Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Notes On Connective Tissue
Uploaded by
Akshitaa PandeyOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Notes On Connective Tissue
Uploaded by
Akshitaa PandeyCopyright:
Available Formats
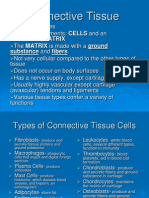
CONNECTIVE TISSUES
Tissues that connect, support, bind and separates other tissues or organs are
called CONNECTIVE TISSUE
• These tissues have few cells embedded in the intercellular spaces
filled with a substance called matrix or ground substance.
• The ground substance may be in the following forms:
Semi solid form – Connective tissue proper
Solid form - Skeletal system
Liquid form- Blood
Connective tissue proper are of 3 types
a Areolar tissue (net like)- holds organs together, connects skin with
underlying organs
b Adipose tissue ( fat tissue) Acts as a shock absorber, insulates,
stores energy as fat. Found under the skin and around internal organs
c Fibrous tissue- Ligaments and tendons
• Ligaments
• It is flexible and highly elastic.
• Poor blood supply.
• Found in These tissues are yellow in colour,( due to bundles of protein)
hence they are also called yellow fibrous tissue.
• It joins the bones to bones.
• knees, ankles, elbows, shoulders
Tendons
• These tissues are white in colour (little blood supply) hence they are also
called white fibrous tissue.
• It joins muscles to bones.
• It is strong and non-flexible.
• Poor blood supply.
• Located all over the body from head to feet. Achilles heel is the largest
tendon connecting the calf muscle to the heel bone.
You might also like
- Cds Day1Document15 pagesCds Day1Rajkamal ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6Document36 pagesChapter 6Nur-aine Hajijul100% (1)
- Connective Tissues: Rochelle M. Delos Santos Ii-A1 Bs-BiologyDocument54 pagesConnective Tissues: Rochelle M. Delos Santos Ii-A1 Bs-BiologyJordan Ramos100% (1)
- Animal Tissues Notes3 9 CbseDocument2 pagesAnimal Tissues Notes3 9 CbseSrijita RoyNo ratings yet
- Animal TissueDocument6 pagesAnimal TissueSarveshrau MagentharauNo ratings yet
- Tissues Cells Are Organized Into Groups and Layers Called TissuesDocument23 pagesTissues Cells Are Organized Into Groups and Layers Called TissuesDani AnyikaNo ratings yet
- Connective Tissue: by Muhammad SalmanDocument21 pagesConnective Tissue: by Muhammad SalmanAmber ZahidNo ratings yet
- Structures and Functions of Animal Tissues and Cell ModificationDocument105 pagesStructures and Functions of Animal Tissues and Cell ModificationArvie Jay Castillo100% (1)
- Connective TissueDocument21 pagesConnective TissueBeyhNo ratings yet
- Topic Types of Connective Tissues in Human BodyDocument13 pagesTopic Types of Connective Tissues in Human Bodysaeed qurashiNo ratings yet
- Tissue Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument35 pagesTissue Anatomy and Physiologysnp88100% (1)
- Lab Report Ayham FaisalDocument7 pagesLab Report Ayham Faisalayham omariNo ratings yet
- TissuesDocument60 pagesTissuesANDREI JESHA GINEZNo ratings yet
- Bio 2 Homeostasis 1mar17Document58 pagesBio 2 Homeostasis 1mar17nicoleNo ratings yet
- Different Body Tissues: By: Group 4Document25 pagesDifferent Body Tissues: By: Group 4Aisha Mae Cañete JawadNo ratings yet
- Cell Tissue TypesDocument48 pagesCell Tissue Typeschristian josh magtarayoNo ratings yet
- Connective Tisssue (General)Document29 pagesConnective Tisssue (General)James ChabuNo ratings yet
- BIOL223-Lab 9Document53 pagesBIOL223-Lab 9chicken fries100% (1)
- Animal Tissue PPT by KanishkaDocument20 pagesAnimal Tissue PPT by KanishkaKanishka SharmaNo ratings yet
- ?????????? ??????Document6 pages?????????? ??????DEBASISH MOHANTYNo ratings yet
- Connective TissueDocument2 pagesConnective Tissueiananicole.b30No ratings yet
- Connective TissuesDocument6 pagesConnective TissuesAmmar ShahidNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1: Animals' Specialized StructuresDocument58 pagesLesson 1: Animals' Specialized StructuresPhoenixNo ratings yet
- Animal TissueDocument45 pagesAnimal TissueAyesha YusopNo ratings yet
- Animal Tissue GKDocument6 pagesAnimal Tissue GKlakshya GandhiNo ratings yet
- Connective TissuesDocument18 pagesConnective TissuesLakwatserong GuroNo ratings yet
- Animal TissuesDocument7 pagesAnimal TissuesBeaNo ratings yet
- Tissues of The Human BodyDocument51 pagesTissues of The Human BodyKubun Ginta GintingNo ratings yet
- 00 Life Sciences Grade 10 PPT Connective TissuesDocument28 pages00 Life Sciences Grade 10 PPT Connective TissuesCleopatra NomathamsanqaNo ratings yet
