Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Meng 116 Machine Design Ii Long Examination 1 Instructions
Uploaded by
Collano M. Noel RogieOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Meng 116 Machine Design Ii Long Examination 1 Instructions
Uploaded by
Collano M. Noel RogieCopyright:
Available Formats
MEng 116
Machine Design II
Long Examination 1
INSTRUCTIONS:
• This exam is open for 3 days and has no time limit.
• Provide the correct solutions and answers to the given problems.
• Solutions should be encoded. However, complex equations may be handwritten if
deemed difficult to encode.
• Submit the PDF form of your answer sheet in VSUEE Long Examination 1 (Turnitin
Assignment page) with the file name “lastnameLE1.pdf”
• CHEATING or ANY FORM OF ACADEMIC DISHONESTY is highly discouraged.
If caught, you will be immediately dropped and possibly be expelled from the
university.
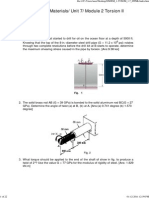
1. A 2 7/16-in. countershaft in a machine shop transmits 52 hp at 315 rpm. It is made
of AISI 1117, as rolled, and supported upon bearing A and B, 59-in. apart. Pulley
C receives the power via a horizontal belt, and pulley D delivers it vertically
downward (Figure 1). Calculate N based on the Octahedral Shear Stress theory
considering varying stresses.
Figure 1. Countershaft
2. A 3-in rotating shaft as shown (Figure 2) carries a bevel gear whose mean is D m
= 10 in and which is keyed (profile) to the left end. Acting on the gear are a radial
force G = 1570.8 lb, a driving force Q = 3141.6 lb. The thrust force is taken by the
right-hand bearing. Let a = 5 in. and L = 15 in.; material, AISI C1040, annealed.
Base calculations on the Maximum Shearing Stress theory with variable stress.
Compute the indicated design factor N. With the use of a sketch, indicate the exact
point of which maximum normal stress occurs.
MEng 116 – Machine Design II LE-001
Figure 2. Shaft
3. A cast-steel (SAE 080, N & T) pulley is keyed to a 2 1/2-in. shaft by means of a
standard square key, 3 1/2-in. long, made of cold-drawn SAE 1015. The shaft is
made of cold-drawn AISI 1045. If the shaft is in virtually pure torsion, and turns at
420 rpm, what horsepower could the assembly safely transmit for steady loading?
4. A pair of carefully cut, full length, 200 involute gears, made of cast iron, ASTM 30,
is transmitting 5 hp at 1150 rpm of the pinion; Np = 24, Ng = 32, Pd = 8, b = 1.5 in.
for the teeth, determine (a) the endurance, (b) the dynamic load, (c) the service
factor.
MEng 116 – Machine Design II LE-001
You might also like
- 6 Shafts PDFDocument23 pages6 Shafts PDFViven SharmaNo ratings yet
- 2020 JC 2 H2 Math Consolidation Test II (Solutions)Document13 pages2020 JC 2 H2 Math Consolidation Test II (Solutions)Timothy HandokoNo ratings yet
- Mech 325 Tutorials (Questions Only)Document54 pagesMech 325 Tutorials (Questions Only)Shahriar Norouzi ZadehNo ratings yet
- Mechanical SpringsDocument33 pagesMechanical SpringsAhmedOMNo ratings yet
- Stress Analysis Problems in S.I. Units: The Commonwealth and International Library: Mechanical Engineering DivisionFrom EverandStress Analysis Problems in S.I. Units: The Commonwealth and International Library: Mechanical Engineering DivisionRating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (4)
