Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Problem 13.147: Given: Find: Solution
Uploaded by
Lucas Baldo Cardoso0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views2 pagesOriginal Title
Problem 13.147
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views2 pagesProblem 13.147: Given: Find: Solution
Uploaded by
Lucas Baldo CardosoCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
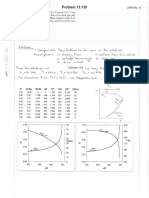
Problem 13.
147 [Difficulty: 4]
Given: Oxygen supplied to astronaut via umbilical
Find: Required entrance pressure and power needed to pump gas through the tube
Solution:
The given or available data is: R = 259.8 J/kg-K
cp = 909.4 J/kg-K
k = 1.4
Q= 10 L/min
D= 1 cm
L= 15 m
f= 0.01
T1 = 20 °C
T1 = 293 K
T2 = 293 K
p2 = 30 kPa
Equations and Computations:
At the exit of the pipe we can calculate the density:
ρ2 = 0.39411 kg/m3
so the mass flow rate is:
m= 6.568E-05 kg/s
The pipe area is:
A= 7.854E-05 m2
Therefore, the flow velocity is:
V2 = 2.12 m/s
The local sound speed is:
c2 = 326.5 m/s
So the Mach number is:
M 2 = 0.006500
From the exit Mach number we can calculate:
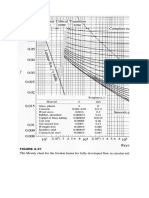
T 02/T 2 = 1.0000
fL 2/D = 16893.2
Given the length, diameter, and friction factor, we know:
fL 1-2/D = 15.0
Therefore: fL 1/D = 16908.2
So from this information we can calculate the entrance Mach number:
M 1 = 0.006498
fL 1/D = 16908.2
(We use Solver to calculate the Mach number based on the friction length)
The entrance sound speed is the same as that at the exit:
c1 = 326.5 m/s
So the flow velocity is:
V1 = 2.12 m/s
We can calculate the pressure ratio from the velocity ratio:
p1 = 30.0 kPa
From the entrance Mach number we can calculate:
T 01/T 1 = 1.0000
So the entrance and exit stagnation temperatures are:
T 01 = 293.00 K
T 02 = 293.00 K
The work needed to pump the gas through the pipeline would be:
W = 1.3073E-07 W
W = 0.1307 microwatts
You might also like
- Natural gas pipe pressure and powerDocument2 pagesNatural gas pipe pressure and powerLucas Baldo CardosoNo ratings yet
- Sizing a Flare Stack and Calculating Flame Distortion from Wind VelocityDocument49 pagesSizing a Flare Stack and Calculating Flame Distortion from Wind VelocityBayu AjipNo ratings yet
- (Unit 5) Me 366 Solutions Manual (28 - 05 - 2021)Document10 pages(Unit 5) Me 366 Solutions Manual (28 - 05 - 2021)somenewguyonthewebNo ratings yet
- Calc Reformer Skin Max Temp PDFDocument3 pagesCalc Reformer Skin Max Temp PDFirfanlarikhotmailcomNo ratings yet
- Pompa (P - 01)Document7 pagesPompa (P - 01)Henrikus Bhanutanaya WNo ratings yet
- Module 5 L2Document9 pagesModule 5 L2varun shaNo ratings yet
- 414CC3 - Excel Template - Prelim Shell and Tube Heat Exchanger Design - Si - UnitsDocument4 pages414CC3 - Excel Template - Prelim Shell and Tube Heat Exchanger Design - Si - Unitsvazzoleralex6884No ratings yet
- 9 SolutionsDocument6 pages9 SolutionsKathleen HalwachsNo ratings yet
- Compressor discharge pressure calculation and multi-stage compressor kWDocument30 pagesCompressor discharge pressure calculation and multi-stage compressor kWyamen-691904No ratings yet
- Condenser CalculationsDocument9 pagesCondenser CalculationsAngelo Imbo100% (2)
- J.R.Manel Sashikala PDFDocument27 pagesJ.R.Manel Sashikala PDFManel SashikalaNo ratings yet
- Tut CentrifugalDocument23 pagesTut CentrifugalDepepanshu MahajanNo ratings yet
- Fundamental Numerical Values Made SimpleDocument64 pagesFundamental Numerical Values Made SimpleFaiz Daud100% (1)
- HX Example1 PDFDocument5 pagesHX Example1 PDFSteveNo ratings yet
