Professional Documents
Culture Documents
2 Susceptible: Transmission Based Precautions Guideline
Uploaded by
paulaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
2 Susceptible: Transmission Based Precautions Guideline
Uploaded by
paulaCopyright:
Available Formats
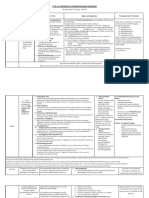
Transmission Based Precautions Guideline Questions: Contact Infection Control (ext 36596 or 36753)
Contact Droplet Airborne Isolation (door must be kept shut)
Required PPE: Gown and gloves Required PPE: mask daily check for negative air pressure
Infection / Disease Duration of precautions Infection / Disease Duration of precautions Infection / Disease Duration of precautions Room must be unoccupied for a minimum of 69 minutes.
Abscess, wounds, pressure ulcer Until drainage stops or can be Impetigo 24 hours after initiation of effective therapy Diphtheria Pharyngeal Until completion of antibiotics (14 days) and Terminal clean can occur during this time, but PPE must be worn
(decubitis ulcer, pressure sore) contained with dressing 2 negative cultures 24 hours apart Required PPE: N95 Respirator or PAPR (located in AOD)
Visitors will wear mask
Burkholderia cepacia Duration of hospitalization Lice: Head (pediculosis) and body Until 24 hrs after initiation of effective Epiglottitis, due to H. influenzae b 24 hours after initiation of effective therapy
therapy (when no lice is found) Infection / Disease Duration of precautions
Conjunctivitis acute viral Duration of illness (7-14 days) *Multidrug-resistant organisms (MDROs): 48hrs after completion of antibiotics and Influenza 7 days after onset or 24 hours after not Tuberculosis (TB) M. tuberculosis: 3 consecutive negative AFB sputum smears
MRSA, VRE, CRE, ESBL, MDR- Acinetobacter, have no open wounds/ulcers or indwelling presenting with respiratory signs and pulmonary or laryngeal --> confirmed collected on separate days; patient has been
organism ≤ 2 susceptible device with + MDRO symptoms (which ever is longer) on effective treatment
Diphtheria Cutaneous Until completion of antibiotics (14 Poliomyelitis Duration of illness (3 weeks) Meningitis: Haemophilus influenzae type b, 24 hours after initiation of effective therapy Tuberculosis (TB) M. tuberculosis: When likelyhood of infectious TB disease is
days) and 2 negative cultures 24 Neisseria meningitidis, meningococcal pulmonary or laryngeal --> suspected deemed negligible, and EITHER: 1. another
hours apart disease (sepsis, pneumonia, meningitis) diagnosis explains clinical syndrome, or
2. results of 3 sputum AFB smears are
negative and PCR negative
Furunculosis, staphylococcal Until drainage stops or can be Scabies and bed bugs 24 hours after initiation of effective therapy Mumps (infectious parotitis) 5 days after the onset of swelling Measles (rubeola) 14 days
contained with dressing
Herpes simplex (Herpesvirus Until lesions dry and crusted (2-3 Scalded skin syndrome Duration of illness (7-10 days) Mycoplasma pneumonia (IgM) Duration of illness (1-4 weeks) Contact and Airborne
hominis): Mucocutaneous, weeks) door must be kept shut; daily check for negative air pressure; room must be unoccupied
disseminated or primary, severe for a minimum of 69 minutes. Terminal clean can occur during this time, but PPE must be
worn
Herpes zoster (shingles): localized Duration of illness (2-4 weeks) Vaccinia: adverse events following Until lesions are dry and crusted over, scabs Pertussis (whooping cough) 5 days after initiation of effective antibiotic
Required PPE: Gown, N95 or PAPR (located in AOD or ED), and gloves
in intact immune system vaccination) have seperated therapy
Visitors will wear mask
Plague (Yersenia pestis ): pneumonic 48 hrs after initiation of effective antibiotic
Enteric Contact Isolation (TruD upon discharge) Contact and Droplet
therapy Infection / Disease Duration of precautions
Pneumonia: Meningococcal, pneumococcal, 24 hrs after initiation of effective therapy Aspergillosis: Massive soft tissue infection
Required PPE: Gown and gloves Required PPE: Gown, mask, and gloves
Strep Group A (Not from respiratory tract)
Rhinovirus (common cold) Duration of illness (7-10 days) Herpes zoster (varicella - zoster), shingles: Duration of illness (2-4 weeks)
Disseminated in any patient, localized in
Infection / Disease Duration of precautions Infection / Disease Duration of precautions immunocompromised
Clostridium difficile 48 hours after completion of Human metapneumovirus (if not presenting Duration of illness (7 days) Rubella (German measles) 7 days after onset of rash Monkeypox Until lesions crusted (4 weeks)
(C. diff) antibiotics and no complaints of with respiratory signs & symptoms Contact
diarrhea. Patient must be transferred only)
to a new room.