- MECH 344 - Final Exam (Winter 2021)Document4 pagesMECH 344 - Final Exam (Winter 2021)Puneet Rudhar100% (1)
- Me 301 Chapter 10Document28 pagesMe 301 Chapter 10Melissa RokaNo ratings yet
- Project ProblemsDocument9 pagesProject Problemsvivek geddamNo ratings yet
- Design Work 9 - Shaft Design Under Combined LoadingsDocument22 pagesDesign Work 9 - Shaft Design Under Combined LoadingsEngr Ghulam MustafaNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 1Document2 pagesWorksheet 1dagimawgchew777No ratings yet
- CEMDEF40 Module 8 - Torsion On Statically Indeterminate Members Non-Circular and Thin-Walled MmebersDocument14 pagesCEMDEF40 Module 8 - Torsion On Statically Indeterminate Members Non-Circular and Thin-Walled MmebersengrrrrNo ratings yet
- Design For Static Load: Design of Machine Elements Module-IDocument13 pagesDesign For Static Load: Design of Machine Elements Module-InikhilasoknNo ratings yet
- Problemario1-Diseã o Mecanico1Document4 pagesProblemario1-Diseã o Mecanico1Gerardo BocanegraNo ratings yet
- ME2233 Mechanics of Materials - I: Credit Hours - 3 Spring 2016 Lecture 2 (Week 2)Document26 pagesME2233 Mechanics of Materials - I: Credit Hours - 3 Spring 2016 Lecture 2 (Week 2)Chaudhry Muhammad AliNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2Document2 pagesAssignment 2just0% (2)
- Question Paper ME1-FDocument3 pagesQuestion Paper ME1-FbrainmanthansNo ratings yet
- MD1 Plate 9 Columns Nov2022Document1 pageMD1 Plate 9 Columns Nov2022Matthew Dale BalisiNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Springs: Machine Design IIDocument72 pagesMechanical Springs: Machine Design IIsainandhaNo ratings yet
- Problems s5Document5 pagesProblems s5zangue billy jamesNo ratings yet
- Strength of Materials/ Unit 7/ Module 2 Torsion II: Problem SetDocument22 pagesStrength of Materials/ Unit 7/ Module 2 Torsion II: Problem Setneeru143No ratings yet
- Torsion 01Document20 pagesTorsion 01Danielle Ruthie GalitNo ratings yet
- Assignment Shaft DesignDocument4 pagesAssignment Shaft DesignHasham Mehmood100% (1)
- Tut 1 CH 6Document6 pagesTut 1 CH 6SpidyNo ratings yet
- Problem Sets Shafts Keys and CouplingDocument4 pagesProblem Sets Shafts Keys and CouplingJay Ann TondoNo ratings yet
- ShaftsDocument1 pageShaftsJim Lester AmodiaNo ratings yet
- Review ProblemDocument35 pagesReview ProblemKANOKPOL URAIPANNo ratings yet
- 1 PBDocument8 pages1 PBkwinten TambeurNo ratings yet
- End Semester SY Question Paper MDD May 2021Document3 pagesEnd Semester SY Question Paper MDD May 2021FelishiaNo ratings yet
- 2019A MEC6B5-GR1 Deber5Document4 pages2019A MEC6B5-GR1 Deber5Daniel19970513No ratings yet
- Analysis of Simple StressesDocument39 pagesAnalysis of Simple StressesEduCartNo ratings yet
- MTP 5Document4 pagesMTP 5tinku singhNo ratings yet
- Machine Element II Worksheet 1Document2 pagesMachine Element II Worksheet 1Hanan ShayiboNo ratings yet
- Assignment - 2 - MEC391 (A) - Fall 2022Document2 pagesAssignment - 2 - MEC391 (A) - Fall 2022ah himelNo ratings yet
- Machine Design Answer KeyDocument16 pagesMachine Design Answer KeyK.KESAVARAJ HICET STAFF MCTSNo ratings yet
- Final Exam MCT3214 Nov09Document6 pagesFinal Exam MCT3214 Nov09Deerah Aziz100% (1)
- Sheet 2Document5 pagesSheet 2Abdalla Mohamed AbdallaNo ratings yet
