Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Concrete Technology Assignment # (10) : Submitted By: Honey I.D #: 119661 Date:31-10-2017
Uploaded by
Lavender Honey0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 views2 pagesThis document discusses concrete technology and specifically chemical reactions of aggregates that can cause detrimental expansion and cracking in concrete. It describes the alkali-silica reaction where reactive silica in aggregates reacts with alkalis from cement in the presence of moisture to form an expansive gel. It also discusses tests to identify potentially reactive aggregates like petrographic examination and mortar bar tests. It concludes with ways to prevent alkali-silica reaction damage like avoiding high alkali cement, reactive aggregates, and controlling water access.
Original Description:
Original Title
10_119661-10-30.10.2017
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document discusses concrete technology and specifically chemical reactions of aggregates that can cause detrimental expansion and cracking in concrete. It describes the alkali-silica reaction where reactive silica in aggregates reacts with alkalis from cement in the presence of moisture to form an expansive gel. It also discusses tests to identify potentially reactive aggregates like petrographic examination and mortar bar tests. It concludes with ways to prevent alkali-silica reaction damage like avoiding high alkali cement, reactive aggregates, and controlling water access.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 views2 pagesConcrete Technology Assignment # (10) : Submitted By: Honey I.D #: 119661 Date:31-10-2017
Uploaded by
Lavender HoneyThis document discusses concrete technology and specifically chemical reactions of aggregates that can cause detrimental expansion and cracking in concrete. It describes the alkali-silica reaction where reactive silica in aggregates reacts with alkalis from cement in the presence of moisture to form an expansive gel. It also discusses tests to identify potentially reactive aggregates like petrographic examination and mortar bar tests. It concludes with ways to prevent alkali-silica reaction damage like avoiding high alkali cement, reactive aggregates, and controlling water access.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
Concrete Technology
Assignment #(10)
Submitted by: Honey
I.D #: 119661
Date:31-10-2017
School of Engineering and Technology,
Asian Institute of Technology,Thailand
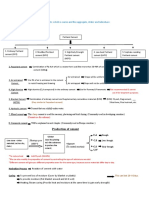
Chemical Reactions of Aggregates
Other aggregate Reactions
Alkali-Carbonate Reaction Alkali-Silica Reaction
1. Hydration of anhydrous MgO,
(Certain Carbonate Rocks (OH- associated with
CaO, CaSO4
participate in reactions with Alkalies from the cement
2. Oxidation of Pyrite
alkalies and produce and certain siliceous
3. Metallic Iron as contaminant
detrimental expansion and constituents from the
4. Reactions from organic impurities
cracking.) aggregate)
ASR Gel which Concrete
Alkalis Reactive Silica Moisture
expands Cracking
Sodium (Na+) Amorphous Water found in pore Creation of Alkali-Silica Gel
Potassium(K+) silica spaces in concrete 1. Aggregate in solution, pre ASR
Main Sources: Main Sources: Main Sources: damage
Portland Opal, Addition of water to 2. Surface of aggregate is attacked by
cement, Cherts , concrete mixture, OH-
