Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Sensitive Electronic Loads
Uploaded by
alvin meOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Sensitive Electronic Loads
Uploaded by
alvin meCopyright:
Available Formats
Technical Application Papers
1.1 Sensitive electronic loads 1.3 Cables and maximum transmissible power
1 Advantages of Low Voltage DC distribution systems
Commercial buildings, such as office buildings, often A grounded three-phase AC system requires five wires—
have a large amount of nonlinear electronic loads, such three phase conductors, one neutral, and one ground. A
as lighting, computers, monitors, and adjustable-speed DC system requires three wires—two phase conductors
drives for air conditioning. and one ground. An existing five-wire AC cable in a retrofit
Special office buildings, such as banks and data centers, DC system can be used in two different configurations.
have critical computer systems which must be operating The first is to use two wires for each pole and one for
“24-7” and must not be affected by transients and out- ground.
ages on the utility power grid. The other alternative is to use one for each pole, two
A common way to protect these loads is to install on- for neutral and one for ground, with the load connected
line uninterruptible power supplies (UPSs) and standby between one pole and neutral.
diesel-generator sets. The UPSs are used to protect the Considering the maximum transmissible power, the DC
loads from transients and short interruptions with dura- distribution solutions (distribution with 2 or 3 conductors)
tion up to approximately 0.5 h. may be compared with the traditional AC distribution, that
The losses of a UPS are in the range 5–10%. in Italy is usually made by three-phase cable lines with
The installed UPSs must also be able to handle distorted 4 conductors (3 phase conductors and the neutral with
currents from nonlinear loads, and they must therefore a smaller cross section), with a nominal voltage of 400V.
be overrated. The transmissible power for the various systems can be
If, instead, DC distribution is used, a single converter is expressed as follows:
utilized to supply the loads, and additional losses can be – traditional AC - =
reduced. Since loads are supplied with DC, the rectifiers – DC with 3 conductors - 3 = 2∙ 3∙ 3
inside the loads can be removed and the losses can be – DC with 2 conductors - 2 = 2∙ 2
lowered. where VDC3 is the voltage between the positive or nega-
tive pole and neutral conductor, while VDC2 is the voltage
between the two poles. Assuming VAC = 400 V; VDC3 =
1.2 Distributed generation 400 V; VDC2 = 800 V, for the comparison between the AC
and DC distribution, the following hypotheses are made:
The number of alternative generation sources connected – the cables, with the same section in all the examined
to the distribution system increases. Some of them, such cases, are loaded up to their thermal limit current, so
as photovoltaic and fuel cells, produce DC, and they can that IAC = IDC3 = IDC2;
easily be connected to a DC distribution system directly, – the whole load is connected at the end of the line and
or through a DC/DC converter. Microturbines generating the possible presence of DG is neglected;
high-frequency AC are also easier to connect to a DC – the power factor of the AC loads is 0.9.
system than to an AC system, where generating a syn- The comparison between the two systems, AC and DC
chronized sinusoidal AC current is required. The electric with 3 conductors, shows that in DC a power 1.28 times
power output of a wind turbine can be kept at a maximum larger than that in AC can be transported.
if the speed of the turbine is allowed to vary. If the shaft The same result is obtained in case of 2-wire DC distri-
is connected to the generator through a gearbox, the bution system.
ability to vary the speed is limited. To increase the speed The relationships between the AC and DC transmissible
range, an AC/DC/AC converter can be used, which is an powers are the following:
expensive solution. A cheaper and simpler solution is to
3 2∙ 3 2 2
connect an AC/DC converter to a DC grid. Other types of = = [1.1]
generators operating with varying speed are small hydro 3∙ ∙ 3∙ ∙
and tidal generators.
