Professional Documents
Culture Documents
As Biology Answers
Uploaded by
Wael TareqOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
As Biology Answers
Uploaded by
Wael TareqCopyright:
Available Formats
1. Galactosaemia is an inherited disorder that produces an inability to metabolise galactose.
Babies
with galactosaemia vomit soon after they have started to breast feed because of the production of
metabolic toxins. If it is not treated it can result in mental retardation. The babies obtain the
galactose because it is a sub-unit of lactose which is present in milk.
(a) (i) State the general formula for disaccharide.
C12 H22 O11;
(1 marks)
(ii) Name the chemical process by which lactose is broken down into its constituent
sub-units.
hydrolysis / eq;
(1 marks)
(iii) State one chemical difference between lactose and maltose.
lactose consists of glucose + galactose, maltose consists of glucose only /
lactose contains galactose but maltose does not;
(1 marks)
(b) Suggest a simple treatment for a baby who has galactosaemia and give a reason for
your answer.
use non-human milk / named example / artificial / powdered; no lactose / no
galactose / add enzymes to break down galactose; replace (lactose) with
another sugar;
(2 marks)
[Total 5 marks]
David Kaunda High School 1
2. The diagram below shows some of the stages in protein synthesis and secretion in a
mammalian cell.
(a) (i) Name the processes taking place during stages A and B.
A transcription;
B translation;
(2 marks)
(ii) Name the process by which protein is secreted in stage F.
exocytosis / reverse pinocytosis;
(1 marks)
(b) Describe the part played by transfer RNA in the formation of the polypeptide chain during
stage B.
tRNA has an unpaired triplet of bases / anticodon; attaches to / binds to
mRNA codon / complementary bases; tRNA carries a specific amino acid;
which becomes part of polypeptide / reference to formation of peptide bonds;
(3 marks)
[Total 6 marks]
David Kaunda High School 2
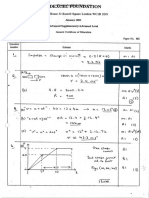
3. The graph below shows how the quantity of DNA, measured in arbitrary units, varies with time
during the different phases of the cell cycle in an animal cell.
6
D N A / a rb itr a ry u n its
4
Q u a n tity o f
G 1 S G 2
In te rp h a s e M ito sis I n te rp h a s e
(a) Interphase is made up of two growth phases, G 1 and G2, separated by an intermediate
phase, S.
(i) Explain what is happening within the cell during phase S.
quantity of DNA doubles;
replication of DNA / chromosomes;
preparation for mitosis / nuclear division / cell division / asexual
reproduction;
(2 marks)
(ii) State one process other than cell growth which occurs during phase G 2.
mitochondria divide / energy stores increase / ATP produced / respiration /
duplication of centrioles / spindle begins to form / protein synthesis;
(1 marks)
(b) Account for the changes in the quantity of DNA in the cell during mitosis.
DNA content halves / returns to original level;
DNA / chromosomes / chromatids shared between (daughter) cells / nuclei;
during cell division / cytokinesis;
(2 marks)
[Total 5 marks]
4. The table below refers to some features of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells.
David Kaunda High School 3
If the feature is present, place a tick () in the appropriate box and if the feature is absent, place
a cross (x) in the appropriate box.
F e a tu re P ro k a ry o tic c e ll E u k a ry o tic c e ll
N u c le a r e n v e lo p e ;
C e ll s u rfa c e m e m b ra n e ;
R ib o s o m e s ;
M ic ro tu b u le s ;
M ito c h o n d ria ;
[Total 5 marks]
5. The graphs below show the relationship between pH and the relative activity of three different
protein digesting enzymes: trypsin, pepsin and papain.
R e la tiv e
a c tiv ity T ry p s in
6 8 10
pH
R e la tiv e P e p s in R e la tiv e P a p a in
a c tiv ity a c tiv ity
2 4 6 4 6 8
pH pH
(a) Explain why changes in pH usually affect the activity of the enzymes.
pH affects ionisation / changes / ionic bonds / hydrogen bonds; this affects
shape of enzyme / active site; could affect ionisation of substrate; affects
formation of enzyme - substrate complexes; enzymes may be denatured at
extremes of pH / at unsuitable pH values;
David Kaunda High School 4
(3 marks)
David Kaunda High School 5
(b) Comment on the effect of changes in pH on the activity of trypsin, pepsin and papain.
trypsin has an optimum activity at pH 8 (range 7.5 - 8.5);
pepsin has an optimum activity at pH 2 (range 1.5 - 2);
activity decreases on either side of the optimum;
activity of papain is not affected by changes in pH;
papain has a relatively high activity over pH range 4 to 8 / has no optimum pH;
(4 marks)
(c) Which of these three enzymes would be most suitable to use as a meat tenderiser?
Give an explanation for your answer.
papain; has a high activity over wide range of pH values; optima of
pH 2 or 8 are unsuitable for culinary use / trypsin (or pepsin) has too
specific pH requirements;
alternative:
trypsin;
pH optimum close to that of meat / blood;
(2 marks)
(d) Rennin, an enzyme extracted from the stomach of calves, is used in the manufacture of
cheese. Maxiren®, an enzyme similar to rennin, is produced by gene technology.
State two advantages of using Maxiren®, instead of rennin in cheese manufacture.
1 may be cheaper to produce / extract;
easier to extract;
2 can be produced in large quantities / faster;
ethical considerations / suitable for vegetarians;
microbial enzymes are temperature stable;
standardised quality / enzyme always the same / purer;
(2 marks)
[Total 11 marks]
6. Read through the following account of carbohydrate digestion then write on the dotted lines the
most appropriate word or words to complete the account.
Digestion of starch starts in the ............mouth / buccal cavity;............ where it is
hydrolysed to.........maltose / dextrins;.......... by the enzyme ................amylase;....
This process is halted in the stomach but continues in the duodenum, catalysed by an
enzyme secreted by the .........pancreas;............... . Also in the duodenum, sucrose is
hydrolysed to ...............glucose;....................... and ................fructose;............. by
enzymes produced by secretory cells in the duodenum wall.
[Total 6 marks]
David Kaunda High School 6
7. Give an account of the ways in which human activities lead to the pollution of water.
sewage / waste organic matter from poor treatment / agricultural / industrial
spillage;
nitrate from agricultural fertilisers;
leaching into / (dissolve) in run-off water;
*growth of algae;
oil from ships / drilling / oil spillage;
less light so less photosynthesis;
effect on plumage / skin / fur;
warm water from industry / power stations / cooling of machinery / eq;
some organisms grow faster / less well / die due to temperature changes;
oxygen less soluble;
detergents domestic / industrial source / oil treatment;
acid rain from combustion / eq of fossil fuel / named eq;
reduces pH of lakes / eq / increases aluminium concentration;
pesticides from agricultural use;
named heavy metal / heavy metals from industry / chemical processes;
radioactive materials / isotopes from nuclear reactions;
oestrogenic compounds from surfactants / plastics industry / pesticides /
DDT;
abnormal development / hermaphroditism in fish;
THE FOLLOWING POINTS COULD BE CREDITED ONCE ONLY WITHIN AN
APPROPRIATE CONTEXT
(organic matter) utilised by bacteria which grow / increase in number;
(increased respiration) uses up more oxygen / increase in B.O.D;
eutrophication / death of other organisms;
toxic effect of substance on organisms;
bio accumulation reference;
effect on / disruption of food chain / web;
*growth of algae was a general point, credited once in an appropriate context.
[Total 10 marks]
8. The diagram below shows a section of a human heart at a specific stage in the cardiac cycle.
David Kaunda High School 7
(a) Name the stage of the cardiac cycle shown in the diagram and give two reasons for
your choice.
Name of stage: diastole / atrial systole;
Reason 1: aortic / pulmonary artery / semilunar valve(s) closed;
Reason 2: atrioventricular / mitral / tricuspid valve(s) open;
(3 marks)
(b) Give one function of each of the parts A and B.
P a rt F u n c tio n
A p r e v e n ts v a lv e in v e r tin g ;
a d ju s ts t e n s io n in A /n a m e /c o n t r a c ts
B to p u ll o n A ;
(2 marks)
[Total 5 marks]
9. The table below refers to three different plant cells found in stems. Complete the table by
writing the appropriate word or words in the empty boxes.
C e ll ty p e O n e c h a ra c te ris tic
O n e fu n c tio n
s tru c tu ra l fe a tu re
tr a n s lo c a tio n /
s ie v e p la te /n o n u c le u s /
S ie v e tu b e e le m e n t tra n s p o rt o f s u c ro s e /
fe w o r g a n e lle s ;
a m in o a c id s ;
lig n ifie d /n o c e ll c o n te n ts / T ra n s p o rt o f w a te r
v e s s e l / tr a c h e id ; n o e n d w a ll (if v e s s e l); a n d m in e ra l io n s
c o lle n c h y m a c e ll;
W a lls th ic k e n e d in th e S u p p o rt
c o rn ers
[Total 5 marks]
10. Records of human fertility for the period 1930 - 1990 have shown changes in the sperm counts
of normal men.
David Kaunda High School 8
The table below summarises the changing percentages of men with high or low sperm counts
over the period of sixty years.
High sperm count > 100 × 106 sperm cm-3
Low sperm count < 20 × 106 sperm cm--3
M e n w ith M e n w ith
T im e p e rio d
h ig h s p e rm c o u n ts / % lo w s p e rm c o u n ts / %
1930 – 1950 50 5
1951 – 1960 45 4
1961 – 1970 28 14
1971 – 1980 21 11
1981 – 1990 15 18
(a) (i) Comment on the changes in the percentage of men with high sperm counts during
the period 1930 to 1990.
percentage falling / fall of 35%;
biggest drop in sixties / between 1951-1970;
some evidence of flattening / ref to figures;
(2 marks)
(ii) Compare the figures for men with low sperm counts with those with high sperm
counts over the same period.
lower percentage of men with low sperm counts at beginning;
numbers increasing during the period / increased by 13%; both fall 1971 - 80;
fall in percentage of men with high sperm counts in greater than rise in
percentage of men with low sperm counts / converse;
biggest rise in numbers in sixties / corresponds with drop in numbers of men
with high sperm counts / fluctuations in numbers of men with low sperm
counts; after 1980 figures similar;
(3 marks)
(b) Explain why it is necessary for large numbers of sperms to be produced when only one
sperm is required to bring about fertilisation.
large numbers do not reach fallopian tubes / site of fertilisation;
many sperm die; ref to conditions / pH in vagina;
enzymes needed for activation of sperm / ref capacitation;
many sperm may be abnormal / reduced mobility;
(2 marks)
(c) Exposure of pregnant women to high levels of certain oestrogens during early pregnancy
can result in reproductive disorders in their male offspring.
It appears that a number of compounds in the environment can mimic the action of
oestrogens when ingested. Such compounds, termed oestrogenic chemicals, are found in
pesticides, such as DDT and PCBs, and also in the breakdown products of certain
detergents. They accumulate in the fatty tissue and have the same effect as oestrogens,
which play a major role in the menstrual cycle.
David Kaunda High School 9
(i) Describe the normal role of oestrogens in the menstrual cycle.
stimulated by FSH; stimulates repair of the endometrium / lining of uterus;
inhibits FSH production; stimulates LH production; leads to ovulation;
(3 marks)
(ii) Suggest how the oestrogenic chemicals pass from the mother to the
developing fetus.
in maternal blood / blood stream;
when fat stores mobilised / broken down;
correct ref to diffusion; correct ref to placenta;
uptake into fetal circulation / fetal blood;
into umbilical vein;
(3 marks)
[Total 13 marks]
11. (a) The diagrams below represent the chromosomes during stages in the process of mitosis.
Write the letters in the order that represents the sequence in which these stages occur.
BDACFE/DACFEB:
(1 marks)
(b) State two ways in which meiosis differs from mitosis.
1 pairing of homologous chromosomes / eq;
chiasmata formation / crossing over occurs;
2 chromosome number halved / haploid cells formed;
two divisions to complete process / four cells formed;
The converse of these points allowed if a clear reference to mitosis was
made.
(2 marks)
David Kaunda High School 10
(c) Explain the significance of mitosis in living organisms.
production of genetically identical cells;
daughter cells have same function as parent cell;
for growth / repair;
for asexual reproduction / clone formation;
rapid reproduction in favourable conditions;
(3 marks)
[Total 6 marks]
12. An experiment was carried out to investigate the relationship between the diameter of stomatal
aperture and the rate of transpiration in still air and in moving air.
Leaves of a dicotyledonous plant were used. One set of leaves was kept in still air and another
set was exposed to moving air generated by an electric fan. The stomatal transpiration was
measured as water loss in nanograms (ng) per second per cm2 of the leaf surface for stomatal
aperture in the range 0 to 20m in diameter.
The results are shown in the table below. Each value is the mean of many readings.
S to m a ta l tra n s p ira tio n / n g s –1 c m –2
S to m a ta l a p e rtu re / m
In s till a ir In m o v in g a ir
0 .0 5 10
2 .5 30 60
5 .0 40 90
7 .5 50 125
1 0 .0 55 150
1 5 .0 65 200
2 0 .0 70 250
(a) (i) Plot the data in suitable graphical form on the graph paper opposite.
(5 marks)
(ii) Using data from your graph, calculate the percentage change in stomatal
transpiration in moving air compared to still air when the stomatal aperture is
12.5m. Show your working.
61 1, 175 1; (check with candidate’s graph)
175 61
100;
61
Answer 186.8%
(3 marks)
David Kaunda High School 11
250
m o v in g a ir
m a rk s fo r
axes:
200 r ig h t w a y
ro u n d ,
c o r r e c tly la b e lle d
s c a le :
s u ita b le ,
–2
m o re th a n ½
m
paper used
–1c
S to m a ta l tr a n s p ir a t io n n g s
150 key:
fo r th e c u rv e s
p o in ts :
p lo tte d a c c u r a te ly
c u rv e :
p o in ts jo in e d
r e a lly w it h
100 r u le d lin e s
s till a ir
50
0 5 10 15 20
S to m a ta l a p e rtu re / m
David Kaunda High School 12
(b) (i) Comment on the relationship between stomatal transpiration and aperture diameter
in still air.
overall increase in transpiration as pore size increases / converse;
aperture of pore up to 7.5 m in diameter / steep increase in transpiration /
greatest rate of change;
above 7.5 m increase in diameter / aperture of pore has less effect;
(2 marks)
(ii) Describe two ways in which the results for moving air differ from those for still air.
more water loss through transpiration / curve steeper;
OR transpiration greater / faster;
continues increasing / linear relationship / rate does not decrease.
(2 marks)
(c) Suggest an explanation for the differences in stomatal transpiration in still air and in
moving air.
in moving air, water vapour removed from vicinity of leaf surface / in still air,
water vapour stays near leaf surface;
steeper concentration gradient / diffusion gradient / converse for still air;
so more water vapour lost / faster rate of transpiration / converse for still air;
the wider the aperture the more water vapour is lost / converse;
(3 marks)
[Total 15 marks]
13. (Biology)
The diagram below shows a potometer which can be used to measure the rate of water uptake by
plants.
David Kaunda High School 13
(a) Describe, with full practical details, how you would use this apparatus to measure the rate
of water uptake per unit area of leaf for this plant.
open tap to allow water column to fill capillary tube; check for leaks with tap
closed/eq ;
equilibration ;
note level of water column/meniscus on scale;
record distance moved along scale in fixed time/time taken for column to
travel fixed distance;
reset water column by opening tap;
repeat at least 3 times;
calculate (mean) volume of water taken up qualified;
suitable method of measuring leaf area described / eg draw round leaves on
graph paper and count squares of known volume
(6 marks)
(b) State three precautions which should be taken when setting up this experiment.
maintain constant conditions surrounding the plant;
at least two of temperature/light/humidity / air movement named;
check apparatus is free from bubbles / air locks / completely filled with water /
eq;
read bottom of the meniscus / eq;
fix plant firmly to prevent movement which could affect reading;
cut stem under water;
(3 marks)
[Total 9 marks]
14. The table below refers to three organic compounds found in cell organelles.
If the compound is found in the organelle, place a tick () in the appropriate box and if the
compound is not found in the organelle, place a cross (x) in the appropriate box.
O rg a n e lle P h o s p h o lip id D N A RN A
R ib o s o m e ;
C h lo ro p la s t ;
S m o o th e n d o p la s m ic ;
re tic u lu m
M ito c h o n d rio n ;
[Total 4 marks]
David Kaunda High School 14
15. The diagram below shows the structure of part of a molecule of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA).
C
O
O
O
O
B D
O
O
O
A O
(a) Name the parts labelled A, B, C and D.
A deoxyribose;
B phosphate / phosphate group;
C organic base / named example / purine / pyrimidine;
D hydrogen bond / dipole - dipole link;
(4 marks)
(b) (i) On the diagram, draw a ring around one nucleotide.
(1 mark)
(ii) What type of chemical reaction is involved in the formation of a molecule of DNA
from nucleotides?
condensation / dehydration / polymerisation;
(1 mark)
[Total 6 marks]
16. The diagram below shows part of a messenger RNA (mRNA) molecule.
U A C C G A C C U U A A
(a) (i) How many codons are shown in this section of mRNA?
four / 4;
(1 mark)
(ii) What is specified by a sequence of codons in an mRNA molecule?
sequence / order of amino acids / primary structure of polypeptide / protein;
(1 mark)
David Kaunda High School 15
(b) A tRNA molecule carries a complementary base sequence for a particular codon.
(i) Write the complementary sequence for the first codon in the mRNA sequence given
above.
AUG;
(1 mark)
(ii) Describe the role of tRNA molecules in the process of protein synthesis.
tRNA has an unpaired triplet of bases / anticodon;
attaches / binds / joins to MRNA codon / triplet of bases;
tRNA carries a specific / eq. amino acid;
correct reference to formation of peptide bond /
OR amino acids joined by peptide bond;
(3 marks)
[Total 6 marks]
17. Give an account of the structure and functions of polysaccharides in living organisms.
[Total 10 marks]
1 (a) polysaccharides consist of monosaccharides joined;
(b) by glycosidic bonds;
(c) correct general formula for polysaccharide;
2 correct details of bond formation / accept from clear diagram;
3 glucose in starch / glycogen / 1-4 linkages;
4 glucose in cellulose / 1-4 linkages;
5 starch consists of amylose and amylopectin;
6 amylase is unbranched / amylopectin branched;
7 glycogen branched;
8 cellulose unbranched;
9 starch / glycogen are storage carbohydrates;
10 (a) starch in plants;
(b) glycogen in animals / liver / muscle;
11 reference to osmotic effects / insolubility;
12 (a) can be broken down to glucose;
(b) glucose / starch / glycogen as source of energy;
13 cellulose in plant cell wall;
14 hydrogen bonding between hydroxyl groups of adjacent chains;
15 forming microfibrils;
16 has high tensile strength / reference to structural support;
17 credit for 2 other polysaccharides; e.g. callose, inulin, pectins,
peptidoglycans, chitin; name and correct function / location.
18 cellulose as roughage;
David Kaunda High School 16
18. The diagram below shows the structure of a chloroplast, as seen using the electron microscope.
(a) Name the parts labelled A, B and C.
A chloroplast envelope / double / outer membrane / inter-membranous space;
B stroma;
C thylakoids / granum / granal lamellae;
(3 marks)
(b) The actual length of this chloroplast is 2.5 m. Calculate the magnification of this
diagram. Show your working.
(78 to 80 × 103) 2.5 ;
(measurement)
Answer 31 200 to 32 000.
(2 marks)
[Total 5 marks]
19. The diagram below shows some of the processes involved in the cycling of nitrogen in an
ecosystem.
A tm o s p h e ric n itro g e n
O rg a n is m T O rg a n is m S
A m m o n ia
Y
N itra te
A m m o n ia P la n t p ro te in
(a) (i) State the genus of one organism represented by the letter S and one organism
represented by the letter T in the diagram.
S Rhizobium / Azotobacter / Anabaena / Clostridium;
T Pseudomonas / Bacillus / Thiobacillus;
(2 marks)
David Kaunda High School 17
(ii) Name the processes represented by the arrows X and Y.
X decomposition / putrefaction / decay / deamination;
Y denitrification;
(2 marks)
(b) Explain how excessive use of nitrate fertilisers might lead to eutrophication of a lake.
nitrates are soluble / dissolve / leach / washed out of soil;
nitrates stimulate plant growth / eq;
algal bloom / eq. and then die / decompose;
by aerobic bacteria which then increase in number / grow / eq;
oxygen level decreases / O2 used by bacteria / higher B.O.D;
(3 marks)
[Total 7 marks]
20. A group of students wanted to produce a pyramid of fresh biomass for a field. They carried out
the procedure described below.
A fine mesh cage was used to enclose part of the field. All the plant material inside the cage was
cut down to ground level and weighed. All the animals in the enclosed area were collected and
identified. They were then sorted into herbivores or carnivores and weighed.
The fresh biomass of the organisms present is given in the table below.
O rg a n is m s F re s h b io m a s s / g
G re e n p la n ts 2250
H e rb iv o re s 240
C a rn iv o re s 38
(a) (i) Use the data in the table to construct a pyramid of fresh biomass on the graph paper
below.
symmetrical diagram with correct orientation;
correct proportions;
(2 marks)
David Kaunda High School 18
(ii) Calculate the percentage loss in fresh biomass between the green plants and the
herbivores. Show your working.
(2010 2250) × 100
OR [(2250 – 240) 2250 marks] × 100
OR 100 – (240 2250);
Answer 89.3%
(2 marks)
(iii) Give two reasons for the loss in mass between green plants and carnivores.
1 not all of an organism eaten / dead organisms;
loss of undigested material;
2 loss as CO2 / from respiration;
loss as urea / urine / excretion;
(2 marks)
(b) Suggest three sources of error in determining pyramids of fresh biomass in this way.
dead organisms may not be collected / converse;
some / organisms / parts of organisms may not be collected / eg roots / seeds;
reference to variable distribution of organisms / area may not be represented;
no repetition has been carried out / only one sample taken;
seasonal distribution / diurnal distribution / time reference;
animals may be at more than one trophic level / difficult to allocate organisms
to a trophic level;
(3 marks)
(c) Explain why only a small percentage of the light energy that falls on green plants is
incorporated into biomass.
reflected / transmitted / eq;
converted into heat energy / used to evaporate water;
some wavelengths not utilised by chlorophyll / in photosynthesis; reference
to biochemical efficiency;
(2 marks)
[Total 11 marks]
David Kaunda High School 19
21. The diagram below shows the relationship between the metabolic rate of a human being and the
environmental temperature.
4
M e ta b o lic ra te 2
/ a rb itra ry u n its
0
0 20 22 24 26 28 30 32
E n v iro n m e n ta l te m p e ra tu re / ºC
(a) Explain why the metabolic rate decreases between environmental temperatures of
20 C and 27 C.
less difference between air temperature and body temperature;
less heat loss from the body;
less heat generation;
(2 marks)
(b) State the term used to describe the range of environmental temperatures within which
metabolic rate is at a minimum.
thermoneutral zone;
(1 mark)
(c) Comment on the change in metabolic rate when the environmental temperature rises
above 31 C.
increases / steep rise / eq;
secretion of sweat;
requires energy;
(2 marks)
[Total 5 marks]
22. The table below refers to the structure and functions of xylem vessels and phloem sieve tubes
in plants.
David Kaunda High School 20
If the statement is correct, place a tick () in the appropriate box and if the statement is incorrect,
place a cross (x) in the appropriate box.
S ta te m e n t X y le m v e s s e ls P h o le m s ie v e tu b e s
P o s s e s s liv in g c o n te n ts
P ro v id e s u p p o rt
C o m p o s e d o f c e lls fu s e d
to g e th e r e n d to e n d
W a lls c o n ta in lig n in
[Total 4 marks]
23. Read through the following account of the hormonal control of the human menstrual cycle and
then write on the dotted lines the most appropriate word or words to complete the account.
The release of ….... FSH / follitropin / follicle stimulating hormone; …....from the anterior
pituitary gland induces the development of primary follicles. Another hormone from the
anterior pituitary gland stimulates the thecal cells to produce …. oestrogen / oestradiol;....
which controls the repair of the …..…..endometrium / uterus lining / womb lining; ……..
after menstruation. At ovulation, a .....secondary oocyte;..... is released from the mature
follicle. The remaining follicular cells form the ......... corpus luteum / yellow body;......... ,
which begins to secrete ....……….progesterone;..………., inhibiting the release of the
hormones from the anterior pituitary gland.
[Total 6 marks]
David Kaunda High School 21
24. All the cells in the blood come from just one type of cell, the multipotential stem cell. When the
stem cell divides one of the two daughter cells may go on to give rise to other types of cell,
whereas the other daughter cell remains a stem cell.
Adapted from The triumph of the embryo, Wolpert 1991
(a) Suggest one region of the body where the stem cells referred to in the above extract
are formed.
bone marrow;
(1 mark)
(b) Name two types of blood cells that are phagocytic.
1 granulocyte / granular polymorph / neutrophil / eosinophil;
2 monocyte;
(2 marks)
(c) Which cellular component of blood begins the process of blood clotting?
Platelet / thrombocyte;
(1 mark)
(d) Suggest why, when a stem cell divides, it is important that one daughter cell remains a
stem cell.
to enable continued formation of blood cells / eq;
(1 mark)
[Total 5 marks]
25. Compare the mechanisms for gas exchange in flowering plants and mammals.
1 gas exchange in both takes place over respiratory surface;
2 ref. to lungs in mammals;
3 ref. to (spongy) mesophyll of leaves in plants;
4 access to respiratory surface via trachea / bronchi / eq. in mammals;
5 access to respiratory surface via stomata / pores / between guard cells
in flowering plants / eq;
6 ref to lenticels / corky tissue in woody stems;
7 active drawing in of air / ventilation mechanism in mammals / eq;
8 credit for details of ventilation mechanism;
9 passive movement / diffusion of gases in plants;
David Kaunda High School 22
10 respiratory surface / gas exchange surface must be large;
11 ref to alveoli in mammals (as large surface);
12 ref to spongy mesophyll in flowering plants (as large surface);
13 thin surfaces aid rapid diffusion / short diffusion paths;
14 alveoli one cell thick in mammals;
15 thin cell walls in mesophyll of plants;
16 moist surfaces aid diffusion of gases / eq;
17 film of moisture lines alveolar surface;
18 plant cell walls moist;
19 respiratory surfaces must be permeable to gases;
20 capillary network around alveoli / eq. in mammals;
21 maintains high concentration gradient / eq;
22 enables more rapid / higher diffusion rate;
[Points 20, 21 and 22 are linked marks]
[Total 10 marks]
26. The table below refers to two types of epithelial tissue found in humans.
If the statement is correct, place a tick () in the appropriate box. If it the statement is incorrect,
place a cross (x) in the appropriate box.
E p ith e liu m
S ta te m e n t
Squam ous C u b o id
C e lls a re b o n d e d to a b a s e m e n t m e m b ra n e ;
C e lls a re w id e r th a n th e y a re ta ll ;
N u c le i a re fla tte n e d ;
A ll c e lls p o s s e s s c ilia ;
[Total 4 marks]
27. Describe the mechanisms and control of the digestion of carbohydrates.
1 mechanical digestion / food broken down by teeth;
2 increasing surface area for enzyme action;
3 mixing food with saliva;
4 increases contact with food / substrate;
5 salivary amylase converts starch to maltose;
6 saliva release initiated by sight / smell / taste of food;
7 initiated by cranial reflex action;
8 food in duodenum;
9 triggers release of hormone pancreozymin / secretin;
10 from duodenal mucosa;
David Kaunda High School 23
11 secretin increases flow of hydrogen carbonate;
12 release of pancreatic juice / enzymes;
13 pancreatic amylase converts starch to maltose;
14 release of intestinal juice / succus entericus;
15 from walls of ileum / small intestine;
16 maltase converts maltose to glucose;
17 sucrase converts to sucrose to glucose and fructose;
18 lactase converts lactose to glucose and galactose;
19 one correct reference to hydrolysing enzymes;
20 one correct reference to peristalsis;
[Total 10 marks]
28. Some people become ill if they drink milk or milk products as they do not secrete the enzyme
lactase in their intestine. This is known as lactose intolerance.
Lactose, present in milk, is converted to glucose and galactose by the action of the enzyme lactase.
In an investigation, milk was passed at different rates over lactase immobilised in beads of
sodium alginate. The rate of glucose production was measured at each flow rate.
The apparatus used is shown in the diagram below.
David Kaunda High School 24
The results are shown in the graph below.
5
4
R a te o f
g lu c o s e
p ro d u c tio n 3
/ a rb itra ry
u n its 2
0
0 5 10 15 20 25 30
R a te o f m ilk flo w / c m m in –1
3
(a) (i) Describe the effect of the rate of flow of milk on the rate of glucose production.
maximum rate between 15 – 20cm3 min-1;
rate decreases either side of maximum / increases to maximum
then decreases;
rapid increase at 5-10 cm3 min-1 flow rate / rapid decrease
at 25 – 28 cm3 min-1 / eq;
(2 marks)
(ii) Suggest two reasons why variations in the rate of flow of milk should produce
this effect.
1 too fast means insufficient time for enzyme to act on lactose / eq;
2 too slow means galactose / glucose / products will accumulate and
inhibit reaction / eq;
(2 marks)
(b) (i) Explain what is meant by enzyme immobilisation.
enzyme bound to a surface / ref to entrapment / eq;
not allowed to mix with its substrate in solution;
(2 marks)
(ii) Suggest two advantages of using immobilised enzymes in commercial processes.
enzyme retained / can be re-used / eq;
enzyme more heat stable / pH stable / eq;
does not contaminate product / can easily be separated from product;
less enzyme needed (therefore reduces cost);
can control rate of reaction.
(2 marks)
(c) (i) Suggest why it may be advantageous to treat milk with lactase during the
manufacture of dairy products.
removes lactose from milk;
makes milk / milk products sweeter;
makes dairy products available for lactose intolerant people;
(2 marks)
David Kaunda High School 25
(ii) Suggest why most people with lactose intolerance only develop the illness
after infancy.
lactase present in gut of young infants / lactose present in natural milk so
young infants produce lactase;
(1 mark)
[Total 11 marks]
29. The diagram below represents the lower jaw of an herbivorous mammal.
(a) Name the parts labelled A, B and C.
A molar tooth;
B diastema;
C incisor tooth;
(3 marks)
(b) State three features shown on the diagram which are characteristic of herbivore dentition.
ridged surface to cheek / molar teeth;
flattened crowns / large surface area to cheek teeth;
diastema / ref to gap for mastication;
small / angled incisors;
small / reduced canines;
(3 marks)
[Total 6 marks]
30. An experiment was carried out to determine the effect of temperature on the activity of an
enzyme digesting the protein gelatin.
Gelatin was incubated with the enzyme at a range of temperatures from 5 C to 60 C. The rate
of amino acid production was measured over a three-hour period.
David Kaunda High School 26
The results are shown in the table below, expressed as rate of amino acid production in
mg dm-3 h-1
R a te o f p ro d u c tio n o f a m in o a c id
T e m p e ra tu re / ºC
/ m g d m –3 h –1
5 14
1 0 19
1 5 24
2 0 31
2 5 40
3 0 51
3 5 68
4 0 93
4 5 98
5 0 89
6 0 33
David Kaunda High School 27
(a) (i) Plot the data on the graph paper below.
100
90
80
70
60
50
40
30
20
10
0
0 10 20 30 40 50 60
(4 marks)
David Kaunda High School 28
(ii) Comment on the effect of temperature on the activity of the enzyme as shown in the
graph.
rate increased exponentially / eq. until 40 °C;
slower / eq. increase to 45 °C / maximum / optimum rate at 45 °C / reaches a
peak at 45 C;
reference to steep / eq fall / ref to specified figures / after 45 C / 50 °C / after
optimum / OR correct ref to specified figs and temperatures;
reference to (kinetic) energy / movement of molecules / eq;
reference to denaturing of enzymes at higher temperatures;
(3 marks)
(b) The experiment was continued at 45 C for a further 7 hours. At the end of this time, an
additional 292 mg dm-3 of amino acid had accumulated.
(i) Calculate the mean rate of reaction during the 10 hours at 45 C.
[(3x98) + 292] 10 =) 58.6 / 59 mg dm –3h–1
(1 mark)
(ii) Give two possible reasons for the difference between the rate at the end of 10 hours
and the rate after 3 hours incubation.
1 substrate / gelatin / protein used up;
enzyme (starts to) denature(s);
2 inhibition by end product of reaction / ref to equilibrium reached / eq;
(2 marks)
(c) Protein-digesting enzymes can be used as an ingredient in biological washing powders.
Suggest how the results of this experiment could be used to design a suitable washing
programme using a biological washing powder.
set programme at (40-) 45 C / optimum temperature;
ref to short time / up to 3 hours for washing cycle;
bring wash up to temperature before adding washing powder / ref to
pre-wash with powder;
(2 marks)
[Total 12 marks]
31. Write an essay on the following topic
The flow of energy through an ecosystem (Bio, HBio)
entry of energy into ecosystem via sunlight collected by chlorophyll, photosystems comment
on light-dependent stage of photosynthesis green plants as primary producers comment
on chemosynthetic bacteria -
role of algae in aquatic ecosystems role of grassland and woodland in terrestrial ecosystems
role of consumers, herbivores and carnivores concept of food chains and food webs
examples flow of energy-rich molecules through consumer levels energy loss at each
transfer explained -
comment on pyramids of energy limitation of number of levels role of
detritivores and decomposers comment on detritivore food chains compared
to producer based food chains S= 13 = B = 2 C = 2
[Total 15 marks]
David Kaunda High School 29
32. Write an essay on the following topic
Regulation of water in flowering plants (Bio)
comment on the need to prevent water loss in terrestrial plants reference to transpiration and
role of stomata drought endurers have structural adaptations to dry conditions result in
reduction in transpiration rate waxy cuticle reduction in numbers of stomata, sunken
stomata rolled leaves -
reduction in leaf surface, leaves reduced to spines leaf shedding in dry season, dry conditions
physiological adaptations to dry conditions alteration of stomatal rhythms drought
evaders little activity during dry season seeds lie dormant until rainfall short life cycles -
reference to storage of water in very dry conditions water storage tissue in
tubers succulent leaves, stems deep, extensive root systems credit for
specific example discussed S = 13, B = 2, C = 2
[Total 15 marks]
33. Write an essay on the following topic
The adaptations of humans to life at high altitude (Hbio)
Introduction:
reference to high altitude stress due to reduced atmospheric pressure high solar radiation,
reduced oxygen availability, low temperatures -
Adaptations to hypoxia:
increase in rate/depth of breathing oxygen tension in alveoli similar to external air increased
blood flow through lungs more red cells increased haemoglobin in red cells increased
capillaries in tissues -
more myoglobin in muscles respiratory centres in brain relatively insensitive to oxygen lack
due to exposure to low oxygen in early life prevents chronic mountain sickness barrel-
chested, can house larger lungs -
Other adaptations:
dark-skinned for protection from high solar radiation epicanthic folds protect
eyes from UV light small stature, low SA/V ratio prevents heat loss allowed
some credit for reference to acclimatisation to high altitude eg mountain
climbers, athletes training at high altitude.
S = 13, B = 2, C = 2
[Total 15 marks]
34. An experiment was carried out to determine the effect of temperature on the activity of an
enzyme digesting the protein gelatin.
Gelatin was incubated with enzyme at a range of temperatures from 5 C to 60 C. The rate of
amino acid production was measured over a three-hour period.
David Kaunda High School 30
The results are shown in the table below, expressed as rate of amino acid production in
mg dm-3 h-1
R a te o f p ro d u c tio n o f a m in o a c id
T e m p e ra tu re / ºC
/ m g d m –3 h –1
5 1 4
1 0 1 9
1 5 2 4
2 0 3 1
2 5 4 0
3 0 5 1
3 5 6 8
4 0 9 3
4 5 9 8
5 0 8 9
6 0 3 3
David Kaunda High School 31
(a) (i) Plot the data on the graph paper below.
100
90
80
70
60
50
40
30
20
10
0
0 10 20 30 40 50 60
(4 marks)
David Kaunda High School 32
(ii) Comment on the effect of temperature on the activity of the enzyme as shown in the
graph.
rate increased exponentially / eq. until 40 C;
slower / eq. increase to 45 C / maximum / optimum rate at 45 C / reaches a
peak at 45 C;
reference to steep / eq fall / ref to specified figures / after 45 C /50 C / after
optimum / OR correct ref to specified figs and temperatures;
reference to (Kinetic) energy / movement of molecules / eq;
reference to denaturing of enzymes at higher temperatures;
(3 marks)
(b) The experiment was continued at 45 C for a further 7 hours. At the end of this time, an
additional 292 mg dm-3 of amino acid had accumulated.
(i) Calculate the mean rate of reaction during the 10 hours at 45 C.
[(3x98) + 292] 10 =) 58.6 / 59 mg dm –3h–1
(1 mark)
(ii) Give two possible reasons for the difference between the rate at the end of 10 hours
and the rate after 3 hours incubation.
1 substrate / gelatin / protein used up;
enzyme (starts to) denature(s);
2 inhibition by end product of reaction / ref to equilibrium reached / eq;
(2 marks)
(c) Protein-digesting enzymes can be used as an ingredient in biological washing powders.
(i) Suggest how the results of this experiment could be used to design a suitable
washing programme using a biological washing powder.
set programme at (40-) 45 C / optimum temperature;
ref to short time / up to 3 hours for washing cycle;
bring wash up to temperature before adding washing powder / ref to
pre-wash with powder;
(2 marks)
(ii) Suggest possible advantages of using biological washing powders rather than non-
biological detergents.
works at/can be used at lower temperatures;
so energy-saving;
less harmful / damaging to fabrics / eq;
better at getting rid of organic / specific stains;
ref to environmental effect / biodegradable / no / less phosphate / eq;
(2 marks)
[Total 14 marks]
David Kaunda High School 33
35. (a) Cell A in the diagram below has two pairs of chromosomes.
Cell B, C and D have each arisen from A by cell division.
(i) For each of the cells labelled B and C, identify the type of cell division which has
occurred to produce the cell. In each case give a reason for your answer.
Cell B
Type of division Mitosis;
Reason no reduction in chromosome number / same number of
chromosomes / both diploid / still diploid / identical to Cell A;
Cell C
Type of division meiosis / reduction division;
Reason chromosome number halved / crossing over has occurred /
haploid / chromosomes different from A;
(2 marks)
(ii) Explain the reasons for the difference between the parts labelled P and Q in cells
C and D.
homologous chromosomes pair / synapsis occurs / bivalents formed;
chiasma formed / crossing over took place;
exchange of materials / genes / genetic information between chromatids;
(3 marks)
(b) State one way in which oogenesis differs from spermatogenesis.
one egg cell produced (in oogenesis) four spermatoza in spermatogenesis
polar bodies formed in oogenesis / not in spermatogenesis;
oogenesis in embryo / spermatogenesis from puberty onwards / final division
of oogenesis after fertilisation / not in spermatogenesis;
(1 mark)
(c) State two ways in which embryo development in flowering plants differs from embryo
development in humans.
1 double fertilisation in plants / ref to two male nuclei involved / only
one in human;
plant embryo develops in seed / human embryo develops in uterus;
David Kaunda High School 34
2 embryo supplied with food store / eq in plant / ref to food via placenta /
eq in humans;
dormant stage of development of plant embryo / no dormant stage
in humans;
(2 marks)
[Total 8 marks]
36. The graph below shows the oxygen dissociation curve for the pigment haemoglobin in a human.
The loading tension is the partial pressure of oxygen at which 95 % of the pigment is saturated
with oxygen. The unloading tension is the partial pressure at which 50% of the pigment is
saturated with oxygen.
100
90
80
70
60
P e rc e n ta g e
oxygen
50
s a tu ra tio n o f
h a e m o g lo b in
40
30
20
10
0
0 2 4 6 8 10 12
P a rtia l p re s s u re o f o x y g e n / k P a
(a) Explain why haemoglobin is an efficient respiratory pigment.
has an affinity for oxygen in high pp / concentration / tension of 02 / OR
haemoglobin combines with oxygen;
gives up oxygen (readily) at low pp / low 02 / high concentration of CO2;
(2 marks)
(b) (i) From the graph determine the difference between the loading and unloading
tensions of the haemoglobin. Show your working.
loading tension 10.8 kPa (allow from 10.6 to 10.8)
unloading tension 3.5 kPa (allow from 3.4 to 3.6);
Answer 7.3 kPa;
(2 marks)
David Kaunda High School 35
(ii) Give one location in the human body where partial pressures lower than the
unloading tension may be reached. Give a reason for your answer.
Location any body tissue / organ except lungs;
Reason oxygen being used up / reference to respiration / respiring tissue;
(2 marks)
(c) Suggest what effects increasing concentrations of carbon dioxide in the blood would have
on the loading and unloading tensions of human haemoglobin. Give reasons for your
answers.
curve shifts to right;
(increasing carbon dioxide makes) Hb less efficient at taking up oxygen;
Hb has to be exposed to higher pp / eq. O2 in order to reach loading tension /
loading tension higher;
increasing carbon dioxide makes Hb release 02 at higher pp / eq. of oxygen;
so unloading tension higher / eq;
credit reference to some detail / eg H ion production inducing release of 0 2
from haemoglobin;
(4 marks)
(d) The oxygen dissociation curve for fetal haemoglobin lies to the left of the curve for adult
haemoglobin. Suggest an explanation for this difference.
has higher affinity for oxygen than mother’s blood / haemoglobin;
in order to be able to take up oxygen from mother’s blood / haemoglobin via
placenta;
(2 marks)
(e) State three ways in which carbon dioxide is transported in the blood.
1 in solution / dissolved in the plasma;
2 as hydrogen carbonate / bicarbonate ions;
3 associated with the haemoglobin / as carbamino - haemoglobin;
(3 marks)
[Total 15 marks]
37. (Human Biology)
(a) Describe how you would collect a sample of expired air from a person in order to carry
out an analysis of its composition.
insert tube in suitable container under clear tube of atmospheric air;
breathe out through tube to fill container / empty polythene bag / balloon:
(2 marks)
David Kaunda High School 36
(b) Give a full account of the experimental method you would use to determine the
proportions of carbon dioxide and oxygen in a sample of expired air.
scheme assumes use of J tube but some (alternative) marking points could
apply to a gas burette experiment
fill tube with water / fill burette with water
container of expired air under water; insert J tube and draw in small sample
of expired air / insert tube and partially fill burette with expired air; form
bubble by drawing in water; measure length of air bubble / read off volume of
air on burette ; named carbon dioxide absorber; expel water to leave bubble
only and draw up small amount of absorber / inject carbon dioxide absorber
through rubber seal; mix with absorber / allow time for absorption; ref
equilibration of pressure in burette ; measure new length of bubble / read new
volume on burette; calculate reduction in bubble length / volume ; repeat with
named oxygen absorber (e.g. alkaline pyrogallol) ; ref temperature
equilibration;
(8 marks)
(c) Describe three limitations of your experimental method.
small temperature changes cause large changes in gas volumes ; small
volumes in tubes difficult to measure accurately; proportion of carbon
dioxide is very small / difficult to measure ; gases can dissolve in the water;
incomplete absorption of gases;
(3 marks)
[Total 13 marks]
38. The table below refers to components of the cell surface membrane (plasma membrane) and to
their roles in transporting substances across the membrane.
Complete the table by inserting an appropriate word or words in the empty boxes.
C om ponent S u b u n its C h e m ic a l b o n d R o le in tra n s p o rt
b e tw e e n s u b u n its
F a tty a c id s , g ly c e ro l R e f. t o v e s ic le
a n d p h o s p h a te e s te r; fo r m a tio n /c y to s is /
P h o s p h o lip id c h y lo m ic r o n s / r e f. to
d if fu s io n ;
m o n o s a c c h a r id e /
C a r b o h y d ra te s id e n a m e d e .g . o f a g ly c o s id ic ; R e c e p to r
c h a in m o n o s a c c h a r id e /
re f. to p e n to s e /h e x o s e ;
R e f. to c h a n n e ls /p o r e s
a m in o a c id s ; a llo w in g p a s s a g e /
P e p tid e
P ro te in fa c ilita t e d d iff u s io n /
re c e p to r/e n z y m e /
c a r r ie r /a c tiv e tr a n s p o r t;
[Total 6 marks]
David Kaunda High School 37
39. The diagram below shows the structure of a bacterial cell as seen using an electron microscope.
(a) Name the parts labelled A, B and C
A Flagellum / flagella;
B (peptidoglycan) / cell wall;
C (circular) DNA / chromosome / nucleoid;
(3 marks)
[Total 3 marks]
40. Read through the following passage on the cell cycle and mitosis, then write on the dotted lines
the most appropriate word or words to complete the passage.
In the cell cycle, replication of DNA takes place during ……. interphase / S phase;…….
At the beginning of prophase the chromosomes become visible and can be seen to consist
of two ……. chromatids;……. joined at the ............centromere;.....….. .
The ...........nucleolus / nucleoli;......... and nuclear membrane disappear and a spindle
develops in the cell.
The chromosomes become attached to the spindle at the equator during
..........metaphase;............ . At anaphase one copy of each chromosome is pulled
towards each ...........pole / end / aster;........... of the spindle. The final phase, called
telophase, involves the formation of two new nuclei. In plant cells the two daughter
cells are separated by the formation of a .…... cell plate / cell wall / phragmoplast /
middle lamella;...…… .
[Total 7 marks]
David Kaunda High School 38
41. The monosaccharides glucose and fructose are reducing sugars. Sucrose is a disaccharide which
is not a reducing sugar.
The Benedict’s test is used to detect reducing sugars. When reducing sugars are boiled with
Benedict’s solution a red precipitate is produced. This precipitate can be filtered from the
solution, dried and weighed. If excess Benedict’s solution is used, the mass of precipitate
produced is proportional to the concentration of reducing sugar in the solution. The enzyme
sucrase is a hydrolase and does not reach with Benedict’s solution.
(a) In an experiment, sucrase was added to a solution of sucrose and incubated for five
minutes. The Benedict’s test was then carried out on the resulting solution and a red
precipitate was produced.
Suggest an explanation for this result.
sucrase breaks down / hydrolyses / eq. sucrose / substrate;
to glucose and fructose / to monosaccharides;
(2 marks)
(b) A further experiment was carried out to investigate the effect of silver nitrate on the
activity of sucrase. The procedure described above was repeated, but different
concentrations of silver nitrate were added to the sucrase. The solutions were kept at the
same pH for the same time. The mass of precipitate produced by the Benedict’s test at
each concentration was measured. The results are shown in the table below.
C o n c e n tra tio n o f s ilv e r n itra te M a s s o f p re c ip ita te
/ m o l d m –3 / m g
0 (c o n tro l) 50
1 0 –6 37
–5
10 27
1 0 –4 10
(i) Calculate the percentage decrease in the mass of precipitate produced in the
solution containing 10-5 mol dm-3 silver nitrate compared with the control test.
Show your working.
(23 50) × 100 / eq;
Answer 46%;
(2 marks)
(ii) Suggest an explanation for the effect of the silver nitrate solution on the activity of
the enzyme sucrase.
silver nitrate is an inhibitor;
block / affects shape of active site;
substrate no longer able to bind;
reduces rate of reaction;
(2 marks)
David Kaunda High School 39
(c) (i) Explain why it is important to maintain constant pH when investigating
enzyme activity.
(changes in pH) affect formation of enzyme-substrate complexes;
changes shape / tertiary structure / 3D structure / eq. of enzyme / active site
by changing (hydrogen) bonding / charges / ionisation;
ref to optimum pH / eq;
(2 marks)
(ii) State three precautions, other than maintaining constant pH, which should be taken
to produce reliable results in the above investigation.
1 constant / same temperature;
equilibration of enzyme and substrate;
same volume of Benedict’s;
same time of heating with Benedict’s;
same temperature for heating with Benedicts;
2 same filtration / drying method;
dry precipitate to constant mass;
same volume of sucrose;
same volume of sucrase;
3 same concentration of sucrose;
same concentration of sucrase;
leave enzyme and substrate for same time to react;
use same volume of silver nitrate;
replication;
(3 marks)
[Total 11 marks]
42. The diagram below shows a transverse section of a leaf of Ammophila arenaria, which is a
xerophyte. The photomicrograph shows the details of the area indicated by the box on
the diagram.
(a) Name the parts labelled A and B.
A vascular bundle / vascular tissue / vein / xylem and phloem / eq.
B epidermis / epidermal cell;
(2 marks)
David Kaunda High School 40
(b) Describe two xeromorphic features shown in this leaf and, in each case, indicate how the
feature helps to reduce transpiration.
presence of hairs / eq. of epidermis / surface;
reduce air movement / trap air / trap water vapour / humidity ref;
thick cuticle; reduces evaporation / diffusion of water / water loss;
leaf rolled / eq;
reduces external / exposed surface area / reduction in air movement /
humidity ref;
hinge cells;
roll / eq. leaf in dry conditions;
stomata few / sunken in pits / on inner epidermis;
reduced water loss through pores / eq;
(4 marks)
[Total 6 marks]
43. Give an account of the roles of bacteria in the nitrogen cycle.
[Total 10 marks]
1 (importance of) decomposers;
2 putrefaction / breakdown of organic matter / organisms,
plants / animals;
3 release ammonia from proteins / eq;
4 saprotrophic / saprophytic bacteria;
5 nitrification as an oxidation process;
6 (oxidation of) ammonia to nitrite / nitrate (III);
8 by Nitrosomonas;
9 (oxidation of) nitrite / nitrate (III) to nitrate / nitrate (V);
11 by Nitrobacter;
12 denitrification;
13 conversion of nitrate / nitrate (V) to nitrogen / dinitrogen;
14 by eg Pseudomonas / Bacillus;
15 nitrogen fixation;
16 conversion of nitrogen / eq to ammonia / other form of
combined nitrogen;
17 by (free living) soil bacteria;
18 eg Azotobacter / Clostridium / Bacillus / Klebsiella / eq;
19 by mutualistic / symbiotic / eq bacteria;
20 eg Rhizobium;
21 in root nodules / associated with legumes / eq;
22 makes nitrogen compounds / nitrates available to (green) plants;
David Kaunda High School 41
44. The photomicrograph below shows part of the lower epidermis of a leaf of Kalanchoe.
The area shown is 0.0108 mm2.
(a) Identify the structures labelled P, Q and R.
P cell wall / cellulose wall;
Q epidermal cell / vacuole;
R guard cell / stoma;
(3 marks)
(b) Calculate the number of stomata per mm 2 of the lower epidermis, assuming that they are
evenly distributed. Show your working.
3
;
0.0108 Answer 277.78 / 277.8 / 278;
(2 marks)
[Total 5 marks]
David Kaunda High School 42
45. The diagram below shows the structure of part of a mammalian placenta and the umbilical cord,
which is attached to a developing fetus.
(a) State two substances which would be present in a higher concentration in the umbilical
vein than in the umbilical artery.
1 oxygen / oxyhaemoglobin; amino acids / named eg;
proteins; glucose / blood sugar;
vitamins / named eg;
2 mineral salts / minerals / named eg;
antibodies;
lipids / fatty acids / glycerol / micelles;
(2 marks)
(b) The cavity labelled X contains maternal blood. Suggest why it is an advantage for this
blood to be in a cavity rather than in a vessel.
increases area of contact / surface area between maternal blood and fetal
capillaries / eq. / reduced diffusion distance qualified;
thus facilitating / making easier exchange of materials between blood of
fetus and mother / eq. / correct reference to making diffusion between the two
easier;
(2 marks)
[Total 4 marks]
David Kaunda High School 43
46. Read through the following passage about enzymes and their industrial uses, then write on the
dotted lines the most appropriate word or words to complete the account.
As much as 75% of the world’s adult population maybe unable to tolerate and digest the
sugar in milk, and so this sugar is removed during the manufacture of some milk
products. This is done using the enzyme ........lactase / -galactosidase;....... which
hydrolyses the milk sugar into ...........…..glucose;…................ and
..............galactose;.................... . Unlike the sugar in milk, these are both
............monosaccharide;.............. sugars. They are both .......sweeter / more soluble;......
than milk sugar, so milk products treated in this way are particularly useful in the
manufacture of confectionery.
[Total 5 marks]
47. The diagram below shows the structure of a liver cell as seen using an electron microscope.
(a) Name the parts labelled in A, B, C and D.
A plasma membrane / cell membrane / cell surface membrane;
B centriole(s) / microtubule(s) / centrosome;
C Golgi apparatus / Golgi body / smooth ER;
D rough ER / ribosome;
(4 marks)
David Kaunda High School 44
(b) The magnification of this diagram is 12 000. Calculate the actual length of the
mitochondrion labelled M, giving your answer in m. Show your working.
(Accept measurement between 11 and 12 mm)
11 12 000; OR 12 12 000;
= 0.92; = 1.0;
(2 marks)
[Total 6 marks]
48. The diagram below shows the structure of a lipid molecule.
H O
H C O C
H C O C
O
H C O C
H
A B
(a) (i) Name the parts labelled A and B.
A glycerol / propan–1, 2,.3–triol;
B fatty acid(s) / fatty acid chain;
(2 marks)
(ii) Name this type of lipid.
triglyceride;
(1 mark)
(iii) Name the chemical reaction used to form the bonds between A and B.
condensation / esterification;
(1 mark)
(b) (i) State one function of this type of lipid in living organisms.
energy store / energy source / insulation / waterproofing / production of
metabolic water / buoyancy / protection;
(1 mark)
(ii) State one feature of the molecules of this type of lipid which makes them suitable
for the function you have given.
insoluble / non-polar / high energy value / poor heat conductor / low density /
less dense than water;
[points in (b)(ii) need to be correctly linked to the answer given in (b)(i)]
(1 mark)
[Total 6 marks]
David Kaunda High School 45
49. The photomicrograph below shows plant cells which have undergone division during the
formation of pollen grains.
(a) Name the type of division shown in the photomicrograph.
meiosis / reduction division;
(1 mark)
(b) (i) Name one location in a flowering plant in which this type of division occurs.
anther / ovule / pollen sac / microsporangium / megasporangium;
(1 mark)
(ii) Name one location in mammals in which this type of division occurs.
ovary / testis / seminiferous tubule;
(1 mark)
(c) Give two reasons why this type of cell division is important in living organisms.
1 halves chromosome number / produces haploid cells / haploid
gametes;
2 reference to genetic variation;
(2 marks)
[Total 5 marks]
David Kaunda High School 46
50. The statements in the table below refer to three polysaccharide molecules. If the statement is
correct, place a tick () in the appropriate box and if the statement is incorrect, place a cross ( x)
in the appropriate box.
