Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Maximum AC Current Absorption
Uploaded by
alvin meOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Maximum AC Current Absorption
Uploaded by
alvin meCopyright:
Available Formats
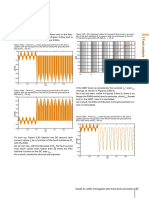
To sum up, Figure 3.33 depicts the DC short circuit cur- value of 800V.
rent values Isc as a function of the fault resistance Rsc. Moreover, since Iac1 is lower than in Case 1a (Figure 3.36),
3 Fault analysis
As we can see, with the decrease of Rsc, the short circuit the ESS allows the FEC to reach its maximum AC current
current may reach values up to 10 times the FEC nominal absorption for lower Rsc values. This is better from the
current on the DC side Idcn, As a result, protective devices electronic component current point of view.
are required.
Figure 3.34 – Trend of Vdc voltage during a short circuit on DC side
in Case 1b
Figure 3.33 - DC short circuit current values Isc as a function of the fault
resistance Rsc (FEC contribution, Idcn = 125 A) 900
1400
850
1200 800
1000 750 820
Vdc [V]
800 700 810
Isc [A]
600 650 800
600
400 790
550
200 780
02 03 04 05
500
0 0.2 0.3 0.4 0.5 0.6 0.7 0.8 0.9 1
t [s]
100 10 1 0.1 0.01 0.001
Rsc [Ω]
Figure 3.35 – Trend of Isc current during a short circuit on DC side
in Case 1b
3.1.2 Behavior with ESS 10
The same cases of the previous section will be analyzed 9
hereunder in order to see what changes during a short 8
circuit adding the ESS, which is inserted in parallel to the 7
DC-Bus at t = 0.25s, while the fault still occurs at t = 0.5s2. 6
5
Isc [A]
Case 1b 4
For Rsc values such that the FEC is able to maintain the Vdc 3
at the nominal value Vdcn, the fault current Isc = Vdcn/Rsc 2
remains at the same value of Case 1a. 1
Therefore, the presence of the ESS does not contribute 0
to increase the short circuit current. 0.2 0.3 0.4 0.5 0.6 0.7 0.8 0.9 1
t [s]
Nevertheless, since the power amounts delivered to the
load RL and to the fault Rsc are now shared between the
Figure 3.36 – Trend of Iac1 current during a short circuit on DC
FEC and the ESS, the current absorbed from the grid side in Case 1b
Iac1 decreases. 250
200
Since Vdc remains at its nominal value of 800V (Figure
150
3.34), assuming Rsc = 100Ω, the fault current Isc is still
100
8A like in Case 1a (Figure 3.35).
50
The ESS connection causes a transient DC-Bus voltage
Iac [A]
increase over the nominal value (Figure 3.34), but the 0
FEC control intervenes to bring back the Vdc to the set -50
-100
2
See Annex B for the behavior in fault condition of the DC/DC converter that interfaces -150
the ESS with the DC-Bus. In particular, the converter parallel capacitance can be added
-200
to Cdc series in order to have the total capacitance contribution.
