Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Elements, Compounds and Mixtures
Uploaded by
chivukula KarthikOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Elements, Compounds and Mixtures
Uploaded by
chivukula KarthikCopyright:
Available Formats
Downloaded from https://www.ncertbooksolutions.
com/
Elements, Compounds and Mixtures
Points to Remember:
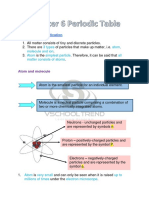
• Every substance is made up of very tiny particles, called molecules. Molecules are
formed from even smaller particles called atoms.
• Element—
(a) Element is the simplest pure substance. It cannot be divided further into
simpler substances by any chemical method, e.g. oxygen, hydrogen, sulphur, etc.
(b) At present 116 elements are known, of which 92 are natural elements.
• Based on their properties, elements are classified into: metals, non-metals,
metalloids, noble gases.
• Metals are ductile, malleable, good conductors of heat and electricity, high melting
om
and boiling points. Metals are sonorous, e.g., Iron, Gold, Silver, etc.
Non-metals are solids and brittle in nature, bad conductor of heat and electricity
.c
•
(exception Graphite) low melting and boiling points, e.g. sulphur, carbon,
ns
hydrogen, etc.
io
• Metalloids— These elements show properties of both metals and non-metals.
t
lu
They are hard solids, e.g. Boron, Silicon, Arsenic.
so
• Inert or noble gases— These elements do not react chemically with other
elements or compounds are called noble (Inert) gases, e.g., helium, neon, argon,
k
oo
etc.
• Symbols of Elements— Each element is denoted by a symbol usually to first
rtb
letter.
ce
Examples: Oxygen by O, Hydrogen by H.
• Atom— “An Atom is the smallest particle of an element that can take part in a
.n
chemical reaction but may or may not have independent existence.”
w
The atom of an element exhibits all the properties of that element.
w
• Molecule— A molecule is the smallest particle of a pure substance of element or
//w
compound which has independent existence. It exhibits all the properties of pure
s:
substance.
tp
• Atomicity— The number of atoms of an element that join together to form a
molecule of that element is known as the atomicity.
ht
• Molecular Formula— of an element is the symbolic representation of its
molecule. It indicates the number of atoms present in it. e.g. Magnesium oxide
– MgO.
Downloaded from https://www.ncertbooksolutions.com/
Downloaded from https://www.ncertbooksolutions.com/
Exercise 3(A)
Question 1.
Define: (a) Elements (b) Compounds
Answer:
(a) Elements: Element is a substance which cannot be broken further into simpler
substances and has a definite set of properties. Elements are made up of only one kind
of atoms.
(b) Compounds: Compounds are pure substances composed of two or more elements
in definite proportion by mass and has properties, entirely different from those of its
constituents elements.
Compound, are made up of different types of atoms combined chemically.
om
Question 2.
Give two examples for each of the following:
.c
(a) Metals (b) Non-metals
ns
(c) Metalloids (d) Inert gases
io
Answer:
t
lu
(a) Metals: Iron, silver, gold. so
(b) Non-metals: Carbon, sulphur, oxygen.
(c) Metalloids: Antimony, silicon, boron.
k
oo
(d) Inert gases: Helium, argon, neon.
rtb
Question 3.
ce
Differentiate between:
.n
(a) Pure and impure substances
w
(b) Homogenous and heterogenous substances
w
Answer:
//w
(a) Pure substances —
s:
1. Pure substances have definite composition and definite physical and chemical
tp
properties.
ht
2. They are all homogeneous i.e. their composition is uniform throughout the bulk.
3. Examples: Elements and compounds.
Impure substances —
1. Impure substances are made up of two or more pure substances mixed together
in any proportion.
2. They may be homogeneous or hetergeneous i.e. their composition is not uniform
throughout the bulk.
3. They are all mixtures.
Examples: air, sea water, petroleum, a solution of sugar in water are all impure
substances.
Downloaded from https://www.ncertbooksolutions.com/
Downloaded from https://www.ncertbooksolutions.com/
(b) Homogeneous mixture — is a mixture where the components that make up the
mixture are uniformly distributed throughout the mixture.
Example — air, sugar water, rain water.
Heterogeneous mixture — is a mixture, where the components of the mixture are not
uniform or have localized regios with different properties.
Example—Cereal in milk, vegetable soup.
Question 4.
