Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Advantages of Low Voltage DC Distribution Systems
Uploaded by
alvin me0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
57 views1 page1. Low voltage DC distribution systems have advantages over AC systems due to advances in power conversion technology. DC can be distributed over longer distances at higher voltages with lower losses compared to AC.
2. Many modern loads contain power electronics and rectifiers to convert AC to DC, which reduces efficiency. Using DC distribution avoids this conversion and improves power quality.
3. A DC system allows flexible integration of renewable generation and energy storage, enables continuous power supply during outages, and facilitates bidirectional power flow.
Original Description:
Original Title
Advantages of Low Voltage DC distribution systems
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Document1. Low voltage DC distribution systems have advantages over AC systems due to advances in power conversion technology. DC can be distributed over longer distances at higher voltages with lower losses compared to AC.
2. Many modern loads contain power electronics and rectifiers to convert AC to DC, which reduces efficiency. Using DC distribution avoids this conversion and improves power quality.
3. A DC system allows flexible integration of renewable generation and energy storage, enables continuous power supply during outages, and facilitates bidirectional power flow.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
57 views1 pageAdvantages of Low Voltage DC Distribution Systems
Uploaded by
alvin me1. Low voltage DC distribution systems have advantages over AC systems due to advances in power conversion technology. DC can be distributed over longer distances at higher voltages with lower losses compared to AC.
2. Many modern loads contain power electronics and rectifiers to convert AC to DC, which reduces efficiency. Using DC distribution avoids this conversion and improves power quality.
3. A DC system allows flexible integration of renewable generation and energy storage, enables continuous power supply during outages, and facilitates bidirectional power flow.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
1 Advantages of Low Voltage DC distribution systems
At the end of the 19th century, AC started replacing voltage to the load using a DC/DC converter. SMPS can
DC in power distribution, mainly because AC was more be operated with both AC and DC without any design
1 Advantages of Low Voltage DC distribution systems
easily transformed between different voltage levels and modifications since the actual frequency range typically
transmitted over long distances. includes 47-63 Hz and DC.
These conversions allow high-voltage, low-current power With DC distribution, it is also possible to improve the
distribution that minimizes losses and enables central customer-end power quality. The main reason is that
power plants with sufficient scale to be maximally cost- inverters on the customer-side are able to maintain the
effective. voltage level at the defined values, even if the DC link
Advances in power conversion technology, including DC voltage varies, as long as the voltage is above the mini-
power rectification, however, have eroded the dominance mum value. Tolerance to voltage variation is therefore
of AC power because of conversion advantages. improved.
When AC was introduced, loads were mostly resistive. It is also possible to eliminate power outages resulting
Today, however, many loads utilize power electronics. from reconnections in the electrical power system, but
Most power-electronic loads contain a diode rectifier to this requires some energy to supply the inverter or in-
convert the supplying AC voltage to DC. This introduces verters during the loss-of-mains situation. These energy
non-sinusoidal currents into the grid, which in turn dete- storages can be directly connected to the DC link, and
riorates power quality. By using appropriate DC voltages it is possible to use a common storage for all inverters
to supply these loads, the rectifier can be removed from or a separate storage for every inverter. This also makes
the loads. This reduces energy losses and brings savings it possible for a customer to individually select the size
without lowering power quality. of the energy storage.
A low-voltage distribution network is traditionally based Considering a DC-distribution system with centralized
on a three-phase 400 V AC system. Because of the low AC/DC power conversion like in Figure 1.1, the proposed
voltage, 20/0.4 kV transformers have to be installed close AC/DC interface does not affect the utility power quality
enough to the customer to avoid too high transmission in terms of low-frequency harmonics, and it has voltage-
losses. The use of a higher AC or DC voltage in the LV dip ride-through capability.
network increases the power transmission capacity and Furthermore, the chosen topology allows bi-directional
permits longer distances. power flow, which can be of interest if the DC system
The use of a higher AC voltage level increases the trans- includes power sources, and allows easy connection of
mission capacity of an aerial or underground cable with energy storage as a countermeasure for power outages.
