive evolution are natural
selection and genetic drift.
Roots
Roots act like straws absorbing water and minerals from
the soil. Tiny root hairs stick out of the root, helping in
the absorption. Roots help to anchor the plant in the
soil so it does not fall over. Roots also store extra food
for future use.
Stems
Stems do many things. They support the plant. They act
like the plant's plumbing system, conducting water and
nutrients from the roots and food in the form of glucose
from the leaves to other plant parts. Stems can be
herbaceous like the bendable stem of a daisy or woody
like the trunk of an oak tree.
Leaves
Most plants' food is made in their leaves. Leaves are
designed to capture sunlight which the plant uses to
make food through a process called photosynthesis.
Flowers
Flowers are the reproductive part of most plants.
Flowers contain pollen and tiny eggs called ovules. After
pollination of the flower and fertilization of the ovule,
the ovule develops into a fruit.
Fruit
Fruit provides a covering for seeds. Fruit can be fleshy
like an apple or hard like a nut.
Seeds
Seeds contain new plants. Seeds form in fruit.
You might also like
- PCR Lab ProtocolDocument5 pagesPCR Lab Protocolhk8atema1lNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in Environmental ScienceDocument7 pagesReviewer in Environmental ScienceAlexándra NicoleNo ratings yet
- Biology NotesDocument32 pagesBiology NotesTaylor BonnetNo ratings yet
- Book - DODDS - ROBERTS - 1985-Experiments in Plant Tissue CultureDocument250 pagesBook - DODDS - ROBERTS - 1985-Experiments in Plant Tissue Culturehosana_rrNo ratings yet
- 01 Unifying Themes of LifeDocument13 pages01 Unifying Themes of LifeFiona Alano100% (2)
- Bio 101-Exam2KeyDocument10 pagesBio 101-Exam2KeyRobbie GroveNo ratings yet
- Buku EvolusiDocument446 pagesBuku Evolusigian septhayudi100% (1)
- Demons in Eden: The Paradox of Plant DiversityFrom EverandDemons in Eden: The Paradox of Plant DiversityRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5)
- WB8 Sci SAMPLE-74-138Document65 pagesWB8 Sci SAMPLE-74-138lengocthuytien0725No ratings yet
- Nat Reviewer For Life Science 2022-2023Document6 pagesNat Reviewer For Life Science 2022-2023Johnren Godinez BoocNo ratings yet
- B3 L 49 QGN YOatnd 4 D Ci UCDocument22 pagesB3 L 49 QGN YOatnd 4 D Ci UCVenu GopalNo ratings yet
- 1.1 What Is Life? Characteristics of Living SystemsDocument6 pages1.1 What Is Life? Characteristics of Living Systemsspencer_jordan_2No ratings yet
- Plant Diversity 1Document39 pagesPlant Diversity 1Harold BuenvenidaNo ratings yet
- Biological Classification Class 11 Notes BiologyDocument6 pagesBiological Classification Class 11 Notes BiologyVyjayanthiNo ratings yet
- Bio ReviewerDocument4 pagesBio ReviewerZyrine Jane JolindonNo ratings yet
- Adaptation and Evolution PowerpointDocument64 pagesAdaptation and Evolution Powerpointapi-263357086No ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Components of EcosystemDocument28 pagesChapter 2 - Components of EcosystemJudy Ann SibayanNo ratings yet
- RRL BookkeepingDocument2 pagesRRL BookkeepingNasha RelatoNo ratings yet
- HEREDITYDocument7 pagesHEREDITYKUBER KUMAR KHANDELWALNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 PDFDocument19 pagesLecture 1 PDFzainab alNo ratings yet
- Biological ClassificationDocument4 pagesBiological ClassificationYashwanthNo ratings yet
- Coping With Hydrometeological Hazard TyphoonDocument2 pagesCoping With Hydrometeological Hazard TyphoonAlexander ValoisNo ratings yet
- Characteristics of Living ThingsDocument13 pagesCharacteristics of Living ThingsZheela EsmaelNo ratings yet