-250
0.4 0.45 0.5 0.55 0.6 0.65
t [s]
Faults in LVDC microgrids with front-end converters 23
You might also like
- Faults in LVDC Microgrids With Front-End Converters: G G DCN G G GDocument1 pageFaults in LVDC Microgrids With Front-End Converters: G G DCN G G Galvin meNo ratings yet
- LVDC Microgrid BehaviorDocument1 pageLVDC Microgrid Behavioralvin meNo ratings yet
- Waveform of The AC CurrentDocument1 pageWaveform of The AC Currentalvin meNo ratings yet
- Battery Fuse 2019Document44 pagesBattery Fuse 2019Firas ouhichiNo ratings yet
- Methodology For Controlling Multi-Level Converter Topologies With SCALE™-2 IGBT DriversDocument4 pagesMethodology For Controlling Multi-Level Converter Topologies With SCALE™-2 IGBT DriversfgokcegozNo ratings yet
- Department of Electrical Engineering, IIT Delhi ELL100 Introduction To Electrical Engg: Problem Set 10Document3 pagesDepartment of Electrical Engineering, IIT Delhi ELL100 Introduction To Electrical Engg: Problem Set 10Osim AbesNo ratings yet
- AN521 Intoduction To IGBTDocument10 pagesAN521 Intoduction To IGBTBuelnitaNo ratings yet
- Become A Master ElectricianDocument7 pagesBecome A Master ElectricianShazmaniaNo ratings yet
- PART B: Measure Voltage and Current in Circuit ObjectivesDocument3 pagesPART B: Measure Voltage and Current in Circuit ObjectivesYap Yu XuanNo ratings yet
- 9 Transistor Inverter Applications IDocument7 pages9 Transistor Inverter Applications IanswetNo ratings yet
- Case 2a: Sin Sin (6.3) 106.6Document1 pageCase 2a: Sin Sin (6.3) 106.6alvin meNo ratings yet
- Technical Application Papers: Faults in LVDC Microgrids With Front-End ConvertersDocument1 pageTechnical Application Papers: Faults in LVDC Microgrids With Front-End Convertersalvin meNo ratings yet
- Mje13003 D On Semi PDFDocument8 pagesMje13003 D On Semi PDFblueword66No ratings yet
- Experiment in Basics of Electronic TechnologyDocument12 pagesExperiment in Basics of Electronic TechnologyMehedi HasanNo ratings yet
- Testing For Current Transformer ParametersDocument2 pagesTesting For Current Transformer Parameters322399mk7086No ratings yet
- Battery FuseDocument40 pagesBattery Fuseajeet.ajju2017No ratings yet
- New Era University: "Volt - Ampere Characteristics of Long-Shunt Compound Motor"Document6 pagesNew Era University: "Volt - Ampere Characteristics of Long-Shunt Compound Motor"Hamim Relacion ManamparanNo ratings yet
- Acb Ae - SW Series 2019-10Document1 pageAcb Ae - SW Series 2019-10valerieNo ratings yet
- Pys PracDocument9 pagesPys PracpfaneloNo ratings yet
- S Series DatasheetDocument2 pagesS Series DatasheetAroldo PereiraNo ratings yet
- Sbd10c 100f (Power Supply TV Led)Document6 pagesSbd10c 100f (Power Supply TV Led)Saharuddin SangkalaNo ratings yet
- Power Ring Film Capacitor™ 1000 F, 600 VDCDocument4 pagesPower Ring Film Capacitor™ 1000 F, 600 VDChyu2123No ratings yet
- Exp 8Document9 pagesExp 8neelu marturuNo ratings yet
- 21967, Water pp424 425 PDFDocument2 pages21967, Water pp424 425 PDFCece SantosNo ratings yet
- NTE2640 Silicon NPN Transistor Color TV Horizontal Deflection OutputDocument2 pagesNTE2640 Silicon NPN Transistor Color TV Horizontal Deflection OutputLeonel MartinezNo ratings yet
- FeedBackREPORT PDFDocument9 pagesFeedBackREPORT PDFمحمد رضا محسن سعيد -B-No ratings yet
- Technical Application Papers: Faults in LVDC Microgrids With Front-End ConvertersDocument1 pageTechnical Application Papers: Faults in LVDC Microgrids With Front-End Convertersalvin meNo ratings yet
- SBD20C100T/F - Datasheet: 20A, 100V Schottky RectifierDocument7 pagesSBD20C100T/F - Datasheet: 20A, 100V Schottky RectifierFreddy CamposNo ratings yet
