Professional Documents
Culture Documents
PMLS2 - Familiarization in Phlebo
Uploaded by
Corinne Bautista Reniva0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
119 views3 pages1) Blood collection equipment includes vein locating devices, tourniquets, needles of varying gauges, and evacuated tube systems.
2) Antiseptics like alcohol and iodine are used to clean skin and disinfect equipment. Phlebotomy needles come in multi-sample or hypodermic varieties.
3) Blood tubes contain additives to prevent clotting or enhance coagulation and are color coded for easy identification. The evacuated tube system allows blood to flow directly into tubes while the syringe system transfers blood via syringe.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Document1) Blood collection equipment includes vein locating devices, tourniquets, needles of varying gauges, and evacuated tube systems.
2) Antiseptics like alcohol and iodine are used to clean skin and disinfect equipment. Phlebotomy needles come in multi-sample or hypodermic varieties.
3) Blood tubes contain additives to prevent clotting or enhance coagulation and are color coded for easy identification. The evacuated tube system allows blood to flow directly into tubes while the syringe system transfers blood via syringe.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
119 views3 pagesPMLS2 - Familiarization in Phlebo
Uploaded by
Corinne Bautista Reniva1) Blood collection equipment includes vein locating devices, tourniquets, needles of varying gauges, and evacuated tube systems.
2) Antiseptics like alcohol and iodine are used to clean skin and disinfect equipment. Phlebotomy needles come in multi-sample or hypodermic varieties.
3) Blood tubes contain additives to prevent clotting or enhance coagulation and are color coded for easy identification. The evacuated tube system allows blood to flow directly into tubes while the syringe system transfers blood via syringe.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
PRINCIPLES OF MEDICAL LABORATORY SCIENCE 2
[TRANS] LESSON 4: BLOOD COLLECTION EQUIPMENT, ADDITIVES, AND ORDER OF DRAW
1. Vein-locating devices: transillumination portable devices
that use infrared light to locate veins
OUTLINE 2. Tourniquet: constricting device applied to patient’s arm
I General Blood Collection Equipment & Supplies prior to venipuncture
II Venipuncture Equipment Inflates veins by restricting venous blood
A Antiseptics and Disinfectants
flow
III Phlebotomy Needles
IV Syringe System and Evacuated Tube System (ETS) 3. Needles: for withdrawing blood
Components Multi-sample, hypodermic, winged infusion
V Categories of Additives Used in Blood Collection 4. Needle gauge: according to diameter of lumen
VI Order of Draw Higher the number = smaller needle
diameter
21 gauge: commonly used
GENERAL BLOOD COLLECTION EQUIPMENT Length: 1-1.5 inches
AND SUPPLIES With color coded caps and equipped with
safety features: resheating, blunting, and
Table 1. Equipment & Supplies retraction devices
Equipment Use 5. Evacuated tube system (ETS): closed collection system
Blood- For outpatient department Multi-sample, adapter, evacuated tubes
drawing - With bed or padded table for heelstick : allows blood to flow directly to the tube
station procedure
- For “stat” cases ANTISEPTICS & DISINFECTANTS
Equipment - Early morning phlebotomy rounds Environmental and Protection Agency (EPA) registered
carrier - Left in the hallway to avoid nosocomial Sodium hypochlorite with 1:100 dilution – “chlorox:
