Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Form and Movement: The Axial Skeletal
Uploaded by
Monkey LoverOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Form and Movement: The Axial Skeletal
Uploaded by
Monkey LoverCopyright:
Available Formats
4.
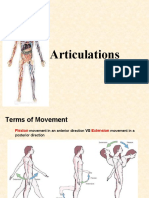
Form and Movement
The axial skeletal consists of the vertebral column, cranium, ribcage and sternum comprise the
axial skeleton. skull, ribcage, vertebral column
The appendicular skeleton consists of the scapula, clavicle, pelvis and limb bones. scapula
(shoulder blade), clavicle (collar bone), pelvis (under vertebral column) and limbs.
Long bones (e.g. femur, humerus) :
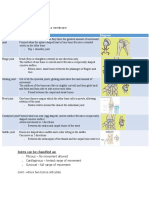
Joints:
The point where two bones meet is called a joint
Their functions include:
- keeping the ends of bones together, so that they do not separate
- reducing friction between the ends of moving bones
- a shock-absorbing surface between the two bones
Hinge joint:
- 1. Present in elbow.
- 2. Prevents movement through more than 180°. Movement is only in one plane.
Ball and socket joint:
- 1. Present at the shoulder and hip.
- 2. Allows for movement in three planes and around 360°.
Cartilaginous Intervertebral Joint:
- 1. Present at the vertebral column.
- 2. This is where the discs of cartilage can be squashed to allow for some movement.
Synovial joint:
- 1. Most joints are synovial joints and they are needed to allow for the smooth
movement of the bones against each other.
- 2. It has smooth articular cartilage at the ends of the bones to reduce friction and to
act also as a shock absorber.
- 3. A synovial joint also contains synovial fluid which lubricates the ends of the bones
reducing friction.
- 4. It also contains ligaments which wrap around the two bones. These are used to hold
the bones in place.
How a muscle induces movement:
- When a muscle contracts, a tendon pulls a bone making it move. Muscles usually work
in antagonistic pairs e.g. the biceps moves the radius up and the triceps moves it
down.
-
Nutrients needed for muscle and bone growth:
- Muscles:
- 1. Protein
- 2. Vitamin D
- Bones:
- 1. Calcium
- 2. Vitamin D
- 3. Phosphate
Symptoms and causes of Osteoporosis
- It is when the bones loose calcium salts and become porous and less dense so that they
break easily. Women are more vulnerable to osteoporosis as after menopause due to
change in in hormone levels. There is no cure, but it can be helped with good diet, calcium
and vitamin D supplements and treatment with hormones. Oestrogen levels fall therefore
osteoblasts can’t produce enough bones and eventually osteoclasts overpower them. In
men high testosterone levels protect bones.
- Treatment: Calcium and vitamin D supplement. Good diet. Exercise.
You might also like
- Principals of Anatomy Energy Systems IncDocument224 pagesPrincipals of Anatomy Energy Systems Inckevinramirezzz365No ratings yet
- Education Notes 6Document4 pagesEducation Notes 6Rwynn MemoryNo ratings yet
- Skeletal SystemDocument19 pagesSkeletal Systemsmbdy tbhhhNo ratings yet
- Skeletal SystemDocument29 pagesSkeletal SystemMB LoterteNo ratings yet
- 01 The Human Skeleton 2014 - WebDocument33 pages01 The Human Skeleton 2014 - Webapi-240330821No ratings yet
- Human Joints and Muscle ClassificationDocument16 pagesHuman Joints and Muscle ClassificationReemNo ratings yet
- Skeletal SystemDocument29 pagesSkeletal SystemCrii XiaNo ratings yet
- The Body in Sport - LearnerDocument31 pagesThe Body in Sport - Learnerplumbs23No ratings yet
