Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Mitochondria: Mitochondrion
Uploaded by
Alexander0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
23 views5 pagesOriginal Title
Mitochondria
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
23 views5 pagesMitochondria: Mitochondrion
Uploaded by
AlexanderCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 5
Mitochondria
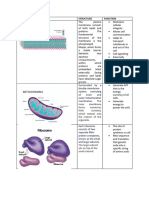
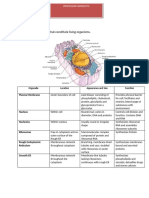
Structure
Mitochondrion is the site of the
Krebs cycle & the electron
Mitochondria has rod-shaped or These cristae give the inner
filamentous organelles. membrane a large total surface
area.
Mitochondria have length from
Cristae in mitochondria from
1-2 µ m & width at 0.1-0.5 µm.
different types of cell. In general,
Each mitochondrion is surrounded mitochondria from active cells
by an envelope of 2 phospholipid have longer, more densely packed
membranes. cristae than mitochondria from
less active cells
Smooth outer membrane to
decrease the resistance during
moving and an inner membrane
which much folded inwards to form
cristae.
The two membranes have different compositions & properties.
■The outer membrane is relatively permeable to small molecules
■ The inner membrane is less permeable.
Inner membranal space
The inner membrane is studded The inner membranal space is the
with tiny spheres about 9 nm in site of the electron transport chain
The space between the 2 membranes of the envelope usually has a lower pH than the matrix of&the
diameter, which are attached to the contains the protein
mitochondrion as anecessary
result
inner membrane ofbythe
stalks for this.
protons that are released into the intermembrane space by the activity of the electron transport chain.
The spheres are the enzyme The intermembrane space is the
ATPsynthase. site for the linked reaction
Matrix
The matrix of the mitochondrion Matrix contains small (70 S )
is the site of the Krebs cycle. ribosomes & several identical copies
of looped
Matrix contains theDNA
mitochondrial .
enzymes
needed for the cycle.
ATP
ATP is formed in the matrix by
the activity of ATPsynthase on
The energy for the production of ATP comes from the proton gradient
between the intermembrane space & the matrix.
The ATP can be used for all the energy-requiring reactions of the cell,
both inside & outside the mitochondria
ATP→ ADP+ P+energy
What is ATP?
ATP is a source of energy. When ATP hydrolyzed by ATPase, ATP gives out one
inorganic phosphate group to release energy.
The energy released is not due to the broken of phosphate bond but to changes in
chemical potential energy created by breaking the bond.
What are the differences between mitochondria and chloroplast?
Features Mitochondria Chloroplast
Liquid inside the organelle Matrix Stroma
Inner membrane Cristae, folded Smooth
Function Cellular respiration Photosynthesis
Available In plant cells and animal cells In plant cell only
Products CO2 & H2O O2 & glucose
Granules Present as granules Present as starch granules
Membrane Cristae Stacks of thylakoid
Site of reaction Photosynthesis & photorespiration Oxidative phosphorylation, beta
oxidation, photorespiration, etc.
Why ATP is a universal energy currency?
■ ATP is small & soluble, so it can easily transport from one cell to another.
■ ATP is stable since it only release energy when being hydrolyzed by the enzyme ATPase.
■ ATP can easily break down to give energy
■ Act as a short-term energy storing
■ The build-up & breakdown of ATP is a reversible reaction. So ATP has high rate of turnover
Why is energy needed?
Energy is required for activities in cells to happen.
