Professional Documents
Culture Documents
4.0 Water Sources
Uploaded by
umi amira0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 views4 pagesOriginal Title
4.0 WATER SOURCES
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 views4 pages4.0 Water Sources
Uploaded by
umi amiraCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 4
SAB 2912-Water Treatment
4.0 WATER SOURCES AND QUANTITY
Water sources
- Water on the earth surface – 78%
- From 78%
o 97.2% sea water
o 2.5% ice water
o 0.65% surface water
- Water sources that commonly used:
o surface water; rivers and lakes
o groundwater
o sea water
Water Quantity
- The average daily per capita water consumption: 280 litre/person/day
- It depends on: place & time
- Factors affecting water usage:
o Economic level of consumer
o Water Tariff
o Efficiency of water supply system (quantity, pressure)
o Climate
- Volume of water commonly used:
o City (> 10 000 persons); 230 – 320 litre/person/day
o Suburban; 130 – 230 litre/person/day
o Urban; 135 – 180 litre/person/day
o Heavy Industries; 45 000 litre/ha/day
o Light industries; 22 000 litre/ha/day
©Faculty of Civil Engineering 26
SAB 2912-Water Treatment
- Municipal water demand is commonly classified according to the nature of
the usage. The ordinary classifications are:
o Domestic
o Commercial and Industrial
o Public use
o Loss and waste
o Fire Demand
- Formula for estimating water consumption per capita in one area:
KAP = Q / P where
Q = volume of water supplied to that area
P = population in that area
Relation of Water Quantity and Population
- Since population is always a relevant factor in estimating future water use, it
is necessary to predict, in some manner, what the future population will be.
- The hypothesis of geometric method assumes that percentage of growth
population is constant
- Geometric Method:
-
r = (Pn / Po) 1/m – 1 where
r = the percentage of growth population and r is a constant (in decimal)
= 0.025 (for Malaysia)
m = period of the projection = n – 0
Po = the present population (year 0)
Pn = the population at some time in the future (year n) where n > 0
©Faculty of Civil Engineering 27
SAB 2912-Water Treatment
- Basic formula for estimating future average daily water demand:
WDn = Pn x Cn x fn + WDT(n) where
WDn = total water demand at the end of year n
Pn = the population at the end of year n
Cn = daily water demand per capita at the end of year n
fn = service factors at the end of year n
WDT(n) = daily water demand for other uses (such as for industrial,
commercial etc.)
SERVICE FACTORS
State Urban Rural
1985 1993 2000 1985 2000 2008
Johor 0.92 0.99 0.99 0.61 0.78 0.85
Kedah 0.95 0.99 0.99 0.58 0.92 0.95
Kelantan 0.65 0.82 0.99 0.30 0.50 0.70
Melaka 0.99 0.99 0.99 0.82 0.85 0.95
N. Sembilan 0.89 0.99 0.99 0.75 0.86 0.95
Pahang 0.95 0.99 0.99 0.65 0.80 0.90
Perak 0.9 0.99 0.99 0.75 0.80 0.90
Perlis 0.93 0.99 0.99 0.50 0.93 0.95
P.Pinang 0.98 0.99 0.99 0.85 0.87 0.95
Sabah 0.99 0.99 0.99 0.38 0.55 075
Sarawak 0.95 0.99 0.99 0.33 0.40 0.70
Selangor 0.95 0.99 0.99 0.73 0.80 0.90
Terengganu 0.85 0.92 0.99 0.40 0.82 0.95
©Faculty of Civil Engineering 28
SAB 2912-Water Treatment
Malaysia 0.93 0.99 0.99 0.58 0.74 0.86
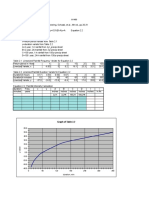
Example 1
Population in the year 1960 = 33,300 persons
Population in the year 1990 = 67,300 persons
Heavy Industrial Area = 40ha.
Light Industrial Area = 75 ha.
