Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Questions-Composition: The Chemical Classification of Matter
Uploaded by
hannahOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Questions-Composition: The Chemical Classification of Matter
Uploaded by
hannahCopyright:
Available Formats
Questions-Composition: The Chemical Classification of Matter
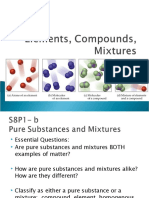
Why is it important for chemists to classify matter by putting it into different categories?
-In order to make sense of the tremendous amount of information that we can learn about matter,
chemists have developed categories of kinds of matter in which to organize the information.
Chemists classify by state (solid, liquid, gas) but what is meant by “composition”?
-Chemical composition refers to the identity and relative number of the chemical elements that
make up any particular compound.
What are the 2 major categories that chemists classify all matter?
-Matter is classified into two broad categories: pure substances and mixtures.
Define pure substance.
-A material that has a constant composition and has consistent properties throughout the sample.
Name + describe the 2 types of pure substances.
-There are two types of pure substances that are Elements and Compounds. A pure substance that
has only one kind of atom and cannot be broken into two or more simpler substances by physical
or chemical means is an element. A pure substance, basically composed of two or more elements
and chemically combined in a fixed proportion is called a compound.
Give 2 examples for each.
-Element~Iron and silver.
Compound~Water and methane.
Why do you think “elements” can not be broken down into simpler substances?
-Any substance that contains only one kind of an atom is known as an element. Elements are
already in their simplest form.
Although elements and compounds are both Pure Substances. Name 2 very clear differences
between them.
-An element is a substance that contains only ONE type of atom, whereas a compound is a pure
substance that contains 2 or more elements that are chemically combined.
Define mixture.
-Mixtures are physical combinations of pure substances that have no definite or constant
composition.
Name and describe 2 main types of mixtures.
-Mixtures can be either homogeneous or heterogeneous: A homogeneous mixture is a solid,
liquid, or gaseous mixture that has the same proportions of its components throughout any given
sample. A heterogeneous mixture is simply any mixture that is not uniform in composition.
Colloids, mechanical mixtures and suspensions are “Heterogeneous Mixtures”. What is the
difference between these 3 types of heterogeneous mixtures + give 2 examples.
-Mechanical mixtures and suspensions particles are big enough to see, whereas colloids particles
can not be seen with the naked eye. Mechanical mixtures and suspensions settle out, whereas
colloids do not settle out.
Homogeneous mixtures “look” pure. Why aren’t they?
-All pure substances are said to be homogeneous but not all homogeneous mixtures are pure. A
pure substance is made up of a single element or compound and has a definite composition.
Homogeneous mixtures are made up of uniform compositions of a variety of compounds, but can
be separated into individual components upon physical separation processes.
Give 3 examples.
-Homogeneous mixtures include: corn oil, sugar water, and pure water.
You might also like
- Chapter 1 OutlineDocument4 pagesChapter 1 Outlinedill1233No ratings yet
- Efficient Water Use for AgricultureDocument20 pagesEfficient Water Use for Agriculturesymphonic8260% (15)
- Is Matter Around Us PureDocument11 pagesIs Matter Around Us Purelohitha chary100% (1)