S ta te m e n t S ta rc h G ly c o g e n C e llu lo s e
P o ly m e r o f – g lu c o s e ;
G ly c o s id ic b o n d s p re s e n t ;
U n b ra n c h e d c h a in s o n ly ;
E n e rg y s to re in a n im a l c e lls ;
[Total 4 marks]
51. Give an account of the factors affecting enzyme activity.
1. enzymes are protein catalysts;
2. comment on complementary shape of active site and substrate / lock
and key mechanism / eq;
3. increasing temperature increases kinetic energy / movement of
molecules;
4. increases chances of enzyme substrate interactions / collisions;
5. increases rate of reaction up to an optimum;
6. above this enzyme is denatured / ref to denaturation;
7. disruption of (hydrogen) bonding;
8. changes in pH affect enzyme activity / work within narrow range of pH;
9. by altering the charges / ionisation / bonding in the molecule;
10. changes shape of active site;
11. activity decreases on either side of optimum;
12. enzyme may be denatured at extreme pH values / eq;
13. increasing enzyme concentration increases rate of reaction;
14. as more active sites available;
15. increasing substrate concentration increases rate of reaction;
16. up to an optimum rate / ref to Vmax;
17. inhibitors are substances which decrease enzyme activity;
David Kaunda High School 47
18. competitive inhibitions have similar shape to substrate / eq;
19. can block active site temporarily / reversibly;
20. credit reference to named example;
21. irreversible inhibitions permanently inactivate enzymes /
non-competitive inhibitors attach to places other than active site;
22. credit reference to named example;
23. credit reference to co-factors / co-enzymes / activators;
[Total 10 marks]
52. The table below refers to some enzymes involved in the digestion of carbohydrates in the human
digestive system. Complete the table by writing the correct word or words in the empty boxes.
N am e of enzym e S ite o f p ro d u c tio n P ro d u c ts o f re a c tio n
la c ta s e ; W a ll o f in te s tin e G lu c o s e + g a la c to s e
S u c ra se w a ll o f in t e s tin e ; g lu c o s e + fr u c t o s e ;
a m y la s e ; P a n c rea s M a lto s e
[Total 4 marks]
53. The diagram below shows the quantity of energy flowing through a food chain in a terrestrial
ecosystem. The figures given are kJ m-2 yr-1
In c id e n t S u n lig h t
6
3 1 0
G re e n p la n ts 1800 100 In s e c tiv o ro u s
4 C a te rp illa rs
N P P = 1 .8 x 1 0 b ird s
(a) Calculate the percentage of the incident energy which becomes available as the net
primary production (NPP) of green plants. Show your working.
1.8 10 4 18000
100 100
3 10 6 OR 3,000,000 OR eq;
Answer 0.6 (%);
(2 marks)
(b) Give two reasons why not all the energy of the incident sunlight is incorporated into
biomass of green plants.
1 light reflected from plant / from leaf / not absorbed by plant / leaf eq;
energy used to evaporate (water) / heat plant / eq;
2 light transmitted / eq; light of wrong wavelength;
photosynthesis / biochemical processes inefficient;
released by plant respiration;
(2 marks)
David Kaunda High School 48
(c) Using the information shown in the diagram, explain why the biomass of insectivorous
birds is usually very much less than the biomass of caterpillars.
1800 kJ transferred to caterpillars only 100 kJ to birds / calculation of loss /
amount transferred (5.6%);
any reference to energy loss;
ref to loss of energy / biomass as respiration / excretion / in movement / eq;
(2 marks)
[Total 6 marks]
54. Read through the following account about acid rain and renewable energy sources, then write on
the dotted lines the most appropriate word or words to complete the account.
Acid rain has been linked to an increase in ……….Sulphur dioxide / carbon dioxide /
nitrogen oxides;…………….in the atmosphere. This increase is mainly due to the
burning of ..........fossil fuels;.......... such as .....coal / oil / gas / petrol / eq;..... .
One way of reducing the problem may be to use biogas produced by microorganisms kept in
warm ..............……...anaerobic;....…............ conditions. These microorganisms convert
.........biomass / organic waste / eq;...... into this renewable energy source.
[Total 5 marks]
55. The diagram below shows a part of the beef tapeworm Taenia saginata.
(a) Explain the importance of the part labelled A in the life of the tapeworm.
holds on to gut wall / eq;
to prevent removal (from host);
ref to peristalsis;
(2 marks)
David Kaunda High School 49
(b) (i) Describe how the tapeworm obtains its nutrition.
ref to parasitism;
(host’s) food absorbed through body wall / cuticle/ eq;
food digested by host / eq;
(2 marks)
(ii) How does the nutrition of Rhizopus differ from that of the tapeworm?
Rhizopus is a saprobiont / saprophyte / description / eq;
digests own food / extracellular digestion / eq;
(2 marks)
[Total 6 marks]
56. Give an account of the causes and effects of desertification.
[Total 10 marks]
1 areas usually already semi-arid / have low rainfall / eq;
2 climate change / reduction in rainfall;
3 possible link to greenhouse effect / global warming;
4 increase in greenhouse gases / named example;
5 overgrazing (by domestic animals) / eq;
6 removal of trees / scrub / woody vegetation;
7 used as firewood / charcoal / fuel;
8 (a) conversion of grass / and for agriculture / agricultural land / eq;
(b) use of unsuitable crop / overcropping / monoculture /
inappropriate farming method used
9 leads to soil erosion;
10 (a) stops recycling of nutrients / loss of nutrients
(b) decrease in soil fertility;
11 irrigation / eq (of marginal land) can lead to salt accumulation
or salination;
12 plants unable to grow due to osmotic effects;
13 loss of plants can have effect on climate;
14 reduced transpiration;
15 lowering of relative humidity / eq;
16 (further) reduction of rainfall in area / in locality / eq;
17 (a) size of populations decreases;
(b) there is a reduction / change in species diversity;
18 loss of ecological riches / habitat / eq;
19 any suitable ref to human population pressure / human activity;
20 extraction of too much water from rivers / aquifers / eq;
21 construction of dams / other interference with water flow;
57. The table below refers to four hormones associated with the human menstrual cycle.
If the statement is correct, place a tick ( ) in the appropriate box and if the statement is
incorrect place a cross (x) in the appropriate box.
David Kaunda High School 50
David Kaunda High School 51
H o rm o n e S e c re te d b y o v a rie s R e a c h e s h ig h e s t le v e l in
b lo o d b e fo re o v u la tio n
F o llic le s tim u la tin g ;
h o rm o n e (F S H )
L u te in is in g h o rm o n e (L H ) ;
O e s tro g e n ;
P ro g e s te ro n e ;
[Total 4 marks]
58. The graph below shows the oxygen dissociation curve of haemoglobin from a mammal at two
different temperatures (38C and 43C).
100
90
3 8 ºC
80
4 3 ºC
70
60
P e rc e n ta g e s a tu ra tio n
o f h a e m o g lo b in w ith 50
oxygen
40
30
20
10
0
0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14
P a rtia l p re s s u re o f o x y g e n / k P a
(a) (i) From the graph find the percentage saturation of haemoglobin in blood from an area
of the body where the temperature is 43C and the partial pressure of oxygen is a 4
kPa.
any value between 17.0 and 18.0%;
(1 mark)
David Kaunda High School 52
(ii) Blood that is fully (100%) saturated with oxygen carries 105cm3 of oxygen in 1
dm3 (litre) of blood.
Calculate the volume of oxygen released from 1 dm3 of blood when blood that has
become 90% saturated at 38C reaches a part of the body where the temperature is
43C and the partial pressure of oxygen is 4 kPa. Show your working.
90 – 18 = 72;
105 × 72/100;
75.6 cm3
(3 marks)
(b) Suggest how this effect of temperature on the oxygen dissociation curve of haemoglobin
might be advantageous to the mammal.
increased rate of respiration / OR metabolic rate increase / eq gives more heat
energy / eq;
causing haemoglobin to release more oxygen / release oxygen faster / eq;
(2 marks)
[Total 6 marks]
David Kaunda High School 53
59. An investigation was carried out into the relationship between the rate of water absorption and
the rate of transpiration in sunflower plants at various times of the day. The results are shown in
the diagram below.
60
50
40
R a te o f tra n s p ira tio n
o r a b s o rp tio n o f 3 0
w a te r p e r p la n t /
g h –1
20
10
0
0800 1000 1200 1400 1600 1800 2000 2200 2400 0200 0400 0600
noon m id n ig h t
T im e o f d a y (2 4 h o u r c lo c k )
K ey
T ra n s p ira tio n ra te
R a te o f w a te r a b s o rp tio n
(a) (i) Describe the changes in the rate of transpiration that took place during the
experiment.
rise from 0800 hours to 1400 hours / peaks at 1400 / peaks at 51g h -1;
falls from 1400 hours to 2000/2200 hours / eq;
then remains steady / small fluctuations /
or correct reference to figures;
(3 marks)
David Kaunda High School 54
(ii) Suggest why these changes occurred.
ref. to loss of water vapour / eq;
stomatal opening / closing / changes in stomatal aperture;
changes in light intensity;
changes in temperature;
changes in wind speed;
changes in humidity levels;
(2 marks)
(b) Comment on the relationship between the rate of transpiration and the rate of water
absorption during the experiment.
similar shaped curves / eq; transpiration reaches higher level / eq; water
absorption to the right of transpiration / eq;
transpiration rate affects water absorption rate;
water moves from area of high in soil to lower in atmosphere / eq;
(2 marks)
(c) Describe a simple method that you could use in the laboratory to measure the rate of
transpiration of a flowering plant.
insert cut shoot into potometer;
under water / or ref to water-tight seal;
ref to control of external conditions / light constant / temp constant;
equilibration;
record rate of movement of water column in capillary tube / eq;
assumes rate of water absorbed is proportional to rate of transpiration;
calculation of volume of water absorbed in given time;
replication qualified / eg to find mean / increase reliability;
[Credit for an alternative method using a well-watered potted plant
and measuring weight loss]
(4 marks)
[Total 11 marks]
David Kaunda High School 55
60. The diagram below represents changes in the relative length of different parts of the body during
the growth of a human male.
(a) (i) Compare the relative size of the head of a two-month fetus with that of
a new-born baby.
head of fetus is twice that of newborn/head of fetus is half of baby while
newborn is quarter / 50% compared to 25%;
(1 mark)
(ii) Suggest two reasons for the difference you describe.
1 early development of brain / sense organs in head;
rest of body/limbs grow more slowly;
2 since not needed for locomotion before birth / in uterus;
(2 marks)
(b) (i) Compare the relative size of three different parts of the body of a six year old and a
twenty five year old.
1 head of 25-year old (relatively) smaller (than 6 year old);
limbs of 25-year old (relatively) longer;
2 body / trunk of 25-year old (relatively) longer;
genitalia of 25-year old (relatively) larger;
3 shoulders of 25-year old (relatively) larger/wider;
(3 marks)
(ii) Give two factors that influence the growth of the body from six to twenty five
years.
1 androgens / testosterone;
growth hormone / somatotrophin;
genetic inheritance;
2 thyroxine / corticosteroids;
supply of nutrients / food / diet;
effects of exercise;
(2 marks)
David Kaunda High School 56
(c) Human growth can be studied by measuring changes in height or changes in mass.
Explain why neither of these is an ideal method for measuring growth.
different parts of body/organs grow at different rates;
growth in height not always accompanied by growth in mass/growth in mass
during growth spurts follows growth in height;
people with same height may have different mass / people with same mass
may be of different heights;
mass may be subject to temporary fluctuations / eq` / obesity / pregnancy /
menstrual cycle which do not reflect any growth;
difficult to measure height in young babies;
(4 marks)
[Total 12 marks]
61. Write an essay on the following topic.
The structure and functions of cell surface membranes (Bio, Hbio)
structure and function of cell surface membranes:
Introduction could include:
outline of fluid mosaic model -
communication with external medium, barrier -
controls exchange of material -
fluid mosaic model:
phospholipids and orientation -
proteins, glycocalyx, channels -
microvilli -
passage through the membrane:
diffusion, facilitated diffusion, Na/K -
osmosis, active transport, ATPase -
lipid soluble molecules, adrenaline
polar molecules through pores, channels -
Vesicles:
cytosis -
endocytosis, phagocytosis, pinocytosis -
exocytosis, secretory vesicles others:
glycosides as receptors, insulin-
adhesion between cells -
immunological response S = 13, B = 2,C = 2
[Total 15 marks]
62. Write an essay on the following topic.
The effects of extremes of temperatures on humans (HBio)
effect concept
of extremes
Introduction
mechanisms
TNZ of
oftemperature
could include
of thermoregulation
heat
\ thermoneutral humans:
loss and
zone - gain
27-31 °C from the environment -
David Kaunda High School 57
-
heat stress:
salt loss and heat cramp -
effects of dehydration -
low tolerance to rise in core temperature -
anterior hypothalamic stimulation -
effects on respiration rate -
anorexia compounds effects -
apathy and inertia -
critical temperature 27 °C -
lethal body core temp 25 °C -
42/3 °C -
cold stress:
effects on cutaneous blood circulation -
cold injury, frost bite, trench foot -
wind chill effects -
hypothermia described -
posterior hypothalamic stimulation -
tolerance to decrease in core temperature -
heat production when head temperature falls -
Credit references to adaptations of natives
surface area to vol. ratio -
hair type -
tolerance to core temp change -
adipose tissue S = 13, B = 2,C = 2
[Total 15 marks]
63. An experiment was carried out to compare the uptake of nitrogen in soyabean seedlings grown
in an atmosphere enriched with carbon dioxide with that of seedlings grown in a normal
atmosphere (control plants). Soyabeans belong to Papilionaceae (legumes) and all the
experimental plants had root nodules containing Rhizobium.
At the beginning of the experiment, the seedlings were 25 days old. The total amount of
nitrogen incorporated into compounds in the plants was then measured at intervals until the
plants were 100 days old.
David Kaunda High School 58
The results of the experiment are shown in the graph below.
900
800
700
60 0
M ean m ass
o f n itro g e n 50 0
in c o rp o ra te d
in to
com pounds 40 0
in a p la n t / m g
30 0
200
100
0
0 20 40 60 80 100
A ge / days
K ey
E n ric h e d w ith c a rb o n d io x id e
N o rm a l a tm o s p h e re
(a) (i) Of the nitrogen incorporated into compounds in the control plants, 75% was taken
up from the soil. State the form in which this nitrogen was taken up by the plants.
nitrate(s) (ions) / N03- / ammonium (ions) / NH4+;
(1 mark)
(ii) Explain how the control plants obtained the remaining 25% of their nitrogen.
Rhizobium / OR bacteria in root nodules able to use / fix
(atmospheric) nitrogen;
reduced / converted to ammonia / ammonium;
combine with organic acids / OR to make amino acids / OR
ref to nitrogenase enzyme;
(2 marks)
(b) (i) Compare the effect of the atmosphere enriched with carbon dioxide with that of the
normal atmosphere on the mass of nitrogen incorporated into the seedlings.
no difference until day 36 / OR for first 10/11 days;
amount of nitrogen fixed is (then) greater in CO2 enriched;
in CO2 enriched rate of increase greater / difference greater
with time / accept converse for normal;
David Kaunda High School 59
in CO2 enriched no plateau / levelling off / eq but in
normal air levels / figures / 36-60 / remains at 20 mg;
in CO2 enriched smaller / eq increase after 90 days but in
normal air not much increase after 80 days /eq;
credit correct attempt to work out %age increase / do something
with the figures;
(3 marks)
(ii) Suggest one reason for any differences you observe.
more CO2 so more photosynthesis / eq;
(1 mark)
(c) A possible application of gene technology would be to incorporate genes for nitrogen
fixation into cereal plants.
Suggest the possible benefits of such an application.
increase in yield / more crop;
cereals could grow on low nitrate / eq soils;
less / no need to use (inorganic) fertiliser;
environmental benefit qualified e.g. less nitrate to be leached /
less eutrophication / eq;
(2 marks)
[Total 9 marks]
64. Write an essay on the following topic.
Atmospheric pollution
general points:
definition - fouling of air by materials harmful to living organisms -
reasons for increase in pollution -
sources of pollutants / industry / motor vehicles / domestic fires -
use of fossil fuels -
natural causes such as volcanoes -
can be solids, liquids or gases -
ozone depletion:
reference to the use of CFCs -
how they get into the atmosphere -
decompose to form chlorine atoms which cause breakdown of ozone -
effects of ozone depletion -
preventative measures -
greenhouse
able
some -effect:
reference
greenhouse
CFCs toheat
comment tointo
absorb
preventativeon possibility
gases
sources
and eg
possible
measures of
emit
space of
water
but global
vapour
these
heat warming
- - due
/ carbon
- emissions
some
climatic back
effectsdown to accumulation
todioxide
the / methane
Earth's /of
surface -greenhouse
nitrous oxide /gases
ozone- /
David Kaunda High School 60
-
acid rain:
formed from sulphur dioxide and oxides of nitrogen from industrial processes eq -
oxidised in the air to form sulphuric and nitric acids -
may be catalysed by ozone / hydrogen peroxide / ammonia -
wind may blow pollutants hundreds of miles from industrial areas -
rain then falls on woodland and affects conifers -
soils affected because ammonium sulphate liberates toxic aluminium ions -
lowers pH of lakes -
causes change in algae and affects fish stocks -
knock-on effect of aluminium such as senile dementia / Alzheimer' s / Parkinson's disease
-
may give reference to:
particulate pollutants such as smoke -
radioactive dust -
removal of toxic gases from car exhausts by catalytic converters -
lead-free petrol -
flue-gas and fuel desulphurisation as preventative measures Scientific
content = 17, Balance = 3, Coherence/clarity = 3
(20 marks)
65. (Biology)
(a) Describe, with full practical details, how you would compare the density of stomata on the
leaves of plants of the same species growing in sunlit and in shaded conditions.
locate suitable sunlit and shaded area containing chosen species / grow
plants in light and shade; check locations for other possible named
variable(s) / same conditions for growth stated condition; select stated
number of leaves (minimum 5); standardised method of leaf selection (eg
third branch from apex second leaf from tip / eq) / ref to random sampling;
standardised selection of location on leaf for counting; stomata counted on
lower / both surfaces; nail varnish painted on and peeled off / strip of
epidermis peeled off / use of adhesive; mounted on slide with cover ship /
sellotape eq; examine under microscope qualified (eg focussing detail use of
graticule); numbers in one field or view counted / ref measured area counts;
ref repeats qualified; calculation of means; compare means statistically
(eg t test / Mann-Whitney U);
(8 marks)
(b) State three limitations of your experimental method.
other named variable could affect stomatal numbers / ref named uncontrolled
variables in the field (eg temperature, soil pH, age of leaves) (allow two);;
difficult to strip off epidermis in some leaves / nail varnish unsuitable for
hairy leaves / eq; some stomata difficult to count (eg too numerous);
deficiency of technique given in (a) (allow once);
(3 marks)
[Total 11 marks]
David Kaunda High School 61
66. (Human Biology)
(a) Describe with full practical details, how you would investigate the effect of physical
activity on human breathing rate.
standard selection of subjects (eg same age / same sex / fitness level);
at least five subjects used; definition of one breath / what is counted
(eg inspiration and expiration); use of spirometer qualified / by observation
using stopwatch eq; measured in stated time / as breaths per minute;
standardised rest before counting described; standard activity / exercise
described (eg using a treadmill); rate of activity / use of metronome / eq; for
stated time; breathing rate remeasured immediately after exercise / monitored
during exercise; counting repeated to obtain mean; breathing rate
measurements repeated at timed intervals / repeat with same subjects after
recovery; compare means statistically (eg t test / Mann Whitney-U);
(8 marks)
(b) State three limitations of your experimental method.
breathing rate under voluntary control / can be altered by subject;
rate changes rapidly after exercise stops and is difficult to measure;
breathing rate affected by medical conditions (asthma etc) /
relevant example;
allow max 2 other variables not given in (a);;
depth of breathing can also be changed;
detail of technique not given in (a) (allow once);
(3 marks)
[Total 11 marks]
67. The table below refers to the first and second divisions of meiosis.
If the statement is correct, place a tick () in the appropriate box and if the statement is
incorrect, place a cross (X) in the appropriate box.
-
Statement First division of Second division of
meiosis meiosis
Pairing of homologous chromosomes Ö X;
occurs.
Chromosomes consist of pairs of Ö Ö;
chromatids during prophase
Chiasmata are formed. Ö X;
Chromatids are separated. Ö Ö;
Independent assortment of Ö X;
chromosomes occurs.
[Total 5 marks]
David Kaunda High School 62
68. Read the following passage about the palisade cells of a leaf and write on the dotted lines the
most appropriate word or words to complete the passage.
The palisade cell is typical of plant cells in that it has three structures,
cell wall; vacuole / tonoplast and
chloroplasts / plastids;
plasmodesmata;
starch grain / starch granules;
(accept structures in any order)
none of which is present in animal cells. In common
with animal cells, plant cells (such as palisade cells) have membrane-bound organelles
which are not present in prokaryotic / bacterial cells. In a leaf, palisade cells are
grouped together as a layer just below the epidermis forming a
tissue / mesophyll the function of which is to carry out photosynthesis.
[Total 5 marks]
69. Polypeptides are synthesised from amino acids. The diagram below shows the molecular
structure of an amino acid.
H H O
N C C
H R O H
(a) (i) In the space below, draw a molecular diagram to show how this amino acid reacts
with another amino acid to produce a dipeptide.
both amino acids drawn correctly / two residues correct;
removal of water shown correctly;
correct structure of dipeptide
(3 marks)
I. Name the type of reaction involved.
condensation / polymerisation;
(1 mark)
(b) State two functions of the R groups in a polypeptide chain.
(i) bonding / interactions within molecules / specific examples of bonds
.g. S S or H bonds;
(ii) forming active sites; ref to tertiary structure; interactions with
substrate / receptors; form receptors in membranes;
affect solubility; can act as buffers;
(2 marks)
[Total 6 marks]
70. Catalase is an enzyme which breaks down hydrogen peroxide into oxygen and water. The
activity of catalase can be measured by soaking small discs of filter paper in a solution
containing the enzyme. The discs are immediately submerged in a dilute solution of hydrogen
peroxide. The filter paper discs sink at first but float to the surface as oxygen bubbles are
produced. The reciprocal of the time taken for the discs to rise to the surface indicates the rate of
reaction.
David Kaunda High School 63
An experiment was carried out to investigate the effect of substrate concentration on the activity
of catalase. A filter paper disc was soaked in a solution containing catalase, and then submerged
in a buffer solution containing hydrogen peroxide. The time taken for the disc to rise to the
surface was recorded. This experiment was repeated using a range of concentrations of hydrogen
peroxide.
The results are shown in the graph below.
0 .2 0
0 .1 5
R a te o f
r e a c ti o n 0 .1 0
/s -1
0 .0 5
0 .0 0
0 20 40 60 80 100 120 140 160 180
C o n c e n tra tio n o f h y d ro g e n p e ro x id e / m m o l d m 3
(a) State why a buffer solution was used in this experiment.
to keep pH constant / enzymes are affected by pH;
(1 mark)
(b) (i) Describe the relationship between the rate of reaction and the concentration of
hydrogen peroxide as shown by the graph.
rate increases as substrate concn increases;
steady / constant / linear increase between 20 to 80* mmol dm 3;
then begins to level off;
(*accept any quoted figure in this range)
(3 marks)
(ii) Explain this relationship between substrate concentration and the rate of reaction.
as substrate concn increases, the number of collisions / number
of enzyme-substrata complexes will increase; therefore the
rate will increase;
until all enzymes in use / limited number of active sites;
rate then remains constant / reaches a maximum / reference to Vmax :
(3 marks)
(c) Describe how a solution containing 160 mmol of hydrogen peroxide per dm 3 would be
diluted to prepare a solution containing 80 mmol of hydrogen peroxide per dm3.
use equal volumes of hydrogen peroxide solution;
and distilled / deionised water / buffer solution :
(accept suggested volumes)
(2 marks)
David Kaunda High School 64
(d) Describe how this experiment could be modified to investigate the effect of temperature
on the activity of catalase.
use a water bath;
suggested range of temperatures (at least 3 stated);
use same volume / depth of hydrogen peroxide;
allow substrate / enzyme to equilibrate before adding filter
paper disc; ref to uniformity of discs;
use constant enzyme concentration;
repeat at each temperature;
plot a graph of rate of reaction against temperature;
(4 marks)
[Total 13 marks]
71. Read through the account of the production of gasohol then write on the dotted lines the most
appropriate word or words to complete the account.
Gasohol is a mixture of petrol and ethyl alcohol/alcohol which is produced by microorganisms
such as yeast/saccharomyces. during the anaerobic respiration of glucose. The glucose can
be obtained from any carbohydrate/plant source, such as suitable, named plant eg
potato/named carbohydrate
[Total 5 marks]
72. The diagram below shows part of the nitrogen cycle.
N itr o g e n g a s in th e
a tm o s p h e re
D
A
B C
A m m o n ia N itrite N itr ite
(a) Name a genus of bacteria which is responsible for each of the reactions A, B, C and D.
A Clostridium/Rhizobium/Bacillus/Azotobacter/Klebsiella/etc;
B Nitrosomonas/Nitrococcus/etc;
C Nitrobacter/Nitrospina/etc;
D Pseudomonas/Bacillus/Thiobacillus/etc;
(4 marks)
(b) Describe the conditions in which the bacteria responsible for reaction D will thrive.
anaerobic/eq;
waterlogged soil/marsh/bog/eq;
(2 marks)
[Total 6 marks]
David Kaunda High School 65
73. The diagram below shows a part of a transverse section through the ileum as seen using a low
magnification with a light microscope.
(a) Name the parts labelled A, B and C.
A Villus/Villi/mucosa;
B Submucosa/connective tissue;
C muscle/muscularis externa;
(3 marks)
(b) Describe the function of part C.
peristalsis/described;
movement of gut contents/eq;
mixes food/eq;
brings villi into close contact with contents
(2 marks)
[Total 5 marks]
74. Acid rain is a matter of serious environmental concern. Sulphuric acid is present in acid rain and
has adverse effects on both plants and animals.
(a) (i) Name two acidic components of acid rain other than sulphuric acid.
1 nitric acid; nitrous acid;
2.carbonic acid; sulphurous acid;
(2 marks)
David Kaunda High School 66
(ii) Describe how acid rain is formed.
burning/eq of fossil fuels or named eg;
production of/eq carbon dioxide/sulphur dioxide;
nitrogen oxides from car exhausts/eq;
gas(es) combines with water to produce (dilute) acid;
(3 marks)
(b) An experiment was carried out to investigate the effect of dilute sulphuric acid on the
growth of cress seedlings. Batches of seeds were sown in glass dishes on filter paper to
which dilute sulphuric acid was added. The dishes were then incubated. The root and
shoot lengths were measured after 65 hours. The results are shown in the table below.
Sulphuric acid concentration Mean root length Mean shoot length
/ mol dm–3 / mm / mm
0 55.5 25.2
1 × 10–³ 63.4 18.4
3 × 10–³ 6.5 9.5
4 × 10–³ 2.0 4.6
6 × 10–³ 2.8 0.8
7 × 10–³ 1.5 0.5
8 × 10–³ 1.3 0.3
9 × 10–³ 1.3 0.0
1 × 10–2 1.0 0.0
Adapted from Fleet, Jones and Petter, J.B.E.1987
(i) Describe the relationship between the concentration of sulphuric acid and the
growth of roots as shown by the results in the table.
as concentration increases root length decreases/eq;
growth in 1 × 10 3 molar causes an increase;
a suitable comment about an anomalous result;.
(2 marks)
(ii) Compare the effects of sulphuric acid on the growth of roots and shoots.
both decrease;
no shoot growth above 8 × 10 3 molar but roots do/eq;
shoots more sensitive/eq/converse for roots;
all concentrations decrease shoot growth;
(3 marks)
David Kaunda High School 67
(iii) Suggest two reasons why cress seedlings are suitable for investigating the effect of
acid rain on plants.
1 grow quickly/rapid germination;
easy to grow/large numbers can be grown/easy to measure;
2 easy to control other variables;
easy to treat/whole plant can be exposed/eq;
(2 marks)
[Total 12 marks]
75. Give an account of the adaptations shown by human populations to life in extremes of
temperature.
1. skin colour related to heat radiation/loss from body/eq;
2. ref to nose shape eg narrow in low temperature;
3. related to temperature of air entering/leaving lungs;
4. low temp., straight hair/high temp., coiled hair;
5. related to heat loss from neck/head;
6. ref to high/low amount subcutaneous fat;
7. related to (thermal) insulation;
8. low temp., short and stocky/short limbs/eq;
9. high temp., tall and thin/long limbs/eq;
10. related to surface area and degree of heat loss;
11. correct ref to surface are to volume ratio;
12. high temp., behavioural adaptations eg sleep/shade;
13. low temp., reduced bradycardia (lower heart rate);
14a. correct ref to level of sweating;
14b. heat loss due to vaporisation;
15. correct ref to vaso constriction/vasodilation;
16a. loose/no clothing in high temp.;
16b. pale/light clothing reflect heat;
17. thick/many layers/eg of clothing in cold temp.;
18. housing qualified eg thick walls for insulation/small windows
reduce wind
19. high activity in low temp./low activity in high temp.;
20. increased food intake in cold temp./decrease in high/
increased water intake in high temp.
21. use of fire in cold.
[Total 10 marks]
76. The table below shows features of arteries, veins and capillaries.
If the statement is correct, place a tick () in the appropriate box and if the statement is incorrect
place a cross (X) in the appropriate box.
Feature Arteries Veins Capillaries
Walls permeable X X
Collagen fibres present in walls X
Endothelium present
Series of valves present X X
[Total 4 marks]
David Kaunda High School 68
77. The diagram below shows some of the cells involved in the loss of water from part of a leaf.
(a) Name the tissues labelled P and Q on the diagram.
P. xylem;
Q spongy mesophyll;
(2 marks)
(b) The table below shows the concentrations of potassium ions in some of the cells shown in
the diagram when the stoma is open and when the stoma is closed.
Cell Concentration of potassium ions / abitrary units
Stoma closed Stoma open
Guard cell 95 448
Cell X 156 293
Cell Y 199 98
Cell Z 448 73
(i) Describe the changes that take place in the concentrations of
potassium ions in cells X, Y and Z when the stoma opens.
falls in Y/ or Z / moves out of Y / or Z;
rises in X / moves into X;
credit for correct manipulation of figures.
(2 marks)
(ii) Explain how these changes in potassium ion concentration are related
to the mechanism for the opening of the stoma.
active transport of K+ ions into guard cell;
correct lowering of water potential/eq.;
water enters guard cell by osmosis;
increase in turgidity/eq.;
causes bending of guard cells/eq.
(3 marks)
[Total 7 marks]
David Kaunda High School 69
78. (a) State three characteristic features of gas exchange surfaces.
1 large surface area;
2 thin lining;
(partially) permeable (lining);
covered by film of moisture.
(3 marks)
3 Describe how the process of inspiration (breathing in) takes place
in mammals.
contraction of diaphragm muscles lowers / flattens diaphragm;
contraction of external intercostal muscles raises ribcage;
volume of thorax / lungs increases thus intrapulmonic pressure
falls / eq.
reference to control by medulla / eq.
(3 marks)
[Total 6 marks]
79. The diagram below shows a flower of the grass Festuca pratensis
(a) Name the parts labelled J and K.
J stigma;
K anther;
(2 marks)
(b) State three features, shown on the diagram, which indicate that this flower is wind-
pollinated
1. anthers outside flower / protruding / eq.;
large anthers;
2 stigma outside flower / protruding / eq.;
3 feathery/eq stigma / OR stigma has large surface area.
(3 marks)
[Total 5 marks]
David Kaunda High School 70
80. The diagram below shows the mean volumes of water ingested, secreted, absorbed and egested
by the human digestive system in one day (24 hours)
1 .5 d m 3
in g e s te d
O esophagus 1 .5 d m 3
in s a liv a
2 .0 d m 3
in g a s tric
S to m a c h
ju ic e
0 .5 d m 3 A
in b ile
S m a ll
in te stin e 1 .5 d m 3
Y in b ile X
1 .5 d m 3
in in te s tin a l
ju ic e
3
0 .3 5 d m
C o lo n
R e c tu m
0 .1 5 d m 3
in fa e c e s
(a) (i) Name the gland labelled A
liver;
(1 mark)
(ii) Name secretion X
pancreatic juice;
David Kaunda High School 71
(1 mark)
(b) Calculate the mean volume of water absorbed by the small intestine in one day,
represented by Y on the diagram. Show your working.
(1.5 + 1.5 + 2.0 + 0.5 + 1.5 + 1.5) (0.35 + 0.15)
OR 8.5 0.5;
Answer 8.0 dm3
(2 marks)
(c) Comment on the mean volumes of water absorbed each day by the small intestine and the
colon.
more water absorbed in small intestine / correct manipulation of figures;
large surface area for absorption;
reference villi / microvilli;
colon partially dehydrates / solidifies faeces / eq.;
efficient water absorption essential to maintain water balance of body
./. to prevent dehydration / eq.
(3 marks)
[Total 7 marks]
81. An investigation was carried out into the effect of ingestion of ice on thermoregulatory
mechanisms in humans. Volunteers ingested quantities of ice three times during the
investigation. Measurements were then taken of their skin temperature, core temperature and the
rate of heat loss as a result of sweating. The external temperature was 45 C
The results are shown in the graphs below.
In g e stio n In g e s tio n I n g e s tio n
o f ic e o f ic e o f ic e
3 8 .0
T e m p e ra tu re
/ ºC
3 7 .5
3 7 .0
0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70
T im e / m in u te s
David Kaunda High School 72
In g e s tio n In g e s tio n I n g e s tio n
o f ic e o f ic e o f ic e
300
R a te o f
h e a t lo s s 250
as a
r e s u lt o f 200
s w e a tin g
/ Jsec –1
150
100
0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70
T im e / m in u te s
(a) (i) Describe the effect of ingestion of ice on core temperature
ingestion of ice causes fall in core temperature;
correct reference to graph / temp. drop / time taken calculated;
fluctuation after second ingestion different from fluctuation after
first / any correct difference.
(2 marks)
(ii) Describe the relationship between skin temperature and the rate of heat loss due to
sweating
both oscillate / fluctuates / eq.;
as rate of heat loss begins to fall before skin temperature rises;
rise in skin temperature followed by increase in rate of heat loss.
(3 marks)
(b) (i) Explain how sweating causes heat loss.
water evaporates from skin surface;
takes heat from body;
reference latent heat of evaporation.
(3 marks)
(ii) Describe and explain the relationship between ingestion of ice and skin temperature
ingestion of ice followed by rise in skin temperature;
ingestion of ice causes fall in core temperature;
detected by thermoreceptors; in hypothalamus;
inhibits mechanisms causing heat loss from skin / sweating / vasodilation;
skin temperature rises.
(3 marks)
[Total 11 marks]
David Kaunda High School 73
82. Read through the following passage on the use of enzymes in the extraction of juice from fruit,
then write on the dotted lines the most appropriate word or words to complete the account.
Enzymes made by microorganisms may be used in commercial processes. In order to
speed up the extraction of juice from fruit, enzymes called pectinases / cellulases
are used. The fruit is first chopped up / eq. and then the enzymes are added to break down the
pectin / cellulose present in the cell walls. These enzymes help to make the extracted juice
clearer / clarified / eq.
[Total 5 marks]
83. The table below gives descriptions of some of the characteristic features of mammalian
herbivores related to their nutrition.
Complete the table by stating the name of the structure to which each description refers.
Description Structure
open roots of teeth;
Allows continual growth of teeth
ridges on cheek teeth / eq.
Permits efficient grinding and crushing of circular jaw movement;
plant food
diastema / description;
Allows manipulation of food in the mouth
during chewing
rumen / caecum;
Is the site of cellulose digestion by
microorganisms
[Total 4 marks]
84. Write an essay on the following topic.
factors affecting enzyme activity:
temperature:
increase increases rate of reaction
in the range 0 - 40C
ref to optimum temperature
ref to temperature coefficient / Q IO
kinetic effect explained in terms of collisions / complex formation
denaturation explained in terms of high temp and bonding -
pH:
change affects H-bonds
correct reference to effect on shape of active site
reference to optimum pH
named examples of enzymes and pH range
effect of extremes of pH -
enzyme concentration:
increase increases rate
explained in terms of numbers of active sites
reference to substrate concentration as a limiting factor -
substrate
increase concentration:
maximumincreases
reference to enzymerate
explained in
concentration
terms of turnover
as a limiting
numbers of enzyme
factor
David Kaunda High School 74
-
inhibition:
reference irreversible by heavy metals
reference competitive inhibition
named examples -S = 13, B = 2, C = 2
[Total 15 marks]
85. Write an essay on the following topic.
pollution of water by organic material and fertilisers:
organic:
source inadequately treated,
untreated sewage, organic
fertilisers
source industrial spillage,
outflow inorganic:
nitrates and phosphates
source agricultural use
reference to solubility
explanation of leaching,
effects
nitrates and phosphates as
nutrients for algae
explanation of algal bloom
death and decay of algal
material
dead algae, sewage, organic
material as a nutrient source
for bacteria
bacterial growth and effect on
BOD -BOD explained
effect on other organisms
such as reduced oxygen
level, reduced light
description of
eutrophication
references to health effects of
nitrates, nitrates in drinking
water,
ref to indicator organisms
methods of reducing or
treating polluted water S= 13,
B= 2, C= 2
[Total 15 marks]
David Kaunda High School 75
86. Cystic fibrosis is a genetic disorder caused by a mutation in the gene which codes for a protein
known as the CFTR protein. This protein is involved in the transport of chloride ions through the
cell surface membrane.
The diagram below shows how the normal CFTR protein is believed to function in the cell
surface membrane.
C F T R p r o te in
O u te r s u rfa c e
m e m b ra n e
P a rt o f
c e ll s u rfa c e
m em b ran e
In n e r su rfa c e
m e m b ra n e
ATP ATP
A T P b in d in g s ite s
ATP ATP
A D P P i A D P P i
P i = in o rg a n ic p h o s p h a te
(a) (i) Describe the sequence of events that takes place when ATP is present.
ATP binds to CFTR protein / binding sites;
ATP hydrolysed / eq. to ADP Pi;
changes shape of protein / opens (ion) channel / eq.
(3 marks)
(ii) What is the function of ATP in this sequence of events?
to provide energy.
(1 mark)
David Kaunda High School 76
(b) One symptom of cystic fibrosis is the production of very sticky, thick mucus which cannot
easily be moved. This occurs particularly in the lungs, pancreas and testes.
Suggest an explanation for each of the following.
(i) Many people affected by cystic fibrosis suffer from repeated lung infections.
thick mucus hinders removal of bacteria / pathogens from the lung.
(1 mark)
(ii) Reduced ability to digest starch in the small intestine is common among people
affected by cystic fibrosis.
mucus impedes the release of (pancreatic) amylase (into the duodenum).
(1 mark)
(iii) 95% of males affected by cystic fibrosis are infertile.
mucus hinders the passage / mobility of the spermatozoa.
(1 mark)
[Total 7 marks]
87. Write an essay on the following.
gas exchange in animals and flowering plants:
introduction:
necessity for gas exchange
oxygen needed for aerobic respiration in both plants and animals
carbon dioxide as a waste product of respiration needs to be eliminated reference to the
consequences
carbon dioxide uptake in plants for photosynthesis
oxygen as a waste product of this process
reference to differences in net gas exchange at different times of day -
gas exchange surfaces:
large surface area explained
reference to thickness in relation to diffusion paths of gases
must be permeable for gases to pass through -
gas exchange in -animals:
oxygen obtained from air or water
need for special respiratory pigments
reference to haemoglobin
respiratory / gas exchange surface needs to have good blood supply / eq
structures associated with gas exchange in mammals described
mechanism of ventilation in mammals described
structures and mechanisms in insects
factors affecting rate of gas exchange -
gas exchange in flowering plants:
reference to external structure of leaf
internal structure with reference to stomata, intercellular air spaces
diffusion of gases explained
mechanism of gas exchange
lenticels S = 17, B = 3, C = 3
[Total 20 marks]
David Kaunda High School 77
88. Write an essay on the following.
Breathing, gas exchange and the role of respiratory pigments:
introduction:
necessity for gas exchange
oxygen needed for aerobic respiration
carbon dioxide as a waste product
outline structure of respiratory system
need for ventilation
need for respiratory pigment for transport of gases -
breathing
structure of respiratory system
trachea, bronchi, bronchioles, alveoli
histology of alveolus
mechanism of ventilation
roles of diaphragm and intercostal muscles
control of breathing via respiratory centre -
gas exchange:
adaptations of alveoli as surfaces for gas exchange
thin, moist vascularised, ventilated to maintian diffusion gradient
large surface area -
respiratory pigments
references to:
haemoglobin
myoglobin
fetal haemoglobin
transport of oxygen and carbon dioxide
the oxygen dissociation curve
significance of Bohr effect S = 17, B = 3, C = 3
[Total 20 marks]
David Kaunda High School 78
89. The diagram below shows the process of DNA replication.
X { Y
(a) Name the parts labelled X and Y.
X nucleotide;
Y (organic / nitrogenous) base / purine / pyrimidine;
(2 marks)
David Kaunda High School 79
(b) Name one enzyme involved in DNA replication and state the type of reaction it catalyses.
Enzyme (DNA) ligase / polymerase;
Reaction condensation / polymerisation;
(2 marks)
(c) Suggest why DNA replication is described as semi-conservative.
Newly synthesised molecule has one parental / original / template strand / has
half of the original;
(1 mark)
(d) Name the stage of the cell cycle during which DNA replication occurs.
S / synthesis phase / interphase;
(1 mark)
[Total 6 marks]
90. The diagrams below illustrate one model of enzyme action.
} A
E nzym e S u b s tra te s E n z y m e -s u b s tra te E n z y m e -p ro d u c t P ro d u c ts
c o m p le x c o m p le x
(a) Name the part of the enzyme labelled A.
active site;
(1 mark)
(b) Explain how this model can account for enzyme specificity.
active site / part A has a particular / specific shape; only the substrate will fit
and form products;
(2 marks)
(c) With reference to this model, explain the effect of a competitive inhibitor on an enzyme-
catalysed reaction.
competitive inhibitor has a similar shape to substrate / same shape as
substrate / can fit into active site;
prevents the substrate combining / blocks the active site;
reduces the rate / slows reaction;
(2 marks)
[Total 5 marks]
David Kaunda High School 80
91. The table below refers to two organic molecules.
If the statement is correct for the molecule, place a tick () in the appropriate box. If it is
incorrect, place a cross (X) in the appropriate box.
Statement Triglyceride Glycogen
Contains only carbon ;
hydrogen and oxygen
Glycosidic bonds present ;
Soluble in water ;
Provides storage of energy ;
Occurs in flowering plants
;
and animals
[Total 5 marks]
92. An experiment was carried out with cells of carrot tissue to determine the effect of temperature
on the absorption of potassium ions.
Slices of carrot tissue were immersed in a potassium chloride solution of known concentration.
The changes in concentration of potassium ions in the solution were determined at intervals for 6
hours. From these measurements, the mass of potassium ions taken in by the carrot cells was
found. The experiment was carried out at 2°C and 20°C. The solutions were aerated
continuously.
David Kaunda High School 81
The results are shown in the graph below. Absorption of potassium ions is given as micrograms
of potassium per gram of fresh mass of carrot tissue (g g–1).
700
600
A t 2 0 ºC
500
400
K + a b s o rp tio n
/ µ g g -1 f r e s h m a s s
300
200
A t 2 ºC
x x
x
100 x
0 x
0 1 2 3 4 5 6
T im e / h o u rs
(a) During the first hour, some of the potassium ions enter the cells by diffusion. State two
conditions which are necessary for a substance to enter a cell by diffusion.
1. membrane must be permeable to substance;
must be a concentration gradient / higher outside cell than inside;
2. substance must be in solution / a gas / a liquid;
(2 marks)
(b) (i) Calculate the mean rate of absorption of potassium ions at 20°C, between 2 and 6
hours. Show your working.
640 – 295 OR 345;
° 4;
= 86.25 g g–1 hour–1;
(3 marks)
David Kaunda High School 82
(ii) Compare the rates of absorption of potassium ions at 2°C and 20°C during this
experiment.
fastest uptake occurs at start / both decrease;
rate of uptake at 20°C is greater than at 2°C converse;
uptake at 20°C continues, levels off at 2°C;
credit manipulation of figures, e.g. final mass taken up at 20°C greater than at
2°C quoting Two figures from graph;
(3 marks)
(iii) Suggest an explanation for the differences in the rates of absorption of potassium
ions at the two temperatures.
reference to increase in temperature increasing movement / kinetic energy /
OR converse;
(So) faster / eq. diffusion at higher temperature; diffusion no longer occurs
when there is no concentration gradient / eq.;
ions also taken up by active transport / ref. to ion pumps;
active transport increases at higher temperatures;
reference to increased respiration / increased ATP;
uses more K+ higher temperature;
(3 marks)
[Total 11 marks]
93. Give an account of the process of mitosis.
1. daughter cells have same number of chromosomes as parent cell / are
genetically identical to parent cell;
2. concerned with growth / repair / replacement of tissues / asexual
reproduction;
3. reference to cell cycle consisting of interphase, mitosis, cell division;
4. named stages in correct sequence;
5. (during prophase) chromosomes condense / eq.;
6. each consists of a pair of chromatids joined by centromere;
7. reference to centrioles;
8. formation of spindle;
9. by microtubules;
10. disappearance of nucleolus / nucleoli;
11. breakdown of nuclear envelope;
12. (at metaphase) chromosomes attached to spindle fibres;
13. lined up at equator of cell;
14. (at anaphase) centromeres split / duplicate;
15. separation of chromatids;
16. daughter chromosomes / chromatids pulled to opposite poles of cell;
17. (at telophase) chromosomes / chromatids reach poles of cell;
18. uncoil / eq.;
David Kaunda High School 83
19. formation of nuclear membrane;
20. (daughter) nuclei formed;
21. followed by cytokinesis (in animal cells) / or description;
22. formation of a cell plate / eq. in plant cells;
[Total 10 marks]
94. The diagram below shows an organism of the genus Rhizopus.
(a) Name the major taxonomic group to which this organism belongs and give one external
feature characteristic of this group.
Group fungi / Zygomycota;
Feature hyphae / mycelium / sporangia;
(2 marks)
(b) Describe the role of part A in the nutrition of the organism.
penetration of / anchorage on substrate / food source / eq.;
secretion / eq. / release of enzymes;
absorption / eq.;
(2 marks)
(c) Explain how parasitic nutrition differs from the nutrition of Rhizopus.
nutrients already soluble / absorption only / eq.;
Source of nutrients is a living organism / host;
detrimental effect on host / eq.;
Rhizopus saprobiont / feeds on dead / decaying matter;
(2 marks)
[Total 6 marks]
David Kaunda High School 84
95. (a) The table below shows mean values for primary productivity for four ecosystems:
temperate deciduous forest, tropical forest, temperate grassland, and intensively cultivated
land in temperate region.
Ecosystem Primary productivity / kJ m–2 yr–1
Temperate deciduous forest 26 000
Tropical forest 40 000
Temperate grassland 15 000
Intensively cultivated land in a
temperate region 30 000
(i) Suggest two reasons to account for the higher primary productivity of a tropical
forest compared with a temperate forest.
1. higher / constant temperature / no / little seasonal change / eq.;
higher plant density; higher water availability / rainfall / eq.;
2. evergreen / eq. plants / temperate trees have no leaves for part of
year / eq;
more light (energy) / intensity / eq;
(2 marks)
(ii) Suggest explanations for the difference in primary productivity between temperate
grassland and intensively cultivated land.
crops all same type of plant / monoculture;
use of crop rotation / fertilisers applied / eq; irrigation / eq.;
pests / diseases controlled / eq;
crop varieties / plants selected for high yield;
replanting after harvest;
(3 marks)
(b) Describe how you would estimate the fresh biomass of the producers in a grassland
ecosystem.
take several / random samples;
use of quadrat of stated / eq. size;
remove / eq. plants / OR count the number of plants;
remove all consumers / remove soil;
weigh to find (fresh) mass / OR weigh one no. of plants / OR multiply number
of plants by value from table of biomass;
multiply by area of grassland / eq;
(4 marks)
David Kaunda High School 85
(c) Suggest why productivity of an ecosystem is measured in units of energy rather than units
of biomass.
biomass includes inorganic component / eq;
water content is variable / makes it less accurate / eq.;
productivity in energy units is true reflection of energy capture / eq;
(2 marks)
[Total 11 marks]
96. Give an account of the causes and effects of pollution of water by sewage.
1. overproduction / eq. of sewage related to population growth / animal
density / eq;
2. agricultural spillage / eq;
3. failure of / no sewage treatment / flooding / into sea;
4. sewage described (two contents from faeces, urine, detergents / eq.);
5. sewage is nutrient / carbohydrate source / eq.;
6. for bacterial / fungal growth / eq;
7. causes increased BOD;
8. due to increase in aerobic respiration;
9. causing decrease in oxygen concentration;
10. effect on other organisms / named e.g.;
11. effect on food chain / web described / eq.;
12. anaerobes / organisms tolerating low oxygen survive / increase;
13. NO3 / PO4 from sewage;
14. ref. to eutrophication;
15. effect on algal growth / ref. to algal bloom;
16. causes reduced light penetration (in context to turbidity) + algal
blooms;
17. effect on other photoautotrophs described;
18. death / decay of algae;
19. pathogenic / eq. bacteria / virus / eq. present in sewage;
20. named eg of pathogen (cholera / typhoid / hepatitis)
21. toxic / eq. heavy metals / named eg present in sewage;
22. oestrogens and their effect;
23. economic consequences of pollution;
[Total 10 marks]
David Kaunda High School 86
97. Explain the meaning of each of the following terms.
(a) Heat cramp
heat generation due to exercise;
heat loss by increased sweating causes increased loss of water /
dehydration;
increased loss of electrolytes / sodium / eq. / need to replace sats;
change in electrolyte balance in blood / eq;
(uncontrolled) muscular contraction / stomach cramps / eq;
(3 marks)
(b) Frostbite
dramatic / eq. lowering of surface tissue / eq. temperature / due to very low air
temperature / low air temp. plus wind;
reduced blood flow to extremities / skin;
formation of ice in cells / tissues / tissues freeze;
disruption / death of tissues / cells bursting / necrosis;
ref. to gangrene;
most common in toes / fingers / ears / nose / eq.;
(3 marks)
[Total 6 marks]
98. The diagram below shows the outline or a process for the production of gasohol.
C o rn
e x tra c t A m y la s e Y east
F e r m e n te r D is tilla tio n G asoho l
(a) Explain why amylase is added to the fermenter.
converts starch / amylose; to maltose;
for respiration of carbon / carbohydrate source / eq;
(2 marks)
(b) Name one constituent of gasohol.
ethanol / eq: / petrol;
(1 mark)
(c) Give two benefits of using gasohol, rather than petrol, as fuel.
1. readily available / no imports needed;
renewable energy source / petrol non-renewable / eq.;
2. less air pollution / less sulphur content / less So2 production;
utilises waste product / cheaper;
(2 marks)
David Kaunda High School 87
David Kaunda High School 88
(d) Suggest one product of economic importance, other than gasohol, which could be
obtained from the fermenter.
yeast / animal feed / fertiliser / SCP / alcohol / CO 2 / eq;
(1 mark)
[Total 6 marks]
99. At high altitudes, atmospheric pressure is lower than at sea level. This means that people living
at high altitude have less oxygen available to them compared with those living at low altitude.
The table below shows the results of three measurements made on blood of normal individuals
resident at each of three different altitudes.
Percentage saturation Oxygen content of Haemoglobin in
Altitude / m of arterial blood with arterial blood / cm3 blood / g per 100
oxygen per 100 cm3 cm3
150 94.2 18.3 15.5
.3
3700 88.2 19.9 17.4
4375 83.5 20.9 18.6
(a) (i) How does the percentage saturation of arterial blood with oxygen change with
increasing altitude?
decreases;
(1 mark)
(ii) Using the information in the table, explain how people living at high altitude have
adapted to the low oxygen availability.
haemoglobin greater; so more oxygen carried;
12 / 20 % more haemoglobin / some manipulation of data;
9 / 14 % more oxygen carried / manipulation of data;
(3 marks)
(iii) State one feature, other than those shown in the table, which enables high altitude
residents to overcome the problem of low availability of oxygen.
greater lung capacity / increased cardiac output / stroke volume / more rbc /
increased diphospho-glycerate / hyperventilation / barrel chested;
(1 mark)
(b) State three environmental factors, other than availability of oxygen, which vary between
sea level and high altitude sites at the same latitude.
1. humidity;
temperature;
2. wind speed;
3. solar radiation / UV light / eq;
(3 marks)
David Kaunda High School 89
(c) A visitor to high altitude from sea level may suffer from mountain sickness.
State three symptoms of mountain sickness.
1. hyperventilation / breathlessness / eq;
increased cardiac output / eq;
2. pulmonary oedema / eq;
nausea / eq;
3. headaches / eq. / impaired mental activity / lethargy;
(3 marks)
[Total 11 marks]
100. The diagram below shows a germinating pollen grain and a mature ovule from a flower of the
Papilionaceae. Some nuclei have been labelled.
(a) Describe how pollination usually occurs in the Papilionaceae.
insect attracted / eq. / to flower by scent / colour / nectar;
lands on wing petals / depresses keel petal;
anthers / stamens dust / eq. pollen on to insect’s abdomen;
pollen carried to another stigma / carpel;
(2 marks)
(b) Give the letter of the nucleus which fuses with a male nucleus to form each of the
following.
The zygote D;
The endosperm G;
(2 marks)
David Kaunda High School 90
(c) Describe one mechanism which prevents self-fertilisation in flowering plants.
dichogamy / male and female parts nature at different times;
any two protanding / eg.; pollen shed before stigma is nature;
dichogamy / male and female parts nature at different times;
any two protogyny / eg.; stigma withered / ripe before pollen shed;
Paired marking
structure of flower prevents pollen landing on stigma;
explanation of heterostyly;
points
ref. to dioecious plants; self-pollination impossible;
self-incompatibility / sterility; no pollen germination;
(2 marks)
[Total 6 marks]
101. The diagram below shows a longitudinal section of two cells of phloem tissue in a plant stem.
(a) Name the cells labelled A and B in the diagram.
A sieve tube element;
B companion cell;
(2 marks)
(b) (i) State the function of phloem in a plant.
Transport / translocation of sucrose / amino
acids / organic solutes / eq.;
(1 mark)
David Kaunda High School 91
(ii) Describe how aphids can be used to investigate the function of phloem.
Allow aphids to feed by inserting stylets / eq. into phloem;
anaesthetise aphids;
remove bodies of aphids leaving stylets / eq. in position;
collect fluid that exudes from stylets;
analyse fluid / credit details of technique / eq.;
(3 marks)
[Total 6 marks]
102. The graphs below show the changes in pressure in the aorta and in the left and right ventricles of
the heart, during the cardiac cycle. Time 0 indicates the start of atrial contraction.