infection o 1 is to 10
1. Non-sterile o 100 ml: 10ml = hypochlorite (?)
2. Disposable latex For spills: 10% dilution is used
3. Nitrile o Contact time: 10 mins
Gloves 4. Neoprene Antiseptics:
5. Polyethylene o 70% ethyl alcohol
6. Vinyl o 70% isopropyl alcohol
7. Liners (if prone to allergies) because of its properties; water acts a
- Prevents sepsis denature/catalyst to penetrate the walls of
Antiseptics
- Applied onto skin of patient the bacteria; helps in penetration in killing
Disinfectants - Sanitizes instruments and materials the bacteria
- Clean 2x2 inch gauze folded in fourths o Benzalkonium chloride
- Hold pressure after blood coll o Chlorhexidine gluconate: for larger surfaces
Gauze pads
- Has fluid proof backing
o Hydrogen peroxide
**Cotton - can remove platelets on area
o Povidone-iodine: for alcohol test
Can be used once bleeding has stopped
o Tincture iodine
Bandages - Paper, cloth, knitted tape can be used
over folded gauze
1x3 inch PHLEBOTOMY NEEDLES
glass For blood films in hematology Multi-sample needles: used in ETS; equipped w/ safety
microscope determination features
slides o Color-coded needles that do not have safety
Pen with non features must be used with tube holders that have
Ball point pen for labelling specimens safety features
smear ink
Watch with Hypodermic needle: used in syringe system; different
Monitor collection time and to time tests gauges and lengths
timer
Sharps Winged infusion set (butterfly): for difficult veins,
Receptacle for needles, syringes, lancets pediatric or elderly patients; more flexible
disposal
and other sharp objects Wings: for easy manipulation of shallow
containers
To transport blood and other specimens to angle insertion
the lab o ½ to ¾ inch stainless needles
Biohazard o 23 to 25 gauge
- Leak-proof
bags
- Outide pocket for requisitons and other o 5 to 12 inch tubing
documentations o Luer attachment for syringes
o Multi-sampler luer adapter for ETS
VENIPUNCTURE EQUIPMENT
RENIVA | MLS1-5 1
PRINCIPLES OF MEDICAL LABORATORY
SYRINGE SYSTEM & EVACUATED TUBE SYSTEM
COMPONENTS
SCIENCE
Enhance coagulation in serum specimen tubes
2 types of activators: clotting 2
factors (thrombin) and
substances that provide more surface for platelet
SYRINGE SYSTEM activation (silica and inert clays [celite] )
Alternative method when drawing blood with small or
difficult veins; THIXOTROPIC GEL SEPARATOR
Transferred to tubes using a syringe transfer device which From metabolizing subs.
is attached to the hub of the syringe Moves between cells, serum or plasma when centrifuged
Syringe transfer device: w/o stopper removal TRACE ELEMENT FREE TUBES
Traditional method
Royal blue stoppers
o syringe needle w/ resheating feature o Trace element tests, toxicology studies, nutrient
o syringe divided into graduated barrel and plunger
determination
Plunger is pulled back slowly = vacuum
Uses hypodermic needle and sterile plastic syringe w/ COLOR CODING IN IDENTIFYING ADDITIVES IN
Luer lock tip BLOOD COLLECTION TUBES
o common syringes: 2ml, 5ml, 10ml
Additive: placed in tube to prevent clotting and to
preserve components
EVACUATED TUBE SYSTEM
Considered most efficient system Table No. Color Coding for Tube Caps
Piercing one end of the double-pointed needle into the Cap Color Specification