- Elements Compounds MixturesDocument18 pagesElements Compounds MixturesDONABEL ESPANONo ratings yet
- Matter PrintableDocument7 pagesMatter Printableapi-310503032No ratings yet
- Elements, Molecules, Compounds, and MixturesDocument43 pagesElements, Molecules, Compounds, and Mixtureswidya sariNo ratings yet
- Classifying MatterDocument31 pagesClassifying MatterAlyssa Crizel CalotesNo ratings yet
- Describing Matter 13-1 Notes Part 2Document7 pagesDescribing Matter 13-1 Notes Part 2Chenie CoronelNo ratings yet
- LEX-115-01 Chemical Technology ClassDocument4 pagesLEX-115-01 Chemical Technology ClassMARLY DAYANARA CASADO CABRALNo ratings yet
- What Is Matter - FinalDocument22 pagesWhat Is Matter - FinalKyle N. BalansagNo ratings yet
- Science 7 ReviewerDocument8 pagesScience 7 ReviewerClarice PalattaoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Introduction To ChemistryDocument3 pagesChapter 1 Introduction To ChemistryMicaela DNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 - Matter and Energy CharacteristicsDocument4 pagesUnit 2 - Matter and Energy CharacteristicsTwice OnceNo ratings yet
- Reading 1 CLASSIFICATION OF MATTERDocument1 pageReading 1 CLASSIFICATION OF MATTERThu Ngân TrầnNo ratings yet
- 2 Elements Compounds Mixtures 2Document36 pages2 Elements Compounds Mixtures 2samantharox13No ratings yet
- Mariano Marcos State University: PCHM 121Document17 pagesMariano Marcos State University: PCHM 121KaizenNo ratings yet
- The 5 Main Branches of ChemistryDocument18 pagesThe 5 Main Branches of ChemistryMohammad khalidNo ratings yet
- Chemistry - Building Matter From AtomsDocument17 pagesChemistry - Building Matter From AtomsAgra AnggrainiNo ratings yet
- 2020 Classification Reading and MapsDocument5 pages2020 Classification Reading and MapsAndre LangagneNo ratings yet
- Topic 1. Elements, Compounds and Mixtures.: What Is Chemistry?Document24 pagesTopic 1. Elements, Compounds and Mixtures.: What Is Chemistry?Lee enzoNo ratings yet
- Module 1 ScienceDocument18 pagesModule 1 ScienceLuisa SevillaNo ratings yet
- Physics An Chemistry 3rd ESO - Unit3Document22 pagesPhysics An Chemistry 3rd ESO - Unit3humanNo ratings yet
- CLASSIFICATION OF MATTER RevisedDocument23 pagesCLASSIFICATION OF MATTER RevisedTrisha Rae GarciaNo ratings yet
- Aim1 T What Is MatterDocument1 pageAim1 T What Is Matterapi-299809358No ratings yet
- Chem (Lec)Document2 pagesChem (Lec)Dalgom's WifeNo ratings yet
- Study Material: Downloaded From VedantuDocument11 pagesStudy Material: Downloaded From VedantuShankar MahadevanNo ratings yet
- Free Study Materials for All Classes & BoardsDocument10 pagesFree Study Materials for All Classes & BoardsAnkit kumarNo ratings yet
- Study Materials: Vedantu Innovations Pvt. Ltd. Score High With A Personal Teacher, Learn LIVE Online!Document10 pagesStudy Materials: Vedantu Innovations Pvt. Ltd. Score High With A Personal Teacher, Learn LIVE Online!sarwath sultanaNo ratings yet
- CHEMISTRY-WPS OfficeDocument5 pagesCHEMISTRY-WPS OfficeTricia RubayaNo ratings yet
- Sophisticated ChemistryDocument9 pagesSophisticated ChemistryKingsleyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Classifying MatterDocument14 pagesChapter 2 Classifying Matteranneth renteriaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry For EngineersDocument21 pagesChemistry For Engineersjustnothing010100No ratings yet
- Intro To BiologyDocument14 pagesIntro To BiologyDawar Aziz MemonNo ratings yet
- Module 3 Basic Concepts in ScienceDocument51 pagesModule 3 Basic Concepts in Sciencehs4fptm82gNo ratings yet
- Some Basic Concept of Chemistry QuesDocument40 pagesSome Basic Concept of Chemistry QuesSaadiya HussainNo ratings yet