Rotavirus After 48 hrs of symptom free Multidrug-resistant organisms (MDROs): 48hrs after completion of antibiotics and Parvovirus B19 (Erythema infectiosum) Immunocompromised: Hospital duration Severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) 10 days after resolution of fever if
MRSA,VRE,CRE,ESBL,MDR- Acinetobacter, have no open wounds/ulcers or indwelling Others: 7 days respiratory symptoms are absent or
organism ≤2 suspectible with positive device with + MDRO improving
respiratory track results
Noroviruses After 48 hrs of symptom free Parainfluenza virus infection: Duration of illness (approx 4 months) Streptococcal group A Toxic shock syndrome 24 hours after initiation of effective therapy Smallpox (variola) All scabs have crusted and separated (3-4
immunocompromised (TSS) weeks)
Hepatitis A 3 weeks Pneumonia: Adenovirus Duration of illness (3 weeks) Tuberculosis (TB) M. tuberculosis, When patient on effective therapy, drainage
Extrapulmonary, draining lesion has ceased or has 3 consecutive negative
Contact time: AFB sputum smears collected on separate
Contact time: 4 minutes days
Hepatitis E 30 days Respiratory syncytial virus (RSV): Duration of illness (4 weeks) 2 minutes Chickenpox (varicella zoster) Until lesions dry and crusted (4-7 days)
immunocompromised
Anthrax cutaneous Duration of illness (12 days); Hand Group A Streptococcus: pneumonia, skin, 24 hours after initiation of effective therapy Viral hemorrhagic fevers: Duration of hospitalization
washing with soap and water 60 wound, or burn, invasive disease and until drainage stops or can be contained Lassa, Ebola, Marburg, Crimean-Congo
seconds by dressing
Bleach protocol (TruD upon discharge) Upon initiation of isolation, PPE should be made available at all times
Amebiasis diapered/incontinent patients Use dedicated or single use disposable patient equipment. When this is not possible, disinfection of common use items must be performed
Gastroenteritis: Bacterial/viral not diapered/incontinent patients Masks should be not worn around the neck; isolation gowns must be fastened on the back
listed under Enteric Contact Gown and gloves should not be worn in the hallway
Unexplained diarrhea: patients After 48 hrs of symptom free Linen: Should be double bagged for bed bugs, lice, and scabies
who do not meet Cdiff testing Prior to patient transport, transport equipment should have clean linen and be wiped down. Patients should wear a mask and be changed into a clean hospital gown
If contact isolation is discontinued, patient should be moved to a new room; Isolation sign will be removed by EVS after room has been cleaned
MRSA nares:No isolation required; Nozin BID
MDRO history: follow MDRO history isolation guideline
https://www.cdc.gov/infectioncontrol/pdf/guidelines/isolation-guidelines-H.pdf CDIFF history: No isolation required unless presenting with diarrhea
Transmission Based Precautions Guideline Questions: Contact Infection Control (ext 36596 or 36753)
Standard Precautions Infants/young children
Universal PPE: what you think is required for the task being performed Bronchiolitis Contact/Droplet
Enteroviral (Group A and B Coxsackie viruses Contact
Infection / Disease Infection / Disease Infection / Disease Infection / Disease Infection / Disease Infection / Disease and Echo viruses)
Abscess: If dressing covers and Colorado Tick fever Hantavirus pulmonary syndrome Meliodiosis: all forms Rickettsial fevers: tickborne (Rocky Trichuriasis: whipworm disease Contact
contains drainage Mountain spotted fever, tickborne Typhus
fever) Necrotizing enterocolitis