vein and other end into the stopper of the evacuated tube Red No additive
to allow the flow of blood into the tube Orange Coagulant
Numerous tubes in single venipuncture Yellow Coagulant & Separation Gel
Green Heparin Sodium
EVACUATED TUBE Light green Heparin Lithium
Prevents exposure of specimen to contaminants Purple EDTA Coagulant
Color coded tubes filled with predetermined volume of Light blue Sodium Citrate 1:9
blood by vacuum Black Sodium Citrate 1:4
Used in both ETS and syringe method Potassium Oxalate Monohydrate and
Grey
Can be additive or non-additive Sodium Fluoride
Different sizes and volume; glass or plastic
Usage depends on: age, size and condition of vein, ORDER OF DRAW
volume of blood needed Order that must be followed when collecting blood
samples to prevent cross contamination, especially when
Threaded portion: attached to tube holder w/ the sleeve dealing with multiple collection tubes
that retracts when the needle goes through the tube
stopper
o Sleeve: slides back once tube is removed to
prevent leakage
CATEGORIES OF ADDITIVES USED IN BLOOD
COLLECTION
Tube should be inverted 3-10 times after collection
ANTICOAGULANTS
“blood thinners”, prevent blood clots
2 methods: precipitation of calcium or by preventing
thrombin formation
Types: Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA), Citrate,
Heparin, Oxalates
SPECIAL USE ANTICOAGULANTS
Acid citrate dextrose
Citrate phosphate dextrose
Sodium polyanethol
ANTIGLYCOLYTIC AGENTS **If butterfly is used: citrate tube is first
Prevent breakdown of glucose by blood cells or glycolysis
Sodium fluoride: most common; preserves glucose and
prevents growth of bacteria
o Usually with potassium oxalate for rapid
REFERENCES
response
CLOT ACTIVATORS Notes from the discussion by Prof. Amy Puaso
De La Salle Medical and Health Sciences Institute
RENIVA | MLS1-5
powerpoint presentation: 2
PRINCIPLES OF MEDICAL LABORATORY SCIENCE 2
RENIVA | MLS1-5 3
You might also like
- BLOOD COLLECTION EQUIPMENT & TECHNIQUESDocument6 pagesBLOOD COLLECTION EQUIPMENT & TECHNIQUESJewel Jehd AlegriaNo ratings yet
- Blood Collection Equipment, Additives, and Order of Draw PDFDocument9 pagesBlood Collection Equipment, Additives, and Order of Draw PDFjanielleNo ratings yet
- Exercise 5 Hematocrit DeterminationDocument7 pagesExercise 5 Hematocrit DeterminationJam RamosNo ratings yet
- CPH Lab - Prelim TransesDocument4 pagesCPH Lab - Prelim TransesLOUISSE ANNE MONIQUE L. CAYLONo ratings yet
- Manual AubfDocument4 pagesManual AubfNoraine Princess Tabangcora100% (2)
- Medical Technology Roles and HistoryDocument9 pagesMedical Technology Roles and Historyain't your saintessNo ratings yet
- PMLS 2 Handling and Processing of Non Blood Specimens For LaboratoryDocument8 pagesPMLS 2 Handling and Processing of Non Blood Specimens For LaboratoryXyrelle NavarroNo ratings yet
- M2 MLSP 2 LectureDocument5 pagesM2 MLSP 2 LectureChai tea100% (1)
- Venipuncture Equipment GuideDocument141 pagesVenipuncture Equipment GuideKhelly Joshua UyNo ratings yet
- Aubf Module 3 Laboratory Assignment - Macabanding - PrincessDocument5 pagesAubf Module 3 Laboratory Assignment - Macabanding - PrincessNailah MacabandingNo ratings yet
- 6 Ra 1517Document56 pages6 Ra 1517Jay Andrea Vea Dayuday-IsraelNo ratings yet
