Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Eukaryotic Cell Structures
Uploaded by
cathyzeng11200 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views3 pagesThis document describes the structure and function of key organelles in eukaryotic cells. It lists the plasma membrane, cytoplasm, 80S ribosomes, nucleus, chromosomes, mitochondria, vacuoles, lysosomes, rough endoplasmic reticulum, smooth endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, and cytoskeleton. The plasma membrane controls what enters and exits the cell. The nucleus contains chromosomes and allows mRNA to enter the cytoplasm. Mitochondria produce ATP through aerobic respiration.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document describes the structure and function of key organelles in eukaryotic cells. It lists the plasma membrane, cytoplasm, 80S ribosomes, nucleus, chromosomes, mitochondria, vacuoles, lysosomes, rough endoplasmic reticulum, smooth endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, and cytoskeleton. The plasma membrane controls what enters and exits the cell. The nucleus contains chromosomes and allows mRNA to enter the cytoplasm. Mitochondria produce ATP through aerobic respiration.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views3 pagesEukaryotic Cell Structures
Uploaded by
cathyzeng1120This document describes the structure and function of key organelles in eukaryotic cells. It lists the plasma membrane, cytoplasm, 80S ribosomes, nucleus, chromosomes, mitochondria, vacuoles, lysosomes, rough endoplasmic reticulum, smooth endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, and cytoskeleton. The plasma membrane controls what enters and exits the cell. The nucleus contains chromosomes and allows mRNA to enter the cytoplasm. Mitochondria produce ATP through aerobic respiration.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
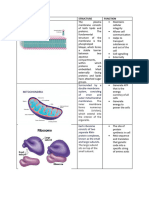
Eukaryotic Cell Structure
Structure Function Electron micrograph image
Plasma membrane The plasma membrane
controls what enters and
exits the cell. The plasma
membrane is composed of
phospholipids.
Cytoplasm Most of the metabolism that
occurs in the cell occurs in
the cytoplasm. The
cytoplasm is mostly
composed of water.
80S Ribosomes The 80S ribosomes are
responsible for protein
synthesis.
Nucleus Chromosomes associated
with histone proteins are
located in the nucleus. The
nucleus has a double
membrane with pores which
allow mRNA to enter the
cytoplasm
Chromosomes Chromosomes are
composed of DNA wrapped
around histone proteins.
The DNA is the genetic
material with information for
growth and development of
the cell.
Mitochondrion Aerobic respiration,
producing ATP.
Vacuoles Plants have large vacuoles
involved in storing nutrients.
Small vacuoles are found in
animal cells and are
involved in the removal of
waste.
Lysosome Lysosomes are specialised
vesicles, which contain
enzymes. They are involved
in the digestion of large
molecules.
Rough Endoplasmic The rough endoplasmic
Reticulum reticulum is a membrane
structure with ribosomes
attached. It is the site of
protein synthesis, and is
involved in transporting
proteins to the Golgi
Apparatus.
Smooth endoplasmic The smooth endplasmic
reticulum reticulum is a membrane
structure without ribisomes
attached. It is involved in
lipid synthesis, and
detoxification.
Golgi Apparatus The Golgi Apparatus
modifies and packages
proteins to be exported from
the cell.
Cytoskeleton The cytoskeleton is
composed of protein
microtubules, and is
involved in maintaining cell
shape, moving organelles,
and nuclear division (mitosis
and meiosis).