- Stem Lesson 1 Gen Chem Pure SubsDocument15 pagesStem Lesson 1 Gen Chem Pure SubsYvonne CuevasNo ratings yet
- Elements Compound MixtureDocument42 pagesElements Compound MixtureRecilia MarthaNo ratings yet
- Basic Chemistry Key Terms Collection by Saya Minn ThantDocument8 pagesBasic Chemistry Key Terms Collection by Saya Minn ThantMinn ThantNo ratings yet
- CH 4. Some Basic Concepts of Chemistry (Chem +1)Document43 pagesCH 4. Some Basic Concepts of Chemistry (Chem +1)Dipin Preet SinghNo ratings yet
- CH 4. Some Basic Concepts of Chemistry (Chem +1)Document43 pagesCH 4. Some Basic Concepts of Chemistry (Chem +1)James FrancisNo ratings yet
- HTTPSBMC - unideb.hupublicdocuments2022!09!132BMCI Lecture Week2 Compounds Mixtures PDFDocument82 pagesHTTPSBMC - unideb.hupublicdocuments2022!09!132BMCI Lecture Week2 Compounds Mixtures PDFayoubNo ratings yet
- Classifying MaterialsDocument26 pagesClassifying MaterialsAyush Singh RathoreNo ratings yet
- Unit 3. Mixtures and Pure SubstancesDocument36 pagesUnit 3. Mixtures and Pure SubstancesArman VillagraciaNo ratings yet
- ReviewerDocument7 pagesReviewerJohn Nicolo P. GurangoNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 101 MatterDocument3 pagesChemistry 101 MatterTroy SaguinNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1.3 Pure Substances and MixturesDocument2 pagesLesson 1.3 Pure Substances and MixturesAndrea MurielNo ratings yet
- Elements_and_Compounds_Notes_Lesson_1Document3 pagesElements_and_Compounds_Notes_Lesson_1ehan.ilrnestersNo ratings yet
- Spec I Task 4 Classification of MatterDocument11 pagesSpec I Task 4 Classification of MatterJERIEL MARTIREZNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Chapter 1 ReviewDocument3 pagesChemistry Chapter 1 ReviewMarcia MurilloNo ratings yet
- Grade 9 Science - Notre Dame College School: John Dalton - The Guy Who Came Up With Particle TheoryDocument25 pagesGrade 9 Science - Notre Dame College School: John Dalton - The Guy Who Came Up With Particle Theorymonsieurkevin30No ratings yet
- Elements and CompoundsDocument29 pagesElements and CompoundsMa Luisa VillaruelNo ratings yet
- Some Basic Concepts of ChemistryDocument8 pagesSome Basic Concepts of ChemistryJatinNo ratings yet
- Ecological Concepts of Matter and EnergyDocument3 pagesEcological Concepts of Matter and EnergymashihoNo ratings yet
- Chemistry: Article Theory of MatterDocument19 pagesChemistry: Article Theory of MatterLizzy XeryuuNo ratings yet
- Class 11 Chemistry CH - 1Document11 pagesClass 11 Chemistry CH - 1WAVER ELECTRiCNo ratings yet
- Self-Instructed Module in Science 6Document21 pagesSelf-Instructed Module in Science 6NikkiBoy Reyes BernabeNo ratings yet
- Notes - Mixtures and Pure SubstancesDocument32 pagesNotes - Mixtures and Pure Substancesapi-326942798No ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Lecture Outline on MatterDocument29 pagesChapter 1 Lecture Outline on MatterSelene VerhofstadNo ratings yet
- Particle Nature of MatterDocument22 pagesParticle Nature of MatterEve JoyceNo ratings yet
- Elements, Compounds and Mixtures ExplainedDocument53 pagesElements, Compounds and Mixtures ExplainedAsma AkterNo ratings yet
- Chemical Reaction of Aluminum and Copper ChlorideDocument3 pagesChemical Reaction of Aluminum and Copper ChloridehannahNo ratings yet
- Reporting Errors and Experimental Results Best Estimate +/-UncertaintyDocument3 pagesReporting Errors and Experimental Results Best Estimate +/-UncertaintyhannahNo ratings yet
- The HobbitDocument1 pageThe HobbithannahNo ratings yet
- Thinking Questions Regarding Genetic Screening and TherapyDocument3 pagesThinking Questions Regarding Genetic Screening and TherapyhannahNo ratings yet
