Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Technical Application Papers: Faults in LVDC Microgrids With Front-End Converters
Uploaded by
alvin meOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Technical Application Papers: Faults in LVDC Microgrids With Front-End Converters
Uploaded by
alvin meCopyright:
Available Formats
Technical Application Papers
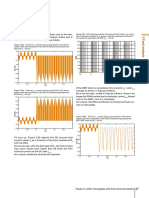
Iac1 is shifted by a value equal to one-third the fault cur- Figure 3.69b – Trend of Isw2 current during a ground fault on DC side in
systems with the neutral point of the MV/LV transformer grounded without
rent DC component.
3 Fault analysis
ESS and PV plant and with Rg = 50 mΩ
Such component may cause several problems, such as 1400
the saturation of MV/LV transformer ferromagnetic core. 1200
In steady-state conditions, Iac1 does not remain positive
1000
for all its period: this still involves the conduction of the
800
anodic star freewheeling diodes.
600
Since the converter works like a diode rectifier, even the
Isw2 [A]
voltage at AC terminals trends to a square waveform due 400
to over-modulation effect (Figure 3.68). 200
0
Figure 3.68 – Trend of the voltage at AC converter terminal Vconv during
a ground fault on DC side in systems with the neutral point of the MV/LV -200
transformer grounded without ESS and PV plant and with Rg = 50 mΩ
-400
600
-600
0.4 0.45 0.5 0.55 0.6 0.65
400 t [s]
200
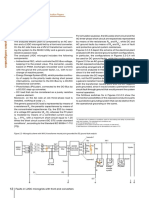
In converters sold on the market, when the current in
Vconv [V]
0 one of IGBTs tends to exceed the overload limits, a block
command is sent to all converter IGBTs.
-200
Then, since all IGBTs are switched off, and only free-
-400 wheeling diodes still remain in conduction, the converter
-600
works as a non-controlled diode rectifier. With the IGBT
block the DC capacitor discharge contribution to the
-500 ground fault current is limited.
-1000 Nevertheless, the ground fault current remains practically
0.2 0.3 0.4 0.5 0.6 0.7 0.8 0.9 1
t [s]
unchanged and equal to that in Figure 3.63, because,
even without IGBT block, such current already flows only
If we look at the currents Isw1 (Figure 3.69a) and Isw2 (Fig- through the cathodic star freewheeling diodes (Figure
ure 3.69b), we note that the DC component of the fault 3.70a). On the contrary, Isw2 (Figure 3.70b) changes, since
current flows through the freewheeling diodes of the now the current can flow only through the freewheeling
cathodic star, while the DC component in the freewheel- diodes and there is no longer any PWM control.
ing diodes of the anodic star is only the DC load current. Even the trend of the AC absorbed current Iac1 is similar
Moreover, Figures 3.69a-b show clearly the non-PWM to that of a diode rectifier with a predominant DC com-
control for wide time intervals, due to over-modulation. ponent due to the fault (Figure 3.71).
Figure 3.69a – Trend of Isw1 current during a ground fault on DC side in Figure 3.70a – Trend of Isw1 current during a ground fault on DC side in
systems with the neutral point of the MV/LV transformer grounded without systems with the neutral point of the MV/LV transformer grounded with
ESS and PV plant and with Rg = 50 mΩ IGBT block, without ESS and PV plant and with Rg = 50 mΩ
400 400
200 200
0 0
-200 -200
-400 -400
Isw1 [A]
Isw1 [A]
-600 -600
-800 -800
-1000 -1000
-1200 -1200
-1400 -1400
0.4 0.45 0.5 0.55 0.6 0.65 0.4 0.45 0.5 0.55 0.6 0.65
t [s] t [s]
32 Faults in LVDC microgrids with front-end converters