You might also like
- Cell Structure and Cell OrganisationDocument27 pagesCell Structure and Cell OrganisationAzmaniza AdnanNo ratings yet
- Dokumen - Tips - Cell Structure Functions Introduction Eucaryotic Cell StructureDocument31 pagesDokumen - Tips - Cell Structure Functions Introduction Eucaryotic Cell StructureJairra Jae LunaNo ratings yet
- Chem 104D MidtermsDocument27 pagesChem 104D MidtermsCASTAÑEDA, Jameela AnneNo ratings yet
- 2nd Lec Cell Structure and FunctionDocument15 pages2nd Lec Cell Structure and FunctionArslan AliNo ratings yet
- Cell WallDocument5 pagesCell WallGoal Digger Squad VlogNo ratings yet
- Chap 5 FullDocument130 pagesChap 5 Fullgaelle tannous100% (1)
- Eukaryotic Cells: Chapter 7-2: Cell StructureDocument10 pagesEukaryotic Cells: Chapter 7-2: Cell Structurejmunozbio@yahoo.comNo ratings yet
- UNIT 2 Notes PDFDocument88 pagesUNIT 2 Notes PDFAjNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure - Note GCCDocument12 pagesCell Structure - Note GCCInshaNo ratings yet
- Topic 2 NotesDocument53 pagesTopic 2 Notessuperhigh06No ratings yet
- Cell Organelle CardsDocument6 pagesCell Organelle CardsVienne MonroidNo ratings yet
- MicroDocument5 pagesMicrotahashahzad9901No ratings yet
- Chapter 1-Cell BiologyDocument43 pagesChapter 1-Cell Biologyapi-374357No ratings yet
- The Cell: Endomembrane System, Mitochondria, Chloroplasts, Cytoskeleton and Extracellular ComponentsDocument65 pagesThe Cell: Endomembrane System, Mitochondria, Chloroplasts, Cytoskeleton and Extracellular ComponentsMeljean Kalaw CastilloNo ratings yet
- 1.2 Ultrastructure of Cells (Main)Document46 pages1.2 Ultrastructure of Cells (Main)MeryemNo ratings yet
- Structural and Functional Manifestation of LifeDocument6 pagesStructural and Functional Manifestation of LifeKaila StefanieNo ratings yet
- Cell Organelles Structure & FunctionDocument4 pagesCell Organelles Structure & FunctionDaniel ChinNo ratings yet
- What Are Cell OrganellesDocument19 pagesWhat Are Cell OrganellesMaraon CharitaNo ratings yet
- Central Mindanao University Department of Biology: "The CellDocument6 pagesCentral Mindanao University Department of Biology: "The CellNEIL MARTINEZNo ratings yet
- Bio Chapter 2Document57 pagesBio Chapter 2Xue Yi LamNo ratings yet
- Upload It 1Document5 pagesUpload It 1John Rey Bandong100% (1)
- CELLFIEDocument4 pagesCELLFIEako at ang exoNo ratings yet
- Lesso N 2: Organe LlesDocument19 pagesLesso N 2: Organe LlesMicha E.No ratings yet
- Cell Organelles - Structure and FunctionDocument6 pagesCell Organelles - Structure and FunctionKaryl Marie Rodas JaminNo ratings yet
- 2 Biology 1-2-07 Pro Vs Eu CellsDocument11 pages2 Biology 1-2-07 Pro Vs Eu CellsMartin ClydeNo ratings yet
- Functional Anatomy of Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsDocument70 pagesFunctional Anatomy of Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsTrixie De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure and FunctionDocument32 pagesCell Structure and Functionnaveedalikhoso365100% (1)
- Cell Structure and FunctionsDocument4 pagesCell Structure and FunctionsDanilo JR. BuaquiñaNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotic & Eukaryotic CellDocument49 pagesProkaryotic & Eukaryotic CellArthe RajarajanNo ratings yet
- HDTD-B-4 - Cell OrganellesDocument43 pagesHDTD-B-4 - Cell OrganellesMariam Qais100% (1)
- Introduction CellDocument48 pagesIntroduction CellabdNo ratings yet
- Cell Structures & Organelles FunctionsDocument9 pagesCell Structures & Organelles Functionsnasimzand78100% (1)