- Xi - Ut-I CH.02Document21 pagesXi - Ut-I CH.02Gargi SapteNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Reproduction NotesDocument10 pagesChapter 1 Reproduction NotesPoornimaNo ratings yet
- Odyssey High School Biology VocabularyDocument24 pagesOdyssey High School Biology VocabularyHanQian WangNo ratings yet
- General EducationDocument15 pagesGeneral EducationMelarce Magallanes LazarteNo ratings yet
- ECOLOGY & Climatic FactorsDocument17 pagesECOLOGY & Climatic Factorsrajshgupta01No ratings yet
- APES Carolina & Bianca's Review of Evolution & BiodiversityDocument16 pagesAPES Carolina & Bianca's Review of Evolution & BiodiversityRobert FlynnNo ratings yet
- Life: Plants: Ben Joshua R. Mancile December 13, 2021 BS Human Biology Botafun N04Document2 pagesLife: Plants: Ben Joshua R. Mancile December 13, 2021 BS Human Biology Botafun N04Ben Joshua MancileNo ratings yet
- Exam Study NotesDocument36 pagesExam Study Notescierrayeh12No ratings yet
- Biology 1.3 NotesDocument3 pagesBiology 1.3 NotesBino The RavenNo ratings yet
- Ecosystem Ch20Document6 pagesEcosystem Ch20瞧你那个亚子No ratings yet
- General Biology 2 4 Quarter: Valerie Ross Pinlac Stem 11 GalileoDocument18 pagesGeneral Biology 2 4 Quarter: Valerie Ross Pinlac Stem 11 GalileoInned NylNo ratings yet
- Zooplankton Past Paer 2018Document18 pagesZooplankton Past Paer 2018Raheela SamooNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document9 pagesChapter 1Anirudh CNo ratings yet
- Haneeza Louise N. Macaraeg Garnet BDocument1 pageHaneeza Louise N. Macaraeg Garnet BxavierNo ratings yet
- CH-2 - Biological Classification - NotesDocument9 pagesCH-2 - Biological Classification - NotesketakiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Biodiversity Form 2 KSSMDocument20 pagesChapter 1 Biodiversity Form 2 KSSMayak jamaludinNo ratings yet
- EnvironmentDocument56 pagesEnvironmentSay KyekNo ratings yet
- Chalky Environment Brought About byDocument2 pagesChalky Environment Brought About bymariejuanaNo ratings yet
- Protists Review WSDocument4 pagesProtists Review WSIZ - 12JR 1013186 Lincoln Alexander SSNo ratings yet
- Insect Ecology Integrated Pest Management Dec. 3 2023Document16 pagesInsect Ecology Integrated Pest Management Dec. 3 2023bedalea07No ratings yet
- CBSE NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Biology Chapter 2Document5 pagesCBSE NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Biology Chapter 2niranjan swamyNo ratings yet
- Education LeadersGuide-Tundra LetterDocument57 pagesEducation LeadersGuide-Tundra LetterahammillNo ratings yet
- Unifying Themes in The Study of LifeDocument12 pagesUnifying Themes in The Study of LifeReyes KathleenNo ratings yet
- BiosphereDocument52 pagesBiosphereapi-306763520No ratings yet
- Biological Diversity 1Document108 pagesBiological Diversity 1Dave McMordieNo ratings yet
- Blueprints of LifeDocument27 pagesBlueprints of Lifeanonymous1No ratings yet
- ProkaryoticDocument2 pagesProkaryoticGievel Enoroba LopezNo ratings yet
- 11biological ClassificationDocument23 pages11biological ClassificationSreenjoy ChakrabortyNo ratings yet
- There Are 3 Main Steps To CloningDocument10 pagesThere Are 3 Main Steps To CloningwaqasadilNo ratings yet
- Plants and The Colonization of LandDocument38 pagesPlants and The Colonization of LandNacorNo ratings yet
- Ento 232 Printed NotesDocument60 pagesEnto 232 Printed NotesAkshay PatilNo ratings yet
- 2 BiologyDocument18 pages2 BiologyAlexandra EscalonaNo ratings yet
- Botany W2Document9 pagesBotany W2Mariel AnaNo ratings yet
- Nematological ExaminationDocument19 pagesNematological ExaminationEduardo MiguelesNo ratings yet
- Biological ClassfificationDocument10 pagesBiological Classfificationmaryak3050No ratings yet
- Characteristics of LifeDocument3 pagesCharacteristics of Lifewyszynki87No ratings yet