- Alinsunurin - PMLS2 - Prelim ExamDocument10 pagesAlinsunurin - PMLS2 - Prelim ExamFrankenstein MelancholyNo ratings yet
- Parasitology Preservation MethodsDocument5 pagesParasitology Preservation MethodsAinah Charina TapicNo ratings yet
- PMLS Lesson 3Document8 pagesPMLS Lesson 3Sheen GabatoNo ratings yet
- Venipuncture A Process of Collecting or "Drawing" Blood From A Vein ofDocument38 pagesVenipuncture A Process of Collecting or "Drawing" Blood From A Vein ofVera June RañesesNo ratings yet
- Cytogenetics - Prelim TransesDocument15 pagesCytogenetics - Prelim TransesLOUISSE ANNE MONIQUE L. CAYLONo ratings yet
- MEDT02 Lesson 2 - Safety in PhlebotomyDocument5 pagesMEDT02 Lesson 2 - Safety in PhlebotomySHELDY AGONCILLONo ratings yet
- PMLS 2 Lesson 7Document3 pagesPMLS 2 Lesson 7Jam LozanoNo ratings yet
- Clinical Parasitology Trans 07 Lecture PDFDocument14 pagesClinical Parasitology Trans 07 Lecture PDFSt. DymphaMaralit, Joyce Anne L.No ratings yet
- Clinical Parasitology Mid Term TransDocument11 pagesClinical Parasitology Mid Term TransBelle LatNo ratings yet
- Medical Technology CoursesDocument3 pagesMedical Technology CoursesAly Bint SmbsNo ratings yet
- Case Study 4 RevisedDocument9 pagesCase Study 4 RevisedHearts heavy Moms spaghettiNo ratings yet
- General Approach in Investigation of Haemostasis: Lecture 2: Bleeding TimeDocument28 pagesGeneral Approach in Investigation of Haemostasis: Lecture 2: Bleeding TimeClorence John Yumul FerrerNo ratings yet
- Histopath Lab ActivityDocument5 pagesHistopath Lab ActivityRakia PillayNo ratings yet
- Classifying Variables & Identifying Experimental TermsDocument2 pagesClassifying Variables & Identifying Experimental TermsRochelle Onelia BaldeNo ratings yet
- AO No. 59 vs AO 2021-0037: A Comparison of Clinical Laboratory RegulationsDocument37 pagesAO No. 59 vs AO 2021-0037: A Comparison of Clinical Laboratory RegulationsAlbar B. SiladNo ratings yet
- CMO No 06, S. 2008Document6 pagesCMO No 06, S. 2008orangebackpack100% (1)
- Module # 2 Medical Terminologies and Abbreviations and Ethics in The ProfessionDocument6 pagesModule # 2 Medical Terminologies and Abbreviations and Ethics in The ProfessionJonice NavarroNo ratings yet
- Medical Technology Profession in the PhilippinesDocument24 pagesMedical Technology Profession in the PhilippinesJr BalagtasNo ratings yet
- Transes Anaphy LEC (Activity 5 HISTOLOGY)Document6 pagesTranses Anaphy LEC (Activity 5 HISTOLOGY)Reign Saplaco100% (1)
- Urine Specific Gravity MeasurementsDocument1 pageUrine Specific Gravity MeasurementsDennis ValdezNo ratings yet
- Genetics and Cytogenetics NotesDocument2 pagesGenetics and Cytogenetics NotesDanNo ratings yet
- Ancient Lab Practices and Disease DiagnosisDocument17 pagesAncient Lab Practices and Disease DiagnosisJulius FrondaNo ratings yet
- PMLS1 Chapter 5 Medical Tech CurriculumDocument5 pagesPMLS1 Chapter 5 Medical Tech CurriculumEloisa LourdesNo ratings yet
- VITAL SIGNS ReviewDocument4 pagesVITAL SIGNS ReviewA CNo ratings yet
- Test For Secondary HemostasisDocument32 pagesTest For Secondary Hemostasistitania izaNo ratings yet
- Parasitology and Clinical MicrosDocument16 pagesParasitology and Clinical MicrosErvette May Niño MahinayNo ratings yet
- MEDT02 Lesson 1Document4 pagesMEDT02 Lesson 1SHELDY AGONCILLONo ratings yet