You might also like
- Faults in LVDC Microgrids With Front-End Converters: G G DCN G G GDocument1 pageFaults in LVDC Microgrids With Front-End Converters: G G DCN G G Galvin meNo ratings yet
- Systems With The DC Mid-Point Grounded: Technical Application PapersDocument1 pageSystems With The DC Mid-Point Grounded: Technical Application Papersalvin meNo ratings yet
- Modeling of IGBT Resistive and Inductive Turn On BehaviorDocument26 pagesModeling of IGBT Resistive and Inductive Turn On BehaviorKunal RajaNo ratings yet
- Behavior With PV PlantDocument1 pageBehavior With PV Plantalvin meNo ratings yet
- Waveform of The AC CurrentDocument1 pageWaveform of The AC Currentalvin meNo ratings yet
- LVDC Microgrid BehaviorDocument1 pageLVDC Microgrid Behavioralvin meNo ratings yet
- Uow - Power Electronics 4 - 2017Document25 pagesUow - Power Electronics 4 - 2017FUCKYOUNo ratings yet
- 12 - Snubber CircuitsDocument10 pages12 - Snubber CircuitsSwifty SpotNo ratings yet
- Comparison Between Ideal and Practical Differentiators Using Operational AmplifierDocument13 pagesComparison Between Ideal and Practical Differentiators Using Operational AmplifierIJRASETPublicationsNo ratings yet
- Structure of Fast Power Diodes 49-53 - SemikronDocument7 pagesStructure of Fast Power Diodes 49-53 - SemikronPelotaDeTrapoNo ratings yet
- Aula10 Chave - Seccionadora - SchneiderDocument5 pagesAula10 Chave - Seccionadora - SchneiderDidier ColinNo ratings yet
- MCCB AdjustableDocument19 pagesMCCB Adjustableheri fauziNo ratings yet
- ActivitiesDocument24 pagesActivitiesanshkourav991No ratings yet
- Electrical 2Document136 pagesElectrical 2Sifa Tsalsabila HasyifahNo ratings yet
- 300 Series 400 Amp Service Entrance Sub PackageDocument67 pages300 Series 400 Amp Service Entrance Sub Packagenitroxx7No ratings yet
- 01 Schneider-Acti9 PDFDocument3 pages01 Schneider-Acti9 PDFNguyen AnhNo ratings yet
- Module 1Document21 pagesModule 1yakomi suraNo ratings yet
- Synchronous Rectification For Forward ConvertersDocument19 pagesSynchronous Rectification For Forward ConvertersfabianoaddorNo ratings yet
- Power Loss CalculationDocument7 pagesPower Loss CalculationDivya PagidimarriNo ratings yet
- Oiltap® V: On-Load Tap-Changer For Regulating TransformersDocument4 pagesOiltap® V: On-Load Tap-Changer For Regulating TransformersAshraf NazifNo ratings yet
- MR2520 DatasheetDocument7 pagesMR2520 DatasheetOxkar YetiNo ratings yet
- Phase-Shifted Cascaded Dual-Buck AC-AC Converter With Less Number of InductorsDocument13 pagesPhase-Shifted Cascaded Dual-Buck AC-AC Converter With Less Number of InductorsNguyễn Hữu MinhNo ratings yet
- Systems With The DC Negative Pole Grounded: dc1 DC/R Convdc2Document1 pageSystems With The DC Negative Pole Grounded: dc1 DC/R Convdc2alvin meNo ratings yet
- Module-Type Switching Rectifier For Cathodic Protection of Underground and Maritime Metallic StructuresDocument9 pagesModule-Type Switching Rectifier For Cathodic Protection of Underground and Maritime Metallic StructuresRizky RNo ratings yet
- Battery Fuse 2019Document44 pagesBattery Fuse 2019Firas ouhichiNo ratings yet
- Electronics Experiment 8Document4 pagesElectronics Experiment 8Dulce DeNo ratings yet
- iC60L Circuit Breakers (Curve B, C, K, Z)Document1 pageiC60L Circuit Breakers (Curve B, C, K, Z)Diego PeñaNo ratings yet
- Plug in Termination System (Rpit) : Up To 52 KV, For Gas Insulated SwitchgearDocument2 pagesPlug in Termination System (Rpit) : Up To 52 KV, For Gas Insulated SwitchgearAnonymous SOQFPWBNo ratings yet