- Biological ClassificationDocument27 pagesBiological Classificationsachit choudharyNo ratings yet
- Notes On Broad Topic Vid For BioDocument8 pagesNotes On Broad Topic Vid For Bioatwaroo.educationNo ratings yet
- General Biology 2Document5 pagesGeneral Biology 2Fern Nicole TagatacNo ratings yet
- What Is The Basic Structural and Functional Unit of LifeDocument14 pagesWhat Is The Basic Structural and Functional Unit of LifeZheela EsmaelNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 Evolution Chapter 7 Power Points Student Note 2020 ModifiedDocument38 pagesUnit 3 Evolution Chapter 7 Power Points Student Note 2020 Modifiedlotte worldNo ratings yet
- Lab Activity 1.2 - DNA Extraction-1Document3 pagesLab Activity 1.2 - DNA Extraction-1alexander justin tanhuecoNo ratings yet
- Haa Nipa Question Bank (Proposed) - FinalDocument3 pagesHaa Nipa Question Bank (Proposed) - FinalZahidul HassanNo ratings yet
- BH3 Mimetics in AML TherapyDocument22 pagesBH3 Mimetics in AML TherapyAbhilash ReddyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 Preview - DNA: Multiple ChoiceDocument5 pagesChapter 9 Preview - DNA: Multiple ChoiceyeateshwarriorNo ratings yet
- Exercise 3Document6 pagesExercise 3Gwyneth Marie DayaganNo ratings yet
- CME Brochure 21 Feb 2015Document2 pagesCME Brochure 21 Feb 2015ParameshParamamNo ratings yet
- 2 Basic Microbiological TestsDocument6 pages2 Basic Microbiological TestsMuhamadNabilFikriJamaluddinNo ratings yet
- Bio 120 Exer 9-10Document4 pagesBio 120 Exer 9-10Asi JenNo ratings yet
- Cebitor 2012Document52 pagesCebitor 2012Vanessa MirandaNo ratings yet
- UCSB MCDB 1A-Syllabus - Fall 2018Document5 pagesUCSB MCDB 1A-Syllabus - Fall 2018Matthew C. ChanNo ratings yet
- 0610 Nov 02 QP 2 Cells, Tissue)Document2 pages0610 Nov 02 QP 2 Cells, Tissue)Ahmed Kaleem Khan Niazi100% (1)
- Evidence For Evolution SlidesDocument11 pagesEvidence For Evolution Slidesapi-2631978100% (1)
- Botany SummaryDocument6 pagesBotany SummaryKristiooyNo ratings yet
- Intercellular CommunicationDocument8 pagesIntercellular CommunicationDina MaulidaNo ratings yet
- Areas and Branches of Medicine, Pharmacology and Its Classification, TerminologyDocument9 pagesAreas and Branches of Medicine, Pharmacology and Its Classification, TerminologyCentral Asian StudiesNo ratings yet
- BIOM1050: Receptors, Neurons, Synapses & Nervous Systems Cell Communication & Receptor FamiliesDocument12 pagesBIOM1050: Receptors, Neurons, Synapses & Nervous Systems Cell Communication & Receptor FamiliesmichelleNo ratings yet
- 4 - Penyakit Tidak Menular - Faktor RisikoDocument51 pages4 - Penyakit Tidak Menular - Faktor RisikoCandra GumilarNo ratings yet
- (R) Varicella VirusDocument8 pages(R) Varicella VirusEkkim Al KindiNo ratings yet
- UC's MotionsDocument37 pagesUC's MotionsjssherkowNo ratings yet
- 7th Impurities Genotoxic, Nitrosamine & Beyond - Final Agenda (Digital Version)Document8 pages7th Impurities Genotoxic, Nitrosamine & Beyond - Final Agenda (Digital Version)Debjani DuttaNo ratings yet
- Tugasan Epraktikal XBDM4103 Mei 2021Document6 pagesTugasan Epraktikal XBDM4103 Mei 2021norfilzahNo ratings yet
- L5 - Gene InteractionDocument23 pagesL5 - Gene Interactioncora o brien100% (1)
- Course Outline For Pharmacology in Dentistry 2013-14Document5 pagesCourse Outline For Pharmacology in Dentistry 2013-14entistdeNo ratings yet
- Experiment 1Document9 pagesExperiment 1Froileth PulidoNo ratings yet
- Definition of Cell CultureDocument36 pagesDefinition of Cell CultureGladys AilingNo ratings yet
- Best Practices For Variant Calling in Clinical Sequencing: Review Open AccessDocument13 pagesBest Practices For Variant Calling in Clinical Sequencing: Review Open AccessAhmad SolihinNo ratings yet