- Analog Circuits-I LABDocument10 pagesAnalog Circuits-I LABIron PatriotNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Amplifier1Document20 pagesMagnetic Amplifier1Aryan BatraNo ratings yet
- University of Engineering and Technology, Lahore Department of Electrical EngineeringDocument6 pagesUniversity of Engineering and Technology, Lahore Department of Electrical EngineeringZbNo ratings yet
- EMI RFI Suppression Capacitors Film IEC 60384-14 International StandardDocument1 pageEMI RFI Suppression Capacitors Film IEC 60384-14 International StandardmubafawNo ratings yet
- Embedded DRAM Using C-Axis-Aligned Crystalline In-Ga-Zn Oxide FET With 1.8V-Power-Supply VoltageDocument8 pagesEmbedded DRAM Using C-Axis-Aligned Crystalline In-Ga-Zn Oxide FET With 1.8V-Power-Supply VoltageRabbi HasnatNo ratings yet
- 2e274k PDFDocument3 pages2e274k PDFFabio MacielNo ratings yet
- Is Now Part ofDocument13 pagesIs Now Part ofRizkiWiraPratamaNo ratings yet
- TEP Cálculo de IccDocument6 pagesTEP Cálculo de IccHector RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Power Plant and Water Pumping - OS SastryDocument83 pagesPower Plant and Water Pumping - OS SastrySAEL SOLARNo ratings yet
- Nte 384Document2 pagesNte 384Rohit SharmaNo ratings yet
- Sinewave Inverter DC Capacitor Ripple CurrentDocument6 pagesSinewave Inverter DC Capacitor Ripple Currentshalu29No ratings yet
- 1.4kesd5.0 Thru 1.4kesd170ca Axial-Lead TvsDocument5 pages1.4kesd5.0 Thru 1.4kesd170ca Axial-Lead Tvshoang_tuanNo ratings yet
- DF1506S Hyecs00447-1Document2 pagesDF1506S Hyecs00447-1trantungson80No ratings yet
- NTE2365 Silicon NPN Transistor High Voltage Horizontal Deflection OutputDocument2 pagesNTE2365 Silicon NPN Transistor High Voltage Horizontal Deflection OutputAbel RodriguezNo ratings yet
- EAD410 Practical 1 TheoreticalDocument5 pagesEAD410 Practical 1 Theoreticalu18348794No ratings yet
- Analog Communication Systems.: Major Semester AssignmentDocument20 pagesAnalog Communication Systems.: Major Semester AssignmentMaryam BabarNo ratings yet
- C 5386Document2 pagesC 5386Esteban CortezNo ratings yet
- EEN-612: Electrical Transients in Power Systems: Tutorial-03Document2 pagesEEN-612: Electrical Transients in Power Systems: Tutorial-03sohit srivastavaNo ratings yet
- 8P1. Fatigue Analysis of An Aluminium 2024-T3 Structure With Quality Index K 4.0Document4 pages8P1. Fatigue Analysis of An Aluminium 2024-T3 Structure With Quality Index K 4.0RGFENo ratings yet
- 1.5KE6.8 - 1.5KE440CA Series: 1500 Watt Axial Transient Voltage SuppressorsDocument3 pages1.5KE6.8 - 1.5KE440CA Series: 1500 Watt Axial Transient Voltage SuppressorsHerberth BarriosNo ratings yet
- Interposing CT Connections in 3-ph TRDocument12 pagesInterposing CT Connections in 3-ph TRMohammedSaadaniHassaniNo ratings yet
- Yuk AyiricilarDocument13 pagesYuk AyiricilarEsat SÖNMEZNo ratings yet
- Current Transformer 12 9120119789Document3 pagesCurrent Transformer 12 9120119789Hoài Sơn LêNo ratings yet
- Calculator TechniquesDocument8 pagesCalculator TechniquesRafael DeocuarizaNo ratings yet
- Nte 876Document2 pagesNte 876julio quatriniNo ratings yet
- Features: High Voltage:vceo 300V Small Collector Output Capacitance: Cob 3.0pF (Typ)Document3 pagesFeatures: High Voltage:vceo 300V Small Collector Output Capacitance: Cob 3.0pF (Typ)Kinyer Isai ManaureNo ratings yet
- Fmmt449 Sot 23v2Document3 pagesFmmt449 Sot 23v2XJ YangNo ratings yet
- Zinc Oxide Varistors - A Review.: American Ceramic Society Bulletin April 1986Document43 pagesZinc Oxide Varistors - A Review.: American Ceramic Society Bulletin April 1986Nguyen Trung HuyNo ratings yet
- RS601 SeCoSDocument2 pagesRS601 SeCoSmarina anastasovaNo ratings yet