Write the chemical name of the following and also give their molecular formulae:
(a) Baking soda (b) Vinegar
(c) Marble (d) Sand
Answer:
(a) Sodium bicarbonate (Baking soda) — NaHCO3
om
(b) Acetic acid (Vinegar) — CH3COOH
.c
(c) Calcium carbonate (Marble) — CaCO3
ns
(d) Silicon dioxide (Sand) — SiO2
tio
Question 5.
Name:
lu
so
(a) a soft metal
k
(b) a metal which is brittle
oo
(c) a non-metal which is lustrous
rtb
(d) a liquid metal
(e) a metal which is a poor conductor of electricity.
ce
(f) a non-metal which is a good conductor of electricity.
.n
(g) a liquid non-metal
w
(h) the hardest naturally occurring substance
w
(i) an inert gas
//w
Answer:
(a) Gold
s:
(b) Zinc
tp
(c) Iodine
ht
(d) Mercury
(e) Tungsten
(f) Graphite
(g) Bromine
(h) Diamond
(i) Neon, helium
Question 6.
How is sodium chloride different from its constituent elements ?
Answer:
The properties of sodium chloride are completely different from those of sodium and
chlorine. Sodium is a soft, highly reactive metal. Chlorine is a poisonous non-metallic
Downloaded from https://www.ncertbooksolutions.com/
Downloaded from https://www.ncertbooksolutions.com/
gas while sodium chloride is a very useful non poisonous compound which is added to
our food to get minerals and also to add taste to it.
Question 7.
Why is iron sulphide a compound ?
Answer:
Iron sulphide is a compound which can be broken into the elements iron and sulphur they both
have different properties. The properties of compound are entirely different from there of its
constituents elements.
Exercise 3(B)
Question 1.
Classify the following substances into compounds and mixtures:
om
Answer:
Carbon dioxide, air, water, milk, common, salt, blood, fruit juice, iron sulphide.
.c
Carbon dioxide — (Compound)
ns
air — (Mixture)
io
water — (Compound)
t
milk — (Mixture)
common salt — (Compound)
lu
so
blood — (Mixture)
k
fruit juice — (Mixture)
oo
iron sulphide — (Compound)
rtb
ce
Question 2.
.n
Give one example for each of the following types of mixtures
(a) solid-solid homogenous mixture
w
w
(b) solid-liquid heterogenous mixture
//w
(c) misicible liquids
(d) liquid-gas homogenous mixture
s:
Answer:
tp
(a) Solid-solid homogenous mixture — Alloys of metals e.g. brass, bronze stainless
ht
steel etc.
(b) Solid-liquid heterogenous mixture — Sand and water, mud and water, sugar and oil.
(c) Misicible liquids — water and ethanol.
(d) Liquid-gas homogenous mixture — Air
Question 3.
Suggest a suitable technique to separate the constituents of the following mixtures. Also
give the reason for selecting the particular method.
(a) Salt from sea water
(b) Ammonium chloride from sand
(c) Chalk powder from water
(d) Iron from sulphur
(e) Water and alcohol
Downloaded from https://www.ncertbooksolutions.com/
Downloaded from https://www.ncertbooksolutions.com/
(f) Sodium chloride and potassium nitrate
(g) Calcium carbonate and sodium chloride
Answer:
(a) The technique used to separate the salt from seawater is Evaporation.
Reason – Because this method is used to separate the components of the
homogeneous solid-liquid mixture. In this method, sea water is collected in a shallow
bed and allowed to evaporate in the sun. When all the water is evaporated, salt is left
behind. By this method, we only get solid and liquid is evaporated in its vapour form.
(b) Technique used to separate Ammonium chloride from sand is sublimation.
Because this method is used for solid mixtures in which one of the components can
sublime on heating. In this method, Ammonium chloride changes into vapours on
om
heating and salt is left behind.
.c
ns
(c) Technique used to separate chalk powder from water is filtration.
Reason – Because this process is used to separate the components of a
io
heterogeneous solid-liquid mixture in which solids are lights and insoluble in liquids.
t
lu
Substances used as filters are sand filter paper at C. These filters allows the liquid to
so
pass through them, but not solids.
k
oo
(d) Technique to separate iron from sulpher is magnetic separation.
rtb
Because, this method is used when one of the component of mixture is Iron. Iron gets
ce
attracted towards the magnet and hence get separated.
.n
(e) Technique used to separate water and Alcohol is Fractional Distillation.
w
w
Because in this method, the vapours of water is left behind in the original vessel as the
//w
alcohol boils at lower temperature than water. Thus these two liquids can be separated.
s:
(f) Technique used is Fractional-crystallisation.
tp
Because: This method is used when solubility of solid components of mixture and
ht
different in the same solvent. Here, sodium chloride and potassium nitrate. Both are
soluble in water but solubility of potassium nitrate is more.