the same cross-section area. With DC, this capacity can
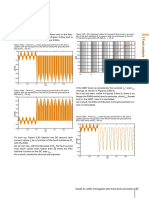
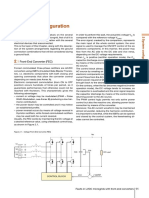
be further increased. Figure 1.1 – A DC distribution system with centralized AC/DC power
conversion
The main reason is the higher voltage level allowed, be-
AC/DC interface Residential DC grid
cause the effective value with DC voltage can be 1500
V, while it is 1000 V in AC. Besides, some other losses AC mains DC mains
Electronic
can be reduced by using DC voltage. The inductance loads
of the transmission line does not have an impact in the
steady-state condition, when the voltage drop in the Energy Variable
storage speed drive
line is smaller. With DC there is also no skin effect, so
transmission line resistance and voltage drop decrease.
Resistive
Moreover, considering the transition from AC to DC sys- loads
tems, most of the loads used today can operate equally
well with a DC supply as with an AC supply. For example, Energy
Generation storage
universal machines, which are used in household ap-
pliances such as electric mixers and vacuum cleaners,
have the same configuration as a series magnetized DC Generation
machine and work both in AC and DC. Generation
Electronic loads, which can be found in computer equip-
ment, battery chargers and lighting, work properly in the
ranges 100-240 V and 50-60 Hz, and this is accomplished
by using a switch mode power supply (SMPS). SMPS
first rectifies the voltage and then adjusts the rectified
Faults in LVDC microgrids with front-end converters 5
You might also like
- Bidirectional DC DC ConverterDocument5 pagesBidirectional DC DC ConverterJAIRAJ MIRASHINo ratings yet
- HVDC Group FinalDocument14 pagesHVDC Group FinalGitta JoshuaNo ratings yet
- Comparative Evaluation of HVDC and HVAC Transmission SystemsDocument5 pagesComparative Evaluation of HVDC and HVAC Transmission SystemsNidhiNo ratings yet
- Applications: Sockets Switches Fixtur Es Diode BridgeDocument4 pagesApplications: Sockets Switches Fixtur Es Diode BridgeChristian CuevasNo ratings yet
- Challenges Faced in HVDC SystemsDocument12 pagesChallenges Faced in HVDC SystemsPKNo ratings yet
- HVDC Transmission Systems UNIT-1: Comparison of AC and DC TransmissionDocument57 pagesHVDC Transmission Systems UNIT-1: Comparison of AC and DC TransmissionSaurabhNo ratings yet
- DC Power Transmission Technology ExplainedDocument10 pagesDC Power Transmission Technology ExplainedHARE KRISHNANo ratings yet
- AC&DC Transmission Lines COMPARASION: TransformersDocument2 pagesAC&DC Transmission Lines COMPARASION: TransformersممشطNo ratings yet
- Cseb ReportDocument25 pagesCseb Reportshchan530% (1)
- EHVAC-HVDC Presentation - Unit 3Document20 pagesEHVAC-HVDC Presentation - Unit 3JungkookNo ratings yet
- A Nonisolated Step-Up DC-AC Converter With Reduced Leakage Current For Grid-Connected Photovoltaic SystemsDocument8 pagesA Nonisolated Step-Up DC-AC Converter With Reduced Leakage Current For Grid-Connected Photovoltaic SystemsMiréli Binder VendruscoloNo ratings yet
- DC Power Transmission TechnologyDocument10 pagesDC Power Transmission TechnologyDrVikas Singh BhadoriaNo ratings yet
- DC-DC Convertors ExplainedDocument6 pagesDC-DC Convertors ExplainedFlorin CristiNo ratings yet
- DC and AC UPS Comparison IEEE Paper 071220 - FDocument6 pagesDC and AC UPS Comparison IEEE Paper 071220 - FChandan KumarNo ratings yet