Acquired human Conjuctivitis: Acute bacterial - Helicobacter pylori Meningitis: fungal, Listeria monocytogenes, Rickettsial pox (vesicular rickettsiosis) Tularemia: draining lesion, pulmonary Contact/Droplet
immunodeficiency syndrome Chlamydiaand gonococcal Streptococcus pneumoniae
(AIDS/HIV) Parainfluenza virus infection
Actinomycosis Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (CJD, vCJD), Hepatitis viral: Type B, C, D, G Molluscum contagiosum Ringworm (dermatophytosis, Typhus: Rickettsia prowazekii (Epidemic or Pneumonia: H. influenzae, type b Droplet
Prion disease, Transmissible dermatomycosis, tinea) If an outbreak, use Louse-borne Typhus), R. typhi
spongiform encephalopathy Contact precautions
Anthrax: Pulmonary Cryptococcosis Histoplasmosis Mucormycosis Roseola infantum (exanthem subitum; Zygomycosis (phycomycosis, mucormycosis) Droplet
caused by HHV 6) Group A Strep: pharyngititis, scarlet fever
Arthropod-borne: viral Cysticercosis Hookworm Mycobacteria (nontuberculosis): atypical, Schistosomiasis (bilharziasis) Contact
encephalitides (eastern, wester, Pulmonary, wound
Venezuelan equine
encephalomyelitis; St. Louis,
Congenital rubella
California encephalitis;West Nile
Virus) and viral fevers (dengue,
yellow fever, Colorado tick fever)
Ascariasis Cytomegalovirus (CMV) infection Herpes simplex (Herpesvirus hominis ): Nocardiosis: draining lesions or other Sporotrichosis Enteroviral (all etiologies ie, group A and B Contact
encephalitis, mucocutaneous, recurrent presentations Coxsackie viruses except, polio)
(oral, skin, genital) Hand, foot, and mouth disease (diapered /
incontinent children)
Babesiosis Echinococcosis (hydatidosis) Kawasaki syndrome Orf Strongyloidiasis
Blastomycosis: North American Endometritis (endomyometritis) Legionnaires' disease Plague (Yersinia pestis ): Bubonic Syphilis
cutaneous or pulmoary
Brucellosis: undulant, Malta, Enterobiasis (pinworm disease, Leprosy (Hansen's disease) Pneumonia: Chlamydia, fungal, Haemophilus Tapeworm disease: Hymenolepis nana,
Mediterranean fever oxyuriasis) influenzae (type b) adults, Legionella spp, Taenia solium (pork), other
Pneumocystitis jiroveci/carinii, S. aureus,
Candidiasis: all forms including Epstein-Barr virus infection, including Leptospirosis Psittacosis (ornithosis): Chlamydia psittaci Tetanus
mucocutaneous infectious mononucleosis
Cat-scratch fever: benign Food poisoning: Botulism, C. Lice: Pubic Q fever Toxic shock syndrome (TSS): S. aureus
inoculation lymphoreticulosis perfringens, C. welchii , staphlococcal
Cellulitis Gonorrhea Listeriosis (Listeria monocytogenes ) Rabies Toxoplasmosis
Chancroid: soft chancre; H. Granuloma inguinale (Donovanosis, Lyme disease Rat-bite fever: Streptobacillus moniliformis Trachoma: acute
ducreyi granuloma venereum) disease, Spirillum minus disease
Chlamydia trachomatis: Group A Streptococcus : Endometritis Lymphocytic choriomeningitis Relapsing fever Trench mouth: Vincent's angina
Conjunctivitis, genital, pneumonia (puerperal sepsis)
(infants ≤3 months)
Closed-cavity infection: no drain or Group B Streptococcus : Neonatal Lymphogranuloma venereum Reye's Syndrome Trichinosis
closed drainage system
Coccidioidomycosis (Valley fever): Guillain-Barre syndrome Malaria Rheumatic fever Trichomoniasis
Draining lesions, pneumonia
MRSA nares:No isolation required; Nozin BID
MDRO history: follow MDRO history isolation guideline
https://www.cdc.gov/infectioncontrol/pdf/guidelines/isolation-guidelines-H.pdf CDIFF history: No isolation required unless presenting with diarrhea
You might also like
- Infectious Disease - BoardsDocument8 pagesInfectious Disease - BoardsSoojung NamNo ratings yet