(g) Technique used is Solvent Extraction Method: Because, by this method, salts get
dissolve in water while calcium carbonate being insoluble in water settles down in the
container. And hence get separated about.
Question 4.
(a) Define mixture.
(b) Why is it necessary to separate the constituents of a mixture.
(c) State four differences between compounds and mixtures.
Answer:
Downloaded from https://www.ncertbooksolutions.com/
Downloaded from https://www.ncertbooksolutions.com/
(a) “Mixtures can be defined as. a kind of matter which is formed by mixing two or more
pure substances (elements and compounds) in any proportion, such that they do not
undergo any chemical change and retain their individual properties. Therefore they are
impure substances.
(b) Because: The mixtures contain unwanted substances which may be harmful and may
degrade the properties of mixtures. So we, need to separated them and extract useful
substances.
This is necessary because
(i) It removes unwanted and harmful substances
(ii) to obtain pure and useful substances them.
Example: Sea water is rich in common salt which is an important ingredient of our food to add
om
taste and nutrients. But sea water, cannot be directly used to get the salt.
Hence, it is necessary to separate both.
.c
(c) Compound
ns
io
1. A compound is formed from its constituent elements as a result of chemical
t
reaction.
lu
so
2. A compound is always homogeneous in nature.
k
3. In a compound the elements are present in a fixed ratio by weight.
oo
4. The components of a compound can’t be separated by physical methods but can
rtb
be separated by chemical methods only.
5. The properties of a compound are different from those of its elements.
ce
6. The formation of a compound from its elements is accompanied by energy
.n
changes.
w
w
Mixture
//w
1. A mixture is obtained form its (elements, compounds) components as a result of
s:
physical change.
tp
2. The mixtures can be homogeneous or heterogeneous.
ht
3. In a mixture the components can be present in any ratio.
4. The components of a mixture can be separated by physical methods only.
5. The properties of a mixture lie between those of-its components.
6. The formation of a mixture from its constituents is not accompanied by energy
changes.
Question 5.
(a) What is chromatography ? For which type of mixture is it used ?
(b) What are the advantages of chromatography.
Answer:
(a) This is one of the latest techniques to separate the coloured components of a
mixture when all the components are very similar in their properties. Example:
Components of ink are separated by this method. Ink is a mixture of different dyes,
Downloaded from https://www.ncertbooksolutions.com/
Downloaded from https://www.ncertbooksolutions.com/
which are separated by chromatography because some of the dyes are less soluble and
some are more soluble in a solvent.
(b)
1. A very small quantity of the substance can be separated.
2. Components with very similar physical and chemical properties can be separated.
3. It identifies the different constitutes of a mixture.
4. It also helps in quantitive estimation of components of a mixture.
6. Choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below:
(a) a mixture of sand and ammonium chloride can be separated by
om
.c
1. filtration
ns
2. distillation
3. sublimation
io
4. crystallisation
t
lu
so
(b) A pair of metalloids are
k
oo
1. Na and Mg
rtb
2. B and Si
3. C and P
ce
4. HeandAr
.n
w
(c) Which of the following property is not shown by compounds?
w
//w
1. They are heterogeneous.
s:
2. They are homogeneous.
tp
3. They have definite molecular formulae.
ht
4. They have fixed melting and boiling points.
(d) A solvent of Iodine is
1. Water
2. Kerosene oil
3. Alcohol
4. Petrol
Downloaded from https://www.ncertbooksolutions.com/
Downloaded from https://www.ncertbooksolutions.com/
(e) Which of the gas is highly soluble in water ?
1. Ammonia
2. Nitrogen
3. Carbon monoxide
4. Oxygen
ADDITIONAL QUESTIONS
Check Your Progress 1
Fill in the blanks.
om
1. A pure substance has definite composition and constant properties.
2. Mixtures can be heterogeneous or homogenous.
.c
3. Use of a sieve to separate the components of a mixture of solids is based on the
ns
difference in the size of the components.
4. Winnowing is used when the constituents of a mixture of solids have difference in
io
their weights.
t
lu
5. Iodine, camphor, naphthalene, ammonium chloride and dry ice are some
so
substances that sublimate.
k
oo
Check Your Progress 2
rtb
ce
Question 1.
Filtraction is a method used to separate fine particles of EEE.. solid from a liquid.
.n
Answer:
w
Filtraction is a method used to separate fine particles of insoluble solid from a liquid.
w
//w
Question 2.
s:
Loading is basically speeding up EEEE
tp
Answer:
ht
Loading is basically speeding up sedimentation.