(a) Compare the changes in pressure in the left ventricle with those in the right ventricle,
giving reasons for the differences.
both rise and fall back to 0 kPa in 0.5 seconds / eq.;
greater change in pressure in left ventricle / smaller changes in right
ventricle;
credit correct ref. to figures / range / difference / eq.;
left ventricle contracts more strongly / eq. / right ventricle contracts less
strongly eq.;
left ventricle has more cardiac muscle in wall / right ventricle has less;
to pump blood around the body / less distance to lungs / left ventricle pumps
blood further;
so that pressure in the lungs is less;
(4 marks)
David Kaunda High School 92
(b) Compare the changes in the pressure in the aorta with those in the left ventricle, giving
reasons for the differences.
steep / rapid rise in both;
pressure in aorta rises later than in ventricle / starts higher in the aorta;
greater rise in left ventricle / converse / use of figures;
slight time delay in blood passing out of ventricle into aorta;
steeper fall in left ventricle / converse;
gradual fall between 0.4 and 0.8 / 0.9 sec / from 14 / 15 to 10 / 11 kPa is aorta;
caused by elastic recoil of aorta wall;
closure of semilunar / aortic value;
(3 marks)
(c) On the graph of changes in pressure in the aorta and left ventricle, show by means of an
arrow when the aortic semilunar valve closes.
arrow placed top of left ventricle curve / cross over point of aorta curve and
ventricle curve;
(1 mark)
(d) Cardiac muscle is described as myogenic. Explain how the cardiac cycle is coordinated
within the heart.
initiated by sino-atrial node / eq.;
wave of electrical excitation / eq. spreads across atria;
stimulates contraction of (cardiac muscle of) atria;
passes to ventricles via atrio-ventricular node / AVN;
non-conductive tissue / eq. elsewhere between atria and ventricles;
some reference to time delay at AVN;
thus atrial systole occurs before ventricular systole;
excitation / eq. passes down purkinje tissue / bundle of His;
ventricles contract from base / apex;
(4 marks)
[Total 12 marks]
David Kaunda High School 93
103. The uptake of water by a leafy shoot can be investigated using a potometer as shown in the
diagram below.
(a) (i) What assumption is made when this apparatus is used to investigate the rate of
transpiration?
water loss / transpiration equals / is proportional to water uptake;
(1 mark)
(ii) State two precautions which must be taken setting up and using this apparatus.
1. cut stem under water;
assemble apparatus under water;
render apparatus water tight / air tight with vaseline / wax;
2. (run water through capillary to) eliminate air bubbles;
ensure leaves / eq. are dry;
control of variables / one variable specified; ref. to equilibration;
(2 marks)
(b) Using this apparatus, four experiments were carried out with the same shoot in the order
given below.
A Still air, leaves untreated
B Moving air, leaves untreated
C Still air, lower surface of leaf covered with grease
D Moving air, lower surface of leaf covered with grease
Temperature and light intensity were kept constant during the investigation.
David Kaunda High School 94
The results are shown in the graph below.
200
B
D is ta n c e m o v e d b y m e n is c u s / m m
150
100
50
D
C
0
0 5 10 15 20 25 30
T im e / m in
The mean rate of water uptake during experiment A was 3.2 mm 3 per minute.
The cross-sectional area of the bore of the capillary tube is 0.8 mm 2. Calculate the mean
rate of water uptake by the shoot during experiment B. Show your working.
(meniscus moves) 180 mm (in 30 minutes);
180 180
0 .8 3 .2
30 120 ;
Answer 4.8 mm3 min–1;
(3 marks)
(c) (i) Describe and explain the effect of moving air on the rate of water uptake in
experiment B.
rate of water loss / transpiration / water uptake increased;
credit comparative reference to figures;
more water vapour blown away / eq.;
thus increasing / maintaining concentration gradient / eq;
causing faster / more diffusion;
(3 marks)
David Kaunda High School 95
(ii) Suggest an explanation for the different effects of moving air in experiments
B and D.
moving air causes more water vapour to be lost from B than D / less from
D than B / eq.;
more water (vapour) lost through stomata;
more stomata on lower surface of leaves;
grease prevents water loss through / blocks
these stomata / acts as a barrier;
(3 marks)
[Total 12 marks]
104. The diagram below shows some of the events which take place in the ovary and oviduct
(Fallopian tube) around the time of fertilisation.
(a) Name the following.
(i) The process labelled A
ovulation;
(1 mark)
(ii) The type of nuclear division taking place at D and E
mitosis;
(1 mark)
(iii) The structure labelled X
corpus luteum / yellow body;
(1 mark)
(iv) One hormone produced by structure X
progesterone / oestrogen;
(1 mark)
David Kaunda High School 96
(b) On the diagram, use the letter F to label the region where fertilisation took place.
Anywhere along line B in funnel to top of first cell;
(1 mark)
[Total 5 marks]
105. An investigation was carried out into the action of amylase in different regions of the human
alimentary canal.
Six petri dishes were partly filled with agar to which starch had been added and the agar was
allowed to set. A well as then created in the centre of each dish by removing a cylinder of the
agar.
5 cm3 samples of the contents of different regions of the alimentary canal were obtained and
labelled as follows.
A - Oesophagus
B - Stomach
C - Duodenum
D - Ileum
E - Colon
2 cm3 of sample A were placed in the central well of one of the petri dishes. This is shown in the
diagram below.
2 c m 3 o f a lim e n ta r y A g a r a n d s ta r c h
c a n a l c o n te n ts
in w e ll
P e tr i d is h
The dish was covered with a lid and placed in an incubator at 35C for 60 minutes, after which
time the surface was flooded with iodine solution. After 3 minutes, the iodine was washed off.
Iodine causes agar containing starch to turn blue-back in colour.
The width of the area of agar which was light brown in colour (distance X) was measured and
recorded. Samples B, C, D and E were treated in exactly the same way. A control dish was set up
with 2 cm3 of distilled water in the central well.
The results are shown in the table and diagram below.
S u rfa c e v ie w o f p e tr i d is h B lu e -b la c k
a re a
S a m p le D is ta n c e X / m m
A 5 .5 D is ta n c e X
B 0 C e n tr a l w e ll
in a g a r
C 6 .5 L ig h t b ro w n
a re a
D 6 .0
E 1 .0
The control stained blue-black and had no light brown coloration.
David Kaunda High School 97
(a) (i) What is the effect of amylase on starch?
digestion / hydrolysis / breakdown to maltose;
(1 mark)
(ii) Explain how this effect is shown in the experiment.
reduction / loss of colour / becomes light brown / eq.;
shows less starch / starch has been changed;
(2 marks)
(iii) What is the purpose of the control?
to show that it is the amylase that causes loss of starch / eq.;
(1 mark)
(b) (i) Name the source of the amylase present in sample A.
saliva / salivary gland(s);
(1 mark)
(ii) Name the sample which shows the most amylase activity and explain why amylase
activity is greatest in this region of the alimentary canal.
C / duodenum; pancreatic juice present / secreted;
contains much amylase;
some reference to optimal pH for amylase in duodenum;
(3 marks)
(c) Suggest an explanation for the results obtained for the sample from the stomach.
(salivary) amylase denatured / inactivated;
by low pH / HCl / acidity of stomach;
no amylase secreted by stomach / stomach mainly concerned with protein
digestion;
(2 marks)
[Total 10 marks]
106. Human Biology
Haemoglobin in mammals is made up of four polypeptide chains, two identical chains and two
identical chains. The sequence of amino acids in these chains has been determined for a
number of different mammals.
Table 1 below shows a sequence of fifteen amino acids in an chain from four different
primates: a chimpanzee, a human, a gorilla and an orang-utan.
Table 1
Primate Amino acid sequence
Chimpanzee KAAWGKVGAHAGEYG
Gorilla KAAWGKVGAHAGDYG
Human KAAWGKVGAHAGEYG
Orang-utan KTAWGKVGAHAGDYG
Key: A = alanine D = asparagine E = glutamic acid G = glucine H = histidine
K = lysine T = threonine V = valine W = tryptophan Y = tryrosine
David Kaunda High School 98
David Kaunda High School 99
(a) (i) What differences are there between the amino acid sequence for the orang-utan and
the chimpanzee?
orang-utan has T / threonine instead of A / alanine and has D / asparagine
instead of E / glutamic acid / T and D / chimp has A and E;
(1 mark)
(ii) Name one other pair of primates in the table in which there is a difference in the
amino acid sequence.
chimpanzee and gorilla / gorilla and human / orang-utan and gorilla / orang-
utan and human;
(1 mark)
(b) Comparisons of amino acid sequences have been used to determine evolutionary
(phylogenetic) relationship in the primates.
(i) Using evidence given in Table 1, complete the evolutionary tree diagram below to
show the possible evolutionary relationship between chimpanzees, gorillas, humans
and orang-utans.
o r a n g -u ta n ;
C om m on
a n c e s to r C h im p a n z e e
hum an;
g o r illa ;
(3 marks)
(ii) Give two ways in which the data in Table 1 support your suggested evolutionary
relationship.
1. human and chimp have (exactly) same / eq. sequence (so must be
together);
gorilla differs by one amino acid so more closely related to humans;
2. orang-utan more differences / 2 amino acids so not as close as
gorilla / eq;
(2 marks)
David Kaunda High School 100
(c) When human blood serum is injected into a rabbit, the rabbit produces antibodies against
human serum proteins. When blood serum from humans and other mammals is mixed
with rabbit serum containing these antibodies, precipitation occurs.
Table 2 below shows the percentage precipitation when this rabbit serum was mixed with
serum from a human, a gibbon, a spider monkey and a hedgehog.
Table 2
Mammal Percentage precipitation
Human 100
Gibbon 79
Spider monkey 58
Hedgehog 17
What do these data suggest about the phylogenetic relationship of the four mammals in
Table 2?
gibbon closest to human;
hedge hog distantly / eq. related (to human);
spider monkey more distant than gibbon (to human)
(2 marks)
(d) (i) Describe how fossils can be used to provide evidence for human evolution.
sequence of changes can be seen;
ref. to dating of fossils;
skeleton / eq. shows trend from quadripedal to bipedal locomotion / eq.;
changes in hands show evolution of dexterity;
changes in jaws / teeth show changes in diet;
changes in skull / eq. show evolution of brain;
(3 marks)
(ii) Give one disadvantage of the use of fossils in providing evidence for human
evolution.
incomplete record / eq. incomplete / eq. fossils / unreliable dating / fossil
displacement;
(1 mark)
[Total 13 marks]
107. Write an essay on the following topic.
The structure and functions of lipids (Bio, HBio)
structure:
triglycerides
fatty acids
glycerol
phospholipids
types - fats, as- esters
- – oils,
saturated,
waxes,-unsaturated -
steroids, phospholipids
David Kaunda High School 101
-
functions:
source -
fats in diet -
consequences on health -
water insolubility -
waterproofing as waxes in leaves, insect cuticle, oils in hair and feather -
energy storage -
component of adipose tissue, oils in seeds -
relative calorific value -
source of metabolic water on oxidation -
contribution to buoyancy in aquatic mammals -
contribution to thermal insulation -
component of cell membranes -
phospholipid bilayer, hydrophilic, hydrophobic, orientation, micelles -
contribution to structure and vesicle formation, fusion -
contribution to electrical insulation -
cholesterol and membrane stability -
metabolic control -
steroid hormones S = 13, B = 2, C =2
[Total 15 marks]
108. Write an essay on the following.
Lipids in organism
Lipids in living organism
lipids as water insoluble substances -
triglycerides as esters -
fatty acids / saturated and unsaturated -
glycerol -
fats / oils / waxes / phospholipids / steroids -
triglycerides as energy store -
relative calorific value -
fats in the diet -
fat storage in mammals -
fat as an insulator -
for buoyancy in aquatic mammals -
storage of oils in plants / eg in seeds -
formation of metabolic water by oxidation of fats -
waxes as waterproofing in leaves / insect exoskeleton -
phosholipids as constituents of cell membranes -
neurones and myelination -
steroids / testosterone / oestrogen and progesterone S = 17, B = 3, C = 3
[Total 20 marks]
David Kaunda High School 102
109. Write an essay on the following.
Lipids in humans
Lipids in living organism
lipids as water insoluble substances -
triglycerides as esters -
fatty acids / saturated and unsaturated -
glycerol -
fats / oils / waxes / phospholipids / steroids -
triglycerides as energy store -
relative calorific value -
fats in the diet -
fat storage in mammals -
fat as an insulator -
for buoyancy in aquatic mammals -
storage of oils in plants / eg in seeds -
formation of metabolic water by oxidation of fats -
waxes as waterproofing in leaves / insect exoskeleton -
phosholipids as constituents of cell membranes -
neurones and myelination -
steroids / testosterone / oestrogen and progesterone S = 17, B = 3, C = 3
[Total 20 marks]
110. The table below refers to features of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells.
If the feature is present place a tick () in the appropriate box and if the feature is absent, place a
cross (x) in the appropriate box.
Feature Prokaryotic cell Eukaryotic
Endoplasmic reticulum x
Mesosome x
Ribosomes
Golgi apparatus x
[Total 4 marks]
David Kaunda High School 103
111. The diagram below shows a plant cell which is undergoing mitosis.
(a) name the parts labelled A, B, C, and D.
A cell wall;
B spindle (fibre) / microtubule:
C centromere;
D chromatid / (daughter) chromosome;
(4 marks)
(b) name the stage of meiosis shown in this diagram.
Anaphase;
(1 mark)
[Total 5 marks]
112. Glucose oxidase is an enzyme which catalyses the oxidation of glucose from gluconic acid and
hydrogen peroxide.
An experiment was carried out to investigate the effect of pH on the activity of glucose oxidase.
The activity of this enzyme was determined at a range of pH values. The results are shown in the
graph below.
5
A c tiv ity o f e n z y m e /a r b itr a r y u n its
0
4 5 6 7 8 9
pH
(a) (i) State how the different pH values could be obtained in this experiment.
reference to use of buffer solutions;
(1 mark)
David Kaunda High School 104
(ii) Describe the effect of changes in pH on the activity of this enzyme.
optimum / eq is pH6;
activity decreases on either side of optimum; little activity av pH4 /
pH 8 / extremes;
(2 marks)
(iii) Explain why changes in pH affect the activity of enzymes.
reference to charges / ionisation of R groups / eq / hydrogen bounding /
ionic bonding;
affects shape of active side;
affects binding with substrate; denaturation at extreme values;
(3 marks)
(b) Glucose oxidase with another enzyme, peroxidase, can be used to measure the
concentration of glucose in solutions.
The solution to be tested is first incubated with glucose oxidase, and then with peroxidase,
plus an indicator which changes colour when it is oxidised. Peroxidase breaks down the
hydrogen peroxide formed by glucose oxidase, and simultaneously changes the colour of
the indicator.
The intensity of the colour produced is directly proportional to the concentration of
glucose in the solution, as shown in the graph below.
I n te n s ity o f c o lo u r p r o d u c e d /a rb itr a r y u n its
0
0 0 .1 0 .2 0 .3 0 .4 0 .5 0 .6
G lu c o s e c o n c e n tr a tio n ( % )
(i) From the graph, determine the concentration of glucose corresponding to a colour
intensity of 6.5 arbitrary units.
0.56 %; (accept values 0.55 to 0.56%)
(1 mark)
David Kaunda High School 105
(ii) Describe how this method could be used to compare the concentration of glucose in
two samples of fruit juice.
use same / equal volumes* of fruit juice; add same volume* / concentration of
glucose oxidase to each;
incubate for standard / stated time / stated constant temperature;
add same volume* / concentration peroxidase + indicator; read intensity of
colour;
use graph to find glucose concentrations;
[* accept stated volumes, but not amounts]
(4 marks)
[Total 11 marks]
113. Give an account of the biological significance of polysaccharides.
1. polysaccharides consist of many monosaccharides;
2. joined by glycosidic bonds;
3. (a) credit details of formation glycosidic bond showing condensation;
3. (b) reference to insolubility of polysaccharides;
4. starch storage in plants;
5. two forms of starch, amylose and amylopectin;
6. glycogen storage in animals;
7. glucose in starch / glycogen;
8. these can be broken down to provide glucose / monosacch for
energy / respiration;
9. ref. to no osmotic effect of polysaccharides;
10. ref. to compact shape of glycogen / starch for storage;
11. cellulose in plant cell walls;
12. cellulose contains for glucose;
13. cellulose forms long unbranched chains;
14. hydrogen bounding between chains;
15. ref to orientation of chains in layers / microfibrils of cell wall
conferring strength;
16. ref. to chitin in cell walls of fungi / exoskeleton of arthropods;
17. ref. to murein in bacterial cell walls;
18. polysaccharides attached to proteins / lipids in cell surface
membranes;
19. ref. to cell identification / recognition;
20. credit specific example such as determination of A an B blood groups;
[Total 10 marks]
David Kaunda High School 106
114. Read through the following passage about pollution of fresh water by raw sewage, then write on
the dotted lines the most appropriate word or words to complete the account.
Sewage contains mineral ions such as nitrates and phosphates / eq; and also suspended organic
solids. If raw sewage flows into a river, the suspended solids are broken down by bacteria /
appropriate named; resulting in a decrease in the concentration of dissolved oxygen in the
water. The volume of oxygen used by a sample of water is known as the biochemical / oxygen,
biological demand; which steadily increases; as the organic solids start to be broken down.
Mineral ions stimulate the growth of algae which can reduce the growth of submerged plants, by
reducing the amount of (sun) light; reaching them.
[Total 5 marks]
115. Give an account of the flow of energy through of food web.
1. source of energy sunlight;
2. absorbed by photosynthetic pigments / named pigments;
3. converted to chemical / bond energy / used in formation ATP;
4. (energy) in the form of organic compounds / carbohydrates / named eg;
5. by photosynthesis in producers / green plants;
6. ref. to GPP + explanation / elaborations;
7. utilisation by producers / used in respiration by plants / eq;
8. any ref. to hear / energy losses from metabolism. respiration;
9. ref. to NPP + explanation / elaboration;
10. energy passed on / eq. by feeding relationships / eq; food chains /
trophic levels
11. less energy at top of food chain / eq;
12. efficiency about 10%;
13. ref. to losses due to muscle contraction / locomotion / eq;
14. (energy) in the form of inedible / indigestible material / eq / not all eaten
by next trophic level;
15. ref. to energy in forces / egested material;
16. utilisation of dead organisms by decomposers / eq;
17. energy in the form of excretory material;
18. named excretory material / urea;
19. losses to fossilisation;
20. ref. to chemoautotrophs;
[Total 10 marks]
David Kaunda High School 107
116. The photograph below shows a native woman from a high altitude region (3200 m) in
western China.
(Photograph by Erica Larkcom)
Describe and explain three ways in which native people, such as this woman, are adapted or
acclimatised to living at high altitudes.
1. increased lung volume / eq. / total blood volume;
(linked to) increased pulmonary diffusing capacity / eq;
increased chest size / eq;
(linked to) increased lung volume / eq;
2. higher red blood cell count / volume / number rbc;
(linked to) increased carriage / eq of oxygen;
higher haemoglobin concentration;
(linked to) increased oxygen carrying capacity;
higher affinity / eq. of haemoglobin for oxygen / eq;
(linked to) saturation of blood at low pO2;
3. increased cardiac output / heart rate / stroke volume;
(linked to) increased blood flow;¤
increased pigmentation / eq;
(linked to) protection against UV;
(Any THREE pairs for 2 marks each.)
[Total 6 marks]
David Kaunda High School 108
117. An investigation was carried out into the effect of exposure to low environmental temperatures
on core body temperatures. Two groups of males were studied: Europeans from a temperate
climate and aborigines from a climate with hot days and cold nights. Both groups were exposed
to an air temperature of 5 oC during a night of eight hours. The results are shown in the grap
below.
38
C o r e te m p e ra tu r e / ºC
36
34
0 2 4 6 8
– – – – A b o rig e n e s E u ro p ea n s
T im e / h o u rs
(a) Explain the meaning of the term core body temperature.
temperature at centre of body / deep in body / eq;
kept within narrow limits;
example of temperature range (accept within range 36 o – 38oC)
(2 marks)
(b) Suggest one reason for using male individuals only in this investigation.
reduce number of variables / eq / female % far higher and could affect heat
loss / eq / menstrual cycle ref / ovulation;
(1 mark)
(c) (i) Describe the differences between the shapes of the two curves.
European drops more quickly in first hour / only drops in 1 st hour;
European remains more constant / changes less (after 1.5 hours);
Aborigine has steadier fall for 8 hours / eq;
European falls by approx 1oC, Aborigine falls by more than 2oC / falls x 2;
(3 marks)
(ii) Suggest how these differences may be related to the climate in which the aborigines
normally live.
aborigines tolerate lower core temperature during cold nights / eq;
body heats up in morning as air temperatures rise;
aborigines have less need of cooling mechanisms in morning as core
temperature increases / eq.
(2 marks)
David Kaunda High School 109
(d) Between 4 and 5 hours exposure the mean core body temperatures remain constant.
Explain how this is brought about.
increased metabolic rate / thermogenesis;
exercise / shivering;
hair erection / vaso constriction;
(2 marks)
(e) Describe the effect on the body if the core temperature drops below 28 oC.
hypothermia;
reduced cardiac / heart rate / output;
reduced blood flow to coronary / cerebral circulations;
increased urine output / cold diuresis;
difficulty walking / co-ordinating movement / fatigue;
loss of consciousness / mental confusion / disturbed vision;
(3 marks)
[Total 13 marks]
118. The table below refers to features of three types of cells present in mammalian blood. If the
feature is correct place a tick () in the appropriate box, and if the feature is not correct place a
cross (x) in the appropriate box.
Feature Erythrocyte Lymphocyte Neutrophil
Has a labed nucleus ;
Contains haemoglobin ;
Produces antibodies ;
Shows amoeboid movement ;
Can destroy bacteria by
phagocytosis
[Total 5 marks]
David Kaunda High School 110
119. Explain the significance of each of the following in the life cycle of flowering plants.
(a) Protandry and protogyny.
in protandry anthers / pollen / stamens ripen / mature / eq;
before stigma matures, and in protogyny stigma
matures before anthers / eq;
increases likelihood of cross pollination / fertilisation;
reduces likelihood of self pollination / fertilisation;
encourages outbreeding / reduces inbreeding;
increased likelihood of heterozygosity / heterosis;
ref. to hybrid vigour / variability;
(3 marks)
(b) Mitosis and meiosis
mitosis involved in (vegetative) growth / repair;
asexual reproduction / formation of genetically identical cells;
meiosis involved in gamete formation / sexual reproduction / genetic variation
/ eq;
produces microspores / megaspores / haploid cells / eq;
(3 marks)
[Total 6 marks]
120. The diagram below shows a longitudinal section through part of the small intestine.
(a) Name the following.
(i) The type of epithelium in the layer labelled P.
columnar;
David Kaunda High School 111
(1 mark)
(ii) The region labelled Q
crypt of Lieberkuhn;
(1 mark)
(b) Explain the function of the longitudinal and circular muscle layers.
peristalsis / description;
movement of chyme along intestine;
OR
segmentary movements / pendular movements;
churn / mix chyme / bring chyme into contact with
lung of small intestine / eq;
(2 marks)
[Total 4 marks]
121. Explain each of the following.
(a) The significance of mitosis and meiosis in gametogenesis
mitosis involved in multiplication proliferation;
produces many primary spermatocytes / spermatogonia / oocytes / oogonia;
meiosis involved in production of secondary spermatocytes . spermatids / 2ry
oocytes / ovum;
halves chromosome number in gametes / produces haploid cells / retains
diploid on fertilisation;
ref genetic variation;
(3 marks)
(b) The roles of prolactin and oxytocin in lactation.
prolactin stimulates milk production by mammary glands;
prolactin stimulates release / secretion / eq of milk into ducts of mammary
glands;
oxytocin stimulates milk release / ejection / eq;
prolactin / oxytocin release stimulated by sucking / eq;
oxytocin release inhibited by stress / eq;
(3 marks)
[Total 6 marks]
David Kaunda High School 112
122. The tissues and organs of a pregnant woman use more oxygen than those of a non-pregnant
woman. The graph below shows the increase in oxygen used by some tissues and organs in the
woman’s body at the end of pregnancy compared with before she became pregnant.
7
–1
m in
6
3
In c re a s e in o x y g e n u s e d /c m
3
U te r in e m u s c le
2
P la c e n ta
K id n e y s
H e a rt
1
0
T i s s u e s a n d o r g a n s i n t h e w o m a n 's b o d y
(a) Calculate the total increase in the volume of oxygen used in one minute by all the tissues
and organs shown on the graph. Show your working.
3.6 + 3.8 + 7.0 + 7.2;
21.6 cm3 (min–1);
(2 marks)
(b) Explain how oxygen passes from the mother to the fetus.
through / via / passes across placenta;
by diffusion;
from maternal blood / haemoglobin to fetal blood / haemoglobin;
fetal haemoglobin has dissociation curve to left of maternal haemoglobin;
fetal haemoglobin has highest affinity for oxygen than maternal haemoglobin;
(4 marks)
David Kaunda High School 113
(c) Suggest why the use of oxygen by the woman’s heart and kidneys increases during
pregnancy.
Heart increased O2 consumption / Co2 production by other organs;
so greater volume / eq. of blood needs to be pumped;
therefore more energy / eq. needed for increased contraction of
cardiac muscle;
Kidneys eliminating fetal urea / N2 waste;
therefore increased ultrafiltration / volume of filtrate;
more energy / ATP / respiration;
(if not given above)
needed for reabsorption (from filtrate);
(4 marks)
[Total 10 marks]
123. A comparison was made between the volume of juice which could be extracted from the same
mass of three varieties of apples, with and without pectinase. In this comparison, the same mass
of pectinase was added to apples from each variety. The results are shown in the graph below.
200
150
3
V o lu m e o f ju ic e / c m
100
50
0
V a rie ty V a rie ty V a rie ty
A B C
K ey
W ith o u t p e c tin a s e W ith p e c tin a s e
(a) (i) Calculate the percentage difference in volume of the juice extracted without
pectinase from variety A compared to the volume extracted from variety C. Show
your working.
90 - 60 / 30; (allow 90/91 - 60/61)
30 30
90 × 100 60 × 100;
33.3% Less from C; 50% more from A
Answer …………………………
(3 marks)
David Kaunda High School 114
David Kaunda High School 115
(ii) Explain the effect of the use of the pectinase on the volume of juice extracted from
the apples.
pectinase increases the volume of juice/makes it easier to extract the
juice/eq.;
enzyme catalyses the break down of pectin in cell walls;
(2 marks)
(b) The effect of increasing the mass of the pectinase used on the volume of juice extracted
was then investigated.
The results are shown in the graph below.
100
80
3
V o lu m e o f ju ic e /c m
60
40
20
0
0 1 2 3 4 5 6
M a s s o f p e c tin a s e /a rb itr a ry u n its
Using the information available from both graphs, suggest how a manufacturer of apple
juice could make use of these results.
increase in concentration of the enzyme increases the volume of juice
extracted;
use variety B/eq.;
add up to 4/4.5 units of pectinase;
above 4.5/5.0 increase in concentration does not increase the volume much;
(3 marks)
(c) Suggest two factors, other than apple variety and use of pectinase, which could affect the
extraction of juice from apples.
1. temperature (at which process carried out);
pH; crushing / chopping/pressure used;
2. ripeness of apples;
age of apples / ref. to storage time;
(2 marks)
[Total 10 marks]
David Kaunda High School 116
124. Write an essay on the following topic.
The roles of RNA in protein synthesis (Bio, Hbio)
Introduction could include
- reference to basic structure of RNA
- types of RNA
- protein coded for in DNA but made in cytoplasm
- mRNA enables DNA integrity to be maintained
- reference to transcription and translation
Transcription
- occurs in nucleus
- unzipping of section of DNA/cistron
- synthesis of mRNA, role of RNA polymerase
- reference to role of nuclear pores
Translation
- occurs in cytoplasm, free and on RER
- ribosome structure, sub-units, rRNA, proteins, A and P sites
- ribosome activity, peptide bonds, polysomes
- mRNA codons, sites for binding, control, initiation, termination
- tRNA structure, anticodon, internal bonding
- tRNA activity, AA complex, anticodon-codon
- protein structure, peptide and other bonds
- potein use, in cytoplasm, role of secretory vesicles
S=13 marks
B= 2 marks
C= 2 marks
[Total 15 marks]
125. Write an essay on the following topic.
Atmospheric pollution (Bio, Hbio)
Introduction could include
- balance of gases is important
- pollutants cause imbalance, give rise to ozone
depletion/greenhouse effect/acid rain
- source of pollutants, combustion, propellants, utilisation
of organisms
Ozone depletion
- reaction between chlorine and nitrogen oxides
- mainly due to chlorofluorocarbon/CFC
- used in refrigerants an cleaning products
- ozone layer filters out UV(B) light
- contributes to development of mutations, skin tumours
David Kaunda High School 117
Greenhouse effect
- short wave radiation converted to long wave
- greenhouse gases act as heat absorbers
- greenhouse gases, carbon dioxide, ozone,
methane, water vapour
- carbon dioxide – roles of combustion, respiration
and photosynthesis
- methane – anaerobic breakdown, methanogenic
bacteria, organic waste
- results in higher global temperature
- expansion of water, melting ice caps
- changing in weather patterns
Acid rain
- acidic gases – carbon dioxide, oxides of nitrogen and sulphur
- sources of these gases
- details of chemical reaction with water
- precipitation in rain
- effects on soil, water pH, release of metal ions, oxidation of
chlorophyll
- allow reference to particulate pollutants, carbon monoxide
S =13 marks
B= 2 marks
C= 2 marks
Total 15 marks]
126. The diagram below shows a vertical section through a flower of the family Papilionaceae.
(a) State one function for each of the parts labelled A and B.
A. encloses/protects flower bud;
B. gives rise to seed/contains/produces female gamete/eq.;
(2 marks)
David Kaunda High School 118
(b) This flower is insect-pollinated. Describe three features, visible on the diagram, which are
characteristic of insect-pollinated flowers.
1. large petals / description of petals;
2. knob like / eq. stigma;
3. enclosed stigma / stigma inside flower;
4. enclosed stamens / stamens inside flower;
(3 marks)
(c) (i) State one similarity between a human sperm and a male gamete from a
flowering plant.
both haploid;
(1 mark)
(ii) State one difference between a human sperm and a male gamete from a
flowering plant.
plant male gamete within pollen grain / human sperm mobile / human sperm
has flagellum / ref. to structural difference;
(1 mark)
[Total 7 marks]
127. In coastal regions, are the tide goes out, pools of seawater containing plants animals are left
amongst the rocks. These are known as rock pools and can be considered as containing isolated
communities of organisms until the next high tide.
An investigation was carried out into the numbers and masses of organisms at each trophic level
present in a rock pool. All the visible organisms were identified, counted and their fresh mass
determined. Each organism was assigned to trophic level, as listed below.
Producers – red and brown seaweeds
Primary consumers – herbivores and detritus feeders, including limpets and sand hoppers
Secondary consumers – carnivores including starfish, crabs, whelks and scaleworms
The results are shown in the table below.
Trophic level Numbers of organisms Biomass of organisms / g
Producers 148 1450
Primary consumers 174 206
Secondary consumers 28 108
(a) Using the graph paper opposite, construct a pyramid of numbers and a pyramid of fresh
biomass for the rock pool community. You are advised to use a separate scale for each
pyramid.
(6 mark marks)
(b) (i) State one way in which the two pyramids are similar.
secondary consumers less numerous/less
biomass/blocks smaller/eq.;
(1 mark)
David Kaunda High School 119
(ii) Suggest which of the two pyramids gives the more useful information about the
relationship between the organisms in the rock pool, giving a reason for your answer.
pyramid of biomass more useful;
plant numbers quite small but larger biomass/numbers of herbivores and
detritus feeders large but smaller biomass/some ref. to variability in size of
organisms;
(2 marks)
David Kaunda High School 120
P y r a m id o f n u m b e r s
S e c o n d a ry c o n s u m e rs
P rim a ry
c o n s u m e rs
P ro d u c e rs
S c a le
S = s u ita b le s c a le ; re p r e s e n ts
n u m e r ic a l in d ic a t io n ; 1 0 o r g a n is m s
A = a c c u ra c y o f e a c h ;
B = b lo c k s c e n tr e d ;
L = tr o p h ic le v e ls la b e lle d ;
P y r a m id o f b io m a s s
S c a le
re p r e s e n ts
5 0 g ra m s
S e c o n d a ry c o n s u m e rs
P rim a r y c o n s u m e r s
P ro d u c e rs
David Kaunda High School 121
(c) (i) Suggest and explain two ways in which the results of this investigation might
be unreliable.
1. animals can move in / move out / nos. change when tide comes in;
so information only true at time of sampling/eq.;
2. not all the plants and animals may be visible;
so figures could be inaccurate/not all counted;
detritus from other sources could enter rock pool;
So detritus feeders could have other sources of food;
(4 marks)
(ii) Suggest two abiotic factors which could change in the rock pool from the time it
became isolated, when the tide went out, to the time when it was submerged again.
1. salinity; temperature; CO2 (concentration);
2. pH; water level/volume of rock pool; light intensity; oxygen/dissolved 02;
fresh biomass contains variable amounts of
dry mass more reliable/eq.;
organisms assigned to wrong trophic level;
difficult to establish how they feed/eq.;
(2 marks)
[Total 15 marks]
128. Write an essay on the following.
The movement of molecules and ions through membranes
General introduction
Expect some discussion of most of the areas below with suitable
examples
reasons for movement, uptake into cells, release of substances from
cells, involved with metabolism, synthesis, elimination of waste
products
membrane structure, details of fluid mosaic model, concept of
permeability, hydrophobic nature of fatty acid chains
definition of diffusion, explanation, conditions under which diffusion is
effective, reference to distance, concentration gradients, suitable
examples of diffusion
facilitated diffusion, reference to carrier proteins, suitable example
osmosis as a special case of diffusion, description of conditions,
reference to water potential in plant cells
active transport, definition, conditions, expect reference to the need for
energy, some description of mechanism, reference to situations where
active transport is important
endocytosis and exocytosis
S = 17 marks
B = 3 marks
C = 3 marks
[Total 20 marks]
David Kaunda High School 122
129. mitochondrion 1
ribosomes 1
chloroplast 1
centrioles / centrosome / basal body 1
nucleus 1
[5]
130. specificity / specific 1
active site / active centre 1
high/eq temperature / extreme/ eq pH / heavy metals /
bonds being broken / non–competitive inhibitors / irreversible inhibitors 1
an inhibitor / reaction products 1
oxidoreductases 1
[5]
131. (a) (i) A = glycerol 1
B = fatty acid (residue) 1
(ii) hydrolysis 1
(b) polar (molecules) / hydrophilic heads/eq & hydrophobic tails/eq 1
form a bilayer / bimolecular double layer
[accept from clear diagram] 1
(polar/hydrophilic) heads outside / (non–polar/hydrophobic) tails inside 1
[6]
132. (a) (i) protein / polypeptide / enzyme / named protein / a peptide hormone 1
(ii) (R.E.R. has) ribosomes/eq 1
(ribosomes / R.E.R. are) site of protein synthesis 1
(iii) (after 10 mins) proteins / polypeptides move to Golgi apparatus max 3
where protein is modified/eq /OR credit for suitable example
of modification such as glycoprotein formation
and enclosed in membranes to form vesicles / eq /OR ref. to packaging
so most activity in vesicles after 45 minutes
(iv) amino acids moving (diffusing) between sites / max 2
not being used / remain in the cytoplasm
proteins used in other parts of cells / not all proteins go to the Golgi /
e.g. of other use / moving between sites
proteins also synthesised in mitochondria / mitochondria have
ribosomes / ref. to free ribosomes/not attached to R.E.R.
ref. to amino acids being broken down / metabolised/ eq
David Kaunda High School 123
(b) exocytosis max 3
vesicles move to cell membrane
(membrane of) vesicle fuses/eq with cell membrane
so contents of vesicle now outside cell / release of contents
[accept from clearly labelled diagrams]
[11]
133. 1. DNA is a polynucleotide / polymer – monomers
called nucleotides / any ref to DNA made of nucleotides 1
2. nucleotide consists of deoxyribose, phosphate and a base 1
[labelled diagram]
3. bases are adenine, guanine, cytosine and thymine
requires correct spellings; penalise “thiamine” spelling once 1
4. A and G are purines 1
5. C and T are pyrimidines 1
6. DNA is a double/eq helix 1
7. phosphate – sugar linked to form strands / sugar–phosphate backbone /
ref. to phospho–diester bonds / [labelled diagram] 1
8. strands are antiparallel / run in opposite directions [labelled diagram] 1
9. pairing of A with T and of G with C [labelled diagram] 1
10. hydrogen bonding between base pairs [labelled diagram] 1
11. replication semi–conservative /
1 old & 1 new strand in each daughter molecule 1
12. replication occurs during interphase / S phase 1
13. strands separate by breaking H bonds [labelled diagram] 1
14. correct involvement of / new strand synthesised by DNA polymerase 1
15. complementary base–pairing in daughter strands / use
of correct base pairing to give accurate copy /eq 1
16. reference to unwinding / separation of the strands by helicase 1
17. 5’ to 3’ direction of synthesis by DNA polymerase 1
18. lagging /eq strand sections joined by ligase 1
Clearly annotated diagrams could include points other than those indicated above max 10
[10]
134. (a) (117 to 119) ÷ 0.8 /OR 11.7 to 11.9 ÷ 0.08 1
Answer: 146 to 149 /OR ×146 to ×149
[allow consequential errors, but no mark if units given] 1
(2)
David Kaunda High School 124
(b) Any TWO pairs: feature & related explanation
[second mark dependent on the first]
thick (waxy) cuticle 1
reduces evaporation / diffusion / impermeable / waterproof /
prevents water passing through /eq 1
(epidermal) hairs 1
traps humid*/moist air* / ref. to diffusion gradient /
reduces air flow near surface /eq 1
leaf rolled / curled / hinged (qualified) / coiled [not curved] 1
reduces exposed surface area / traps humid / moist air* /
water vapour* / ref. diffusion gradient /
reduces air flow near surface / encloses stomata / eq 1
[*not refs. to moisture / water loss]
leaves small / as spines / deciduous / leaves lost 1
reduces surface area for evaporation / diffusion 1
few stomata 1
less area for diffusion 1
stomata in pits / sunken /eq 1
traps humid air /eq 1
stomata closed in day / in daylight [allow converse] 1
less evaporation / diffusion /eq 1
cells have mucilage /OR more sucrose/solute / salts 1
cells have lower / less evaporation /eq 1
(max 4)
[6]
135. amylase[not salivary] 1
maltose[not disaccharide] 1
villi / ileum / duodenum / crypts of Lieberkuhn
[ignore refs. to small intestine] 1
glucose /OR fructose 1
fructose /OR glucose 1
[5]
136. (a) known / stated volume of water sampled
/OR description: e.g. sweep net a fixed distance / eq 1
organisms sorted / separated into
trophic levels / consumer groups /eq 1
organisms in each group/eq weighed
/OR description: count mass average 1
several samples to obtain a mean /eq 1
(max 3)
[ignore refs. to drying]
David Kaunda High School 125
418.0 26.8
100
(b) (i) 418
391.2
100
or 418
26.8
100 100
418 1
Answer 93.58 to 93.6 (%) [not 94, no consequential error] 1
(2)
(ii) respiration / loss as carbon dioxide 1
not all organism eaten / death / losses to decomposers 1
not all that is eaten is digestible / egestion / faeces / eq 1
excretion /eq [Allow urine / urea] 1
[ignore refs. to heat / energy / locomotion / movement]
(max 2)
[7]
137. (a) (i) no change/constant / 4 cm3 hr–1 up to 7.00 / first 6 hrs 1
×14 / rapid / steep/eq increase /OR 12.9 – 13.0 cm3 hr–1
to 11.30 / 11.45 / 12.00 / midday 1
stable / little change / plateau /eq to 13.00 / 13.45 / 14.00 1
stepped falls /eq to 21.00 – 22.00 1
reaches starting level / back to 4 cm3 hr–1 1
(max 3)
(ii) as sun rises / temperature rises /eq stomata open / water loss increases 1
water uptake increases because transpiration increases 1
water potential of root cells/eq decreases 1
rate goes down due to wilting of leaves / closing of stomata 1
credit refs. to uptake by osmosis 1
(max 2)
[Allow converses, ignore refs. to photosynthesis, raining]
(b) (i) increase starts /eq at the same time / approx. 7.00 /
increase & then decrease / both high / peak in day / light / both low at night / both
constant up to approx 7.00 / first 6–7 hrs 1
(ii) phosphate uptake increases as water uptake decreasing/ eq 1
increase in phosphate uptake takes longer / less steady
(than water uptake) / interrupted 1
phosphate uptake remain higher towards the end of the day/
does not return to starting rate 1
maximum/ peak at different times /eq 1
(max 2)
David Kaunda High School 126
(c) DNA 1
RNA 1
nucleic acid / nucleotide [for (1), IF neither DNA/RNA given] 1
phospholipids / cell membrane / lipid bilayer 1
RubP 1
contribution to water potential /eq 1
root development 1
some protein [not “protein” only] 1
(max 2)
[ignore refs. to phosph. glucose / ADP / AMP]
[10]
138. 1. nitrogen gas cannot be used by plants / is inert /eq 1
2. nitrate / NH4 taken up by plants / producers, used in protein / AA /
nucleic acid synthesis 1
3. ref. to consumers obtaining nitrogen in proteins / AAs / eq from
plants / producers 1
4. putrefaction / decay / decomposition / breakdown of organic matter
/eq by saprobiontic / saprophytic / saprotrophic organisms / bacteria / fungi
[not detritivores] 1
5. ref. to nitrification / nitrifying [in right context, qualified] 1
6. organic N / urea / protein converted / reduced to ammonium ions/ ammonia 1
7. ammonium / ammonia oxidised / converted to nitrite / N3 1
8. by Nitrosomonas / Nitrosococcus 1
[7 & 8 must be linked for]
9. nitrite / N3 oxidised / converted to nitrate / N5 1
10. by Nitrobacter / Nitrococcus 1
[9 & 10 must be linked for]
11. denitrification / denitrifying [in right context, qualified] 1
12. nitrates to nitrogen (gas) 1
13. by Pseudomonas / Thiobacillus 1
14. under poorly aerated / anaerobic conditions / eq 1
15. for example, waterlogged soil / conditions / bog / marsh / compacted soil 1
16. nitrogen fixation [in right context, qualified] 1
17. Rhizobium /OR named blue–green / cyanobacteria
in root nodules / mutualistic / symbiotic
converts N2 to ammonia / nitrogen–containing organic compounds 1
David Kaunda High School 127
18. Azotobacter / Bacillus / Clostridium / Klebsiella
/OR named blue–green / cyanobacteria
free–living / in soil / converts N2 to ammonia / nitrogen–containing
organic compounds 1
19. lightning reference 1
(max 10)
[points can be credited from clear diagrams]
[10]
139. (a) (i) convection / wind chill 1
(ii) shivering / increased metabolic rate 1
(b) reduced blood flow / circulation (to exposed parts) / vasoconstriction 1
tissues freeze / ice crystals form / frostbite 1
cells burst / cell death 1
gangrene / loss of toes / fingers/eq extremities 1
[ignore refs. to behaviour, clothes]
(max 3)
(c) hypothermia
[not hyperthermia] 1
[6]
140. (a) (i) constant / directly proportional linear increase with time / day / ref.
to % increase or gradient / 0.04 day–1 / 35% 1
no. of blood cells continues to increase after max altitude reached / eq 1
(2)
(ii) increase to 60 days, but at lower rate / peak production 60 days/ eq
/ (then) decreases and levels off 1
body acclimatised to altitude 1
(2)
(iii) number of blood cells decreases as soon as / immediately altitude
decreases / ref. day 80 1
constant / linear rate of decrease / inversely proportional 1
decrease more rapid than the increase / steeper gradient 1
number of red blood cells higher at the end than start/ eq 1
(max 2)
(b) lower pO2 at high altitude /eq 1
more red blood cells to increase the carrying capacity of blood /
carry more O2 / more Hb to carry O2 1
ref. O2 for respiration 1
(max 2)
David Kaunda High School 128
(c) headache / lack of concentration / mental alertness/ eq / dizziness 1
rapid heart beat / palpitations 1
nausea / vomiting 1
muscle weakness / exhaustion
[ignore tiredness refs] 1
fluid retention / swollen limbs / reduced urinary output /
increased ADH production 1
hyperventilation / increased frequency of breaths/ eq 1
(max 3)
[11]
141. (a) an S–shaped / sigmoid curve 1
steepest part of the curve in region of partial pressure of oxygen found
in (respiring) tissues /eq 1
haemoglobin releases O2 at low / lower pO2 1
a small change in pO2 causes a large change in % saturation / large %
released / large % uptake of O2 1
at high pO2 / in lungs there is nearly 100% saturation 1
(max 3)
(accept O2 concentration or O2 tension for partial pressure)
(b) (i) 57 – 45 1
= 12 (%) (allow consequential error) 1
(2)
(ii) More CO2 released/eq (as tissue) becomes more active /eq 1
(dissociation) curve
(of haemoglobin) moves to right 1
More oxygen released / more oxyhaemoglobin
dissociation / decreased affinity for O2 1
(accept converses of the above points)
Enables more rapid respiration / metabolism /
activity at same partial pressure of oxygen 1
(max 3)
(c) Oxygen store / reserve /deposit (not “supply”) 1
Only releases O2 / dissociates at very low O2 tensions /
partial pressure of oxygen below one kPa 1
Enables aerobic respiration to continue /
muscle to continue activity / continue to contract
at (very) low (blood) oxygen levels /eq 1
(3)
[ignore “myoglobin has a higher affinity for O2 than
haemoglobin”,
references to diffusion gradients]
[11]
David Kaunda High School 129
142. (a) break open cells / break cell walls / release cell contents / eq 1
increase surface area for pectinase / enzyme to work 1
increase/eq volume / quantity / rate of flow of juice 1
(max 2)
(b) (pectinase) breaks down / hydrolyses
pectin / middle lamella (not “softens”) 1
therefore: juice extracted more quickly / easily / OR more juice extracted 1
(2)
(c) reference to presence of pectins (still remaining in juice) 1
(pectinase) clarifies juice / removes cloudiness / reduces viscosity/ eq
(not “smoother”, “softer”) 1
(2)
[6]
143. (a) (i) (Type) meiosis / meiotic / reduction OR meiosis ll 1
(Stage) anaphase ll OR anaphase 1
(2)
(apply list rule)
(ii) position of centromere correctly indicated and labelled 1
(b) (a generative nucleus) 7 1
(an endosperm cell) 21 1
(a leaf epidermal cell) 14 1
(a phloem companion cell) 14 1
(4)
[7]
144. Water Pollution
Introduction to include references to water as a habitat, physical and chemical factors human
activities which lead to pollution of water sewage, (outline of treatment and) inadequate
treatment leading to pollution components of sewage and their environmental effects
suspended solids, effect of light penetration -
nitrogenous compounds, references to eutrophication, algal blooms BOD phosphates
possible pesticide residues and reference to oestrogenic compounds
microorganisms
detergents
effect on species diversity -
agricultural run–off nitrates and phosphates, environmental effects of leaching
pesticide residues -
oil pollution spillage and effects of oil on aquatic organisms
treatment of oil spillage -
thermalonpollution
rain
effects effects of
fish and leaching aquatic ecosystems, including referencescauses
on ions and effects
to changes in pH, acid
David Kaunda High School 130
expect discussion of most areas above, illustrated with suitable examples
Scientific content 17
Balance 3
Coherence 3
[Total 20 marks]
145. Transport systems in mammals and flowering plants
Introduction to include references to the need for transport systems and substances transported
(emphasis is on systems)
transport in mammals, double circulatory system, pulmonary and systemic circulation outline
structure and function of the heart, cardiac muscle and
co–ordination of heart beat blood vessels
structure and function of arteries, capillaries and veins
exchange between capillaries, tissue fluid and cells -
haemoglobin and oxygen transport, including the oxygen dissociation curve
*
transport of carbon dioxide *
transport of metabolites and metabolic wastes *
transport of hormones *
lymph *
*[points worthy of credit, but not essential to a good account]
transport in flowering plants, osmosis, xylem and phloem uptake and transport of
water and mineral ions roles of stomata
transport of organic solutes, the mass flow hypothesis
[evidence of translation of organic solutes ]
Conclusion could include an overview of the differences between transport in mammals and
transport in flowering plants.
Expect discussion of most of the areas above, illustrated with suitable examples
Scientific content 17
Balance 3
Coherence 3
[Total 20 marks]
146. (a) A Provides (developing gametes with) mechanical / metabolic support
/ nutrients / removes excess cytoplasm / phagocytosis /
“protection” qualified 1
B divides by mitosis to give spermatogonia / gametes/ eq 1
(2)
(b) (i) TWO of: C, D, E 2
(ii) TWO of: A, B, F 2
David Kaunda High School 131
David Kaunda High School 132
(c) (one 1º oocyte) gives rise to 1 ovum/eq,
(one 1º spermatocyte) gives rise to 4 spermatozoa/ eq 1
unequal meiotic division / polar body formation in oogenesis,
not in spermatogenesis 1
(stimulus of) fertilisation needed to complete final division / second
meiotic division of oogenesis, not so in spermatogenesis 1
most oogonia degenerate / do not develop into ova/eq ,
not so for spermatogonia/eq 1
greater growth involved in formation of 1º oocyte 1
correct reference to timing difference e.g. oogenesis starts in
embryo / fetus, spermatogenesis from puberty onwards 1
(max 2)
[8]
147. Transport systems in humans
General points / introduction :
transport system needed in large animals such as humans diffusion / active transport too slow
reference substances carried
outline of heart structure
cardiac muscle
cardiac cycle
control of cardiac cycle -
structure and function of arteries, veins and capillaries exchange of substances between
capillaries and tissues double circulatory system types
of blood cells transport of oxygen by erythrocytes
haemoglobin dissociation curve -
mechanisms of carbon dioxide transport role of plasma
formation of lymph
lymphatic system, structure and function
Expect discussion of most of the areas above, illustrated with suitable examples
Scientific content 17
Balance 3
Coherence 3
[Total 20 marks]
148. (a) A phospholipid ;
B protein ;
C glycoprotein ; 3
(b) act as a marker / antigen / recognition site ;
other molecules combine with it / detecting similar / non-self cells ;
OR
reference to receptor / binding site ;
other (specific) molecules / named e.g. / combine with it ; 2
[5]
David Kaunda High School 133
149. solvent ;
enter / diffuse into /eq ;
insoluble /osmotically inert / non-polar /eq ;
lipids / triglycerides / fats / oils ;
glycogen ;
plant ;
[6]
150. (a) Stage l = transcription ;
Stage 2 = translation ; 2
(b) ribosome(s) / RER ; 1
(c) tRNA carries amino acid /eq ;specific amino acids link with specific tRNAs /eq ;
tRNA has anticodon / specific base triplet ;pairs with /eq codon /
complementary triplet of mRNA ;peptide bond formed
when bond to tRNA broken /eq ; max 3
[6]
151. (a) (i) activity at 65 ºC = 35 (units), activity at 75 ºC = 47 (units) ;
percentage increase = (12 ÷ 35) × 100 ;34.28 / 34.3 (%) ; 3
(ii) increasing temperature increases kinetic energy / movement of molecules;
increases chances of collision / formation of enzyme-substrate complexes;
therefore activity increases ;optimum at 75 ºC;
above optimum enzyme becoming denatured /eq;
so active site distorted / changed in shape /
no longer complements substrate /eq ; max 4
(iii) stable at high temperatures / less likely to be denatured;
temperature control less important;
can be used continually / ref.. to high productivity / faster;
reduced risk of contamination by (other) microorganisms max 2
(b) activity will stop / decrease /eq ;heavy metals are inhibitors /
disrupt internal bonding / tertiary structure / denature enzymes ; 2
[11]
152. (a) (i) synthesis / building up / production of organic molecules / starch /
sugar / sucrose /carbohydrate / any correct named organic molecule ;
made in photosynthesis / light (energy) converted to chemical- / bond-
energy ; 2
(ii) [(14.5 × 104) ÷ (251 × 104)] × 100
OR 14.5 ÷ 215 × 100
OR alternative method to correct answer ;
= 5.77 (%) to 5.8 (%) ; 2
(b) respiration / metabolism in plant / rice grass ;
plant death / ref. to decomposition / not all plants / plant parts eaten by insects ;
not all plant material digested / ref. to faeces / defecation / indigestibility ; max 2
[6]
David Kaunda High School 134
153. (a) keep out oxygen / maintain anaerobic conditions/eq ;
constant/eq temperature / keeps heat in /eq / for favourable temperature ;
prevent gas escaping /eq ; max 2
(b) (i) 0 – 10 days
bacteria produce CO2 / organic acids / named e.g. / ref. to bact. acetogenesis / eq;
CO2 / organic acids increase acidity / causes pH to fall ;
10 – 45 days
organic acids / named e.g. converted to methane / ref. to bact. methanogenesis/ eq ;
acids used up/eq, causing pH to rise ; max 3
(ii) initial increase due to CO2 ;
from aerobic respiration / bacteria / aerobes ;
production falls due to less O2 / anaerobic /
pH falls /eq more organic acids ;
(then) production rises due to methane production ;
suitable conditions for anaerobes / these bacteria / anaerobic respiration ;
as temperature rises / pH is low / pH changes ;
last few days, substrate /eq depleted / no more organic acids,
so production falls ; max 3
(c) little or no sulphur in biogas / no sulphur dioxide / trioxide produced ;
less / no contribution to acid rain ;
renewable (biomass) ;
uses waste products / substrates / named waste product readily available/ eq ;
(production) cheaper / time reference /
less damaging to land e.g. no mining ; max 3
Allow clear statements relating converse for fossil fuels
[11]
154. 1. Felled for timber / paper / use as fuel / eq ;
2. Cleared for urban/eq development / more houses / ref. to industrial use;
3. Cleared for described agricultural use ;
4. Natural disasters / lightning strikes / hurricanes / qual. (natural) forest
fire /eq / failure of regeneration because of climate change / eq ;
5. Erosion of soil because of absence of tree roots ;
6. Increased flooding / run-off / silting of rivers ;
7. Loss of humus/eq from soil // loss of soil texture /eq //
nutrients lost / not recycled / leached from soil ;
8. Causes desertification ;
9. Loss of / change in habitat / ecosystem ;
10. Possible extinction/eq of other organisms / decrease in biodiversity / species diversity ;
11. Carbon dioxide levels increase if (cleared by) burning / eq ;
David Kaunda High School 135
12. Less photosynthesis so less carbon dioxide removed /eq ;
13. Some detail of greenhouse effect ;
14. Reduced transpiration / affects local climate /eq ;
15. Reference to loss of future products e.g. undiscovered drugs /
loss of genetic resource ;
[10]
155. hypothalamus thermoregulatory centre ;
blood flow / supply /eq ;
evaporates ;
cramps ;
(upper/high) critical / lethal ;
[5]
156. (a) (i) A spermatogonium / spermatogonia ;
B permatid / spermatids ; 2
(ii) M indicated between secondary spermatocyte and cell B ; 1
(b) FSH / testosterone / LH / ICSH / GnRH ; 1
(c) TWO of :flagellum (for locomotion) ;acrosome
(hydrolytic enzymes to penetrate egg membrane) / lysosome;
large / many mitochondria (to provide ATP) ; max 2
[6]
157. guard ;
potassium / K+ ;
more negative / lower / less ;
(cell) walls ;
open /eq ;
[5]
158. (a) TWO of:
single layer of cells / endothelium / simple epithelium ;cells very
thin / flattened / squamous ;presence of pores ;selectively /
partially permeable / permeable to small molecules ; max 2
(b) drains into lymph(atic) capillaries / vessels / duct // lacteals;
to form lymph ;moves in lymphatic vessels by skeletal muscle / local body movement;
reference to valves / one way flaps in lymphatic vessels /
filtered through nodes ;lymph returned to venous system
(via thoracic ducts / into subclavian veins) ; max 3
(c) increased / high blood pressure /
decrease in plasma proteins / colloidal
concentration / protein deficient diet /
increased capillary permeability /
blocked lymph vessels ; 1
[6]
David Kaunda High School 136
159. (a) A Sino atrial node / SA node / SAN ;
B Atrioventricular node / AV node / AVN ; 2
(b) (0.16 – 0.04 = ) 0.12 seconds ; 1
(c) spreads across atria (first) so atria contract (first) / atrial systole (first);
passes to ventricles via the AV node / through B;
non-conductive tissue between atria and ventricles/ eq;
passes to apex / bottom of ventricles ;figures quoted /
ref. to delay at AV node / conduction to ventricles;
ventricles contract after atria / ventricular systole after atrial systole ; max 4
[7]
160. (a) (i) progesterone curve low from day 0 to day 14 ;
peak between day 14 and day 28 ; 2
(ii) corpus luteum / yellow body / wall / cells of follicle ; 1
(b) (i) (27 – 2) ÷ 30 ;
= 0.83 ng per cm3 per week ; 2
(ii) oestrogen rises through 30 week period / 10 – 40 weeks ;
progesterone rises to week 35 then falls ;
progesterone concentration always higher than oestrogen concentration ;
credit correct manipulation or comparison of figures ; max 3
(iii) maintains endometrium
prevents menstruation ;
inhibits release of FSH / ovulation ;
inhibits contraction of muscle in uterine wall / inhibits oxytocin action ;
concentration drops at birth / ref. to development of milk glands / inhibits
prolactin ; max 3
[11]
161. (a) (i) 42.7 ; 1
(ii) more juice extracted with cellulase only than with pectinase only / eq ;
same volume extracted with cellulase+pectinase mixture
as with cellulase only ; 2
(b) ref. to pectins in middle lamella and/or cellulose in cell walls ;
pectinase hydrolyses / breaks down/eq pectins ;
cellulase hydrolyses / breaks down/eq cellulose ;
cell contents / juices released from cell
(as cell walls broken down / softened /eq) ; 3
(c) variety ;
ripeness ;
size of pieces / surface area /eq ;
pressure applied ;
temperature ;
freshness / length of storage time ; max 2
David Kaunda High School 137
(d) no contamination of juice with enzyme /eq ;
enzyme can be used several times ;
ref. to continuous flow ;
less enzyme needed ;
ref. to increased stability to pH / temperature / less likely to denature ; 3
[11]
162. (a) (i) galactose ; 1
(ii) 0.24 ÷ 4.8 × 100 ;
5% ; 2
(b) some people do not produce lactase ;
(therefore) cannot digest lactose / are lactose intolerant ;
milk / milk products still available to them /
ref. to they would get diarrhoea/eq if normal milk ingested ; max 2
[5]
163. The roles of microorganisms in the cycling of materials in an ecosystem
Introduction could include
The need for recycling –
Ref. to main cycles of carbon and nitrogen –
Nitrogen cycle
Nitrogen fixation –
Details of Rhizobium and legumes –
Free-living Azotobacter –
Reduction of nitrogen to ammonia –
Nitrification by Nitrosomonas and Nitrobacter –
Ammonia to nitrite to nitrate –
Nitrate used for production of amino acids, proteins –
Denitrification by Pseudomonas in anaerobic conditions –
Ref. to waterlogging, compaction –
Nitrate to nitrogen gas –
Putrefaction conversion of amino acids, proteins to ammonia –
Carbon cycle
Decomposition by bacteria, fungi –
Hydrolytic enzymes, cellulase –
Carbohydrate conversion to carbon dioxide –
Aerobic respiration –
Recycling materials in dead organisms –
Ref. to effect on BOD in aquatic media –
Eutrophication explained –
Anaerobic respiration –
Biogas and methanogenic bacteria –
Fossilisation
Photosynthetic bacteria –
Scientific content: max 13
Balance: max 2
Coherence: max 2
[15]
David Kaunda High School 138
OUTLINE SCHEME FOR MARKING ESSAYS
Scientific content
Above average
13 Excellent
11 Good
Essays in this category demonstrate a sound understanding of the topic, contain a
significant amount of material relevant to two or more units of the specification, and
suitable examples where appropriate.