- Ee 176.1 Experiment No.1Document5 pagesEe 176.1 Experiment No.1Jade Albert G. FalladoNo ratings yet
- 420kV, 40 KA For 1 Sec. Triple Pole, Double Break, Motor Operated IsolatorDocument14 pages420kV, 40 KA For 1 Sec. Triple Pole, Double Break, Motor Operated Isolatorrajinikanth19100% (1)
- iC60N Circuit Breakers (Curve B, C, D)Document1 pageiC60N Circuit Breakers (Curve B, C, D)Dimaz IrawanNo ratings yet
- HV320Document9 pagesHV320Jean DiazNo ratings yet
- IC60LDocument5 pagesIC60LJan SebastianNo ratings yet
- Resonant OcnverterDocument7 pagesResonant Ocnvertersatyam swarup dubeyNo ratings yet
- Technical Application Papers: Faults in LVDC Microgrids With Front-End ConvertersDocument1 pageTechnical Application Papers: Faults in LVDC Microgrids With Front-End Convertersalvin meNo ratings yet
- IGBT Module Selection and ApplicationDocument7 pagesIGBT Module Selection and Applicationvdsantos74No ratings yet
- Contactors and Contactor Assemblies: Contactors For Special Applications SiriusDocument24 pagesContactors and Contactor Assemblies: Contactors For Special Applications SiriuschochoroyNo ratings yet
- ABB MCCB CatelogueDocument34 pagesABB MCCB CatelogueThusitha RanawanaNo ratings yet
- Ee0041l Finals (Fa) VillanuevaDocument18 pagesEe0041l Finals (Fa) VillanuevaKYLE LEIGHZANDER VICENTENo ratings yet
- Sic He Rungs Last T RennerDocument36 pagesSic He Rungs Last T Rennerpracticante crcNo ratings yet
- 1sdc210033d0204 TC Tmax XT Iec enDocument348 pages1sdc210033d0204 TC Tmax XT Iec enBolivar MartinezNo ratings yet
- Contactores de VacioDocument8 pagesContactores de VacioVictor TaveraNo ratings yet
- Ls CDocument4 pagesLs CkylegazeNo ratings yet
- Trabajo Ferrer Mendoza Carlos Peñaranda Roman JoelDocument10 pagesTrabajo Ferrer Mendoza Carlos Peñaranda Roman JoelCarlos Antonio Ferrer MendozaNo ratings yet
- Ic60 Catalouge (Lma)Document12 pagesIc60 Catalouge (Lma)Akozba Selim ÖzdemirNo ratings yet
- N Differential Protection Schemes For Auto-TransformersDocument42 pagesN Differential Protection Schemes For Auto-TransformerschetanNo ratings yet
- Flyer 023Document4 pagesFlyer 023Pankaj Kumar SinghNo ratings yet
- Principles and Applications of The ICL7660 CMOS Voltage Converter PDFDocument10 pagesPrinciples and Applications of The ICL7660 CMOS Voltage Converter PDFPeter JordanNo ratings yet
- DC-DC Converter Implementation With Wide Output Voltage OperationDocument12 pagesDC-DC Converter Implementation With Wide Output Voltage OperationsaptadipNo ratings yet
- Ir2155 PDFDocument7 pagesIr2155 PDFagrajitNo ratings yet
- Ir2301 (S) & (PBF) : High and Low Side DriverDocument18 pagesIr2301 (S) & (PBF) : High and Low Side DriverDr Zeljko DespotovicNo ratings yet
- Half-Bridge Driver Ir2111 PDFDocument8 pagesHalf-Bridge Driver Ir2111 PDFRida DTNo ratings yet
- 2CCS893001R0804 s803n c80Document4 pages2CCS893001R0804 s803n c80André Gogola VilarinhoNo ratings yet
- Comparison of IGBT and GTO For High Power Inverters PDFDocument9 pagesComparison of IGBT and GTO For High Power Inverters PDFLuis Eduardo RibeiroNo ratings yet
- Features: Ebs-040Sxxxbte 40W Class I/Ii Programmable Ip20 Driver With DaliDocument13 pagesFeatures: Ebs-040Sxxxbte 40W Class I/Ii Programmable Ip20 Driver With DaliAbraham Seco ArmestoNo ratings yet
- 03 ACB SACE Emax 2 - ABBDocument34 pages03 ACB SACE Emax 2 - ABBVũ Hữu PhongNo ratings yet
- Outdoor LBS - R-Series-FlyerDocument4 pagesOutdoor LBS - R-Series-FlyerKmj KmjNo ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2No ratings yet