- Communicable Disease Nursing Part II Diseases (1) 2Document21 pagesCommunicable Disease Nursing Part II Diseases (1) 2MK LiNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan For SarsDocument5 pagesNursing Care Plan For SarsKeith Wesley Ybut100% (2)
- Aerosol Generating Medical ProceduresDocument6 pagesAerosol Generating Medical Proceduresdhira anindita100% (1)
- Lecture 7 - Nosocomial PneumoniaDocument30 pagesLecture 7 - Nosocomial PneumoniaKartika Rezky100% (2)
- Exposure Risk Assessment and Management of Health Care WorkersDocument33 pagesExposure Risk Assessment and Management of Health Care WorkersCreativ WorxNo ratings yet
- COVID 19 Nurse's POVDocument3 pagesCOVID 19 Nurse's POVMarie Antionette MondragonNo ratings yet
- Ent Ward - NCPDocument5 pagesEnt Ward - NCPWendee PadillaNo ratings yet
- 3B Ids 2Document32 pages3B Ids 2LA BriguelaNo ratings yet
- Infection Control Audit Workshop 2021Document21 pagesInfection Control Audit Workshop 2021Nuraina SabdaniNo ratings yet
- Anesthesia Management and Perioperative Infection Control in Patients With The Novel CoronavirusDocument12 pagesAnesthesia Management and Perioperative Infection Control in Patients With The Novel CoronaviruswidiastrikNo ratings yet
- Final Pneumonia AlgorithmDocument1 pageFinal Pneumonia AlgorithmWajih FarhanNo ratings yet
- Cte #2: Matrix of Communicable DiseasesDocument7 pagesCte #2: Matrix of Communicable Diseasesjoannamae molagaNo ratings yet
- Quarantine Protocol PPE Proximity GuidelinesDocument2 pagesQuarantine Protocol PPE Proximity GuidelinespaulaNo ratings yet
- Ventilator: Associated Pneumonia (VAP)Document36 pagesVentilator: Associated Pneumonia (VAP)D. Melba S.S ChinnaNo ratings yet
- NR 224 Week 1 Instuctor Unit 1 Questions and AnswersDocument7 pagesNR 224 Week 1 Instuctor Unit 1 Questions and AnswersJesse JohnsonNo ratings yet
- Prelims - GMJ RLE - Module 2 III DisorderDocument1 pagePrelims - GMJ RLE - Module 2 III DisorderjuiceNo ratings yet
- DIPTHERIADocument2 pagesDIPTHERIADr KhatidjaNo ratings yet
- Theory PointersDocument89 pagesTheory Pointerslala byuNo ratings yet
- Infeksi Nosokomial: DR Hendra S. Spu Bag Bedah/Smf Urologi Rsud Ulin BanjarmasinDocument27 pagesInfeksi Nosokomial: DR Hendra S. Spu Bag Bedah/Smf Urologi Rsud Ulin BanjarmasinArini MulianaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care of Patients With Respiratory Comunicable DiseasesDocument74 pagesNursing Care of Patients With Respiratory Comunicable DiseasesGiselle EstoquiaNo ratings yet
- Handouts CD Prof. RojasDocument6 pagesHandouts CD Prof. RojasChallen CulturaNo ratings yet
- ICC AUDIT TOOL AND TRIAGE ALGORHYTHM DGMC - WPS PDF Convert PDFDocument40 pagesICC AUDIT TOOL AND TRIAGE ALGORHYTHM DGMC - WPS PDF Convert PDFWendy Dela PenaNo ratings yet
- Emerging Infections: Mers-Cov Ebola Avian FluDocument65 pagesEmerging Infections: Mers-Cov Ebola Avian Flurizko pNo ratings yet
- CNS+Infection+ +Fatima+SeparaDocument20 pagesCNS+Infection+ +Fatima+SeparaMarc Lorenz SeparaNo ratings yet
- Guideline For Isolation PrecautionsDocument4 pagesGuideline For Isolation PrecautionsJoebert BangsoyNo ratings yet
- DiphtheriaDocument3 pagesDiphtheriakpkr603No ratings yet
- Airborne PrecautionDocument2 pagesAirborne PrecautionEckry SilverNo ratings yet
- Diphtheria: Sabah Mohsin Al-Maamuri MDDocument3 pagesDiphtheria: Sabah Mohsin Al-Maamuri MDAmmar AlnajjarNo ratings yet
- Standard Operating Procedure For Handling of Corona Virus Disease (Covid-19) PatientsDocument6 pagesStandard Operating Procedure For Handling of Corona Virus Disease (Covid-19) PatientsHiJackNo ratings yet
- DiphtheriaDocument15 pagesDiphtheriaelka.kgmaNo ratings yet
- Pan 13863Document5 pagesPan 13863hanady shehataNo ratings yet