Daily water demand per
capita at the end of year 2015 = 280 L/capita/day
Assume service factor = 0.99
Estimate the total average daily water demand in the year 2015
Solution:
1 1
P m
67.3 30
r n 1 1 0.024
Po 33.3
P2015 = P1960 (1 + r)m = 33300 (1 + 0.024)55
= 122727 123,000 persons
WDn = Pn x Cn x fn + WDT(n)
WDT(n) = 40 x 45,000 + 75 x 22,000
= 3.45 x 106 L/day
WDn = 123,000 x 280 x 0.99 + 3.45 x 106
= 37.5 x 106 L/day = 38.4 MLD
©Faculty of Civil Engineering 29
You might also like
- Aakash Social Science ModuleDocument295 pagesAakash Social Science ModuleASHISH NAIK100% (1)
- Financial AnalisysDocument12 pagesFinancial AnalisysMuhamad FajriNo ratings yet
- Water SupplyDocument112 pagesWater Supplyyasas89100% (6)
- 3.MScWSDSE CourseDocument242 pages3.MScWSDSE CourseHawi EtanaNo ratings yet
- Source:: Sugarloaf - Nbed.nb - Ca/sites/sugarloaf - Nbed.nb - Ca/... / 8 - Types - of - GlobalizationDocument12 pagesSource:: Sugarloaf - Nbed.nb - Ca/sites/sugarloaf - Nbed.nb - Ca/... / 8 - Types - of - GlobalizationKuroha KokonoseNo ratings yet
- 4.0 Water Sources and Quality-2Document13 pages4.0 Water Sources and Quality-2Zul ImiNo ratings yet
- Civil731 Tutorial4 - Frank Ho-Hyung KangDocument3 pagesCivil731 Tutorial4 - Frank Ho-Hyung Kangaaronjason8992No ratings yet
- Water Management Assignment: Karthik C.SDocument7 pagesWater Management Assignment: Karthik C.SKarthik ChandrasekaranNo ratings yet
- Stormwater Drainage DesignDocument7 pagesStormwater Drainage Designarasee araNo ratings yet
- Proposed Morcellement For For Residential Purposes AT Helvetia, Cote D'OrDocument28 pagesProposed Morcellement For For Residential Purposes AT Helvetia, Cote D'OrArvin BhurtunNo ratings yet
- Impact of Climate Change On Water Resources of Nepal and Role of WECSDocument50 pagesImpact of Climate Change On Water Resources of Nepal and Role of WECSVijay RajuNo ratings yet
- Tutorial I and II SolutionsDocument4 pagesTutorial I and II SolutionsMin Thiha SoeNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2Document29 pagesLecture 2Yaseen Talal Mosalam GahamaNo ratings yet
- Sollution For Assignment 1Document6 pagesSollution For Assignment 1liceNo ratings yet
- PopulationDocument17 pagesPopulationJoud RamadanNo ratings yet
- Goa - State PresentationDocument29 pagesGoa - State Presentationrajesh kandimallaNo ratings yet
- Development of Utah's Small MS4 Storm Water Retention StandardDocument47 pagesDevelopment of Utah's Small MS4 Storm Water Retention StandardSean CrossNo ratings yet
- Guided by - DR .V. S. PradhanDocument25 pagesGuided by - DR .V. S. PradhanSnehil KajariaNo ratings yet
- Jurnal NSL - Simulasi Pengaruh Tata Guna Lahan Terhadap Debit Banjir Di DASDocument8 pagesJurnal NSL - Simulasi Pengaruh Tata Guna Lahan Terhadap Debit Banjir Di DASMuih NuzulNo ratings yet
- Ehnes Estimation of Design Flows For PDFDocument35 pagesEhnes Estimation of Design Flows For PDFDylan PowellNo ratings yet
- 2023 Test 1 MemoDocument4 pages2023 Test 1 MemoFrancine NaickerNo ratings yet
- 2-Solved Problems - Water DemandDocument12 pages2-Solved Problems - Water Demandf2c95225d3No ratings yet
- KMPDocument16 pagesKMPAnil KumarNo ratings yet
- 1511261268Document14 pages1511261268RajNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document12 pagesChapter 4Rushed Alama100% (1)
- 2 BSC Iriigation Engineering Design 2021 22 230329 175202Document155 pages2 BSC Iriigation Engineering Design 2021 22 230329 175202Benjamin DagbeyNo ratings yet
- 1. 관개기본기초Document65 pages1. 관개기본기초김정민No ratings yet
- UntitledDocument15 pagesUntitledAfiq AimanNo ratings yet
- Caustic TankDocument5 pagesCaustic TankMuhammad Aftab AhmedNo ratings yet
- Workshop On Hydrology: Associate Professor in Land and Water Development UNESCO-IHE Institute For Water EducationDocument62 pagesWorkshop On Hydrology: Associate Professor in Land and Water Development UNESCO-IHE Institute For Water EducationAloumi HichamNo ratings yet