- Yield & Plasticity Ex Sheet 2021Document1 pageYield & Plasticity Ex Sheet 2021Enda O'ConnellNo ratings yet
- Module 4 TorsionDocument62 pagesModule 4 TorsionPRINZE SEREGUINENo ratings yet
- Sheet 6Document4 pagesSheet 6Abdalla Mohamed Abdalla100% (1)
- Special Mid Term Exam CET204Document3 pagesSpecial Mid Term Exam CET204zNo ratings yet
- Assignment 7221 MD-IIIDocument2 pagesAssignment 7221 MD-IIIkalikaNo ratings yet
- ME3104 DPTE EndSemDocument3 pagesME3104 DPTE EndSemPriyojit GhoshNo ratings yet
- CIVE-441 Steel Design (I) : Homework Assignment # 7Document26 pagesCIVE-441 Steel Design (I) : Homework Assignment # 7Mohamed GamalNo ratings yet
- Practice Exam 2Document7 pagesPractice Exam 2azizieh5701No ratings yet
- 12me52 MQP-1Document3 pages12me52 MQP-1SumitKumarNo ratings yet
- Lecture 8 & 9 - TorsionDocument12 pagesLecture 8 & 9 - TorsionHowell TungolNo ratings yet
- Fatigue Loading ExamplesDocument6 pagesFatigue Loading ExampleskillyriaNo ratings yet
- Design and Analysis of Crankshaft For Single Cylinder 4-Stroke Deisel EngineDocument3 pagesDesign and Analysis of Crankshaft For Single Cylinder 4-Stroke Deisel EngineChetan GuptaNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2Document2 pagesAssignment 2Suman MandalNo ratings yet
- Design and Analysis of Fixture For Heavy Shell TiltingDocument5 pagesDesign and Analysis of Fixture For Heavy Shell Tiltinggkdora574No ratings yet
- NR 10105 Engineering MechanicsDocument13 pagesNR 10105 Engineering MechanicsVijay PrakashNo ratings yet
- EMT 3102 SUPP Solids & Structural Mechanics 1 SUPPDocument4 pagesEMT 3102 SUPP Solids & Structural Mechanics 1 SUPPGausss TjNo ratings yet
- Design of Machine Element 211012010732Document2 pagesDesign of Machine Element 211012010732Abhishek KumarNo ratings yet
- Portfolio in MD1 - VALE Jenille Jane TDocument74 pagesPortfolio in MD1 - VALE Jenille Jane TEdmundo AbatNo ratings yet
- Advanced Steel Design - HW - 3 - Mastan1Document4 pagesAdvanced Steel Design - HW - 3 - Mastan1YogeshUnde0% (1)
- Mdid Lab ManualDocument48 pagesMdid Lab Manualjaimin777No ratings yet
- Design Analysis and Fabrication of Hydra PDFDocument9 pagesDesign Analysis and Fabrication of Hydra PDFMac NyandoroNo ratings yet
- Macine Element I Worksheet For Final ExamDocument4 pagesMacine Element I Worksheet For Final Examdagimawgchew777No ratings yet
- Lec01-Springs (Ch10)Document32 pagesLec01-Springs (Ch10)Kiril AckovskiNo ratings yet
- DME-Module 3-Ktunotes - inDocument52 pagesDME-Module 3-Ktunotes - inLinto VargheseNo ratings yet
- Unit - II Tension Members: Two Mark Question and AnswersDocument7 pagesUnit - II Tension Members: Two Mark Question and AnswersSourabh SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- SCTS 11 - 2sem22 23 - Module 3 - Learning Task. Collano..Document3 pagesSCTS 11 - 2sem22 23 - Module 3 - Learning Task. Collano..Collano M. Noel RogieNo ratings yet
- Final Balcon PlanDocument1 pageFinal Balcon PlanCollano M. Noel RogieNo ratings yet
- Final 2nd Floor PlanDocument1 pageFinal 2nd Floor PlanCollano M. Noel RogieNo ratings yet
- SCTS 11pdfDocument2 pagesSCTS 11pdfCollano M. Noel RogieNo ratings yet
- SCTS 112pdfDocument1 pageSCTS 112pdfCollano M. Noel RogieNo ratings yet
- Final Isometric ViewDocument1 pageFinal Isometric ViewCollano M. Noel RogieNo ratings yet