By increasing the length of the line, the DC solutions can
Using a DC distribution system makes it easier to incor-
transport an amount of electric power up to 2.2÷3.9 times
porate more local energy storage and sources, either
the one in AC. It can be concluded that with the same
standby power generation, which is used only when there
extension of the distribution network, the DC solutions
is a fault on the utility grid, or distributed generation (DG)
can supply a larger load, while with the same load, the
(small-scale energy sources) which are operated more
DC distribution systems can have a greater extension
or less continuously.
than the AC one.
To connect an energy source to a DC system only the
voltage has to be controlled.
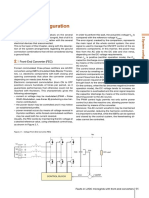
6 Faults in LVDC microgrids with front-end converters
You might also like
- It Is Quite Another Electricity: Transmitting by One Wire and Without GroundingFrom EverandIt Is Quite Another Electricity: Transmitting by One Wire and Without GroundingNo ratings yet
- Comparative Evaluation of HVDC and HVAC Transmission SystemsDocument5 pagesComparative Evaluation of HVDC and HVAC Transmission SystemsNidhiNo ratings yet
- Advantages of Low Voltage DC Distribution SystemsDocument1 pageAdvantages of Low Voltage DC Distribution Systemsalvin meNo ratings yet
- Fault Scenario Simulation in A Feeder: Transmission and Distribution of Electrical PowerDocument32 pagesFault Scenario Simulation in A Feeder: Transmission and Distribution of Electrical PowerriteshtiroleNo ratings yet
- Modelling and Co-Ordination Control of Hybrid Grid: S. Lakshmi Devi K. SudheerDocument8 pagesModelling and Co-Ordination Control of Hybrid Grid: S. Lakshmi Devi K. SudheerAdriano NavarroNo ratings yet
- PS2 HDocument10 pagesPS2 Hasifchandarki.official72No ratings yet
- High Voltage Direct Current (HVDC) Transmission Line SystemDocument30 pagesHigh Voltage Direct Current (HVDC) Transmission Line SystemzakiNo ratings yet
- Wind Energy ConversionDocument7 pagesWind Energy ConversionMurtadha KadhimNo ratings yet
- Documents: HVDC ContrDocument92 pagesDocuments: HVDC Contrvenkilaxmi9No ratings yet
- Submitted To: Subject Manual of Lab WorkDocument61 pagesSubmitted To: Subject Manual of Lab WorkRana FaizanNo ratings yet
- Comparative Evaluation of HVDC and HVAC Transmission SystemsDocument5 pagesComparative Evaluation of HVDC and HVAC Transmission SystemsZak TahirkheliNo ratings yet
- Marano Marcolini2009Document5 pagesMarano Marcolini2009Paolo FlorentinNo ratings yet
- HVDC Transmission Systems UNIT-1: Comparison of AC and DC TransmissionDocument57 pagesHVDC Transmission Systems UNIT-1: Comparison of AC and DC TransmissionSaurabhNo ratings yet
- Submitted To: Subject Manual of Lab WorkDocument62 pagesSubmitted To: Subject Manual of Lab WorkRana FaizanNo ratings yet
- Lecture HVDCDocument19 pagesLecture HVDCRakibul IslamNo ratings yet
- A Bidirectional DC-DC Converter For An Energy Storage System With Galvanic IsolationDocument8 pagesA Bidirectional DC-DC Converter For An Energy Storage System With Galvanic IsolationKrishnaChaitanyaNo ratings yet
- Cseb ReportDocument25 pagesCseb Reportshchan530% (1)
- Minization LossesDocument5 pagesMinization LossesRtc NasikNo ratings yet
