Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Micro
Uploaded by
tahashahzad99010 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views5 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views5 pagesMicro
Uploaded by
tahashahzad9901Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 5
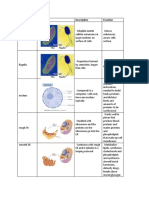
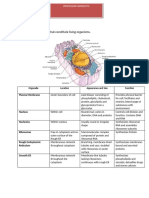
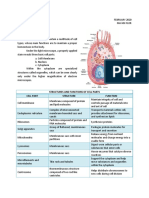
CELL ORGANELLE STRUCTURE FUNCTION
Plasma membrane The plasma Maintains
membrane consists cellular
of both lipids and integrity
proteins. The Allows cell
fundamental communication
structure of the Helps to
membrane is the transport
phospholipid substances in
bilayer, which forms and out of the
a stable barrier cell
between two Cell signalling
aqueous Externally
compartments, facing proteins
within which act as receptors
proteins are
embedded. Most
externally facing
proteins and lipids
have attached sugar
groups.
Surrounded by a Generate ATP
double-membrane that is the
system, consisting energy
of inner and currency of all
outer mitochondrial cells
membranes. The Generate
inner membrane energy to
forms numerous power the cells
folds (cristae),
which extend into
the interior of the
organelle.
Each ribosome The site of
consists of two protein
separate RNA- synthesis in cell
protein complexes, RNA sequence
known as the small and translates
and large subunits. that genetic
The large subunit code into a
sits on top of the specific string
small subunit. of amino acids
Rough Endoplasmic reticulum A series of Involved
convoluted, associated with
flattened like many roles in
membrane sheets protein
(called cisternae) synthesis
that arise near the Post
nucleus and extend translational
across the modifications
cytoplasm. Sections Folding and
of the cisternae sorting
contain ribosomes,
held together by
microtubules of the
cytoskeleton.
Smooth endoplasmic reticulum Meshwork of fine Synthesis of
disklike tubular lipids, steroids,
membrane vesicles, and
part of a continuous carbohydrates
membrane Metabolism of
organelle within the exogenous
cytoplasm of substances,
eukaryotic cells such as drugs
or toxins
Lysosomes are Functions as
acidic membrane- the digestive
bound organelles system of the
found within cells, cell
usually around 1 Degrades the
micrometre in material taken
length. Lysosomes up from outside
contain numerous Digest obsolete
hydrolytic enzymes components of
which catalyse the cell itself
hydrolysis reactions.
Membranous sacs Detoxify a
of catalase and number of toxic
oxidase enzyme substances
Plays important
role in
metabolism
Helps in
signalling
Golgi Body A stack of flattened A factory in
tubules and vesicles which proteins
close to the nucleus received from
the ER are
further
processed and
sorted for
transport to
their eventual
destinations
Microtubules Dimers of α- and β- Determine cell
tubulin polymerize shape
to form Determine
microtubules, which variety of cell
are composed of 13 movements,
protofilaments including cell
assembled around a locomotion
hollow core. Intercellular
transport of
organelles
Separation of
chromosome
during mitosis
Centriole Most centrioles are Play a role in
made up of nine organising
circularly arranged microtubules
triplet Help determine
microtubules. A the locations of
triplet microtubule nucleus and
has a complete other
microtubule (the A- organelles in
tubule) onto which the cell
two additional
partial microtubules
are assembled (the
B- and the C-
tubules,
respectively).
Cilia Membrane- Help the cell
bounded, centriole- move around in
derived projections cellular fluids
from the cell Helps fluid
surface that contain move past the
a microtubule cell
cytoskeleton, the
ciliary axoneme,
surrounded by a
ciliary membrane.