- Design and Analysis of High-Gain MV DC-DC Converters for PV IntegrationDocument5 pagesDesign and Analysis of High-Gain MV DC-DC Converters for PV IntegrationHussain K. SayedNo ratings yet
- Notes (04 - 01 - 2020 - 729032330)Document62 pagesNotes (04 - 01 - 2020 - 729032330)pearzinNo ratings yet
- Comparative Study of HVDC and HVAC For A Bulk Power TransmissionDocument6 pagesComparative Study of HVDC and HVAC For A Bulk Power TransmissionNidhiNo ratings yet
- HVDC Transmission Systems: Benefits of DC over AC for Long Distance Power TransmissionDocument56 pagesHVDC Transmission Systems: Benefits of DC over AC for Long Distance Power Transmissionmahi100% (2)
- LECTURE NOTES ON HVDC TRANSMISSION SYSTEMSDocument61 pagesLECTURE NOTES ON HVDC TRANSMISSION SYSTEMSThulasi PrasadNo ratings yet
- (ZHU 20) 6kW DCDCDocument15 pages(ZHU 20) 6kW DCDCXiaoShan LIUNo ratings yet
- Comparison HVDC EHVACDocument2 pagesComparison HVDC EHVACgoyal.167009No ratings yet
- Name: Pooja Dubey Course: EEE Roll No:120104026Document22 pagesName: Pooja Dubey Course: EEE Roll No:120104026Bvijaya krishnaNo ratings yet
- DC-Bus Voltage Regulation and Power Compensation With Bi-Directional Inverter in DC-Microgrid ApplicationsDocument8 pagesDC-Bus Voltage Regulation and Power Compensation With Bi-Directional Inverter in DC-Microgrid ApplicationsAbi Yusuf AuliaNo ratings yet
- SmpsDocument6 pagesSmpsMadhu46dNo ratings yet
- Modelling and Co-Ordination Control of Hybrid Grid: S. Lakshmi Devi K. SudheerDocument8 pagesModelling and Co-Ordination Control of Hybrid Grid: S. Lakshmi Devi K. SudheerAdriano NavarroNo ratings yet
- 229 HVDC NoteDocument58 pages229 HVDC NoteSubhashree RoutNo ratings yet
- Hvts AssignmentDocument12 pagesHvts AssignmentrashmisbhumbareNo ratings yet
- Power SupplyDocument9 pagesPower SupplyMuhammed HuzaifaNo ratings yet
- Section B AbdurehmanDocument32 pagesSection B AbdurehmansyabseeshoesNo ratings yet
- DC Power Transmission TechnologyDocument15 pagesDC Power Transmission TechnologySal Excel60% (5)
- Stand Alone Solar Power Generation SysteDocument7 pagesStand Alone Solar Power Generation SystekarthicktamilmaniNo ratings yet
- Unit-1-Basic Concepts Analysis of HVDC ConverterDocument23 pagesUnit-1-Basic Concepts Analysis of HVDC Converterravikumar_ranganNo ratings yet
- AC and DC - Julius P. de MesaDocument2 pagesAC and DC - Julius P. de MesaJulius De MesaNo ratings yet
- Sensitive Electronic LoadsDocument1 pageSensitive Electronic Loadsalvin meNo ratings yet
- High Voltage Direct Current Transmission (HVDC)Document18 pagesHigh Voltage Direct Current Transmission (HVDC)Aurongo NasirNo ratings yet
- Processes: Analysis of A Series-Parallel Resonant Converter For DC Microgrid ApplicationsDocument14 pagesProcesses: Analysis of A Series-Parallel Resonant Converter For DC Microgrid ApplicationsMohmed khaja HussainNo ratings yet
- (Edit) Power Supply TypesDocument8 pages(Edit) Power Supply Typeshazel violetNo ratings yet
- StevenChuLecture pg88Document1 pageStevenChuLecture pg88Robert Ssettuba BrownNo ratings yet
- AC vs DC: Differences Between Alternating and Direct CurrentDocument4 pagesAC vs DC: Differences Between Alternating and Direct CurrentAmirul AizadNo ratings yet
- AC-DC Power Conversion TechniquesDocument67 pagesAC-DC Power Conversion TechniquesJilly ArasuNo ratings yet
- PS2 HDocument10 pagesPS2 Hasifchandarki.official72No ratings yet