- 3 290 PaperDocument6 pages3 290 PaperEdo EdićNo ratings yet
- Power Transmission CapacityDocument2 pagesPower Transmission Capacityintiw_23No ratings yet
- Elimination of SynchronizationDocument1 pageElimination of Synchronizationalvin meNo ratings yet
- Taller Parcial Electronica de PotenciaDocument4 pagesTaller Parcial Electronica de PotenciaMaria Isabel Martinez NorenaNo ratings yet
- Ned Mohan: Minneapolis 2002Document19 pagesNed Mohan: Minneapolis 2002Anoop InnocentNo ratings yet
- Module - 3 - NotesDocument41 pagesModule - 3 - NotesBUNTI MN100% (1)
- UNIT-2 Introduction To Facts: Need For Transmission Networks InterconnectionsDocument13 pagesUNIT-2 Introduction To Facts: Need For Transmission Networks Interconnectionspadma kalyan RelaNo ratings yet
- HVDC NotesDocument56 pagesHVDC Notesmahi100% (2)
- Low Voltage DC Distribution - Are We Ready Yet?Document6 pagesLow Voltage DC Distribution - Are We Ready Yet?pavan gangwarNo ratings yet
- Self-Powered 380V DC Sic Solid-State Circuit Breaker and Fault Current LimiterDocument9 pagesSelf-Powered 380V DC Sic Solid-State Circuit Breaker and Fault Current LimiterTRIAD TECHNO SERVICESNo ratings yet
- Dual Active Bridge Based Reduced Stage Multiport DC AC Converter For PV-Battery SystemsDocument11 pagesDual Active Bridge Based Reduced Stage Multiport DC AC Converter For PV-Battery Systemstengfei.sunNo ratings yet
- 7-Chapter 2 PDFDocument30 pages7-Chapter 2 PDFsirishaNo ratings yet
- Design and Implementation of A Sic Based Contactless Battery Charger For Electric VehiclesDocument7 pagesDesign and Implementation of A Sic Based Contactless Battery Charger For Electric VehiclesGOOGLE RECURIMENTNo ratings yet
- DC MachinesDocument9 pagesDC MachinesSIVARASU RATHINAVELUNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document57 pagesChapter 1MikatechNo ratings yet
- Grounding Configurations of DC Nanogrid and Study of Dual-Buck-Boost Ac/Dc ConverterDocument4 pagesGrounding Configurations of DC Nanogrid and Study of Dual-Buck-Boost Ac/Dc ConverterSegNo ratings yet
- Chapter IDocument51 pagesChapter ImartazemeduNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1-: Suresh Babu AdiandhraDocument4 pagesChapter 1-: Suresh Babu AdiandhraFreedom YenesewNo ratings yet
- HVDC Transmission: Advanced Power ElectronicsDocument75 pagesHVDC Transmission: Advanced Power ElectronicsBvijaya krishnaNo ratings yet
- 1 110-04 PDFDocument8 pages1 110-04 PDFAkinbode Sunday OluwagbengaNo ratings yet
- AC Fault Ride-Through of MMC VSC-HVDC SystemsDocument6 pagesAC Fault Ride-Through of MMC VSC-HVDC Systemsas147No ratings yet
- Iuga 2019Document4 pagesIuga 2019Alioth F.a.mNo ratings yet
- HVDC Group FinalDocument14 pagesHVDC Group FinalGitta JoshuaNo ratings yet
- Hvts AssignmentDocument12 pagesHvts AssignmentrashmisbhumbareNo ratings yet
- Igh-Voltage DC Relay: FTR-J2/FTR-K2W SeriesDocument4 pagesIgh-Voltage DC Relay: FTR-J2/FTR-K2W SeriesAkong KudetNo ratings yet
- Combination of Interleaved Single-Input Multiple-Output DC-DC ConvertersDocument11 pagesCombination of Interleaved Single-Input Multiple-Output DC-DC ConvertersAshish kumar N HNo ratings yet
- 3 Phase DistributionDocument13 pages3 Phase DistributionAnil BhattaNo ratings yet