- Pre-Analytical Consideration in PhlebotomyDocument3 pagesPre-Analytical Consideration in PhlebotomyJacinta Malamion100% (1)
- Principles of Medical Laboratory Science Practice 1Document30 pagesPrinciples of Medical Laboratory Science Practice 1JACOB AQUINTEYNo ratings yet
- Animal Form & FunctionDocument157 pagesAnimal Form & FunctionRenz Soledad100% (1)
- Pharmad1 - Chapter 1Document7 pagesPharmad1 - Chapter 1Elaine SombranoNo ratings yet
- ProteinsDocument8 pagesProteinsNara100% (1)
- Cartilage: Ethel Marie M. Mangada, RMTDocument34 pagesCartilage: Ethel Marie M. Mangada, RMTAesthetics MinNo ratings yet
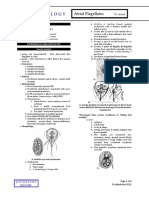
- Parasitology Lecture 4 - Atrial FlagellatesDocument4 pagesParasitology Lecture 4 - Atrial Flagellatesmiguel cuevasNo ratings yet
- CMO14 3mt01Document75 pagesCMO14 3mt01makike100% (2)
- RA 4688 Clinical Laboratory Law REVIEWERDocument9 pagesRA 4688 Clinical Laboratory Law REVIEWERKAREN DELA CRUZNo ratings yet
- Lesson 11 Arterial PunctureDocument42 pagesLesson 11 Arterial Punctureitz RageNo ratings yet
- FixationDocument5 pagesFixationMargalet Aguinaldo100% (1)
- Module 11 - Features of Cardiology Information Systems and Radiology Information SystemsDocument9 pagesModule 11 - Features of Cardiology Information Systems and Radiology Information SystemsZuriel San PedroNo ratings yet
- HTMLE SEMINAR NOTES DOC. ORTEGA - CompressedDocument35 pagesHTMLE SEMINAR NOTES DOC. ORTEGA - CompressedNISSI JUNE T. UNGABNo ratings yet
- 3.1 Where Do Research Ideas Come FromDocument1 page3.1 Where Do Research Ideas Come Fromsheran ballesteros100% (1)
- AUBF Microscopic Exam Part 2&3Document13 pagesAUBF Microscopic Exam Part 2&3Anya IgnacioNo ratings yet
- Basic Diagnostic CytologyDocument45 pagesBasic Diagnostic CytologyIrah Birung LorenzoNo ratings yet
- Types of Culture MediaDocument7 pagesTypes of Culture MediaSurbhi GuptaNo ratings yet
- Exercise 3Document6 pagesExercise 3Gwyneth Marie DayaganNo ratings yet
- Health Information Systems: Lesson 5Document7 pagesHealth Information Systems: Lesson 5Jennifer Ledesma-Pido100% (2)
- 1 VenipunctureDocument42 pages1 VenipunctureQuennie Abellon QuimanNo ratings yet
- PMLS2 - Familiarization in PhleboDocument2 pagesPMLS2 - Familiarization in PhleboCorinne Felice RenivaNo ratings yet
- Blood Collection Equipment & Order of Draw GuideDocument2 pagesBlood Collection Equipment & Order of Draw GuideCASSANDRA P. ONGCONo ratings yet
- Lesson 1: Computer 101: Health InformaticsDocument4 pagesLesson 1: Computer 101: Health InformaticsCorinne Bautista RenivaNo ratings yet
- CPH LAB ScreeningDocument6 pagesCPH LAB ScreeningCorinne Bautista RenivaNo ratings yet
- MIDTERM - Ethics Feelings Values and ImpartialityDocument3 pagesMIDTERM - Ethics Feelings Values and ImpartialityCorinne Bautista RenivaNo ratings yet
- Moral Development ReviewerDocument3 pagesMoral Development ReviewerCorinne Bautista RenivaNo ratings yet
- GE Chem Nucleic Acids and Proteins ReviewerDocument5 pagesGE Chem Nucleic Acids and Proteins ReviewerCorinne Bautista RenivaNo ratings yet
- PMLS2-Infection ControlDocument3 pagesPMLS2-Infection ControlCorinne Bautista RenivaNo ratings yet