- COLLANO1Document1 pageCOLLANO1Collano M. Noel RogieNo ratings yet
- 10-24-22 ConductionDocument28 pages10-24-22 ConductionCollano M. Noel RogieNo ratings yet
- Final ViewsDocument1 pageFinal ViewsCollano M. Noel RogieNo ratings yet
- Final 1st Floor PlanDocument1 pageFinal 1st Floor PlanCollano M. Noel RogieNo ratings yet
- Collano Floor PlanDocument2 pagesCollano Floor PlanCollano M. Noel RogieNo ratings yet
- HT AssignmentDocument12 pagesHT AssignmentCollano M. Noel RogieNo ratings yet
- COLLANO2Document7 pagesCOLLANO2Collano M. Noel RogieNo ratings yet
- Numerical Analysis in Engineering: Taylor SeriesDocument36 pagesNumerical Analysis in Engineering: Taylor SeriesCollano M. Noel RogieNo ratings yet
- MEng 111e Learning Task No2Document5 pagesMEng 111e Learning Task No2Collano M. Noel RogieNo ratings yet
- Numerical Methods: Introduction, Discrete Algebra, Accuracy, ErrorsDocument40 pagesNumerical Methods: Introduction, Discrete Algebra, Accuracy, ErrorsCollano M. Noel RogieNo ratings yet
- Boiler Other Steam Plant AccessoriesDocument5 pagesBoiler Other Steam Plant AccessoriesCollano M. Noel RogieNo ratings yet
- 3-4 RA 8495 Article IVDocument22 pages3-4 RA 8495 Article IVCollano M. Noel RogieNo ratings yet
- Numerical Analysis in Engineering: Taylor SeriesDocument28 pagesNumerical Analysis in Engineering: Taylor SeriesCollano M. Noel RogieNo ratings yet
- 2 The Mechanical Engineering ProfessionDocument11 pages2 The Mechanical Engineering ProfessionCollano M. Noel RogieNo ratings yet
- 3-5 RA 8495 Article VDocument11 pages3-5 RA 8495 Article VCollano M. Noel RogieNo ratings yet
- Diesel Hydro PowerDocument6 pagesDiesel Hydro PowerCollano M. Noel RogieNo ratings yet
- Module 1, Lesson 1.1 INDUSTRIAL PLANT DESIGN ASPECTSDocument5 pagesModule 1, Lesson 1.1 INDUSTRIAL PLANT DESIGN ASPECTSCollano M. Noel RogieNo ratings yet
- 3-1 RA 8495 Article IDocument27 pages3-1 RA 8495 Article ICollano M. Noel RogieNo ratings yet
- Module 1, Lesson 1.2Document15 pagesModule 1, Lesson 1.2Collano M. Noel RogieNo ratings yet
- 3-2 RA 8495 Article IIDocument19 pages3-2 RA 8495 Article IICollano M. Noel RogieNo ratings yet
- Mod. 3, Less 3.2, Turb. PerfDocument25 pagesMod. 3, Less 3.2, Turb. PerfCollano M. Noel RogieNo ratings yet
- Milk Is Carefully Produced at The Milking at The PCC (Philippine CarabaoDocument1 pageMilk Is Carefully Produced at The Milking at The PCC (Philippine CarabaoCollano M. Noel RogieNo ratings yet
- ME Laboratory No. 2 Compressors or Turbine With Different EfficienciesDocument9 pagesME Laboratory No. 2 Compressors or Turbine With Different EfficienciesCollano M. Noel RogieNo ratings yet
- MEng 151 - Mechanical Engineering Laboratory II ME Laboratory No. 2 ManualDocument13 pagesMEng 151 - Mechanical Engineering Laboratory II ME Laboratory No. 2 ManualCollano M. Noel RogieNo ratings yet
- Operating Process For Access To Gas Insulated SwitchgearDocument19 pagesOperating Process For Access To Gas Insulated SwitchgearMaharajaNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 3 - Kinematics EquationsDocument2 pagesWorksheet 3 - Kinematics EquationsGezem GigantoNo ratings yet
- Mathematics - Iii - Feb - 2022 - 3 - MechDocument2 pagesMathematics - Iii - Feb - 2022 - 3 - MechLakshmi PithaniNo ratings yet