- Workshop On Hydrology: Associate Professor in Land and Water Development UNESCO-IHE Institute For Water EducationDocument62 pagesWorkshop On Hydrology: Associate Professor in Land and Water Development UNESCO-IHE Institute For Water EducationAloumi HichamNo ratings yet
- Workshop On Hydrology: Associate Professor in Land and Water Development UNESCO-IHE Institute For Water EducationDocument62 pagesWorkshop On Hydrology: Associate Professor in Land and Water Development UNESCO-IHE Institute For Water EducationBoos yousufNo ratings yet
- Storm-Drainage - On RunoffDocument20 pagesStorm-Drainage - On Runoffrosalesapril0214No ratings yet
- Rainfall-Runoff Analysis Using The Soil Conservation Service Curve Number MethodDocument31 pagesRainfall-Runoff Analysis Using The Soil Conservation Service Curve Number MethodCarlos GrupotecNo ratings yet
- Sludge Treatment of WaterDocument11 pagesSludge Treatment of WaterWinsam Amiel Cejudo100% (1)
- Water Stabilization PondsDocument16 pagesWater Stabilization PondsLawrence MagagaNo ratings yet
- Towards Sustainable Energy in The Power Sector EditDocument25 pagesTowards Sustainable Energy in The Power Sector EditCentre for Poverty AnalysisNo ratings yet
- Supply and Demand Gap AnalysisDocument18 pagesSupply and Demand Gap AnalysisJustine Anthony SalazarNo ratings yet
- Precipitation Intensity: Graph of Table 2.2Document12 pagesPrecipitation Intensity: Graph of Table 2.2Jong Dollente Jr.No ratings yet
- Nandyal Municipality - Action Plan For Reduce of Water LossesDocument10 pagesNandyal Municipality - Action Plan For Reduce of Water LossesRammohanraoRangarajulaNo ratings yet
- Supply and Demand Gap AnalysisDocument18 pagesSupply and Demand Gap AnalysisKimberly OngNo ratings yet
- Alternative Budget 2019-20 (FINAL)Document30 pagesAlternative Budget 2019-20 (FINAL)Matt MaloneyNo ratings yet
- Details Attached at Annex "A"Document3 pagesDetails Attached at Annex "A"usmanmughal111No ratings yet
- jm20110609 GamioDocument27 pagesjm20110609 GamioWilian Armando Leon CabanaNo ratings yet
- 3 Lecture Wastewater Characteristic AnalysisDocument41 pages3 Lecture Wastewater Characteristic AnalysiszeyadNo ratings yet
- Clean Water Distribution Network System Planning in Coblong Sub-District, Bandung CityDocument10 pagesClean Water Distribution Network System Planning in Coblong Sub-District, Bandung CityBerlyan BesoniNo ratings yet
- Surat WaterDocument49 pagesSurat WaterAASTHA KHURANA SVNITNo ratings yet
- Bonview Catchment MUSIC ModelingDocument22 pagesBonview Catchment MUSIC ModelingRita HasanNo ratings yet
- C. 27-CLP03H - Technical ReportDocument6 pagesC. 27-CLP03H - Technical ReportJoanna Robles NicodemusNo ratings yet
- Class Project: Kothagudem Municipal Council Bhadradi DistrictDocument22 pagesClass Project: Kothagudem Municipal Council Bhadradi Districtabdul khaliqNo ratings yet
- Target Report For Kalamnuri For FY 2016-2017Document2 pagesTarget Report For Kalamnuri For FY 2016-2017Anonymous d6tUk8QZNo ratings yet
- Goemorphology 4NDocument6 pagesGoemorphology 4Nshuvobosu262No ratings yet
- Run Off CoefficientDocument8 pagesRun Off CoefficientConstruction BranchNo ratings yet
- Drainahe SystemDocument11 pagesDrainahe SystemJanissaries NivercaNo ratings yet
- Water Supply Engineering: 1 Assignment Eng. Ahmad Alzoubi: Group Work: 2 Students/assignmentDocument10 pagesWater Supply Engineering: 1 Assignment Eng. Ahmad Alzoubi: Group Work: 2 Students/assignmentHeba BazlamitNo ratings yet
- Cabrera 111Document14 pagesCabrera 111uroskNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document66 pagesChapter 2Mohamad Ridhwan Bin ZahriNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 Water QuantityDocument10 pagesLecture 2 Water QuantityDakheel maleko100% (1)
- Page 1 of 4: Design & Calculation Drawing Results Viva-Voce Record Total 30 40 10 10 10 100Document4 pagesPage 1 of 4: Design & Calculation Drawing Results Viva-Voce Record Total 30 40 10 10 10 100UthraNo ratings yet
- C. 27-CLP03H - Technical Report ReviewedDocument6 pagesC. 27-CLP03H - Technical Report ReviewedJoanna Robles NicodemusNo ratings yet