- GLOBAL HECTARE: ASSESSING HUMAN FLOURISHING AND DEVELOPMENTDocument5 pagesGLOBAL HECTARE: ASSESSING HUMAN FLOURISHING AND DEVELOPMENTCorinne Bautista Reniva100% (1)
- Health Planning: Steps and ToolsDocument4 pagesHealth Planning: Steps and ToolsCorinne Bautista RenivaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry For Allied Health Professionals (Lab)Document3 pagesChemistry For Allied Health Professionals (Lab)Corinne Bautista RenivaNo ratings yet
- GE Chem Carbohydrates ReviewerDocument3 pagesGE Chem Carbohydrates ReviewerCorinne Bautista RenivaNo ratings yet
- STS The Good Life ReviewerDocument2 pagesSTS The Good Life ReviewerCorinne Bautista RenivaNo ratings yet
- GE Chem COVID VaccinesDocument5 pagesGE Chem COVID VaccinesCorinne Bautista RenivaNo ratings yet
- GE Chem COVID VaccinesDocument5 pagesGE Chem COVID VaccinesCorinne Bautista RenivaNo ratings yet
- STS The Good Life ReviewerDocument2 pagesSTS The Good Life ReviewerCorinne Bautista RenivaNo ratings yet
- GLOBAL HECTARE: ASSESSING HUMAN FLOURISHING AND DEVELOPMENTDocument5 pagesGLOBAL HECTARE: ASSESSING HUMAN FLOURISHING AND DEVELOPMENTCorinne Bautista Reniva100% (1)
- Demography and Population EstimatesDocument4 pagesDemography and Population EstimatesCorinne Bautista RenivaNo ratings yet
- PMLS2 LEC - Circulatory SystemDocument4 pagesPMLS2 LEC - Circulatory SystemCorinne Bautista RenivaNo ratings yet
- STS Human Condition ReviewerDocument2 pagesSTS Human Condition ReviewerCorinne Bautista RenivaNo ratings yet
- CPH LAB ScreeningDocument6 pagesCPH LAB ScreeningCorinne Bautista RenivaNo ratings yet
- Health Planning: Steps and ToolsDocument4 pagesHealth Planning: Steps and ToolsCorinne Bautista RenivaNo ratings yet
- CPH Lab Data CollectionDocument4 pagesCPH Lab Data CollectionCorinne Bautista RenivaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1: Computer 101: Health InformaticsDocument4 pagesLesson 1: Computer 101: Health InformaticsCorinne Bautista RenivaNo ratings yet
- CPH LAB Disease Prevention and ControlDocument4 pagesCPH LAB Disease Prevention and ControlCorinne Bautista RenivaNo ratings yet
- PMLS2-Infection ControlDocument3 pagesPMLS2-Infection ControlCorinne Bautista RenivaNo ratings yet
- Sodium Chlorite, Which Is "Activated" With Citric Acid To Form Chlorine Dioxide. Sodium Hypochlorite (Caustic Soda And), CalciumDocument4 pagesSodium Chlorite, Which Is "Activated" With Citric Acid To Form Chlorine Dioxide. Sodium Hypochlorite (Caustic Soda And), CalciumSophia Eryca GeagaNo ratings yet
- Class 11 Chemistry Test Consolidated Test ReviewDocument21 pagesClass 11 Chemistry Test Consolidated Test ReviewRAVI ANANTHAKRISHNANNo ratings yet
- Determination of Hydrogen Peroxide Decompositon (16 Hours at 96 °C)Document3 pagesDetermination of Hydrogen Peroxide Decompositon (16 Hours at 96 °C)U6 Rayon RamoutarsinghNo ratings yet
- Wolff Kishner Reduction - MECHDocument2 pagesWolff Kishner Reduction - MECHbaskhemNo ratings yet
- 00 IPC TM650 Contents October 2004Document8 pages00 IPC TM650 Contents October 2004Emanuel KszenicsNo ratings yet
- Exam Style Answers 26 Asal Chem CBDocument2 pagesExam Style Answers 26 Asal Chem CBHaoyu XuNo ratings yet
- Lead Drier Replacement in Solvent Based Alkyd Decorative PaintsDocument24 pagesLead Drier Replacement in Solvent Based Alkyd Decorative PaintsIwan TirtaNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry 2: ElectrochemistryDocument12 pagesGeneral Chemistry 2: ElectrochemistrySteinerNo ratings yet