- Power Upgrading of Transmission Lines by Combining Ac & DCDocument68 pagesPower Upgrading of Transmission Lines by Combining Ac & DCrashidmd42100% (2)
- Lec. 2Document15 pagesLec. 2Ihssan JamallNo ratings yet
- 229 HVDC NoteDocument58 pages229 HVDC NoteSubhashree RoutNo ratings yet
- Whitepaper Switching of Filter Circuits With Vacuum SwitchesDocument8 pagesWhitepaper Switching of Filter Circuits With Vacuum Switchesvijayeee82No ratings yet
- Comparison HVDC EHVACDocument2 pagesComparison HVDC EHVACgoyal.167009No ratings yet
- 1SDC007113G0201 - QT14 2021 - enDocument72 pages1SDC007113G0201 - QT14 2021 - enyessica PadronNo ratings yet
- HVDC Transmission Technology For Sustainable Power Supply: J. Dorn H. Gambach, D. RetzmannDocument6 pagesHVDC Transmission Technology For Sustainable Power Supply: J. Dorn H. Gambach, D. RetzmannSiti SitiNo ratings yet
- Bidirectional 12kV To 1.2kV DC-DC Converter For Renewable Energy ApplicationsDocument8 pagesBidirectional 12kV To 1.2kV DC-DC Converter For Renewable Energy ApplicationsJyothiPunemNo ratings yet
- UNIT-1 Introduction To Facts: Need For Transmission Networks InterconnectionsDocument13 pagesUNIT-1 Introduction To Facts: Need For Transmission Networks InterconnectionsChetan KotwalNo ratings yet
- Comparative Evaluation of HVDC and HVAC Transmission SystemsDocument6 pagesComparative Evaluation of HVDC and HVAC Transmission SystemssajuaanalsaNo ratings yet
- Transmission and Distribution SchemeDocument4 pagesTransmission and Distribution SchemeearhyathNo ratings yet
- Nepal Electricity Authority (NEA) Transmission Network and Its LossesDocument3 pagesNepal Electricity Authority (NEA) Transmission Network and Its LossesUkesh ShresthaNo ratings yet
- HVDC Feeder Solution For Electric Railways: L. Abrahamsson, T. Kjellqvist, S. OstlundDocument10 pagesHVDC Feeder Solution For Electric Railways: L. Abrahamsson, T. Kjellqvist, S. OstlundAhmad TaheriNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Power System ProtectionFrom EverandIntroduction to Power System ProtectionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Own The Culture - Yamaha Mio Soul I125Document3 pagesOwn The Culture - Yamaha Mio Soul I125alvin me0% (1)
- Aerox Smart Key BatteryDocument1 pageAerox Smart Key Batteryalvin meNo ratings yet
- Systems With The DC Mid-Point Grounded: Technical Application PapersDocument1 pageSystems With The DC Mid-Point Grounded: Technical Application Papersalvin meNo ratings yet
- Aerox Smart Key SystemDocument1 pageAerox Smart Key Systemalvin meNo ratings yet
- Aerox Seat Opening and ClosingDocument1 pageAerox Seat Opening and Closingalvin meNo ratings yet
- Aerox Stop and Start SystemDocument1 pageAerox Stop and Start Systemalvin meNo ratings yet
- Technical Specs - Yamaha Mio Soul I125Document3 pagesTechnical Specs - Yamaha Mio Soul I125alvin meNo ratings yet
- Aerox Restarting The EngineDocument1 pageAerox Restarting The Enginealvin meNo ratings yet
- 2.5 2 1.41 Iconv: Faults in LVDC Microgrids With Front-End ConvertersDocument1 page2.5 2 1.41 Iconv: Faults in LVDC Microgrids With Front-End Convertersalvin meNo ratings yet
- Technical Application Papers: Faults in LVDC Microgrids With Front-End ConvertersDocument1 pageTechnical Application Papers: Faults in LVDC Microgrids With Front-End Convertersalvin meNo ratings yet
