Professional Documents
Culture Documents
2.5 2 1.41 Iconv: Faults in LVDC Microgrids With Front-End Converters
Uploaded by
alvin meOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
2.5 2 1.41 Iconv: Faults in LVDC Microgrids With Front-End Converters
Uploaded by
alvin meCopyright:
Available Formats
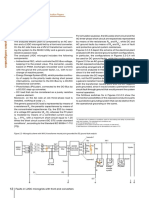
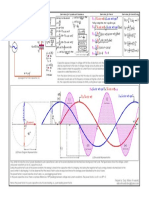
To preserve the integrity of the semiconductors, all Figure 3.
106 - AC current waveform when the power supplied is equal to
converters limit the instantaneous value of the current, the maximum value and with a bolted short circuit
3 Fault analysis
which is usually set at a higher value than the value given 2.5
by (3.14). 2
1.41 Iconvmax
As a consequence, as the grid voltage falls below the
1.5
prescribed minimum values, the current passes first from
a sinusoidal to a trapezoidal shape, then to a squared 1
one as shown in Figures. 3.104-3.105-3.106. 0.5
10 ms 20 ms
0
Figure 3.104 – AC current waveform when the power supplied is equal to
the maximum value and V1 > 85% V1n -0.5
-1
2.5
-1.5
2
1.41 Iconvmax
-2
1.5
-2.5
1
0.5
10 ms 20 ms
0 Hence, in case of an AC short circuit, the converter sup-
-0.5 plies a current of 50%-100% more than the rated value.
-1 Considering the FEC used in this study, the maximum
current supplied during an AC short circuit is:
-1.5
-2 = =1.7 ∙ = 1.7 ∙ 144 = 245 [3.15]
-2.5
This consideration does not take into account of the
Figure 3.105 - AC current waveform when the power supplied is equal to presence of capacitors possibly installed on the converter
the maximum value and V1 < 85% V1n
AC side: such capacitors would increase the short circuit
2.5
current peak due to their discharge.
2
1.41 Iconvmax Besides, in the particular case of n-converters installed in
1.5 parallel, if an AC side short-circuit occurred on the paral-
1
leling bar, the fault current would be about n-times the
value of in (3.14) and consequently the protective device
0.5
10 ms 20 ms should have an adequate breaking capacity.
0
-0.5
-1
-1.5
-2
-2.5
Faults in LVDC microgrids with front-end converters 43
You might also like
- Analysis and Design of Multicell DC/DC Converters Using Vectorized ModelsFrom EverandAnalysis and Design of Multicell DC/DC Converters Using Vectorized ModelsNo ratings yet
- Influence of System Parameters Using Fuse Protection of Regenerative DC DrivesFrom EverandInfluence of System Parameters Using Fuse Protection of Regenerative DC DrivesNo ratings yet
- IEC 61000-4-x Guidelines 2015Document109 pagesIEC 61000-4-x Guidelines 2015Robert LegaultNo ratings yet
- IEC 61000-4-4 Burst Electrical Fast Transient / Burst Immunity TestDocument64 pagesIEC 61000-4-4 Burst Electrical Fast Transient / Burst Immunity TestopinzonNo ratings yet
- Instrument Transformers For Relaying: W. A. ElmoreDocument13 pagesInstrument Transformers For Relaying: W. A. ElmoreAbhishek RajputNo ratings yet
- Protection of Feeders: Er - Sandeep Yadav, Xen, Protection Division, HVPNL, GurgaonDocument19 pagesProtection of Feeders: Er - Sandeep Yadav, Xen, Protection Division, HVPNL, Gurgaonsandeepy_27100% (1)
- Sympathetic Inrush CurrentDocument6 pagesSympathetic Inrush CurrentRajitha BoppaNo ratings yet
- SGP Notes Part 2Document39 pagesSGP Notes Part 2Krishna SinghNo ratings yet
- Overcurrent Relay PDFDocument17 pagesOvercurrent Relay PDFtranhuutuongNo ratings yet
- Assignment-Iv: (I) Operating Time of Feeder RelayDocument4 pagesAssignment-Iv: (I) Operating Time of Feeder RelayPrasenjit Dey100% (1)
- Overcurrent - Relay Setting 3Document17 pagesOvercurrent - Relay Setting 3Shrikant KajaleNo ratings yet
- Type CV Voltage RelayDocument28 pagesType CV Voltage Relayหนุ่ม วัยทองNo ratings yet
- SGP Notes Part 2Document31 pagesSGP Notes Part 2Ganpat GehlotNo ratings yet
- Tutorial T1 ImpedanceDocument2 pagesTutorial T1 Impedanceseshubabu_999No ratings yet