- Design of Distillation ColumnDocument21 pagesDesign of Distillation Columnusmanafzal246100% (1)
- Pump problem set solutions and calculationsDocument10 pagesPump problem set solutions and calculationsJames Nevin GoNo ratings yet
- Mach Numbers and Flow PropertiesDocument4 pagesMach Numbers and Flow PropertiesSyed Qassam Mustafa SadiqullahNo ratings yet
- Calculation Note Pondasi Tower Crosing NusakambanganDocument49 pagesCalculation Note Pondasi Tower Crosing Nusakambanganolis.uikNo ratings yet
- Where, The Temperature Ratio, Capacity Ratio, R A Value of 0.8 Is Generally Not AcceptedDocument43 pagesWhere, The Temperature Ratio, Capacity Ratio, R A Value of 0.8 Is Generally Not AcceptedAditya DeokarNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 - 16 MarkDocument23 pagesUnit 1 - 16 MarkShanhoodNo ratings yet
- Sag Tension Calculation IEEE STD 605 2008Document8 pagesSag Tension Calculation IEEE STD 605 2008Hassen LazharNo ratings yet
- Shell Tube Heat Exchanger DesignDocument7 pagesShell Tube Heat Exchanger DesignMakhdoom Ibad HashmiNo ratings yet
- Types of condensers and design calculationsDocument17 pagesTypes of condensers and design calculationsfarhaNo ratings yet
- Monteron Jaji C4 2Document15 pagesMonteron Jaji C4 2John Lloyd TulopNo ratings yet
- Chapter8-Assignment and SolutionDocument6 pagesChapter8-Assignment and SolutionDavid100% (1)
- Chapter 17Document57 pagesChapter 17MS schNo ratings yet
- Gambar Skema HE: Example 12.1Document5 pagesGambar Skema HE: Example 12.1FarisNo ratings yet
- Temperature Distributions in Solids and in Laminar FlowDocument4 pagesTemperature Distributions in Solids and in Laminar FlowSambasiva Rao KaturiNo ratings yet
- Proprietary Material Ited Distribution Permitted Only To Teachers and Educators For Course Preparation. If You Are A Student Using This Manual, You Are Using It Without PermissionDocument1 pageProprietary Material Ited Distribution Permitted Only To Teachers and Educators For Course Preparation. If You Are A Student Using This Manual, You Are Using It Without PermissionJorge Corrales RhenalsNo ratings yet
- Spek HE SolidDocument8 pagesSpek HE SolidMumahmmad Rizwan RNo ratings yet
- IntroductionDocument17 pagesIntroductionMitul PrajapatiNo ratings yet
- Shell and Tube Heat Exchanger Design CalculationsDocument6 pagesShell and Tube Heat Exchanger Design CalculationsnileshNo ratings yet
- Rotary Screw Compressor Discussion and Calculations: NotesDocument9 pagesRotary Screw Compressor Discussion and Calculations: Notesfarshad100% (2)
- Heat Exchanger Design CalculationsDocument8 pagesHeat Exchanger Design Calculationskikokiko KarimNo ratings yet
- Design Stripper Column ProcessDocument10 pagesDesign Stripper Column ProcessAhmed HassanNo ratings yet
- Solutions 3 17Document2 pagesSolutions 3 17EDM MAGIC100% (1)
- S K Mondal: Key: (A) SolDocument28 pagesS K Mondal: Key: (A) SolChaitanya Kishore ChitikenaNo ratings yet
- 5.3 Design of Waste Heat Boiler: (13) : DataDocument7 pages5.3 Design of Waste Heat Boiler: (13) : Datamoni beeNo ratings yet
- Structural Design and Computations: Certified By: ApprovedDocument13 pagesStructural Design and Computations: Certified By: ApprovedJesusAntonioJugosNo ratings yet
- Heater Lowers Methanol Temp from 95C to 40CDocument30 pagesHeater Lowers Methanol Temp from 95C to 40CHamdan ShdNo ratings yet
- تمرن فصل 7Document11 pagesتمرن فصل 7mohammadNo ratings yet
- Thermo 5th Chap17 P096Document19 pagesThermo 5th Chap17 P096UTA - Std - Elvin ChantreNo ratings yet