Average
9 Slightly above average
7 Average
5 Slightly below average
Essays in this category contain factually correct and relevant material. Some areas
should show a progression from GCSE, particularly if a mark of 9 is awarded.
Below average
3 Some correct facts
1 Very few correct facts
0 No correct information
Essays in this category contain few relevant facts. The material that has been included
has little depth and barely reaches the standard expected at GCSE.
S = 13 marks
Balance
2 A balanced essay covering all the main areas outlined
Some discussion of each area covered with, suitable examples where applicable
Material all relevant to the topic
Few, if any, errors
1 Most of the main areas of the topic covered, but possibly one or two lacking
Some discussion of each of the areas chosen
Some irrelevance, either in the areas chosen or in the material within an area
Some errors
0 Very limited account, possibly only one aspect chosen
Material mostly irrelevant
Large number of errors
B = 2 marks
David Kaunda High School 139
Coherence
2 Material logically presented, with little or no repetition
Essay has coherence, ideas are developed well; continuous prose used throughout
Essay has an introduction and a conclusion, summing up the main points
Technical terms have been used correctly
Spelling, punctuation and grammar are sound
1 Material is presented in an orderly way and some ideas developed
Continuous prose used throughout
The introduction and conclusion may be present, but brief
Technical terms are used and generally in the correct context
Spelling, punctuation and grammar are generally sound
0 Essay style not used
Material in note form or numbered points
Very poor standard of spelling, punctuation and grammar
C = 2 marks
[max 15]
164. The roles of carbohydrates in living organisms
Introduction could include
Mono, di, polysaccharides –
Ref. production by photosynthesis –
Ultimate source from producers –
Heterotrophs obtain them from producers –
Ref. energy source, conversion to other organic molecules, storage, support –
Roles
Transport –
Size and relative solubility –
Glucose in animals, sucrose in plants –
Osmotic effects described –
Metabolism
Role in Calvin cycle –
Carbon dioxide fixation and RuBP
Regeneration from triose –
Triose conversion to other compounds –
Respiration and energy release –
Ref. glycolysis –
Ref. TCA –
Synthesis of other organic compounds e.g. lipids, amino acids –
Role of pentoses in nucleic acids –
David Kaunda High School 140
Storage
Solubility , compaction , non-osmotic effects –
Starch in plants –
Glycogen in animals –
Support / other
Plants and cellulose cell wall –
Bacteria and peptidoglycans –
Fungi and chitin –
Glycosides and cell recognition , receptors –
Scientific content: max 13
Balance: max 2
Coherence: max 2
[15]
OUTLINE SCHEME FOR MARKING ESSAYS
Scientific content
Above average
13 Excellent
11 Good
Essays in this category demonstrate a sound understanding of the topic, contain a
significant amount of material relevant to two or more units of the specification, and
suitable examples where appropriate.
Average
9 Slightly above average
7 Average
5 Slightly below average
Essays in this category contain factually correct and relevant material. Some areas
should show a progression from GCSE, particularly if a mark of 9 is awarded.
Below average
3 Some correct facts
1 Very few correct facts
0 No correct information
Essays in this category contain few relevant facts. The material that has been included
has little depth and barely reaches the standard expected at GCSE.
S = 13 marks
David Kaunda High School 141
Balance
2 A balanced essay covering all the main areas outlined
Some discussion of each area covered with, suitable examples where applicable
Material all relevant to the topic
Few, if any, errors
1 Most of the main areas of the topic covered, but possibly one or two lacking
Some discussion of each of the areas chosen
Some irrelevance, either in the areas chosen or in the material within an area
Some errors
0 Very limited account, possibly only one aspect chosen
Material mostly irrelevant
Large number of errors
B = 2 marks
Coherence
2 Material logically presented, with little or no repetition
Essay has coherence, ideas are developed well; continuous prose used throughout
Essay has an introduction and a conclusion, summing up the main points
Technical terms have been used correctly
Spelling, punctuation and grammar are sound
1 Material is presented in an orderly way and some ideas developed
Continuous prose used throughout
The introduction and conclusion may be present, but brief
Technical terms are used and generally in the correct context
Spelling, punctuation and grammar are generally sound
0 Essay style not used
Material in note form or numbered points
Very poor standard of spelling, punctuation and grammar
C = 2 marks
[max 15]
165. (a) most gain in height during the first year ;
due to cell multiplication / cell enlargement ; 2
(b) (i) max height gain for girls = 9.2 cm ;
(10.4 – 9.2 = ) 1.2 cm ; 2
(ii) height gain at 16 = 2.8 cm ;
176 + 2.8 = 178.8 cm ; 2
(c) increase in length of the long bones / ref. to growth of femur / eq ;
by growth of bones / formation of more bone tissue / eq ;
credit ref. to production of cartilage /
location of part of bone where growth takes place ;
growth of the trunk ; max 2
(d) in both there will be more skeleton/eq which adds to mass ;
in boys development of more muscle tissue ;
influenced by testosterone / androgens / male hormones ;
in girls development of more fatty tissue /eq ;
influenced by oestrogen ;
increase in sex hormones increases the secretion of growth hormone ; max 4
David Kaunda High School 142
(e) brain / head / CNS ;
rapid growth / most growth during first 5 years / figures quoted ;
does not have an adolescent growth spurt / not affected by sex hormones ;
reproductive organs /eq ;
very little growth / development before puberty ;
growth at puberty affected by sex hormones ;
lymphoid tissue / thymus /eq ;
maximum growth rate before adolescence / in children ;
then declines to adult value / affected by sex hormones ; 3
[15]
166.
Structures Liver cell Leaf palisade cell
Mitochondria ;
Starch grains X ;
Microtubules ;
Golgi apparatus ;
Glycogen granules X;
X is incorrect. If there are no crosses, assume blanks are crosses. If a mixture of ticks and
crosses, blanks are incorrect.
[5]
167. (a) Maltose ; 1
(b) Disaccharide / reducing sugar ; 1
(c) Glycosidic (ignore qualifications, e.g. 1- 4) ; 1
David Kaunda High School 143
(d) (i) Form plant cell walls / structural support in plants ; 1
(ii) Second mark depends on first, cannot get second mar
unless linked to a structural point.
correct structural point ; link to relevant function ;
1. large molecules / many glucoses insoluble ;
linked / polymer ;
2. (forms) straight / unbranched chains ; high (tensile) strength / “strong”
forms microfibrils / forms fibres ;
3. cross links / (hydrogen) bonds, between high (tensile) strength / forms
molecules ; microfibrils / forms fibres ;
4. forms microfibrils ; high strength / forms fibres ;
5. (1-4) glucose links ; difficult to digest ;
6. many glucoses linked ; cellulose can be hydrolysed and
(glucose) used in respiration ;
max 2
[6]
168. (a) A = chromatid ;
B = centromere ;
C = centriole ; 3
(b) (i) Mitosis (Check spelling) ; 1
(ii) (Homologous) chromosomes not paired / no chiasma / no crossing-over / no
bivalents / results in two diploid cells / cells which have four chromosomes /
chromatids ; 1
(c) Increase number of cells / growth / replace cells / repair (of tissues) (not cells) ;
Genetically identical daughter cells /eq same chromosomes / same diploid number DNA in
each cell /eq clones ;
Asexual reproduction ; max 2
[7]
169. (a) A = glycoprotein / glycosidic chain / carbohydrate ;
B = phospholipid (but not “phospholipid bilayer”) ; 2
(b) (i) More sodium (ions) enters when ATP present / fewer when no ATP ;
Faster uptake when ATP present / slower when no ATP ;
Maximum concentration not reached with ATP, but max. with no ATP / description ;
Correct use of figures, e.g. with ATP 10 (to 20) times faster / 5.7(AU) more with
ATP, at 5 minutes / two comparative figures quoted ;
Fastest rate in first minute in both ; max 3
David Kaunda High School 144
(ii) Sodium (ions) moved against / up the concentration gradient ;
Active transport / uptake ;
ATP needed to provide energy ;
To enable sodium / potassium pump to operate / to enable change in shape of
protein carrier / transport protein ;
(Some) diffusion occurs /eq passive transport ; 4
(c) To keep rate of reactions involved constant /eq temperature
affects rate of movement / diffusion across membrane /
affects kinetic energy / changes permeability of membranes /
affects enzyme activity / enzymes denatured at high / extreme temperature ; 1
[10]
170. (a) Points in (a) need not be paired
Change diameter of nozzle (e.g. “use a needle” ) / of syringe ;
Smaller nozzle ® smaller beads ;
Change flow rate / pressure applied to syringe ;
Faster flow / more pressure ® smaller beads;
Change alginate viscosity / concentration ;
Lower viscosity ® smaller beads ; 2
(b) Increase rate ;
Greater surface area (of beads) / reduces flow rate ;
Increased contact between enzyme and substrate / eq ;
More active sites available ;
If a single bead used: less enzyme ; Decrease in rate ;
Less contact between enzyme and substrate / fewer active sites ; 3
(c) (i) Increased concentration increases rate of reaction / increased rate of
production of glucose ;
No increase in rate above 0.15 mol dm-3 /eq (e.g. max. or highest) ;
Reference to increased number of collisions with active sites / enzyme ;
(At higher concentrations) rate limited by number of
active sites /eq all active sites occupied /
concentration of enzyme limiting rate ; max 3
(ii) Flow rate ;
Affects time for contact between enzyme and substrate / eq ;
OR
pH ; Affects bonding in enzyme / shape of enzyme / active sites ;
Denatured at extremes of pH ; max 2
David Kaunda High School 145
(d) (i) Production of lactose-free / lactose reduced milk / dairy products /
named e.g. kitten / cat milk / production of glucose / fructose /
galactose from whey ; 1
(ii) Continuous production ;
Uses less enzyme / re-use of enzyme /eq can easily remove enzyme ;
Avoids contamination of product /
can easily separate enzyme from products ;
More stable ; max 2
[13]
171. 1 Correct reference to translation ;
2 mRNA becomes attached /eq to ribosome (in cytoplasm) ;
3 Reference to ribosome attachment site / P site or S’end / sequence / eq start sequence
(AUG) ;
4 tRNA in cytoplasm attached to specific /eq amino acid ;
5 Reference to structure of tRNA / anticodon on tRNA ;
6 tRNA (carries amino acid) to the ribosome /eq ;
7 Complementary /eq anti-codon of tRNA lines up with codon of mRNA ;
8 Two tRNA molecules held in position /eq (may be implied) ;
9 Amino acids joined by peptide bond(s) ;
10 Reference to enzyme / enzyme complex in ribosome / ATP in loading tRNA ;
11 tRNA free / released to pick up another amino acid / re-used / recycled ;
12 Ribosome moves along mRNA until reaches end / stop codon / non-sense codon / eq
(UAA, UGA, UAG) ;
13 Polypeptide chain produced ;
14 (Polypeptide) chain twisted / folded to form protein / reference to a - helix / b pleated
sheet etc ;
15 Reference to polysomes or description / free and RER ribosomes / reference to
modification (post-translation) by Golgi ;
(Accept 2, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 11, 13, and 15 from diagram. Diagrams must be appropriately labelled to
gain mark.)
[max 10]
172. (a) (i) Mutualism / symbiosis ; 1
(ii) Rhizobium ; 1
David Kaunda High School 146
(b) (i) Nitrogen is fixed by bacteria / by Rhizobium / nitrogen fixing bacteria ;
Reduced / converted into ammonia / ammonium / NH4+ / NH3 ;
By nitrogenase ;
Reference to anaerobic conditions /eq ;
Converted into amino acids / protein /eq ;
By addition to carbohydrate /eq from plant ; max 3
(ii) Needs less nitrate / nitrogen from soil / can grow on nitrogen / nitrate
deficient soil ; 1
[6]
173. (a) (i) Nitrates / phosphates / urea / ammonium / accept chemical symbols ; 1
(ii) Competition for light /(other plants) block / shade light ;
Other plants unable to photosynthesise / less photosynthesis ;
Competition for carbon dioxide ; max 2
(b) Increased source / more food /eq for bacteria / bacteria decompose dead algae ; 1
(c) Bacteria respire aerobically / using O2 for respiration /eq ;
Uses up / depletes / reduces / lowers oxygen levels / BOD increases ;
Fish / aquatic animals / aerobic organisms die due to lack of oxygen
(stated or implied) ; Increase in anaerobic organisms /
decrease in biodiversity ; max 2
[6]
174. (a) Freezing of peripheral tissues / extremities / toes / nose / ears / fingers ;
Frostbitten area hard / painless / numb ;
Ice kills / damages tissues / cells ;
Gangrene may occur (when tissues have thawed) ;
Ice crystals can damage cell membrane / ice formation causes dehydration ; max 3
(b) (i) Rapid fall, between 0.25 and 0.5 hours / at start / after immersion ;
More gradual fall between 0.5 hours and 0.75 hours ;
Then regular fluctuations ;
Credit any two correct temperature references
from graph / one difference ; max 3
(ii) Temperature reduction reduces heat loss from core ;
Reduces likelihood of hypothermia ;
Temperature increase prevents tissue damage / frostbite in finger ;
Correct reference to either vasoconstriction / vasodilation ; 3
David Kaunda High School 147
(c) Increased metabolic rate ;
More heat energy released ;
Core temperature drops when sleeping ;
Reduced energy expenditure ;
Hgher blood flow to hands and feet ;
Reduces likelihood of frostbite / retains mobility of digits ;
Stocky / short build /eq ;
Reduces surface area: volume /eq ;
More subcutaneous fat / more fat under skin ;
For insulation / reduces heat loss ;
Brown fat qualified ;
Increased metabolic rate / generate heat ; 2×2
[13]
175. (a) Protandry
Male organs / stamens / anthers mature or ripen before stigma /
carpel / ovary / ovule / female organs
Pollen shed before stigma ripe
Correct named examples include: daisy, white deadnettle, canterbury bell,
rosebay willowherb, sage, geranium, ivy
Protogyny
Female organs / stigma / carpel matures or ripens before stamens /
anthers / male parts (not gametes)
Stigma ripe before pollen shed
Correct named examples include: bluebell, plantain, grasses,
reference to cereals, horse chestnut, honeysuckle fig wort,
wild arum lily, lords and ladies max 3
(b) Sieve tube elements
Wall contains cellulose
Contain cytoplasm / living (contents)
Sieve plates present
Transport organic solutes / sucrose / amino acids
Active /eq processes involved in transport
Transport is up and down /eq the plants
Xylem vessel elements
Wall contains (cellulose and) lignin
No living (contents) / dead
No end walls /eq present
Transport water and mineral (ions) / two named examples
No active process involved / transpiration stream
Transport is in one direction /eq max 3
[6]
David Kaunda High School 148
176. (a) (i) Absorbs carbon dioxide ;
So volume of oxygen used can be found / (decrease in volume due to) oxygen
uptake /eq; 2
(ii) To reset oil drop / position oil drop / calibrate capillary tube ; 1
(iii) To maintain constant temperature ; Temperature affects kinetic energy/
movement of molecules ;
Rate of respiration varies with temperature ;
Gas volume affected by changes in temperature ;
Temperature affects enzyme activity / metabolism ; 3
(b) 43 × 0.9 / 38.7 ;
÷ 15 ;
= 2.58 (mm3 oxygen per minute) / 2.6 / 2.574 ;
Allow consequential error. 3
(c) Need to know mass / weight / volume / number of seeds ;
Different masses would give different rates /eq ; 2
[11]
177. Give an account of the structure and functions of mammalian blood cells
Erythrocytes / red blood cells
1. Correct reference to shape as biconcave disc /eq ;
2. Large surface area for (gas) diffusion ;
3. No nucleus ;
4. Reference to flexibility / small size to enable cells to pass through capillaries ;
5. Oxygen combines with haemoglobin to form oxyhaemoglobin / HbO 8 ;
6. Reference to reversible affinity of haemoglobin for oxygen / Bohr effect ;
7. Red blood cells also involved in transport of carbon dioxide ;
8. HCO3- formed in red cells / reference to carbonic anhydrase ;
9. Carbon dioxide transported as carbaminohaemoglobin ;
Leucocytes / White Blood Cells
10. General statement about role in defence against disease ;
11. Have a nucleus ;
12. Some are phagocytic ;
13. Correctly named phagocytic cell e.g. neutrophil / monocyte / eosinophil ;
14. Secretion of antibodies by lymphocytes ;
15. In response to presence of antigens / antibodies combine with antigens ;
Accept marks from good, well-labelled diagrams.
[10]
David Kaunda High School 149
178. (a) Squamous
Cells flat / thin
Nucleus central
No microvilli / cilia
Allows rapid diffusion
Location e.g. buccal cavity / inside of cheek / Bowman’s capsule / alveolus /
capillaries / lining of blood vessels
Columnar
Cells tall / narrow ;
Nucleus basal ;
May have microvilli / cilia ;
Allows secretion / absorption ;
Location e.g. small / large intestine / named part of intestine (not oesophagus) /
trachea / bronchus ; max 3
[3]
179. (a) Soda lime removes / absorbs carbon dioxide ;
Prevents carbon dioxide accumulating in spirometer / reference to harmful effect of
carbon dioxide (not rebreathed) ;
Can find volume of oxygen used ; max 2
(b) Subject needs to use a nose clip ;
Chamber / spirometer filled with oxygen ;
Subject breathes in and out via mouthpiece ;
Lid moves up and down ;
Switch on chart recorder ;
Movement recorded on chart / paper (recorder) ;
Reference to calibration to find volumes / volumes read from chart ; max 4
(c) (i) Volume / amount of air breathed in or out / inspired or expired ;
At rest / with each breath ; 2
(ii) 420 to 440 cm3 / 940 - 450 = 490 cm3 ; 1
(iii) Number of breaths = 7 in 20 seconds ;
7 × 440 cm3 = 3080 cm3 ;
(Minute volume) = 3080 × 3 = 9240 cm3 (per minute) ;
[Allow consequential error for figure in (c) (ii). If only correct idea in
(c) (iii) is to obtain result in a minute, allow this mark. ] 3
[12]
180. Phospholipids ;
Proteins ;
(Mono)saccharide / sugar / carbohydrate / named monosaccharide ;
Receptors / recognition sites /eq antigens ;
Endocytosis / phagocytosis pinocytosis ;
[5]
David Kaunda High School 150
181.
Statement Glycolysis Krebs cycle
C6 compounds are involved ;
Pyruvic acid is produced X;
Carbon dioxide is produced X ;
ATP is hydrolysed X;
Reduced co-enzyme is produced ;
[5]
182. (a) A Crista ;
B (Outer) membrane envelope / (double) membrane ;
C Intermembrane space /eq inner membrane / envelope (if not given for B) ; 3
(b) Krebs /eq cycle / link reaction 1
(c) Accept measurement of 104 to 106 mm
105 1 1000
6
105 1
or 6 10
–3
10.5 0.1
or 6 10
–4
(Allow for consequential error for measurements outside range if calculated correctly) ;
= 17 333 to 17 667 ; 2
[6]
183. (a) Monohybrid involves one character, dihybrid two characters /eq ;
Monohybrid one gene / locus, dihybrid two genes / loci /eq // monohybird one pair of
alleles,dihybrid two pairs of alleles involved ;
Credit for examples genotypes / phenotypes of both;
Monohybrid reference to allelic interaction at one locus /dihybrid gene interaction
between two loci / reference to epistasis (accept “eye colour” for monohybrid) ;
Heterozygous cross monohybrid gives 3:1, dihybrid 9:3:3:1 (accept correct ratios for other
specified crosses) ; Max 3
David Kaunda High School 151
(b) Continuous has (complete) range of measurements / phenotypes, discontinuous only a few
categories /eq ;
Continuous is polygenic / controlled by a large number of genes, discontinuous one / only
a few genes ;
Continuous likely to / may be influenced by the environment, discontinuous little / no
environmental influence ;
Credit for examples of both (accept “eye colour”/“coat colour in mice” for
discontinuous) ;
Allow 1st and 4th points if shown on clearly labelled sketch graphs. Axes must be
labelled. Max 3
[6]
184. (a) Mutation I - deletion;
Mutation II - insertion / addition / duplication 2
(b) Alanine ; 1
(c) If only mutation I occurred then all the following amino acid / codon / triplets / bases
sequence would be altered / frame shifted / eq Mutation II corrects mutation I only the
sequence between the two mutations is altered / eq 2
(d) Mutagen / mutagenic (agent) 1
[6]
185. (a) Must be heterozygous to score mark in (a)
Aa / XA Xa / X A Xa /eq: 1
(b) Only males have the disease / disorder /eq (accept converse) ;
(Probably) carried on the X chromosome ;
Male sufferers are produced from unaffected/ eq parents ;
Recessive only expressed when no dominant allele is present / eq
females may be carriers;
Male has only one locus / allele for the disease /
disorder / no locus on Y /eq ; Max 3
(c) Person 3 / father is XAY/eq ;
(As) person 4 / mother is carrier / XAXa / Aa / heterozygous ;
Person 5 / son inherits Y from person 3 / father /eq ;
And Xa / recessive allele / disorder from person 4 / mother / eq Max 3
David Kaunda High School 152
(d) Accept marks from genetic diagram. If unclear whether mother is AA or Aa, can only
score mark for person 6’s genotype.
Person 6 / father is XA Y / A /eq
Person 7 / mother is carrier /eq is heterozygous / Aa ;
All the females / daughters will be unaffected / eq ;
Half /eq of the sons / males will be unaffected /eq (or converse) ;
There is a one in four /eq chance (but not ratios)
of producing a sufferer (or converse) Max 4
[11]
186. (a) 7; 1
(b) (Repeat the experiment at) a range of closer pHs (between 6 and 8) ; 1
(c) In very /eq acidic conditions / high concentration of H+ ;
Reference to changes in R group / side group ionisation charge /eq ;
Bonding disrupted /eq ;
Shape of enzyme / active site /eq denaturation /eq ;
Substrate / urea does not bond /eq with active site ; Max 3
(d) (Change in pH) affects shape of enzyme / active site ;
Enzyme-substrate complex formed less efficiently / eq ; 2
(e) Use (buffer solution) pH7 (throughout) / optimum pH ;
Same / stated volume / concentration of urease / enzyme ;
Range of concentrations of urea / substrate ;
Use the same / stated volume of urea / substrate ;
Named variable kept constant / e.g. time, temperature /
same volume of buffer; Max 4
[11]
187. All points must be made in an appropriate context
1 Produces cells with haploid number of chromosomes / eq produces gametes in animals /
spores in plants / halves chromosome number;
2 Leads to genetic variation ;
3 Pairing of homologous chromosomes / reference to bivalent (in interphase or prophase 1) ;
4 Named stages in correct sequence for either 1st or 2nd division ;
5 Description of chiasmata / description of crossing over;
6 (Elaboration of spindle formation) e.g. reference to centrioles, microtubules
7 (Prophase) e.g. condensation of chromosomes / disintegration of nuclear envelope /
disappearance of nucleolus ;
David Kaunda High School 153
8 (Metaphase 1) e.g. attachment /eq of pairs of chromosomes / bivalents to spindle fibres /
at equator ;
9 (Anaphase 1) e.g. separation of pairs of chromatids / eq homologous sets of chromosomes ;
10 (Telophase 1) e.g. chromosomes /eq at poles / decondensation / nuclear membrane reforms
/ spindle disintegrates ;
11 (2nd prophase) duplication of centrioles / reference to chromosome state (i.e. number) ;
12 (2nd metaphase) e.g. spindles at right angles / attachment of (individual) chromosomes ;
13 (2nd anaphase) e.g. separation of sister chromatids / eq (clearly described)
14 (2nd telophase ) e.g. reintegration /eq of nuclear envelope / spindle disintegrates ;
15 Division of cytoplasm / decondensation / cytokinesis in animals / formation of cell
plate /eq in plants
[10]
188. Hairs ;
Stomata / stomatal pores ;
Cuticle ;
Surface area ;
Xerophytes / xeromorphs ;
[5]
189. (a) The tendency for water to move out of a solution /eq // a measure of the free energy of
H2O molecules in a solution ;
Pure water has the highest water potential / solutions have negative water potentials //
pure / distilled water has a water potential of zero ;
(Water potential) determined / affected by solute concentration and (hydrostatic)
pressure /eq (accept equation if terms are explained) Max 2
(b) (i) Plasmolysed / plasmolysis 1
(ii) Water potential of solution outside lower / more negative than inside the cell ;
Water moves out (of cell) through partially / selectively permeable membrane;
Volume of the cell / or protoplast / vacuole decreases / shrinks // cell (surface)
membrane/eq protoplast comes away from cell wall ;
Remains attached at plasmodesmata Max 3
(iii) Sucrose solution / bathing solution 1
[7]
190. (a) Too many plants are eaten /eq over-grazing kills / removes plants ;
Trampling destroys plants / causes compaction (of soil);
So nutrients / organic matter not returned to soil / reduces air spaces ; Max 2
(b) Lack / absence of (plant) roots to bind soil ;
(Surface) soil exposed because of lack of surface vegetation ;
Trampling (by animals) loosens soil surface; Max 2
David Kaunda High School 154
David Kaunda High School 155
(c) Wood / timber for burning /eq fuel /charcoal ;
Wood for building /eq timber / furniture ;
Branches /eq; for fodder /eq ;
Clearance for farming /eq ;
Clearance for urbanisation / eq Max 2
[6]
191. (a) Maltose ; 1
(b) Maltase ; 1
(c) Microvilli (epithelial) mucosa / cells on surface of villi / brush borders ; 1
(d) Long, providing large surface area / folding of wall gives large surface area ;
Villi, increase surface area ;
Villi with (smooth) muscle fibres increase contact with the food ;
Microvilli / brush borders increase surface area ;
Extensive /eq; capillary network /eq; to carry away food / glucose /
maintain concentration gradients/eq ;
Presence of transport proteins / channels/eq in cell membranes; Max 3
[6]
192. (a) Kills useful insects /eq natural predators / disrupts food chains communities / eq ;
May harm actual crop ;
Requires equipment to apply to fields / health and safety implications / eq ;
Residues /eq can harm human consumers;
Repeat application / resurgence of pest ;
Development of resistance ;
Bioaccumulation if persistent / non-biodegradable ; Max 3
(b) (i) Overall steady / linear increase ;
Harvest / yield doubles / mean increase million tonnes / yr / eq
1975-1977 shows a plateau /eq slower increase 85-87 /
highest rate of increase between 81-83 / 81-85 ; Max 2
(ii) Pest increasing / amount of rice grown increases ;
Pests attracted to / breed in / feed on rice ;
Pests developing resistance to pesticides ;
Apply greater variety of pesticides to kill pests /
more frequent applications / reference to resurgence ;
Increases availability of pesticides / increased awareness of benefits ; Max 3
David Kaunda High School 156
(c) Natural predators no longer killed by pesticide ;
(They) prey on /eq rice pests ;
Reference to lack of side effects of pesticides on rice growth ;
Change in rice variety to higher yielding / disease pest resistant ones / shorter life cycle ;
(Greater) use of fertilisers (farmers spending less on pesticides) ;
Use of biological control methods ; Max 3
[11]
193. (a) (Grass) not mowed / grazed by domestic animals / livestock / eq ;
Shrub seedlings allowed to grow / not eaten /eq ;
Reference to leaf lifter from shrubs smothering grasses / shading effect : Max 2
(b) [(19-8)/8] × 100 ;
137.5 (%) ; 2
(c) Reference to canopy layer in woodland / more layers in woods;
Increase in number of niches / habitats ;
Increase in different types of food ;
Increase in different types of nesting / roosting site ; Max 2
(d) Accept points in converse but must state in ‘shrub community’ ;
More predators (in pine) ;
Birds may have larger territories Greater diversity may cause increased competition ;
Decrease in nesting / roosting sites ;
Leaf lifter more acidic, supports fewer (insect) species as food for birds /
less food available ; Max 2
(e) (Secondary) succession; 1
(f) Cutting of trees / deforestation /eq ;
Introduction of new species / aliens / disease (e.g. Dutch elm) ;
Natural disaster / flooding / storm damage / volcanic activity / fire / eq;
Climate change / acid rain; Max 2
[11]
David Kaunda High School 157
194. All points must be made in an appropriate context
1 Definition of acid rain (rain / snow / precipitate that is more acidic than normal / lower
than pH 5) (allow pH 5.6) ;
2 Caused by burning fossil fuels from industry / vehicles / release of sulphur dioxide /
nitrogen oxides ;
3 Chemicals react and produce acids / specified acid that dissolve in water (droplets) e.g.
H2O + SO2 H2SO3;
4 Reference to acid rain damaging buildings /eq ;
5 Areas with naturally acidic soil / highlands / pine conifer forests most affected / eq ;
6 Damage to plant cuticle / needles // leaves die / eq fall / die back of branches ;
7 Soil acidity increased, causing leaching of nutrients / aluminium / metal ions released ;
8 Root damage;
9 Lack of nutrients, causes trees to be weaker / more susceptible to disease /
drought / frost ;
10 Acidification /eq pH decrease of lake / river water;
11 Aluminium ions damage fish gills;
12 Acidity affects eggs of fish / amphibians // enzyme inhibition // pH effect;
13 Reduced calcium levels in water / soil affects crustacea / molluscs leaching of calcium
from soil results in fewer earthworms ;
14 Loss of plankton / effect on food chain / biodiversity [specific point] / affects soil
microorganisms ;
15 Reference to release of heavy metals / specified metal e.g. Cu / Pb / cadmium / Al / Hg
affecting human health ;
[10]
195. Knapping ;
Erectus ;
Neanderthal ;
Cutting / skinning / shearing / sawing ;
Palaeolithic ;
[5]
David Kaunda High School 158
196.
New world monkeys Flat nose / wide nostrils // Prehensile tail ;
nostrils facing out //
no ischial callosites ;
Old world monkeys Downward facing nose / nostrils / narrow nostrils // Tail absent or non
prehensile ;
nostrils close together //
ischial callosites / sitting pads on buttocks /eq ;
[4]
197. (a) (424/1216) × 100 ;
= 34.9 % / 34.87 ; 2
(b) 15-19 age range includes females starting menstruation /
reaching child bearing age /eq ;
TFR indicates the number of children that these females will have / eq ;
If multiply TFR by 15-19 population size, get estimate of population ; Max 2
(c) Contraception //
smaller families / conception later in life older mothers /
decreasing birth rate / TFR decrease indicates lower population / eq //
women being educated / have careers / eq //
greater income ; 1
(d) Better medical facilities / hospitals / more likely to have a baby in hospital /
better ante natal care ; 1
[6]
198. (a) Difficulty breathing / short of breath ;
Headache ;
Lack of concentration / dizziness / lack of coordination/ difficulty in decision making ;
Palpitations /eq ;
Nausea / vomiting ;
Muscle weakness;
Fluid retention / oedema / swollen limbs / reduced urinary output ; Max 3
(b) Using oxygen supply;
Ascending in stages slowly / taking rests ;
Use of decompression chamber /eq before visit / stay at altitude before ; Max 2
David Kaunda High School 159
(c) Hyperventilation ;
Tidal volume /eq increased / depth of breathing increased ;
Increase in heart rate / cardiac output / decrease in stroke volume ;
More / increased production of RBC ;
Increased haemoglobin ;
Increased blood volume; Max 2
[7]
199. (a) To acclimatise / become used to the conditions / adjust idea /eq ;
So that heart rate was / results being measured were due to that concentration / eq ;
To settle down after being handled (needs qualification) ; Max 2
(b) To obtain a mean / average value (at each concentration) ;
To make results more reliable ;
Eliminate / reduce variations between individual Daphnia /
anomalous results ; Max 2
(c) Temperature may affect rate of uptake of compound ;
Will alter rate of metabolism /eq respiration ;
Which will alter rate of heart beat /eq ;
Reference to temperature affecting enzyme activity ; Max 2
(d) That increasing the concentration of the oestrogenic compound
decreased the rate of heart beat / inverse relationship / eq //converse ;
The decrease is steady / linear /eq reference to less change
from 9 –12, than up to 9 /eq 2
(e) Could make them move more slowly ;
Could make them easier to catch / decrease population ;
Could cause them to die / increased mortality /eq ;
Affect their (overall) metabolic rate / rate of respiration ; Max 2
(f) (i) Rate of photosynthesis increases with increasing concentration /
direct relationship reference ; 1
(ii) Accumulate within the tissues of Elodea ;
Get passed on to plant-eating insects / fish / herbivores ;
Eventually accumulate in trout / salmon / fish /eq consumed by humans ;
OR
Increased 1° productivity / in Elodea ;
More food available for herbivores ;
Reference to more food available for humans ;
(Accept converse points if (f)(i) is incorrect) Max 2
[13]
David Kaunda High School 160
200. Outline Scheme For Marking Essay Questions
Scientific content
Above average
13 Excellent
11 Good
Essays in this category demonstrate a sound understanding of the topic, contain a
significant amount of material relevant to two or more units of the specification,
and suitable examples where appropriate.
Average
9 Slightly above average
7 Average
5 Slightly below average
Essays in this category contain factually correct and relevant material. Some areas
should show a progression from GCSE, particularly if a mark of 9 is awarded.
Below average
3 Some correct facts
1 Very few correct facts
0 No correct information
Essays in this category contain few relevant facts. The material that has been
included has little depth and barely reaches the standard expected at GCSE.
S = 13
Balance
3 A balanced essay covering all the main areas outlined
Some discussion of each area covered with, suitable examples where applicable
Material all relevant to the topic
Few, if any, errors
2 Most of the main areas of the topic covered, but possibly one or two lacking
Some discussion of each of the areas chosen
Some irrelevance, either in the areas chosen or in the material within an area
Some errors
1 Only a few aspects of the topic discussed, so unbalanced
Limited discussion of the areas chosen
Irrelevant material included
Errors present
0 Very limited account, possibly only one aspect chosen
Material mostly irrelevant
Large number of errors
B=3
David Kaunda High School 161
Coherence
3 Material logically presented, with little or no repetition.
Essay has coherence, ideas are developed well ; continuous prose used throughout.
Essay has an introduction and a conclusion, summing up the main points.
Technical terms have been used correctly
Spelling, punctuation and grammar are sound
2 Material is presented in an orderly way and some ideas developed
Continuous prose used throughout
The introduction and conclusion may be present, but brief
Technical terms are used and generally in the correct context
Spelling, punctuation and grammar are generally sound
1 Material not very well organised and ideas do not follow logically
Essay lacks proper introduction and/or conclusion
There may be some numbered points or headings
Poor use or lack of technical terms
Spelling, punctuation and grammar of a poor standard
0 Essay style not used
Material in note form or numbered points
Very poor standard of spelling, punctuation and grammar
C=2
[15]
The functions of proteins in living organisms
General points
amino acids, formation of the peptide bond and polypeptides primary, secondary and
tertiary structure fibrous and globular proteins conjugated proteins Enzymes
illustrated with specific examples in metabolic pathways, such as hexokinase and ribulose
bisphosphate carboxylase role of enzymes in DNA replication enzymes in digestion -
Structural proteins
microtubules, membrane proteins, histones Hormones
Insulin, glucagon, ADH Transport
channel proteins and ion pumps haemoglobin -
Contractile proteins
actin and myosin, roles in muscle contraction Other functions
antibodies storage in plants myoglobin S = 13 marks B = 2 marks C = 2
[max 15]
201. Outline Scheme For Marking Essay Questions
Scientific content
Above average
13 Excellent
11 Good
Essays in this category demonstrate a sound understanding of the topic, contain a
significant amount of material relevant to two or more units of the specification,
and suitable examples where appropriate.
David Kaunda High School 162
David Kaunda High School 163
Average
9 Slightly above average
7 Average
5 Slightly below average
Essays in this category contain factually correct and relevant material. Some areas
should show a progression from GCSE, particularly if a mark of 9 is awarded.
Below average
3 Some correct facts
1 Very few correct facts
0 No correct information
Essays in this category contain few relevant facts. The material that has been
included has little depth and barely reaches the standard expected at GCSE.
S = 13
Balance
3 A balanced essay covering all the main areas outlined
Some discussion of each area covered with, suitable examples where applicable
Material all relevant to the topic
Few, if any, errors
2 Most of the main areas of the topic covered, but possibly one or two lacking
Some discussion of each of the areas chosen
Some irrelevance, either in the areas chosen or in the material within an area
Some errors
1 Only a few aspects of the topic discussed, so unbalanced
Limited discussion of the areas chosen
Irrelevant material included
Errors present
0 Very limited account, possibly only one aspect chosen
Material mostly irrelevant
Large number of errors
B=3
Coherence
3 Material logically presented, with little or no repetition.
Essay has coherence, ideas are developed well ; continuous prose used throughout.
Essay has an introduction and a conclusion, summing up the main points.
Technical terms have been used correctly
Spelling, punctuation and grammar are sound
2 Material is presented in an orderly way and some ideas developed
Continuous prose used throughout
The introduction and conclusion may be present, but brief
Technical terms are used and generally in the correct context
Spelling, punctuation and grammar are generally sound
David Kaunda High School 164
1 Material not very well organised and ideas do not follow logically
Essay lacks proper introduction and/or conclusion
There may be some numbered points or headings
Poor use or lack of technical terms
Spelling, punctuation and grammar of a poor standard
0 Essay style not used
Material in note form or numbered points
Very poor standard of spelling, punctuation and grammar
C=2
[15]
Natural Selection and the effects of environmental change.
Expect descriptions and discussion within all or most of the following areas:
Natural selection (Expect some references to genes / alleles in better answers)
Variety amongst individuals of same species An individual has many different characteristics which
affect its survival Some characteristics give individuals an advantage More likely to survive and
breed / survival of the fittest Offspring inherit the characteristics Characteristics become more
common in the population Certain characteristics can be selected for, or selected against -
Environment and selection pressures
Environmental factors affect survival / exerts selection pressure Examples of environmental factors
such as change in climate, pollution, predation, food Changes in an environmental variable will
favour certain characteristics References to differential mortality and natality Stabilising
selection (no environmental change, less variation) Directional selection (gradual environmental
change. favouring particular characteristic) Leads to isolation and speciation -
Range of specific examples such as:
Industrial melanism in peppered moth Metal tolerance in plants in spoil heaps
Resistance to insecticide / warfarin / antibiotics / myxomatosis
S = 13 marks B = 2 marks C = 2
[max 15]
202. Outline Scheme For Marking Essay Questions
Scientific content
Above average
13 Excellent
11 Good
Essays in this category demonstrate a sound understanding of the topic, contain a
significant amount of material relevant to two or more units of the specification,
and suitable examples where appropriate.
Average
9 Slightly above average
7 Average
5 Slightly below average
Essays in this category contain factually correct and relevant material. Some areas
should show a progression from GCSE, particularly if a mark of 9 is awarded.
David Kaunda High School 165
Below average
3 Some correct facts
1 Very few correct facts
0 No correct information
Essays in this category contain few relevant facts. The material that has been
included has little depth and barely reaches the standard expected at GCSE.
S = 13
Balance
3 A balanced essay covering all the main areas outlined
Some discussion of each area covered with, suitable examples where applicable
Material all relevant to the topic
Few, if any, errors
2 Most of the main areas of the topic covered, but possibly one or two lacking
Some discussion of each of the areas chosen
Some irrelevance, either in the areas chosen or in the material within an area
Some errors
1 Only a few aspects of the topic discussed, so unbalanced
Limited discussion of the areas chosen
Irrelevant material included
Errors present
0 Very limited account, possibly only one aspect chosen
Material mostly irrelevant
Large number of errors
B=3
Coherence
3 Material logically presented, with little or no repetition.
Essay has coherence, ideas are developed well ; continuous prose used throughout.
Essay has an introduction and a conclusion, summing up the main points.
Technical terms have been used correctly
Spelling, punctuation and grammar are sound
2 Material is presented in an orderly way and some ideas developed
Continuous prose used throughout
The introduction and conclusion may be present, but brief
Technical terms are used and generally in the correct context
Spelling, punctuation and grammar are generally sound
1 Material not very well organised and ideas do not follow logically
Essay lacks proper introduction and/or conclusion
There may be some numbered points or headings
Poor use or lack of technical terms
Spelling, punctuation and grammar of a poor standard
0 Essay style not used
Material in note form or numbered points
Very poor standard of spelling, punctuation and grammar
C=2
[15]
David Kaunda High School 166
Structural changes in the evolution of hominids
General points
Increase in brain size and cranial capacity Other changes in skull such as cranium more domed, teeth
small /eq flatter, jaw shallower.Brow ridges less pronounced
Skeletal changes concerning bipedalism, such as femur not vertical / inward pointing, centre of hip,
knee and ankle in straight line, foot can be placed under centre of gravity, gives striding gait,
legs stay parallel Pelvis shorter / smaller, better hip rotation, more compact muscle attachment,
keeps body from leaning forward Big toe is parallel with other toes, not opposable, gives wider
platform for support balance
Evolution of the hand and opposable thumb Ratio of first finger to thumb
Reference to other features such as bones more robust thicker giving better support for whole body
mass /eq Flatter face Nose shape -
Details of these changes in:
The Australopithecines
Homo habilis
Homo erectus
Early Homo sapiens
Homo neanderthalensis
Homo sapiens sapiens
S = 13 marks B = 2 marks C = 2
[max 15]
203. (a) (i) 1. Add enzyme to sodium alginate solution ;
2. Drop into solution with calcium ions (any salt) (allow credit for correct
alternative method) ;
3. (Strain off beads) and place in column /eq ;
4. Use same beads throughout /equal number / mass of same size bead ;
5. Use of buffer solutions ;
6. Suitable pH values, at least 5 with 1 above pH7 ;
7. Run buffer through column before starting ;
8. Standard concentration of lactose ;
9. Equilibrate at stated suitable temperature before adding to column ;
10. Use the same column for each solution (even if different beads) ;
11. Add same volume of lactose solution (to column) ;
12. Test drops of solution separately with indicator strips ;
13. Time to get standard colour / colour after stated time ;
14. Preparation of standard colour(s) / use of standard colour chart ;
15. Rinse column / beads between tests ;
16. Repetition of whole experiment ; Max 9
David Kaunda High School 167
If enzyme not immobilised
allow points 5, 6, 8, 11, 13, 14, 16 and the following alternative points
4a. Use of same volume and concentration of lactase ;
9a. Equilibrate and test in water bath at stated suitable temp ;
Allow only to max 7
(a) (ii) Tabulation ;
Columns / rows with units where appropriate ;
Calculation of means ;
Calculation of rate by suitable means /eq 1/time ;
Line graph ;
Axes - pH on x, time or rate on y / intensity of colour ; Max 4
(b) Temperature difficult to control /eq ;
Rate of flow can vary / gets slower /eq ;
Possible loss of enzyme from beads ;
Sample drop size may vary ;
Beads not fully washed / previous solution may penetrate beads /
beads may vary (if different ones used) ;
End point / colour standards subjective ; Max 2
[15]
204. Treat with warm HCl;
Name of suitable stain e.g. orcein, Schiffs, Leishman’s, fuelgen, Toluidine blue ;
Detail of removal of suitable region of root tip 1.5 mm (max) ;
Break up tissue with glass rod /eq ;
Allow time for staining / warm to intensify orcein stain. ;
Cover with cover slip ;
Place in folded filter paper /eq ;
Apply firm pressure / press with thumb on cover slip ;
Avoid moving cover slip /eq ;
[max 7]
David Kaunda High School 168
205. (a) 404 4 /eq ;
= 101 for all four /eq ; 2
(b)
Phenotype Observed (O) Expected (E) O-E (O E ) 2
E
Coloured, full 190 101 89 78.4
Coloured, shrunken 9 101 –92 83.8
Colourless, full 7 101 –94 87.5
Colourless, shrunken 198 101 97 93.2
Total 404 404 342.9
Correct values O-E (including sign) ;
All four calculated values correct ;
Correct value for X2 ;
Allow consequential errors from part (a) and through part (b) Max 3
(c) Difference between observed and expected is significant / not due to chance ;
Value of X2 greater than 5% value /eq ;
Allow correct alternative for incorrect values. 2
(d) Too many coloured full and colourless shrunken phenotypes / too few coloured shrunken
and colourless full ;
Genes are linked ;
On the same chromosome ;
Not usually separated by meiosis / only by chiasmata /
when crossing over occurs ;
Alleles for Coloured full / colourless shrunken together /
reference to genotypes of parents of the heterozygous plant ; Max 3
If result of calculation of X2 is less than 7.185, allow the following
Genes are not linked ;
Carried on different chromosomes. ;
Show independent assortment / inherited independently ; 3
[10]
David Kaunda High School 169
206. (a) M - Magnification correct within agreed limits (120-130 mm wide 115-125 mm vertical) ;
P - Proportions of drawing correct within agreed limits
(approximately equal horizontal and vertical) ;
N - Neat drawing, no cells, no sketchy lines ;
T - all four tissues shown clearly (epidermis and exodermis, vascular bundles, central
vascular bundle, parenchyma) ;
A - Accurate selected detail e.g. corners drawn accurately -
no gross inaccuracy ; Max 5
(b) Stated diameter within agreed limits (82 mm – 84 mm) 1
(c) Correct diameter calculated (2.05 mm - 2.1 mm) ;
Allow correct calculation from candidate’s answer to (b) 1
(d) Answer to (b) divided by answer to (c) or using scale line
Correct calculation from their figures ; 1
[8]
207. (Nuclear) membrane / envelope;
Glycogen ;
Lipids / fats / triglycerides oils
Plasmids ;
Flagellum /flagella;
[5]
208.
Disaccharide Constituent Monomers One role in living
organisms
Glucose and galactose
Maltose Energy / food source in
(germinating) seeds
Sucrose Glucose and fructose
[5]
209. (a) A Crista / cristae
B (Outer) membrane/inter-membrane space / eq envelope;
C Matrix ; 3
(b) Aerobic respiration / description /eq link reaction / Krebs cycle
oxidative phosphorylation / electron transport chain;
Production of ATP; 2
[5]
David Kaunda High School 170
210. (a) (Linear) sequence / order / arrangement / pattern of amino acids; 2
(b) Description of H bond / attraction between dipoles e.g + and – /
weak electrostatic bond
Between H and O;
In amine and carboxyl groups
Reference to the helix / secondary structure / - sheet/ – strand ;
(Bond between) R groups in coiling / tertiary stucture / 3D shape Max 3
(c) Long chain / long strand / fibrils / reference to linear molecule
Repeating sequence of amino acids;
Many parallel strands lie side by side / eq;
Reference to a helix / (pleated) sheet;
Collagen has triple helix; Max 3
[8]
211. (a) Palisade (mesophyll);
Reference to elongated shape / presence of (large numbers of)
chloroplasts / location e.g. near top / near upper surface
under / below epidermis / vertically orientated 2
(b) Photosynthesis / description of process 1
(c) Magnification [between 55 - 75mm] M;
Proportions [height – 2½ - 3½ × width] P ;
Drawn correct two cells only; D ;
Cell wall, varying thickness / chloroplasts shown C ;
Nucleus [approximately correct position] N ; 5
[8]
212. (a) A - chromatid;
B- centromere; 2
(b) Anaphase;
Chromatids separate / centromere splits
Move / pulled to (opposite) poles / ends of cell / ends of spindle to centrioles ;
By spindle fibres / microtubules 3
(c) Daughter cells genetically identical (to parent cell) /maintains
chromosome number/eq; 1
David Kaunda High School 171
(d) Interphase / G1 / S / G2 / cytokinesis / cleavage
If interphase or named stage - growth/synthesis of organelles
synthesis / replication of DNA / division of organelles
OR
If cytokinesis - division of the cytoplasm / formation of cell plate in plants ;
Points linked. [if give ‘telophase’and then describe division of
cytoplasm allow second mark] 2
[8]
213. (a) 7 1
(b) Repeat experiment at a range of pH values at closer intervals / at
smaller intervals of pH /eq (on either side of the optimum) 1
(c) In very /eq acidic conditions / high concentration of H+;
Reference to changes in R group ionisation /eq
Bonding disrupted /eq;
Enzyme / active site changes shape / tertiary structure changes denaturation ;
Substrate / urea does not bond /eq with active site; 3
(d) Shape affected more at pH 9 than 8 / more denaturation at pH9 than 8 H converse ;
Enzyme-substrate complex formed less efficiently / eq 2
(e) Use (buffer solution) pH7 throughout / optimum pH ;
Same / stated concentration / volume of urea / substrate
Range of concentrations of urease / enzyme;
Use the same / stated volume of urease / enzyme;
Named variable (e.g. time / temperature / volume of buffer) kept
constant Max 4
[11]
214. (a) A Phosphate
B Deoxyribose
C (Organic) base / thymine / adenine;
D Hydrogen bond / H bond; 4
(b) Total percentage of C + G = 84 %;
Therefore T will be (100 – 84) ÷2;
= 8%; 3
(c) (i) CGC\AGU\ACG;; 2
[all correct = 2 marks, 1 error1 mark]
(ii) 3; 1
[10]
David Kaunda High School 172
215. All points must be in an appropriate context
Diffusion
1 (Molecules / ions) move down / with a concentration gradient
2 Rate increased by larger concentration difference / higher temperatures / smaller
molecules or ions / larger surface area of membrane / small diffusion distance (or
converse) ;
3 Credit example of diffusion e.g. oxygen, carbon dioxide, water;
Facilitated diffusion 4(Molecules / ions) move down/ with a concentration gradient/eq
5 Requires protein channel / carrier in membrane;
6 Credit example of facilitated diffusion, such as glucose / amino acids / named ion
Osmosis
7 Movement of water;
8 From high / less negative water potential / to low / more negative water potential
//eq;
9 Across partially permeable /eq membrane;
Active transport
10 (Molecules / ions) move up / against concentration gradient;
11 Requires protein channel / carrier in membrane;
12 Credit further details of mechanism of active transport;
13Credit example of active transport, such as sodium / potassium / proton pumps;
Endocytosis / exocytosis /pinocytosis / phagocytosis 14 Description of process;
15 Active transport / endocytosis / etc require ATP / energy;
OR
Diffusion / facilitated diffusion / osmosis do not require ATP / energy;
[10]
216. No mark scheme available
217. No mark scheme available
218. No mark scheme available
219. No mark scheme available
David Kaunda High School 173
220. No mark scheme available
221. No mark scheme available
222. No mark scheme available
223. No mark scheme available
224. No mark scheme available
225. No mark scheme available
226. No mark scheme available
227. No mark scheme available
David Kaunda High School 174
228. No mark scheme available
229. No mark scheme available
230. No mark scheme available
231. No mark scheme available
232.