- Systems With The DC Negative Pole Grounded: dc1 DC/R Convdc2Document1 pageSystems With The DC Negative Pole Grounded: dc1 DC/R Convdc2alvin meNo ratings yet
- Technical Application Papers: Faults in LVDC Microgrids With Front-End ConvertersDocument1 pageTechnical Application Papers: Faults in LVDC Microgrids With Front-End Convertersalvin meNo ratings yet
- Technical Application Papers: Behavior With PV PlantDocument1 pageTechnical Application Papers: Behavior With PV Plantalvin meNo ratings yet
- DC Component Values of The Ground Fault CurrentDocument1 pageDC Component Values of The Ground Fault Currentalvin meNo ratings yet
- High Fault Resistance R With ESS (S1 OFF, S2 ON) : Technical Application PapersDocument1 pageHigh Fault Resistance R With ESS (S1 OFF, S2 ON) : Technical Application Papersalvin meNo ratings yet
- Low Fault Resistance R With ESS (S1 ON, S2 ON/OFF) : Faults in LVDC Microgrids With Front-End ConvertersDocument1 pageLow Fault Resistance R With ESS (S1 ON, S2 ON/OFF) : Faults in LVDC Microgrids With Front-End Convertersalvin meNo ratings yet
- High Fault ResistanceDocument1 pageHigh Fault Resistancealvin meNo ratings yet
- Technical Application Papers: Faults in LVDC Microgrids With Front-End ConvertersDocument1 pageTechnical Application Papers: Faults in LVDC Microgrids With Front-End Convertersalvin meNo ratings yet
- Maximum AC Current AbsorptionDocument1 pageMaximum AC Current Absorptionalvin meNo ratings yet
- Low Fault Resistance R With ESS (S1 ON, S2 ON/OFF) : Faults in LVDC Microgrids With Front-End ConvertersDocument1 pageLow Fault Resistance R With ESS (S1 ON, S2 ON/OFF) : Faults in LVDC Microgrids With Front-End Convertersalvin meNo ratings yet
- Faults in LVDC Microgrids With Front-End Converters: G G DCN G G GDocument1 pageFaults in LVDC Microgrids With Front-End Converters: G G DCN G G Galvin meNo ratings yet
- Faults in LVDC Microgrids With Front-End Converters: G G DCN G G GDocument1 pageFaults in LVDC Microgrids With Front-End Converters: G G DCN G G Galvin meNo ratings yet
- Technical Application Papers: Faults in LVDC Microgrids With Front-End ConvertersDocument1 pageTechnical Application Papers: Faults in LVDC Microgrids With Front-End Convertersalvin meNo ratings yet
- Case 2a: Sin Sin (6.3) 106.6Document1 pageCase 2a: Sin Sin (6.3) 106.6alvin meNo ratings yet
- DC Ground Fault AnalysisDocument1 pageDC Ground Fault Analysisalvin meNo ratings yet
- LVDC Microgrid BehaviorDocument1 pageLVDC Microgrid Behavioralvin meNo ratings yet
- Behavior With PV PlantDocument1 pageBehavior With PV Plantalvin meNo ratings yet
- Waveform of The AC CurrentDocument1 pageWaveform of The AC Currentalvin meNo ratings yet
- 2 System Configuration: Front-End Converter (FEC)Document1 page2 System Configuration: Front-End Converter (FEC)alvin meNo ratings yet
- Hazard of Direct CurrentDocument1 pageHazard of Direct Currentalvin meNo ratings yet
- An Intelligent Approach of The Fish Feeding SystemDocument13 pagesAn Intelligent Approach of The Fish Feeding SystemAdeyinka OluwoNo ratings yet
- Yusra Hanif: Lecturer Computer Science Concordia College SahiwalDocument21 pagesYusra Hanif: Lecturer Computer Science Concordia College SahiwalYusraNo ratings yet