- Caracteristicas XTDocument15 pagesCaracteristicas XTdanielliram993No ratings yet
- Electricity in Fish Research and Management: Theory and PracticeFrom EverandElectricity in Fish Research and Management: Theory and PracticeNo ratings yet
- Aerox Smart Key BatteryDocument1 pageAerox Smart Key Batteryalvin meNo ratings yet
- Technical Specs - Yamaha Mio Soul I125Document3 pagesTechnical Specs - Yamaha Mio Soul I125alvin meNo ratings yet
- Aerox Stop and Start SystemDocument1 pageAerox Stop and Start Systemalvin meNo ratings yet
- Aerox Restarting The EngineDocument1 pageAerox Restarting The Enginealvin meNo ratings yet
- Aerox Seat Opening and ClosingDocument1 pageAerox Seat Opening and Closingalvin meNo ratings yet
- Own The Culture - Yamaha Mio Soul I125Document3 pagesOwn The Culture - Yamaha Mio Soul I125alvin me0% (1)
- Technical Application Papers: Faults in LVDC Microgrids With Front-End ConvertersDocument1 pageTechnical Application Papers: Faults in LVDC Microgrids With Front-End Convertersalvin meNo ratings yet
- Systems With The DC Mid-Point Grounded: Technical Application PapersDocument1 pageSystems With The DC Mid-Point Grounded: Technical Application Papersalvin meNo ratings yet
- Aerox Smart Key SystemDocument1 pageAerox Smart Key Systemalvin meNo ratings yet
- Systems With The DC Negative Pole Grounded: dc1 DC/R Convdc2Document1 pageSystems With The DC Negative Pole Grounded: dc1 DC/R Convdc2alvin meNo ratings yet
- Technical Application Papers: Behavior With PV PlantDocument1 pageTechnical Application Papers: Behavior With PV Plantalvin meNo ratings yet
- Behavior With PV PlantDocument1 pageBehavior With PV Plantalvin meNo ratings yet
- 2.5 2 1.41 Iconv: Faults in LVDC Microgrids With Front-End ConvertersDocument1 page2.5 2 1.41 Iconv: Faults in LVDC Microgrids With Front-End Convertersalvin meNo ratings yet
- DC Component Values of The Ground Fault CurrentDocument1 pageDC Component Values of The Ground Fault Currentalvin meNo ratings yet
- High Fault Resistance R With ESS (S1 OFF, S2 ON) : Technical Application PapersDocument1 pageHigh Fault Resistance R With ESS (S1 OFF, S2 ON) : Technical Application Papersalvin meNo ratings yet
- Low Fault Resistance R With ESS (S1 ON, S2 ON/OFF) : Faults in LVDC Microgrids With Front-End ConvertersDocument1 pageLow Fault Resistance R With ESS (S1 ON, S2 ON/OFF) : Faults in LVDC Microgrids With Front-End Convertersalvin meNo ratings yet
- Technical Application Papers: Faults in LVDC Microgrids With Front-End ConvertersDocument1 pageTechnical Application Papers: Faults in LVDC Microgrids With Front-End Convertersalvin meNo ratings yet
- Low Fault Resistance R With ESS (S1 ON, S2 ON/OFF) : Faults in LVDC Microgrids With Front-End ConvertersDocument1 pageLow Fault Resistance R With ESS (S1 ON, S2 ON/OFF) : Faults in LVDC Microgrids With Front-End Convertersalvin meNo ratings yet
- Technical Application Papers: Faults in LVDC Microgrids With Front-End ConvertersDocument1 pageTechnical Application Papers: Faults in LVDC Microgrids With Front-End Convertersalvin meNo ratings yet
- Technical Application Papers: Faults in LVDC Microgrids With Front-End ConvertersDocument1 pageTechnical Application Papers: Faults in LVDC Microgrids With Front-End Convertersalvin meNo ratings yet
- High Fault ResistanceDocument1 pageHigh Fault Resistancealvin meNo ratings yet
- Case 2a: Sin Sin (6.3) 106.6Document1 pageCase 2a: Sin Sin (6.3) 106.6alvin meNo ratings yet
- Hazard of Direct CurrentDocument1 pageHazard of Direct Currentalvin meNo ratings yet
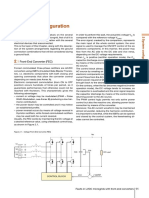