Process Takes place against Requires energy in
a concentration the form of ATP
gradient
Diffusion X X
Facilitated diffusion X X
Osmosis X X
Active transport
Any two correct boxes for one mark
[4]
233. Condensation / polymerisation ;
Deoxyribose ;
Thymine ; [watch spelling]
(double) helix ;
Hydrogen ; [accept H]
[5]
David Kaunda High School 175
234.
Name of organelle Description Function
Transport of lipids / storage
Stack / group / eq, of, of lipids / modification of
(flattened / curved), lipids /
cisternae /tubules / sacs ; formation of glycoproteins /
modification of proteins /
formation of secretory / eq
vesicles / formation of
lysosomes / transport of
carbohydrates ;
Centrioles / centrosome;
Mitochondria ; Aerobic respiration / ATP
production / ETC / oxidative
phosphorylation / Krebs
cycle;
[5]
235. (a) Phospholipid ; 1
(b) A Glycerol / propan 1,2,3 triol ;
B Ester bond / ester linkage ; 2
(c) Insoluble in water / does not dissolve in water / non-polar ; 1
(d) (Fluid because) phospholipids move (around membrane) ;
(Mosaic because) membrane contains proteins /
glycoproteins (lying amongst phospholipids) / eq ; 2
[6]
236. (a) anaphase ;
prophase ;
telophase ;
metaphase ;
[if ‘I’ or ‘II’, penalise ONCE] 4
(b) (i) (G lasts) 7.0 hrs (and cell cycle time is 14 hrs) / 18-11 ;
7 × 100 ÷ 14 ;
= 50 % ; 3
(ii) B;
DNA replication / DNA mass beginning to, increase / double ; 2
[9]
237. (a) (Solution) heated / boiled (with Benedict’s solution / reagent ;
Green / yellow / orange / red / brown (precipitate) ; 2
(b) Heat with acid or add sucrase ;
Neutralise or incubate [if using enzyme] ;
David Kaunda High School 176
(Heat with) Benedict’s / repeat test / eq ; 3
(c) Same / stated, volumes of each (test) solution ;
Same / stated, volume Benedict’s solution (to each) ;
Stated / same , time / temperature (for heating) / boil in waterbath;
Weigh precipitate / colour comparison / reference to
colorimeter comparison / time taken to reach standard
or same colour / reference to rate of colour change ; max 3
[8]
238. (a) central C with R and H attached by single bonds ;
NH2 and COOH attached to carbon by single bonds ;
[accept NH3+ and /or COO–] 2
(b) (i) A Ribosomes ;
B Rough ER ;
C Golgi apparatus ; 3
(ii) (Rises by 15 units in 15 minutes)
Rate = 15 ÷ 15 ; [accept other correct figures]
=1;
unit per min ;
[allow unit mark if figures from incorrect curve] 3
(c) Radioactivity will continue to drop in (all) organelles ;
Reference to half life (of isotope) / natural drop in radioactivity over time ;
Moved out of cell / exocytosis / secreted ;
As protein / named example ;
Radioactivity will not reach zero ;
Because some, amino acids / proteins, incorporated ;max 3
[11]
239. (a) Glucose ;
Fructose ; 2
[allow either way round]
(b) Same slope / mass of products , at lower temperatures / below 43°C ; 1
(c) (Activity of) both increases as temp. increases up to 45°C ;
Credit manipulated figures from graph up to 43°C;
Peak / optimum , at 43 to 45°C / lower for solution
and 51 to 52°C / higher for immobilised ;
Comparison of figures between 42 °C – 60°C ;
Activity ceases at 60°C / lower for solution and 69
to70°C / higher for immobilised ; max 3
David Kaunda High School 177
(d) Immobilised enzyme / more stable (at high
temperatures) ;
Because held in position / eq ; 2
(e) Constant / stated, temperature / time for both ; (below 43 °C )
Same / stated volume / concentration, of sucrose
solution / substrate ;
Same / stated volume / concentration, of enzyme / sucrose ;
Use buffers over range of pH ;
Mass of products determined ;
Plot graph of mass of products against pH for sucrase
solution and immobilised sucrase ; max 4
[12]
240. Award marking points only in correct context
1 Consists of amino acids held together by peptide bonds (in either) ;
2 Insulin is globular and collagen is fibrous ;
3 Hydrogen bonds hold, secondary structure / (alpha) helix / beta strands, in shape (in
either) ;
4 R groups determine, tertiary / 3D, shape (in either) ;
5 Reference to named type of bonding in tertiary structure ;
Insulin
6 Relatively small protein / 51 amino acids ;
7 Reference to, alpha helix / beta sheet ;
8 Two polypeptide chains / A chain and B chain ;
9 Reference to disulphide bonds ;
10 Reference to binding site for cell membrane receptor ;
Collagen
11 Relatively large protein / over 1000 amino acids ;
12 3 polypeptide chains / triple helix ; [ignore alpha here]
13 Hydrogen bonds between chains ;
14 Regular amino acid sequence / repeating sequence ;
15 Molecules form (micro)fibres / cross-linking between molecules ;
[10]
David Kaunda High School 178
241.
Feature Haemoglobin Myoglobin
Is carried in the
blood.
X
Transports oxygen
X
Acts as an oxygen
store in muscle
X
Transports carbon
dioxide
X
Any two correct boxes for one mark
[4]
242. (a) A right atrium ; [accept right auricle]
B (pulmonary) semilunar valve ;
C mitral / biscupid / (left) av, valve ; 3
(b) 1 Reference to, pacemaker / SA node / SAN ;
2 (Wave of) excitation / eq, in (walls) of atria ;
3 Causes contraction of (muscle in) atria (walls) ;
4 Delay at, AV node / AVN ;
5 Conducted to ventricles via, bundles of His / Purkyne fibres ; max 4
[7]
243. (a) A – villus ; [accept villi]
B – lymph vessel / lacteal ; [accept lymph capillary]
C – crypt (of Lieberkuhn) ; 3
(b) (Villi / microvilli, provide) large surface area ;
To increase rate of absorption / uptake;
Simple / single layered, epithelium / single layer of cells;
Provides short (diffusion) pathway / distance ;
Presence of capillaries ;
To absorb / transport, amino acids / glucose / any other
correctly named substance
David Kaunda High School 179
or
To maintain, diffusion gradient / concentration gradient;
Capillaries near surface ;
Provides short (diffusion) pathway / distance;
Presence of lacteal ;
To absorb / transport, fatty acids / lipids / fats
/ oils / fat
soluble vitamins ;
Presence of (smooth) muscle ;
To assist, contact with contents / mixing; 2+2
max 4
(c) Amylase ;
Lining / epithelium / mucosa, of small intestine / ileum /
duodenum ;
Glucose + galactose ;
Glucose + fructose ; 4
[11]
244. (a) One peak before day 14 ;
One peak after day 14 ;
[If more than 2 peaks, (1 mark) only] 2
(b) Corpus luteum / yellow body / ovary ; 1
(c) Maintenance of, endometrium / lining of uterus /
secretory phase / inhibits, LH / FSH secretion /
inhibits the, LH / FSH releasing hormone /eq ; 1
(d) Regression / degeneration / eq, of corpus luteum /
yellow body ;
Because less LH present / secretion of LH inhibited /
inhibition of LH releasing factor ; 2
(e) Remains high / continues to increase / does not
decrease ;
Because, corpus luteum / yellow body, persists / eq ;
Correct reference to human chorionic gonadotrophin
/ HCG ; max 2
[8]
David Kaunda High School 180
245. Note: Do not credit 'reduce water loss' alone, as this is stated in the question.
Thick cuticle ;
Impermeable to water or
Reduces, transpiration / diffusion of water (vapour) /
reduces evaporation ;
Few stomata / stomata on inside of leaf ;
Reduces, transpiration / diffusion of water (vapour) /
reduces evaporation ;
Leaf rolled / eq ;
Reduces (exposed) surface area / stomata open into
enclosed space / maintains high humidity inside leaf /
reduces transpiration / reduces evaporation ;
Stomata in pits / sunken stomata ;
Reduce air movement / increase humidity / reduces
transpiration / reduces evaporation ;
Presence of hairs / eq ;
Reduce air movement / trap moist air (next to leaf) /
reduce diffusion (gradient) / reduces transpiration /
reduces evaporation ;
Presence of hinge cells ;
To curl leaf ; 2+2+2
[6]
246. (a) Transfer of pollen (grains) ;
From anther to stigma ;
By named agent, e.g. wind / water / insect / animal ; max 2
(b) Large anthers ;
Large numbers of pollen (grains) produced ;
Exposed / swinging / versatile, anthers / long filaments /
exposed stamens ;
Pollen shed into air / shaken by wind ;
Exposed / feathery, stigmas ;
Large surface area to, catch / trap, pollen (grains from the air) ; 2+2
max 4
(c) Protandry /male /eq parts ripen before female /eq ;
Protogyny / female /eq parts ripen before male /eq;
[male and female parts ripen at different times = 1 mark]
Dioecious plants / individual plants either male or female ; max 3
[9]
247. (a) Tubifex / sludgeworm / rat-tailed larva /
midge larva / Chironomus larva / bloodworm / gnat larva /
mosquito larva; 1
David Kaunda High School 181
(b) Haemoglobin / respiratory pigment (in blood) ;
Picks up oxygen (at low external oxygen
concentrations) / very high affinity for oxygen ;
Very thin body wall ;
Short oxygen (diffusion) pathway ;
Blood (vessels) near body surface ;
Short oxygen (diffusion) pathway ;
Waving tail ;
Circulates water next to body / eq. ;
Reference to breathing tube / eq ;
Goes to surface / to obtain oxygen from the air ; 2+2
max 4
Presence of hairs / wing cases / elytra ;
To trap an air bubble ;
[Credit other correct example]
[5]
248. (a) To provide oxygen ;
For aerobic respiration ;
Reference to requirement for ATP (produced by
respiration) ; max 2
(b) 38.1 ÷ 7.29 ;
= 5.2 ; [accept 5.23] 2
(c) They are taken up, by active transport / active uptake /
actively ;
Because the concentration in cell sap is higher than
concentration in culture solution / ions are taken up
against a concentration gradient ; 2
(d) (i) Concentrations of ions increases as temperature
increases ;
Credit any quantitative description ; 2
(ii) (Increase in temperature) increases, kinetic energy /
movement (of ions);
Increases enzyme activity ;
Increases, (rate of) respiration / production of ATP ;
Increases (rate of) collisions of ions with transporter
protein / eq ; max 2
[10]
David Kaunda High School 182
249. Accept points only in correct context
1 Carbon dioxide in and oxygen out during, day / light and
carbon dioxide out and oxygen in during, night / darkness ;
2 Photosynthesis and respiration during day but only respiration at night ;
3 (During day) photosynthesis provides (more than enough) oxygen for respiration/ eq ;
4 Gases / oxygen / carbon dioxide, enter / leave, through stomata ;
5 (Passive) movement, down concentration gradient / by diffusion ;
6 Guard cells control opening of stomata ;
7 Description of mechanism of, opening / closing ; [e.g. changes in turgor / movement of
potassium / protons / pH / water]
8 Influence of an environmental factor on, opening / closing stomata ;
9 Large surface area provided by, flat leaf / spongy mesophyll cells ;
10 Air spaces allow, rapid / easy, diffusion within leaf ;
11 Thin leaf for, rapid diffusion / short (diffusion) pathway ;
12 Thin cell walls (in mesophyll) for, rapid diffusion / short (diffusion) pathway;
13 Moist, cell surface / walls (of mesophyll), to enable gases [accept named gas] to dissolve ;
14 Reference to gas exchange in roots ;
15 Reference to lenticels in woody stems / eq ;
Credit any point from well drawn and annotated drawings
[10]
250. (a) 1 Increase in, body mass / length / size / height ;
2 Irreversible / permanent, increase ;
3 By cell multiplication / division / enlargement / mitosis;
4 Reference to increase in complexity ; max 2
(b) (i) CNS / brain, has developed early / converse (other
parts of body develop later) ;
Rest of body growing faster than head ;
Reference to ease of birth ; max 2
(ii) Growth hormone / somatotrophin / androgens /
testosterone /oestrogen /thyroxine ; 1
[5]
251. (a) Concentration (of sodium ions) decreases ;
Credit quantitative comment, e.g. 90 mmol per dm3 ; 2
(b) Sodium (re)absorbed (by cells in duct) / diffuses out ; 1
David Kaunda High School 183
(c) Evaporation ;
Reference to latent heat ;
Heat taken from, skin / blood / body ; max 2
[5]
252. (a) Oxygen (in inspired) air diffuses into blood from
alveolar (air) ;
Carbon dioxide diffuses out of blood into alveoli ;
Oxygen used in respiration / carbon dioxide produced
in respiration ; 3
(b) Breathing / ventilation rate, will increase / become quicker
/ faster / more rapid ;
Depth of breathing / tidal volume increases /
Carbon dioxide , detected by / stimulates, chemoreceptors ; max 2
(c) Percentage oxygen will increase ;
% Carbon dioxide will decrease ;
Reference to increased alveolar ventilation / eq. ; max 2
(d) (i) Car exhaust / cigarettes / tobacco smoke / gas appliances /
incomplete burning of fuel ; 1
(ii) Combined / binds , with haemoglobin ;
As carboxyhaemoglobin ;
Irreversibly / reference to higher affinity for Hb than
oxygen / eq ; max 2
[10]
253. (a) (i) Accept answer in range 0.26 to 0.28 kg ; 1
(ii) (Placental mass at 10 weeks) = 0.1 (kg) and (at 40
weeks) = 0.47 to 0.48 (kg) ;
(Increase) = 0.37 to 0.38 (kg) ;
(% increase) = 0.38 × 100 ÷ 0.1 = 380 (%) ;
or 0.37 × 100 ÷ 0.1 = 370 (%) 3
(b) 1 Both increase throughout / from 14-40 weeks ;
2 Increase (in mass) of both is the same, for first few
weeks / up to 12-14 weeks / mass stays same in both
up to 12-14 weeks ;
3 Then fetal mass increases more rapidly than placental mass ;
4 Rate of change of placental mass is relatively constant
(between 14 - 40 weeks) but rate of change of fetal
mass increases at 18 (or 28) weeks ;
5 Comparative use of figures relating to change in mass ; max 3
David Kaunda High School 184
(c) 1 At placenta, mother’s blood (with drug) in close
contact / doesn’t mix with fetal / baby blood / eq ;
2 Placenta permeable to drug / in placenta drug diffuses /
passes from mother’s to fetal / baby blood ;
3 Drug could affect, metabolism / activity, of fetus /
baby ;
4 Fetal / baby liver not developed enough to remove drug ; max 3
[10]
254. Allow points only in correct context
1 High altitude defined as above 3000 m ;
2 Acclimatisation defined ;
3 Reference to low partial pressure / p.p.O2 of oxygen ;
4 Increase in, breathing rate / depth of breathing / ventilation / tidal volume /
hyperventilation ;
5 Increase in, cardiac output / heart rate / stroke volume / blood pressure ;
6 Increase in, pulmonary / lung, diffusion capacity ;
7 By increase in lung surface area ;
8 By increase in, pulmonary / lung / alveolar, capillaries ;
9 Increased haemoglobin (in red blood cells) / increase in number of R.B.C ;
10 Reference to erythropoetin ;
11 Linked to increased oxygen transport ;
12 Correct reference to shift in dissociation curve / higher affinity for O 2 by haemoglobin
13 Reference to vasoconstriction ;
14 Reduces heat loss through, radiation / convection ;
15 Increased pigmentation of skin protects against ultraviolet ;
[max 10]
255. (a) side to side / rotating / circular movement ;
ridges (of enamel) ;
act as cutting edges / grinding (action/surface); max 2
(b) manipulation of, grass / food ;
to expose different surfaces to teeth / eq;
keep chewed grass separate from fresh grass ; max 2
David Kaunda High School 185
(c) fermentation / breakdown / digestion of, cellulose /
fibrous material / cell walls
or reference to cellulase ;
by, microorganisms / gut fauna / bacteria / protozoa ;
regurgitation / rechewing / storage or time for action of
bacteria / idea of second digestion ; max 2
[6]
256. (a) fuel / energy source / charcoal / burning for purpose ;
building material / reference to specific structural use /
construction / furniture ;
paper making ;
turpentine / named chemical product from wood ;
ignore 'timber', medicines, rubber max 2
(b) agriculture / cultivation / industrial use / urbanisation ;
reference to patterns showing planted crops / rows /roads /
terraces / increased population / increased demand for
food / economic reasons ; 2
(c) (biodiversity) reduced / fewer, species / varieties / types / eq.
reference to loss of habitats / niche / disruption of food
chains; 2
(d) fewer, trees / plants, less photosynthesis ;
reference to absorption of carbon dioxide by, trees / plants
/ photosynthesis ;
burning (of trees) releases carbon dioxide ;
rotting / decay, (of felled trees) / respiration, releases
carbon dioxide or soil disturbance releases carbon dioxide ; max 3
(e) Using, trees / forest, in such a way as not to, destroy /
reduce / use it up ;
Over a (relatively) long time period (minimum 5 years) ;
Timber is, cut / eq. at the same rate as it can be, grown /
regenerated / replanted / eq.;
Example – e.g. coppicing / selective felling / rubber
tapping / pollarding / replanting / reforestation ; max 3
[12]
257. (a) biomass
weight / mass, of, organisms / plants & animals ;
productivity
rate at which biomass / materials produced /
synthesised / energy incorporated / energy transferred
(into a trophic level) (could be expressed as per unit time ) ; 2
David Kaunda High School 186
(b) (i) grazed - (increase of) 150 so rate is 150 / 32 =
4.7 / 4.69 g m–2 day–1
ungrazed - (decrease of) 130 so rate is 130 / 32 =
4.1 / 4.06 g m–2 day–1
(note – allow 31 days, giving 4.8 and – 4.19 )
change for both correctly read (could be 200-50/ 32
and 300-430/32) ;
correct rate calculation for grazing ;
correct rate for ungrazed with negative sign ;
correct units for either ;
(allow consequential error if wrong reading but correct maths) 4
(ii) no / lack of, compensatory growth ;
competition for light / long leaves shading other leaves /
less light penetration ;
reduced photosynthesis ;
competition for, water / nutrients / minerals ;
leaves dying ;
grass being grazed by, birds / insects (that can fly in) ; max 3
(c) (i) 0.5 arbitrary units ; 1
(ii) (large numbers of) animals, trample/crush, grass ;
overgrazing / too many grasses/plants eaten/damaged /
reference to exceeding carrying capacity ;
grasses unable to recover / few leaves so little
photosynthesis / takes longer to grow back ;
too much excreta / dung / urine /eq ;
reference to soil compaction + qualification ; max 3
(d) fewer, grazing animals / named grazers / herbivores
killed, so numbers increase ;
leads to, overgrazing / more grasses/plants eaten /
reduction in numbers of primary producers ;
grassland has reduced / less productivity ;
leads to, grass shortage/ reduced biomass of grass,
fewer / death of grazing animals / grazing animals
migrate / reduced reproduction rate ;
increase in numbers of other/named carnivores / decrease in scavengers / named
scavengers ; max 3
David Kaunda High School 187
(e) (Converted to) ammonium;
by, decomposers / saprophytes / bacteria / fungi /
putrefying bacteria ;
(ammonium) oxidised to nitrite ;
by nitrifying bacteria (allow once) / Nitrosomonas / Nitrococcus ;
(nitrites) oxidised to nitrate ;
by nitrifying bacteria / Nitrobacter ;
Note can use chemical symbols but must be correct max 4
[20]
258. (a) A Plasma membrane / cell membrane / cell surface membrane;
B Centriole(s) / microtubule(s) / centrosome;
C Golgi apparatus / Golgi body / smooth ER;
D Rough ER / ribosome; 4
(b) (Accept measurement between 11 and 12 mm)
11 ÷ 12 000; OR 12 ÷ 12 000;
= 0.92; = 1.0 2
[6]
259. (a) A Glycerol / propan - 1, 2, 3 - triol
B Fatty acid (s) / fatty acid chain 2
(b) Triglyceride 1
(c) Condensation / esterification 1
(d) Energy store or source / insulation /waterproofing /
production of metabolic water / buoyancy / protection; 1
(e) insoluble / non-polar / high energy value / poor heat conductor /
low density / less dense than water (points in (e) need to be correctly
linked to the answer given in (d)) 1
[6]
260.
Statement Starch Glycogen Cellulose
Polymer of aglucose
Glycosidic bonds present
Unbranched chains only
Energy store in animal cells
[4]
David Kaunda High School 188
261. (a) Diffusion of water molecules;
Through a partially permeable membrane;
From a region of high concentration of water molecules to a region of lower;
concentration of water molecules/eq in terms of water potential; 3
(b) Means whereby polar molecules are transported across membranes;
Molecules bind with transport proteins;
Transport protein changes shape and moves molecule across membrane;
No metabolic energy required; 3
[6]
262. (a) A = Flagellum;
C = (Peptidoglycan) cell wall;
D = (Circular) DNA / chromosome / nucleoid; 3
(b) B = location of enzymes associated with aerobic respiration;
C = maintains shape / protection / etc;
E = storage of carbohydrate / eq; 3
[6]
263. (a) (Lower) epidermis of leaf;
Stomata allow gaseous exchange / eq;
Protection from desiccation / eq;
Allows penetration of light to photosynthetic mesophyll; 3
(b) Correct size / magnification;
Correct proportions;
Minimum number of cells / both stomata and cells touching;
Cell wall thickness appropriate;
Accurate detail of cell contents in guard cell; 5
[8]
264. (a) Protein / polypeptide / eq 1
(b) RER has ribosomes;
Site of protein synthesis; 2
(c) Proteins / polypeptides / move to Golgi apparatus;
Ref. to protein modification;
Enclosed in membranes to form vesicles;
So most activity in vesicles after 45 minutes; 3
(d) Amino acids moving between sites / eq;
Amino acids being broken down / metabolised;
Proteins used in other parts of cells / eq;
Proteins also synthesised in mitochondria / eq; 3
(e) Exocytosis;
Vesicles move to cell membrane;
Vesicle fuses with cell mebrane;
Contents released outside cell; 3
[11]
265. (a) To keep pH constant / enzymes are affected by pH 1
David Kaunda High School 189
(b) Rate increases as substrate concentration increases
Steady / constant / linear increase between 20 to 80* mmol dm–3;
Then begins to level off;
(*accept any quoted figure in this range) 3
(c) As substrate concentration increases, the number of collisions / number of
enzyme - substrate complexes will increase;
Therefore the rate will increase;
Until all enzymes in use / limited number of active sites;
Rate then remains constant / reaches a maximum / ref to V max; 3
(d) Use equal volumes of hydrogen peroxide solution;
And distilled / deionised water / buffer solution;
(accept suggested volumes); 2
(e) Use a water bath;
Suggested range of temperatures (at least 3 stated)
Use same substrate concentration;
Use same volume / depth of hydrogen peroxide
Allow substrate / enzyme to equilibrate before adding filter paper disc
Ref. to uniformity of discs;
Use constant enzyme concentration;
Repeat at each temperature;
Plot a graph of rate of reaction against temperature; 4
[13]
266. 1 Daughter cells have same number of chromosomes as parent cell / are genetically
identical to parent cell;
2 Concerned with growth / repair / replacement of tissues / asexual reproduction;
3 Reference to cell cycle consisting of interphase, mitosis, cell division
4 (During prophase) chromosomes condense / eq so each consists of a pair of chromatids
joined by centromere;
5 Reference to centrioles / movement / position
6 Formation of spindle by microtubules;
7 Disappearance of nucleus / nucleoli
8 Breakdown of nuclear envelope;
9 (At metaphase) chromosomes attached to spindle fibres
10 Lined up at equator of cell :
11 1 (At anaphase) centromeres split / duplicate / separation of chromatids
12 Daughter chromosomes / chromatids pulled to opposite poles of cell (at telophase)
chromosomes / chromatids reach poles of cell;
13 Formation of nuclear membrane / (daughter) nuclei formed;
14 Followed by cytokinesis (in animal cells) / or description
15 Formation of a cell plate / eq in plant cells;
[10]
267. (a) Large surface area;
Thin lining;
(Partially) permeable (lining);
Covered by film of moisture; 3
David Kaunda High School 190
(b) Contraction of diaphragm muscles lowers / flattens diaphragm;
Contraction of external intercostal muscles raises ribcage;
Volume of thorax / lungs increases thus intrapulmonic pressure;
falls / eq;
Ref. to control by medulla / eq; 3
[6]
268. (a) A = (Aortic) semilunar valve;
B = Bicuspid / mitral / valve / left atrioventricular valve; 2
(b) Diastole / atrial systole;
Aortic / pulmonary artery / semilunar valve(s) closed;
Atrioventricular / mitral / tricuspid valve(s) open; 3
(c) X = prevents valve inverting;
Y = adjusts tension in valve / contracts to pull on valve; 2
[7]
269. (a) Percentage falling / fall of 35%;
Biggest drop in sixties/ between 1951-1970;
Some evidence of flattening / ref. to figures; 2
(b) Lower percentage of men with low sperm counts at beginning;
Numbers increasing during the period / increased by 13%;
Both fall 1971-1980;
Fall in percentage of men with high sperm counts is greater than
rise in percentage of men with low sperm counts / converse;
Biggest rise in numbers in sixties/ corresponds with drop in
numbers of men with high sperm counts / fluctuations in numbers
of men with low sperm counts;
After 1980 figures similar; 3
(c) Large numbers do not reach fallopian tubes / site of fertilisation
Many sperm die;
Ref. to conditions / pH in vagina;
Enzymes needed for activation of sperm / ref. capacitation;
Many sperm may be abnormal / reduced mobility; 2
(d) (i) Stimulated by FSH;
Stimulates repair of the endometrium / lining of uterus;
Inhibits FSH production;
Stimulates LH production;
Leads to ovulation; 3
(ii) In maternal blood / blood stream;
When fat stores mobilised / broken down;
Correct ref. to diffusion;
Correct ref. to placenta;
Uptake into fetal circulation / fetal blood;
Into umbilical vein; 3
[13]
270. (a) Any value between 17.0 and 18.0% 1
(b) 90 – 18 = 72
105 × 72 ÷ 100
75.6 cm3; 3
David Kaunda High School 191
(c) Increased rate of respiration / or metabolic rate increase / e.q./ gives more heat energy /
eq;
Causing haemoglobin to release more oxygen / release oxygen faster / eq 2
(d) Curve drawn to the left of the other two;
Steeper 2
[8]
271. (a) D;
G; 2
(b) Petals/ no petals;
Sepals / no sepals;
Fixed stamens / loose stamens / eq
Knob-like stigma / feathery stigma
Short filaments/ long filaments 2
(c) Any two from:
Dichogamy / male and female parts mature at different times;
Protandry / eq;
Pollen shed before stigma is mature
Any two from:
Dichogamy / male and female parts mature at different times;
Protogyny / eq;
Stigma withers / ripe before pollen shed
Paired marking points:
Structure of flower prevents pollen landing on stigma
Explanation of heterostyly
Ref. to dioecious plants;
Self-pollination impossible;
Self-incompatibility / sterility;
No pollen germination; 2
[6]
272.
Phloem sieve
Statement Xylem vessels
tubes
Possess living contents
Provide support
Composed of cells fused together
end to end
Walls contain lignin
[4]
David Kaunda High School 192
273. (a) P = xylem;
Q = spongy mesophyll; 2
(b) Falls in Y / or Z / moves out of Y / or Z;
Rises in X /moves into X;
Credit for correct manipulation of figures; 2
(c) Active transport of K+ ions into guard cell;
Correct ref. to lowering of water potential / eq;
Water enters guard cells by osmosis;
Increase in turgidity / eq;
Causes bending of guard cells/ eq; 3
[7]
274. (a) Water loss / transpiration equals / is proportional to water uptake; 1
(b) Cut stem underwater;
Assemble apparatus under water;
Render apparatus water tight / air tight with vaseline / wax;
(Run water through capillary to) eliminate air bubbles;
Ensure leaves / eq are dry;
Control of variables one variable specified;
Ref. to equilibration; 2
(c) (Meniscus moves) 180 mm (in 30 minutes);
(180 ÷ 30) × 0.8 / (180 ÷ 120) × 3.2
4.8 mm3 min–1; 3
(d) Moving air causes more water vapour to be lost from B than D /
less from D than B / eq;
More water (vapour) lost through stomata;
More stomata on lower surface of leaves;
Grease prevents water loss through / blocks these stomata / acts as a barrier 3
[9]
275. 1 Lower / more variable concentrations of oxygen in water than in air / eq ref. To
solubility;
2 Very low / anaerobic conditions in mud / undisturbed water / eq;
3 Disturbance / photosynthesising plants increases oxygen levels;
4 In small invertebrates / eq surface area to volume ratio important for efficient diffusion /
e.g. protozoa / coelenterates absorb oxygen all over surface exposed to water;
5 Flattened body shapes increase surface area to volume ratios / so planarians /
leeches can absorb sufficient oxygen;
6 Gills provide larger surfaces for gas exchange in some aquatic insect larvae / named
e.g.s such as caddis fly larvae;
7 Some depend on tracheae located at hind end of insect;
David Kaunda High School 193
8 Ref. to breathing tubes and siphons in suitable e.g.s such as rat-tailed maggots / eq;
9 Problems of waterlogging overcome by the presence of hairs / eq;
10 Small insects depend on diffusion, larger ones often show ventilation movements;
11 Some take air down into the water / ref. to air bubbles / trapped air/ description or
reference to an example such as water beetle;
12 Ref. to molluscs as being typical of better aerated water;
13 Pulmonates need to come to surface for air / eq;
14 Possession of respiratory pigments aids absorption / retention of oxygen respiratory
pigments/ haemoglobin has affinity for oxygen at low pps;
15 Found in Tubifex worms / midge larvae in still water / Tubifex worms also show
ventilation movements / waving tails around to increase uptake of oxygen;
[10]
276. (a) A = secondary oocyte;
B = Graafian follicle;
C = primary oocyte / eq; 3
(b) Mitosis 1
(c) FSH / eq 1
[5]
277. (a) Caused by a reduction in the amount of organic material in bone tissue;
Due to lack of stress / inactivity in older people;
Deficiency of protein in diet;
Deficiency of Vitamin D, so Ca and P not absorbed;
Reduced secretion of oestrogen in post-menopausal women; 3
(b) Wearing away of the cartilage at the joints;
Causes pain / eq; 2
[5]
278.
E p ith e liu m
S ta te m e n t
S quam ous C u b o id a l
C e lls a re b o n d e d to a b a s e m e n t × × ;
m e m b ra n e
C e lls a r e w id e r th a n th e y a r e × ;
ta ll
N u c le i a re fla tte n e d × ;
A ll c e lls p o s s e s s c ilia ;
[4]
279. (a) Head of fetus is relatively twice size of that of new-born /
is half of body while new born is quarter / 50% compared to 25%; 1
(b) Early development of brain / sense organs in head;
Rest of body / limbs grow more slowly;
Since not needed for locomotion before birth / in uterus; 2
David Kaunda High School 194
(c) Head of 25 year old (relatively) smaller (than 6 year old);
Limbs of 25 year old (relatively) longer;
Body / trunk of 25 year old (relatively) longer;
Genitalia of 25 year old (relatively) larger;
Shoulders of 25 year old (relatively) larger / wider; 3
(d) Androgens / testosterone;
Growth hormone / somatotrophin;
Genetic inheritance;
Thyroxine / corticosteroids;
Supply of nutrients / food / diet;
Effects of exercise; 2
(e) Different parts of body / organs grow at different rates;
Growth in height not always accompanied by growth in mass / growth in mass during
growth spurts follows growth in height;
People with same height may have different mass / people with same mass may be of
different heights;
Mass may be subject to temporary fluctuations / eq / obesity/ pregnancy menstrual cycle
which do not reflect any growth;
Difficult to measure height in young babies; 4
[12]
280. 1 Skin colour related to heat radiation / loss from body / eq;
2 Ref. to nose shape e.g. narrow in low temperature / related to
temperature of air entering / leaving lungs;
3 Low temperature, straight hair / high temperature coiled hair;
4 Related to heat loss from neck head;
5 Ref. to high / low amount of subcutaneous fat / related to (thermal) insulation;
6 Low temperature, short and stocky / short limbs eq // high temperature, tall and thin /
long limbs / eq;
7 Related to surface area and degree of heat loss / correct ref. to surface area to volume
ratio;
8 High temperature, behavioural adaptations e.g. sleep / shade
9 Low temperature, reduced bradycardia (lower heart rate);
10 Correct ref. to level of sweating / heat loss due to vaporisation
11 Correct ref. to vasoconstriction / vasodilation;
12 Loose / no clothing in high temperature / pale / light clothing reflects heat / thick / many
layers / eq of clothing in cold temperature;
13 Housing qualified e.g. thick walls for insulation / small windows reduce wind;
14 Increased food intake in low temperature / decrease in high / increased water intake in
high temperature
15 Use of fire in cold
[10]
281. (a) Holds on to gut wall / eq;
To prevent removal (from host);
Ref. to peristalsis; 2
David Kaunda High School 195
(b) Ref. to parasitism;
(Host’s) food absorbed through body wall / cuticle / eq;
Food digested by host/ eq; 2
(c) Rhizopus is a saprobiont / saprophyte / description / eq;
Digests own food / extracellular digestion / eq; 2
[6]
282. (a) Loss of vegetation cover;
Exposed soils dry out;
Soil erosion;
Soils blown over surrounding land;
Salinisation; 3
(b) More animals kept / increasing human population /
restricted migration due to national borders /
falling rainfall has upset the balance / lower levels of recovery by plants; 1
(c) More water available for crops;
Growing crops less suited to climate / cash crops;
Increased irrigation;
More vegetation so more grazing animals;
Human migration into region;
Population increase above carrying capacity; 2
(d) Crop failure;
Widespread famine;
Loss of vegetation cover;
Increased rate of desertification; 2
(e) Increasing global temperatures;
Shift in climate belts;
Lower rainfall; 2
(f) Planting trees shelter belts;
Agroforestry (trees and crops);
Building earth banks / bunds to stop water running off;
Terrace sloping land;
Cover soil with mulches / plastic to reduce evaporation;
Grow drought resistant / salt tolerant crops;
Use native species of animals which tend not to overgraze; 2
[12]
283. (a) Burning fossil fuels in power stations / cars;
Release of sulphur dioxide and nitrogen oxides;
Release of ozone / hydrocarbons;
React together to form acids dissolved in rain;
Specific gas linked to a named acid / eq; 4
(b) pH level stable at approx. 5.6-5.8 for more than 75 years;
Decrease in pH only occurred since 1975;
Drop of more than one pH unit;
Spread of industry;
Burning more fossil fuels;
Increased power generation / more power stations;
Clearance of forests from the area;
Not due to Industrial Revolution as changes too recent; 4
David Kaunda High School 196
David Kaunda High School 197
(c) Other changes in water quality;
Misidentification;
Disturbance of the sediment by animals;
In-wash of diatoms from streams; 1
(d) Affects larger organisms, especially fish and amphibians;
Affects gills of fish;
Due to increased mucus production;
Reduces viability of the fish and amphibian eggs / eq; 3
(e) When aluminium concentration is at 0, the survivorship is nearly 100 with both
treatments;
For both treatments, as aluminium concentration increases survivorship of fry decreases;
Greater survivorship at higher levels of aluminium with the higher calcium concentration;
In high calcium and high aluminium, survivorship is greater at lower pH;
In low calcium and high aluminium, survivorship is greater at pH 5.4; 4
(f) Aluminium comes from soil;
Liming soil will neutralise run-off into the lake;
Longer lasting effect;
Liming water is short-term as more acidity drains
into the lake from surrounding streams and slopes / eq; 2
(g) Legislation / large combustion plant plants directive;
Fitting flue gas desulphurisation filters to chimneys of power stations;
Fitting catalytic converters to cars / emission standards on engines; 2
[20]
284.
Feature Prokaryotic Cell Eukaryotic cell
Cell surface membrane
Plasmids X
Ribosomes
Mitochondria X
[4]
Any two correct boxes for one mark
Blanks are incorrect
Circle correct answers
Put in appropriate number of ticks for total mark
David Kaunda High School 198
285. amino acids / polypeptides / peptides ;
peptide ; [not dipeptide] [accept peptide / hydrogen / disulphide / ionic if peptide or
polypeptides given above]
condensation / polymerisation ;
() helix / (alpha) helix ;
hydrogen / H ;
[5]
286. (a) (net) movement / eq of, molecules / ions / particles / gases / solute / named
example ;
from high concentration to low concentration / down a concentration gradient ;
[ignore references to membrane] 2
(b) concentration gradient / eq ;
temperature ;
(diffusion) distance / thickness (of membrane) ; [not ‘size’]
permeability (of membrane) ;
surface area (of membrane) ;
size of, molecules / ions / particles ;
polarity / solubility in lipids / eq ; 2
(c) (active transport) up / against concentration gradient / from low to high
concentrations / involves carriers / ATP / energy / respiration ; 1
[5]
287. (a) 1. (mRNA) is a copy of DNA ;
2. (copy of) part of DNA / eq ;
3. (copy of) one strand / sense strand ;
4. mRNA is complementary (to DNA) / mRNA made up of complementary
bases ;
5. mRNA strand, built / formed (looking for idea that mRNA strand is put
together during the process) / reference to enzyme ;
6. carries genetic code to, cytoplasm / out of nucleus / to ribosome ; 3
(b) 1. genetic information / base sequence / code, in mRNA determines
amino acid sequence ;
2. codons / base triplet on mRNA ;
3. determines amino acid ;
4. (codons) pair with, complementary triplet / anticodons, on tRNA ;
5. reference to start / stop codons / sequences / binding sequences ;
6. occurs on ribosomes ; 3
[6]
288. (a) centrioles / centrosomes ;
asters ;
no cell wall ;
[ignore chloroplasts and vacuole] 2
(b) A chromatid / chromosome / daughter chromosome ;
B spindle (fibres) / microtubules ; 2
(c) anaphase ; [ignore I or II] 1
David Kaunda High School 199
(d) 80 ÷ 1000 ; [accept 80 to 83 or 8 to 8.3]
0.08 mm / 0.008 cm / 80 m ; [accept answer consistent with measurement] 2
[7]
289. (a) pH ;
enzyme concentration ;
enzyme (solution) volume ;
substrate (solution) volume ;
total volume ; 2
(b) more collisions / complexes ;
with, enzyme / active site (and substrate) ;
in unit time / eq ; 2
(c) enzymes are working as fast as they can / reference to Vmax ;
all active sites occupied / eq ;
substrate concentration is no longer a limiting factor ;
enzyme concentration is limiting ; 2
(d) line on graph begins at zero and is below original line ;
less kinetic energy / molecules moving more slowly ;
fewer collisions (between enzyme and substrate) ;
less energetic collisions ;
in unit time / eq ; 3
[9]
290. (a) prevent, entry / exit, of water ;
by osmosis ;
which may affect / eq, organelles ; 2
(b)
Pellet Organelle
A nuclei ;
B mitochondria ;
C ribosomes ;
2
(c) glucose / monosaccharides / disaccharides / sugar ;
glycogen ;
proteins / (poly)peptides ;
enzymes / suitable named example ;
ions / named example ;
amino acids / named example ;
lipids / phospholipids / triglycerides / fats ;
microtubules / centrioles ;
microfilaments ;
RNA / mRNA / tRNA ;
[accept other correct substances present in liver cells] 2
David Kaunda High School 200
(d) two membranes shown [M] ;
inner membrane shown folded [F] ;
membrane / envelope ;
intermembranal space ;
cristae ;
matrix ;
ribosomes / DNA, in matrix ;
stalked particles / ATPase ; 4
(e) to produce (large amounts) of ATP ;
by, aerobic respiration / Krebs cycle / electron transport chain ;
(because) liver cells are (metabolically) very active / eq ; 2
[12]
291. (a) A phosphate ;
B pentose / ribose / deoxyribose / 5C sugar ;
C purine / pyrimidine / (organic) base / named example ; [watch spelling] 3
(b) U C G G C AG G G C AG ; ;
[one mistake = 1 mark, two mistakes = 0] 2
(c) making new DNA / copying DNA ;
makes identical copies ;
new molecule has one old and one new strand ;
DNA strands separate / eq ;
each strand acts as a template ;
individual nucleotides line up against (old) strand ;
complementary base pairing ;
nucleotides joined (by DNA polymerase) ; 4
(d) one eighth / 12.5% ;
eight strands have been formed from each original strand / eq ; 2
(e) interphase / S phase ; 1
[12]
David Kaunda High School 201
292. Accept points only in correct context
1. phospholipid bilayer ;
2. polar / phosphate / hydrophilic (groups of phospholipids) face outwards ;
3. nonpolar / hydrophobic / fatty acid tails face inwards ;
4. reference to cholesterol ;
5. molecules can move around ;
6. proteins present in membrane ;
7. qualification of the location of these proteins ;
8. glycosidic / carbohydrate side chains on lipids / proteins / glycolipids /
glycoproteins / glycocalyx ;
9. involvement of proteins in transport (across membrane) ;
10. by active transport / facilitated diffusion described (e.g. reference to
attachment / change in shape) ;
11. some proteins are enzymes ;
12. partially / selectively permeable / eq ;
13. reference to cell-cell interaction / recognition / antigens ;
14. reference to receptors for hormones / neurotransmitters ;
15. vesicle fusion / formation / description of membrane involvement in
exo- or endo-cytosis ;
[10]
293. (a) neutrophil / polymorph / granulocyte / eosinophil ;
defence against disease / eq ;
phagocytosis / engulfing / description ; [but not if secretion of antibodies
included]
microorganisms / bacteria / pathogens / microbes /
cell debris / eq ; [ignore viruses] 3
(b) large surface area (to volume ratio) ;
reference to biconcave shape ;
for increased, diffusion / uptake / release ;
of, oxygen / carbon dioxide / respiratory gases ; 3
[6]
294. (a) large surface area ; increases diffusion ;
thin (wall) / single cell ; reduces diffusion distance ;
reference to surfactant ; stops adhesion / eq ;
reference to capillaries ; maintains, diffusion /
concentration gradient ; 2+2
(b) external intercostal muscles contract ;
diaphragm (muscle) contracts ;
volume of thorax increases ;
pressure decreases ; 3
[7]
295. (a) number of chromosomes halved / haploid number (n) formed / 23 ;
so that diploid number (2n) restored at fertilisation / in zygote / 46 ;
reference to genetic variation ; 2
(b) secondary oocyte ; 1
(c) oestrogen ;
progesterone ; 2
David Kaunda High School 202
David Kaunda High School 203
(d) oogenesis cyclical AND spermatogenesis continuous ;
oogenesis starts in fetus AND spermatogenesis in puberty ;
polar bodies formed in oogenesis AND not in spermatogenesis ;
oogenesis completed after sperm entry ;
one egg produced AND four sperm produced ; oogenesis stops at
menopause AND spermatogenesis continues ; 2
[7]
296. (a) (TL) 10.6 to 10.8 kPa ;
(TU) 3.5 kPa ; [penalise once if no units] 2
(b) loading tension increases ;
unloading tension increases ;
[‘both increase’ = 2 marks] 2
(c) any named organ / reference to cells / tissue (not ‘lungs’) ;
reference to respiration / metabolism ; 2
(d) has greater affinity for oxygen / eq ;
therefore takes up oxygen from mother ;
from mother’s haemoglobin / red cells ;
reference to transfer of oxygen across placenta ; 3
[9]
297. (a) A vascular bundle ;
B xylem (vessel) ; 2
(b) storage of gases / air / oxygen / carbon dioxide ;
gas exchange / gas diffusion / gas movement ;
buoyancy / eq ; 2
(c) submerged:
less resistance to water flow ;
less likely to be damaged by water currents / eq ;
reference to gas exchange ;
large surface area ;
floating:
large surface area ;
(increased) exposure to air ;
(increased) light trapping ;
reference to photosynthesis ;
stomata on upper surface ; 4
any FOUR points for 4 marks
[8]
298. (a) A anther ;
B stigma ; 2
(b) acts as a landing platform / eq ;
colourful / conspicuous / markings / scented ;
to attract insects / any suitable animal ;
pollen brushed from insect on to part B / stigma ; 3
[5]
David Kaunda High School 204
299. (a) A sieve tube / sieve element ;
B companion (cell) ; 2
(b) reference to presence of sieve plates / pores / small amount of cytoplasm /
lack of nucleus / few organelles ;
to allow transport, from cell to cell / of organic solutes ;
plasmodesmata (connecting to companion cell) ;
allows passage of substances between cell B and cell A ; 2
(c) (i) comparative comment for each solute e.g.
sucrose - none in xylem, high concentration in phloem ;
sodium - higher concentration in phloem ;
nitrate - none in phloem but present in xylem ; 2
(ii) to roots / underground storage organs ;
converted to starch for storage ;
to growing regions / growing shoots / new leaves / flower buds / other cells /
eq ;
as a respiratory substrate / synthesis of cell walls / to provide ATP / as fuel
for growth ;
to seeds / fruits ;
as fuel for growth / carbohydrate storage / provides sweetness ;
to flowers ;
for nectar ; 2
[8]
300. (a) (i) draw round leaf on graph / squared paper / grid ;
count squares ; 2
(ii) remove epidermis / use nail varnish film ;
use microscope ;
count number of stomata in unit area / given area / field of view ;
repeat and find mean ;
divide area (of field of view) into 1 and find number per cm 2 / appropriate
calculation ; 4
(b) rate of water loss increases as number of stomata increases ; 1
David Kaunda High School 205
(c) temperature ;
increase gives more (kinetic) energy / movement to water molecules ;
on surface of spongy mesophyll cells ;
greater evaporation (into air spaces) ;
increases diffusion gradient / rate (of water vapour through stomata) ;
wind / air movement ;
increases / speeds removal of water vapour / humid air ;
from (leaf) surface/ stomata ;
increases diffusion gradient (of water vapour through stomata) ;
decreases boundary layer ;
humidity ;
increase means more water vapour around leaf / stomata ;
reduces diffusion gradient (of water vapour through stomata) ;
light intensity ;
increase causes stomata to open / widen ;
so more diffusion of water vapour ;
from air spaces (in spongy mesophyll) ;
water stress / extremely high temperature / high winds ;
stomata close ;
less diffusion ;
[Accept converse points where appropriate] 3
[10]
301. Accept points only in correct context
1. presence of villi increases surface area ;
2. presence of microvilli / brush border (on epithelial cells) ;
3. (1 or 2) increase the rate of uptake / diffusion / absorption ;
4. single layer of (epithelial) cells / simple epithelium ;
5. reduces diffusion distance ;
6. presence of capillaries to, maintain diffusion gradient / concentration gradient ;
7. reference to muscle, (layers) and peristalsis / segmentation / movement ;
8. amylase (from pancreas) breaks down starch to maltose ;
9. maltase breaks down maltose to glucose ;
10. sucrase breaks down sucrose to glucose and fructose ;
11. lactase breaks down lactose to glucose and galactose ;
12. enzymes in brush border / produced by cells in lining of ileum ;
13. reference to, carrier proteins / transport proteins, in cell membranes ;
14. correct reference to sodium co-transport / facilitated diffusion / active
transport (into epithelial cells) ;
15. diffusion of monosaccharides / named monosaccharide (into blood) ;
[10]
302. (a) more protein and less fat and carbohydrate ; [accept converse] 1
(b) contains antibodies / immunoglobulins ;
confers immunity (on baby) ;
passive immunity ;
more protein for growth / development ; 3
(c) oxytocin ; 1
[5]
David Kaunda High School 206
303. (a) reference to (impulse) conduction between atria and ventricles ;
delay at AV node ;
allows ventricles to fill before contraction ; 2
(b) distance from one P wave to next (or R to R) is 56 to 58 ;
heart rate = 60 × 50 / 56 to 58 ;
= 51.7 (52) to 53.8 (54) beats per minute ; 3
[5]
304. (a) short term change ;
not inherited / not genetic ;
reversible / eq ;
in response to a changed environmental / seasonal / climatic condition ;
example of condition and change ; 3
(b) (i) initial rapid increase, rate of increase slows then increases again ;
as temperature increases (mean percentage increase in) sweat production
increases or
greatest mean percentage increase at 38.5 C ;
use of figures, i.e. calculate percentage increase between any two
temperatures ;
(percentage) increase at 2 hours not twice that at 1 hour /
words to that effect / acclimatisation occurring ; 2
(ii) sweat glands in dermis (of skin) ;
stimulated by increased temperature ;
by (nerve) impulses from hypothalamus ;
body heat removed by evaporation / vaporisation ;
of water (from skin surface) ; 3
(iii) excessive salts / ion loss or heat cramp or dehydration ; 1
[9]
305. (a) to absorb / remove carbon dioxide or prevent build-up of carbon dioxide ; 1
(b) fill spirometer with oxygen ;
reference to use of a nose clip ;
person breathes in as fully as possible ;
then out as fully as possible ;
pen records movement of lid on chart ;
vital capacity read from chart / recorded on chart ; 4
(c) (i) volume of air breathed in or out ;
in one breath / at rest / eq ; 2
(ii) 500 × 18 ;
= 9000 cm3 / 9 dm3 ; 2
(iii) tidal volume increases ;
breathing rate increases ;
carbon dioxide increases in the blood ;
carbon dioxide stimulates breathing ; 3
[12]
David Kaunda High School 207
306. (a) suitable table ;
rows and columns correct with units ;
correct calculations of percentage change in mass ;;
(1 error = 1 mark, 2 errors = 0 marks)
Concentration of sucrose / mol dm– Mass at start / g Final mass / g Percentage change in
3 mass
0 14.58 14.56 0
0.25 14.27 15.76 10.4
0.50 16.25 19.49 19.9
1.00 14.43 19.32 33.8
1.50 14.61 21.64 48.0
2.00 16.20 24.63 52.0
4
(b) line graph drawn ;
axes correctly labelled, with concentration on horizontal and percentage change on
vertical axes ;
all points plotted correctly ;
points joined with suitable lines / if histogram, bars must touch ;
[if histogram max 3 marks, last three points] 4
(c) overall increase comment ;
from 0 to 0.5 mol dm–3 / 0.5 to 1.5 mol dm–3 linear increase in
% mass change / (if line of best fit), 0 to value between 0.5 to 0.75 linear / eq,
increase in % mass change ;
above 1.5 mol dm–3 increase is less steep / (if line of best fit),
above 0.5 to 0.75 increase less steep / non-linear ;
[all above values taken from graphs] 2
(d) Maintain constant temperature (throughout) ;
Reference to identical lengths / specific dimension of visking tubing ;
dry / blot / eq. tubing before weighing ;
check seal for leaks ;
rinse tubing in distilled water after adding sugar solutions ; 2
(e) water (molecules) move by osmosis / diffuse ;
across / through selectively / partially permeable membrane ;
[NOT semi-permeable]
Correct reference to water potential / solute potential gradients / eq ; 2
[14]
David Kaunda High School 208
307. (a) 1. method of immobilisation described (alginate in solution of Ca 2+ ions) ;
2. solution of lactase prepared ;
3. same concentration of lactase in both ;
4. equal volumes / mass of both used in tests ;
5. both tested without treatment (allow at room temperature) ;
6. method of heat treatment described e.g. water bath ;
7. good range of temperatures (minimum 5, from 30-100°C, excluding
room temperature) ;
8. stated same time of treatment for each minimum 1 minute ;
9. samples cooled to standard temperature before activity tested ;
10. tested by adding to same / stated volume of lactose ;
11. same concentration of lactose each time ;
12. left / incubate for same time ;
13. reference to named method of testing for glucose produced,
e.g. test strips (diabur) / quantitative Benedicts’ test ;
14. details of quantitative method, such as mass of precipitate with
Benedicts’ / reference to colour scales for test strips ;
15. repeat whole procedure ; 9
(b) suitable table with correct rows and columns ;
line graph (bar chart if only one temperature treatment in method) ;
correctly orientated axes with labels and units ;
suitable method of rate calculation described e.g. Concentration of glucose
detected divided by incubation time ; 3
(c) difficult to standardise alginate bead sizes ;
difficult to standardise concentration in beads and solution ;
difficult to standardise time of heat treatment / higher temperatures take
longer to heat up / take longer to cool to standard temperature ;
difficult to determine end point ;
alginate / calcium ions may affect rate of reaction ;
investigate effect of different bead sizes ;
investigate the effect on other enzymes ;
investigate effect at different lactase concentrations ;
use smaller increments of temperature (around point of denaturation) ; 6
[18]
308. (a) secondary consumer / top consumer / carnivore ;
primary consumer / herbivore ;
[ignore examples] 2
(b) reference to method of sampling / quadrats / eq ;
count plants ;
collect animals/organisms from given area / eq ;
identify all the animals found (in sample) ;
determine whether each is primary or secondary consumer / sort into trophic levels ;
count number of primary / secondary consumers (in sample) ; 4
(c) reference to energy loss ;
only small percentage / approx. 10-15 %, of energy transferred between levels ;
reference to suitable reason for energy loss ; 2
[8]
David Kaunda High School 209
309. (a) (taken up from atmosphere) 93 + 121 = 214 ;
(released into atmosphere) 90 + 120 + 1.6 + 0.1 + 5.5 = 217.2 ;
difference = 3.2 Gt (year–1 ) ;
[allow consequential error] 3
(b) planting of trees ;
reference to photosynthesis ;
carbon locked up in trees / reference to lignin or wood or cellulose ;
trees live for long time / hundreds of years ;
plants / trees die and become buried in swamps / eq ;
peat forms ;
fossil fuel forms ;
reference to shells / exoskeletons / limestone / calcareous rock ;
reference to carbon sink (anywhere) ; 4
(c) reference 93 Gt taken in, 90 Gt released / net of 3 Gt taken up / eq ;
some carbon, taken up by marine animals ;
forms calcium carbonate / forms shell / exoskeleton ;
example of marine animal (diatoms, corals, molluscs etc) ;
used in photosynthesis ;
of algae / plankton ;
marine organisms die and form sediment on seabed / settle on sea bed / eq ;
(sediments form) fossils / limestone / calcareous rock / chalk / oil / gas ; 4
(d) improved fuel efficiency / eq ;
increased use of public transport / eq ;
burn hydrogen / ethanol / gasohol / biogas (rather than petrol / oil ) ;
produce / use (electricity) from nuclear / solar / wind / water / geothermal / wood / energy
crop / straw / renewable energy ;
burning gas / methane in power station rather than oil / coal ;
reference to planting trees / forests / afforestation ; 3
[14]
310. (a) 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 10, 10, 25, 12, 6, 9, 6, 6, 4 ;
total = 88 ;
[allow consequential error] 2
(b) site 1 score higher than site 2 ;
score for site 1 2.5 / nearly 3 times more than site 2 ;
site 1 less polluted than site 2 ;
site 1 score indicates moderate pollution, site 2 indicates very severe pollution ;
site 1 score indicates moderate water quality, site 2 indicates very poor water/river
quality ;
greater species diversity / more invertebrate groups / more species in site 1/
reference to one specific named example (but must be comparative) ;
those with species index number 10 all found in site 1 /
none found in site 2 / eq ; 4
(c) some invertebrates miss the net / too small to catch ;
some invertebrates may not be dislodged / disturbed / animals may bury themselves
deeper in mud ;
some animals washed down from upstream ;
reference to non standard technique (e.g. length of kicking) ; 2
(d) pollutants affect oxygen levels / environmental conditions ;
different tolerances to pollutants / oxygen / eq ;
(therefore) only live / survive in conditions which suit them ;
invertebrates easy to sample / count / catch ; 2
David Kaunda High School 210
(e) reference to leaching / draining of fertiliser / nitrates / slurry / soil into river ;
(fertiliser) contains nitrates / phosphates ;
leads to, nutrient enrichment / eutrophication (of river / water) ;
reference to increased algal growth / bloom on surface of water ;
reference to blocking out light to submerged plants ;
causes reduced photosynthesis (in submerged plants) ;
algae / plants die and decompose ;
(so more) oxygen depletion due to bacteria / eq ;
pesticides / eq, kill / are toxic ; 4
(f) detergents / washing / cleaning materials (contain phosphates) ;
sewage (contains phosphates) ; 2
[16]
311.