- Tissues 1Document42 pagesTissues 1Patricia JalbanNo ratings yet
- Handout Animal Tissues 2023 2024Document4 pagesHandout Animal Tissues 2023 2024reece sayamNo ratings yet
- Tissue: The Living Fabric: Chapter 4 - Part BDocument10 pagesTissue: The Living Fabric: Chapter 4 - Part BJonathan HigginbothamNo ratings yet
- Animal TissuesDocument13 pagesAnimal TissuesYudatami TiaraNo ratings yet
- Genbio1 Unit1 Chapter2 (Animal Cells) 1Document26 pagesGenbio1 Unit1 Chapter2 (Animal Cells) 1Sofia EgbalicNo ratings yet
- Anatomy - TissuesDocument43 pagesAnatomy - TissuesGleceree Filomeno100% (1)
- Connective TissueDocument34 pagesConnective TissueLizette Joy Cuilan-Camilo100% (1)
- Samarjeet FA-1 Activity ScienceDocument16 pagesSamarjeet FA-1 Activity ScienceSamarjeet BaliyanNo ratings yet
- Cell OrganizationDocument8 pagesCell OrganizationKiele Nicole Calansingin100% (1)
- Gen BioDocument3 pagesGen BioalulodizeeNo ratings yet
- Animal TissuesDocument94 pagesAnimal TissuesMercel MacasinagNo ratings yet
- Cell Types: Plant and Animal TissuesDocument40 pagesCell Types: Plant and Animal TissuesMARY ANN PANGANNo ratings yet
- Animal TissueDocument26 pagesAnimal TissueReanne MeregildoNo ratings yet
- Plant Tissue: Epidermis (Outermost Covering) Simple Tissues: Epidermis TissueDocument6 pagesPlant Tissue: Epidermis (Outermost Covering) Simple Tissues: Epidermis TissueBhoomika GoyalNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5 Tissues, Cell CyclesDocument90 pagesLecture 5 Tissues, Cell Cyclesaidar.seralinNo ratings yet
- Handout 3.1 Cell Animal Vs Plant TissueDocument60 pagesHandout 3.1 Cell Animal Vs Plant Tissuearianeleurienee.poralanNo ratings yet
- TI UE: Epithelial TissueDocument7 pagesTI UE: Epithelial TissueDeep RoyNo ratings yet
- Tissues of Body: Chapter # 3Document20 pagesTissues of Body: Chapter # 3Mrym NbNo ratings yet
- Animal TissueDocument28 pagesAnimal TissueArjunNo ratings yet
- 9 A NewDocument62 pages9 A NewPrejith KNo ratings yet
- Unifying Concepts of Animal Structure and Function: Unit 5 Chapter 21Document76 pagesUnifying Concepts of Animal Structure and Function: Unit 5 Chapter 21Run GaoNo ratings yet
- Tissues: - TissueDocument61 pagesTissues: - Tissueuday xeroxNo ratings yet
- Connective Tissues Presented By: D F Wangila ConnectiveDocument27 pagesConnective Tissues Presented By: D F Wangila ConnectiveGeorge MunyendoNo ratings yet
- Structural Organisation in AnimalsDocument61 pagesStructural Organisation in AnimalsGanesh PatilNo ratings yet
- Connective Tissue ProperDocument15 pagesConnective Tissue ProperFilkal BasnetNo ratings yet
- Secret MineralizeDocument2 pagesSecret MineralizeMaricris CosmeNo ratings yet
- Animal Tissue: Haroen RasyidDocument41 pagesAnimal Tissue: Haroen Rasyidenkidani100% (1)
- Grade Ix Biology Animal Tissues 2021Document55 pagesGrade Ix Biology Animal Tissues 2021Purvi Prakash KNo ratings yet
- TISSUESDocument8 pagesTISSUESanmolmuskan2020No ratings yet
- Connective TissueDocument4 pagesConnective TissueLANGWAEMILLNo ratings yet
- Of Mice and MenDocument12 pagesOf Mice and MenAkshitaa PandeyNo ratings yet
- You're Losing Me (Capo 5)Document5 pagesYou're Losing Me (Capo 5)Akshitaa PandeyNo ratings yet
- Lulu Part 1Document2 pagesLulu Part 1Akshitaa PandeyNo ratings yet
- CSI Wildlife - Tracking Poachers - Case 1Document2 pagesCSI Wildlife - Tracking Poachers - Case 1Akshitaa PandeyNo ratings yet
- Belle Du Seigneur p.1Document4 pagesBelle Du Seigneur p.1Akshitaa PandeyNo ratings yet
- On Va Au Vieux CarreDocument2 pagesOn Va Au Vieux CarreAkshitaa PandeyNo ratings yet
- Building Food ChainsDocument5 pagesBuilding Food ChainsAkshitaa PandeyNo ratings yet
- Homes in DetroitDocument5 pagesHomes in DetroitAkshitaa PandeyNo ratings yet
- History of The N-WordDocument3 pagesHistory of The N-WordAkshitaa PandeyNo ratings yet
- Places To Visit in DubaiDocument1 pagePlaces To Visit in DubaiAkshitaa PandeyNo ratings yet
- Grouped Da A: (Or U) TDocument6 pagesGrouped Da A: (Or U) TAkshitaa PandeyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Matter and Its CompositionDocument4 pagesChapter 1 Matter and Its CompositionAkshitaa PandeyNo ratings yet
- Grade 9 Latitude and LongitudeDocument15 pagesGrade 9 Latitude and LongitudeAkshitaa PandeyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Matter and Its Composition: Arrangement of Molecules: Comparative Study in Solid, Liquid and GasDocument3 pagesChapter 1 Matter and Its Composition: Arrangement of Molecules: Comparative Study in Solid, Liquid and GasAkshitaa PandeyNo ratings yet