- Pumps Sheet-1-SolutionDocument12 pagesPumps Sheet-1-Solutionamrahmes123No ratings yet
- Shell Diameter Calculation and Heat Exchanger DesignDocument26 pagesShell Diameter Calculation and Heat Exchanger Designpavan100% (1)
- Chapter 8 - TutorialDocument4 pagesChapter 8 - TutorialDavidNo ratings yet
- Problem 3.86Document2 pagesProblem 3.86Luis Gustavo Pilco GarciaNo ratings yet
- Thermal Lab-2 Manual CompletedDocument69 pagesThermal Lab-2 Manual CompletedSiva RamanNo ratings yet
- Week 11 Examples, MEMODocument7 pagesWeek 11 Examples, MEMOlehlabileNo ratings yet
- ECE 309 Tutorial # 4 First Law of Thermodynamics: Control VolumesDocument6 pagesECE 309 Tutorial # 4 First Law of Thermodynamics: Control VolumesSaran JiNo ratings yet
- Lec23 PDFDocument44 pagesLec23 PDFSyed YousufuddinNo ratings yet
- Solution Assignment MENG580 Chapter 11Document4 pagesSolution Assignment MENG580 Chapter 11ahmadNo ratings yet
- Tata Consulting Engineers LimitedDocument24 pagesTata Consulting Engineers LimitedNitish TakalkarNo ratings yet
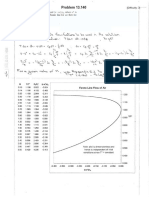
- Problem 13.146: Given: Find: SolutionDocument2 pagesProblem 13.146: Given: Find: SolutionLucas Baldo CardosoNo ratings yet
- Merancang Propeller untuk MV. CETAK MEDIADocument31 pagesMerancang Propeller untuk MV. CETAK MEDIAJustice FagNo ratings yet
- Module 7: Solved ProblemsDocument15 pagesModule 7: Solved Problemscaptainhass67% (6)
- Feynman Lectures Simplified 2C: Electromagnetism: in Relativity & in Dense MatterFrom EverandFeynman Lectures Simplified 2C: Electromagnetism: in Relativity & in Dense MatterNo ratings yet
- Exercises in Electronics: Operational Amplifier CircuitsFrom EverandExercises in Electronics: Operational Amplifier CircuitsRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- Solution Manual for an Introduction to Equilibrium ThermodynamicsFrom EverandSolution Manual for an Introduction to Equilibrium ThermodynamicsNo ratings yet
- Problem 13.146: Given: Find: SolutionDocument2 pagesProblem 13.146: Given: Find: SolutionLucas Baldo CardosoNo ratings yet
- Problem 13.139kDocument1 pageProblem 13.139kLucas Baldo CardosoNo ratings yet
- Problem 13.141: (Difficulty: 4) Part 1/2Document2 pagesProblem 13.141: (Difficulty: 4) Part 1/2Lucas Baldo CardosoNo ratings yet
- Problem 13.144Document1 pageProblem 13.144Lucas Baldo CardosoNo ratings yet
- Problem 13.143 Fanno Line FlowDocument2 pagesProblem 13.143 Fanno Line FlowLucas Baldo CardosoNo ratings yet
- Problem 1.5Document1 pageProblem 1.5Lucas Baldo CardosoNo ratings yet
- Problem 13.140kkDocument1 pageProblem 13.140kkLucas Baldo CardosoNo ratings yet
- Problem 13.142: Given: Find: SolutionDocument1 pageProblem 13.142: Given: Find: SolutionLucas Baldo CardosoNo ratings yet
- Problem 1.4: Open-Ended Problem StatementDocument1 pageProblem 1.4: Open-Ended Problem Statementlbro7291No ratings yet
- Conservation Laws ExplainedDocument1 pageConservation Laws ExplainedAldo AldoNo ratings yet
- Problem 1.3: Open-Ended Problem StatementDocument1 pageProblem 1.3: Open-Ended Problem Statementlbro7291No ratings yet
- Problem 1.7 PDFDocument1 pageProblem 1.7 PDFCaioPaesNo ratings yet
- Syllabus CoperativeDocument22 pagesSyllabus CoperativeSiva LingamNo ratings yet
- Course: School Leadership (8618) : Assignment No. 1Document13 pagesCourse: School Leadership (8618) : Assignment No. 1Suliman KhiljiNo ratings yet
- SAM+ Guidance DocumentDocument23 pagesSAM+ Guidance DocumentLaura Rosero0% (1)
- Mini Project DocumentationDocument43 pagesMini Project Documentationmgitecetech100% (6)