Statement Sucrose Maltose
Contains glucose
Is a reducing sugar
Contains glycosidic bonds
Is transported in the
phloem of flowering plants
Encircle CORRECT answers
Any TWO correct responses = 1 mark
Blanks and ambiguous ticks are incorrect
Put correct numbers of ticks to correspond with total mark
[4]
312. H2O ;
(di)polar ;
Hydrogen / H ;
Solvent ;
(specific) heat capacity ;
[not latent heat capacity]
[5]
313. (a) A flagellum ;
B DNA / (bacterial) chromosome ;
C cell wall ; 3
David Kaunda High School 211
(b)
Marking Prokaryotic cell Eukaryotic cell
point
1 Smaller Larger ;
2 Do not have a nucleus / nucleolus / Have a nucleus / nuclear envelope /
have a nucleoid nucleolus (allow description) / no
nucleoid ;
3 Do not have membrane-bound Have membrane-bound organelles /
organelles / absence of named presence of named membrane-bound
organelle organelle ;
- 4 Smaller / 70S ribosomes Larger / 80S ribosomes ;
5 Mesosomes / description of No mesosomes ;
infoldings
6 Circular DNA Linear DNA ;
- 7 No histones / chromosomes Histones / chromosomes ;
8 Murein / mucopeptide / Cellulose cell walls (if present) ;
peptidoglycan cell walls / no
cellulose
9 Flagellum with no microtubules / Flagellum with microtubules / 9+2
eq / reference to basal structure arrangement / reference to basal
structure ;
3
[6]
314. (a) Making more DNA ;
Molecule unwinds / strands separate ;
Each strand acts as a template / eq ;
Each molecule contains, one parental/ one new / one daughter strand ;
New DNA is identical to original DNA / identical to each other / eq ; max 3
(b) Folding of secondary structure / eq ;
To form irregular / 3D / globular shape ;
Maintained by, hydrogen / ionic / disulphide bonds / eq ;
Bonding determined by R-groups ;
Shape is important for function ; max 3
[6]
David Kaunda High School 212
315. (a) 14 mm (allow 12 - 15 mm) ;
÷ 800 ;
= 17.5 / 18.0 ; 3
[allow consequential error]
(b) Only 2 cells drawn (D);
Both cells with correct magnification (M) ;
Nucleus of A has correct shape (N) ;
Drawn with single line and no additional details / structures (L) ; 4
[7]
316. (a) Reference to named stain (acetic orcein / acetocarmine / Feulgens / Schiffs) ;
Warm / heat ;
Break open tip with (mounted) needle /eq ;
Mount in stain / acid / water ;
(gently) squash under coverslip / eq ; max 4
(b) (i) A; 1
(ii) C; 1
(c) Synthesis / division / multiplication of organelles (or named organelle) ;
Growth ;
Replication of DNA/ chromosomes ;
Protein synthesis / name of specific protein being synthesised ;
Any normal cell activities, named example (e.g. respiration) ; max 2
[8]
317. (a) (i) Movement down concentration gradient / eq ;
Involves protein in membrane ; 2
(ii) (Active transport) requires, ATP/ energy ;
(Active transport) occurs against/up the concentration gradient ; 2
(b) (i) (0.05 mol dm-3 =) 90% and (0.07 mol dm-3 =) 15% ;
Difference = (90-15) = 75% ;
[allow 14% reading, no consequential error] 2
(ii) Water potential of solution is more than that of red blood cells /
allow converse ;
Water enters the cells ;
By osmosis / down water potential gradient ;
Expansion of cytoplasm / eq / increasing pressure /
stretching the membrane ; max 3
(iii) Shrink / shrivel up / crenate / eq / water would move out / exosmosis ; 1
(c) Cell wall ;
Resists expansion / eq ; 2
[12]
318. (a) (i) The production of juice is increased / more juice is produced ;
Four times as much / 15 cm3 more juice was produced ;
The rate of production increases / the graph has a steeper line with
pectinase ;
Production lasts longer ; 2
David Kaunda High School 213
(ii) Enzyme digests/breaks down/ hydrolyses pectin ;
In cell walls ;
Allowing release of juice / reference to permeability ; 2
(b) (i) Inhibitor has similar shape to, substrate / pectin ;
Binds to active site ;
Prevents entry of / competition with, substrate ; 2
(ii) More juice released / juice released faster ;
Increased enzyme activity / decreased inhibition ; 2
(c) 1. Use same type / variety of apples ;
2. Same / stated mass / volume of pulp ;
3. Range of temperatures / at least three stated temperatures ;
4. Same / stated volume / concentration of enzyme / pectinase ;
5. Same time / stated time period ;
6. Measure volume of juice extracted ;
7. Plot graph of volume of apple juice vs. temperature ; 4
[12]
319. ACCEPT POINTS ONLY IN CORRECT CONTEXT
1. Contain carbon, hydrogen and oxygen ;
2. Insoluble (in water) / hydrophobic ;
3. Triglycerides consist of glycerol plus three fatty acids ;
4. Joined by condensation reactions / formation of ester bonds ;
5. Correct reference to saturated and unsaturated fatty acids ;
6. Phospholipids consist of glycerol plus two fatty acids and a phosphate group ;
7. Reference to non-polar/hydrophobic tails/fatty acids and polar/hydrophilic
heads/phosphates of phospholipids ;
8. Correct orientation of phospholipids, in cell membrane / phospholipids bilayer ;
9. Role of phospholipids in cell membrane (fluidity/permeability etc) / role of
surfactants ;
10. Energy stores ;
11. Reference to energy from fats / oils, compared with carbohydrates ;
12. (mechanical) protection / packing qualified ;
13. Insulation qualified (either electrical or thermal) ;
14. Buoyancy ;
15. Qualified reference to waterproofing / protection against entry of pathogens in plants ;
[10]
320.
Found at highest level in blood
Hormone Secreted by ovary
after fertilisation
Oestrogen or
Follicle stimulating hormone
(FSH)
Progesterone
Luteinising hormone (LH)
Oxytocin
Encircle CORRECT answers
David Kaunda High School 214
Any TWO correct responses =1 mark
Blanks and ambiguous ticks are incorrect
Put correct numbers of ticks to correspond with total mark
[5]
321. (a) A is, an artery / named artery, and B is, a vein / named vein ; 1
(b) (Lining / wall) one cell thick ;
Thin cells / simple epithelium / squamous epithelium ;
Alternative to first two marking points – Thin walls ;
Pores ;
Selectively / partially permeable ; 2
(c) For transport / eq of, solutes / named solute / nutrients / molecules,
to / from, cells / tissues ;
OR
Movement of waste products / named waste product from cells ; 1
(d) Increased blood pressure / hydrostatic pressure / hypertension /
increased capillary permeability / decrease in plasma protein /
colloidal osmotic pressure / protein / amino acid deficient diet /
blocked lymphatic vessels / faulty valves in lymphatic vessels ; 1
[5]
322. (a) A Villus ;
B Mucosa ;
C Submucosa ;
All three correct =(2 marks)
Two correct = (1 mark)
One correct = (0 marks) 2
(b) [A] 1. Completes digestion ;
2. Named enzyme + substrate + product ;
3. Reference to membrane bound enzymes on, villi /
microvilli ;
4. Absorption ;
5. Of glucose / amino acids / monosaccharides / vitamins / water /
minerals / eq into, blood / capillaries ;
6. Of fats / lipids / fatty acids / glycerol / fat soluble vitamins / into
lacteals / lymph / lymph vessels ;
7. Diffusion / concentration gradient, maintained by movement of villi /
presence of capillaries ;
8. Production of mucus + function (lubrication / protection from
digestion) ; 4
David Kaunda High School 215
[Muscularis externa] Causes peristalsis / waves of contraction /
rhythmic contraction ;
Moves food / contents through ileum ;
Mixes food with (digestive) enzymes ;
Segmentation ;
Delays passage of contents / food through gut /
reverse peristalsis ;
More time for digestion / absorption ; 2
[8]
323. (a) Arrow drawn between point where ventricular pressure curve
starts to rise and where curve cuts 5 kPa line ; 1
(b) 60 ÷ 1.0 ; [accept equivalent calculations]
= 60 beats per minute ; [accept range 60 to 64] 2
(c) Reference to closure of semilunar valve ;
Elasticity / eq of aorta wall ;
Recoil (in aorta) maintains pressure ;
Reference to refilling / relaxation of ventricle ; 3
(d) Right ventricle pumps blood to lungs ;
Left ventricle pumps blood all around the body ;
Correct reference to relative thickness of ventricular walls ;
Correct reference to pressure in relation to lungs / body /
e.g. more pressure needed to pump blood round body /
converse OR less resistance to blood flow in lungs
/ converse ; 3
[9]
324. (a) A Guard cell ;
B Epidermal cell / epidermis cell / subsidiary cell ; 2
(b) (i) In cell A the concentration (of potassium) is higher when the stoma is
open / converse statement ;
In cell B the concentration (of potassium) is higher when the stoma is closed
/ converse statement ;
When stoma is closed concentration (of potassium) is lower in cell A than in
cell B / converse statement ;
When stoma is open concentration (of potassium) is higher in cell A than in
cell B / converse statement ;
Credit quantitative manipulated comparison e.g. difference calculated
(Allow once) ; 2
[accept named cells in place of A / B]
[allow consequential error if cells labelled
incorrectly in part (a)]
(ii) Increased concentration of potassium ions reduces solute potential / eq ;
Water moves into (guard) cell ;
By osmosis / down water potential gradient / down diffusion gradient ;
[accept diffusion gradient if “water” is understood]
Increases turgor / hydrostatic pressure, of guard cells / A /
makes cells turgid (therefore stomata open) ; 3
[7]
David Kaunda High School 216
325. (a) A Pollen tube ;
B Tube nucleus ; 2
(b) One, fuses / fertilises / combines, with female nucleus / egg cell / eq ;
To form zygote ;
Which is diploid ;
One fuses with polar nuclei / fusion nucleus / primary endosperm nucleus ;
To form endosperm (nucleus) ;
Which is triploid / 3n ; 4
(c) (i) 15% ; 1
(ii) (Germination rate of) both decreases ;
(Germination rate of) Bauhinia always greater than that of Camellia /
/ converse ; [greater at all concentrations must be implied]
(Germination rate of) Camellia reaches zero at 25%, Bauhinia minimum at
30% / does not reach zero / eq ;
Above 30 % / this (germination rate of) Bauhinia (starts to) increase
(Camellia stays at zero) ; 3
[10]
326. Presence of respiratory pigment / haemoglobin ;
To take up oxygen (at low partial pressures) / high affinity for oxygen ;
Presence of breathing tube / siphon / eq ;
To reach the air / to reach above surface ;
Waving tail / eq ;
Circulates water near body / maintains oxygen, diffusion / concentration, gradient ;
Gills ;
Increase surface area ;
Hairs ;
Trap bubble of air ;
Flattened / elongated body ;
Increase surface area ;
Capillaries close to surface / thin body wall ;
Short diffusion distance ; 2+2
[4]
327. (a) A Epidermis / epidermal cells / piliferous layer / root hair cells ;
B Cortex ;
C Endodermis ;
D Xylem ; 2
[any two correct answers for 1 mark]
(b) 1. Osmosis ;
2. (across cortex) down water potential gradient ;
3. Symplastic route explained / vacuolar route explained ;
4. Apoplastic route explained ;
5. Reference to plasmodesmata ;
6. Reference to function of endodermis / cell C / Casparian strip
(e.g. controlling water uptake) ;
7. Reference to transpiration stream / cohesion tension theory (qualified) ;
8. Reference pores / pits allows water into xylem ; 4
David Kaunda High School 217
(c) (i) Active transport / uptake ;
Energy / ATP, used ;
Ions moved, against / up, concentration gradient ;
Respiration provides ATP ;
Aerobic / oxygen required ;
Some uptake without aeration ; 4
(ii) No active transport ;
Diffusion only ;
Transporters / carriers / ion channels, absent / reduced ;
Smaller surface area / with root hairs, larger surface area ;
Lack of / fewer, mitochondria ; 2
[accept converse points]
[12]
328. ACCEPT POINTS ONLY IN CORRECT CONTEXT
ALVEOLI
1. (general features of gas exchange surface) large surface area + thin ;
2. (large surface by) numerous alveoli ; [must be related to large surface area]
3. (alveolar wall) one cell thick / reference to, simple / squamous, epithelium ;
4. Capillaries near alveoli / cover / surround alveoli ; [idea of capillaries close
to alveoli must be conveyed]
5. Gases move by diffusion ;
6. Carbon dioxide concentration in blood greater than in, alveolar air / air
in alveoli, therefore diffuses to alveolar air / converse for oxygen ;
INSPIRATION
7. Air inspired by contraction of external intercostal muscles ;
8. Diaphragm (muscles) contract ;
9. Thoracic / chest cavity / lungs increase in volume / lungs inflate ;
10. Thoracic / chest cavity / lungs decrease in pressure ;
EXPIRATION
11. Air expelled by, relaxation of external intercostal muscles / diaphragm /
contraction of internal intercostal muscles / contraction of abdominal
muscles / elastic recoil of lungs ;
12. Thoracic cavity / lungs, decrease in volume / deflate and increase in pressure ;
OTHER POINTS
13. Reference to stretch receptors / chemoreceptors ;
14. Reference to control by medulla / breathing / inspiration centres / respiratory centre ;
15. Surfactants prevent, collapse of / adhesion of, alveoli ;
[Accept points from diagrams, but only if well annotated]
[10]
329. (a) 43 / 44 seconds ; 1
(b) Air pressure / pO2 ;
Decreases ;
Temperature ;
Decreases ;
[It gets colder = 2 marks]
David Kaunda High School 218
Wind speed / force ;
Increases ;
Humidity ;
Decreases ;
UV / Solar radiation ;
Increases / stronger ; 2+2
(c) Reference to acclimatisation ;
Increased numbers of red blood cells ;
Increased haemoglobin (concentration) ;
Increased oxygen-carrying capacity of blood ;
Use of oxygen cylinders / eq ;
Hyperventilation / eq ;
Increased pulmonary capillaries / increased pulmonary diffusion capacity ; 3
[8]
330. (a) Low bone mass / density ;
Loss of calcium from bones ;
Increased brittleness of bones ;
Loss of bone strength / weakening of bones / fragile bone ;
Increased risk of fracture ; 3
(b) Exercise ;
Reference to dietary calcium / vitamin D ;
Reduced alcohol intake ;
Stop smoking ;
HRT ; 3
[6]
331. (a) B Spermatagonium ;
C Spermatid / spermatocyte ; 2
(b) (i) C/D; 1
(ii) Meiosis I / reduction division ;
Homologous chromosomes ;
Attachment to spindle fibres ;
Separate in, metaphase (I) / anaphase (I) ;
To two opposite, poles / ends of cells ; 4
(c) Flagellum / tail – locomotion / eq ;
Acrosome – (hydrolytic) enzymes to penetrate egg membrane / eq ;
Large / many, mitochondria to provide, energy / ATP ; 2
[9]
332. (a) (i) Hypothalamus ; 1
(ii) Hypothermia ; 1
(b) (i) Temperature stayed the same from 0 to 5 minutes ;
Increased from 5 to 20 minutes / peaks at 20 minutes ;
Then temperature decreased from 20 to 40 minutes ;
Same at the end as at start ; [accept time references]
Credit any quantitative description
(e.g. temperature increased by 0.9oC from start to 20 minutes) ; 3
David Kaunda High School 219
(ii) 0 to 20 minutes
Temperature of water higher than body temperature ;
Heat gained by conduction ;
Therefore temperature increased ;
Reference to sweating being ineffective in water as a way to reduce
body temperature ;
20 to 40 minutes
Correct reference to vasodilatation ;
Increased heat loss by radiation ;
Increased sweating ;
Reference to evaporation (of water) ;
Correct reference to latent heat ;
Therefore body temperature decreased / body cools ; 5
[10]
333. (a)
Concentration of sodium metabisulphate (grams dm–3)
75 50 25 5 2.5 Distilled
water
Final mass (g) 1.74 1.76 1.81 2.11 2.81 3.41
Initial mass (g) 1.65 1.66 1.68 1.66 1.67 1.65
Difference 0.09 0.10 0.13 0.45 1.14 1.76
in mass (g)
% change 5.45 6.02 7.74 27.11 68.26 106.67
Neat table correctly formatted (shaded columns optional) ;
Correct rows and columns with labels and units ;
Difference in mass correctly calculated / accept % change ; 4
(1 error = 1 Mark, 2 errors = 0 Marks)
(b) Axes – correct orientation and labels ;
Scale – use of more than half paper and correct scale ;
Plot – all points plotted correctly ;
Line – well drawn through all points ; 4
(c) Trends and patterns
1. All concentrations sulphur dioxide cause lower increase in mass ;
2. The more concentrated the sodium metabisulphite the lower the increase
in mass ;
3. Mass differences are all less than in distilled water ;
4. Little further effect above 25g / dm3 / majority of effect achieved
below 25g / dm3 / eq ;
Conclusions
5. Sulphur dioxide in atmosphere will inhibit plant growth (accept ‘growth’) /
limit increase of mass in plants ;
6. (even) low concentrations of sulphur dioxide will have this effect ;
7. Reference to lowering pH affecting enzymes ; 4
David Kaunda High School 220
(d) 1. Seeds not placed equal distances apart ;
2. Number of non-germinated seeds not counted / comparison
more effective between germinated seeds ;
3. Seed size in each sample may be different / seeds may come
from various sources / seeds not from same batch ;
4. All parts of seedlings not taken from filter paper / filter paper
carried with seedlings ;
5. Water content may vary ;
6. Actual sulphur dioxide concentration not measured / may vary ;
7. No reference to control of environmental factors , 2
[14]
334. (a) 1. Same concentration of each amylase ;
2. Same volume of amylase used in each test ;
3. Standardised starch solution volume and concentration ;
4. Stated temperature for each test (15 – 50°C );
5. Method of achieving standard temperature e.g. water bath ;
6. All solutions equilibrated at chosen temperature before mixing ;
7. Suitable range of pH values (min 5 values spread must be at least 5>9) ;
8. Use of buffer solutions ;
9. Method of measuring end point named e.g. disappearance of starch /
quantitative Benedict’s test ;
10. Detail of measurement of end point e.g. drops tested with standard iodine
every minute / excess Benedict’s and mass of precipitate / use of iodine
with colorimeter ;
11. Repeat at each pH ;
12. Repeat whole procedure with alternative enzyme (watch for this in
earlier description) ; 9
(b) Suitable table with correct rows and columns to match suggested method ;
Bar chart / accept line graph where rates have been measured ;
Correct orientation of the axes with labels and units ;
Reference to rate calculation 1 / t etc. ; 3
(c) Limitations
End point difficult to measure accurately ;
Difficult to control concentrations of different enzymes / eq ;
Difficult to carry out iodine tests at short intervals / time taken to carry out
Benedict’s tests limits accuracy ;
Difficult to adjust concentrations to get measurable timings / eq ;
Different enzymes may have different optimum temperatures ;
Further work
Use different / wider range of volumes / concentrations / pH values ;
Compare results with / test other amylases ;
Test to see if pH effect is permanent / reversible ;
Research actual pH conditions for proposed use ; 6
[18]
335. (a) (root) nodules ; 1
(b) Rhizobium ; 1
(c) Mutualism / mutualistic / symbiosis / symbiotic ; 1
David Kaunda High School 221
(d) 1. Reference to nitrogen fixation ;
2. Reference to anaerobic process / eq ;
3. (Nitrogen fixed is) converted / synthesised to amino acids / proteins ;
4. Nitrogen combined with hydrogen ions (from carbohydrates) to give
ammonium / ammonia (allow use of correct formulae)
(also allow nitrogen reduced to form ammonia / ammonium) ;
5. Reference to nitrogenase ;
6. Ammonium / ammonia combined with glutamate / organic acid to give
glutamine / amino acid ; 3
[6]
336. (a) Amylase hydrolyses / breaks down, starch ;
Maltose / glucose / sugar is produced (from starch) ;
Reference to fermentation / respiration ;
Reference to anaerobic / anoxic / absence of oxygen ; 2
(b) Added / mixed with petrol / petroleum / gasoline ;
Usually 10 to 20% ethanol ;
Correct reference to gasohol ; 2
(c) (i) 1. General trend is a rise / eq ;
2. Decrease from 1994 / 1996 ;
3. Increase back to ± 1994 level in 1998 ;
4. Manipulation of figures (must have units) ;
5. Reference to plateau / levelling out in 1982 – 84 / 1988 – 1990 ; 3
(ii) Poor crop / corn yield ;
Corn more expensive / corn needed for food / rise in production costs ;
Tax changes / eq ;
Less demand / more public transport / fewer uses of cars / eq ;
Reference to another additive / motor fuel / hydrogen / methane /
LPG / introduced on the market ;
Cost of oil / petrol decreased ; 2
(d) 1. Reference to carbon dioxide used in photosynthesis ;
2. Carbon dioxide from ethanol only removed from atmosphere recently / eq ;
3. But carbon dioxide from fossil fuels removed a long time ago / eq ;
4. Reference ethanol renewable / fossil fuels non renewable / eq ;
5. Only other waste product from ethanol is water ;
6. Named example of waste product from fossil fuels (allow any air
pollutant from fossil fuels) / reference to damage from extraction of
fossils fuels / reference to unspecified pollutant causing acid rain ; 2
(e) Biogas / methane ; 1
[12]
337. (a) Rain has a pH less than 5.6 / rain that is more acidic than usual / normal ; 1
(b) Sulphur dioxide ; [allow formula]
Nitrogen oxides ; [allow formulae] 2
David Kaunda High School 222
(c)
Germany UK
Stayed same / remained constant / eq Percentages fluctuated / varied from year to
over the three years year / fluctuated more ;
Percentage of healthy forest stayed constant at 50% Percentage of healthy forests rose from 60 to
80 % then fell to 40 % ;
In 1984 approx. 50% healthy trees 60 % healthy trees / 10 % more healthy
forests ; [allow comparison of other
categories or descriptive comparison]
In 1985, 50 % healthy trees 80 % healthy ; [allow comparison of other
categories or descriptive comparison]
In 1986, approx. 50 % healthy trees 40% healthy ; [allow comparison of other
categories or descriptive comparison]
In both countries, percentage of severely damaged
forests was less than 10 % ;
[Values from graph – allow some leeway on readings] 3
(d) Tree = Norway spruce ;
Explanation:
Largest percentage of healthy trees /
lowest percentage in the moderate category ; 2
(e) 1. Needles / leaves damaged / fall off ;
2. Reference to cuticle damage ;
3. Die-back of crown / branches ;
4. Reduced photosynthesis ;
5. Less carbohydrate / food moved to roots ;
6. Reduced root growth / roots damaged / reference to damage of mycorrhiza ;
7. Reduced uptake of nutrients from the soil ;
8. Tree more susceptible to frost / drought / disease ;
9. Leaching / eq of nutrients / minerals from soil ; max 4
(f) (i) 21 –25 ; 1
(ii) During first 10 years, tree health improved / increased to 14 % or 9%
fewer trees moderately or severely damaged / eq ; [actual figure will
depend on answer to f (i)]
Between 1996 and 1997, 5% more trees severely / moderately damaged /
increase from 14 to 19 % of severely / moderately damaged trees / eq ;
[allow figures for 1996-1998]
Tree health stable / same / didn't change by much between 1997,
1998 or 1999 ;
[allow 1998 – 1999 if used 1996-1998 in previous mark point]
No / little overall change between 1986 and 1999 ; max 2
David Kaunda High School 223
(iii) (1986-1996) improvement due to legislation / Government initiatives
/ Clean Air Act / eq ;
Filters / scrubbers on power stations to remove sulphur dioxide / eq ;
Catalytic converters on cars / low sulphur fuel ;
(1996) fall in health due to weather / dry summer / wet autumn /
climate change ;
More cars due to more people / greater car ownership / more car miles ;
Reference to industry (in reasonable context) ;
Use of alternative fuels / energy sources / named source / nuclear ;
1996 anomalous result / change in survey techniques ; Max 2
Note answer needs to indicate whether the reason is related to
an increase in health or a decrease
(g) 1. Trees / producers / autotrophs, are source of energy for food chain
/ web / reference to using light energy to make own food / eq ;
2. Primary consumers / herbivores / named herbivore, feed on producer ;
3. If producers / eq die, primary consumers / herbivores / named herbivore,
starve / die / move away / eat other food source ;
4. (this causes) Secondary / tertiary consumer / carnivore / named carnivore,
to starve / die / move away / eat other foods ;
5. Reference to loss of habitat / fewer nesting / roosting sites for animals /
birds / mammals ;
6. (leads to) Loss of biodiversity / loss of species /
disruption of food chain / web ; 3
[20]
338.
Component DNA mRNA
Cytosine present
Uracil present
Pentose sugar present
Is single stranded
[Any two correct = 1 mark]
[Blanks and alterations are incorrect]
[4]
339. Sequence / order ;
Peptide ;
Condensation / polymerisation ;
Hydrogen / H ;
(di)sulphide / covalent ; [accept sulphur]
R groups / side chains / sulphur / SH groups / thiol groups ;
[6]
David Kaunda High School 224
340. (a) Genetically identical ;
(identical) to {each other / the parent cell} ; 2
(b)
1
(c) Daughter cells {suitable / eq} for surviving in the present conditions /
preserves desirable characteristics / eq ;
Rapid / eq ;
Only one parent is needed ; 2
[5]
341. (a) To {remove / digest} {protein / named example / blood / gravy / eggs} ;
(proteins broken down to) peptides / amino acids ;
Correct reference to solubility ;
Less {heat / energy} required / lower temperature needed /
less damage to material ; 3
(b) Do not denature at temperatures that the detergents work at / greater stability ;
Optimum temperature is higher / works faster than other
enzymes at higher temperature ;
Stains easier to shift at high temperatures ;
Have longer shelf-life / eq ; 2
(c) Enzymes will only {be released / start working} {during washing procedure / when
needed} ;
Less danger of harm to users ;
Increases stability of the enzyme ; 2
[7]
342. (a) Breaks the hydrogen bonds (between the strands) ; 1
(b) Condensation / polymerisation ; 1
(c) Interphase / S phase / synthesis phase ; 1
David Kaunda High School 225
(d) Correct diagram, as below ; 3
C e n tro m e re : ;
C h r o m a tid ;
[accept constriction for centromere]
[accept single line for chromatid]
[6]
343. (a) {Fatty acid / tails} are {hydrophobic / non-polar} ;
(so orientate themselves) away from {water / polar environment} ;
{Phosphate / heads} are {hydrophilic / polar} ;
(so can) interact with {water / polar environment} ; 3
(b) Correct measurement ; [27 mm or 37 / 38 mm]
Divide by magnification ;
Correct conversion to m ; [answer = 0.009 or 0.012 / 0.013] 3
(c) Carbohydrate: Cell recognition / cell adhesion / eq ; 1
Protein: Transport of molecules / eq OR
receptor for hormone / eq OR enzymes ; 1
[8]
344. (a) (i) (single) membrane ;
Contains {hydrolytic / digestive / zymogen} enzymes ;
[accept suitable named enzyme]
Reference to size (accept up to 1 m) ; 2
(ii) Isolation of enzymes ;
Break down / eq of {ingested material / bacteria} ;
Autolysis / self-digestion ;
Breakdown of (old) organelles ; 2
(b) 0 – 10 hours Increase in radioactivity ;
10 – 12 hours Amount of radioactivity remains constant ;
After 12 hours Fall in amount of radioactivity ;
OR
0 – 8 hours Increase in radioactivity ;
8 – 14 hours Amount of radioactivity remains relatively constant ;
After 14 hours Fall in amount of radioactivity ;
No radioactivity present in white blood cells at the beginning and some
remaining inside white blood cells at the end ; 3
(c) (hydrolytic enzymes) digesting the bacteria ; 1
David Kaunda High School 226
(d) Degraded bacteria are expelled from cell / eq ;
By exocytosis ;
Digested molecules are (still) radioactively-labelled ; 2
(e) Not all bacteria engulfed / some {radioactivity / labelled amino acids}
still present in supernatant / eq ; 1
[11]
345. (a) Less active after inhibitor is added ;
Comparative use of figures (calculation of rates) ; 2
(b) Inhibitor attaches to part of enzyme molecule {other than active site / allosteric site} ;
Alters shape of active site / eq ;
So substrate cannot bind / enzyme-substrate complex cannot form / eq ;
Slows rate of reaction ; 3
(c) Decrease rate further ;
Because it will affect more of the enzyme molecules ;
OR
Stop reaction ;
Because it will affect all of the enzyme molecules ; 2
(d) So that rate of reaction without the inhibitor was known /
{acclimatisation / equilibration idea} /
to compare results before and after inhibitor was added ; 1
(e) {Suitable / optimum} temperature for the activity of the enzyme ;
(fluctuations) would alter rate of oxygen uptake ;
(fluctuations) would alter (rate of) enzyme activity ; 2
(f) To keep the pH constant ;
Fluctuations in pH could affect enzyme activity ;
Variations in pH could alter the ionic charges ;
Substrate molecules could be prevented from binding at the active site ; 2
(g) The concentration of the enzyme in the root tips might not be the same /
difficult to make sure that the enzyme concentration is the same in all the
samples / size of root tips vary / different stages of development / different
metabolic rates / different quantities of stored energy / reference to different
genotypes / kept in different conditions before experiment ; 1
[13]
David Kaunda High School 227
346. Points accepted in correct context only
1. Polysaccharides are {polymers / eq} of monosaccharides / correct
general formula (C6H10O5)n ;
2. Linked by glycosidic bonds ;
3. (monomers are) -glucose in {starch / glycogen} ;
4. -glucose in cellulose ;
5. Starch made up of amylose and amylopectin ;
6. Credit reference to structure of {amylose / amylopectin} ;
7. Glycogen branched chains ;
8. Cellulose unbranched ;
9. Starch is an energy store in plants ;
10. Glycogen is an energy store in animals ;
11. (Starch or glycogen) broken down to glucose for respiration ;
12. Cellulose in plant cell walls ;
13. Hydrogen bonding between (adjacent) {chains / molecules} ;
14. Forms microfibrils ;
15. With high tensile strength / reference to turgor ;
[10]
347.
Enzyme Site of secretion Product(s)
Pancreas / salivary glands ; Maltose ;
Lactase ;
{Lining / epithelium / mucosa}
of {small intestine / ileum /
duodenum} ;
[4]
348. (a) Spontaneous / automatic (contraction) / self-stimulating ;
No {nerve impulse / eq} required / no nerve stimulation ; 2
(b) (i) A SAN / sino-atrial node / pacemaker ;
B AVN / atrio-ventricular node ;
C Bundle of His / Purkyne fibres / Purkinje tissue ; 3
(ii) 1. {SAN / A / pacemaker} initiates impulse / eq ;
2. {Impulse / eq} to {AVN / B} then delay ;
3. So atrial {systole / contraction} before ventricular systole / ventricles
fill with blood before systole ;
4. {Bundle of His / C} conducts impulse to (base of) ventricles ;
5. Which contract from {apex / eq} upwards ; 3
[8]
349. (a) {Blood / hydrostatic} pressure ;
Forces water (and solutes) out (of capillary) ;
Reference to pores / permeability of capillary wall / eq /
single cell layer of capillary wall / squamous epithelium ; 2
(b) (i) Potassium and sulphate ions have the same concentration
(in plasma and tissue fluid) ;
Higher concentration of protein in plasma
David Kaunda High School 228
(than in tissue fluid) / converse ; 2
(ii) 1. Capillary (freely) permeable to ions / eq ;
2. (because) ions are small ;
3. Capillary (much) less permeable to proteins ;
4. (because) proteins large ;
5. Therefore most stay in {capillaries / plasma} /
cannot pass through pores ; 3
[7]
350. (a) {Embedding / eq} of blastocyst ; [allow embryo]
In endometrium / lining of the uterus ; 2
(b) (i) A Umbilical vein ; 1
(ii) CO2 / carbon dioxide ;
Urea ;
Fetal haemoglobin ; 2
(iii) Large surface area for increased diffusion rate / eq ;
{Very vascular / many capillaries (fetal) / counter current flow}
{no static build up of substances / maintains diffusion gradient} ;
Short distance between maternal and fetal blood for increased transfer ;
{Maternal space / eq} causes slower
blood flow and more time for transfer ; 3
(iv) Oxytocin ; 1
[9]
351. (a) Transfer of pollen from {anther / stamen} ;
To stigma ;
By {wind / named agent} ; 3
(b) Anthers mature first / pollen released first ;
Before {female parts / eq} are {receptive / developed / mature} ;
Favours cross pollination / avoids self-pollination ; 2
[5]
352. (a) Xylem vessel correctly indicated ; 1
(b) 1. Reference to Casparian strip / suberin / waxy layer ;
2. Waterproof ;
3. Water directed from apoplast pathway / eq ;
4. Into symplast pathway / eq ;
5. Reference to regulation of uptake / control of uptake ;
6. Active transport of mineral ions ;
7. Reference to passage cells ; 3
(c) (i) Uptake increases (from 08.00) {to 18.00 / up to 14.00 then ± constant to
18.00} ;
Decreases from 18.00 to {04.00 / 06.00} ;
Credit manipulated figure reference ; 2
(ii) Increase in transpiration / eq ;
Increase in {temperature / wind speed / stomatal opening / light intensity}
OR decrease in humidity ; 2
[8]
David Kaunda High School 229
David Kaunda High School 230
353. (a) A Palisade (mesophyll / layer) ;
B Spongy (mesophyll / layer) ; 2
(b) Large surface area ;
Thin (cell) walls ;
Presence of air spaces ;
Reference to increased rate of diffusion ; 3
(c) (i) 4.076 ÷ 29 ;
= 0.14 / 0.141 mg per cm2 (per hour) ; 2
(ii) Less carbon dioxide released / no CO2 {released / produced} /
CO2 taken up rather than released ;
Because photosynthesis occurs /
carbon dioxide used in photosynthesis / eq ; 2
[9]
354. (a) (Toadfish) 0.3 and (Mackerel) 2.05 ;
kPa ; [at least once] 2
(b) 1. (Species) Toadfish ;
2. (still water likely to have) low concentration of (dissolved) oxygen ;
3. Dissociation curve to the left ;
4. Reference to high affinity for oxygen of haemoglobin ;
5. {To saturate with oxygen / pick up oxygen} at low pO2 / eq ;
6. Toadfish inactive because oxygen is released
only at very low partial pressures ; 4
(c) (i) Correct shape (sigmoid) starting at 0, 0 ;
To the right of the mackerel curve ; 2
(ii) Reference to reduced affinity for oxygen ;
Releases oxygen more readily ;
More oxygen available to {(actively) respiring tissues / active tissue} ; 2
[10]
355. Points accepted in correct context only
1. Occurs in ovaries and testes ;
2. Formation of spindle / reference to centrioles ;
3. (Prophase) condensation of chromosomes / disintegration of nuclear
{membranes / envelope} / disappearance of nucleolus ;
4. (Meiosis I) homologous chromosomes pair / bivalents form ;
5. And attach to spindle at {metaphase plate / equator} ;
6. Each chromosome consists of two chromatids ;
7. Crossing over / chiasma ;
8. (Anaphase I) separation of chromosomes ;
9. To opposite poles of cell ;
10. Pulled by spindle fibres / microtubules ;
11. (Meiosis II) sister chromatids separate ;
12. {Haploid / n} {cells / gametes} formed ;
13. Fertilisation restores {diploid / 2n} number ;
14. Reference to genetic variation ;
15. Reference to the production of four sperm, and one {ovum / egg} plus
{two / three} polar bodies ;
[10]
David Kaunda High School 231
356. (a) Increase in {body mass / length / size / height} ;
Irreversible / permanent (increase) ;
By cell multiplication / division / enlargement / mitosis ;
Reference to increase in complexity / influenced by
{hormones / named example} / reference to allometric growth ; 3
(b) 1. Decrease in fertility / not fertile / ovulation stops / menstruation stops
/ sperm production decreases ;
2. (associated with) decreasing {oestrogen / testosterone} ;
3. Occurs in males and females ;
4. Occurs at approximately {age 50 in females / age 60-65 in males} ;
5. Any feature
e.g. {hot flushes / night sweats / lower sex drive / mood swings} ; 3
[6]
357.
Epithelium Name One location
Cuboidal ; Nephron ;
Alveolus / lining of mouth /
Squamous / pavement ; Bowman’s capsule / lining
blood vessels ;
Columnar ; Ileum / small intestine ;
[The locations given above are the ones named in the
specification, other correct locations will be accepted]
[6]
358. (a) 28 and 52 ;
52 - 28 = 24 dm3 min–1 ; 2
(b) 1. Rate decreases as oxygen concentration increases ;
2. Rate decreases as oxygen increases from 5% to quoted figure ;
3. Little or no change above this figure ;
4. Manipulated figure reference –
relating to change in pulmonary ventilation rate ; 3
(c) 1. Carbon dioxide ;
2. Small changes in the percentage of carbon dioxide produce greater
changes in ventilation than changes in percentage of oxygen / changes
in carbon dioxide have a greater affect than changes in oxygen ;
3. {Little change / eq} as carbon dioxide increases from 0 to about 3 % ;
4. (but) oxygen needs to drop to about 8 % before effect noticed / eq ; 3
[8]
359. (a) (Llama) 4 and (Human) 5.8 ;
kPa ; [at least once] 2
(b) 1. Dissociation curve to the left (of human) ;
2. Haemoglobin has high affinity for oxygen ;
3. Reference to low pO2 at high altitudes ;
4. Therefore {saturates with oxygen / picks up oxygen} at low pO 2 ; 4
David Kaunda High School 232
(c) Correct shape (sigmoid) starts close to zero ;
To the right of human curve ; 2
(d) Number of red cells increases / haemoglobin content increases ;
Increases oxygen carrying capacity of blood / eq ; 2
(e) Vasoconstriction ;
(narrowing) of superficial blood vessels ;
For heat conservation ;
OR
Reduced sweating ;
For water conservation ;
For heat conservation ;
OR
Increase in thyroxine production / shivering ;
Increases metabolic rate ;
More heat production ; 2
[12]
360. (a)
Absorbance / arbitrary units
Temperature / °C Tube A Tube B Mean
25 0.13 0.09 0.11
37 0.17 0.19 0.18
47 0.54 0.58 0.56
56 0.93 0.99 0.96
65 3.42 3.56 3.49
Suitable table ; [shaded columns optional]
Correct rows and columns with labels and units ;
Mean absorbance for each temperature calculated ; ; 4
[1 error = 1 Mark, 2 errors = 0 Marks]
[decimal place inconsistency = 1 error]
(b) Line graph drawn ;
Axes correct orientation and labelled with units (equal to or more than half of paper) ;
All points plotted correctly ;
Line joins points or good line of best fit ; 4
(c) {Loss of pigment / absorbance} increases with temperature ;
Small increase in pigment from 25 – 47 °C ;
Increase larger above 37 °C / very large increase 56 °C / 65 °C ; 2
(d) Discs could be cut from different parts of the root ;
Handling discs could cause damage ;
Discs take different times to reach temperature of water ;
Liquid needs to be mixed well to ensure even dispersion of pigment ; 2
(e) Reference to damage to cell membrane ;
Reference to any protein component of cell membrane ;
Denaturation of protein likely above 56 °C ; 2
[14]
David Kaunda High School 233
361. (a) 1. Standardised apple variety, type used in experiment ;
2. Apple {pulped / crushed / treated in blender}
{for fixed time / in standard manner} ; [allow division of single batch]
3. {Same / stated} {mass / volume} of pulp used in each experiment ;
4. Same volume of pectinase + distilled water and pectinase/cellulase
mixture added each time ;
5. Equal concentration of each enzyme ;
6. Standard method of {mixing / stirring} enzyme with pulp ;
7. Method of temperature control ;
8. Leave mixture for stated time (5 minutes minimum) ;
9. Add pulp and enzyme mixture to filter paper in funnel / eq (accept from diagram) ;
10. Collect juice for {same / stated} time (10 minutes minimum) /
until no more juice runs out ;
11. Method of measuring volume of juice e.g. measuring cylinder ;
12. Credit reference to control with {no enzyme / cellulase only} ;
13. Repeat at least twice (three in total) ; 9
(b) Suitable table with correct rows and columns to match suggested method ;
Bar chart / accept line graphs where rates have been measured ;
Correct orientation of the axes with labels and units ;
Presentation of data is comparative ; 3
(c) Limitations
Different batches of apples may vary / eq ;
Acid pH of apple may affect pectinase and cellulase differently / different {pH /
temperature} optima ;
Total volume of juice takes a long time to collect ;
Further work
Vary proportions of pectinase and cellulase ;
Test effect on {different apple varieties / different fruits} ;
Test effect of other named enzyme on pectinase ;
Test effect of one other factor on juice extraction e.g. temperature /
pH / concentration of enzyme ; 6
[18]
362. Any three
1. a) Incisors in sheep {only on lower jaw / absent on upper jaw} / reference to the horny
pad on the upper jaw
AND
Incisors in dog present on upper and lower jaw ;
b) Reference to {chopping / cropping / cutting / tearing} in sheep OR
{gripping / nibbling} in dog ;
2. a) Canines {small / only in lower jaw / absent} in sheep
AND
Canines {large / pointed} in dog ;
b) Reference to {gripping / piercing / stabbing} in dog ;
3. a) Sheep has a diastema OR {gap / space} between {canines / incisors}
and premolars / position clearly described
AND
Dog has no {diastema / gap} ;
b) Reference to {manipulation / eq} of food (by tongue) in sheep ;
David Kaunda High School 234
4. a) {Premolars / molars / cheek teeth} of sheep {ridged / interlocking / not sharp}
AND
{Premolars / molars / carnassials} of dog {pointed / scissor blades / sharp /
not ridged / not interlocking} ;
Reference to grinding in sheep OR {slicing / shearing / cutting / crushing
bone} in dog ;
[6]
363. (a) Too much land being farmed / over-intensive farming ;
Exceeding carrying capacity ;
Decreasing rainfall ;
Increasing population leads to more demand for {wood for fuel / food} ; 2
(b) 1. Loss of vegetation cover / overgrazing ;
2. Soil erosion / exposed soil blown away ;
3. Increased evaporation (of water) from soil ;
4. Correct reference to {salinisation / salts drawn up into top soil} ;
5. Soil {unable to support plant growth / lack nutrients / eq} ;
6. Lack of moisture in the air leads to change in local rainfall patterns / eq ; 3
(c) 1. Converted to {ammonium ions / ammonia} by {decomposers / putrefaction
/ named organism} / eq ;
2. (ammonium) converted to nitrite ;
3. By {Nitrosomonas / nitrifying bacteria} ;
4. Nitrite converted to nitrate ;
5. By {Nitrobacter / nitrifying bacteria} ; [allow nitrifying bacteria only once]
6. Reference to aerobic conditions /
process or oxidation or in presence of oxygen ; 4
(d) 1. Crops have {nitrogen fixing bacteria / Rhizobium} (in their roots) ;
2. Detail of nitrogen fixation (e.g. nitrogen to ammonia / ammonium / amine
/ amino acids OR reference to nitrogenase) ;
3. Allows crops to be grown on {nutrient poor / deficient / low nitrogen} soils ;
4. {Crop remains / leakage from roots} increases the {nitrogen (compounds) /
named e.g.} in the soil / eq ;
5. {Millet / other crop} synthesises more {protein / seeds / leaves} / eq ; 3
[12]
364. (a) {Range / variety / number} of species in a
{habitat / ecosystem / area / environment} ; 1
(b) (i) 1. (overall) there is a decrease in the (mean) number of seedlings ;
2. Within a fragment there are fewer seedlings at the {edge / corner}
OR converse ;
3. In the 100ha fragment {just over half / 55%} of seedlings at corner
rather than centre ;
4. In the 10ha fragment {more seedlings at corner than at edges /
least at edge} ;
5. The one hectare fragment has {just over half / 55% / mean lower
by 7.7} of the seedlings found in the continuous forest ;
6. Comparison between the continuous forest and centre of
{100ha / 10ha} fragment using manipulated figures ; 3
David Kaunda High School 235
(ii) 1. {More light / less shade} {at edge of fragment / in smaller fragments} ;
2. (so these) shade tolerant trees do not grow so well ;
3. More competition from other trees (species) that can grow where
there is more light ;
4. Eaten by animals from farmland ;
5. (too many) climbing plants growing over them ;
6. On edge there is more exposure to {weather / wind etc.} /
seeds blown away ; 3
(iii) 1. Trees in {edge / corner} less likely to be replaced when they
die than trees in {the centre / continuous forest} ;
2. Composition of the {plant / tree} species in the forest would change ;
3. Light-demanding trees replace the shade tolerant trees / eq ;
4. Reference to the change in the animals of the forest ;
5. Change in biodiversity OR {change / loss} of habitat OR
{gain / new} habitat ; 2
(c) (i) Centre: (1501 + 745 + 684 + 538 + 55 =) 3523 ;
Edge: (2740 + 1308 + 1219 + 944 + 137 =) 6348 ;
(2825 ÷ 3523 × 100 =) 80.2 / 80 / 80.19 (%) ; 3
(ii) Increase {because smaller fragments have more edges / there are
more dead trees in the edges} / eq ; 1
(d) Trees more than 60cm in diameter ;
Reference to figures / greater percentage increase in dead trees ; 2
(e) The mass of {plants / vegetation / producers} ;
Per unit area / kg m–2 ; 2
(f) 1. {Trees / plant biomass} are {producers / autotrophs} ;
2. Less {food / energy} available for {primary consumers / herbivores}
OR less energy through the food chain ;
3. Causing {death by starvation / migration} ;
4. Causing decrease in {populations / numbers} of herbivores ;
5. Affects all the animals in the {food chain / food web} OR affects
{secondary consumers / carnivores / animals higher in the food chain} ; 3
[20]
365. Catalysts ;
Activation energy ;
Substrate ;
Active site ;
Temperature / non-active site-directed inhibitors ;
Change / increase or decrease ;
[only accept decrease if referring to inhibitor]
[6]
David Kaunda High School 236
366. (a)
Cellulose Glycogen
1. -glucose -glucose
2. 4 glycosidic bonds 1, 4 and 1, 6 glycosidic bonds
3. Unbranched / straight / linear Branched / compact / eq
2
(b)
Collagen Insulin
1. Fibrous Globular
2. Three (polypeptide) chains / triple Two (polypeptide) chains / eq
helix
3. Chains held together by hydrogen Chains held together by di-
bonds / chains not held together by di- sulphide bonds / eq
sulphide bonds
4. Large / about 1000 amino acids Small / 51 amino acids
OR length can be variable OR fixed / precise length
5. Repetitive / repeating sequence No repetitive sequence
6. Sequence of amino acids may vary Sequence of amino acids does not
between molecules vary between molecules
2
[4]
367. (a) (i) Red ; 1
(ii) Test 1 shows no reducing sugar (in solution B) ;
In test 2 sugar is hydrolysed / eq ;
In test 2 solution (B) was positive ; 2
(b) 1. Add equal volumes of each solution ;
2. To equal volumes of biuret reagent ;
3. {Purple / lilac} colour produced ;
4. Compare intensity of colour / use a colorimeter ;
5. After same period of time ; 3
[6]
David Kaunda High School 237
368.