Flagella These Help an
supramolecular organism in
structures extend movement
from the cytoplasm Act as sensory
to the cell exterior organs to
and are composed detect
of three major temperature
structural and pH changes
elements, the basal Also used as
body, the hook and secretory
the filament organelle
Microvilli Finger-like Increase
membrane surface area to
protrusions, absorb more
supported by the nutrients
actin cytoskeleton
Nucleolus Dense spherical Produce and
bodies, composed assemble the
of ribosomal RNA cell’s ribosomes
and proteins rRNA and
proteins are
transcribed
here
146 base pairs of To package DNA
DNA, wound in two into a unit
turns around a disk capable of
like complex of 8 fitting within the
proteins that are tight space of a
called histones- a nucleus
nucleosome
You might also like
- Cell Organelles Structure & FunctionDocument4 pagesCell Organelles Structure & FunctionDaniel ChinNo ratings yet
- Cell STRUCTURE and Function Worksheet. HomeworkDocument5 pagesCell STRUCTURE and Function Worksheet. HomeworkMichael WrightNo ratings yet
- Cell Organelles ExplainedDocument4 pagesCell Organelles ExplainedVeronica AlvaradoNo ratings yet
- Cell NotesDocument7 pagesCell NotesBrohi NadeemNo ratings yet
- PHINMA UNIVERSITY OF PANGASINAN COLLEGE OF ALLIED HEALTH SCIENCES BIOCHEMISTRY LAB REPORTDocument4 pagesPHINMA UNIVERSITY OF PANGASINAN COLLEGE OF ALLIED HEALTH SCIENCES BIOCHEMISTRY LAB REPORTCindy Macaranas SorianoNo ratings yet
- Quiz Fms 1 Questions and Answers 1. Describe The Organelle of The Cell (Cytoplasm and Its Components & The Functions of Each Organelles)Document12 pagesQuiz Fms 1 Questions and Answers 1. Describe The Organelle of The Cell (Cytoplasm and Its Components & The Functions of Each Organelles)deaNo ratings yet
- Basic Building Blocks of Life Smallest Living Unit of An OrganismDocument2 pagesBasic Building Blocks of Life Smallest Living Unit of An OrganismkikomagsaysayNo ratings yet
- Cell StructureDocument6 pagesCell StructureZen Kenneth A. PanaliganNo ratings yet
- Organelle ChartDocument3 pagesOrganelle Chartapi-589105148No ratings yet
- Cells Memorization SheatDocument2 pagesCells Memorization SheatNiomi ButtermilkNo ratings yet
- Cell OrganellesDocument12 pagesCell OrganellesVeronica AlvaradoNo ratings yet
- Chap 5 FullDocument130 pagesChap 5 Fullgaelle tannous100% (1)
- The Cell: Endomembrane System, Mitochondria, Chloroplasts, Cytoskeleton and Extracellular ComponentsDocument65 pagesThe Cell: Endomembrane System, Mitochondria, Chloroplasts, Cytoskeleton and Extracellular ComponentsMeljean Kalaw CastilloNo ratings yet
- Cell Organelles - Structure and FunctionDocument6 pagesCell Organelles - Structure and FunctionKaryl Marie Rodas JaminNo ratings yet
- Bio Notes (ZNotes) MYPDocument65 pagesBio Notes (ZNotes) MYPkimaaya vermaNo ratings yet
- AS Biology Revision Pack UNIT 2Document16 pagesAS Biology Revision Pack UNIT 2George Noorland100% (1)
- Eukaryotic Cells: Chapter 7-2: Cell StructureDocument10 pagesEukaryotic Cells: Chapter 7-2: Cell Structurejmunozbio@yahoo.comNo ratings yet
- CellDocument36 pagesCellwnslthmangulad05No ratings yet
- Clinical Hematology Cell Organelles and FunctionsDocument10 pagesClinical Hematology Cell Organelles and FunctionsEmmanuel Tristan OlarteNo ratings yet
- Organelle Present/Absent Description FunctionDocument5 pagesOrganelle Present/Absent Description FunctionTania BacsinNo ratings yet
- Plant Vacuoles Sap Water OsmosisDocument3 pagesPlant Vacuoles Sap Water OsmosisChrister MalonzoNo ratings yet
- Comparison Between Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells Property Prokaryotic Cells Eukaryotic CellsDocument4 pagesComparison Between Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells Property Prokaryotic Cells Eukaryotic CellsKarl Leo Hee YeongNo ratings yet
- Organelle With Solution 2022-23Document1 pageOrganelle With Solution 2022-23LuLaMejorNo ratings yet
- Preliminary Biology NotesDocument36 pagesPreliminary Biology NotesSaad KashifNo ratings yet
- Eukaryotic Cell StructuresDocument3 pagesEukaryotic Cell Structurescathyzeng1120No ratings yet