Deicing agents, Volcanic rocks, Moist environment, 3. Silanol groups (Si-OH) on surface are
Sea water Strained quartz Permeable concrete broken down by OH- into SiO-
molecules
4. Released SiO- molecules attract alkai
Lab Tests for ASR: cations in pore solution, forming a gel
around the aggregate
1. Petrographic Examination (ASTM C295)
5. Alkali-Silica gel takes in water,
(Determination of the presence and quantities of reactive expanding and exerting a force
Materials by Petrographic Examination is helpful in against surrounding concrete
Evaluating potential alkali reactivity.) 6. When expansionary pressure
exceeds the tensile strength of
concrete, the concrete cracks
2. Mortar -Bar Test for potential reactivity (ASTM C227)
Test at 38℃ to in high alkali cement,
Measure Length at 14days,1,2,3,4,6,9,12 months,
Harmful if > 0.05% at 3 months & < 0.10% at 6 months
3. Chemical Test for potential reactivity (ASTM C289)
(Used primarily for the quick evaluation with results being obtained in a few days as
compared with 3-12 months with the Mortar-Bar Test)
1.Avoid High Alkali
How to content 4. Use Lithium
2. Avoid reactive 3. Control
Prevent (use low alkali additives prior to
aggregate access to
ASR Portland cement, placement of
(Amorphous silica) water
Damage Replace cement with concrete
pozzolanic admixture)
You might also like
- Risk AssessmentDocument2 pagesRisk AssessmentFaraiMbudaya0% (1)
- Study Plan For The Mechanical PE ExamDocument2 pagesStudy Plan For The Mechanical PE ExamMatthew Leaper100% (2)
- Doubly Reinforced BeamDocument19 pagesDoubly Reinforced BeamLavender HoneyNo ratings yet
- Design of Doubly Reinforced RC Beam (ACI 318-14) : Particulars Remarks 1 Material Properties Codes and SectionsDocument71 pagesDesign of Doubly Reinforced RC Beam (ACI 318-14) : Particulars Remarks 1 Material Properties Codes and SectionsLavender HoneyNo ratings yet
- Fly Ash Class C Geopolymer BrickDocument8 pagesFly Ash Class C Geopolymer BrickSiti AsmahaniNo ratings yet
- Diagnosis and Control of Alkali-Aggregate Reactions in ConcreteDocument26 pagesDiagnosis and Control of Alkali-Aggregate Reactions in ConcreteIrfan OmarNo ratings yet
- Jotun CourseDocument76 pagesJotun CourseElhusseiny Fouda100% (1)
- Matt FoundationDocument9 pagesMatt FoundationLavender HoneyNo ratings yet
- Technical Discussion - Cutless BearingsDocument7 pagesTechnical Discussion - Cutless BearingsSoodyod Yodyod0% (1)
- VoulhireDocument3 pagesVoulhireLavender HoneyNo ratings yet
- Physical Science 1 1Document58 pagesPhysical Science 1 1Anonymous N0FZEkrSaeNo ratings yet
- The Basics of Deteriorating Concrete at Wastwater Plants-Tips On Causes Repair and ResourcesDocument9 pagesThe Basics of Deteriorating Concrete at Wastwater Plants-Tips On Causes Repair and ResourcesPrakash100% (1)
- CY6251: Engineering Chemistry IIDocument26 pagesCY6251: Engineering Chemistry IIAnkur GuptaNo ratings yet
- Corrosion Process and Effects: Reliance Gas Transportation Infrastructure LTDDocument15 pagesCorrosion Process and Effects: Reliance Gas Transportation Infrastructure LTDRamesh mudunuriNo ratings yet
- Hydrogen in Steel: Effect of Hydrogen on Iron and Steel During Production, Fabrication, and UseFrom EverandHydrogen in Steel: Effect of Hydrogen on Iron and Steel During Production, Fabrication, and UseNo ratings yet
- Alkali-Silicate Reaction in CementDocument33 pagesAlkali-Silicate Reaction in CementAbbasabbasiNo ratings yet