Name of molecule Formula Structure
O
H H ;
Amino acid H H
O
N C C ;
O H
H R
CH3 (CH2)4 COOH
OR
C5 H11 COOH ;
() Glucose /
hexose ; C6 H12 O6 ;
[6]
369. (a) 1. Enzyme is {attached to / trapped in} (material) ;
2. An insoluble (material)
3. Such as {agar gel / cellulose / polyacrylamide} / reference to alginate beads /
eq ; 2
(b) 1. Can be re-used ;
Which reduces overall cost / more economical / eq ;
2. Process is continuous ;
Saves time / can be automated / reduces cost ;
3. Enzymes more stable ;
Less likely to be {denatured / affected by temperature changes / affected by
pH changes} ;
OR
Enzymes can be used at higher temperatures ;
Faster reaction / saves time ;
4. Enzyme does not have to be separated from product ;
Reduces cost / saves time ;
5. More than one enzyme can be fixed in an order ;
Greater control over process / saves time / more efficient ; 4
[6]
370. (a) DNA increases: in interphase / synthesis / S stage / phase ;
Synthesis of new DNA / replication of DNA / eq ;
DNA decreases: in cytokinesis ;
Daughter cells formed ; 4
(b) (i) mRNA is made ;
It is complementary to DNA OR DNA code is copied ; 2
David Kaunda High School 238
David Kaunda High School 239
(ii) Tyr Leu Phe Ser ; ;
[one error = 1 mark, 2 errors = 0 mark] 2
[8]
371. (a) Correct measurement – 78 / 79 ;
Measurement × 1000 (to give µm) ;
÷ 50 ;
[if final answer is incorrect maximum marks = 2] 3
(b) Drawing marks:
D1 Chromosomes drawn correctly ;
D2 Centrioles drawn correctly ;
Label marks:
Chromosomes ;
Centrioles ;
Spindle fibres ; 5
(c) Anaphase ; [ignore reference to I or II] 1
(d) Spindle fibres: Pull {centromeres / chromatids / chromosomes} {apart / to
opposite poles}
OR
{Pull / hold} chromosomes into position ;
Centrioles: {Produce / organise / assemble} spindle (fibres) / microtubules ;
OR
{ Organise / assemble} tubulin ; 2
[11]
372. (a) 1. Uptake of A increases throughout 6 hour period ;
2. Uptake of A is {proportional to time / linear} / rate of uptake of A is constant ;
3. Uptake of B increases then {plateaus / levels off} / rate of uptake of B
decreases ;
4. {Uptake / rate of uptake} of A greater than of B ;
5. Credit manipulation of figures ; 3
(b) 1. Rate of uptake greater at start of experiment as diffusion gradient is high ;
2. Rate of uptake decreases as diffusion gradients lower ;
3. {Line / rate / uptake} plateaus out when concentration of substance B inside
cell is same as concentration outside cell ;
4. Concentration inside cell doesn’t decrease ; 3
(c) (increase in temperature) increases kinetic energy (of molecules) ;
Therefore molecules move faster ; 2
David Kaunda High School 240
(d) 1. Movement (of molecules) against concentration gradient / eq ;
2. Requires {energy / ATP} ;
3. Occurs in one direction ;
4. Involves {carrier / transporter} proteins ;
5. Which span the membrane / eq ;
6. Molecule binds to {protein / carrier} ;
7. {Protein / carrier} changes shape ;
8. Reference to {sodium / proton} pump or other named example ; 5
[13]
373. Bronchioles / alveolar ducts ;
Single / thin / squamous / flattened / type I pneumocyte ;
Increases / eq ;
Blood / capillaries / red blood cells ; 4
[4]
374. (a) Seminiferous {tubule / tube} ; 1
(b) Cell A Primary spermatocyte ;
Cell B Spermatid ; 2
(c) 1. Reducing chromosome number / haploid from diploid / 2n to n / correct
reduction ;
2. So diploid reformed at fertilisation / eq ;
3. Genetic variation ;
4. Four {sperm / gametes} produced ; 3
[6]
375. (a) 1. Rhythmic / sequence (of events) in each heart beat ;
2. {Initiated / controlled} by {pacemaker / SAN (sinoatrial node)} ;
3. Reference to atrial {systole / contraction} ;
4. Reference to ventricular {systole / contraction} ;
5. (complete) diastole / relaxation (of heart) ;
[points 3 to 5 must be in sequence] 3
(b) Coronary artery ;
From aorta ;
Supplies {blood / oxygen / glucose / nutrients / named nutrient} to heart
{muscle / tissue / myocardium} / correct reference to removal of {waste
products / named waste product} by coronary circulation ;
Returns to right atrium / coronary sinus / cardiac veins ; 3
[6]
David Kaunda High School 241
376. (a) (Myoglobin:) 0.6 kPa AND (Haemoglobin:) 3.1 kPa ; [kPa at least once] 1
(b) 1. (Acts as) a store of oxygen ;
2. In muscle ;
3. Releases oxygen at (very) low partial pressure (of oxygen) ;
4. Provides oxygen during strenuous activity / allows muscle to respire
aerobically for longer / eq ;
5. Higher affinity for oxygen (than haemoglobin) ; 3
(c) S-shaped curve starting at 0,0 ;
Drawn to left of haemoglobin curve (but not to the left of the myoglobin
curve) ; 2
(d) (i) Bohr (effect) / Bohr (shift) ; 1
(ii) 1. (at higher partial pressures of carbon dioxide) affinity of haemoglobin is
reduced (for oxygen) ;
2. (therefore) releases oxygen more readily / percentage saturation with oxygen
falls / oxygen dissociates more readily / more oxygen released ;
3. At same partial pressure of oxygen ;
4. Oxygen released to {actively respiring / active / exercising} tissues / eq ;3
[10]
377. (a) P Epidermal (cell) / epidermis cell / subsidiary (cell) ;
Q Guard (cell) ; 2
(b) (Number of stomata present =) 12 ;
÷ 0.069 (calculation mark) ;
= 173.9 / 174 (per mm2) ;
[allow consequential error if the method is correct] 3
(c) (i) (Rate of transpiration) increases (in moving air) / eq ; 1
(ii) 1. Reference to boundary layer ;
2. Humid air (in vicinity of leaf) removed / water vapour removed ;
3. Increases {diffusion gradient / water potential gradient / concentration
gradient} ;
4. Water vapour lost by diffusion ;
[accept converse of points 2 and 3 for still air] 3
[9]
378. (a) 1. Low oxygen (concentration) ;
2. Reference to (breathing) tube / eq ;
3. To obtain oxygen / to exchange oxygen and carbon dioxide ;
4. From above surface of water / from air ;
5. Reference to hairs or lipids to prevent waterlogging of tube ;
6. Reference to {respiratory pigment / haemoglobin} ;
7. With a high affinity for oxygen ; 4
David Kaunda High School 242
(b) Reference to {claws / hooks} (on legs) ;
To hold onto stones / eq ;
Streamlined / flattened shape / aerodynamic / hydrodynamic ;
Less resistance to flowing water / hides under stones ; 2
[6]
379. (a) To {absorb / remove / take up} carbon dioxide ; 1
(b) To move liquid in capillary tube / calibrate scale / set zero / reset ; 1
(c) (i) Reference to {greater movement / eq} at 30 °C (than at 24 °C) ;
[accept converse]
Credit any quantitative manipulated difference (e.g. difference of 40 mm
at 24°C, 76 mm at 30 °C) ; 2
(ii) 1. Reference to keeping temperature constant ;
2. Find volume of oxygen used / measure distance moved on scale ;
3. In a known time / reference to recording time ;
4. Rate = {volume of oxygen / distance moved on scale} ÷ time / plot a graph and
find gradient ;
5. Distance moved indicates volume of oxygen used ; 3
[7]
380. (a) (i) Amylase ; [accept diastase / ptyalin] 1
(ii) Starch converted to {maltose / dextrins} ;
Hydrolysis ;
{Glycosidic bonds / 1, 4 bonds} broken ; 2
(b) As a standard / to compare with other tubes / to check starch does not break
down on its own / eq / to check no reducing sugars present {at start / in
starch} ; 1
(c) (i) No amylase {in stomach / produced by stomach tissue} ; 1
(ii) Amylase produced in pancreas but no amylase produced by duodenum ; 1
David Kaunda High School 243
(d) 1. Glucose ;
2. Diffusion (of glucose) into blood ;
3. Into capillaries ;
4. Reference to movement of blood maintains {diffusion / concentration} gradient ;
5. Carrier proteins / transport proteins ;
6. In {plasma / cell surface } membrane (of {villi / microvilli}) ;
7. Sodium co-transport ;
8. Reference to facilitated diffusion ;
9. Reference to {active transport / pinocytosis / sodium pump} ;
[not Na+ / K+ pump] 6
[12]
381. (a) 1. Europeans show {greatest / fastest} drop in first hour ; [or converse]
2. Aboriginals show {steady / eq} drop (throughout 8 hours) ;
3. Europeans more or less {constant / eq} from 1 hour onwards / fluctuates ;
4. Credit a manipulated quantitative comparison ; 3
(b) 1. (Aboriginals) {tolerant of / adapted to} cold nights ;
2. Allow their body temperature to fall ;
3. No shivering ;
4. Marked vasoconstriction ;
5. Reduces energy requirements / less food required ;
6. Reference to starting day with a lower body temperature to cope with heat
(during day) ; 2
[5]
382. (a) Distance from start of P wave to start of R wave = 8 mm ;
Calculation (e.g. 8 ÷ 50) ;
Time interval = 0.16 seconds ; [accept s]
[allow consequential error] 3
(b) Reference to sending an (electrical) impulse ;
To heart muscle ;
Stimulating contraction / eq ; 2
[5]
383. (a) Birth weight decreases as concentration of lead increases / converse ;
At less than 13 arbitrary units (au) of lead {it has less effect on birth weight /
birth weight fluctuates} ;
Credit reference to use of figures ; 3
(b) In {food / diet / drinks / water} ;
As particles from air / breathed in ; 2
David Kaunda High School 244
David Kaunda High School 245
(c) Increased surface area ;
Causes increase in rate of {diffusion / exchange / active transport} ;
Between maternal and fetal blood ; 2
(d) 1. Separates from {uterus lining / endometrium / myometrium / uterus wall} ;
2. Passed out of vagina (as afterbirth) ;
3. By contraction of {uterine muscle / uterus} ;
4. Reference to {oxytocin / prostaglandins} ; 3
(e) Diet (of mother) ;
Virus / named virus ;
Nicotine / carbon monoxide / smoking ;
Alcohol ;
Heroin ;
Genotype / eq ;
Length of gestation / premature babies are smaller ;
Multiple birth / twins etc. ; 2
[12]
384. (a)
Rate of heart beat / beats minute -1
Time / Water flea 1 Water flea 2 Mean
minutes
0 184 180 182
2 220 222 221
4 232 234 233
6 246 240 243
8 242 240 241
10 230 234 232
Suitable table ; [accept with raw data or means only]
Correct rows and columns with labels and units ; [accept with raw data or
means only]
Mean heart beat rates for each time calculated ; ;
[1 error = 1 mark, 2 errors = 0 marks] 4
(b) F Line graph drawn ;
A Axes correct orientation, scale and labelled with units ;
P All points plotted correctly ;
L Line joins points or good line of best fit through the points ; 4
David Kaunda High School 246
(c) Heart rate increases {most steeply / eq} for first 2 mins ;
Heart rate reaches a maximum {at 6 mins / between 4 – 8 mins} ;
Heart rate declines after 6 mins / eq ;
Heart rate does not return to original level after 10 minutes ; 2
(d) Adrenaline stimulates heart rate ;
Adrenaline less effective after 6 minutes / {adrenaline may become toxic / eq}
/ effect lasts at least 10 minutes ; 2
(e) Environmental factors such as {temperature / oxygen} not controlled ;
Biotic factors such as {size / age etc.} not controlled ;
{Concentration / dilution} of adrenaline when added to water fleas not
controlled ;
Difficult to count (fast) heart rate ; 2
[14]
385. (a) 1. Same concentration of animal and fungal rennin (each time) ;
2. Same volume of animal and fungal rennin (each time) ;
3. Reference to milk of same type, e.g. full fat ;
4. Milk {of same age / from same source / eq} ;
5. Reference to control without enzyme;
6. Use of water bath ;
7. Stated range of temperatures (at least 5 up to max 60°C) ;
8. Equilibration of rennin and milk sample separately at set temperature ;
9. Mixing rennin and milk sample ;
10. Reaction for specific time / time to reach specific {viscosity / thickness} / eq ;
11. Quantitative method for measuring viscosity after specific time e.g. time for
(specific volume of) milk to drain through nozzle of syringe / noting time at
which milk reaches specific measurable viscosity – specific practical suggestion ;
12. Repeat for each stated temperature ; 9
(b) Suitable table with units and correct rows and columns to match suggested
method ;
Line graphs where {rates / time / eq} are presented on the vertical axes ;
Correct orientation of the axes with labels and units ;
Presentation of data is comparative ; 3
(c) Limitations
End point difficult to measure / specific example / eq ;
Gel formation at higher temperatures may occur too quickly to measure ;
Difficult to standardise original {activity / concentration} of different rennins ;
Effect of high temperatures on milk without an enzyme present ;
David Kaunda High School 247
Further work
Use a narrow range of temperatures around optimum ;
{Compare with / use} a wider range of {rennins / enzymes} (from various
sources) ;
Investigate the effect of immobilisation on the optimum temperature of
rennins ;
Reference to the reliability of determination of viscosity by comparing
methods of measuring viscosity ;
{Compare with / use} different sources of milk ;
Investigate the effect of different rennin concentrations ; 6
[18]
386. (a) Small intestine / ileum / duodenum ; 1
(b) Enables {grip / eq} (to region of alimentary canal) ;
Prevents it being carried away by {peristalsis / peristaltic wave / movement of
food through intestine} ; 2
(c) 1. No {mouth / alimentary canal / digestive system / eq} ;
2. Lack of sense {organs / receptors} / reduced nervous system ;
3. {Thick / enzyme-resistant / tough} {tegument / coat / covering / cuticle} /
reference to production of {mucus to protect against enzymes / anti-
enzymes} ;
4. Reference to ability to tolerate {low oxygen / anaerobic conditions} ;
5. Reference to prolific reproductive capacity ;
6. Reference to being a hermaphrodite ;
7. Reference to flat body shape / large surface area to volume ; 2
(d) 1. Rhizopus is a {saprophyte / saprobiont / saprotrophic} ;
2. {Taenia / parasites} {feeds from / lives on} host and Rhizopus {feeds on
/ lives on} {dead material / e.g.} ;
3. {No digestion / no digestive enzymes / food already digested} in Taenia and
{external digestion / secretion of enzymes} {onto / into} food in Rhizopus ;
4. Absorption of food over whole body surface in Taenia and reference to
{mycelium / hyphae / eq} in Rhizopus ; 3
[8]
387. (a) 1. Third / secondary consumers ;
2. Feed (mainly) on {herbivores / primary consumers / e.g.} ;
3. Which feed on {producers / plants} ;
4. They are eaten by {tertiary consumers / foxes / cats / a carnivore} ;
OR
David Kaunda High School 248
5. Fourth / tertiary consumers ;
6. Feed on {carnivores / secondary consumer / named e.g.} ;
7. Which feed on {primary consumers / herbivores} ;
8. They are eaten by {quaternary consumers / foxes / cats / a carnivore} ;
[marks can be gained EITHER from points 1-4 OR from points 5-8] 3
(b) 1. Stoats {larger / heavier} than weasels ;
2. {About / more than} {3x / 3.4x} heavier / mean mass weasel = 75.56g and
stoat = 251.08g / number of both not very different but biomass for stoat
much greater / relevant calculation ; 2
(c) 1. Biomass is the mass of {organisms / animals} ;
2. Large number of small organisms is equivalent to small number of large
organisms / eq / prey are different sizes ;
3. Reference to relevant energy consumed ;
4. Comparisons more {valid / meaningful} / eq ; 2
(d) 1. Mice and voles main food of weasels and rabbits and hares main food of
stoats ;
2. Both eat more or less same quantity of eggs and birds / same quantity of
other prey ;
3. Credit use of two readings for comparison / manipulation to calculate
difference ; 2
(e) 1. Both have {fallen / decreased} ;
2. More rapidly from 1975 to 1980 than later / reference to levelling off after
1980 / reference to stoats level from 1990 but weasels still decreasing / eq ;
3. {Herbivores / 1° consumers / named e.g.} numbers increase because fewer
consumed ;
4. {Foxes / cats / eq} may decrease in numbers because fewer {weasels /
stoats} to eat ;
5. {Foxes / cats / eq} eat more of {other herbivores / named e.g.} / {foxes / cats
/ eq} eat more stoats because weasels still declining ;
6. (Therefore) may increase due to {less competition / more food} ; 3
[12]
388. (a) 1. Rate of / per unit time / quote appropriate units ;
2. Production of {biomass / organic material / photosynthetic products / eq} ; 2
(b) 1. Reference to {fresh nutrients / lots of nutrients} being introduced all the time /
eq ;
2. And recycled / circulated / washed back / eq ;
3. Credit one other appropriate factor (e.g. oxygen, temperature, light, flow of
water) ;
4. Explanation of factor ; 2
David Kaunda High School 249
(c) 1. Reference to {tidal effect / inward movement of sea water} ;
2. So that water in estuary is recycled / eq ;
3. Preventing {fertiliser / pesticide} (from agricultural land) passing out to sea ;
4. Where they would be diluted / eq ; [allow converse] 3
(d) 1. Able to be {broken down / decomposed / digested} ;
2. By the action of {(micro)organisms / detritivores / decomposers / e.g.} ; 2
(e) 1. As distance increases, number of {individuals increases to a peak / species
fall to a trough / eq} ;
2. Eventually both return to original level ;
3. Peak of individuals is more or less same distance as trough for species ;
4. Reference to relevant change in biodiversity ; 3
(f) 1. Extra {nutrients / named e.g.} / eutrophication ;
2. Some {organisms / species / named e.g. / algae / bacteria} increase in number ;
3. Use up {resources / named e.g.} ;
4. Light blocked ;
5. Other {organisms / species} decrease due to lack of {resources / named e.g.} ;
6. Increase in {nutrients / detritus / waste} so conditions {unsuitable for some
species / cause some species die / eq} ; 3
(g) 1. Reference to {pathogenic microorganisms / harmful microorganisms / pathogens} ;
2. Named example of organism or disease ;
3. May contaminate (human) {drinking water / water supplies} ;
4. May contaminate {beaches / swimming areas / food sources} ;
5. Toxins produced by algal blooms ;
6. Reference to {toxic / eq} {chemical / substance / excess nitrates} in sewage ;3
[18]
389.
Carbohydrate One role in living organisms
Glucose;
Form in which plants transport carbohydrate / energy source;
Glycogen;
In plant cell walls;
[4]
David Kaunda High School 250
390. (a) Tissues are groups of (similar) cells performing similar functions;
Organs are a number of tissues that perform a function 2
(b) Magnification is the number of times bigger an image is than
the {specimen / original};
Resolution is the {ability to distinguish two points as separate
points / degree of detail visible} 2
[4]
391. (a) (i) Glycerol / propan 1, 2, 3 triol 1
(ii) Ester 1
(b) (Stearic acid / saturated fatty acids} have more hydrogen atoms;
{Stearic acid / saturated fatty acids} have no double carbon-carbon bonds;
{Stearic acid / saturated fatty acids} have no kinks;
[allow converse statements about unsaturated fatty acids] 2
(c) 1. Energy stores;
Qualification: {More than / twice as much as) carbohydrate
OR Insoluble / compact / minimise mass
OR Subcutaneous / adipose / blubber;
2. Protection / mechanical insulation;
Qualification: Around {organs / named organ}
OR Reference to adipose tissue
OR Ear wax giving protection against infection;
3. Waterproofing;
Qualification: Of skin / fur / feathers / insect cuticle / ear wax
OR Hydrophobic / insoluble / repels water;
4. Electrical insulation;
Qualification: Reference to myelin sheath / nerve cells /
neurones / axons / dendrons
OR Non-polar;
5. Heat insulation;
Qualification: Subcutaneous / adipose / blubber
OR Prevents heat loss from body;
6. Buoyancy;
Qualification: Less dense than {water / muscle};
7. Making beeswax;
Qualification: Formation of honeycomb;
8. Membrane fluidity;
Qualification: Reference to cholesterol;
9. Cell membrane structure;
Qualification: Reference to phospholipids;
10. Reference to hormones;
Qualification: As steroids;
11. Source of metabolic water;
Qualification: Reference to respiration
OR Desert adaptation 2 x 2 mark
[8]
David Kaunda High School 251
392. (a) 1. Contains (r)RNA;
2. And protein;
3. Has two (sub-)units;
4. Binding{site/groove} to accept RNA;
5. 20-30 nm in size; 2
(b) Glycine;
Lysine; 2
R O H R
H O
N C C N C C
H O H
(c) (i) H H
Correct amino acid parts on either side;;
Carbon nitrogen back bone; 3
(ii) Condensation 1
[8]
393. (a) (i) BDAC; 1
(ii) Metaphase; [ignore I and II] 1
(b) (i) DNA replicates;
Cell division / cytokinesis; 2
(ii) Mitosis / G2 and mitosis; 1
(iii) {l5/20} hours; 1
[6]
394. (a) A Nucleus/chromatin/nucleoplasm;
B Mitochondrion; 2
(b) Correctly measured length;
(Length) ÷ 5000;
Correct answer in m; 3
(c) 1. (molecules/proteins) pass into the{cisternae/eq}of the RER;
2. Vesicles {break off (from cisternae) / form};
3. (molecules) carried to Golgi / (vesicles) fuse with Golgi;
4. (proteins) concentrated;
5. Modified / carbohydrate added / become glycoproteins;
6. Vesicles {break away (from Golgi) / move to cell membrane};
7. (vesicles) fuse (with cell membrane);
8. Reference to exocytosis; 5
[10]
David Kaunda High School 252
395. (a) (i) Sucrose is a non-reducing sugar therefore gives negative result
{with Benedict’s reagent / in table 1};
It is hydrolysed into {monosaccharides / glucose and fructose
/ reducing sugars);
The orange precipitate in table 2 indicates a higher concentration
of sucrose / eq; 2
(ii) 1. Maltose is {detected / eq} at a lower concentration;
2. Maltose is a disaccharide;
3. Therefore twice as much glucose after being hydrolysed;
4. Compared to a glucose solution of same (molarity / concentration}
eq; 2
(b) 1. Add {biuret solution (at room temperature) / KOH and CuSO 4};
2. {Stated / equal) volumes of both protein solutions;
3. Control of one other variable (e.g. time, temperature, volume of biuret);
4. Purple / lilac / violet / eq;
5. Intensity comparison / {darker / eq} colour means more protein /
reference to use of calorimeter; 4
[8]
396. (a) Catalyst: 1. (Chemical that) {speeds up / increases rate of} a
reaction;
2. Without itself being changed / used over and over
again / not used up;
Activation energy: 3. Energy needed for a chemical reaction to begin;
4. Enzymes reduce it; 4
(b) (i) Hydrolysis; 1
(ii) Glycosidic (-1,4) 1
(iii) 1. Use water as basis to compare effect;
2. Copper sulphate decreases rate of cellulose breakdown;
3. {Increase in concentration / higher concentrations) decreases
rate of breakdown even more;
4. After six days more cellulose broken down at lower
concentrations;
5. Credit manipulations of data to compare breakdown of
solutions at different concentrations 3
David Kaunda High School 253
(iv) 1. Disulphide bonds maintain {(tertiary/3D)structure/shape};
2. If disulphide bonds break, the active site will be altered;
3. Cellulose will no longer fit into the active site / eq;
4. Cellulose will not be digested;
5. As copper ions increase more enzymes are affected;
6. Reference to non-active site directed inhibitor; 3
[12]
397. (a) 3
Structural feature
Blood vessel Valves present Wall has pores Wall a single
layer of cells
Capillary
Vein
(b) (Elastic recoil) maintains pressure (in artery) (flexibility) to allow for
{blood pressure / pulse}; 1
[4]
398. (a) A Neutrophil / granulocyte;
B Erythrocyte / red blood {corpuscle / cell); 2
(b) {Engulf / eq} {bacteria / pathogens microorganisms};
Reference to intracellular digestion; 2
(c) Transport of respiratory gases;
(Transport) oxygen;
(Transport) carbon dioxide;
Reference to picking up oxygen in lungs and releasing oxygen in (respiring)
tissues / high affinity for oxygen {in lungs / at high pp of oxygen) / converse in
tissues / reference to low affinity for oxygen at high pp of carbon dioxide; 3
[7]
399. (a) Cell structure A Microvilli / brush border;
Function Increase surface area for absorption / (membrane)
{bound / attached} enzymes for digestion;
Cell B {Mucous / goblet} cell;
Function Lubrication for movement of food / mucus production /
protection (of epithelial cells) from digestive enzymes 4
(b) (i) Lactose + lactase;
Sucrose + sucrase; 2
(ii) Glucose and galactose have similar rates of absorption / galactose
has higher absorption than glucose / converse;
Fructose has a lower rate;
Use of manipulated comparative figures; 2
David Kaunda High School 254
David Kaunda High School 255
(iii) {Glucose / galactose} absorbed by active transport, fructose is not /
fewer {(membrane) channels / receptor sites / transport proteins}
for fructose / correct reference to different diffusion gradients; 1
[9]
400. (a) Anaphase;
II; 2
(b) (i) 23; 1
(ii) 46; 1
(iii) 46; 1
(c) 1. In seminiferous tubules (of testis);
2. At puberty / continuous through adult life / 12-16 years to 65-70 years;
3. Reference to {germinal cells / eq} divide by mitosis (to form
spermatogonia);
4. Spermatogonia divide by mitosis;
5. Form {primary spermatocytes /type B};
6. Divide by meiosis I;
7. Form secondary spermatocytes;
8. Divide by meiosis II;
9. Form spermatids;
10. Any reference to {correct male hormone / Sertoli cells} reference
to differentiation of spermatids to sperm; 5
[10]
401. (a) A Palisade mesophyll;
B Spongy mesophyll;
C {Lower / abaxial} epidermis; 3
(b) 1. Contains stomata;
2. Reference to guard cells;
3. (Which) control pore size / eq;
4. (Which) allow diffusion of gases (into and out of leaf);
5. E.g. {carbon dioxide in / oxygen out} during the day / converse at night; 3
[6]
402. (a) (Extensive root system) increases surface area;
For uptake of water;
Near surface so can take up water rapidly when it rains / eq; 2
(b) Storage;
Of water;
Allows easy movement of water through walls / allows expansion of cells; 2
David Kaunda High School 256
(c) Reduced surface area;
Fewer stomata;
Reduces {transpiration / water loss} / converse;
Protection against herbivores / eq;
Spines trap humid air; 3
[7]
403. (a) 1. As temperature increases, uptake of ions also increases;
2. Credit a manipulated point, e.g. uptake increases by 82 mmol per
3
dm from 5 to 30 °C / greatest increase between 10 and 20 °C 2
(b) (i) (42 – 8)
Calculation of percentage;
Answer = 425 (%) 2
(ii) Active transport / eq;
Concentration in cells is (much) higher than in culture solution / eq;
(Suggests) ions are taken up using {energy / ATP};
Against concentration gradient; 3
(c) (Cells) need oxygen / eq;
For (aerobic) respiration / anaerobic if no oxygen;
+ +
To provide {ATP / energy} for active uptake / Na :K pump;
Small uptake due to diffusion 2
[9]
404. (a) Arrow shown at day 14; 1
(b) Progesterone;
{Maintenance / further thickening} of the {endometrium / uterine lining} /
inhibits ovulation / increases {vascularisation / gland activity}
(of endometrium) / inhibits {FSH / LH / oxytocin / uterine contractions}; 2
(c) 1. {Initial / eq} rise in FSH;
2. Stimulates{development/growth} of {follicles/thecal cells/granulosa
cells; [not production or ripening]
3. Which secrete oestrogen;
4. Low oestrogen level gives {negative feedback / inhibition} of FSH;
5. High oestrogen level stimulates production of FSH;
6. Oestrogen stimulates LH production;
7. LH causes {ovulation / release of secondary oocyte};
8. And {development formation production) of corpus luteum; 5
[8]
David Kaunda High School 257
405. (a) Maximum volume of air breathed out;
Following maximum inspiration;
VC = IRV + TV + ERV;; 2
(b) 660 – 230;
3
= 430 cm 2
(c) Increased rate of breathing;
Increased depth of breathing /tidal volume increases; 2
[6]
406. (a) (i) Increases;
Quantitative manipulation of data; 2
(ii) [Increase in:]
Numbers of red {corpuscles cells erythrocytes};
Breathing rate;
Breathing depth;
Cardiac output / heart rate;
Decrease in urinary output;
Increase in blood volume;
Increase in erythropoietin (secretion); 3
(b) Air outside has a low partial pressure of oxygen;
Air in cabins is pressurised to {maintain consciousness / prevent
hypoxia / prevent mental confusion / prevent DVT} / eq; 2
[7]
407. (a) (Eating ice) decreases the core temperature;
By 0.5 °C (first time) / by 0.4 °C (second time); 2
(b) They are inversely related / as rate of sweating decreases, skin temperature
increases;
Credit a manipulated quantitative description; 2
(c) Evaporation of water;
Removes heat from body / reference to latent heat of evaporation; 2
(d) Eating ice reduces the core temperature;
Detected by hypothalamus;
Rate of sweating decreases;
Therefore less heat loss;
So skin temperature increases; 3
[9]
David Kaunda High School 258
408. (a)
Time (h) Mean blood pressure (kPa)
06:00 10.6 / 10.60
09:00 11.3 / 11.30
12:00 11.8 / 11.77
15:00 10.7 / 10.70
18:00 11.7 / 11.67
21:00 11.7 / 11.67
24:00 9.9 / 9.87
Neat table correctly formatted;
Correct rows and columns with labels and units;
[Means correct = 2 marks, 1 error = 1 mark and two errors = 0 marks] 4
(b) A Axes correct orientation and labelled with units;
S Scale correct and more than ½ paper used;
P Plot all points correctly;
L Line well drawn through all points; 4
(c) Trends and patterns:
All volunteers show similar pattern;
Reference to {peak at 12:00 / highest value for all at 12:00};
Lowest value at 24:00 / lowest value for all at 24:00;
Decrease in pressure to 15:00;
Conclusions:
Reference to {daily pattern / circadian rhythm};
Possible link to {activity / sleep}; 4
(d) Allow two marks for other named factors not controlled e.g. feeding,
activity, fitness levels of volunteers ; ;
Measurement intervals too long / pressure could be changing between
measurements; 2
[14]
David Kaunda High School 259
409. (a) 1. Lactose solutions of stated concentrations (min 4 suggested);
2. Same concentrations of both lactases used;
3. Use of buffer at {pH of small intestine / stated pH between 5-9};
4. Suitable method of temperature control at stated temperature 35-40;
5. All solutions equilibrated separately;
6. Stated volumes of lactose and lactase (added to artificial tubing);
7. Reference to mixing solutions / outside of tubing washed with distilled
water (to remove lactose);
8. Reference to use of {glucose testing sticks / Diabur / Diastix};
[allow use of Benedict’s reagent / clinistix]
9. Sampling stated volume of solution;
10. Method of quantitatively measuring {reducing sugar / glucose} eg.
use of standards / time of first appearance of ppt;
11. Repeat at each concentration ;
12. Repeat whole procedure with alternative enzyme; 9
(b) Suitable table with corrects rows and columns with units for raw data to
match suggested method;
Graph of the type that matches the table;
Correct orientation of axes with labels and units;
Reference to rate calculation; 3
(c) Limitations:
Concentration of enzymes difficult to determine accurately;
Difficult to adjust enzyme concentration to give measurable results;
Reference to subjectivity of test e.g. difficult to determine colour if using
glucose testing strips;
Disappearance of lactose not measured;
Experiment does not reflect the mix of substrates and digestive juices of
small intestine; Conditions in intestine may affect lactases in different
ways / microbial lactases may not work in small intestine;
[MAX 4 marks for Limitations]
Further work:
Test enzymes in in vivo conditions:
Use {a wider range of concentrations of lactose specific concentration
found in milk};
Test action of microlactase on milk;
Test action of microlactase on two or more sources of milk e.g. human
colostrum, human milk, cow’s milk etc;
Investigate for presence of symptoms of lactose intolerance when
microlactase used;
[MAX 4 marks for Further work] 6
[18]
David Kaunda High School 260
410. (a) Saprobiontic / saprophytic / saprotrophic / saprobiotic; 1
(b) Hypha / rhizoids / mycelium; 1
(c) 1. {Penetrates / grows across} {food / substrate} or forms large
surface area (in contact with food) / anchors organism on
{substrate / food};
2. {Secretes / releases) enzymes (onto substrate / food);
3. Named enzyme and substrate or product / idea of {hydrolysis /
breakdown} of large compounds to small;
4. Idea of {take in / uptake of / absorbs} {soluble products / named
soluble product} (of digestion);
5. Reference to {external / extracellular} digestion; 3
(d) Heterotrophs {take in / can’t make} organic compounds / eq AND autotrophs
{take in / use} inorganic compounds / synthesise organic compounds;
Heterotrophs rely on other organisms AND autotrophs use {light / external
energy / photosynthesis / eq}; 2
[7]
411. (a) (i) 1. Made up of {biotic components / living components / community
/ eq} AND {environment / habitats / surroundings};
2. Correct reference to {abiotic / physical and chemical} environment;
3. Reference to interaction with {a flow of energy / eq} /
reference to food {chains /webs};
4. Cycling of nutrients; 2
(ii) 1. Feeding level / level within a food {chain / web};
2. Credit two examples e.g. producer and primary consumer;
3. Reference to energy transfer between levels / eq;
4. Determined by the number of transfers of energy to that level / eq; 2
(b) (i) 562 ÷ 600 × 100;
93.67; 2
(ii) 1. Not all of the primary consumer is eaten / reference to inedible
body parts;
2. Reference to dead primary consumers {not being eaten by
consumer at higher trophic level / eq};
3. Losses from {respiration metabolism / heat};
4. Losses from (excretion / urine / egestion / faeces); 2
David Kaunda High School 261
(iii) 1. {Producers / plants / eq} have a {high rate of growth / rapid
reproduction};
2. Short life cycle / producers quickly replaced;
3. Producers have a {high productivity / eq};
4. Reference to large {numbers / mass} of producers eaten;
5. (Biomass) measured at one point in time / eq;
6. Consumers feeding elsewhere;
7. Primary consumers {reproduce quickly / have a high birth rate}; 3
(c) 1. Use quadrat of specified size / sample specified area;
2. Take random samples / reference to number of samples;
3. {Remove / trap / collect} all the {consumers / animals} within
the {quadrat / sample area};
4. Sort into trophic levels;
5. Remove (all) the {plants / producers} within the quadrat
(alternative method: remove one plant and weigh, then count the rest);
6. Clean soil off roots;
7. {Determine eq} the (fresh) mass of {all the trophic levels /
producers and consumers} 4
[15]
412. (a) Reversible damage is {not permanent / eq} and irreversible damage is
{permanent / eq};
Pipeline laying causes damage but {land / soil / eq} replaced;
Building treatment works is permanent because {land cannot be replaced
/ habitat is destroyed}; 2
(b)
Area Type of Area Ecological Units of Reversible Irreversible
development 2 category damage damage damage
/m
p 42 000 42 000
q 2 500 2 500
r 3 000 3 000
s 2 500 2 500
t 10 000
Totals 60 000 18 000 42 000
1. Units of damage calculated for p, q, r, s and t;
2. Damage for area p assigned to irreversible damage and damage for
areas q, r, s and t assigned to reversible damage;
3. Totals correct; 3
David Kaunda High School 262
(c) 1. (Total ecological) damage at Site 1 greater than at Site 2;
2. Reversible damage at Site 2 less than at Site 1 / irreversible damage at Site 2 greater
than at Site 1;
3. Two category 5s at site 2 AND one category 5 at site 1;
4. Manipulation of figures to compare magnitude of damage; 3
(d) Number of {species / different types of organism / different kinds of organism}; 1
(e) 1. Distance from shore / different lengths of pipeline;
2. Tidal movement / tides;
3. {Strength / direction) of currents;
4. Reference to wash back / eq;
5. {Strength / direction} of winds;
6 Wave action;
7 Depth of pipeline / depth of water;
8. Temperature of water / oxygen concentration in water; 3
(f) 1. Addition of {minerals / nitrates / phosphates / nutrients} / reference to
eutrophication;
2. And organic solids;
3. (Leads to) increased growth of {algae / seaweeds / plants / producers};
4. More food for {herbivores / primary consumers};
5. (So) {herbivores / primary consumers} increase in number;
6. More food for carnivorous fish; 4
[16]
413.
Name of organelle Two features of structure One function
Golgi (apparatus /
body);
Cisternae / {flattened / membranous / {Transport / storage} of
network} {sacs / tubules}; proteins / synthesise
Ribosomes; proteins / translation;
(Contains) {thylakoids / lamellae /
grana};
(Contains) {stroma / chlorophyll / DNA
/ starch granules};
(surrounded by) two membranes /
double membrane / envelope;
[6]
414. (a) Hydrogen / H 1
David Kaunda High School 263
(b) Charge is not equally distributed throughout molecule / one part is
positive and the other part is negative};
Hydrogen (atoms) have (slight) positive charges;
Oxygen (atom) has a (slight) negative charge ; 2
(c) Idea that a lot of {energy / heat} is needed to change temperature ;
Temperature of their {environment / habitat} does not {fluctuate / change}
much / reference to {thermostable / thermobuffer};
Reference to effect on metabolic {rate / reactions}; 2
[5]
415. (a) Ribose;
Lactose;
Sucrose; 3
(b) Unbranched chains;
Made up of glucose (molecules);
(Linked by) glycosidic bonds;
1, 4 linkages;
Reference to hydrogen bonds cross-linking chains; 3
[6]
416. (a) Four layers shown with no cells drawn;
Palisade layer narrower than spongy layer;
Epidermal layers similar width to each other and both much narrower than
mesophyll layers; 3
(b) (i) Palisade (mesophyll layer);
Mesophyll = 1 mark
Spongy (mesophyll layer);
Epidermis (upper or tower);
Xylem;
Vascular = 1 mark
Phloem; 2
(ii) It is made up of {several / more than one} tissue; 1
[6]
417. (a) Root tip / shoot tip;
Dividing cells / meristem; 2
(b) (i) To make the {chromosomes / chromatids / DNA} visible; 1
(ii) Acetic orcein / acetocarmine / Feulgens / Schiffs / any other
correctly named stain; 1
(c) To {get a single layer of cells / spread out cells}; 1
[5]
418. (a) (i) Nucleus / nucleoplasm; [allow nucleolus] 1
(ii) Condensation / polymerisation 1
(b) (i) 6; 1
(ii) GCT TGG CGG GCT TAG TGG;;
[all correct = 2 marks, one error = 1 mark, more than one error = 0 marks] 2
David Kaunda High School 264
David Kaunda High School 265
(c) Reference to start codon;
Reference to stop codon;
Reference to post transcription modification; 2
(d) 1. Occurs {on / in} ribosome;
2. Two tRNA molecules (held in position in ribosome);
3. Each carrying a specific amino acid;
4. Anticodons on tRNA;
5. Reference to binding of tRNA to complementary bases on mRNA;
6. Peptide bonds form between amino acids;
7. Ribosome moves along mRNA;
8. Until a stop codon is reached 5
[12]
419. (a) Reference to {alginate beads / other named method of immobilisation};
Description of appropriate method (e.g. mixing urease with alginate,
beads made by dropping into calcium chloride solution); 2
(b) (i) 100 ÷ 30;
3.3 a.u. per minute; 2
(ii) 1. Optimum pH is pH 7 for both immobilised and non-immobilised
urease;
2. The activity of non-immobilised urease is greater than the
immobilised at pH 7;
3. Immobilised urease is more active between pH 2 and 6 and
between pH 8 and 12 / converse;
4. Immobilised urease is active over a wider range of pHs;
5. Correct manipulation of figures to compare the activity of
immobilised urease to non-immobilised urease; 3
(iii) Active over wider range of pH:
Enzyme is more stable;
{Active site / enzyme} less likely to change shape / enzyme less
likely to denature;
Lower maximum activity:
Some {active sites / enzymes} less accessible to substrate; 2
[9]
420. (a) 1. Making more DNA;
2. Strands separate ;
3. Idea that each strand acts as a template / eq;
4. Nucleotides line up against complementary base pairs;
5. (Each) new (daughter) molecule contains one old and one new strand;
6. Reference to molecules being identical to {each other / original parent
molecule}; 4
David Kaunda High School 266
(b) (i) DNA in B is lighter (than the DNA in A) converse;
Because A contains all heavy nitrogen;
B contains both heavy and light nitrogen; 2
(ii) 1. (Bacteria) in B have one heavy and one light strand of
DNA (in each molecule);
2. All newly synthesised strands will contain light
{DNA / nitrogen};
3. Some molecules will consist of only light DNA;
4. Some molecules will consist of one light strand and
one heavy strand;
5. Each type of molecule is present in equal proportions; 3
(iii) Two bands shown in correct position;
Lower band is thinner than the one shown in D and upper band is
thicker than one shown in D; 2
[11]
421. Masticated / chewed / mechanically digested / eq;
Mucus / water;
Amylase / ptyalin;
Maltose / dextrins;
Pancreas; 5
422. (a)
Blood plasma Tissue fluid
Contained in vessels
Very low hydrostatic pressure
Contains white blood cells
[one mark for two correct]
[blanks are marked as incorrect] 3
(b) Reduced {blood / plasma) proteins / reduced named blood protein;
Causes reduced {solute concentration / osmotic pressure} of blood /
increases {water potential / solute potential} of blood / reduced {diffusion
/ concentration / water potential} gradient;
So less water reabsorbed (into capillaries);
[allow converse of points] 2
[5]
423. (a) 1. Maintains {endometrium / lining of uterus};
2. Develops {glands / blood vessels / eq} in {endometrium /
lining of uterus};
3. Inhibits {FSH / LH} (secretion);
4. Inhibits {prolactin / oxytocin}; 2
David Kaunda High School 267
(b) 1. Causes {growth / development maturation} of follicle / production of
Graafian follicle;
2. In ovary;
3. Stimulates oestrogen {secretion / production};
4. By {follicle cells / theca}; 2
(c) 1. Causes muscle contraction for {birth / release of placenta / labour};
2. In {uterus wall / myometrium};
3. Causes (‘muscle’ contraction for) {release / ejection / let down}
of milk;
4. In {mammary gland / breast}; 2
[6]
424. (a) General description of pressure changes;
Decreases to (a minimum) of {–0.29 / –0.3 / –0.31} (kPa);
Then returns to zero (at the end of inspiration);
Suitable time reference (e.g. minimum at 0.8 – 0.9 (s) or
1.62 – 1.7 (s) at end); 3
(b) Changes from {–0.29 / –0.3 / –0.29} (kPa) to {0.29 / 0.3 / 0.31} (kPa);
Overall change of {0.58 – 0.62} kPa;
[units needed once] 2
(c) (i) 1. Contraction of diaphragm;
2. Contraction of external intercostal muscles;
3. Increased volume in {thorax / chest};
4. Decreases pressure ;
5. Pressure rises as air moves in; 3
(ii) 1. Relaxation of diaphragm;
2. And {(external) intercostal muscles / muscles between ribs}
contraction of internal intercostal muscles;
3. Decreased volume in {thorax / chest};
4. Increases pressure;
5. Pressure decreases as air moves out;
6. Reference to {elasticity / elastic fibres}; 3
[11]
425. (a) 1. Thin / squamous / flattened (cells);
2. Decreases diffusion distance;
3. Large surface area (of cells);
4. Increases diffusion;
5. Of {respiratory gases / oxygen / carbon dioxide}; 3
(b) In solution (in the plasma);
Combined with haemoglobin / as carbaminohaemoglobin;
-
As {hydrogencarbonate / HCO3 } (in plasma); 2
(c) Increased {heart rate / diameter of lung (blood) vessels} OR increased
{cardiac output / stroke volume}; 1
[6]
David Kaunda High School 268
426. (a) A Sieve (tube) element;
B Companion (cell); 2
(b) (i) Phloem; 1
(ii) 1. Transport / translocation / eq;
2. Of {organic solutes / correctly named example};
3. From {source to sink / leaves to roots / leaves to growing point / eq};
4. Correct reference to {mass flow (hypothesis) / pressure flow / eq};
5. Correct reference to active process(es) in phloem loading;
6. Correct reference to transfer cells;
7. Correct reference to function of companion cells e.g. metabolic support; 4
[7]
427. (a) P Petal / corolla;
Q Anther;
R Stigma; 3
(b) 1. {Bee / insect} attracted to flower by {petals / colour / scent / nectar};
2. Pollen transferred from {anther / Q} to {stigma / R};
3. Reference to cross pollination as transfer of pollen from one
plant to another;
4. Pin tends to pollinate thrum / converse;
5. Idea that pollen on bee matches position of stigma in the other flower;
6. Correct reference to {stigma above anthers in pin-eyed / below
anthers in thrum-eyed};
7. (Therefore) less likely that pollen is transferred (directly) from anther
to stigma (in the same flower);
8. Self pollination less likely in pin than in thrum because of relative
positions of anther and stigma / converse; 5
[8]
428. (a) Leaves had different initial masses;
Can (therefore) make comparisons; 2
(b) (i) (Percentage change in mass) greater in moving air / converse; 1
(ii) 1. Loss in mass is due to loss of water (from leaf);
2. (Moving air) removes {humid air / eq} from vicinity of leaf / eq;
3. {Maintains / increases} {diffusion gradient / water potential gradient /
concentration gradient};
4. (Moving air) reduces thickness of {boundary layer / diffusion shell};
5. Reducing diffusion distance; 2
David Kaunda High School 269
(c) (i) 1. Reference to {epidermal peel / use of nail varnish};
2. Use of microscope;
3. Count number per {field of view / unit of area};
4. Repeat and find mean;
5. Reference to determining {area of leaf e.g. using graph paper / total number
(of stomata) on area of leaf}; 3
(ii) Directly related / more stomata gives a greater (percentage) change in mass;
Use of comparative manipulated figures (e.g. twice, double); 2
(d) 1. Increased kinetic energy;
2. Greater evaporation;
3. Increases diffusion;
4. Warm air can hold more water vapour than cold air; 2
[12]
429. (a) Hypothalamus; 1
(b) Reference to water temperature lower than body temperature / converse;
Heat lost by conduction (therefore body temperature decreased); 2
(c) (i) Decrease in temperature when swimming was faster than when
tying still ;
Decrease in temperature when swimming was greater than
when lying still;
Credit quantitative comparative difference; 3
(ii) 1. Reference to muscles used (when swimming);
2. Increased {blood flow / vasodilation} to {muscles / limbs};
3. Reference to increased ventilation;
4. (Therefore) increases heat loss from body;
5. Credit reference to the fact that the volunteer was thin therefore
less insulating effect of fat;
6. Idea that warm(ed) water is moved away from body’s surface
temperature gradient maintained; 2
[8]
430. (a) 1. Bone density increases from age 10 to 20;
2. Remains more or less constant from age 20 to {40 / 50} / reaches
a peak at 40 / increases at slower rate from 20 to 40;
3. Then decreases;
4. Reference to change in slope at age 70;
5. Same at 90 years old as at 10 years old; 3
David Kaunda High School 270
(b) 1. Smoking;
2. High alcohol intake;
3. Physical inactivity;
4. Thin body type;
5. Genetic factors;
6. Hormonal diseases, e.g. Cushing’s syndrome;
7. {Removal of / under active) ovaries / early menopause (below 40);
8. Calcium deficient diet / vitamin D deficiency;
9. Prolonged treatment with corticosteroids; 3
(c) 1. {Fertility / ovulation / menstruation} {stops / decreases};
2. (Associated with) decreasing secretion of {oestrogen / progesterone};
3. {Increased / continued} {FSH / LH};
4. Occurs between 40 – 60 ; [accept figure within this range]
5. Any feature e.g. {hot flushes / night sweats / lower sex drive /
mood swings}; 4
[10]
431. (a) A {Graafian / tertiary / mature / secondary} follicle / secondary oocyte;
B Corpus luteum / yellow body; 2
(b) C 23;
D 46; 2
(c) 1. Large surface area;
2. Increased (rate of) exchange / eq;
3. To provide {nutrients / named example / oxygen / etc.};
4. From maternal blood / to fetal blood;
5. Removal of {carbon dioxide / urea / heat};
6. To maternal blood / from fetal blood;
7. Storage of {iron / glycogen);
8. In case of dietary deficiency (in female);
9. Separation of maternal and fetal blood;
10. Protection against high blood pressure of female / reference to
{antibodies / immunological protection} / prevents transfer of (some)
pathogens / eq;
11. Secretion of {oestrogen / progesterone / HCG};
12. To maintain pregnancy; 5
[9]
David Kaunda High School 271
432. (a)
Concentration of Mean time / (Initial) Rate
hydrogen peroxide seconds (s) [ignore units]
–3
/ mmol dm
31.7 20.0 0.05
63.4 9.0 0.11
95.1 6.2 0.16
126.8 5.0 0.20
158.5 4.3 0.23
190.2 4.1 0.24
221.9 4.1 0.24
[shaded column optional]
Suitable table (concentrations and rates);
Correct rows and columns with labels and units [concentrations and rates];
Rates correctly calculated from means;
[1 error = 1 mark, 2 errors = 0 marks] 4
(b) F Line graph drawn;
A Axes correct orientation and labelled with units and using half paper;
P All points plotted correctly;
L Line joins points or good line of best fit through the points; 4
-3
(c) (Initial) rate increases until a concentration of 190.2 mmol dm ;
Rate increases at {constant / almost constant} rate to a concentration of
–3 -3
158.5 mmol dm / rate of increase is less between 158.5 – 190.2 mmol dm ;
Rate {doubles / almost doubles} as concentration doubles between {31.7 and
-3
63.4 / 63.4 and 126.8} mmol dm / manipulation of figures;
–3
Rate remains constant after 190.2 mmol dm ; 2
(d) Hypothesis correct at lower concentrations / eq;
Reference to need to modify hypothesis at higher concentrations (e.g. rate
of increase decreases at higher concentrations);
Reference to active sites becoming saturated at higher concentrations / eq; 2
(e) One variable not controlled e.g. {temperature / pH / lack of temperature
equilibration};
{Concentration / volume} of enzyme not standardised;
Hydrogen peroxide not renewed for second run;
(At high concentrations) time is too short to measure accurately;
End point difficult to determine accurately;
Some oxygen may escape from discs;
Pieces of liver may adhere to discs (altering mass); 2
[14]
David Kaunda High School 272
433. (a) 1. Suitable containers described e.g. petri dishes;
2. Same stated number of plants in each (minimum five);
3. Attempt to standardise Lemna e.g. same number of leaves on each / same mass of
Lemna;
4. pH range within 1 – 8 (minimum five different values);
5. Standard source of water / culture medium / pond / lake water;
6. Method of adjusting pH (accept drops of sulphuric or nitric acid)
7. Same volume of water in each;
8. Temperature and light (intensity) kept same for all samples
9. Cover with transparent cover / maintain water level;
10. Number of leaves counted at intervals / after fixed period;
11. Total time for experiment a minimum of 14 days; 9
(b) Suitable table with correctly labelled rows and columns with units
to match method;
Line graph;
Correctly orientated and labelled axes (check method);
Reference to method of calculating rate of growth; 3
(c) Limitations:
Counted leaves can be different sizes / eq;
Evaporation of water can change pH;
Natural pond / lake water can change pH;
Nutrients in dishes can get used up plants; Max 4 marks
Further work:
Test effect on different water plants;
Weigh mass / dry mass instead of counting leaves;
Examine plants for signs of physical damage;
Investigate actual (pH / water composition) of acidified lakes and ponds; 6
[18]
434. (a) Methane / CH4 1
(b) 1. Reference to {bacteria / microorganism / decomposers / eq};
2. Reference to {respiration / fermentation};
3. Reference anaerobic conditions / lacking O2;
4. Reference to methanogenesis / description of how methane is
produced / reference to methanogenic (bacteria); 2
(c) Fuel / cooking / heating / produce electricity; 1
(d) Fertiliser / manure / compost / enrich soil / idea of soil improvement / eq; 1
[5]
435. (a) Two species / two types of organism;
Benefits both;
Credit another example e.g. alga and fungus / description of how
they benefit; 2
(b) japonicum; 1
David Kaunda High School 273
(c) 66;
3.5; [allow consequential error] 2
(d) 1. (Rhizobium is a) {nitrogen fixing bacterium / nitrogen fixer};
2. Reference to nitrogenase;
3. Converts nitrogen to {ammonia / ammonium (compounds)};
4. Used to form {amino acids / proteins};
5. Idea of addition to those avai lable in soil;
6. (Therefore) more protein for growth; 4
(e) (i) South Dakota had a greater increase in yield / eq;
10 × greater / 6.4% more; 2
(ii) Reference to {climate / weather} may be different / specific climate
reference described
OR
May be difference in {natural Rhizobium / Azobacter / nitrate}
OR
Reference to possibility of {disease / pest / drought};
OR
Different soil types / fertilizer; 1
(f) (i) Individual beans vary in {size / mass) / takes less time / easier / eq; 1
(ii) Reference to {irregular / different} shape of beans / reference to
{they don’t pack down / (air) spaces between them) / variation of
density / idea of mass is related to energy content; 1
[14]
436. (a) {Microorganism / bacteria / protozoa / yeast / fungi} found in the rumen;
Reference to cellulase;
Reference to {mutualistic / symbiotic} relationship;
Food {stays / churned} in {rumen / stomach} for {long time / 5 - 30 hours};
Idea of fermentation / production of acids / production of {glucose / hexose};
Some food regurgitated and {chewed again / chewing the cud}; 3
(b) 175715 – 160572 ÷ 160572 × 100 OR 15143 ÷ 160572 × 100;
= 9.4; [allow 9.43] 2
(c) 1. Both increase;
2. Reference to manipulated figures / 0.8% more / eq;
3. Emissions from dairy cattle and sheep have decreased because
numbers have decreased;
4. Increased emissions from beef cattle because numbers have increased;
5. Change in (animal) diet has altered the emissions from {cattle / sheep};
6. Idea of change in human diet leading to changes in agriculture
e.g. more beef burgers eaten; 3
(d) (Methane) swamps / peat bogs / {paddy / rice} fields / landfill sites /
leaking gas pipes / coal mines / tundra {decomposition of organic material / eq}/
leaking biogas digester;
(Carbon dioxide) respiration / fermentation / combustion of fossil fuels /
combustion of C-containing substances / burning forests; 2
David Kaunda High School 274
(e) 1. Idea that greenhouse gases trap {heat / infrared energy};
2. Correct reference to short and long wave radiation;
3. Which keeps the global temperature at a level that can sustain life / eq
4. Increase in gases causes increase in the {heat / infrared energy)
trapped in the atmosphere / eq; 3
(f) GWP of methane is greater than that of carbon dioxide;
21x; 2
(g) (i) Because the others have increased more / eq; 1
(ii) 1. More {livestock / paddy fields / rice production) leads to
(increased) methane levels / eq;
2. More {waste in landfills / gas pipes / mining / biogas ) leads to
(increased) methane levels;
3. More {fridges / computers / aerosols / fire extinguishers} leads to (increased)
CFCs / eq,
4. More packaging leads to (increased) CFCs;
5. More {car engines / car exhausts / forest fires} leads to (increased)
nitrous oxide;
6. Increased use of (nitrogen / nitrate) fertilisers leads to (increased)
nitrous oxide; 3
[19]
437.
Name of biological Smaller molecules Name of bond joining
molecule from which it is the smaller
made molecules
Fatty acids and Ester;
glycerol;
Cellulose / polysaccharide (1, 4) Glycosidic;
/ disaccharide;
Peptide;
[5]
438. Nuclear {membrane / envelope} / nucleolus;
Centrioles;
Metaphase;
Centromeres / kinetochore / chromosome;
Anaphase;
[5]
David Kaunda High School 275
439. (a) (i) Hydrogen;
Ionic;
Disulphide; 2
(ii) It has two (polypeptide) chains / an A and a B chain / more than
one (polypeptide) chain; 1
(b) (i) {Sequence / order} of amino acids; 1
(ii) 1. Reference to bonds between R groups;
2. The R groups are always in the same position;
3. [Bonds / named bonds} will always form in the same place;
4. Reference to {hydrophilic groups on outside / hydrophobic
groups on inside}; 2
[6]
440. (a) (i) A Flagellum;
B DNA / bacterial chromosome; 2
(ii) Glycogen; 1
(iii) Made of {peptidoglycan / murein} / does not contain cellulose; 1
(b) Correct measurement: {80 / 81} mm;
Correct division: ÷ 6000;
Correct conversion to m;
[Maximum 2 marks if answer is incorrect, correct answer: 13.3 / 13.5] 3
[7]
441. (a) (i) (Inner) membrane of mitochondrion {is folded / forms cristae};
(Inner) membrane of mitochondrion has {ATPase / stalked particles /
electron carriers};
Nuclear membrane has pores;
(Outer) nuclear membrane is continuous with the endoplasmic reticulum;
(Outer) nuclear membrane has ribosomes; 2
(ii) Chloroplast; 1
(b) 1. Cylindrical;
2. Occur in pairs;
3. Lie at 90° to each other;
4. Made of microtubules;
5. Arranged in {triplets / nine groups};
[Maximum 2 marks from marking points 1-5]
6. Reference to spindle formation / organisation;
7. Reference to {microtubule organising centre / assembling the tubulin}; 3
[6]
David Kaunda High School 276
442. (a) (Fluid because) phospholipids move (around membrane);
(Mosaic because) membrane contains {proteins / glycoproteins} (amongst phospholipids);
2
(b) To remove the red pigment released by the cells {cut open / damaged} during preparation;
1
(c) 1. (Increasing bile salt concentration) results in increase of red coloration;
2. No further increase in red coloration {between 1.6% and 2.0% /
after 1.6%};
3. Reference to linear relationship between red coloration and bile
salt concentration up to 0.6%;
4. Reference to change in gradient after 0.6%;
5. Manipulation of figures to compare gradients before and after 0. 6 %; 3
(d) 1. Disruption of membrane by bile salts increases its permeability;
2. Bile salts may emulsify lipids (within membrane);
3. Proteins (in membrane) may be affected;
4. Pigment leaks through (plasma) membrane;
5. Pigment leaks through vacuole membrane;
6. By diffusion;
7. More bile salts, {more cells break down / more membrane disrupted};
8. Reference to plateau as all cells have lost pigment / all membranes
disrupted;
9. Reference to plateau as there is no longer a diffusion gradient; 4
(e) Any ONE of the following regarding Beetroot 2:
was different age
was stored under warmer conditions
was stored in different conditions
had more cells damaged during preparation
had discs with skin still on them
had discs taken from a different region of the beetroot
was different species
contained different concentrations of pigment
was grown in different conditions 1
[11]
David Kaunda High School 277
443. (a) Ring drawn around one phosphate, one sugar and one base (linked together); 1
(b) 1. Part of the DNA molecule unwinds;
2. DNA strands {separate / unzips / H-bonds break};
3. (Mono)nucleotides line up against their complementary bases;
4. Against {sense / one} strand;
5. Reference to RNA polymerase;
6. Individual mononucleotides join up by [condensation reactions /
(phosphodi)ester bonds};
7. mRNA strands separate from DNA molecule;
8. mRNA migrates into cytoplasm / eq; 5
(c) (i) Ribosomes / rough endoplasmic reticulum; 1
(ii) Ring drawn around U C G; 1
[8]
444. (a) Clarifying {wines / vinegar / fruit juices} / improves colour extraction
from fruit skins / peeling fruit skins; 1
(b) (i) Same concentration of enzyme;
Same pH;
Same time for incubation;
Same {type / age} apple;
Same temperature for filtering;
Standardisation of apple chopping; 2
(ii) The line goes up / rate increases;
Because of increase in {kinetic energy / collisions};
Reference to optimum at 40 °C 2
(iii) {Rate of production / line} decreases;
Because bonds break;
Therefore the active site changes shape / reference to denaturing
of enzyme;
Substrate will not fit / enzyme-substrate complex will not form;
Enzyme is denatured at 60 °C;
Reference to optimum at 40 °C; [only allow once, either here or in (b)(ii)] 3
David Kaunda High School 278
(c) (i) Mixture D Line drawn between A and B;
Line levels out at the same maximum as curves A, B and C; 2
(ii) 1. The results show that the rate of reaction depends on the relative
concentrations of inhibitor and substrate / {B / C} have similar
shape curve to A;
2. Faster initial rate at lower concentration of inhibitor;
3. {B / C} give the same yield {as A / when no inhibitor present};
4. This shows the inhibitor must be competitive;
5. Will be binding to active site;
6. Doesn’t stop the reaction completely; 2
[12]
445.