- Water Requirement Analysis Hubli and Dharwad CROPSDocument26 pagesWater Requirement Analysis Hubli and Dharwad CROPSadit.shet23No ratings yet
- Mapping Hazards in Nepal’s Melamchi River: Catchment to Enhance Kathmandu’s Water SecurityFrom EverandMapping Hazards in Nepal’s Melamchi River: Catchment to Enhance Kathmandu’s Water SecurityNo ratings yet
- B PSC Exam: Previous Year Question Papers-MainsDocument18 pagesB PSC Exam: Previous Year Question Papers-Mainssumit kumarNo ratings yet
- Sangre PesadaDocument10 pagesSangre Pesadabarbara8lazaraNo ratings yet
- You've Arrived!!! Welcome To Alfonso Lista!Document3 pagesYou've Arrived!!! Welcome To Alfonso Lista!Korina MarawisNo ratings yet
- EAP Status NewProjectsDocument10 pagesEAP Status NewProjectsSouvik Dalui100% (1)
- Sürdürülebi̇li̇r Kirsal Turi̇zme Bütüncül YaklaşimDocument14 pagesSürdürülebi̇li̇r Kirsal Turi̇zme Bütüncül YaklaşimSüleyman can ASLANNo ratings yet
- Kalabagh Dam CaseDocument11 pagesKalabagh Dam CaseAwami National PartyNo ratings yet
- Electors - Summary - 25.03.2019Document4 pagesElectors - Summary - 25.03.2019Krish ChaituthekingNo ratings yet
- Water, Sources and UsesDocument3 pagesWater, Sources and UsesLabista SmithNo ratings yet
- Ar-July 31Document2 pagesAr-July 31Arvy Stave GraellosNo ratings yet
- GBM Resolution MahaveerDocument1 pageGBM Resolution MahaveerNarendra SinghNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Sustainable Development in Practice - SyllabusDocument5 pagesIntroduction To Sustainable Development in Practice - SyllabusEko SuryantoNo ratings yet
- Materi Belajar Cambridge Kelas 2 TAHUN PELAJARAN 2021/2022Document3 pagesMateri Belajar Cambridge Kelas 2 TAHUN PELAJARAN 2021/2022Ariska YuliNo ratings yet
- The Teen Activist: Artistic FamilyDocument3 pagesThe Teen Activist: Artistic FamilyAli BhraNo ratings yet
- Telangana Ongoing ProjectsDocument302 pagesTelangana Ongoing Projects36 vaishnavi chiluveruNo ratings yet
- Alih Fungsi (Konversi) Penggunaan Tanah Negara Di Kota MalangDocument11 pagesAlih Fungsi (Konversi) Penggunaan Tanah Negara Di Kota MalangFarhan Ahmad Setiyadin PutroNo ratings yet
- Navigating The Complex Tapestry of The Contemporary WorldDocument2 pagesNavigating The Complex Tapestry of The Contemporary WorldAlexie AlmohallasNo ratings yet
- Perilaku Hidup Bersih Dan Sehat (PHBS) Tatanan Rumah Tangga Pada Ibu Di PosyanduDocument6 pagesPerilaku Hidup Bersih Dan Sehat (PHBS) Tatanan Rumah Tangga Pada Ibu Di PosyanduMaulida FajriyahNo ratings yet
- Chalamaih - CRITICAL ANALYSIS OF LIFT IRRIGATION SCHEMES or OPTIMAL MANAGEMENT OF RESOURCESDocument168 pagesChalamaih - CRITICAL ANALYSIS OF LIFT IRRIGATION SCHEMES or OPTIMAL MANAGEMENT OF RESOURCESSoham SantraNo ratings yet
- ASEAN Socio-Cultural Community (Sustainable, Resilient, and Dynamic)Document9 pagesASEAN Socio-Cultural Community (Sustainable, Resilient, and Dynamic)Cayla Jen Basalan BunghanoyNo ratings yet
- Ongoing Investment Projects 1810 EngDocument9 pagesOngoing Investment Projects 1810 EnggvantsaNo ratings yet
- SpringissueDocument8 pagesSpringissueapi-309441596No ratings yet
- A Presentation On Sunkoshi Hydrpower Plant: Prepared By: Sarbaghya Lohala Roll No:33Document22 pagesA Presentation On Sunkoshi Hydrpower Plant: Prepared By: Sarbaghya Lohala Roll No:33Saroj DwaNo ratings yet
- Project Proposal TemplateDocument2 pagesProject Proposal TemplatejorifeberdenuevoespinosaNo ratings yet
- Pipe - Design - Sample With RVT Sizing Doti New SeriesDocument18 pagesPipe - Design - Sample With RVT Sizing Doti New SeriesCivil EngineeringNo ratings yet
- Class 10th Holiday Home WorkDocument4 pagesClass 10th Holiday Home WorkRithwik NambiarNo ratings yet
- Importance of WaterDocument2 pagesImportance of WaterMuddisetty AnandNo ratings yet
- Kirlampudi Mandal CanalsDocument3 pagesKirlampudi Mandal CanalsSaiteja PanyamNo ratings yet
- Critical Verbal Reasoning Practice Test 4Document2 pagesCritical Verbal Reasoning Practice Test 4Detay DanismanlikNo ratings yet