- Bacterial InfectionsDocument7 pagesBacterial InfectionsLarissaNo ratings yet
- Exposed To Covid19 1409Document6 pagesExposed To Covid19 1409A ShahinNo ratings yet
- RabiesDocument28 pagesRabiesrouhanbinrashidNo ratings yet
- Tatalaksana PneumoniaDocument37 pagesTatalaksana PneumoniaAnonymous R6ex8BM0No ratings yet
- COVID Management 17th January 2022 DR Suvrankar Datta AIIMSDocument1 pageCOVID Management 17th January 2022 DR Suvrankar Datta AIIMSWhiteNo ratings yet
- COVID Clinical Management 14012022Document1 pageCOVID Clinical Management 14012022Naina DesaiNo ratings yet
- Rational Use of PPE.Document18 pagesRational Use of PPE.Purvesh DhamiNo ratings yet
- Inbound 9171532219273535705Document6 pagesInbound 9171532219273535705MichelleNo ratings yet
- PPE Policy For COVID-1 - 31 03202Document13 pagesPPE Policy For COVID-1 - 31 03202CFTCNo ratings yet
- Management of Animal BiteDocument61 pagesManagement of Animal BiteSuryaAtmajayaNo ratings yet
- Diphteria, Pertussis and Staphylococcal Infections-1Document15 pagesDiphteria, Pertussis and Staphylococcal Infections-1Nwosu Ogbonna GabrielNo ratings yet
- Isolationwardinhospital 180913070258Document34 pagesIsolationwardinhospital 180913070258Lorna MiroNo ratings yet
- EN - Management of Healthcare Workers Exposed To COVID 19 V3.2Document6 pagesEN - Management of Healthcare Workers Exposed To COVID 19 V3.2Gangotri GayatriNo ratings yet
- Treatment Guidance For COVID-19 - 6 December 2020Document1 pageTreatment Guidance For COVID-19 - 6 December 2020meiraimNo ratings yet
- Communicable DiseaseDocument98 pagesCommunicable DiseasePeach BubbleNo ratings yet
- MERS CoV June2016Document41 pagesMERS CoV June2016riffat shaheenNo ratings yet
- Finals Reviewer: Page - 1Document64 pagesFinals Reviewer: Page - 1Louise DueyNo ratings yet
- Novel Coronavirus 2019: SCCC - SV Staff Accommodation Medical Services DepartmentDocument46 pagesNovel Coronavirus 2019: SCCC - SV Staff Accommodation Medical Services DepartmentnadiNo ratings yet
- Cardiacand Respiratory CMsDocument23 pagesCardiacand Respiratory CMsday alcoberNo ratings yet
- Covid 19Document31 pagesCovid 19Lee BuelaNo ratings yet
- Ppi Terkait Corona Virus (Utk DM) - DR TriDocument34 pagesPpi Terkait Corona Virus (Utk DM) - DR Tritrisna minNo ratings yet
- DiphtheriaDocument11 pagesDiphtheriabrigde_xNo ratings yet
- Infection Control ChartDocument11 pagesInfection Control ChartbrittanyNo ratings yet
- Covid 19 Aerosol Generating ProceduresDocument4 pagesCovid 19 Aerosol Generating ProceduresAhmed Ben BellaNo ratings yet
- Enhanced Contact & Respiratory PPE Proximity Isolation 10.13.20Document1 pageEnhanced Contact & Respiratory PPE Proximity Isolation 10.13.20paulaNo ratings yet
- Diphtheria - AMBOSSDocument8 pagesDiphtheria - AMBOSSSadikNo ratings yet
- Good Health in the Tropics: Advice to Travellers and SettlersFrom EverandGood Health in the Tropics: Advice to Travellers and SettlersNo ratings yet
- 2019 Sir AchDocument177 pages2019 Sir AchpaulaNo ratings yet
- Quarantine Protocol PPE Proximity GuidelinesDocument2 pagesQuarantine Protocol PPE Proximity GuidelinespaulaNo ratings yet
- Interim Guidance - Healthcare Professionals 2019-NCoV - CDCDocument2 pagesInterim Guidance - Healthcare Professionals 2019-NCoV - CDCpaulaNo ratings yet
- FY 2022 Domain Weighting DocumentDocument1 pageFY 2022 Domain Weighting DocumentpaulaNo ratings yet
- Enhanced Contact & Respiratory PPE Proximity Isolation 10.13.20Document1 pageEnhanced Contact & Respiratory PPE Proximity Isolation 10.13.20paulaNo ratings yet
- Utilizing Visual Cues Instrument TransportDocument2 pagesUtilizing Visual Cues Instrument TransportpaulaNo ratings yet