- Unit - IV: Stereochemistry, Reaction Mechanism and Synthesis of Drug MoleculesDocument8 pagesUnit - IV: Stereochemistry, Reaction Mechanism and Synthesis of Drug MoleculesSai shravya GorekarNo ratings yet
- Eshmuno S ResinDocument4 pagesEshmuno S ResinTuyền KimNo ratings yet
- Chemistry MYP 3 Section 3Document15 pagesChemistry MYP 3 Section 3Hadeel IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Material Safety Data Sheet STHAMEX AFFFDocument12 pagesMaterial Safety Data Sheet STHAMEX AFFFAldren GilanaNo ratings yet
- Mekelle University Ethiopian Institute of Technology-Mekelle Department of Chemical Engineering Process EngineeringDocument77 pagesMekelle University Ethiopian Institute of Technology-Mekelle Department of Chemical Engineering Process EngineeringetayhailuNo ratings yet
- Prefeasibility Report For Pigments Manufacturing Plant at Plot No. FS-34, Mahad Five Star Industrial Area, MIDC, Mahad, Raigad, MaharashtraDocument15 pagesPrefeasibility Report For Pigments Manufacturing Plant at Plot No. FS-34, Mahad Five Star Industrial Area, MIDC, Mahad, Raigad, MaharashtrasureshNo ratings yet
- Paper Class VIIDocument3 pagesPaper Class VIIAzib KhanNo ratings yet
- Pathway For Production Ascorbic Acid SynthesisDocument18 pagesPathway For Production Ascorbic Acid SynthesisSantosh Jadhav100% (3)
- A Literature Survey of Methods To Remove IodineDocument91 pagesA Literature Survey of Methods To Remove IodinesekharsamyNo ratings yet
- Clusters, Surfaces, and Catalysis: Gabor A. Somorjai, Anthony M. Contreras, Max Montano, and Robert M. RiouxDocument7 pagesClusters, Surfaces, and Catalysis: Gabor A. Somorjai, Anthony M. Contreras, Max Montano, and Robert M. RiouxDorisNo ratings yet
- Filtration For HPLC Sample Preparation DistributorDocument24 pagesFiltration For HPLC Sample Preparation DistributorTuyết NgânNo ratings yet
- NSTSE 2009 Class VIII SOLVEDDocument15 pagesNSTSE 2009 Class VIII SOLVEDMihir GargNo ratings yet
- Marcinkowska 2017Document24 pagesMarcinkowska 2017Francesco AdingraNo ratings yet
- Unites of Mappina in Soil ClassificationDocument27 pagesUnites of Mappina in Soil ClassificationJulie Faith Aquimba BulanNo ratings yet
- C5049pcleaning of Titanium and Titanium AlloysDocument7 pagesC5049pcleaning of Titanium and Titanium AlloysRubén Eduardo Galindo CarmonaNo ratings yet
- Cu-ETP: C11000 Industrial RolledDocument4 pagesCu-ETP: C11000 Industrial Rolledsrsivaraman81No ratings yet
- Unit 2 Module 2 Gravimetric AnalysisDocument14 pagesUnit 2 Module 2 Gravimetric AnalysisFrank Massiah100% (1)
- Chapter 5 Test BankDocument24 pagesChapter 5 Test Bank陳禹誌No ratings yet
- Biodegradable PolymersDocument4 pagesBiodegradable PolymersArnela HodzicNo ratings yet
- Loudon Chapter 8 & 9 Review: Substitutions and Eliminations: CL Nu CL HDocument6 pagesLoudon Chapter 8 & 9 Review: Substitutions and Eliminations: CL Nu CL HxryceuNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding O1 1-40Document20 pagesChemical Bonding O1 1-40Mahesh choudharyNo ratings yet
- Precipitation Reaction of ProteinsDocument7 pagesPrecipitation Reaction of ProteinsMissy Arabella PameNo ratings yet