Blood
Name of cell One function
cell
Neutrophil / {Phagocytosis (of bacteria /
polymorph (onucleocyte) microbes) / description} / secretion
/ eosinophil / basophil; of {granules / antibacterial /basic
protein / histamine / heparin} /
reference to allergies;
Monocyte; Phagocytosis / forms macrophages
Lymphocyte; {Antibody / immunoglobin /
antitoxins} secretion (in response to
antigens) / synthesis;
[Each box marked independently]
[6]
446. (a) (i) (Chromosomes) condense / become visible / eq;
Presence of homologous chromosome pairs / (form) bivalents / synapsis;
Attach to spindle (fibres) ; [accept once, either here OR in (a)(ii)]
Reference to crossing over / reference to {chiasmata / genetic material
exchanged); 2
(ii) (Chromosomes) arranged at {equator / middle of cell};
{Bivalents / homologous chromosomes / very clear description} start
to separate;
Attach to spindle fibres; [accept once, either here OR in (a)(i)] 2
(iii) Centromeres divide / eq;
Each chromosome separates into two chromatids / the chromatids separate;
(Separated chromatids) move to opposite poles; 2
(b) (i) {Secondary / 2°} oocyte; 1
(ii) {Secondary / 2°} spermatocyte; 1
[8]
David Kaunda High School 279
447. (a) A {Aortic / semi lunar / SL} valve;
B Aorta / aortic arch;
C {Atrio-ventricutar / AV / bicuspid / mitral} valve; 2
(b) 1. {Valves / named valve / C} close;
2. (To) prevent backflow (of blood);
3. Reference to {contraction / systole} of ventricle;
4. Thick (muscular) wall / more muscle;
5. Provides high {pressure / force / eq};
6. To pump blood through {systemic circulation / round body / eq};
7. Reference to elasticity of {aorta / B} (to accommodate blood expelled
from ventricle) / eq; 4
(c) (i) 1. Uterus bigger / more tissue;
2. More muscle development / eq;
3. Reference to {development / maintenance} of {placenta / eq};
4. Reference to development of {fetus / baby};
[Maximum three marks]
(ii) 1. {More / greater} contraction / heart works harder;
2. (Because) {blood / oxygen / nutrients};
3. (Pumped to) {uterus / placenta / fetus / mother’s body}; 4
[10]
448. (a) Pancreas / pancreatic gland; 1
(b) (i) {Hydrolyses / eq} {starch / amylose / amytopectin};
To {maltose dextrins}; 2
(ii) Neutratises acid (from stomach) / provides {optimum pH / eq}
for enzymes idea of suitable conditions for enzyme activity; 1
(c) 1. {Thin / single layer / simpler epithelium;
To increase (rate of) diffusion / short diffusion distance;
2. Reference to {long / folds / villi / microvilli};
To increase surface area;
To increase (rate of) diffusion;
3. Presence of capillaries;
To maintain {diffusion / concentration} gradient;
4. Presence of lacteal;
To {uptake / eq} of {fats / products of fat digestion / eq};
5. Presence of muscle;
To keep contents in contact with the absorbing surface / eq; 5
[9]
David Kaunda High School 280
449. Alveoli:
1. (Thin wall) of {squamous / flattened} epithelium;
2. Decreases diffusion distance;
3. Reference to blood flow in the capillaries;
4. Reference to ventilation / eq;
5. {Maintains / eq} {concentration / diffusion} {gradient / difference} of
{(respiratory) gases / carbon dioxide / oxygen};
[Maximum 4 marks for Alveoli marking points (1 -5)]
Protozoa:
Reference to cell membrane;
Diffusion gradients maintained by {use of oxygen (in respiration) / release of carbon
dioxide (from respiration)};
Reference to movement (cell/water) to maintain diffusion gradient;
[5]
450. (a) Function: Photosynthesis / {absorb / trap} light;
Reason: Near top of leaf;
Cells contain [chloroplasts / chlorophyll};
Reference to densely packed cells; 3
(b) Buoyancy / eq;
Storage of [oxygen carbon dioxide gases)
Allows (rapid) [diffusion / movement) of [gases named e.g.); 2
(c) To enable {diffusion / uptake / exchange} of {gases (from air) / carbon dioxide / oxygen};
If in lower epidermis would let in water; 2
[7]
451. (a) No change with distilled water;
+
Width increased from 0 to 3 hours (with K );
+
Increasing rate change of width (with K );
+
Then remained {constant / more or less constant / eq} (with K ) /
reference to decrease to 4 hours;
Credit quantitative change, e.g. aperture increases by 7.6 m / rate; 3
(b) Potassium ions are causing the stomata to open;
Potassium ions enter guard cells;
(And) decrease the {water / solute} potential;
(So) water enters (guard) cells (by osmosis);
Increased turgor of (guard) cells;
Reference to unequal thickness of (guard) cell walls; 3
[6]
David Kaunda High School 281
452. (a) (i) 61% and 48%; [0.5] 1
(ii) The affinity of haemoglobin for oxygen decreases;
{Causes more oxygen to be released / increased dissociation of oxygen /
oxygen released more readily} (from haemoglobin) / haemoglobin less
saturated with oxygen;
At same partial pressure of oxygen;
(More) oxygen available for {respiration / ATP synthesis}; 3
(b) 1. Diffuses (from tissues) into tissue fluid;
2. Diffuses into {plasma / blood / capillaries};
3. Carbon dioxide in solution / dissolved (in plasma);
4. Red blood cell contains carbonic anhydrase;
5. H2O + CO2 H2CO3;
– +
6. H2CO3 HCO3 + H ;
–
7. HCO3 transported (in plasma / blood);
–
8. Reference to Cl / chloride shift;
+
9. H {buffered / eq} by haemoglobin / haemoglobinic acid reference;
10. CO2 combines with haemoglobin / carbaminohaemoglobin / carbamino
compounds;
11. Reference to reverse in alveoli / CO2 diffuses into {alveoli / alveolar
cavity / air}; 5
[9]
453. Alveoli:
1. (Thin wall) of {squamous / flattened} epithelium;
2. Decreases diffusion distance;
3. Reference to blood flow in the capillaries;
4. Reference to ventilation / eq;
5. {Maintains / eq} {concentration / diffusion} {gradient / difference} of
{(respiratory) gases / carbon dioxide / oxygen};
[Maximum 4 marks for Alveoli marking points (1 - 5)]
Placenta:
1. Reference to thin barrier between placenta and endometrium / eq /
accept reference to chorionic villi;
2. Reference to counter-current flow;
3. Concentration gradient {maintained by / eq} blood flow;
4. Reference to fetal haemoglobin taking up oxygen;
[5]
David Kaunda High School 282
454. 1. Increased lung volume / hyperventilation / barrel-chested / eq;
Increased surface area;
Increases pulmonary diffusing capacity;
Can take up much more oxygen;
2. Increased breathing rate / hyperventilation;
Increases pulmonary ventilation;
3. Increased red blood cell count / eq;
Increases oxygen carrying capacity of blood / eq
4. Increased haemoglobin content;
Increases oxygen carrying capacity;
5. Reduced sweating;
Reduces dehydration / eq;
6. Increased pigmentation of skin;
Reduces damage to skin from UV rays;
7. Reduced stature;
Less surface area for heat loss;
8. Lower thermoneutral zone;
Any reference to adaptation to low temperature;
9. Increased subcutaneous fat;
Reduces heat loss;
10. Increased metabolic rate;
To generate more heat;
11. Increased {HR / CO / SV};
Increased oxygen transport;
12. Increased blood volume;
Increased oxygen transport;
13. Increased pulmonary capillaries;
Increased oxygen uptake;
14. Reference to change in affinity of haemoglobin (for oxygen);
Increases {uptake / release} of oxygen;
[6]
455. (a) More carbohydrate and fat, less protein (in human milk);
[Accept converse for dried milk, or correct combination] 1
(b) Advantages (human milk):
More {carbohydrate / fat} - more energy;
More fat - appropriate fatty acids for nerve development;
Less sodium - less risk of increased blood pressure / hypertension;
Disadvantaqes (human milk):
Less protein – less {growth / developments};
More fat – greater risk of fat associated diseases (in later life);
Less calcium – poorer bone / tooth formation;
Less iron – less haemoglobin production;
[Allow correct converse for dried milk] 3
David Kaunda High School 283
(c) 1. At birth {placenta lost / eq};
2. Progesterone levels fall;
3. (Therefore) progesterone inhibition stops;
4. So prolactin is secreted so prolactin can cause milk
{production / secretion}; 3
[7]
456. (a) 1. Use inorganic materials / eq;
2. {Make / eq} organic materials / eq;
3. Reference to {photosynthesis / using light};
4. Reference to {chemosynthesis / using energy from chemicals}; 2
(b) 1. Production of {organic material / biomass / new tissue / named example};
2. Idea of energy incorporated into a trophic level;
–2 –1 –2 –1
3. KJ m year / kg m year / per (unit) {area / volume} per (unit)
time / eq;
4. Reference to {gross / net} productivity; 2
(c) 1. {Harvesting / using} {trees / forest} in such a way as not to {destroy /
reduce / use it up);
2. (To ensure supply) over a (relatively) long period of time (minimum
5 years);
3. Cutting timber at the same rate as it can be {grown / regenerated /
replanted / eq};
4. Credit suitable example of management programme e.g. {coppicing /
selective felling / pollarding / replanting}; 2
[6]
457. (a) (i) 1. Reference to all decrease;
2. The bigger the mesh, the greater the breakdown / leaves in the
5 mm mesh {broken down / eq} more quickly than the other bags;
3. Leaves in the air broke down the least;
4. In {1 mm / 5 mm mesh} no change after {Nov 1989 / May 1990}
but 0.05 mm continued to break down over entire period / eq;
5. In first six months, leaves remaining in 5 mm mesh was {half / eq}
that remaining in {0.5 mm / 1 mm} mesh / any other valid comparison;
6. Comparison of 0.05 in air and 0.05 in soil;
7. Credit for suitable comparative manipulation of data e.g. 19%
more leaves were broken down in 5 mm mesh compared with
61 % in 1 mm mesh; 4
David Kaunda High School 284
(ii) 1. {Soil animals / organisms / microorganisms / decomposers}
{responsible for the breakdown of the leaves / feed on the leaves};
2. The bigger the mesh, {the more animals / larger animals} are able
to enter the bags to feed on the leaves / eq;
3. Credit a specific example, e.g. worms cannot enter the bags with
smaller mesh;
4. Bag in the air had least breakdown because {fewer / no} {soil
animals / organisms / microorganisms / decomposers} could
get at the leaves / reference to {lack of moisture / dry air} / eq; 2
(b) The higher the nitrogen content {the greater the breakdown / eq};
{Soil animals / microorganisms / decomposers} {more numerous / breed
more / grow more} in leaves with higher nitrogen content OR leaves with
more nitrogen were more {palatable / nutritious} reference to lignin / eq; 2
(c) 1. Decomposition affected by {climate / weather};
2. {Hot / wet} climate increases rate of decomposition so leaves are
broken down quickly;
3. Pine needles {do not break down quickly / harder to break down}
(so build up on forest floor);
4. Rainforest leaves may have high nitrogen content so are broken
down more;
5. Reference to {temperature / pH} and enzyme activity;
6. Pine needles {may contain inhibitory chemicals / are thick / are
waxy / are fibrous / eq}; 3
(d) 1. {Bacteria / microorganisms / fungi} in soil {breakdown / putrefy /
decompose} leaves / reference to bacterial decomposition;
2. Releasing {ammonia / ammonium};
3. {Nitrosomonas / reference to nitrifying bacteria [allow ONCE]}
{converts / oxidise} {ammonia / ammonium) to nitrite;
4. {Nitrobacter / reference to nitrifying bacteria [allow ONCE]}
{converts / oxidise} nitrite to nitrate;
[Maximum 2 marks if any reference to nitrogen fixation or Rhizobium] 3
[14]
458. (a) 1. {Sulphur dioxide / nitrogen oxides};
2. (Produced by) burning {fossil fuels / named fossil fuel};
[Do not allow CO2]
3. {Dissolve / eq} in {moisture / rain / clouds} (in air) ;
[Do not allow for CO2]
4. {Falls / precipitated} as {acid rain / acidic rain} / makes rain acidic;
5. With pH less than 5;
6. Pass into soil and drain into streams that feed into rivers /
fall directly on rivers;
[Maximum 3 marks if neither sulphur dioxide nor nitrogen oxides
mentioned] 4
David Kaunda High School 285
David Kaunda High School 286
(b) 1. Mussel + hoglouse;
2. Able to {tolerate / survive in} {pH lower than 5 / in acidified rivers};
3. Less competition / more {food / space} in context;
4. {Fewer eaten / less predation}; 3
(c) 1. In non-acidified rivers {catch goes up / eq} and {catch falls / eq}
in acidified rivers;
2. Both more or less the same until 1940;
3. Both show similar pattern until {1960 / 1970} reference to particular
change compared between quoted years;
4. Both show some fluctuations;
5. Comparative manipulated data; 3
(d) 1. Reference to eggs affected;
2. So fewer fish hatch / eq;
3. Increased aluminium;
4. (Increases) mucus production by gills;
5. Reduced oxygen uptake / eq;
6. Reference to other heavy metals;
7. Reference to enzyme inhibition (linked to heavy metals);
8. Reference to food chain effects;
9. Specified food chain effect; 4
(e) (i) 125 – 5 = 120 then (120 ÷ 5) × 100; [accept alternative correct methods]
= 2400 (%) 2
(ii) Rivers {flow / eq} and lakes (more or less) have {stationary water / eq};
{Lime neutralised water} {washed away in rivers / not washed
away in lakes};
Reference to more acidic water enters rivers from streams
(after lime washed away) 2
[18]
459. (a)
Disaccharide Monosaccharide
Galactose Glucose Fructose
Sucrose
Maltose
Lactose
[One mark for each correct row] 3
(b) Glycosidic; 1
[4]
David Kaunda High School 287
460. Nitrogen / N;
Peptide;
{Alpha / α} helix;
Hydrogen / H;
R groups / side groups / side chains;
[5]
461. (a) A Nucleus / nucleoplasm / chromatin / nuclear {envelope / membrane};
B Chloroplast / stroma;
C DNA / chromosome / nucleoid; 3
(b) Cell wall of leaf cell is made of cellulose / bacterial cell wall is not made of
cellulose / bacterial cell wall is {peptidoglycan / mucopolysaccharide} /plant
cell wall is not made of peptidoglycan / mucopolysaccharide; 1
(c) To enable cell to move (through medium);
Rotates / eq;
Any valid reason for movement; 2
[6]
462. (a) (i) A Glycoprotein;
B Phospholipid; [do not allow bilayer] 2
(ii) Cell {recognition / attachment} / {receptor / eq} / antigen; 1
(iii) 1. {Fatty acids / tails} are {hydrophobic / non-polar};
2. Idea that fatty acids are in the middle of the bilayer;
3. {Phosphate / heads} are {hydrophilic / polar};
4. Idea that phosphate groups are on the outside of the bilayer;
5. Reference to {cytoplasm / tissue fluid} being {polar / eq} in nature; 3
(b) 1. The membrane is fluid;
2. (Because) {phospholipids /B} are able to move (within membrane);
3. (Therefore) proteins can move (within membrane / phospholipid bilayer);
4. Idea that there is a new arrangement of proteins; 2
[8]
463. (a) 1. Reference to named stain (acetic orcein / acetocarmine /
Feulgens / Schiffs);
2. {Warm / heat} (with the stain / acid);
3. Break open tip (with needle / eq);
4. {Mount / eq} in {stain / acid / water / glycerol};
5. (Gently) squash under coverslip / eq;
6. Warm (gently to intensify stain); 4
David Kaunda High School 288
(b) 1. Telophase is the longest stage;
2. Anaphase is the shortest stage;
3. Correct manipulation of figures to compare any two phases;
4. Any two actual times given e.g. {prophase 29.16 mins /
metaphase 16.80 mins / anaphase 8.40 mins / telophase 33.36 mins}; 3
(c) (Use the equation to) work out actual time of each phase;
Total all four times;
OR
Add up all 4 percentages;
1200
{Substitute into equation / eq} / Multiply by 100 ; 2
[9]
464. (a) Magnification How many times bigger the image is than the real size
of the specimen / eq;
Resolution The ability to distinguish two points as separate points / the
{degree / amount} of detail visible; 2
Number of stage microscope units
(b) Number of eye piece units ;
× 100 (to give correct answer); 2
(c) (i) 300 / 320 (µm); 1
(ii) Two cells drawn with indication of unequal thickening of cell wall;
In correct proportions;
No cell contents shown; 3
[8]
465. (a) (i) (By adding a) buffer (solution);
2
Using the same area of {cloth / 1 cm } / even spraying of cloth; 2
2 3
(ii) Starch and iodine on 1 cm square of cloth and 5 cm of buffer;
3
Add 5 cm of water (instead of enzyme); 2
(b) 1. Change in H+ concentration;
2. (Changes in pH) alter {charges / ionisation} of R groups;
3. Reference to bonds broken / eq;
4. Resulting in change in active site;
5. Reference to {substrate binding / eq} being affected;
6. Reference to (complete) {denaturation / eq} of enzyme at
extreme pHs / eq; 3
David Kaunda High School 289
(c) 1. (It) is a {polymer / polysaccharide / eq};
2. Of α glucose (molecules);
3. (Joined by α) glycosidic links;
4. (It) consists of amylose and amylopectin;
5. Amylose {is unbranched / forms helical shape};
6. Amylopectin is branched (molecule);
7. Amylose has only 1,4 (glycosidic) bonds;
8. Amylopectin contains 1,4 and 1,6 bonds;
9. Starch molecules {can be built up into starch grains /
have a compact shape}; 5
[12]
466. (a) Stack of at least three cisternae;
Cisternae curved / showing {budding / fusing} vesicles / eq;
{Cisternae / sacs / vesicles} labelled; 3
(b) (i) Level of radioactivity falls;
Protein moving out (of the RER); 2
(b) (ii) 1. (In first 20 minutes) there were no secretory vesicles / only
non-radioactive material in vesicles;
2. (Because) radioactive proteins have not yet reached the vesicles;
3. (Because) {proteins / radioactivity / eq} has yet to pass into
Golgi apparatus;
4. From RER (into Golgi);
5. (After 20 minutes) reference to formation of vesicles
(from Golgi) now containing (radioactive) protein; 3
[8]
467. Monocytes / eosinophils / basophils;
Round / rounded / circular / spherical;
Phagocytosis / endocytosis;
Antibodies / immunoglobulins;
[4]
David Kaunda High School 290
468. (a) 1. Pick up and release oxygen;
2. High affinity for O2 at high {pp / concentrations} of O2 / converse;
3. Carries {4 molecules / 8 atoms} of oxygen;
4. Reference to co-operative bonding / eq;
5. Reference to {picks up / transports} CO2 (at high {pp / concentration}
of CO2 / converse);
6. Reference to Bohr effect {qualified / described};
[Maximum 2 marks if referring to red blood cells (rather than
haemoglobin)] 3
(b) 1. O2 storage;
2. {High affinity for O2 / greater affinity for O2 / picks up O2 more readily / eq}
(than haemoglobin);
3. (So) takes up O2 from (circulating) {red blood cells / blood / haemoglobin};
4. Releases O2 at (very) low {pp / concentration } O2;
5. Provides O2 during {strenuous / eq} activity / allows muscle to respire
aerobically for longer; 3
[6]
469. (a) Ventricular systole; 1
(b) 1. Relaxation of atria and ventricles;
2. Reduces pressure (inside heart) / eq;
3. Refilling / eq;
4. AV valves are open;
David Kaunda High School 291
(c) 1. Correct reference to the coronary circulation;
2. Via the coronary artery;
3. From the aorta;
4. Reference to capillaries (within) cardiac muscles;
5. Reference to {red blood cells / haemoglobin} {carrying / releasing}
oxygen; 3
[6]
470. (a) 1. Microvillus / brush border;
2. Large surface area;
3. Increased (rate of) {absorption / diffusion / uptake};
4. Reference to transport proteins; 3
1. Capillary;
2. Reference to thin wall / presence of pores;
3. Reference to {high permeability / short diffusion distance /
increased diffusion};
4. Maintains {diffusion / concentration} gradient (by removal of
absorbed glucose); 3
(b) 1. Concentration of glucose increases (steadily);
2. Rate of glucose absorption does not increase / rate of absorption is
constant;
3. Reference to sodium co-transport mechanism;
4. Reference to (specific glucose) transport protein (on cell surface
membrane);
5. Active transport;
6. {Energy / ATP} required;
7. (Can be absorbed) against a concentration gradient / eq; 4
[10]
471. (a) (i) 1. Oxygen concentration decreases as depth increases /
converse;
2. Reference to greatest change below surface of mud / eq / converse;
3. Credit a quantitative description; 2
David Kaunda High School 292
(ii) 1. Reference to (very) low {oxygen / pO2} (3 cm below surface
of sediment);
2. Presence of {haemoglobin / respiratory pigment};
3. With a high affinity for oxygen;
4. Reference to structure reaching water {at / above} surface (of mud);
5. Idea that they live in burrows and aerate by movement;
6. Reference to anaerobic respiration;
7. Gills qualified; 3
(b) Gills;
(Provide a large surface area) for uptake of oxygen / gas exchange;
OR
Tail (fins);
Adaptation to swimming / eq;
OR
Feet / eq;
Gripping bottom (to move);
OR
Streamline shape;
Less resistance when swimming; 2
[7]
472. (a) Anther / pollen sac / microsporangium / pollen mother cell; 1
(b) Anaphase;
II; 2
(c) 7;
7;
14;
21; 4
[7]
473. (a) (i) Spongy (tissue) / spongy mesophyll; 1
(ii) 1. Large surface area;
2. Cells irregular in shape;
3. Reference to air spaces;
4. Thin (cell) walls (increase rate of diffusion);
5. Reference to diffusion (of gases); 3
David Kaunda High School 293
(b) (i) That the volumes are the same / eq; 1
3
(ii) Difference = 7 (cm );
Calculation mark (7 ÷ 3);
3
= 2.3 cm (per day); [allow CE]
3
[Reference to cm once for full marks]
3
[2.3 cm , with no working = 1 only] 3
[8]
474. (a) (i) M written between secondary follicle and part Q; 1
(ii) Graafian follicle / mature follicle; 1
(iii) Oestrogen;
Progesterone; 2
(b) 1. Sperm in {Fallopian tube / eq};
2. Release of enzymes (from acrosome);
3. Idea that enzymes digest channel on layers around secondary oocyte / eq;
[accept ovum]
4. Fusion of membranes;
5. Reference to second meiotic division (of secondary oocyte);
6. Reference to fusion of two nuclei;
7. Reference to change in permeability of egg membrane; 3
(c) 1. Reference to keeping maternal and fetal blood separate;
2. Protects fetus from high maternal blood pressure / prevents
agglutination;
3. Exchange (of materials) between fetal and maternal blood;
4. Correct reference to exchanges of {respiratory gases / oxygen /
carbon dioxide};
5. Correct reference to transfer of {nutrients / named example};
6. Correct reference to transfer of urea;
7. {Secretion / synthesis} of {hormones / HCG / oestrogen /
progesterone / relaxin};
8. Allows transfer of antibodies (to fetus); 5
[12]
475. (a) Temperature of hand in air stays constant, temperature of hand in
water decreases;
Temperature of hand in air is always higher;
Credit a quantitative comparison (2 figures quoted); 2
David Kaunda High School 294
(b) 1. Reference to temperature gradient between hand and air,
and hand and water;
2. Hand in air stays at 25°C because this is nearly {room / air}
temperature;
3. Hand in water loses heat by conduction (to water) / converse;
4. Decrease in blood flow to hand in water / eq; 2
(c) 1. Decrease in skin blood flow / vasoconstriction;
2. Reduces heat loss (to water);
3. Increase in {metabolism / shivering}.
4. Generates heat; 3
[7]
476. (a) Meiosis;
Chromosome number halved / cell B haploid / crossing over has occurred /
cell B has one pair of chromosomes / 2n n / reference to chromosome
P is different; 2
(b) 1. Homologous chromosomes pair / bivalents form / synapsis occurs;
2. Chiasma forms / crossing over occurs;
3. Exchange of parts / eq;
4. Between chromatids; 3
(c) Seminiferous tubule; 1
[6]
477. (a) Count the number of breaths {per minute / ref. to recording time}; 1
(b) (i) As walking speed increases, ventilation rate increases / eq;
Credit a manipulated quantitative reference; 2
(ii) 1. (Increased exercise) increases (production of) carbon dioxide;
2. Reference to respiratory centre / medulla;
3. Increased production of lactate;
+
4. Decreased blood pH / increase in H ;
5. Increased rate and depth of breathing; 3
(c) Difference: {75 – 72 / 3};
Calculation mark: 3 ÷ 75 × 100;
= 4 (%);
[If 3 ÷ 72 × 100 = 4.17, allow CE] 3
[9]
David Kaunda High School 295
478. (a)
+
Conc. of K ions Total number Number of
-3 % stomata open
(mol dm ) of stomata stomata open
0.0 / distilled water 76 17 22.4 / 22.37
0.010 81 24 29.6 / 29.63
0.025 73 26 35.6 / 35.62
0.050 90 40 44.4 / 44.44
0.100 83 36 43.4 / 43.37
[Shaded columns optional]
Suitable table format;
Rows and columns with correct headings and units;
All percentages correct;; [1 error = 1, 2 errors = 0 marks] 4
(b) F Line graph format;
A Axes correct - scale, orientation and labelled with units;
P All points plotted correctly;
L Suitable line point to point or good curve; 4
+
(c) 22.4% / many stomata open without additional K ions / all concentrations
+
of K ions cause greater opening than distilled water;
-3
Increasing concentration above 0.05 mol dm has no increased effect /
-3
reference to maximum effect at 0.05 mol dm / eq;
-3
Some simple manipulation of data e.g. increasing to 0.05 mol dm doubles
percentage of stomata open (in 15 mins); 2
(d) Hypothesis correct at lower concentrations / eq;
+
Ref to K hypothesis for stomatal opening; 2
(e) Use smaller intervals of concentration (not just more concentrations) /
use high concentrations;
Test effect beyond 15 minutes;
Use different species / types of leaf; 2
[14]
David Kaunda High School 296
479. (a) Mark scheme for biuret reagent method
B1. {Same / same stated} {mass / concentration} of both enzymes;
B2. Dissolved in {same / stated} volume of (distilled) water / {saline /
salt solution};
[allow once only]
B3. Reference to use of buffer (to control pH);
B4. Standardisation of protein source (e.g. volume / concentration / mass /
surface area / eq);
B5. Temperature stated (within 20 °C – 40 °C range);
B6. Use of water bath / stated method(s) of controlling temperature;
B7. Equilibration of solution(s) separately for stated time
(minimum 2 minutes);
B8. Reference to biuret reagent / CuSO4 + NaOH;
B9. Biuret colour change described – violet to blue;
B10. Sample {same / stated} volume at {fixed / specified} time intervals /
same volume of biuret;
B11. Reference to standardising colour of end point (using stated volume
enzyme solution and stated volume of biuret reagent);
B12. Measure time to reach {standard colour [allow blue] / end point}
OR use colorimeter (to record (%) {transmission / absorption});
B13. Repeat at least once for each enzyme;
Alternative marking points 8 and 9 for turbidity method
T8. Named suitable protein source; [not fresh milk]
T9. Turbidity change described – cloudy to clear; 9
(b) Suitable table with units and correct rows and columns to include
raw data to match suggested method;
Mean reaction time OR mean diameter;
Bar chart OR line graph [relevant to data] and comparative;
Correct orientation of axes with labels and units; 3
David Kaunda High School 297
(c) Limitations:
Enzyme Difficult to obtain pure enzyme
OR
Difficult to standardise concentration / eq;
Protein Protein(s) used not same as protein(s) that coat(s) lenses [if not in method]
OR
Comment about difficulty in obtaining (sufficient) lens coating protein;
[if in method]
Control Protein coated on lens may react differently to free protein / protein
coated on lens difficult to assess;
Measure Difficult to decide on end point; [relevant to method]
-ment
Further work:
Investigate proteases (subtilisin and superlitin) on the protein that
covers lenses (if not in method);
Compare findings with another named (described) technique;
Determine optimum conditions for use of enzyme (e.g. pH / temperature);
[must be in context of use in cleaning solution]
Compare the action of other proteases on contact lens protein; 6
[18]
Alternative mark scheme for viscosity method
V1. {Same / same stated} {mass / concentration} of both enzymes;
V2. Dissolved in {same / stated} volume of (distilled) water / {saline /
salt solution};
[allow once only]
V3. Reference to use of buffer (to control pH);
V4. Standardisation of protein source (e.g. volume / concentration / mass /
surface area / eq);
V5. Temperature stated (within 20 °C – 40 °C range);
V6. Use of water bath / stated method(s) of controlling temperature;
V7. Equilibration of solution(s) separately for stated time (minimum 2 minutes);
V8. Statement of what is to be measured e.g. {viscosity / eq};
V9. Measure {viscosity / eq} at {fixed / specified} time intervals /
fixed volume used to measure viscosity;
V10. Reference to standardising end point (with enzyme alone);
V11. Specific detail about viscosity measurements e.g. control of drop size,
nozzle size for drop or burette;
V12. Measure time for {viscosity measurement / eq} to reach standard;
V13. Repeat at least once for each enzyme; 9
David Kaunda High School 298
Alternative mark scheme for photographic film / contact lenses method
P1. {Same / same stated} {mass / concentration} of both enzymes;
P2. Dissolved in {same / stated} volume of (distilled) water / {saline /
salt solution};
[allow once only]
P3. Reference to use of buffer (to control pH);
P4. Standardisation of protein source (e.g. volume / concentration / mass /
surface area / eq);
P5. Temperature stated (within 20 °C – 40 °C range);
P6. Use of water bath / stated method(s) of controlling temperature;
P7. Equilibration of solution(s) separately for stated time
(minimum 2 minutes);
P8. Statement of what is to be measured e.g. release of {colour / silver}
OR reference to {opacity / eq};
P9. {Same / stated} volume of enzyme used;
P10. Reference to end point – black to clear;
P11. Detail about measurement e.g. use a piece of white card / colorimeter;
P12. Measure time to reach standard;
P13. Repeat at least once for each enzyme; 9
Alternative mark scheme for agar method
A1. {Same / stated} {mass / concentration} of both enzymes;
A2. Dissolved in {same / stated} volume of (distilled) water OR
{saline / salt} solution;
A3. Reference to use of buffer (to control pH);
A4. {Same / stated} type of agar OR use of gelatine;
A5. Temperature stated (within 20 °C – 40 °C range);
A6. Use of incubator OR stated method(s) of controlling temperature;
A7. {Agar / gelatine} same {depth / volume} OR well(s) cut to same diameter;
A8. Add {same / stated} volume of enzyme to each well;
A9. Reference to measurement of clear area;
A10. Detail about what is to be measured e.g. several diameters /
largest diameter;
A11. After period of incubation; [24 –48 hours]
A12. Reference to use of control (without enzyme);
A13. Repeat at least once for each enzyme;
[Marking points A1 and A2 must be in the context of both
enzymes being used] 9
David Kaunda High School 299
480. (a) A Combustion / combusting / burning
B Respiration / respire / respiring
C Respiration / respire / respiring
D Photosynthesis / photosynthesise / photosynthesising
[“breathing” negates B or C once]
[1 for each correct pair] 2
(b) 1. {Takes up / locks up / stores} {carbon / carbon dioxide}
(for a long time) / eq;
2. Named example e.g. {peat / coal / limestone / trees / fossil fuel /
chalk / shells}; 2
(c) (i) 1. Increase in {temperature of earth’s surface / mean global
temperature / eq};
2. Carbon dioxide is a greenhouse gas / due to an increase in
greenhouse gases;
3. (Which) {trap / reflect back} {heat / long wave / infra red} (in the
atmosphere);
4. Reference to an {increased / enhanced} greenhouse effect;
5. Reference to valid {effect / consequence} e.g. melting ice caps,
flooding, climate change; 2
(ii) Methane / CH4;
Nitrous oxide / N20;
CFCs (or related gases such as HFC and HCFC);
{Water / H2O} vapour;
Ozone / O3; 2
[8]
481. (a) {Primary / 1° / first} consumer / herbivore / 2 / second / level 2; 1
(b) {38 000 + 48 000 / 86 000} ÷ 92 000 × 100; [accept alternative method]
{93 / 93.48 / 93.478 / 93.5 / 94} (%); 2
(c) 1. Reference to energy loss {at each stage of / between stages of / along}
the {food chain / levels};
2. Only {a small proportion / 6%} of {original plant material / energy}
available to pass on to humans from cattle / eq;
3. Reference to time scale / eq;
4. Only one stage in food chain if {maize / crop} grown (for human
consumption) / human would be primary consumer; 3
(d) 1. {Incisors / canines} {chop / cut / eq};
2. {Hard pad / eq} acts as {chopping surface / eq};
3. Molars {grind / crush};
4. Lower jaw has a {side to side action / circular / eq} / reference to loose
articulation; 3
David Kaunda High School 300
David Kaunda High School 301
(e) 1. Reference to {micro-organisms / bacteria / protozoa / yeast} in rumen;
2. (Microorganism) produce {cellulase / eq};
3. Breaks down {cellulose / cellulobiose} to {sugars / monosaccharides /
other suitable products};
4. Reference to {mutualism / symbiosis};
5. Reference to {regurgitation / chewing cud} allows {several digestion /
increases surface area / better breakdown / further chewing / eq}; 3
[12]
482. (a) 1. Papua New Guinea no change;
2. Brunei and Thailand both decrease;
3. Any relevant comparison between decrease in Thailand and Brunei
e.g. decrease greater for Brunei than Thailand;
4. Any two comparative manipulated figures e.g. 28% for Brunei
and 12% for Thailand between ‘73 and ‘88; 3
(b) 1. Agriculture / named example;
2. Industry / named example;
3. Urbanisation / named example;
4. Fuel / named example;
5. Acid rain;
6. Natural disaster / named example; 2
(c) 1. (Removal of trees) causes loss of protective cover for soil / exposed to
{sun / rain / water / wind};
2. Tree roots {hold soil together / stabilise soil} / reference to
humus binding soil;
3. {Rain / water} {runs off the surface, carrying soil / washes soil away};
4. Wind blows away soil; 3
(d) 1. Less water evaporates from trees into atmosphere / reference to
less transpiration;
2. Less water in soil / more water runs off into {streams / rivers / eq};
3. Causes flooding;
4. Less water vapour in atmosphere so less rain;
5. Leads to {drought / low water table};
6. Reference to disruption of global {climate / rainfall patterns}; 3
David Kaunda High School 302
(e) 1. Idea of damage to forest as trees are removed / eq;
2. Removing trees leaves gaps in canopy;
3. More {light / rain} reaches forest floor;
4. Other species of plants may grow in the spaces / tree seedlings may
grow in the light;
5. Loss of {habitat / nesting site / roosting site} for the animals that live
in the timber trees;
6. Food chain affected / loss of food supply;
7. New habitats created / changes may favour other {plants / animals /
organisms / species} / change in biodiversity; 3
(f) (i) 1. All species show an {immediate / eq} fall in numbers (after logging);
2. Gibbons {recover after two years / do not return to original number};
3. After two years number of Maroon Langur {much higher than before logging
/ then {almost disappear / very low} after 4 years};
4. After 4 years number of White-fronted Langurs {almost double / eq}
(compared with those before logging); 2
(ii) 1. The idea that the decrease is due to disturbance caused by {logging /
machinery / people};
2. {Gibbons / Maroon Langur} need closed forest / need trees
closer together / don’t like more open forest / prefer taller trees;
3. Need trees for {movement through the canopy / food supply / escape
predators};
4. White-fronted Langur {prefers more open forest / out compete
others / better adapted} so numbers increase; 2
[18]
David Kaunda High School 303
You might also like
- Topical Guidebook For GCE O Level Biology 3 Part 2From EverandTopical Guidebook For GCE O Level Biology 3 Part 2Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Biology Unit 1 Edexcel Jan 96-June 05 Mark SchemeDocument97 pagesBiology Unit 1 Edexcel Jan 96-June 05 Mark Schemeapi-372956375% (4)
- Skema Trial 2014 Batu PahatDocument25 pagesSkema Trial 2014 Batu PahatKavinesh GanesanNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry Part Two Mxed AnswersDocument5 pagesBiochemistry Part Two Mxed Answersgauri kanodiaNo ratings yet
- Cell Cycle and Cell Division: Topic 1Document9 pagesCell Cycle and Cell Division: Topic 1Gautam KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Answer All Questions in This Section. Write Your Answers in The Spaces Provided in The Question PaperDocument14 pagesAnswer All Questions in This Section. Write Your Answers in The Spaces Provided in The Question PaperfongNo ratings yet
- Biology p4 Ms March 2021Document12 pagesBiology p4 Ms March 2021afyNo ratings yet
- Cell Cycle and Cell Division - DPP-02Document3 pagesCell Cycle and Cell Division - DPP-02Vishal SorteyNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 - Life Science - June Paper 1 - MemoDocument8 pagesGrade 10 - Life Science - June Paper 1 - MemoJustinCase1991No ratings yet
- Jan 2004 U1Document4 pagesJan 2004 U1api-3726022No ratings yet
- Cell Cycle and Cell Division - DPP 01 (Of Lec 02)Document3 pagesCell Cycle and Cell Division - DPP 01 (Of Lec 02)mankarangharialNo ratings yet
- Parth’s PRARAMBH SCIENCE ACADEMY Cell CycleDocument3 pagesParth’s PRARAMBH SCIENCE ACADEMY Cell CycleHarshadNo ratings yet
- Biology Paper 2 Marking SchemeDocument15 pagesBiology Paper 2 Marking Schemeveronica francisNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure MSDocument5 pagesCell Structure MSsophiaNo ratings yet
- Mitosis and Cell Cycle ADocument3 pagesMitosis and Cell Cycle AKhushi ShahNo ratings yet
- Cell Cycle and Cell Division - DPP-03Document3 pagesCell Cycle and Cell Division - DPP-03Vishal SorteyNo ratings yet
- Ans P2 Johor 2010Document15 pagesAns P2 Johor 2010Rozaini OthmanNo ratings yet
- 1 GCE Biology Marking Scheme January 2007 2Document21 pages1 GCE Biology Marking Scheme January 2007 2semirah anthonyNo ratings yet
- NTA NEET MAIN 101 Speed Tests-278-281Document4 pagesNTA NEET MAIN 101 Speed Tests-278-281Palmurugan MNo ratings yet
- 20210418 Cell Division and Cell Reproduction TIDARATDocument102 pages20210418 Cell Division and Cell Reproduction TIDARATPanyapat SrisawatNo ratings yet
- Practice Test For Botany Class 11Document4 pagesPractice Test For Botany Class 11Debangsu Ghosh100% (1)
- MEIOSIS TEST MEMODocument4 pagesMEIOSIS TEST MEMOMaciaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Cell Division MYM (Answer)Document7 pagesChapter 3 Cell Division MYM (Answer)AISHAH NAZIRAH100% (1)
- Biology Unit 1 & 2 Questions 1996 To 2005 MS PDFDocument97 pagesBiology Unit 1 & 2 Questions 1996 To 2005 MS PDFLeen WaheedhNo ratings yet
- 4551 Biologi Skema Pemarkahan 2018Document15 pages4551 Biologi Skema Pemarkahan 2018danialNo ratings yet
- Concept Strengthening Sheet CSS-10 Botany: Regd. Office: Aakash Tower, 8, Pusa Road, New Delhi-110005, Ph.011-47623456Document13 pagesConcept Strengthening Sheet CSS-10 Botany: Regd. Office: Aakash Tower, 8, Pusa Road, New Delhi-110005, Ph.011-47623456Partha SheeNo ratings yet
- Grade 12 Sba Controlled Test 1Document13 pagesGrade 12 Sba Controlled Test 1aphelelembhele065No ratings yet
- 1 Da S63 M 1 A5 Ycv Pce MF TD CJZ 8 FHMYqs NViDocument12 pages1 Da S63 M 1 A5 Ycv Pce MF TD CJZ 8 FHMYqs NViYaziNo ratings yet
- Biology 1700 Assignment 1Document13 pagesBiology 1700 Assignment 1api-508334317No ratings yet
- Life Sciences P2 May-June 2022 MG EngDocument11 pagesLife Sciences P2 May-June 2022 MG EngDariusNo ratings yet
- M13CDocument10 pagesM13CMiriam LópezNo ratings yet
- Living Enviroment Regents June 2008Document37 pagesLiving Enviroment Regents June 2008DOGGxYO100% (9)
- Cell Biology Mixed Question Quiz AnswersDocument6 pagesCell Biology Mixed Question Quiz Answersjay prakashNo ratings yet
- Mark Scheme (Results) Summer 2007: GCE Biology SNAB (6134/01)Document9 pagesMark Scheme (Results) Summer 2007: GCE Biology SNAB (6134/01)sar34wsNo ratings yet
- Week 2Document2 pagesWeek 2ahmedpadela84No ratings yet
- DNA and Protein Synthesis MS - UpdateDocument5 pagesDNA and Protein Synthesis MS - UpdateAzad AlizadaNo ratings yet
- Life Sciences P2 Sept 2020 GR 12 QPDocument15 pagesLife Sciences P2 Sept 2020 GR 12 QPPBS SibandaNo ratings yet
- M-Caps-02: Botany: NEET - XI StudyingDocument3 pagesM-Caps-02: Botany: NEET - XI StudyingAbhishek Kumar VermaNo ratings yet
- MS Formative 1 Aug 2021Document10 pagesMS Formative 1 Aug 2021Aditya RaoNo ratings yet
- May 2013 MS TZ1Document9 pagesMay 2013 MS TZ1Eda ŞafakNo ratings yet
- Life Sciences NSC P2 QP Nov 2022 EngDocument16 pagesLife Sciences NSC P2 QP Nov 2022 Engsiyethabazondi3No ratings yet
- HMK Cell Division and Specialisation MCQDocument11 pagesHMK Cell Division and Specialisation MCQkatiegale50No ratings yet
- Life Sciences P1 GR 10 Exemplar Memo EngDocument8 pagesLife Sciences P1 GR 10 Exemplar Memo EngstephanseggsyNo ratings yet
- Skema Jawapan StrukturDocument7 pagesSkema Jawapan Strukturmarwani mat nasirNo ratings yet
- Life Sciences P1 2016Document11 pagesLife Sciences P1 2016nkosi3000No ratings yet
- A2AS BIOL Past Papers Mark Schemes Standard January Series 2013 11881Document8 pagesA2AS BIOL Past Papers Mark Schemes Standard January Series 2013 118816nht9f65zcNo ratings yet
- BIOL 182: Cell Division, Genetics and Molecular BiologyDocument7 pagesBIOL 182: Cell Division, Genetics and Molecular BiologyMayaNo ratings yet
- IBL420S - Introduction To Biology - 1st - 2016Document6 pagesIBL420S - Introduction To Biology - 1st - 2016Nyashah FelixNo ratings yet
- Answers To Exam-Style Questions: Topic 1 Topic 2Document9 pagesAnswers To Exam-Style Questions: Topic 1 Topic 2Mahnoor ShahidNo ratings yet
- Paper 2 Nov Res 2012Document10 pagesPaper 2 Nov Res 2012XdNo ratings yet
- Bks IGCB2 Ccuu An01 XxaannDocument8 pagesBks IGCB2 Ccuu An01 XxaannThet Nay OoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Cell Division SB015Document59 pagesChapter 3 Cell Division SB015Muhammad IzuanNo ratings yet
- Cell Cycle QuestionsDocument9 pagesCell Cycle QuestionsParnava Pratihar V BINOY 64No ratings yet
- Revision SB025 Set 1 AnswerDocument12 pagesRevision SB025 Set 1 Answerewine0529No ratings yet
- Cell Division and Cell CycleDocument18 pagesCell Division and Cell CycleAKM KINGNo ratings yet
- Mi H Biology All 2011Document22 pagesMi H Biology All 2011Nathan MwapeNo ratings yet
- Grade 11 - Life Science - November Paper 2-1 - MemoDocument8 pagesGrade 11 - Life Science - November Paper 2-1 - MemoJustinCase19910% (1)
- Monomers and Polymers MS PDFDocument8 pagesMonomers and Polymers MS PDFRaihanNo ratings yet
- Mark Scheme Bio 2 Trial Selangor 2007Document17 pagesMark Scheme Bio 2 Trial Selangor 2007hasimahazitNo ratings yet
- EDEXCEL 6677 MECHANICS M1 JANUARY 2004 MARK SCHEMEDocument4 pagesEDEXCEL 6677 MECHANICS M1 JANUARY 2004 MARK SCHEMEKollol KolllolNo ratings yet
- January 2002 MSDocument3 pagesJanuary 2002 MSWael TareqNo ratings yet
- January 2005 QPDocument13 pagesJanuary 2005 QPWael TareqNo ratings yet
- January 2002 QP - M1 EdexcelDocument6 pagesJanuary 2002 QP - M1 EdexcelAkhlak HossainNo ratings yet
- January 2001 QP - M1 EdexcelDocument5 pagesJanuary 2001 QP - M1 EdexcelAkhlak HossainNo ratings yet
- January 2006 6677 Mechanics M1 Mark SchemeDocument5 pagesJanuary 2006 6677 Mechanics M1 Mark SchemeWael TareqNo ratings yet
- January 2003 QP - M1 EdexcelDocument5 pagesJanuary 2003 QP - M1 EdexcelBryan FuryNo ratings yet
- January 2004 QPDocument6 pagesJanuary 2004 QPWael TareqNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 May19 Till Jan21Document306 pagesUnit 2 May19 Till Jan21Wael TareqNo ratings yet
- PhysicsAndMathsTutor Mechanics Mark SchemeDocument7 pagesPhysicsAndMathsTutor Mechanics Mark SchemeWael TareqNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 May19 Till Jan21Document299 pagesUnit 1 May19 Till Jan21Wael TareqNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 May19 Till Jan21Document189 pagesUnit 3 May19 Till Jan21Wael TareqNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 May19 Till Jan21Document189 pagesUnit 3 May19 Till Jan21Wael TareqNo ratings yet
- January 2001 MSDocument4 pagesJanuary 2001 MSWael TareqNo ratings yet
- Combined 2010 Till 2018 With SpecimenDocument1,615 pagesCombined 2010 Till 2018 With SpecimenWael TareqNo ratings yet
- Mock Examination Al-Rowad International SchoolsDocument14 pagesMock Examination Al-Rowad International SchoolsWael TareqNo ratings yet
- HL Test 2013: Cells (Topics 2.1 To 2.4) : Name - PeriodDocument7 pagesHL Test 2013: Cells (Topics 2.1 To 2.4) : Name - PeriodWael TareqNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 May19 Till Jan21Document299 pagesUnit 1 May19 Till Jan21Wael TareqNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 May19 Till Jan21Document306 pagesUnit 2 May19 Till Jan21Wael TareqNo ratings yet
- As Biol Unit 2 Example QuestionsDocument26 pagesAs Biol Unit 2 Example QuestionsWael TareqNo ratings yet
- 2010 Till 2021Document1,914 pages2010 Till 2021Wael TareqNo ratings yet
- Combined 2010 Till 2018 With SpecimenDocument1,615 pagesCombined 2010 Till 2018 With SpecimenWael TareqNo ratings yet
- LifeDocument35 pagesLifeJannette Jane DavidNo ratings yet
- Antimicrobial Host Defense PeptidesDocument22 pagesAntimicrobial Host Defense PeptidesSherlock HolmesNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Sosial PolitikDocument488 pagesJurnal Sosial PolitikMuhamad MiftachudinNo ratings yet
- MLS 408 Midterms: Mendelian Inheritance and CytogeneticsDocument33 pagesMLS 408 Midterms: Mendelian Inheritance and CytogeneticsLovely Mae EspañolNo ratings yet
- Angiosperms Male Parts of Angiosperms: AntherDocument4 pagesAngiosperms Male Parts of Angiosperms: AntherAriel PononNo ratings yet
- Capsicums - Innovative Uses of An Ancient CropDocument11 pagesCapsicums - Innovative Uses of An Ancient CropMaarioNo ratings yet
- Human Biology, Science, and Society: Lecture Presentation by Suzanne Long, Monroe Community CollegeDocument29 pagesHuman Biology, Science, and Society: Lecture Presentation by Suzanne Long, Monroe Community CollegeTAHA GABRNo ratings yet
- InvasiveAppleSnailsBook2017 FinalDocument424 pagesInvasiveAppleSnailsBook2017 FinalSandraJustinoNo ratings yet
- Government College of Nursing, Jodhpur: Presentation ONDocument7 pagesGovernment College of Nursing, Jodhpur: Presentation ONpriyanka0% (1)
- CHAPTER XI - Gene TherapyDocument4 pagesCHAPTER XI - Gene TherapyKeannoNo ratings yet
- Scientists Discover Childrens Cells Living in Mothers Brains Scientific AmericanDocument1 pageScientists Discover Childrens Cells Living in Mothers Brains Scientific AmericanGosh KaNo ratings yet
- HEMATOLOGYDocument153 pagesHEMATOLOGYmariel clementeNo ratings yet
- Jurnal TranskripsiDocument4 pagesJurnal TranskripsiGisela GloryNo ratings yet
- Philsci Questionnaire FinalDocument15 pagesPhilsci Questionnaire Finalandrea dyanne AzoresNo ratings yet
- BiodiversityDocument34 pagesBiodiversityHerlinaNo ratings yet
- Fphys 10 00287Document9 pagesFphys 10 00287Maria Julia Ogna EgeaNo ratings yet
- IMMUNODIFFUSIONDocument12 pagesIMMUNODIFFUSIONDhaval Shah100% (3)
- 2nd Term Grade 12 English QuestionsDocument10 pages2nd Term Grade 12 English QuestionsTaze UtoroNo ratings yet
- Animal Cells and Plant CellsDocument4 pagesAnimal Cells and Plant CellsPranav BISUMBHERNo ratings yet
- 2019 Book EvolutionaryGenomicsDocument777 pages2019 Book EvolutionaryGenomicsAnonymous zHra6PvNo ratings yet
- Biological OxidationDocument42 pagesBiological OxidationSapana Subedi100% (1)
- Physicochemical and Microbiological Characteristics of El-Guedid From MeatDocument9 pagesPhysicochemical and Microbiological Characteristics of El-Guedid From MeatNatália KoiyamaNo ratings yet
- Class 11 Chapter 3 BryophytesDocument6 pagesClass 11 Chapter 3 BryophytesAshok KumarNo ratings yet
- Medical & Diagnostic Bacteriology: A Guide in Resources Constrained LaboratoriesDocument229 pagesMedical & Diagnostic Bacteriology: A Guide in Resources Constrained LaboratoriesVitus SilagoNo ratings yet
- Leber Hereditary Optic Neuropathy Review of TreatmDocument8 pagesLeber Hereditary Optic Neuropathy Review of Treatmfebyan yohanesNo ratings yet
- One Word Questions - Physiology - Fill Ups and Location Type QuestionsDocument16 pagesOne Word Questions - Physiology - Fill Ups and Location Type Questionss vNo ratings yet
- The Role of IgADocument3 pagesThe Role of IgAullifannuriNo ratings yet
- Kamal Grammar School Biology Test QuestionsDocument5 pagesKamal Grammar School Biology Test QuestionsRafiq AfridiNo ratings yet
- Practical Manual of Developmental BiologyDocument93 pagesPractical Manual of Developmental Biologyarushi4702No ratings yet
- Hepatitis D Virus RNA, Quantitative Real-Time PCR - Test Detail - Quest DiagnosticsDocument2 pagesHepatitis D Virus RNA, Quantitative Real-Time PCR - Test Detail - Quest DiagnosticsevafadillahNo ratings yet
- Alex & Me: How a Scientist and a Parrot Discovered a Hidden World of Animal Intelligence—and Formed a Deep Bond in the ProcessFrom EverandAlex & Me: How a Scientist and a Parrot Discovered a Hidden World of Animal Intelligence—and Formed a Deep Bond in the ProcessNo ratings yet
- Roxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingFrom EverandRoxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- Roxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingFrom EverandRoxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (33)
- World of Wonders: In Praise of Fireflies, Whale Sharks, and Other AstonishmentsFrom EverandWorld of Wonders: In Praise of Fireflies, Whale Sharks, and Other AstonishmentsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (222)
- Fire Season: Field Notes from a Wilderness LookoutFrom EverandFire Season: Field Notes from a Wilderness LookoutRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (142)
- Dark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseFrom EverandDark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (69)
- The Other End of the Leash: Why We Do What We Do Around DogsFrom EverandThe Other End of the Leash: Why We Do What We Do Around DogsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (63)
- Why Fish Don't Exist: A Story of Loss, Love, and the Hidden Order of LifeFrom EverandWhy Fish Don't Exist: A Story of Loss, Love, and the Hidden Order of LifeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (699)
- The Ancestor's Tale: A Pilgrimage to the Dawn of EvolutionFrom EverandThe Ancestor's Tale: A Pilgrimage to the Dawn of EvolutionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (811)
- Wayfinding: The Science and Mystery of How Humans Navigate the WorldFrom EverandWayfinding: The Science and Mystery of How Humans Navigate the WorldRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (18)
- The Mind of Plants: Narratives of Vegetal IntelligenceFrom EverandThe Mind of Plants: Narratives of Vegetal IntelligenceRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (11)
- The Revolutionary Genius of Plants: A New Understanding of Plant Intelligence and BehaviorFrom EverandThe Revolutionary Genius of Plants: A New Understanding of Plant Intelligence and BehaviorRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (137)
- The Hidden Life of Trees: What They Feel, How They CommunicateFrom EverandThe Hidden Life of Trees: What They Feel, How They CommunicateRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1002)
- When You Find Out the World Is Against You: And Other Funny Memories About Awful MomentsFrom EverandWhen You Find Out the World Is Against You: And Other Funny Memories About Awful MomentsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (13)
- The Secret Life of Lobsters: How Fishermen and Scientists Are Unraveling the Mysteries of Our Favorite CrustaceanFrom EverandThe Secret Life of Lobsters: How Fishermen and Scientists Are Unraveling the Mysteries of Our Favorite CrustaceanNo ratings yet
- Come Back, Como: Winning the Heart of a Reluctant DogFrom EverandCome Back, Como: Winning the Heart of a Reluctant DogRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (10)
- Last Child in the Woods: Saving Our Children From Nature-Deficit DisorderFrom EverandLast Child in the Woods: Saving Our Children From Nature-Deficit DisorderRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (283)
- The Rise and Fall of the Dinosaurs: A New History of a Lost WorldFrom EverandThe Rise and Fall of the Dinosaurs: A New History of a Lost WorldRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (593)
- The Lives of Bees: The Untold Story of the Honey Bee in the WildFrom EverandThe Lives of Bees: The Untold Story of the Honey Bee in the WildRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (44)
- Spoiled Rotten America: Outrages of Everyday LifeFrom EverandSpoiled Rotten America: Outrages of Everyday LifeRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (19)