- CellDocument36 pagesCellwnslthmangulad05No ratings yet
- The Cell and Cell Organelles 1Document4 pagesThe Cell and Cell Organelles 1Wennie Fe MartinezNo ratings yet
- CellDocument17 pagesCellAaliyah Quesha LadjamatliNo ratings yet
- LESSONS in BIOCHEMDocument39 pagesLESSONS in BIOCHEMMikhael Jay IglesiasNo ratings yet
- MICROBIOLOGYDocument5 pagesMICROBIOLOGYCia RraNo ratings yet
- Lecture 9. Cell and Cell OrganellesDocument35 pagesLecture 9. Cell and Cell OrganellesSaksham JainNo ratings yet
- Animal Cell: Prokaryotes Are Unicellular Organisms That Lack Organelles or Other InternalDocument6 pagesAnimal Cell: Prokaryotes Are Unicellular Organisms That Lack Organelles or Other InternalJohnson Macayan FernándezNo ratings yet
- Plant and Animal CellsDocument3 pagesPlant and Animal CellsCharisse Sheree PuentenegraNo ratings yet
- Organelle and CellsDocument9 pagesOrganelle and CellsAnjehyn ElleNo ratings yet
- The Basic Unit of LifeDocument18 pagesThe Basic Unit of LifeKenneth Myro GarciaNo ratings yet
- General BiologyDocument14 pagesGeneral BiologyMason DeidriNo ratings yet
- Parts of A Cell 1. NucleusDocument2 pagesParts of A Cell 1. NucleusVon Lester SanchezNo ratings yet
- PL4 Cell CompartmentsDocument11 pagesPL4 Cell CompartmentsJake GopitaNo ratings yet
- Cells, Organelles, Microscopy TechniquesDocument34 pagesCells, Organelles, Microscopy TechniquesJeffrey100% (1)
- Cell STRUCTURE and Function Worksheet. HomeworkDocument5 pagesCell STRUCTURE and Function Worksheet. HomeworkMichael WrightNo ratings yet
- Basic Building Blocks of Life Smallest Living Unit of An OrganismDocument2 pagesBasic Building Blocks of Life Smallest Living Unit of An OrganismkikomagsaysayNo ratings yet
- M4 Check-In Activity 1 - VenusDocument2 pagesM4 Check-In Activity 1 - VenusGrezha Mari VenusNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in BiologyDocument16 pagesReviewer in BiologyAngel CastilloNo ratings yet
- Cellular Biology: Cell Structure and TaxonomyDocument7 pagesCellular Biology: Cell Structure and TaxonomyFelyn Roseann AretaNo ratings yet
- DNA, The Genetic MaterialDocument6 pagesDNA, The Genetic MaterialMarinelle TumanguilNo ratings yet
- Introduction and Pioneers in Microbiology and ParasitologyDocument4 pagesIntroduction and Pioneers in Microbiology and ParasitologyJasmin Pearl AndayaNo ratings yet
- BIO 1 The CellDocument54 pagesBIO 1 The CellElyNo ratings yet
- Premidterms NotesDocument4 pagesPremidterms NotesRenee Andrei Concepcion MozarNo ratings yet
- Biology Prelim NotesDocument47 pagesBiology Prelim NotesAmanie SidawiNo ratings yet
- BiochemistryDocument4 pagesBiochemistryAaliyah Ashley CerboNo ratings yet
- Cell Organelles - Lec. 1Document27 pagesCell Organelles - Lec. 1Hamza KaisNo ratings yet
- 2 Biology 1 - 2 - 07 Pro Vs Eu CellsDocument37 pages2 Biology 1 - 2 - 07 Pro Vs Eu CellsJuan Jaylou AnteNo ratings yet
- The Basics of Cell Life with Max Axiom, Super Scientist: 4D An Augmented Reading Science ExperienceFrom EverandThe Basics of Cell Life with Max Axiom, Super Scientist: 4D An Augmented Reading Science ExperienceNo ratings yet
- Topographic Surveys: Engr. Randy G. PolicarpioDocument34 pagesTopographic Surveys: Engr. Randy G. PolicarpioBj Castro BautistaNo ratings yet
- Running Head: CASE ANALYSIS #22 1Document11 pagesRunning Head: CASE ANALYSIS #22 1Vikram KumarNo ratings yet