- Passive and Discrete Circuits: Newnes Electronics Circuits Pocket Book, Volume 2From EverandPassive and Discrete Circuits: Newnes Electronics Circuits Pocket Book, Volume 2No ratings yet
- Technical Specs - Yamaha Mio Soul I125Document3 pagesTechnical Specs - Yamaha Mio Soul I125alvin meNo ratings yet
- Aerox Seat Opening and ClosingDocument1 pageAerox Seat Opening and Closingalvin meNo ratings yet
- Aerox Stop and Start SystemDocument1 pageAerox Stop and Start Systemalvin meNo ratings yet
- Own The Culture - Yamaha Mio Soul I125Document3 pagesOwn The Culture - Yamaha Mio Soul I125alvin me0% (1)
- Aerox Restarting The EngineDocument1 pageAerox Restarting The Enginealvin meNo ratings yet
- Aerox Smart Key BatteryDocument1 pageAerox Smart Key Batteryalvin meNo ratings yet
- Aerox Smart Key SystemDocument1 pageAerox Smart Key Systemalvin meNo ratings yet
- DC Component Values of The Ground Fault CurrentDocument1 pageDC Component Values of The Ground Fault Currentalvin meNo ratings yet
- 2.5 2 1.41 Iconv: Faults in LVDC Microgrids With Front-End ConvertersDocument1 page2.5 2 1.41 Iconv: Faults in LVDC Microgrids With Front-End Convertersalvin meNo ratings yet
- Systems With The DC Negative Pole Grounded: dc1 DC/R Convdc2Document1 pageSystems With The DC Negative Pole Grounded: dc1 DC/R Convdc2alvin meNo ratings yet
- Technical Application Papers: Faults in LVDC Microgrids With Front-End ConvertersDocument1 pageTechnical Application Papers: Faults in LVDC Microgrids With Front-End Convertersalvin meNo ratings yet
- Technical Application Papers: Behavior With PV PlantDocument1 pageTechnical Application Papers: Behavior With PV Plantalvin meNo ratings yet
- Low Fault Resistance R With ESS (S1 ON, S2 ON/OFF) : Faults in LVDC Microgrids With Front-End ConvertersDocument1 pageLow Fault Resistance R With ESS (S1 ON, S2 ON/OFF) : Faults in LVDC Microgrids With Front-End Convertersalvin meNo ratings yet
- High Fault Resistance R With ESS (S1 OFF, S2 ON) : Technical Application PapersDocument1 pageHigh Fault Resistance R With ESS (S1 OFF, S2 ON) : Technical Application Papersalvin meNo ratings yet
- Low Fault Resistance R With ESS (S1 ON, S2 ON/OFF) : Faults in LVDC Microgrids With Front-End ConvertersDocument1 pageLow Fault Resistance R With ESS (S1 ON, S2 ON/OFF) : Faults in LVDC Microgrids With Front-End Convertersalvin meNo ratings yet
- High Fault ResistanceDocument1 pageHigh Fault Resistancealvin meNo ratings yet
- Technical Application Papers: Faults in LVDC Microgrids With Front-End ConvertersDocument1 pageTechnical Application Papers: Faults in LVDC Microgrids With Front-End Convertersalvin meNo ratings yet
- Technical Application Papers: Faults in LVDC Microgrids With Front-End ConvertersDocument1 pageTechnical Application Papers: Faults in LVDC Microgrids With Front-End Convertersalvin meNo ratings yet
- LVDC Microgrid BehaviorDocument1 pageLVDC Microgrid Behavioralvin meNo ratings yet
- Maximum AC Current AbsorptionDocument1 pageMaximum AC Current Absorptionalvin meNo ratings yet
- Case 2a: Sin Sin (6.3) 106.6Document1 pageCase 2a: Sin Sin (6.3) 106.6alvin meNo ratings yet
- DC Ground Fault AnalysisDocument1 pageDC Ground Fault Analysisalvin meNo ratings yet
- Hazard of Direct CurrentDocument1 pageHazard of Direct Currentalvin meNo ratings yet
- 2 System Configuration: Front-End Converter (FEC)Document1 page2 System Configuration: Front-End Converter (FEC)alvin meNo ratings yet