Type of work Examples
Transporting substances ■ Active transport using Na+-K+ in cell
across the membrane membrane
■ Exocytosis of digested bacteria from
white blood cells
Anabolic reaction- ■ Synthesis of DNA from nucleotides
synthesize of complex ■ Synthesis of proteins from amino
substances from their acids
monomers
Movement ■ Cellular movement of chromosomes
via the spindles
■ Mechanical contraction of muscles
Maintaining body ■ Only occurs in mammals & birds-
temperature-Homeostasis they use thermal heat to keep them
warm
You might also like
- Gamma Ray Spectroscopy ExperimentDocument15 pagesGamma Ray Spectroscopy ExperimentLizelleNiit100% (1)
- Chapter 1 - Quiz 2 Form A: A. B. C. D. E. F. G. H. I. J. K. L. M. N. O. P. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8Document2 pagesChapter 1 - Quiz 2 Form A: A. B. C. D. E. F. G. H. I. J. K. L. M. N. O. P. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8Olalekan Oyekunle0% (1)
- Assignment 1 (Total Marks: 70) EEE 323: Power System IIDocument2 pagesAssignment 1 (Total Marks: 70) EEE 323: Power System IIShahriar SauravNo ratings yet
- Mitochondria and Chloroplasts: Structure and Function - A ReviewDocument18 pagesMitochondria and Chloroplasts: Structure and Function - A ReviewLloyd RebusiNo ratings yet
- Structure and Function of MitochondriaDocument7 pagesStructure and Function of MitochondriaHariniNo ratings yet
- Mitochondria, Aerobic Respiration and Energy GenerationDocument32 pagesMitochondria, Aerobic Respiration and Energy GenerationWai Kwong ChiuNo ratings yet
- By, Devi Priya Sugathan Msc. Biochemistry and Molecular BiologyDocument30 pagesBy, Devi Priya Sugathan Msc. Biochemistry and Molecular BiologysekharurlaNo ratings yet
- Mitochondria and chloroplast functionsDocument13 pagesMitochondria and chloroplast functionsEljenColanggoNo ratings yet
- IB Biology Study NotesDocument134 pagesIB Biology Study NotesManav Parikh100% (2)
- BIO Reviewer - All Abt CellsDocument5 pagesBIO Reviewer - All Abt CellsLeilah Angelique KunkelNo ratings yet
- Mitochondria: Structure and FunctionDocument6 pagesMitochondria: Structure and FunctionHariniNo ratings yet
- Cells 3 PPT 2022 PDFDocument25 pagesCells 3 PPT 2022 PDFNinjaTylerFortniteBlevins 2.0No ratings yet
- Chapter 9 PDFDocument44 pagesChapter 9 PDFFiona SimeonNo ratings yet
- Presentation-The Nature of Life-Stage 2Document33 pagesPresentation-The Nature of Life-Stage 2Manuel CastroNo ratings yet
- MitochondriaDocument16 pagesMitochondriaJassien Moring FlorentinoNo ratings yet
- Evolution and Structure of the Mitochondrion (38 charactersDocument1 pageEvolution and Structure of the Mitochondrion (38 charactersSebastiancody PasuquinNo ratings yet
- 1.2 Ultrastructure of Cells: Define The Term Resolution. Distinguish The Resolution of Light and Electron MicroscopesDocument44 pages1.2 Ultrastructure of Cells: Define The Term Resolution. Distinguish The Resolution of Light and Electron MicroscopesBader Al-SaloumNo ratings yet
- The Parts of The MitochondrionDocument14 pagesThe Parts of The MitochondrionPatrick Rómulo CabilingNo ratings yet
- Mitokondria 1Document40 pagesMitokondria 1Nilam CahyaNo ratings yet
- Mitochondria, Endoplasmic Reticulum, RibosomesDocument39 pagesMitochondria, Endoplasmic Reticulum, Ribosomesanos2002No ratings yet
- 1.2 Ultrastructure of Cells: ProkaryotesDocument8 pages1.2 Ultrastructure of Cells: Prokaryotesdavid tsaiNo ratings yet
- Mitochondrion: (Structure and Function)Document28 pagesMitochondrion: (Structure and Function)jovelyn dahangNo ratings yet
- AS Biology Revision Pack UNIT 2Document16 pagesAS Biology Revision Pack UNIT 2George Noorland100% (1)
- mtDNA encodes proteins for oxidative phosphorylationDocument10 pagesmtDNA encodes proteins for oxidative phosphorylationmelinda garpidaNo ratings yet
- Mitochondria and chloroplasts convert energy for cellsDocument3 pagesMitochondria and chloroplasts convert energy for cellsA CNo ratings yet
- Assessment 1: What Makes ATP Essential To The Organelles and The Cell Itself? Pwede Ba Ma Low Batt Ang ATP? Write Your Answers HereDocument4 pagesAssessment 1: What Makes ATP Essential To The Organelles and The Cell Itself? Pwede Ba Ma Low Batt Ang ATP? Write Your Answers HereAnnie Laiza BacayNo ratings yet