- Skeletal SYatemDocument188 pagesSkeletal SYatemJasmine GañganNo ratings yet
- 511-525chapter 6-8 (2) An Introduction To ArticulationsDocument3 pages511-525chapter 6-8 (2) An Introduction To Articulationstomorrow.today.yesterday .yesterdayNo ratings yet
- The Skeletal SystemDocument4 pagesThe Skeletal SystemJoya Sugue AlforqueNo ratings yet
- Joints Joints: Dr. Dr. Wafaa Wafaa Abdel Abdel Rahman RahmanDocument25 pagesJoints Joints: Dr. Dr. Wafaa Wafaa Abdel Abdel Rahman RahmanImo ElfNo ratings yet
- Skeletal System (2) - 2Document71 pagesSkeletal System (2) - 2alazarademe797No ratings yet
- The Skeletal SystemDocument5 pagesThe Skeletal SystemMika SaldañaNo ratings yet
- Reviewer Skeletal To EndoDocument46 pagesReviewer Skeletal To EndoSophia CaisipNo ratings yet
- What is the Skeletal SystemDocument9 pagesWhat is the Skeletal SystemTishonna DouglasNo ratings yet
- PATHFIT_REVIEWER_TAYLORS-VERSIONDocument10 pagesPATHFIT_REVIEWER_TAYLORS-VERSIONvncbckNo ratings yet
- ORTHO Lec PP1 AnaPhysio - DxtestsDocument102 pagesORTHO Lec PP1 AnaPhysio - DxtestsJoana Patricia Celeres SaplagioNo ratings yet
- 02 Handout 2 (4) 2Document5 pages02 Handout 2 (4) 2Senpai LeonNo ratings yet
- Major Functions::: Compact Bone Spongy Bone and Marrow Which Makes Red and White Blood CellsDocument9 pagesMajor Functions::: Compact Bone Spongy Bone and Marrow Which Makes Red and White Blood CellsSi Aby ReyesNo ratings yet
- Skeletal SystemDocument13 pagesSkeletal Systemariolajose5No ratings yet
- BMED 66 - Movement Joints SUMMARYDocument5 pagesBMED 66 - Movement Joints SUMMARYBSMT 1-1, TAN, NICOLE SELINA L.No ratings yet
- Skeletal System 2: Dr. Garry NiedermayerDocument44 pagesSkeletal System 2: Dr. Garry NiedermayerWeng Sze TingNo ratings yet
- Track EventDocument21 pagesTrack Eventbosshage2No ratings yet
- Joints: Bones in The Shoulder and Chest: Types of Movable JointsDocument2 pagesJoints: Bones in The Shoulder and Chest: Types of Movable JointsLloyd LagadNo ratings yet
- SKELETAL SYSTEM-WPS OfficeDocument7 pagesSKELETAL SYSTEM-WPS OfficeAlan Gandidze MotifNo ratings yet
- Skeletal System NotesDocument4 pagesSkeletal System NotesLeon Abel80% (5)
- Locomotion Notes by AhmedfjDocument3 pagesLocomotion Notes by AhmedfjruesNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Principles of Anatomy and Physiology in SportDocument64 pagesUnit 1 Principles of Anatomy and Physiology in Sportdomhughes1093No ratings yet
- Skeletal System GuideDocument11 pagesSkeletal System GuideBryan JagroopNo ratings yet
- G-8 Skeletal SystemDocument30 pagesG-8 Skeletal SystemMarjun SalinasNo ratings yet
- The Skeleton and MusclesDocument33 pagesThe Skeleton and Musclesapi-406307933No ratings yet
- Pathfit ReviewerDocument7 pagesPathfit ReviewerbantayalagaNo ratings yet
- Skeleton Functions Types Bones Structure ConnectionsDocument3 pagesSkeleton Functions Types Bones Structure ConnectionsJas TingNo ratings yet
- Core 2 ADocument16 pagesCore 2 AJasmiine AlzateeNo ratings yet
- Skeletal SystemDocument7 pagesSkeletal SystemmikeNo ratings yet
- Skeletal System: Christine Bas Sweet Audrey Gwen SamsonDocument39 pagesSkeletal System: Christine Bas Sweet Audrey Gwen SamsonDanielle Kate MadridNo ratings yet
- Topic 1: Anatomy: 1.1 The Skeletal SystemDocument110 pagesTopic 1: Anatomy: 1.1 The Skeletal SystemJayden OoiNo ratings yet
- Skeletal System UpdatedDocument55 pagesSkeletal System UpdatedAlthea OcaslaNo ratings yet
- JointsDocument34 pagesJointsNandhana Kattuparambil SunojNo ratings yet