- ADHD is Awesome: A Guide to (Mostly) Thriving with ADHDFrom EverandADHD is Awesome: A Guide to (Mostly) Thriving with ADHDRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- The Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityFrom EverandThe Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (30)
- Think This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeFrom EverandThink This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeRating: 2 out of 5 stars2/5 (1)
- Love Life: How to Raise Your Standards, Find Your Person, and Live Happily (No Matter What)From EverandLove Life: How to Raise Your Standards, Find Your Person, and Live Happily (No Matter What)Rating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- LIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionFrom EverandLIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (404)
- The Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsFrom EverandThe Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (4)
- Summary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandSummary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (42)
- Raising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsFrom EverandRaising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- By the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsFrom EverandBy the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsNo ratings yet
- Summary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedFrom EverandSummary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (81)
- Raising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsFrom EverandRaising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (170)
- The Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaFrom EverandThe Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- Dark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.From EverandDark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (110)
- Why We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityFrom EverandWhy We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5)
- Summary: Limitless: Upgrade Your Brain, Learn Anything Faster, and Unlock Your Exceptional Life By Jim Kwik: Key Takeaways, Summary and AnalysisFrom EverandSummary: Limitless: Upgrade Your Brain, Learn Anything Faster, and Unlock Your Exceptional Life By Jim Kwik: Key Takeaways, Summary and AnalysisRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (8)
- Empath: The Survival Guide For Highly Sensitive People: Protect Yourself From Narcissists & Toxic Relationships. Discover How to Stop Absorbing Other People's PainFrom EverandEmpath: The Survival Guide For Highly Sensitive People: Protect Yourself From Narcissists & Toxic Relationships. Discover How to Stop Absorbing Other People's PainRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (95)
- The Courage Habit: How to Accept Your Fears, Release the Past, and Live Your Courageous LifeFrom EverandThe Courage Habit: How to Accept Your Fears, Release the Past, and Live Your Courageous LifeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (253)
- Mindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessFrom EverandMindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (328)
- Summary: Thinking, Fast and Slow: by Daniel Kahneman: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedFrom EverandSummary: Thinking, Fast and Slow: by Daniel Kahneman: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (61)
- The Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossFrom EverandThe Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (6)
- The Marshmallow Test: Mastering Self-ControlFrom EverandThe Marshmallow Test: Mastering Self-ControlRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (60)
- Manipulation: The Ultimate Guide To Influence People with Persuasion, Mind Control and NLP With Highly Effective Manipulation TechniquesFrom EverandManipulation: The Ultimate Guide To Influence People with Persuasion, Mind Control and NLP With Highly Effective Manipulation TechniquesRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (1412)
- Cult, A Love Story: Ten Years Inside a Canadian Cult and the Subsequent Long Road of RecoveryFrom EverandCult, A Love Story: Ten Years Inside a Canadian Cult and the Subsequent Long Road of RecoveryRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)