- Digital Omputer Simulation Virtual Current Chopping in Vacuum Circuit BreakersDocument7 pagesDigital Omputer Simulation Virtual Current Chopping in Vacuum Circuit BreakersRorrachoNo ratings yet
- (A) Time Graded (B) Current Graded (C) Combination of Time Graded and Current Graded SystemDocument31 pages(A) Time Graded (B) Current Graded (C) Combination of Time Graded and Current Graded SystemAnuja TipareNo ratings yet
- Technical Poster On Overcurrent Relays GradingDocument1 pageTechnical Poster On Overcurrent Relays GradingEng. HaSeebNo ratings yet
- Power Systems Protection Assignment (EEG 806)Document27 pagesPower Systems Protection Assignment (EEG 806)control roomNo ratings yet
- PWM Motor Speed ControlDocument1 pagePWM Motor Speed ControlRev. Matthew100% (3)
- Zoom 16Document90 pagesZoom 16ATHAR IQBALNo ratings yet
- Impulse Voltage Testing of Power TransformersDocument10 pagesImpulse Voltage Testing of Power TransformerssameekNo ratings yet
- Requirement of Current Transformer in MicomDocument8 pagesRequirement of Current Transformer in MicomnmanikandanNo ratings yet
- Compensation of Earth FaultDocument13 pagesCompensation of Earth FaultA. HassanNo ratings yet
- ABB REF - Protection - RADHD-Notes PDFDocument8 pagesABB REF - Protection - RADHD-Notes PDFEBENo ratings yet
- Generator Breaker Equipped With Vacuum InterruptersDocument4 pagesGenerator Breaker Equipped With Vacuum InterruptersVenna Karthik ReddyNo ratings yet
- CoordinationDocument18 pagesCoordinationKhaled Galal AhmedNo ratings yet
- DK1913 CH10 PDFDocument26 pagesDK1913 CH10 PDFManiraj PerumalNo ratings yet
- ELX303 Exam SolutionsDocument27 pagesELX303 Exam SolutionsNadeesha BandaraNo ratings yet
- Application of Zig-Zag Transformers in A Three-Wire Three-Phase Dynamic Sag Corrector SystemDocument6 pagesApplication of Zig-Zag Transformers in A Three-Wire Three-Phase Dynamic Sag Corrector SystemDolisirNo ratings yet
- Fault Level CalculationsDocument11 pagesFault Level CalculationsSatheesh Kumar NatarajanNo ratings yet
- Cálculo Dos Parâmetros para Diferentes Disposições Do Cabo - Hélder (2011)Document6 pagesCálculo Dos Parâmetros para Diferentes Disposições Do Cabo - Hélder (2011)AndréNo ratings yet
- Earthing Design For High Voltage Installations - A Study PaperDocument40 pagesEarthing Design For High Voltage Installations - A Study PaperAppavoo Subbaiya100% (1)
- ImpedanceDocument2 pagesImpedanceJesús RodríguezNo ratings yet
- Implementation of A High Voltage Power SupplyDocument4 pagesImplementation of A High Voltage Power SupplyJiakeat LiauNo ratings yet
- Short Circuit CalculationsDocument10 pagesShort Circuit CalculationsvenkateshbitraNo ratings yet
- SGP 2Document13 pagesSGP 2BantiNo ratings yet
- Relay Coordination in The Protection of Radially-Connected Power System NetworkDocument5 pagesRelay Coordination in The Protection of Radially-Connected Power System NetworktobyNo ratings yet
- Symmetrical Faults: Instructor: Mohammad Abdul BaseerDocument45 pagesSymmetrical Faults: Instructor: Mohammad Abdul Baseernehal hasnain refathNo ratings yet
- Manual-Relay SettingDocument7 pagesManual-Relay SettingRakesh ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Exercises On Relay Settings - MemoDocument7 pagesExercises On Relay Settings - Memomoses kakwenaNo ratings yet
- Calculations of Short Circuit CurrentsDocument9 pagesCalculations of Short Circuit CurrentsCorneliusmusyokaNo ratings yet
- Impact of Distributed Generation On The Overcurrent Protection Scheme For Radial FeedersDocument21 pagesImpact of Distributed Generation On The Overcurrent Protection Scheme For Radial FeedersTanveer Ul HaqNo ratings yet
- 5 Book Transfoemer Percent ImpedanceDocument6 pages5 Book Transfoemer Percent ImpedanceSLDC DDNo ratings yet
- Broken Delta - U0 SEF 90%Document4 pagesBroken Delta - U0 SEF 90%Jaya AdiwigunaNo ratings yet