- Skeletal and Muscular System OverviewDocument72 pagesSkeletal and Muscular System OverviewMhimi ViduyaNo ratings yet
- Topic 1-Skeletal SystemDocument7 pagesTopic 1-Skeletal Systemadriana060909No ratings yet
- Lecture Guide Assessment-Of-Musculoskeletal-Function HPDocument85 pagesLecture Guide Assessment-Of-Musculoskeletal-Function HPBlessed GarcianoNo ratings yet
- Skeletal System OverviewDocument12 pagesSkeletal System OverviewRenjyl Gay DeguinionNo ratings yet
- m5 Skeletal SystemDocument33 pagesm5 Skeletal Systemapi-464344582No ratings yet
- BonesDocument9 pagesBonesLatt moe ooNo ratings yet
- Document 5Document22 pagesDocument 5dawidkubiak222No ratings yet
- Bones and Joint A&PDocument4 pagesBones and Joint A&Pbayoagunbiade0No ratings yet
- Bones in The Body 1. Skull: Skeletal SystemDocument12 pagesBones in The Body 1. Skull: Skeletal SystemSolemnly SwearrNo ratings yet
- Phy Class 9Document4 pagesPhy Class 9r jeet ranjanNo ratings yet
- Skeletal SystemDocument5 pagesSkeletal SystemWynne Michael David GogoNo ratings yet
- Bones BiomechanicDocument38 pagesBones BiomechanicTEH YU SHIAN SHARONNo ratings yet
- Synovial Joints and FunctionsDocument4 pagesSynovial Joints and FunctionsNinaNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Presentation WeeblyDocument85 pagesUnit 1 Presentation Weeblyapi-276945651No ratings yet
- Lect 1 Intro - MSKDocument75 pagesLect 1 Intro - MSKSivajothyNo ratings yet
- Musculoskeletal System AssessmentDocument75 pagesMusculoskeletal System AssessmentRolinette DaneNo ratings yet
- Form 5 Biology (Chapter 2: Locomotion & Support)Document14 pagesForm 5 Biology (Chapter 2: Locomotion & Support)NorhalizaIsmailNo ratings yet
- Skeletal System Guide - 206 Bones, Functions & Bone Types in 40 CharactersDocument4 pagesSkeletal System Guide - 206 Bones, Functions & Bone Types in 40 CharactersEricBuguinaNo ratings yet
- DefinitionDocument8 pagesDefinitionJamesNo ratings yet
- WBI05 01 Que 20190614Document28 pagesWBI05 01 Que 20190614alialiNo ratings yet
- Oct 20Document28 pagesOct 20Monkey LoverNo ratings yet
- WBI06 01 Que 20190520Document20 pagesWBI06 01 Que 20190520aliali100% (1)
- Biology: Pearson EdexcelDocument16 pagesBiology: Pearson EdexcelrachitNo ratings yet
- IAL Biol WBI05 Jan18 Scientific ArticleDocument8 pagesIAL Biol WBI05 Jan18 Scientific ArticleMoeez AkramNo ratings yet
- P51860a Ial Biology Wbi04 01 Jan18Document28 pagesP51860a Ial Biology Wbi04 01 Jan18Βασιλεία ΕυαγγέλουNo ratings yet
- Biology: Pearson EdexcelDocument16 pagesBiology: Pearson EdexcelrachitNo ratings yet
- Jan21 (4) NewDocument32 pagesJan21 (4) NewMonkey Lover0% (1)
- Wednesday 23 January 2019: BiologyDocument20 pagesWednesday 23 January 2019: Biologyrachit100% (1)
- Tuesday 8 January 2019: BiologyDocument24 pagesTuesday 8 January 2019: BiologyMonkey LoverNo ratings yet
- Homeostatic MechanismsDocument5 pagesHomeostatic MechanismsMonkey LoverNo ratings yet
- 1 HBDocument8 pages1 HBMonkey LoverNo ratings yet
- Reproduction and HeredityDocument10 pagesReproduction and HeredityMonkey LoverNo ratings yet
- Biology: Pearson EdexcelDocument24 pagesBiology: Pearson EdexcelMahmoudAboAlSamenNo ratings yet
- 8 HBDocument4 pages8 HBMonkey LoverNo ratings yet
- 9 HBDocument8 pages9 HBMonkey LoverNo ratings yet
- Respiration and BreathingDocument1 pageRespiration and BreathingMonkey LoverNo ratings yet
- Biological Molecules and Enzyme TestsDocument4 pagesBiological Molecules and Enzyme TestsMonkey LoverNo ratings yet
- 5 HBDocument13 pages5 HBMonkey LoverNo ratings yet
- 6 HBDocument6 pages6 HBMonkey LoverNo ratings yet