- Ethics Updated ImDocument75 pagesEthics Updated ImGraciella MabalingNo ratings yet
- PS 5.1.2 Enthalpy CalculationsDocument3 pagesPS 5.1.2 Enthalpy Calculationsrichard.gross62No ratings yet
- Genetic Algorithms: Department of Computer Science, University of New Mexico, AlbuquerqueDocument4 pagesGenetic Algorithms: Department of Computer Science, University of New Mexico, AlbuquerqueESMAILNo ratings yet
- Laser Shock Forging-A Novel in Situ Method DesignedDocument16 pagesLaser Shock Forging-A Novel in Situ Method DesignedEstefania CovarrubiasNo ratings yet
- A Detailed Lesson Plan in EDUC 6ADocument10 pagesA Detailed Lesson Plan in EDUC 6ARyan Jay Gaviola CalahatNo ratings yet
- 24160-Article Text-39228-1-10-20220603Document10 pages24160-Article Text-39228-1-10-20220603pandji pridjantoNo ratings yet
- Classification of AggregatesDocument17 pagesClassification of AggregatesBerdin, Fresh Sthela AidaNo ratings yet
- SchimmentiDevelopmentalrootsofdissociationpre PrintDocument42 pagesSchimmentiDevelopmentalrootsofdissociationpre PrintZeynep ÖzmeydanNo ratings yet
- MSC Thesis Alan Wijaya 2018Document2 pagesMSC Thesis Alan Wijaya 2018Alan WijayaNo ratings yet
- The No Cry Sleep Solution PDFDocument273 pagesThe No Cry Sleep Solution PDFanastaufan MrNo ratings yet
- Solving Differential Riccati Equations A NonlinearDocument20 pagesSolving Differential Riccati Equations A NonlinearCarlosNo ratings yet
- Science News - June 19, 2021 USADocument36 pagesScience News - June 19, 2021 USAblabla11No ratings yet
- Curiosity in Schools Jiroutetal.2018Document17 pagesCuriosity in Schools Jiroutetal.2018EVA JAZMIN DE LA ROSA RIVERANo ratings yet
- Department of Computer Science Software Engineering Course Offering Fall 2022Document6 pagesDepartment of Computer Science Software Engineering Course Offering Fall 2022Bushi BaloochNo ratings yet
- 3.6.3 Function Block Diagram: 3 Operation TheoryDocument2 pages3.6.3 Function Block Diagram: 3 Operation TheoryAC DCNo ratings yet
- Preliminary Examination - Attempt Review1 PDFDocument11 pagesPreliminary Examination - Attempt Review1 PDFPeter Eclevia0% (1)
- Water Budget Equation Exercise Problems SolvedDocument10 pagesWater Budget Equation Exercise Problems SolvedSheeraz AhmedNo ratings yet
- Interpersonal Communication Self Reflection #1Document5 pagesInterpersonal Communication Self Reflection #1monicawoods705No ratings yet
- EC2204 Signals and Systems University Questions for Five UnitsDocument19 pagesEC2204 Signals and Systems University Questions for Five UnitsCrazy EditingsNo ratings yet
- Russian Common AdjectivesDocument8 pagesRussian Common Adjectivesmoniquebateman20No ratings yet
- GRADE:10: Page 1 of 13Document13 pagesGRADE:10: Page 1 of 13Pujan PatelNo ratings yet
- N164.UCPE12B LANmark - OF - UC - 12x - Singlemode - 9 - 125 - OS2 - PE - BlackDocument2 pagesN164.UCPE12B LANmark - OF - UC - 12x - Singlemode - 9 - 125 - OS2 - PE - BlackRaniaTortueNo ratings yet
- Winmena - DPGDocument1 pageWinmena - DPGFAIYAZ AHMEDNo ratings yet
- Norman Steenrod and William G. Chinn - First Concepts of Topology: The Geometry of Mappings of Segments, Curves, Circles, and DisksDocument170 pagesNorman Steenrod and William G. Chinn - First Concepts of Topology: The Geometry of Mappings of Segments, Curves, Circles, and DisksMi LiaNo ratings yet
- UPP PE Tank Sump Installation GuideDocument32 pagesUPP PE Tank Sump Installation GuidelowiyaunNo ratings yet
- Monthly Magzine JAN 2023Document165 pagesMonthly Magzine JAN 2023charan100% (1)