- The Use of Triggered Current Limitors To Reduce The Prospective Fault Current For High Voltage SystemDocument3 pagesThe Use of Triggered Current Limitors To Reduce The Prospective Fault Current For High Voltage SystemShailesh ChettyNo ratings yet
- Ho-1.1 Fault Analysis 2Document17 pagesHo-1.1 Fault Analysis 2japhet ontongNo ratings yet
- Hgsemi LM331M TRDocument16 pagesHgsemi LM331M TREDU GCNo ratings yet
- Relay ActmDocument24 pagesRelay ActmmukeshhNo ratings yet
- REF Protection UsefulDocument5 pagesREF Protection Usefulss_chinniNo ratings yet
- Generation of High Voltages & CurrentsDocument46 pagesGeneration of High Voltages & Currentssaikarthick023No ratings yet
- Power System ProtectionDocument2 pagesPower System Protection7sn omerNo ratings yet
- Controlled Slew Rate Enhancement Circuit For Error Amplifier in High Frequency DC-DC ConvertersDocument4 pagesControlled Slew Rate Enhancement Circuit For Error Amplifier in High Frequency DC-DC ConvertersKristian BallabaniNo ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2No ratings yet
- Practical Troubleshooting of Electrical Equipment and Control CircuitsFrom EverandPractical Troubleshooting of Electrical Equipment and Control CircuitsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5)
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Rating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (3)
- Aerox Stop and Start SystemDocument1 pageAerox Stop and Start Systemalvin meNo ratings yet
- Aerox Smart Key SystemDocument1 pageAerox Smart Key Systemalvin meNo ratings yet
- Systems With The DC Mid-Point Grounded: Technical Application PapersDocument1 pageSystems With The DC Mid-Point Grounded: Technical Application Papersalvin meNo ratings yet
- Aerox Restarting The EngineDocument1 pageAerox Restarting The Enginealvin meNo ratings yet
- Aerox Seat Opening and ClosingDocument1 pageAerox Seat Opening and Closingalvin meNo ratings yet
- Systems With The DC Negative Pole Grounded: dc1 DC/R Convdc2Document1 pageSystems With The DC Negative Pole Grounded: dc1 DC/R Convdc2alvin meNo ratings yet
- High Fault Resistance R With ESS (S1 OFF, S2 ON) : Technical Application PapersDocument1 pageHigh Fault Resistance R With ESS (S1 OFF, S2 ON) : Technical Application Papersalvin meNo ratings yet
- Waveform of The AC CurrentDocument1 pageWaveform of The AC Currentalvin meNo ratings yet
- High Fault ResistanceDocument1 pageHigh Fault Resistancealvin meNo ratings yet
- Faults in LVDC Microgrids With Front-End Converters: G G DCN G G GDocument1 pageFaults in LVDC Microgrids With Front-End Converters: G G DCN G G Galvin meNo ratings yet
- Elimination of SynchronizationDocument1 pageElimination of Synchronizationalvin meNo ratings yet
- Technical Application Papers: Faults in LVDC Microgrids With Front-End ConvertersDocument1 pageTechnical Application Papers: Faults in LVDC Microgrids With Front-End Convertersalvin meNo ratings yet
- Technical Application Papers: Faults in LVDC Microgrids With Front-End ConvertersDocument1 pageTechnical Application Papers: Faults in LVDC Microgrids With Front-End Convertersalvin meNo ratings yet
- Case 2a: Sin Sin (6.3) 106.6Document1 pageCase 2a: Sin Sin (6.3) 106.6alvin meNo ratings yet
- Behavior With PV PlantDocument1 pageBehavior With PV Plantalvin meNo ratings yet
- DC Ground Fault AnalysisDocument1 pageDC Ground Fault Analysisalvin meNo ratings yet
- Hazard of Direct CurrentDocument1 pageHazard of Direct Currentalvin meNo ratings yet
- Maximum AC Current AbsorptionDocument1 pageMaximum AC Current Absorptionalvin meNo ratings yet
- LVDC Microgrid BehaviorDocument1 pageLVDC Microgrid Behavioralvin meNo ratings yet
- Sensitive Electronic LoadsDocument1 pageSensitive Electronic Loadsalvin meNo ratings yet
- Advantages of Low Voltage DC Distribution SystemsDocument1 pageAdvantages of Low Voltage DC Distribution Systemsalvin meNo ratings yet
- 2 System Configuration: Front-End Converter (FEC)Document1 page2 System Configuration: Front-End Converter (FEC)alvin meNo ratings yet