- Damask: by ChenoneDocument17 pagesDamask: by ChenoneYasir IjazNo ratings yet
- Modal Verbs of Ability and PossibilityDocument12 pagesModal Verbs of Ability and PossibilitymslolinrNo ratings yet
- UniFi Quick GuideDocument2 pagesUniFi Quick GuideAndhika TharunaNo ratings yet
- Episode Transcript: Episode 34 - Chinese Han Lacquer CupDocument2 pagesEpisode Transcript: Episode 34 - Chinese Han Lacquer CupParvathy SubramanianNo ratings yet
- AMX Prodigy Install ManualDocument13 pagesAMX Prodigy Install Manualsundevil2010usa4605No ratings yet
- R35 Credit Analysis Models - AnswersDocument13 pagesR35 Credit Analysis Models - AnswersSakshiNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument17 pagesUntitledSedat100% (1)
- Unit 4 Transistor Frequency ResponseDocument6 pagesUnit 4 Transistor Frequency ResponseShaina MabborangNo ratings yet
- 28 ESL Discussion Topics Adult StudentsDocument14 pages28 ESL Discussion Topics Adult StudentsniallNo ratings yet
- Family School Project Lesson Plan AstrologyDocument3 pagesFamily School Project Lesson Plan Astrologyapi-529488210No ratings yet
- K To 12 Math 7 Curriculum Guide PDFDocument15 pagesK To 12 Math 7 Curriculum Guide PDFEdmar Tan Fabi100% (1)
- Exam C - HANATEC142: SAP Certified Technology Associate - SAP HANA (Edition 2014)Document10 pagesExam C - HANATEC142: SAP Certified Technology Associate - SAP HANA (Edition 2014)SadishNo ratings yet
- Et200sp Im 155 6 PN ST Manual en-US en-USDocument47 pagesEt200sp Im 155 6 PN ST Manual en-US en-USayaz officeNo ratings yet
- GCG Damri SurabayaDocument11 pagesGCG Damri SurabayaEndang SusilawatiNo ratings yet
- Game On Series BibleDocument28 pagesGame On Series Bibleapi-513832615No ratings yet
- STS Reviewer FinalsDocument33 pagesSTS Reviewer FinalsLeiNo ratings yet
- ENGLISH 4 (General & Specific Sentence, Main Idea & Key Sentence) )Document3 pagesENGLISH 4 (General & Specific Sentence, Main Idea & Key Sentence) )Analiza Dequinto BalagosaNo ratings yet
- Amplificadores Automotivos PyramidDocument13 pagesAmplificadores Automotivos Pyramidedusf1000No ratings yet
- KirbyDocument3 pagesKirbyNorhassanah UtosabuayanNo ratings yet
- Geography Paper 1Document7 pagesGeography Paper 1Sudhir TewatiaNo ratings yet
- Molecules of Life PDFDocument113 pagesMolecules of Life PDFArpit Pradhan100% (1)
- Marketing Measurement Done RightDocument16 pagesMarketing Measurement Done RightWasim Ullah0% (1)
- Buy Wholesale China Popular Outdoor Football Boot For Teenagers Casual High Quality Soccer Shoes FG Ag Graffiti Style & FootballDocument1 pageBuy Wholesale China Popular Outdoor Football Boot For Teenagers Casual High Quality Soccer Shoes FG Ag Graffiti Style & Footballjcdc9chh8dNo ratings yet
- Financial Analysis of Ashok LeylandDocument120 pagesFinancial Analysis of Ashok LeylandSiva Kumaravel0% (1)
- Module 1Document64 pagesModule 1Jackyson RajkumarNo ratings yet
- L15 PDFDocument15 pagesL15 PDFlesNo ratings yet
- Esp8285 Datasheet enDocument29 pagesEsp8285 Datasheet enJohn GreenNo ratings yet
- U04 Fxs of Humeral ShaftDocument88 pagesU04 Fxs of Humeral Shaftadrian_mogosNo ratings yet
- Q1. What Is JDBC? Explain Different Types JDBC Drivers With Suitable DiagramDocument64 pagesQ1. What Is JDBC? Explain Different Types JDBC Drivers With Suitable DiagramjyebbwycqmfkuxNo ratings yet
- Why Do Kashmiris Need Self-Determination?: UncategorizedDocument16 pagesWhy Do Kashmiris Need Self-Determination?: UncategorizedFarooq SiddiqiNo ratings yet