- 1 HBDocument8 pages1 HBMonkey LoverNo ratings yet
- 1 HBDocument8 pages1 HBMonkey LoverNo ratings yet
- Substance Move in and Out of Cells by Three WaysDocument2 pagesSubstance Move in and Out of Cells by Three WaysMonkey LoverNo ratings yet
- 1 HBDocument8 pages1 HBMonkey LoverNo ratings yet
- Ping Pong RulesDocument20 pagesPing Pong RulesHelmi Hj IsmuniNo ratings yet
- Worksheet #5: Applicable For Hardcopy ONLYDocument1 pageWorksheet #5: Applicable For Hardcopy ONLYJeff LacasandileNo ratings yet
- CSNZ Title Code ListDocument14 pagesCSNZ Title Code ListLutherweisNo ratings yet
- Kill Death Business Card RankerDocument2 pagesKill Death Business Card RankerDerek ShawNo ratings yet
- November 2020 course scheduleDocument1 pageNovember 2020 course scheduleAmeer sohailNo ratings yet
- Riser's Small Propane Fired ForgeDocument5 pagesRiser's Small Propane Fired ForgeDarko тралалаNo ratings yet
- Rehabilitation: Walking After Total Knee ReplacementDocument10 pagesRehabilitation: Walking After Total Knee ReplacementSandeep DhimanNo ratings yet
- Medial Side of ThighDocument29 pagesMedial Side of ThighAnnapurna BoseNo ratings yet
- Viviana PlazasDocument29 pagesViviana PlazasEricaNo ratings yet
- BreaststrokeDocument3 pagesBreaststrokeznguyen555No ratings yet
- Couatl Herald - Magic ItemsDocument2 pagesCouatl Herald - Magic ItemsDavi Alves MarinhoNo ratings yet
- Mix of Methods Leg Workout by MusclePharm - Muscle & StrengthDocument5 pagesMix of Methods Leg Workout by MusclePharm - Muscle & StrengthMouhNo ratings yet
- Calcium HypochloriteDocument7 pagesCalcium HypochloriteFrancois BresseNo ratings yet
- Dual Clutch Transmission: Visvesvaraya Technology UniversityDocument20 pagesDual Clutch Transmission: Visvesvaraya Technology Universitylhooks.infyNo ratings yet
- Faculty Meeting Minutes 2019Document26 pagesFaculty Meeting Minutes 2019Fobe Lpt NudaloNo ratings yet
- Brochure-Model 1895 SBLDocument2 pagesBrochure-Model 1895 SBLtystar_21No ratings yet
- Subordinate Service Selection Board, Punjab: Forest Guard Roll No. Wise Result of The Exam Held For The Post ofDocument1,552 pagesSubordinate Service Selection Board, Punjab: Forest Guard Roll No. Wise Result of The Exam Held For The Post ofGurtajbir SinghNo ratings yet
- RegulationsDocument10 pagesRegulationsapi-3837942100% (2)
- HP DV 5 IntelDocument44 pagesHP DV 5 IntelValerică HizanuNo ratings yet
- Healing CodesDocument3 pagesHealing CodesZEBADEEE85% (13)
- Gheorghe Hagi (: Romanian PronunciationDocument1 pageGheorghe Hagi (: Romanian PronunciationClaudiu PiuNo ratings yet
- A25d8425 2d66 4de8 Aa82 65e6dc954dfb - Wicked Brief AgentsDocument5 pagesA25d8425 2d66 4de8 Aa82 65e6dc954dfb - Wicked Brief AgentsJessica VellucciNo ratings yet
- Front Loader ChecklistDocument1 pageFront Loader ChecklistMalefane Cortez TlatlaneNo ratings yet
- Ultrasound of Ankle SprainsDocument8 pagesUltrasound of Ankle SprainsVenissa Lee100% (1)
- Recreational Activity (Fitness)Document36 pagesRecreational Activity (Fitness)Rina Lou Lumactud-DumukNo ratings yet
- SC2 PaperCraft: UEF ACU 2Document5 pagesSC2 PaperCraft: UEF ACU 2ali kararNo ratings yet
- Technical: Engine Blueprinting 101 - Part OneDocument4 pagesTechnical: Engine Blueprinting 101 - Part OneRussell GouldenNo ratings yet
- Auto reverse and airbag seat addedDocument7 pagesAuto reverse and airbag seat addedKofetoNo ratings yet
- Race DAODocument3 pagesRace DAOHether StoneNo ratings yet
- Sparepart JanuariDocument14 pagesSparepart JanuariArsana MdNo ratings yet