Question 3.
Name the techniques used to separate a solid from its solution.
Answer:
Sedimentation and Decantation
Question 4.
A separating funnel can be used for separating a mixture of immiscible liquids. True or
false ?
Answer:
True
Downloaded from https://www.ncertbooksolutions.com/
Downloaded from https://www.ncertbooksolutions.com/
Question 5.
During centrifugation, solid particles of the mixture move towards the bottom. True or
false ?
Answer:
True
EXERCISES
Tick the most appropriate answer.
1. The constituents of a mixture are present in
1. a fixed ratio
om
2. a variable ratio,
3. the ratio of 2: 1
.c
4. none of these
ns
io
2. Solutions are
t
lu
so
1. heterogeneous mixtures.
k
2. compounds
oo
3. homogeneous mixtures.
rtb
4. elements.
ce
3. The methods of separating components of a given mixture are based on the
.n
w
1. physical properties and state of the components.
w
2. colour of the components only.
//w
3. state of the components.
s:
4. none of these.
tp
4. Winnowing is the method used to separate
ht
1. chaff from grain.
2. stones from rice
3. oil from water
4. salt from sand
5. During filtration the substance left behind on the filter paper is called
1. distillate
2. filtrate
3. sublimate.
4. residue.
Downloaded from https://www.ncertbooksolutions.com/
Downloaded from https://www.ncertbooksolutions.com/
6. Loading is a process in which
1. impurities become heavy and sink to the bottom.
2. impurities float on the top.
3. impurities vaporize.
4. none of these
7. Fractional distillation is used to separate liquids having an appreciable
difference in their
1. size and shape
2. solubility
3. boiling points.
om
4. none of these
.c
8. The different constituents of an ink are separated by
ns
io
1. handpicking.
t
2. paper chromatography
3. filtration.
lu
so
4. magnetic separation.
k
oo
B. Fill in the blanks.
rtb
ce
1. A pure substance has only one kind of matter.
.n
2. The composition and properties of a homogenous mixture is uniform throughout.
3. An alloy is a homogeneous mixture of two or more metals.
w
w
4. Chalk powder dissolved in water is an example of a Chalk powder dissolved in
//w
water is an example of a suspension.
5. An emulsion is formed when one liquid is dispersed as tiny droplets throughout
s:
another liquid
tp
6. Immiscible liquids are separated by using a separating funnel.
ht
C. Write true or false for each statement. Rewrite the false statements correctly.
Question 1.
All pure substances have characteristic melting and boiling points.
Answer:
True
Question 2.
Milk is an emulsion.
Answer:
True
Downloaded from https://www.ncertbooksolutions.com/
Downloaded from https://www.ncertbooksolutions.com/
Question 3.
A heterogeneous mixture has a uniform composition throughout the mixture.
Answer:
False. A heterogeneous mixture has a non-uniform composition throught the mixture.
Question 4.
The constituents of a mixture can only be separated by chemical means.
Answer:
False. The constituents of a mixture can be separated by chemical means and physical
means.
Question 5.
Handpicking can be used as a separation technique if the particle size of the
om
constituents of the mixture is the same.
Answer:
.c
False. Handpicking can be used as a separation technique if the particle size of the
ns
constituents of the mixture is the not the same.
tio
lu
D. Match the columns. so
k
oo
rtb
ce
.n
w
w
//w
s:
tp
ht
Downloaded from https://www.ncertbooksolutions.com/
Downloaded from https://www.ncertbooksolutions.com/
E. Differentiate between the following.
1. solution and suspension
2. Supernatant liquid and Fill rate
3. Filter Paper and Alum
Answer:
1. Solution and Suspension
Solution
1. It is an example of homogeneous mixture.
2. It is formed when a solid dissolves in liquid.
om
3. For example – sugar dissolved in water.
.c
Suspension
ns
1. It is an example of heterogeneous mixture.
io
2. It is formed when an insoluble solid is added to solvent.
t
lu
3. For example-chalk dissolved in water. so
2. Supernatant liquid and Fill rate
k
oo
Supernatant liquid
rtb
1. It is obtained during sedimentation.
ce
2. It is used to separate mixture of liquid and insoluble solid heavier than liquid.
.n
3. No filter paper is used.
w
w
Filtrate
//w
1. It is obtained during filtration.
s:
2. It is used to separate fine particles of insoluble solids from liquids.
tp
3. filter paper is used.
ht
3. Filter Paper and Alum
Filter Paper
1. It is a special paper fitted in funnel during filtration.
2. It does not dissolve in water.
3. It does not speeds up-loading.
Alum
1. It is a solid which is used to load suspended mud particles in watei.
2. It dissolves easily in water.
3. It speeds up loading
Downloaded from https://www.ncertbooksolutions.com/
Downloaded from https://www.ncertbooksolutions.com/
Write short answers.