- The History of AtomDocument3 pagesThe History of Atomariel frejasNo ratings yet
- Motion in A PlaneDocument15 pagesMotion in A PlaneLokeshNo ratings yet
- MM 439 - 2021 - Assignment-1 SolutionsDocument10 pagesMM 439 - 2021 - Assignment-1 SolutionsAryan MishraNo ratings yet
- Cot - DLP - Science Q3Document4 pagesCot - DLP - Science Q3Nymfreda LequipNo ratings yet
- Grade 9 1st Term 2023 2024 W. 2Document2 pagesGrade 9 1st Term 2023 2024 W. 2Hazem TamerNo ratings yet
- User Manual For Remote Midea Mission II Air ConditionersDocument8 pagesUser Manual For Remote Midea Mission II Air Conditionerscostica_dinaNo ratings yet
- Allplastics - Perspex - Technical DatasheetDocument40 pagesAllplastics - Perspex - Technical DatasheetdscvsddvfvNo ratings yet
- Product Specifications Product Specifications: HWXXX HWXXX - 6516DS 6516DS - VTM VTMDocument2 pagesProduct Specifications Product Specifications: HWXXX HWXXX - 6516DS 6516DS - VTM VTMcesarbayonaNo ratings yet
- The S - Block ElementsDocument1 pageThe S - Block ElementsRunjhunNo ratings yet
- Pulse Measurement: Learning From The BasicsDocument14 pagesPulse Measurement: Learning From The Basicsk ONo ratings yet
- Syllabus in Fluid MechanicsDocument9 pagesSyllabus in Fluid MechanicsAlan BalilaNo ratings yet
- Substation Grounding Grid Design Using ADocument23 pagesSubstation Grounding Grid Design Using ADavid LondoñoNo ratings yet
- ETP4830-A1 Embedded Power User ManualDocument90 pagesETP4830-A1 Embedded Power User ManualBruno SilveiraNo ratings yet
- by Nvs Teacher-States of MatterDocument29 pagesby Nvs Teacher-States of MatterAshlyNo ratings yet
- ADP 2 Lab ManualDocument102 pagesADP 2 Lab ManualKishoremcNo ratings yet
- Five-Phase Inverters With Synchronized PWMDocument7 pagesFive-Phase Inverters With Synchronized PWMBook4AllNo ratings yet
- Tabla de Torque de Diametros Grandes Asme B16 47 Metallic GasketsDocument4 pagesTabla de Torque de Diametros Grandes Asme B16 47 Metallic GasketsQuiroa, Antonio JNo ratings yet
- 3 & 4 Inch Borewell Submersible Installation ProcedureDocument7 pages3 & 4 Inch Borewell Submersible Installation ProcedureRaviNo ratings yet
- Folheto TBS Insulated Lightning Protection 9131887 09-2017 ENDocument44 pagesFolheto TBS Insulated Lightning Protection 9131887 09-2017 ENLuis PintoNo ratings yet
- 9) Expt No - 9 (Halleffect)Document16 pages9) Expt No - 9 (Halleffect)Pollack Prittam ChoudhuryNo ratings yet
- Terrameter-VES Rev5b CompressedDocument2 pagesTerrameter-VES Rev5b CompressedO6U Pharmacy RecordingsNo ratings yet
- Z Transform Pairs and PropertiesDocument2 pagesZ Transform Pairs and PropertiesAicha CherNo ratings yet
- Physico-Chemical Characteristics of Some Lesotho'sDocument7 pagesPhysico-Chemical Characteristics of Some Lesotho'sLeidyNo ratings yet
- Heat Science Class 7 Revision Worksheet: (A) (B) (C) (D) (A) (B) (C) (D) (A) (B) (C) (D)Document3 pagesHeat Science Class 7 Revision Worksheet: (A) (B) (C) (D) (A) (B) (C) (D) (A) (B) (C) (D)Masked GamerNo ratings yet
- Arizona Vortex Kit: User ManualDocument32 pagesArizona Vortex Kit: User ManualTraescoNo ratings yet
- PG M.sc. Chemistry 344 21 Inorganic Chemistry-II MSC ChemistryDocument394 pagesPG M.sc. Chemistry 344 21 Inorganic Chemistry-II MSC ChemistryinuperuvaikalaNo ratings yet