- Petroleum Systems of Indonesia PDFDocument28 pagesPetroleum Systems of Indonesia PDFWahyu Probo Ananto HadiNo ratings yet
- 1 - Designing Ultrasonic Flow MetersDocument183 pages1 - Designing Ultrasonic Flow Metersmunzii100% (1)
- Osmotic Fragility of Red Blood CellsDocument3 pagesOsmotic Fragility of Red Blood Cellschaudhry umar farooqNo ratings yet
- Alkali-Aggregate Reaction (AAR) : Lecture # 8Document20 pagesAlkali-Aggregate Reaction (AAR) : Lecture # 8ashar khanNo ratings yet
- Durability (ARS)Document14 pagesDurability (ARS)Nijynsco KalebNo ratings yet
- Rebuild-Vol 9Document20 pagesRebuild-Vol 9ahtin618No ratings yet
- Alkali Aggregate Reaction, Alkali Carbonate Reaction and Pyrite AttackDocument3 pagesAlkali Aggregate Reaction, Alkali Carbonate Reaction and Pyrite AttackVasanthapragash NadarajhaNo ratings yet
- Alkali Aggregate Reaction in Concrete - Types, Causes, and EffectsDocument7 pagesAlkali Aggregate Reaction in Concrete - Types, Causes, and EffectsPritha DasNo ratings yet
- Natural Pozzolan As A Partial Substitute For Cement in ConcreteDocument11 pagesNatural Pozzolan As A Partial Substitute For Cement in ConcreteHka IsmailNo ratings yet
- Slugging in Pipelines What You NEED To KnowDocument68 pagesSlugging in Pipelines What You NEED To KnowSandeep PetwalNo ratings yet
- CCM Exam 2 ReviewDocument13 pagesCCM Exam 2 ReviewLuis AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Shell PDFDocument11 pagesShell PDFJoel John Day-ongao OlpindoNo ratings yet
- Construction and Building Materials: Lei Jiang, Ditao NiuDocument11 pagesConstruction and Building Materials: Lei Jiang, Ditao NiuXtem AlbNo ratings yet
- Examination of The Effects of LiOH, LiCl, and LiNO3on Alkali-Silica ReactionDocument13 pagesExamination of The Effects of LiOH, LiCl, and LiNO3on Alkali-Silica ReactionyimrhaneNo ratings yet
- Influence of Activator Solution Formulation On Fresh and Hardened Properties of Low Calcium Fly Ash Geopolymer ConcreteDocument9 pagesInfluence of Activator Solution Formulation On Fresh and Hardened Properties of Low Calcium Fly Ash Geopolymer ConcreteHonin AlshaeerNo ratings yet
- Corrosion of Uncoated and Oxide-Coated Basalt Fibre in Different Alkaline Media 2016Document7 pagesCorrosion of Uncoated and Oxide-Coated Basalt Fibre in Different Alkaline Media 2016Ping GeNo ratings yet
- Why Alkali-Activated Materials (AAM) Are NOT Geopolymers ?: Prof. Dr. Joseph Davidovits, Geopolymer InstituteDocument10 pagesWhy Alkali-Activated Materials (AAM) Are NOT Geopolymers ?: Prof. Dr. Joseph Davidovits, Geopolymer InstituteManuel AlejandroNo ratings yet
- Mae 1153 Alkali Silica ReactionDocument5 pagesMae 1153 Alkali Silica ReactionMohammad AL HaririNo ratings yet
- Orange Communication Workshop PresentationDocument13 pagesOrange Communication Workshop PresentationManan BariaNo ratings yet
- Corrosion: Dr. G. S. Ram Pradheep, M.E., PH.D Associate Professor Kongu Engineering College PerunduraiDocument18 pagesCorrosion: Dr. G. S. Ram Pradheep, M.E., PH.D Associate Professor Kongu Engineering College PerunduraiJanarthanan K SNo ratings yet
- Advanced Concrete TechnologyDocument22 pagesAdvanced Concrete TechnologymustafaNo ratings yet
- Impurities in Mixing WaterDocument2 pagesImpurities in Mixing WaterM.IDREES KhanNo ratings yet
- Krizan 2002Document8 pagesKrizan 2002Vidyadhara VNo ratings yet
- Sulfateresistanceofhigh PerformanceconcreteDocument10 pagesSulfateresistanceofhigh PerformanceconcreteMaroof imadNo ratings yet