Question 1.
Is food that we eat a mixture ?
Answer:
Yes food that we eat is a mixture of carbohydrates, proteins, fats, minerals and
vitamins.
Question 2.
Name two methods by which solid-solid mixtures can be separated.
om
Answer:
.c
(i) Winnowing (ii) Hand Picking
ns
io
Question 3.
t
lu
How can you separate iron metal from non-magnetic impurities ?
so
Answer:
k
We can separate iron metal from non-magnetic impurities by the method of magnetic
oo
separation.
rtb
ce
Question 4.
Name the technique that you use if only the solid component of a solution is required.
.n
Answer:
w
Evaporation.
w
//w
Question 5.
Name the substance you will add to speed up sedimentation.
s:
Answer:
tp
Alum
ht
Question 6.
Name the different types of chromatographic techniques.
Answer:
1. Paper Chromatography
2. Column Chromatography
3. Thin Layer Chromatography
4. Gas Chromatography.
Downloaded from https://www.ncertbooksolutions.com/
Downloaded from https://www.ncertbooksolutions.com/
Answer in detail.
Question 1.
What is the difference between a pure substance and a mixture ?
Answer:
A pure substance consists of only one kind of matter, that is. all the particles are same.
It has a definite composition and constant properties. It cannot be split into simpler
substances by physical meAll pure substances have characteristic melting and boiling
points. A pure substance is either a compound or an element.
A Mixture contains two or more substances in any proportion which can be separated
by physical methods. Mixtures are generally of two types:
om
Homogeneous and Heterogeneous.
In a mixture, the constituents can be present in any ratio. They do not have
.c
characteristic melting and boiling points. In a mixture each constituent retain its original
ns
properties. These can be separated by physical means.
io
t
Question 2.
What are the different types of mixtures ?
lu
so
Answer:
k
Mixtures are basically of two types:
oo
(i) Homogeneous (ii) Heterogeneous
rtb
Homogeneous Mixtures: The composition of these mixtures is uniform throughout the
mixture. Besides the properties of the mixture are the same in all the parts of the
ce
mixture, e.g. sugar dissolved in water.
.n
Heterogeneous Mixtures: A heterogenous mixture composition is not uniform
w
throughout the mixture. The properties of the mixture are different in different parts of
w
mixture e.g. chalk dissolved in water.
//w
Question 3.
s:
Why is filtration a better technique than sedimentation and decantation ?
tp
Answer:
ht
Filtration is a better technique than sedimentation and decantation because it can
separate very Fine insoluble particles as compared to the latter. Besides the filtrate
obtained is generally pure solvent. In decantation when we pour out supernatant liquid
there are chances of their getting mixed up with solute particles.
Question 4.
How is distillation method different from evaporation?
Answer:
In distillation and evaporation both the solution is allowed to boil by giving heat.
Evaporation does not involves the collection of vapour thus obtained.Distillation involves
the condensation of the vapour obtained to obtain pure solvent. This is done in specially
designed condensation chamber.
Downloaded from https://www.ncertbooksolutions.com/
Downloaded from https://www.ncertbooksolutions.com/
om
.c
ns
tio
lu
so
Question 5.
What is centrifugation ? Also write the principle on which it works.
k
oo
Answer:
Centrifugation: It is a technique used to speed up sedimentation of fine particles
rtb
suspended in a solid liquid mixture.
ce
Principle: The principle of centrifugation is that an object, when spun at high speed,
experiences an outward force away from the centre of rotation.