- Cell Structure and FunctionDocument32 pagesCell Structure and Functionnaveedalikhoso365100% (1)
- Class 9 Cytoplasm To MitochondriaDocument2 pagesClass 9 Cytoplasm To Mitochondrianivya MariyamnobyNo ratings yet
- Parts of The Cell Worksheet - BiochemistryDocument3 pagesParts of The Cell Worksheet - BiochemistryAnonymous giver100% (1)
- Cell Organelle and Parts Review Table - Chapter 6 Organelle/Cell Function Structure Plant/Animal/Proka Ryote?Document3 pagesCell Organelle and Parts Review Table - Chapter 6 Organelle/Cell Function Structure Plant/Animal/Proka Ryote?Lehman042No ratings yet
- A Specialized Structure Occurring in Most Cells and Separated From The Rest of The Cell by A Double Layer, The Nuclear MembraneDocument3 pagesA Specialized Structure Occurring in Most Cells and Separated From The Rest of The Cell by A Double Layer, The Nuclear MembraneGian Carlo MadriagaNo ratings yet
- CellsDocument9 pagesCellsjasmineNo ratings yet
- F4 C2 NotesDocument15 pagesF4 C2 Notesmarisyayasmin050907No ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Cell Structures & Their Functions: Certain Molecules To Enter/exit The Cell)Document5 pagesChapter 3 Cell Structures & Their Functions: Certain Molecules To Enter/exit The Cell)Gellyace A.No ratings yet
- Anatomy MidwiferyDocument15 pagesAnatomy MidwiferyJohn Ross EsturcoNo ratings yet
- 1.2 Ultrastructure of Cells (Main)Document46 pages1.2 Ultrastructure of Cells (Main)MeryemNo ratings yet
- Chem 104D MidtermsDocument27 pagesChem 104D MidtermsCASTAÑEDA, Jameela AnneNo ratings yet
- PL4 Cell CompartmentsDocument11 pagesPL4 Cell CompartmentsJake GopitaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Cell Review AssignmentDocument8 pagesChapter 4 Cell Review Assignmentsarahmohammed801No ratings yet
- Parts of A Cell 1. NucleusDocument2 pagesParts of A Cell 1. NucleusVon Lester SanchezNo ratings yet
- Benjamin Watson - Summer PiXL Gateway Biology - Cells TRANSITIONDocument15 pagesBenjamin Watson - Summer PiXL Gateway Biology - Cells TRANSITIONboobooNo ratings yet
- Histo Lab Exercise #2Document6 pagesHisto Lab Exercise #2Gela ReyesNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure and Function Answered Review SP 08Document16 pagesCell Structure and Function Answered Review SP 08Yader Camilo Caicedo DelgadoNo ratings yet
- BIO104E-Laboratory Activity. (The Cell)Document5 pagesBIO104E-Laboratory Activity. (The Cell)Stephen AzaresNo ratings yet
- Bmed 105 Cells and Tissues (Notes)Document14 pagesBmed 105 Cells and Tissues (Notes)Jobelle MalihanNo ratings yet
- H2 Biology Notes On Cell Structure Cell Organelles PDFDocument5 pagesH2 Biology Notes On Cell Structure Cell Organelles PDFAnonymous 0iTAS7No ratings yet
- NOTES Unit 3 - The CellDocument7 pagesNOTES Unit 3 - The CellCarina LattoNo ratings yet
- General BiologyDocument14 pagesGeneral BiologyMason DeidriNo ratings yet
- Module 2 LectureDocument13 pagesModule 2 LectureJeal NochefrancaNo ratings yet
- Central Mindanao University Department of Biology: "The CellDocument6 pagesCentral Mindanao University Department of Biology: "The CellNEIL MARTINEZNo ratings yet
- OCR A Level Biology Revision on Cell Structure and MembraneDocument15 pagesOCR A Level Biology Revision on Cell Structure and MembraneRawdatul JannahNo ratings yet
- Structure and Functions of Cells: RibosomesDocument6 pagesStructure and Functions of Cells: RibosomesShakib al molik100% (1)
- Plant and Animal CellsDocument3 pagesPlant and Animal CellsCharisse Sheree PuentenegraNo ratings yet
- 3-Cells and TissuesDocument53 pages3-Cells and TissuesTwelve Forty-fourNo ratings yet
- Lesso N 2: Organe LlesDocument19 pagesLesso N 2: Organe LlesMicha E.No ratings yet
- Prokaryotic Cell Eukaryotic Cell: Botany Lecture Reviewer A. CellsDocument11 pagesProkaryotic Cell Eukaryotic Cell: Botany Lecture Reviewer A. CellsRosemarie OngNo ratings yet
- Histology AssignmentDocument6 pagesHistology AssignmentBryan LebasnonNo ratings yet
- Structural and Functional Manifestation of LifeDocument6 pagesStructural and Functional Manifestation of LifeKaila StefanieNo ratings yet
- Organelle ChartDocument4 pagesOrganelle ChartDetroit MetsNo ratings yet