- Corrosion Durability of Geopolymer Concretes Containing Different Concentrations of Alkaline SolutionDocument10 pagesCorrosion Durability of Geopolymer Concretes Containing Different Concentrations of Alkaline SolutionJHON WILMAR CARDENAS PULIDONo ratings yet
- Construction and Building Materials: P. Štukovnik, V. Bokan Bosiljkov, M. MarinšekDocument12 pagesConstruction and Building Materials: P. Štukovnik, V. Bokan Bosiljkov, M. MarinšekManuel AceroNo ratings yet
- Minerals: Effects of Cations/Anions in Recycled Tailing Water On Cationic Reverse Flotation of Iron OxidesDocument15 pagesMinerals: Effects of Cations/Anions in Recycled Tailing Water On Cationic Reverse Flotation of Iron OxidesBenito Quispe A.No ratings yet
- Kup Wade Patil 2011Document12 pagesKup Wade Patil 2011JHON WILMAR CARDENAS PULIDONo ratings yet
- Pat Soil Final Lab 1Document11 pagesPat Soil Final Lab 1Patrick Anthony Calica JeminezNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S2213343718306201 Main PDFDocument7 pages1 s2.0 S2213343718306201 Main PDFPAULINA AGUIRRENo ratings yet
- Lecture 06 Durability (ASR)Document36 pagesLecture 06 Durability (ASR)Danyal SafdarNo ratings yet
- A Comparative Study Between ASTM C1567 and ASTM C227 To Mitigate Alkali-Silica ReactionDocument8 pagesA Comparative Study Between ASTM C1567 and ASTM C227 To Mitigate Alkali-Silica ReactionMARLON ESPINOZANo ratings yet
- Construction and Building Materials: Xiao Huang, Shuguang Hu, Fazhou Wang, Yunpeng Liu, Yuandong MuDocument8 pagesConstruction and Building Materials: Xiao Huang, Shuguang Hu, Fazhou Wang, Yunpeng Liu, Yuandong MukarskotNo ratings yet
- Effectiveness of New Silica Fume Alkali Activator: Vladimı R Z IvicaDocument5 pagesEffectiveness of New Silica Fume Alkali Activator: Vladimı R Z Ivicataramalik07No ratings yet
- Electrochemical Behaviour Blended Cement Concretes Chloride Environments of Steel in Plain and in Sulphate And/orDocument7 pagesElectrochemical Behaviour Blended Cement Concretes Chloride Environments of Steel in Plain and in Sulphate And/orElizabeth CruzNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of Sulfate Resistance of Portland and High Alumina Cement Mortars Using Hardness TestDocument7 pagesEvaluation of Sulfate Resistance of Portland and High Alumina Cement Mortars Using Hardness TestEphremMelakuNo ratings yet
- 2 - Corrosion Related To CoatingsDocument22 pages2 - Corrosion Related To CoatingsLeon PanjaitanNo ratings yet
- An Experimental Investigation On Fly Ash Blended Cement ConcreteDocument9 pagesAn Experimental Investigation On Fly Ash Blended Cement ConcreteJHON WILMAR CARDENAS PULIDONo ratings yet
- Comparative Study of Conventional Concrete With Micropozz Based Geopolymer Concrete Along With GGBSDocument3 pagesComparative Study of Conventional Concrete With Micropozz Based Geopolymer Concrete Along With GGBSVivek PatvaNo ratings yet
- CONICET Digital Nro. ADocument11 pagesCONICET Digital Nro. ANora al-anssariNo ratings yet
- Materials and Design: R. Walter, M. Bobby KannanDocument5 pagesMaterials and Design: R. Walter, M. Bobby KannanAamir FarooqNo ratings yet
- Sulfate Resistance of High-Performance Concrete: M.J. Shannag, Hussein A. ShaiaDocument7 pagesSulfate Resistance of High-Performance Concrete: M.J. Shannag, Hussein A. ShaiaeliNo ratings yet