- TFT What Students Need To Know GED RLA Extended Response PPT Slides 1Document22 pagesTFT What Students Need To Know GED RLA Extended Response PPT Slides 1AddieBeam100% (1)
- Emma Hudgins CV 2023Document10 pagesEmma Hudgins CV 2023Emma HudginsNo ratings yet
- JurnalDocument17 pagesJurnalBlank - CodeNo ratings yet
- LP Mapeh 7Document16 pagesLP Mapeh 7BIT INTERNATIONAL COLLEGE TALIBON100% (1)
- Memories: By: Andrés Felipe Cárdenas VargasDocument22 pagesMemories: By: Andrés Felipe Cárdenas VargasAndres Felipe Cárdenas VargasNo ratings yet
- Warragamba Dam and Township MapDocument2 pagesWarragamba Dam and Township MapRaveeNo ratings yet
- Grades 11 Daily Lesson LogDocument6 pagesGrades 11 Daily Lesson LogRaquel disomimbaNo ratings yet
- Teen Parenting Brochure AssignmentDocument1 pageTeen Parenting Brochure AssignmentJayricDepalobosNo ratings yet
- Rosaldes Research Paper - EditedversionDocument84 pagesRosaldes Research Paper - EditedversionguerrasashamearlNo ratings yet
- Prodrammes To Achieve Universalisation of Education-SsaDocument16 pagesProdrammes To Achieve Universalisation of Education-SsaSREELEKSHMI AnilNo ratings yet
- Toys HomeworkDocument7 pagesToys Homeworkbdypujtif100% (1)
- Cut-Over Template - SampleDocument16 pagesCut-Over Template - Sampleizkx50% (2)
- Nursing Care Plan: Provide Rest Periods To Promote Relief, Sleep, and RelaxationDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan: Provide Rest Periods To Promote Relief, Sleep, and RelaxationGrace MellaineNo ratings yet
- Busm3255 Strategy Unit 01 Course Notes 2017Document10 pagesBusm3255 Strategy Unit 01 Course Notes 2017taghavi1347No ratings yet
- Atria Salsabila Nur 1847041002 Paper EspDocument15 pagesAtria Salsabila Nur 1847041002 Paper EspatriaNo ratings yet
- PROPOSAL On Online ExaminationDocument18 pagesPROPOSAL On Online ExaminationHardik Gupta100% (2)
- New Microsoft Office Word DocumentDocument14 pagesNew Microsoft Office Word DocumentSourav Sharma0% (1)
- INSDSG Project Management For Instructional DesignersDocument16 pagesINSDSG Project Management For Instructional DesignersApostolos KoutropoulosNo ratings yet
- Research Methods - A Framework For Evidence-Based Clinical Practice-Wendy L. Hurley, Craig R.Document450 pagesResearch Methods - A Framework For Evidence-Based Clinical Practice-Wendy L. Hurley, Craig R.DannyCespedes100% (1)
- DLP 1 and 2Document10 pagesDLP 1 and 2Kareen Carlos GerminianoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2: Importance of Quantitative Research ACROSS FIELDS (Penslar & Porter, 2010)Document59 pagesLesson 2: Importance of Quantitative Research ACROSS FIELDS (Penslar & Porter, 2010)Patrice Del MundoNo ratings yet
- 2012 Test & Score Data Summary For TiBTDocument14 pages2012 Test & Score Data Summary For TiBT研發室No ratings yet
- Suzuki Program Parent Handbook (Revised 2013)Document27 pagesSuzuki Program Parent Handbook (Revised 2013)johaber100% (3)
- Linguistics-Quiz and Compre-18-19 IDocument4 pagesLinguistics-Quiz and Compre-18-19 IDrishtantRaghavNo ratings yet
- Java Web ProgrammingDocument7 pagesJava Web ProgrammingShekhar SaudNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document6 pagesChapter 4Peb BlesNo ratings yet
- TBI Longman Introductory The Paper Test 84 87Document4 pagesTBI Longman Introductory The Paper Test 84 87happinesNo ratings yet
- Rodham, K. (2010) - What Is Health Beahaviour. Health Psychology. New York Palgrave Macmillan.Document18 pagesRodham, K. (2010) - What Is Health Beahaviour. Health Psychology. New York Palgrave Macmillan.Hilda CadenaNo ratings yet