- 02cytology Lecture - Oct2016Document29 pages02cytology Lecture - Oct2016USA EMAILNo ratings yet
- The Nucleus: Structure and FunctionsDocument11 pagesThe Nucleus: Structure and FunctionsRadon WilsonNo ratings yet
- Ultra Structure of An Animal CellDocument16 pagesUltra Structure of An Animal CellArham AdnanNo ratings yet
- MBoC NLSDocument11 pagesMBoC NLSaudiopiazza09No ratings yet
- BIO104E - Laboratory Activity (The Cell)Document5 pagesBIO104E - Laboratory Activity (The Cell)Stephen AzaresNo ratings yet
- Cell Organelle and Parts Review Table - Chapter 6 Organelle/Cell Function Structure Plant/Animal/Proka Ryote?Document3 pagesCell Organelle and Parts Review Table - Chapter 6 Organelle/Cell Function Structure Plant/Animal/Proka Ryote?Lehman042No ratings yet
- A Tour of The CellDocument86 pagesA Tour of The CellRawanNo ratings yet
- BiologyDocument3 pagesBiologyCarlo Jake CarballoNo ratings yet
- The Microstructure of CellsDocument65 pagesThe Microstructure of CellsRufaro SadindiNo ratings yet
- MicroDocument5 pagesMicrotahashahzad9901No ratings yet
- Eukaryotic Cell Organelles and Their FunctionsDocument1 pageEukaryotic Cell Organelles and Their FunctionsShein GonzalesNo ratings yet
- 2 Ultra Structure of CellsDocument49 pages2 Ultra Structure of CellsYousef WardatNo ratings yet
- Answers To Saqs: Cambridge International As Level BiologyDocument2 pagesAnswers To Saqs: Cambridge International As Level BiologyTazeen FatimaNo ratings yet
- 02 - The CellDocument91 pages02 - The CellDASHNo ratings yet
- Clinical Hematology Cell Organelles and FunctionsDocument10 pagesClinical Hematology Cell Organelles and FunctionsEmmanuel Tristan OlarteNo ratings yet
- L4 the+Endomembrane+SystemDocument21 pagesL4 the+Endomembrane+Systembmnyandu2003No ratings yet
- Topic 2 CellsDocument1 pageTopic 2 CellsKandy Anne Castillo AbuanNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3Document153 pagesLecture 3Miya GordNo ratings yet
- Semi Autonomus Nature of Mitochondria 1st YearDocument9 pagesSemi Autonomus Nature of Mitochondria 1st YearTalha ArshadNo ratings yet
- Mitochondria and Chloroplasts Energy Synthesis of ATP Extracellular ATPDocument4 pagesMitochondria and Chloroplasts Energy Synthesis of ATP Extracellular ATPGiancarlo CasabarNo ratings yet
- Cell organelles and their functionsDocument1 pageCell organelles and their functionsNazimNo ratings yet
- MitochondriaDocument32 pagesMitochondriaDayana PrasanthNo ratings yet
- Choloroplast and ribosomeDocument34 pagesCholoroplast and ribosomeAAKASH JANGIDNo ratings yet
- Van Deventer Et Al - 2021Document11 pagesVan Deventer Et Al - 2021SusanaNo ratings yet
- Eukaryotic Cells: Chapter 7-2: Cell StructureDocument10 pagesEukaryotic Cells: Chapter 7-2: Cell Structurejmunozbio@yahoo.comNo ratings yet
- MITOCHONDRIADocument3 pagesMITOCHONDRIACris PachecoNo ratings yet
- The Cell: Structure and FunctionDocument36 pagesThe Cell: Structure and FunctionYla Mae Buo AcejoNo ratings yet
- Inti Sel Dan Ribosom - Bagus PriambodoDocument61 pagesInti Sel Dan Ribosom - Bagus PriambodoAHMAD IQBALNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9, Biols300Document31 pagesChapter 9, Biols300mariamNo ratings yet
- k2. MItochondria - Muzar Z-Des 2016Document29 pagesk2. MItochondria - Muzar Z-Des 2016Khemal MubaraqNo ratings yet
- (Organelles & Cellular Structures) H1 Bio NotesDocument11 pages(Organelles & Cellular Structures) H1 Bio Notesblah blehNo ratings yet
- Topic 1. Cells and Cellular ProcessDocument89 pagesTopic 1. Cells and Cellular ProcessNics PedrezuelaNo ratings yet
- Ribosome Ribosome: Fundamental Medical Science 1 Cell Structure and FunctionDocument20 pagesRibosome Ribosome: Fundamental Medical Science 1 Cell Structure and FunctionezebelluciNo ratings yet
- Weel 4 SurveyDocument29 pagesWeel 4 SurveyAaron MostNo ratings yet
- OCR A Level Biology Revision on Cell Structure and MembraneDocument15 pagesOCR A Level Biology Revision on Cell Structure and MembraneRawdatul JannahNo ratings yet