.n
w
w
//w
s:
tp
ht
Downloaded from https://www.ncertbooksolutions.com/
You might also like
- Chemistry: a QuickStudy Laminated Reference GuideFrom EverandChemistry: a QuickStudy Laminated Reference GuideRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- GCSE Chemistry Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandGCSE Chemistry Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Piano Syllabus 2018-2020 PDFDocument98 pagesPiano Syllabus 2018-2020 PDFJake PaulNo ratings yet
- Sample Paper 1 GR 1 Theory FOR WEB PDFDocument8 pagesSample Paper 1 GR 1 Theory FOR WEB PDFJoelClarinSilorio0% (2)
- Chemistry Reviewer 1 2Document10 pagesChemistry Reviewer 1 2Ian PadillaNo ratings yet
- Inorganic Prac 2Document3 pagesInorganic Prac 2Ray DyerNo ratings yet
- Atoms, Molecules, and IonsDocument44 pagesAtoms, Molecules, and Ionsholley_kennethNo ratings yet
- Naming CompoundsDocument60 pagesNaming CompoundsLorilieNo ratings yet
- Elements, Compounds, Mixtures WorksheetDocument6 pagesElements, Compounds, Mixtures WorksheetAlvianica Nanda Utami100% (1)
- Y9 Chemistry Revision Booklet PDFDocument17 pagesY9 Chemistry Revision Booklet PDFRamesh Adwani0% (1)
- Element and CompoundsDocument14 pagesElement and CompoundsKehekeshan RizwanNo ratings yet
- Extracting MetalsDocument27 pagesExtracting MetalsJojo Hany100% (1)
- Chemical Recycling of PETDocument39 pagesChemical Recycling of PETAmit SinghNo ratings yet
- Selina Concise Chemistry Solutions Class 6 Chapter 4 Elements, Compounds, Symbols and FormulaeDocument31 pagesSelina Concise Chemistry Solutions Class 6 Chapter 4 Elements, Compounds, Symbols and FormulaeFLANTAMOCKNo ratings yet
- Class-7 Dlalal Simplified Elements Compound and Mixtures ICSE Chemistry SolutionsDocument15 pagesClass-7 Dlalal Simplified Elements Compound and Mixtures ICSE Chemistry SolutionssrobeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Atoms and MoleculesDocument34 pagesChapter 3 Atoms and MoleculesManushi ShahNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 3: Atoms and MoleculesDocument15 pagesChapter - 3: Atoms and Moleculesuma mishra0% (1)
- Chemistry Factsheet (OL, IGCSE, MYP) FinalDocument17 pagesChemistry Factsheet (OL, IGCSE, MYP) FinalJustSomeCrackHeadNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 3: Atoms and MoleculesDocument15 pagesChapter - 3: Atoms and MoleculesJanahvi PawarNo ratings yet
- Atoms, Molecules and IonsDocument27 pagesAtoms, Molecules and IonsRechellu ZamboangnonNo ratings yet
- Chemistry: End of Year Exam RevisionDocument9 pagesChemistry: End of Year Exam Revisionapi-354037574No ratings yet
- Syllabus: Name of The Element Latin Name SymbolDocument6 pagesSyllabus: Name of The Element Latin Name Symbolmehlawat_vivekNo ratings yet
- Minjun & Dongha Lesson SheetDocument68 pagesMinjun & Dongha Lesson SheetRicky SaputraNo ratings yet
- 2 Chapter2 PDFDocument80 pages2 Chapter2 PDFNUR AUNI SAHIRA S ROSLINo ratings yet
- Notes Atoms & Molecules PDFDocument3 pagesNotes Atoms & Molecules PDFGaurav SethiNo ratings yet
- Note On Atoms, Molecules, Valency and RadicalsDocument3 pagesNote On Atoms, Molecules, Valency and RadicalsRadiant BrothersNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Class 10 Meatals and NonmetalsDocument9 pagesChemistry Class 10 Meatals and NonmetalsGokulNo ratings yet
- The Periodic Table and ElementsDocument54 pagesThe Periodic Table and ElementsMa Luisa VillaruelNo ratings yet
- Notes Basis Concept of Chem L01-03 PDFDocument7 pagesNotes Basis Concept of Chem L01-03 PDFAbhishek KumarNo ratings yet
- Module 5 Chemical Symbols NotesDocument10 pagesModule 5 Chemical Symbols NotesaerinNo ratings yet
- Y10 Chemical ReactionsDocument30 pagesY10 Chemical Reactionsaleth felicianoNo ratings yet
- EXERCISE ChemistryDocument61 pagesEXERCISE ChemistryAnusha MaityNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document51 pagesChapter 4Pirate CaribbeanNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Unit Test Review Part II ADocument7 pagesChemistry Unit Test Review Part II AreBassistNo ratings yet