- 2 System Configuration: Front-End Converter (FEC)Document1 page2 System Configuration: Front-End Converter (FEC)alvin meNo ratings yet
- DC Ground Fault AnalysisDocument1 pageDC Ground Fault Analysisalvin meNo ratings yet
- RB - A5D2x - Rev1P1 - CARRIER BOARD - SCHEMATICDocument16 pagesRB - A5D2x - Rev1P1 - CARRIER BOARD - SCHEMATICPrajwalNo ratings yet
- New Aqua Calibration CertificateDocument20 pagesNew Aqua Calibration Certificateahmed mohamedNo ratings yet
- Structure and Detailed Syllabus - IT (5th Sem To 8th Sem)Document72 pagesStructure and Detailed Syllabus - IT (5th Sem To 8th Sem)Randy OrtonNo ratings yet
- Trojan HorseDocument6 pagesTrojan Horsemathew roshanNo ratings yet
- Supply Chain Management in Brick-and-Mortar Stores of NepalDocument22 pagesSupply Chain Management in Brick-and-Mortar Stores of NepalTrishna SinghNo ratings yet
- Test Certificates Repair Instructions Service Bulletins (Idms) ConversionsDocument394 pagesTest Certificates Repair Instructions Service Bulletins (Idms) ConversionsGABRIELNo ratings yet
- Drawing List - April-2019Document1 pageDrawing List - April-2019abdul jackilNo ratings yet
- Lessons From Crane RunwaysDocument5 pagesLessons From Crane Runwaysdicktracy11No ratings yet
- PVTsimHelp 20Document197 pagesPVTsimHelp 20JesseNo ratings yet
- Refrigeration Compressor Zr190kce Tfd.Document4 pagesRefrigeration Compressor Zr190kce Tfd.Mlayeh MohamedNo ratings yet
- User's Guide: Magnetic Inductive Flow Meter MAG-VIEW™Document20 pagesUser's Guide: Magnetic Inductive Flow Meter MAG-VIEW™mrdadeNo ratings yet
- 3932-Article Text-21872-2-10-20211223Document19 pages3932-Article Text-21872-2-10-20211223papungNo ratings yet
- LIS - Abbott Architect-90937-105Document98 pagesLIS - Abbott Architect-90937-105jyoti ranjanNo ratings yet
- 1 Year Pressure Vessel Experience ResumeDocument2 pages1 Year Pressure Vessel Experience ResumevivekNo ratings yet
- ZIEHL-ABEGG - FN045-VDA.4I.V7P1 - 175771 - EN - 2019-01-11 Station OneDocument10 pagesZIEHL-ABEGG - FN045-VDA.4I.V7P1 - 175771 - EN - 2019-01-11 Station OneLuiz CarlosNo ratings yet
- AMS User ManualDocument20 pagesAMS User ManualAndújar Báez CésarNo ratings yet
- Computer Science Paper Scheme (Marks Distribution)Document4 pagesComputer Science Paper Scheme (Marks Distribution)Honey BunnyNo ratings yet
- 2023 GIST Undergraduate Admission GuideDocument28 pages2023 GIST Undergraduate Admission GuideZubia NazNo ratings yet
- Gesture MSCDocument52 pagesGesture MSCWahid KhanNo ratings yet
- 3-The Four Dimensions of ServiceDocument13 pages3-The Four Dimensions of Serviceziad i alshowaiterNo ratings yet
- Sizing of DG Unit To Reduce Losses in Radial Distribution - A Case StudyDocument7 pagesSizing of DG Unit To Reduce Losses in Radial Distribution - A Case StudyDizky Christian HadiNo ratings yet
- Wfa - Metric - Tube FittingsDocument75 pagesWfa - Metric - Tube FittingsandywanderNo ratings yet
- HostsDocument1 pageHostsThet Aung Moe50% (2)
- Pe1024-Mb-Mfb030-011200 38 GT#1 MBX PDFDocument1 pagePe1024-Mb-Mfb030-011200 38 GT#1 MBX PDFAldo Quispe HuarachiNo ratings yet
- Ebook - IELTS WT1 (2021)Document14 pagesEbook - IELTS WT1 (2021)Trần Lê Uyên PhươngNo ratings yet
- 1-571 Study Guide - 1000+ QADocument112 pages1-571 Study Guide - 1000+ QAMahmoud Hagag100% (3)
- Introduction To LinuxDocument17 pagesIntroduction To Linuxسليمان الشمريNo ratings yet
- FT ExadropDocument2 pagesFT ExadropABRAHAM MANUEL MEDINA LEYTONNo ratings yet
- Unit 2Document84 pagesUnit 2Ashok (Ak)No ratings yet
- MGS1600GY: Precision Magnetic Track Following Sensor With GyrosopeDocument21 pagesMGS1600GY: Precision Magnetic Track Following Sensor With GyrosopeDwi SaputroNo ratings yet