- Confined Spaces in ConstructionDocument4 pagesConfined Spaces in ConstructionRonald AranhaNo ratings yet
- General Guidelines Structural Silicone Glazing With Sikasil AdhesivesDocument28 pagesGeneral Guidelines Structural Silicone Glazing With Sikasil AdhesivesfasdfaNo ratings yet
- REVIEWER-3RD-GRADIng ApDocument12 pagesREVIEWER-3RD-GRADIng ApElvira Yap100% (1)
- German ATV DVWK A 168E Corrosion of Wastewater Systems Wastewater 1998 PDFDocument51 pagesGerman ATV DVWK A 168E Corrosion of Wastewater Systems Wastewater 1998 PDFJosip Medved100% (1)
- Commissioning Responsibilty Matrix Rev.0 12-Nov-2014Document4 pagesCommissioning Responsibilty Matrix Rev.0 12-Nov-2014Dinesh Radhakrishnan100% (1)
- Sulfaflux - Oilfield H2S Scavenger'sDocument6 pagesSulfaflux - Oilfield H2S Scavenger'sben7251No ratings yet
- Multistoreyed Building 3Document26 pagesMultistoreyed Building 3V.m. RajanNo ratings yet
- Explore the Balmer Series of Hydrogen Emission SpectraDocument5 pagesExplore the Balmer Series of Hydrogen Emission SpectraEddie WinterNo ratings yet
- Fosroc Guncrete E: High Strength, Low Shrinkage, High Build Dry-Spray Applied Repair Mortar Uses Application InstructionsDocument3 pagesFosroc Guncrete E: High Strength, Low Shrinkage, High Build Dry-Spray Applied Repair Mortar Uses Application InstructionsJohnNo ratings yet
- Val Caraig WPQTDocument1 pageVal Caraig WPQTMark Jason M. BrualNo ratings yet
- Reaction Injection Molding (RIM)Document11 pagesReaction Injection Molding (RIM)Mithun KnNo ratings yet
- NCERT Solutions For Class 9 ScienceDocument33 pagesNCERT Solutions For Class 9 ScienceShivang MohtaNo ratings yet
- Badger RCDL DatasheeDocument2 pagesBadger RCDL Datasheeابزار دقیقNo ratings yet
- JC2 (05/06) Physics Common Test 2006 Suggested Answers: Paper 1Document13 pagesJC2 (05/06) Physics Common Test 2006 Suggested Answers: Paper 1wangks1980No ratings yet
- Materials Science and Engineering - A First Course - V. RaghavanDocument53 pagesMaterials Science and Engineering - A First Course - V. RaghavanDhvani Rakeshkumar Shah 4-Yr B.Tech. Chemical Engg., IIT(BHU), VaranasiNo ratings yet
- Salt and SugarDocument9 pagesSalt and Sugarapi-384186386No ratings yet
- Basf Masterbrace Adh 1414 Tds 823008Document3 pagesBasf Masterbrace Adh 1414 Tds 823008Mohamed Abo-ZaidNo ratings yet
- UOP 555-10 Trace Impurities in Benzene by GCDocument11 pagesUOP 555-10 Trace Impurities in Benzene by GCMorteza SepehranNo ratings yet
- Valco Cheminert - VICI - Resolution SystemsDocument56 pagesValco Cheminert - VICI - Resolution SystemsResolution Systems, Inc.No ratings yet
- Horizontal Seperator DesignDocument19 pagesHorizontal Seperator DesignSwaroop VadaliNo ratings yet
- Crystal Defect - Planar Defects WNPDocument33 pagesCrystal Defect - Planar Defects WNPNaufal HNo ratings yet
- Applied Thermodynamics Exam 2018 Wirh SolutionsDocument9 pagesApplied Thermodynamics Exam 2018 Wirh SolutionsFarouk BassaNo ratings yet
- Khan 2017Document6 pagesKhan 2017Mahendra KumarNo ratings yet
- A Practical Handbook of Seawater AnalysisDocument328 pagesA Practical Handbook of Seawater Analysisfdlab100% (2)
- Astm D 1434-1982 Old Method Otr TestDocument12 pagesAstm D 1434-1982 Old Method Otr Testjai soniNo ratings yet
- Che 312 Notebook DistillationDocument19 pagesChe 312 Notebook DistillationUGWU MARYANNNo ratings yet
- CEIC 2002 Exam Preparation Practice Question No. 1 FluxDocument2 pagesCEIC 2002 Exam Preparation Practice Question No. 1 FluxWinnieNo ratings yet
- 22-Article Text-40-3-10-20210527Document5 pages22-Article Text-40-3-10-20210527Wahyu DwilestariNo ratings yet
- HEC-RAS Modeling Course-Day-2Document147 pagesHEC-RAS Modeling Course-Day-2Qaxim ShahNo ratings yet