- HVDC Transmission Systems Compared to AC for Long Distance Power TransmissionDocument20 pagesHVDC Transmission Systems Compared to AC for Long Distance Power TransmissionMr. R. Jagan EEENo ratings yet
- Bidirectional 12kV To 1.2kV DC-DC Converter For Renewable Energy ApplicationsDocument8 pagesBidirectional 12kV To 1.2kV DC-DC Converter For Renewable Energy ApplicationsJyothiPunemNo ratings yet
- HVDC and FACTS - PPT PDFDocument19 pagesHVDC and FACTS - PPT PDFManu KasturiNo ratings yet
- The Advantages of AC Power Over DC PowerDocument2 pagesThe Advantages of AC Power Over DC PowershafibhaiNo ratings yet
- Optimal Integration of An Offshore Wind Farm To A Weak AC GridDocument8 pagesOptimal Integration of An Offshore Wind Farm To A Weak AC GridMadhusudhan SrinivasanNo ratings yet
- IJETR021397Document5 pagesIJETR021397erpublicationNo ratings yet
- DC To DC Pscad ModelDocument6 pagesDC To DC Pscad Modeladyasha acharyaNo ratings yet
- HVDC - Lecture 1Document17 pagesHVDC - Lecture 1yesmuraliNo ratings yet
- 11 2021 13-Z-Source-Based High Step-Up DC-DC Converters For Photovoltaic ApplicationsDocument14 pages11 2021 13-Z-Source-Based High Step-Up DC-DC Converters For Photovoltaic ApplicationsSai RameshNo ratings yet
- IJE_Volume 27_Issue 1_Pages 123-130Document8 pagesIJE_Volume 27_Issue 1_Pages 123-130TamilselvanNo ratings yet
- Ned Mohan: Minneapolis 2002Document19 pagesNed Mohan: Minneapolis 2002Anoop InnocentNo ratings yet
- Analysis of A High-Power, Resonant DC-DC Converter For DC Wind TurbinesDocument4 pagesAnalysis of A High-Power, Resonant DC-DC Converter For DC Wind TurbinesBrightworld ProjectsNo ratings yet
- ANALYSIS OF A HIGH-POWER RESONANT DC-DC CONVERTER FOR DC WINDDocument4 pagesANALYSIS OF A HIGH-POWER RESONANT DC-DC CONVERTER FOR DC WINDBrightworld ProjectsNo ratings yet
- Type of Power SupplyDocument7 pagesType of Power SupplySHah WanHazNo ratings yet
- Elimination of SynchronizationDocument1 pageElimination of Synchronizationalvin meNo ratings yet
- High Step-Down Nonisolated DCDC Converter With Coupled InductorsDocument8 pagesHigh Step-Down Nonisolated DCDC Converter With Coupled InductorsAkobir KamolovNo ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Rating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (3)
- Aerox Smart Key SystemDocument1 pageAerox Smart Key Systemalvin meNo ratings yet
- Aerox Restarting The EngineDocument1 pageAerox Restarting The Enginealvin meNo ratings yet
- Own The Culture - Yamaha Mio Soul I125Document3 pagesOwn The Culture - Yamaha Mio Soul I125alvin me0% (1)
- Technical Specs - Yamaha Mio Soul I125Document3 pagesTechnical Specs - Yamaha Mio Soul I125alvin meNo ratings yet
- Open and close your seat with your smart keyDocument1 pageOpen and close your seat with your smart keyalvin meNo ratings yet
- Aerox Smart Key BatteryDocument1 pageAerox Smart Key Batteryalvin meNo ratings yet
- Fault analysis in grounded DC systemsDocument1 pageFault analysis in grounded DC systemsalvin meNo ratings yet
- Technical Application Papers: Behavior With PV PlantDocument1 pageTechnical Application Papers: Behavior With PV Plantalvin meNo ratings yet
- Stop and Start System OverviewDocument1 pageStop and Start System Overviewalvin meNo ratings yet
- Systems With The DC Mid-Point Grounded: Technical Application PapersDocument1 pageSystems With The DC Mid-Point Grounded: Technical Application Papersalvin meNo ratings yet