- (Organelles & Cellular Structures) H1 Bio NotesDocument11 pages(Organelles & Cellular Structures) H1 Bio Notesblah blehNo ratings yet
- The Basics of Cell Life with Max Axiom, Super Scientist: 4D An Augmented Reading Science ExperienceFrom EverandThe Basics of Cell Life with Max Axiom, Super Scientist: 4D An Augmented Reading Science ExperienceNo ratings yet
- Biology 9 enDocument361 pagesBiology 9 enАсем БисембиеваNo ratings yet
- What Is Resting Membrane Potential?: Mechanism of An Action PotentialDocument5 pagesWhat Is Resting Membrane Potential?: Mechanism of An Action PotentialAli InamNo ratings yet
- Step by Step Anaesthesia in Dentistry Local and GeneralDocument208 pagesStep by Step Anaesthesia in Dentistry Local and Generaldrnadeemulla khanNo ratings yet
- IB Biology HL NotesDocument154 pagesIB Biology HL NotesBobby McFerrin100% (1)
- Cambridge International AS & A Level: Biology 9700/01Document18 pagesCambridge International AS & A Level: Biology 9700/01Raphael JosephNo ratings yet
- Nelson Biology Answers 1Document2 pagesNelson Biology Answers 1ritaNo ratings yet
- Biochem ABO IncompatibilityDocument62 pagesBiochem ABO IncompatibilityChi Samaniego100% (4)
- The Cell Grade 7Document15 pagesThe Cell Grade 7shrestha.aayas234No ratings yet
- General Biology 1 Module 2Document16 pagesGeneral Biology 1 Module 2Ennyliejor YusayNo ratings yet
- BIOLOGYFINALanswers (1stedition)Document61 pagesBIOLOGYFINALanswers (1stedition)Abhinav VermaNo ratings yet
- Strawberry DNA Extraction LabDocument5 pagesStrawberry DNA Extraction Labjackhume4No ratings yet
- Cell Unit of Life - 011321Document73 pagesCell Unit of Life - 011321abhishek KumarNo ratings yet
- Properties and Functions of Water BSB 111Document56 pagesProperties and Functions of Water BSB 111Manak ThakurNo ratings yet
- Module 9 - Weeks 1,2Document15 pagesModule 9 - Weeks 1,2Jomar CarabotNo ratings yet
- Cell Quiz: Eukaryotic Organelles & StructuresDocument7 pagesCell Quiz: Eukaryotic Organelles & StructuresChris GayleNo ratings yet
- Medical VirologyDocument136 pagesMedical VirologysoundharyaNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotes and EukaryotesDocument6 pagesProkaryotes and EukaryotesC Bala DiwakeshNo ratings yet
- Leafy sea dragons camouflage through evolutionDocument16 pagesLeafy sea dragons camouflage through evolutioncryhxNo ratings yet
- LECTURE 1: INTRO TO MICROBIOLOGYDocument12 pagesLECTURE 1: INTRO TO MICROBIOLOGYEinah EinahNo ratings yet
- A Cell Is Like Army CampDocument1 pageA Cell Is Like Army CampOli Memerit0% (1)
- Topic 4 Unit 1 Part2Document16 pagesTopic 4 Unit 1 Part2body fayezNo ratings yet
- IT Bio F4 Topical Test 3 (BL)Document8 pagesIT Bio F4 Topical Test 3 (BL)Ismaliza IshakNo ratings yet
- UIC Fall 2019 BIOS 222 SylDocument4 pagesUIC Fall 2019 BIOS 222 SylNicole WillNo ratings yet
- Mathematical Models in BiophysicsDocument49 pagesMathematical Models in Biophysicsonebyzerooutlook100% (1)
- Science 10 Textbook Unit ADocument132 pagesScience 10 Textbook Unit AessamNo ratings yet
- Life Science Test 1 2021 Grade 10. FinalDocument8 pagesLife Science Test 1 2021 Grade 10. Finaldeveloping habit and lifestyle of praise and worshNo ratings yet
- Biology Quiz: Cell Structure, Organ Systems, Evolution & MoreDocument32 pagesBiology Quiz: Cell Structure, Organ Systems, Evolution & MoreChrisshalyn Sy PinedaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology - The Unity of Form and Function 5th Ed - Saladin (McGraw-Hill, 2009) BBSDocument4 pagesAnatomy and Physiology - The Unity of Form and Function 5th Ed - Saladin (McGraw-Hill, 2009) BBSdixama9519No ratings yet
- CharlesCantorandPaulSchimmel BiophysicalChemistry PartI TheConformationofBiologicalMacromoleculesBiophysicalChemistry1980W.H.freeman Libgen - Li1Document408 pagesCharlesCantorandPaulSchimmel BiophysicalChemistry PartI TheConformationofBiologicalMacromoleculesBiophysicalChemistry1980W.H.freeman Libgen - Li1Riya guptaNo ratings yet
- STROMA, in Botany, Refers To The Colorless Fluid SurroundingDocument2 pagesSTROMA, in Botany, Refers To The Colorless Fluid SurroundingDanilo de MesaNo ratings yet