- Specifications For Tenders TELETASK Systems en V32Document41 pagesSpecifications For Tenders TELETASK Systems en V32Eric ChavesNo ratings yet
- GstarCAD2021 Network License Manager GuideDocument18 pagesGstarCAD2021 Network License Manager Guidegstarcad IndonesiaNo ratings yet
- Smartclass 4800: Tool of Choice For All-In-One Service TestingDocument3 pagesSmartclass 4800: Tool of Choice For All-In-One Service TestingSebastian E. Caro S.No ratings yet
- Windows Registry PresentationDocument22 pagesWindows Registry Presentationvoxpop51No ratings yet
- NSX For VSphere - A Foundation of The SDDCDocument234 pagesNSX For VSphere - A Foundation of The SDDCMahmood RobbinsNo ratings yet
- MCP1640/B/C/D: 0.65V Start-Up Synchronous Boost Regulator With True Output Disconnect or Input/Output Bypass OptionDocument32 pagesMCP1640/B/C/D: 0.65V Start-Up Synchronous Boost Regulator With True Output Disconnect or Input/Output Bypass OptionseseNo ratings yet
- Internet Service Provider (ISP) - Central ZoneDocument5 pagesInternet Service Provider (ISP) - Central ZoneSuvendu SahaNo ratings yet
- 1: Introduction To The Prism Library 5.0 For WPF: #!155chartopicsummary!#Document20 pages1: Introduction To The Prism Library 5.0 For WPF: #!155chartopicsummary!#thorirNo ratings yet
- The Removal and Fitting of Engines in Bus F94: Issue 1Document12 pagesThe Removal and Fitting of Engines in Bus F94: Issue 1RuanNo ratings yet
- BulkSMS Api 6.1Document54 pagesBulkSMS Api 6.1Shashank WadhwaNo ratings yet
- OHPC Balimela Volume 4Document309 pagesOHPC Balimela Volume 4gmdgfkNo ratings yet
- TDocument38 pagesTgauravsharmacl2007No ratings yet
- Cooling Load Rule of ThumbDocument18 pagesCooling Load Rule of ThumbQaz Zaq100% (1)
- Admissions Open 2012: Manipal UniversityDocument1 pageAdmissions Open 2012: Manipal UniversityTFearRush0No ratings yet
- Spin Master BRCH en A00523Document6 pagesSpin Master BRCH en A00523Hendra GunawanNo ratings yet
- Study Plan Chemical Engineering UiTM Shah AlamDocument2 pagesStudy Plan Chemical Engineering UiTM Shah AlamKhairaniNorNo ratings yet
- Operations Management BITS PilaniDocument692 pagesOperations Management BITS Pilanisap6370No ratings yet
- CoTM Harmonized CurriculumDocument106 pagesCoTM Harmonized CurriculumTinsae Mulatu100% (2)
- Ias 2 0 Revc Gold ManualDocument590 pagesIas 2 0 Revc Gold Manualphani22No ratings yet
- 3 8049usaDocument9 pages3 8049usaAsep Dian PermanaNo ratings yet
- List of Instruments and Pressure GaugesDocument1 pageList of Instruments and Pressure Gaugesram dhukeNo ratings yet
- Zend Continuous Delivery BlueprintDocument17 pagesZend Continuous Delivery BlueprintdextervipNo ratings yet
- Stadium FailureDocument1 pageStadium Failurerao_gsv7598No ratings yet
- 2012 Behringer Catalog en v1Document45 pages2012 Behringer Catalog en v1Kang AmorNo ratings yet
- Typewriter To Wordprocessor 1Document18 pagesTypewriter To Wordprocessor 1Wendy NoboaNo ratings yet
- FedEx AnalysisDocument17 pagesFedEx AnalysisAbhimanyu ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Smart City Project ModulesDocument3 pagesSmart City Project Modulesdeepika balichwal0% (1)
- (M5 MAIN) 8086 8088 InstructionSetsDocument153 pages(M5 MAIN) 8086 8088 InstructionSetsAkademiko HelperNo ratings yet