- Technical Application Papers: Faults in LVDC Microgrids With Front-End ConvertersDocument1 pageTechnical Application Papers: Faults in LVDC Microgrids With Front-End Convertersalvin meNo ratings yet
- 2.5 2 1.41 Iconv: Faults in LVDC Microgrids With Front-End ConvertersDocument1 page2.5 2 1.41 Iconv: Faults in LVDC Microgrids With Front-End Convertersalvin meNo ratings yet
- Faults in LVDC Microgrids With Front-End Converters: G G DCN G G GDocument1 pageFaults in LVDC Microgrids With Front-End Converters: G G DCN G G Galvin meNo ratings yet
- DC Component Values of The Ground Fault CurrentDocument1 pageDC Component Values of The Ground Fault Currentalvin meNo ratings yet
- High Fault Resistance R With ESS (S1 OFF, S2 ON) : Technical Application PapersDocument1 pageHigh Fault Resistance R With ESS (S1 OFF, S2 ON) : Technical Application Papersalvin meNo ratings yet
- Low Fault Resistance R With ESS (S1 ON, S2 ON/OFF) : Faults in LVDC Microgrids With Front-End ConvertersDocument1 pageLow Fault Resistance R With ESS (S1 ON, S2 ON/OFF) : Faults in LVDC Microgrids With Front-End Convertersalvin meNo ratings yet
- Behavior With PV PlantDocument1 pageBehavior With PV Plantalvin meNo ratings yet
- Low Fault Resistance R With ESS (S1 ON, S2 ON/OFF) : Faults in LVDC Microgrids With Front-End ConvertersDocument1 pageLow Fault Resistance R With ESS (S1 ON, S2 ON/OFF) : Faults in LVDC Microgrids With Front-End Convertersalvin meNo ratings yet
- Technical Application Papers: Faults in LVDC Microgrids With Front-End ConvertersDocument1 pageTechnical Application Papers: Faults in LVDC Microgrids With Front-End Convertersalvin meNo ratings yet
- Technical Application Papers - Fault Analysis in LVDC MicrogridsDocument1 pageTechnical Application Papers - Fault Analysis in LVDC Microgridsalvin meNo ratings yet
- Technical Application Papers: Faults in LVDC Microgrids With Front-End ConvertersDocument1 pageTechnical Application Papers: Faults in LVDC Microgrids With Front-End Convertersalvin meNo ratings yet
- Case 2a: Sin Sin (6.3) 106.6Document1 pageCase 2a: Sin Sin (6.3) 106.6alvin meNo ratings yet
- Technical Application Papers: Faults in LVDC Microgrids With Front-End ConvertersDocument1 pageTechnical Application Papers: Faults in LVDC Microgrids With Front-End Convertersalvin meNo ratings yet
- DC short circuit analysis with energy storage systemDocument1 pageDC short circuit analysis with energy storage systemalvin meNo ratings yet
- DC Ground Fault AnalysisDocument1 pageDC Ground Fault Analysisalvin meNo ratings yet
- Waveform of The AC CurrentDocument1 pageWaveform of The AC Currentalvin meNo ratings yet
- Faults in LVDC Microgrids With Front-End Converters: G G DCN G G GDocument1 pageFaults in LVDC Microgrids With Front-End Converters: G G DCN G G Galvin meNo ratings yet
- LVDC Microgrid BehaviorDocument1 pageLVDC Microgrid Behavioralvin meNo ratings yet
- Advantages of Low Voltage DC Distribution SystemsDocument1 pageAdvantages of Low Voltage DC Distribution Systemsalvin meNo ratings yet
- LVDC microgrid system and fault configurationDocument1 pageLVDC microgrid system and fault configurationalvin meNo ratings yet
- 3.5V to 9V Step-up Converter Module DN140-01v01Document3 pages3.5V to 9V Step-up Converter Module DN140-01v01José Mendes da SilvaNo ratings yet
- 8DJH Produktblatt EN Screen PDFDocument2 pages8DJH Produktblatt EN Screen PDFHung Cuong PhamNo ratings yet