- R6 - 2011 - Effects of Sodium Chloride Solutions On Compressive Strength Development of Concrete Containing Rice Husk AshDocument8 pagesR6 - 2011 - Effects of Sodium Chloride Solutions On Compressive Strength Development of Concrete Containing Rice Husk Ashshekhar2307No ratings yet
- Study On Fly Ash and GGBS Based Geopolymer Concrete Under Ambient CuringDocument6 pagesStudy On Fly Ash and GGBS Based Geopolymer Concrete Under Ambient CuringkarskotNo ratings yet
- Lec 8Document6 pagesLec 8TOKA TKNo ratings yet
- Influence of Lightweight Aggregate On The Durability and Microstructure of ConcretesDocument1 pageInfluence of Lightweight Aggregate On The Durability and Microstructure of ConcretesWilmer Saith Catalan NoblesNo ratings yet
- An Experimental Work On Concrete by Usage of Calcite Powder As Partial Replacement With CementDocument5 pagesAn Experimental Work On Concrete by Usage of Calcite Powder As Partial Replacement With Cementኦርቶዶክስ ተዋህዶNo ratings yet
- Calor de RXN Rihani1965Document8 pagesCalor de RXN Rihani1965Joha BetancurNo ratings yet
- K2 0-Corrosion PDFDocument49 pagesK2 0-Corrosion PDFsyahmi azharNo ratings yet
- Ren Lai 2019Document22 pagesRen Lai 2019Leandro Jara GamarraNo ratings yet
- 1032 1561 1 PBDocument9 pages1032 1561 1 PBJHON WILMAR CARDENAS PULIDONo ratings yet
- Corrosion: Lydia - Uitm SaDocument9 pagesCorrosion: Lydia - Uitm SaLydiaRH100% (1)
- Assessing, Understanding and Unlocking Supplementary Cementitious MaterialsDocument6 pagesAssessing, Understanding and Unlocking Supplementary Cementitious MaterialsJuan J. Porras BarreroNo ratings yet
- MetalsDocument25 pagesMetalsGwen KoNo ratings yet
- Tendon Adjustment Tolerance-31.3.22Document13 pagesTendon Adjustment Tolerance-31.3.22Lavender HoneyNo ratings yet
- Dubai - 3D Printed House - Post-Tensioning Method For Precast Segmental StructureDocument3 pagesDubai - 3D Printed House - Post-Tensioning Method For Precast Segmental StructureLavender HoneyNo ratings yet
- Wedge Plate 6819M Stress Analysis ReportDocument13 pagesWedge Plate 6819M Stress Analysis ReportLavender HoneyNo ratings yet
- Level B1 Floor Plan: Span SystemsDocument1 pageLevel B1 Floor Plan: Span SystemsLavender HoneyNo ratings yet
- Honey's Work Schedule: The Royal OneDocument2 pagesHoney's Work Schedule: The Royal OneLavender HoneyNo ratings yet
- Vibration Response To Human Induced Dynamic Loading: Stana ŽivanovićDocument18 pagesVibration Response To Human Induced Dynamic Loading: Stana ŽivanovićLavender HoneyNo ratings yet
- Strength Prediction Techniques For Fresh Concrete: Miss Honey ID. 119661 Assignment-6 8.sept.2017Document10 pagesStrength Prediction Techniques For Fresh Concrete: Miss Honey ID. 119661 Assignment-6 8.sept.2017Lavender HoneyNo ratings yet
- Personal Monthly Budget1Document4 pagesPersonal Monthly Budget1Lavender HoneyNo ratings yet
- LNG Nom-Fap Tank's Files: No File FoundDocument2 pagesLNG Nom-Fap Tank's Files: No File FoundLavender HoneyNo ratings yet
- Dubai - 3D Printed House - Required Project InformationDocument2 pagesDubai - 3D Printed House - Required Project InformationLavender HoneyNo ratings yet
- (20201104) Drawings - CamberDocument12 pages(20201104) Drawings - CamberLavender HoneyNo ratings yet
- PTTLNG Tank: Preliminary Inspections and TestsDocument1 pagePTTLNG Tank: Preliminary Inspections and TestsLavender HoneyNo ratings yet
- S11 - X-Direction (Top Slab) : Longitudinal Active Tendons + Surface Pressure + PT Bars (Mpa)Document16 pagesS11 - X-Direction (Top Slab) : Longitudinal Active Tendons + Surface Pressure + PT Bars (Mpa)Lavender HoneyNo ratings yet