- Ambient Temperature Around The Miniature Circuit BreakerDocument1 pageAmbient Temperature Around The Miniature Circuit Breakeralvin meNo ratings yet
- Technical Application Papers: Faults in LVDC Microgrids With Front-End ConvertersDocument1 pageTechnical Application Papers: Faults in LVDC Microgrids With Front-End Convertersalvin meNo ratings yet
- Electrical Distribution NetworksDocument1 pageElectrical Distribution Networksalvin meNo ratings yet
- T19110836 - VEW2000-1.0-VVVF (LEFT) Sanur Building Project Denpasar 3000 3500Document4 pagesT19110836 - VEW2000-1.0-VVVF (LEFT) Sanur Building Project Denpasar 3000 3500DaveNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Status of E&M EquipmentDocument4 pagesManufacturing Status of E&M Equipmenttaimur ahmadNo ratings yet
- Excess Air CalculationDocument11 pagesExcess Air CalculationKarthic Keyan50% (2)
- ABB Surge Arrester POLIM-C N - Data Sheet 1HC0075874 EN ADDocument8 pagesABB Surge Arrester POLIM-C N - Data Sheet 1HC0075874 EN ADA. SajadiNo ratings yet
- Lub Oil SystemDocument20 pagesLub Oil SystemSam83% (6)
- Pure Capacitor (C) in Circuits AC SystemDocument1 pagePure Capacitor (C) in Circuits AC SystemWilson (Electrical Engineer)No ratings yet
- Yanmar Air Cooled, Diesel Generator YDG5001SEDocument37 pagesYanmar Air Cooled, Diesel Generator YDG5001SESunthron Somchai75% (8)
- Teaching and Learning in Primary and Secondary Mathematics: Universiti Teknologi MalaysiaDocument11 pagesTeaching and Learning in Primary and Secondary Mathematics: Universiti Teknologi MalaysiaushaNo ratings yet
- Datasheet Solis-EPM-5G GBR V2,1 2022 09Document2 pagesDatasheet Solis-EPM-5G GBR V2,1 2022 09David QuintanaNo ratings yet
- Kandasamy2015 PDFDocument8 pagesKandasamy2015 PDFsankar peddapatiNo ratings yet
- Data Sheet HiberniumDocument2 pagesData Sheet HiberniumGuy HaliouaNo ratings yet
- Catalog Numbers (AMPS)Document2 pagesCatalog Numbers (AMPS)api-289140720No ratings yet
- MPR300Document4 pagesMPR300KUNALJAY100% (1)
- Powercommand Digital Master Control: FeaturesDocument12 pagesPowercommand Digital Master Control: FeaturesthainarimeNo ratings yet
- ATUM PresentationDocument58 pagesATUM PresentationManoj Kumar SodhaniNo ratings yet
- Solar Quiz: How Much Do You Know About Solar Power?: The Questions: True or False?Document2 pagesSolar Quiz: How Much Do You Know About Solar Power?: The Questions: True or False?Armando Giraldo PradoNo ratings yet
- Boilers - ClassificationDocument77 pagesBoilers - Classificationkabbilaash kumarNo ratings yet
- Wiring of MCB, Elcb, RCCB, MCCB MANUALDocument7 pagesWiring of MCB, Elcb, RCCB, MCCB MANUALSreenidhi Srungaram100% (1)
- Energy & PowerDocument20 pagesEnergy & PowerBilal AhmadNo ratings yet
- Dr. Sagar'sDocument263 pagesDr. Sagar'sdhakar_ravi1No ratings yet
- Power Sector Economics and PlanningDocument123 pagesPower Sector Economics and Planningsundaram upadhyayNo ratings yet
- LED Lighting Solutions GuideDocument16 pagesLED Lighting Solutions Guideseyedamir mohammadiNo ratings yet
- Development and Test of The LOX-LNG Regenerative Cooled Rocket EngineDocument4 pagesDevelopment and Test of The LOX-LNG Regenerative Cooled Rocket EnginePabloreimonteNo ratings yet
- JKR Specs L-S1 Specification For Low Internal Electrical Installation May-2011 Rev.2Document114 pagesJKR Specs L-S1 Specification For Low Internal Electrical Installation May-2011 Rev.2Leong Km86% (7)
- 1Document299 pages1鄧豆No ratings yet
- Golap 2014 PDFDocument6 pagesGolap 2014 PDFgolapkantideyNo ratings yet
- User'S Manual: MODEL: MMA160/200Document9 pagesUser'S Manual: MODEL: MMA160/200Vlaovic GoranNo ratings yet
- Centrifugal Pumps Training CourseDocument125 pagesCentrifugal Pumps Training CourseHECTOR IBARRA100% (3)
- Sciencedirect Sciencedirect SciencedirectDocument8 pagesSciencedirect Sciencedirect SciencedirectÖğr. Gör. Yasin BEKTAŞNo ratings yet
- 2020.practice QQT FRQsDocument6 pages2020.practice QQT FRQstoxxic21No ratings yet