- f1 Chapter 6 Periodic TableDocument9 pagesf1 Chapter 6 Periodic TableshshshchinNo ratings yet
- 1 - Atoms, Molecules and StoichiometryDocument80 pages1 - Atoms, Molecules and StoichiometryHenry ChongNo ratings yet
- 32e06 Sains f1 c6 Bi Edit Done (Revised) (Verified) Done - CompressedDocument18 pages32e06 Sains f1 c6 Bi Edit Done (Revised) (Verified) Done - CompressedannabellNo ratings yet
- Y10 Science - Unit 2 ChemistryDocument30 pagesY10 Science - Unit 2 ChemistryCharmaine LIENo ratings yet
- Some Basic Concept of ChemistryDocument81 pagesSome Basic Concept of ChemistryZaid KhanNo ratings yet
- Atom Element and Atomic StructrureDocument48 pagesAtom Element and Atomic StructrureMindOfPrinceNo ratings yet
- Grade - 10 Term - I - Metals and Non-Metals Questionnaire - 2021-22Document5 pagesGrade - 10 Term - I - Metals and Non-Metals Questionnaire - 2021-22AnilNo ratings yet
- Elements and Compounds: Classification of MatterDocument5 pagesElements and Compounds: Classification of Matter2023hb74041No ratings yet
- Chemistry Factsheet OL and IGDocument16 pagesChemistry Factsheet OL and IGsaad nasirNo ratings yet
- Question Bank Elements, Compounds and MixturesDocument32 pagesQuestion Bank Elements, Compounds and MixturesPravat TiadiNo ratings yet
- Elements Compounds and MixturesDocument12 pagesElements Compounds and MixturesMarie LopesNo ratings yet
- Adge 2021 General Inorganic ChemDocument11 pagesAdge 2021 General Inorganic ChemHILVANO, HEIDEE B.No ratings yet
- Chemistry PendahuluanDocument63 pagesChemistry PendahuluanRani PuspitaNo ratings yet
- CH 4 - The Periodic Table and ElementsDocument50 pagesCH 4 - The Periodic Table and ElementsSJ ClassesNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Endurance Race 5070Document29 pagesChemistry Endurance Race 507024avesh.kumarNo ratings yet
- 10 Science Notes 03 Metals and Non Metals 1Document9 pages10 Science Notes 03 Metals and Non Metals 1varunNo ratings yet
- 10chemistry General Trial Test AnsDocument6 pages10chemistry General Trial Test AnsMNo ratings yet
- Ch. 11 Chemical BondsDocument33 pagesCh. 11 Chemical BondsNick Andrew Dequilla NiervaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1.2 Writing and Naming of Compounds-Group UploadDocument60 pagesLesson 1.2 Writing and Naming of Compounds-Group UploadMike MarquisNo ratings yet
- 2 Solutions Mixed Together Form A SolidDocument14 pages2 Solutions Mixed Together Form A SolidJoshua BlumbergNo ratings yet
- CH 5 ChemDocument29 pagesCH 5 ChemCaroline SueperNo ratings yet
- Structure of The AtomDocument15 pagesStructure of The AtomJeetNo ratings yet
- Crystals, Ions & Solids: CHEM091Document67 pagesCrystals, Ions & Solids: CHEM091Saltanat TurarovaNo ratings yet
- Atoms, Molecules, and IonsDocument86 pagesAtoms, Molecules, and IonsRoseman TumaliuanNo ratings yet
- Hindi Atoms & Molecules in One Shot AnubhaDocument112 pagesHindi Atoms & Molecules in One Shot AnubhaDushyant SinghNo ratings yet
- Calculations Involving Balanced Chemical EquationsDocument107 pagesCalculations Involving Balanced Chemical Equationsmain.20002245No ratings yet
- Int Wet-1Document8 pagesInt Wet-1Rsrao JNo ratings yet
- Quarter1 Lesson2-Week2Document83 pagesQuarter1 Lesson2-Week2Rea Magsael RogadorNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Matter and Measurement - 548154241Document35 pagesChapter 1 - Matter and Measurement - 548154241Elvis ChanNo ratings yet
- Periodic Table NotesDocument27 pagesPeriodic Table Noteschaitanya goyalNo ratings yet
- 4.chemzone - Formulas and Names of CompoundsDocument14 pages4.chemzone - Formulas and Names of CompoundsIANo ratings yet
- India Climate Notes BKLDocument12 pagesIndia Climate Notes BKLchivukula Karthik100% (1)
- Physical and Chemical Changes: AnswerDocument11 pagesPhysical and Chemical Changes: Answerchivukula KarthikNo ratings yet