- 18.8.2017 LectureDocument2 pages18.8.2017 LectureLavender HoneyNo ratings yet
- Design of Steel Stool by SAP2000: Finite Shell Element Model Applied LoadingDocument8 pagesDesign of Steel Stool by SAP2000: Finite Shell Element Model Applied LoadingLavender HoneyNo ratings yet
- Combine FootingDocument98 pagesCombine FootingLavender HoneyNo ratings yet
- NA Topic3 BridgeDesignSeminar ColomboMarch2016Document141 pagesNA Topic3 BridgeDesignSeminar ColomboMarch2016Lavender HoneyNo ratings yet
- Lateral Loading CalculationsDocument8 pagesLateral Loading CalculationsLavender HoneyNo ratings yet
- Assignment For BCH3356Document2 pagesAssignment For BCH3356farehaNo ratings yet
- TurbidityDocument4 pagesTurbiditylaxminarayanNo ratings yet
- Metalcraft 4Document90 pagesMetalcraft 4Ana DuranNo ratings yet
- Paper MT Ii PDFDocument1 pagePaper MT Ii PDFiscristin26No ratings yet
- 1Document117 pages1Madhavi VyasNo ratings yet
- Environmentally Friendly Cooling With Heat: Ecoo 2.0: The Classic of Adsorption RefrigerationDocument3 pagesEnvironmentally Friendly Cooling With Heat: Ecoo 2.0: The Classic of Adsorption RefrigerationGokulSubramanianNo ratings yet
- Model Paper Engg - Chemistry 1 1 r16Document1 pageModel Paper Engg - Chemistry 1 1 r16vrkoradaNo ratings yet
- AIATS Schedule (2011, 2012)Document7 pagesAIATS Schedule (2011, 2012)goelbharatNo ratings yet
- Internship Report On Railway Coach FactoryDocument39 pagesInternship Report On Railway Coach FactoryJyotiraj ThakuriaNo ratings yet
- Rxn10 - FEMLAB-Fixed Bed ReactorDocument15 pagesRxn10 - FEMLAB-Fixed Bed ReactorvijendranbNo ratings yet
- Material Design and Characterization of High Performance Pervious ConcreteDocument10 pagesMaterial Design and Characterization of High Performance Pervious Concreteqwefqwefqwe fqwefqwNo ratings yet
- Salt Analysis-Vi Aluminum SulphateDocument3 pagesSalt Analysis-Vi Aluminum SulphateNANNo ratings yet
- Directional Spray Nozzles, Open: Type D3 Protectospray@ - L/2" NPTDocument6 pagesDirectional Spray Nozzles, Open: Type D3 Protectospray@ - L/2" NPTKrishna N HNo ratings yet
- Centrifugal PumpsDocument26 pagesCentrifugal PumpsromwamaNo ratings yet
- Low Power CMOS VLSI Circuit Design (LPVD) : Dr. Veena S ChakravarthiDocument43 pagesLow Power CMOS VLSI Circuit Design (LPVD) : Dr. Veena S ChakravarthiVeena SridharNo ratings yet
- Indion 850 Resin Engg Data SheetDocument6 pagesIndion 850 Resin Engg Data SheetsoumitrabanNo ratings yet
- Periodic Table Sig Fig B WDocument1 pagePeriodic Table Sig Fig B WRicardo VelozNo ratings yet
- 14 List of Products For Cert of Fitness (1) DNVDocument23 pages14 List of Products For Cert of Fitness (1) DNVCrywul Suitswitt FazhNo ratings yet
- Influence of Acerola Pulp Concentration On Mead Production by Saccharomyces Cerevisiae AWRI 796Document8 pagesInfluence of Acerola Pulp Concentration On Mead Production by Saccharomyces Cerevisiae AWRI 796mashelyNo ratings yet
- Processes 02 00265 v2 PDFDocument28 pagesProcesses 02 00265 v2 PDFGu VhvNo ratings yet
- Technical SpecificationDocument10 pagesTechnical SpecificationLUCAS ADOLFONo ratings yet
- Vacuum Super Insulated Heat Storage Up To 400 °C: January 2015Document11 pagesVacuum Super Insulated Heat Storage Up To 400 °C: January 2015Arvin SlayerNo ratings yet
- 99ebook Com Msg00388 PDFDocument15 pages99ebook Com Msg00388 PDFM Sarmad KhanNo ratings yet