- Getting Started With Android DevelopmentDocument90 pagesGetting Started With Android DevelopmentAnubhav Kumar100% (1)
- PD Flow FilesDocument2 pagesPD Flow FilespdnoobNo ratings yet
- Mil STD 756bDocument100 pagesMil STD 756bbitconcepts9781No ratings yet
- Ericsson Counters and FormulaDocument2 pagesEricsson Counters and FormulaIdowu OjoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Concepts of Radiologic ScienceDocument4 pagesChapter 1 Concepts of Radiologic ScienceCzarinaSy80% (5)
- KSZ8041RNL Hardware Design Checklist 00002702ADocument14 pagesKSZ8041RNL Hardware Design Checklist 00002702ArajasekaranNo ratings yet
- ConclusionDocument14 pagesConclusionRajat JainNo ratings yet
- DVA T4 DatasheetDocument3 pagesDVA T4 DatasheetGöestaf Zar0% (1)
- 1150-003 MIG - Flux Core - Stick Welder - Dual Voltage, 200 AmpDocument46 pages1150-003 MIG - Flux Core - Stick Welder - Dual Voltage, 200 AmpSiamakNo ratings yet
- Datasheet CT 4MDocument2 pagesDatasheet CT 4MYessa FitraNo ratings yet
- MS2-User Manual FalconDocument19 pagesMS2-User Manual FalconFatmir Enila FerhatiNo ratings yet
- Electrical LibraryDocument355 pagesElectrical LibraryRubén Blanco CarreraNo ratings yet
- RTL8822CEDocument96 pagesRTL8822CE박희만No ratings yet
- Pluto 0001X & Pluto 0002X-EN-20210701 - WithrayDocument2 pagesPluto 0001X & Pluto 0002X-EN-20210701 - WithrayyksNo ratings yet
- Avionic SystemsDocument10 pagesAvionic Systemsgelliott7639No ratings yet
- Load Flow Analysis For Three Phase Unbalanced Distribution Feeders Using MatlabDocument5 pagesLoad Flow Analysis For Three Phase Unbalanced Distribution Feeders Using MatlabEdna LópezNo ratings yet
- Excitation Systems Generators: Excitation Systems 1. 0 ObjectivesDocument10 pagesExcitation Systems Generators: Excitation Systems 1. 0 ObjectivesAnonymous dqbb02DUhNo ratings yet
- Optimizing P-Channels for Switching and RectificationDocument5 pagesOptimizing P-Channels for Switching and RectificationTim PriceNo ratings yet
- Engineering Standard: IPS-E-EL-100Document137 pagesEngineering Standard: IPS-E-EL-100Fatholla SalehiNo ratings yet
- Dokumen - Tips - Aladin Diagnostic Software For The Diwa 5 Transmission Turbo Aladin Diagnostic PDFDocument4 pagesDokumen - Tips - Aladin Diagnostic Software For The Diwa 5 Transmission Turbo Aladin Diagnostic PDFDiego CaceresNo ratings yet
- Signal Operations in The Corps and Army: Department Field Manual WARDocument76 pagesSignal Operations in The Corps and Army: Department Field Manual WARBarry FollandNo ratings yet
- PS09 - SP077 - Lima - Considerations Regarding Electrically Close Static Var Compensators With Adaptive Controllers Joint Operation and PerformanceDocument10 pagesPS09 - SP077 - Lima - Considerations Regarding Electrically Close Static Var Compensators With Adaptive Controllers Joint Operation and PerformanceFernando Cattan JusanNo ratings yet
- 10348Document54 pages10348sania2011No ratings yet
- Job 1 SksoDocument5 pagesJob 1 SksoFajAr OkTaNo ratings yet
- Photoelectric Sensor SolutionsDocument13 pagesPhotoelectric Sensor SolutionsHa RbNo ratings yet
- K85005-0125 - Remote Booster Power SuppliesDocument4 pagesK85005-0125 - Remote Booster Power SuppliesRafael AraújoNo ratings yet
- Osisense XX Xx518a3pam12Document6 pagesOsisense XX Xx518a3pam12Paulinho CezarNo ratings yet
- The Following Table Lists The 8051 Instructions by HEX CodeDocument5 pagesThe Following Table Lists The 8051 Instructions by HEX CodeBruce_Jass_3739No ratings yet