- Short Question & Answers: Class 8 History L-9Document1 pageShort Question & Answers: Class 8 History L-9chivukula KarthikNo ratings yet
- Acetophenone Uses: Acute EffectsDocument3 pagesAcetophenone Uses: Acute EffectsRahul JadhavNo ratings yet
- An Examination of The Physical Properties of Pure Magnesium StearateDocument10 pagesAn Examination of The Physical Properties of Pure Magnesium StearateAstrid Carolina Gutierrez ShimabukuroNo ratings yet
- PHD Thesis - Eugene Atiemo (Final)Document210 pagesPHD Thesis - Eugene Atiemo (Final)desalegn aberaNo ratings yet
- Complexes of 2,4 Diamino 6-Hydroxy PyrimidineDocument40 pagesComplexes of 2,4 Diamino 6-Hydroxy Pyrimidinepulimamidi SarithareddyNo ratings yet
- 5.3 Calculation Questions PDFDocument27 pages5.3 Calculation Questions PDFCornflake 25No ratings yet
- Optimalisasi Pit Limit Penambangan Mineral Nikel Laterit PT ANTAM Tbk. Unit Bisnis Penambangan Nikel Di Site Pomalaa Sulawesi Tenggara Di Front XDocument12 pagesOptimalisasi Pit Limit Penambangan Mineral Nikel Laterit PT ANTAM Tbk. Unit Bisnis Penambangan Nikel Di Site Pomalaa Sulawesi Tenggara Di Front XAris MunandarNo ratings yet
- Resource Management Strategy of Limestone by Evolution of Nil Waste ProcessDocument3 pagesResource Management Strategy of Limestone by Evolution of Nil Waste ProcessravibelavadiNo ratings yet
- 2002 Thallium Review 2002 JEMEPDocument34 pages2002 Thallium Review 2002 JEMEPMINANo ratings yet
- SuggestedAnswers T08 EDocument6 pagesSuggestedAnswers T08 EkelvinNo ratings yet
- 1 Formulae Equations and Amount of Substance IedxcelDocument14 pages1 Formulae Equations and Amount of Substance IedxcelAdel GamerNo ratings yet
- Crystals 10 00612 PDFDocument26 pagesCrystals 10 00612 PDFDaniel Quintana GaviriaNo ratings yet
- IS1350-Part 4 - 1Document27 pagesIS1350-Part 4 - 1Stacy WilsonNo ratings yet
- Vasco 6000 EsiteDocument2 pagesVasco 6000 EsiteBruno GomesNo ratings yet
- Synergism of Clay and Heteropoly Acids As Nano-Catalysts For The Development of Green Processes With Potential Industrial ApplicationsDocument21 pagesSynergism of Clay and Heteropoly Acids As Nano-Catalysts For The Development of Green Processes With Potential Industrial ApplicationsJOSEPH HERBERT MABELNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry Lab 3Document4 pagesOrganic Chemistry Lab 3Presley OmorodionNo ratings yet
- Purification of Al (OH) 3 Synthesized by Bayer Process For Preparation of High Purity Alumina As Sapphire Raw MaterialDocument4 pagesPurification of Al (OH) 3 Synthesized by Bayer Process For Preparation of High Purity Alumina As Sapphire Raw Materialhaisamdo100% (1)
- Synthesis and Characterisation of Tetra-Tetrazole MacrocyclesDocument8 pagesSynthesis and Characterisation of Tetra-Tetrazole MacrocyclesroxideNo ratings yet
- Butadieno A04 431-1Document16 pagesButadieno A04 431-1Tasneem MNo ratings yet
- Danh Muc Hoa Chat Đối Chiếu Giữa Nhà Thầu Và Phòng Phân Tích TanichemDocument11 pagesDanh Muc Hoa Chat Đối Chiếu Giữa Nhà Thầu Và Phòng Phân Tích TanichemMai PhuNo ratings yet
- 116CH18Document21 pages116CH18girma245selaleNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S2452223620301115 MainDocument10 pages1 s2.0 S2452223620301115 MainDrawing and Artistic DecorationsNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan Mar 01, 2021Document15 pagesAdobe Scan Mar 01, 2021Mayank MishraNo ratings yet
- Pre Board Chemistry 12thDocument2 pagesPre Board Chemistry 12thSyed Raza Hassan GardeziNo ratings yet
- The Iodometric Estimation of MercaptansDocument2 pagesThe Iodometric Estimation of MercaptansSteven Alvarez AguilarNo ratings yet
- Radical Chain Polymerization: " Molecule Empire Building' by Radical' Groups"Document54 pagesRadical Chain Polymerization: " Molecule Empire Building' by Radical' Groups"bunnyNo ratings yet
- Modul KimiaDocument57 pagesModul KimiaAZIE207No ratings yet
- Department of Chemistry-Experi. 1Document13 pagesDepartment of Chemistry-Experi. 1ThabisoNo ratings yet