- MitochondriaDocument14 pagesMitochondriaPhoebe KimNo ratings yet
- Cell Motility: From Molecules to OrganismsFrom EverandCell Motility: From Molecules to OrganismsAnne RidleyNo ratings yet
- Respiratory substrates: Glucose, lipids, amino acids and their energy valuesDocument2 pagesRespiratory substrates: Glucose, lipids, amino acids and their energy valuesAlexanderNo ratings yet
- Respiration ExperimentDocument5 pagesRespiration ExperimentAlexanderNo ratings yet
- Aerobic RespirationDocument10 pagesAerobic RespirationAlexanderNo ratings yet
- Anerobic Respiration: Anaerobic Energy Density CalorieDocument5 pagesAnerobic Respiration: Anaerobic Energy Density CalorieAlexanderNo ratings yet
- The Sound of MusicDocument6 pagesThe Sound of MusicRajdeep MukherjeeNo ratings yet
- TR019999012181 enDocument37 pagesTR019999012181 enAliTronic1972No ratings yet
- Facts on Timber Engineering and StructuresDocument73 pagesFacts on Timber Engineering and StructuresNaresworo NugrohoNo ratings yet
- Nominal Pipe Size, Nominal Diameter & Outside Diameter For PipesDocument1 pageNominal Pipe Size, Nominal Diameter & Outside Diameter For PipesmdnorNo ratings yet
- Intel Processors PDFDocument33 pagesIntel Processors PDFbiplab royNo ratings yet
- NCE - Lesson 61 (A)Document8 pagesNCE - Lesson 61 (A)Zahir Pacasum-OmarNo ratings yet
- Unit 1.Pptx Autosaved 5bf659481837fDocument39 pagesUnit 1.Pptx Autosaved 5bf659481837fBernadith Manaday BabaloNo ratings yet
- Sunningdale School Notes Summer 2022Document12 pagesSunningdale School Notes Summer 2022sunningdaleschoolNo ratings yet
- Wiring Diagrams Model Yk (Style G) Liquid Chillers Optiview Control Center With SSS, LV VSD W/ Modbus, & MV VSDDocument30 pagesWiring Diagrams Model Yk (Style G) Liquid Chillers Optiview Control Center With SSS, LV VSD W/ Modbus, & MV VSDAbdulSattarNo ratings yet
- Analyzing the Effects of Changing the Values of a, b, and c in the Equation of a Quadratic Function on Its GraphDocument13 pagesAnalyzing the Effects of Changing the Values of a, b, and c in the Equation of a Quadratic Function on Its GraphRamil NacarioNo ratings yet
- Manual stack emission monitoring standardDocument29 pagesManual stack emission monitoring standardsantisal11No ratings yet
- Off Road and Military Vehicles Off Road Vehicles Agrale Marruaam200 1Document2 pagesOff Road and Military Vehicles Off Road Vehicles Agrale Marruaam200 1Victor SilvaNo ratings yet
- Bitumen Water ProofingDocument23 pagesBitumen Water ProofingAkshthagowda848_1952No ratings yet
- Modul 1 - Pengantar Remote SensingDocument60 pagesModul 1 - Pengantar Remote SensingNgurah Ade KalyanaNo ratings yet
- Phylum Chordata TransesDocument2 pagesPhylum Chordata TransesMaribel Ramos InterinoNo ratings yet
- Feed Water Heater ModellingDocument64 pagesFeed Water Heater ModellingSIVA KAVYANo ratings yet
- Vdocuments - MX - Control Systems by Nagrath Gopal Solution Manual PDFDocument128 pagesVdocuments - MX - Control Systems by Nagrath Gopal Solution Manual PDFPriyadarshini SahooNo ratings yet
- Development Length ACI 318-14 v2.0Document5 pagesDevelopment Length ACI 318-14 v2.0Raymund Dale P. BallenasNo ratings yet
- 456/1 Mathematics Paper 1 June /july 2012 HoursDocument4 pages456/1 Mathematics Paper 1 June /july 2012 HoursBaguma MichaelNo ratings yet
- 2015 - 3 Lennar Concord Proposal PDFDocument148 pages2015 - 3 Lennar Concord Proposal PDFEric LiptonNo ratings yet
- Quantum Free Electron Theory: Sommerfeld's ModelDocument8 pagesQuantum Free Electron Theory: Sommerfeld's ModelNeelam KapoorNo ratings yet
- Model AnswerDocument27 pagesModel AnswerdishaNo ratings yet
- Life Saving Appliance: Personal Life-Saving Appliances Lifeboats & Rescue Boats LiferaftsDocument18 pagesLife Saving Appliance: Personal Life-Saving Appliances Lifeboats & Rescue Boats Liferaftsdafa dzaky100% (1)
- Kti Semuanya-DikonversiDocument59 pagesKti Semuanya-DikonversigacikNo ratings yet
- Strength of CSG and TBGDocument10 pagesStrength of CSG and TBGTiffany DacinoNo ratings yet
- VTBS 20-3DDocument1 pageVTBS 20-3Dwong keen faivNo ratings yet
- Syngo - Via: HW Data SheetDocument4 pagesSyngo - Via: HW Data SheetCeoĐứcTrườngNo ratings yet