Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Calculation For Protection Works Project: Construction of Abay Bank Head Quarters Client: Abay Bank S.C
Uploaded by
kidi mollaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Calculation For Protection Works Project: Construction of Abay Bank Head Quarters Client: Abay Bank S.C
Uploaded by
kidi mollaCopyright:
Available Formats
Calculation for Protection Works
Project: Construction of Abay Bank head quarters
Client: Abay Bank S.C.
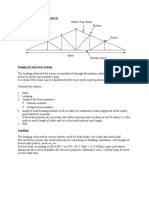
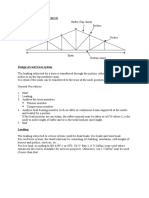
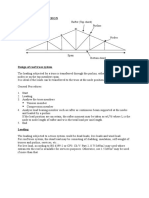
Shown herewith is the sample calculation for the design of protection piles for 22m
excavation (type SP4 as shown on drawings). Reinforced concrete piles supported with
anchors are used to support the lateral load from the excavation.
1. Assumptions
1.1. Material for construction:
Concrete- C25/30 concrete with minimum cylindrical strength of 25MPa for the
piles and C20/25 Concrete with minimum cylindrical strength of 20Mpa for the
shotcrete wall is considered.
Reinforcement steel S400 with minimum yield strength of 400MPa is considered.
1.2. Pile spacing:
Pile center to center spacing of 2.0m is considered.
1.3. Loads:
Load from surcharge
A surcharge load (S) of 10KPa is considered at immediately above the piles and
30kpa surcharge is considered at 5m apart from the piles.
Calculation for protection works Page 1
Lateral load from surcharge is considered as
Ls = Ka (S)
Even though the dominant layer to be supported is basalt which has high angle of
friction, a value of 300 is considered conservatively;
Ka = (1-sin∅)/(1+sin∅) = (1-0.5)/(1+0.5)=0.333
Ls (0-5m) = 0.333 x 10kpa = 3.33kpa
Ls (5-end of excav.) = 0.333 x 30kpa = 10kpa
Lateral load
Soil strata are considered according to the geotechnical investigation report with
analysis parameters considered accordingly;
Since direct shear tests are not conducted in the geotechnical investigation,
estimations from correlations are used to estimate the shear strength parameters.
Calculation for protection works Page 2
Layer 1: is ignored (layer 2 is considered to extend from the top level, NGL)
Layer 2: 0-2m is a clay layer, γ = 21kN/m3 (estimated)
Cu = 4.5N …where N is adjusted SPT value.
Cu = 4.5 x 5 =18 KPa
The active pressure is estimated as
Pa at 0.0m = 0kpa
Pa at 2.0m= γh -2Cu = 21 x 2 – 2x18 = 6kpa
Layer 3: 2m – 5m is a silty sand layer, γ = 20kN/m3 (estimated)
Considering it is a stiff layer as indicated in the geotechnical investigation; angle of
friction is estimated as 300.
Ka = (1-sin∅)/(1+sin∅) = (1-0.5)/(1+0.5)=0.333
Pa at 2.0m = γhka = 20 x 2 x 0.333 = 13.33kpa
Pa at 5.0m = γhka = 20 x 5 x 0.333 = 33.33kpa
Layer 4: 5m-22m is a scoria basalt, γ = 25kN/m3 (estimated)
For the basaltic layer, cohesion is considered as the strength characteristic
parameter.
Literatures give a vast range of values for cohesion in rocks but conservatively a
low value of 250Kpa is considered due to presence of fractures and rock quality
index values.
Calculation for protection works Page 3
Pa at 5m = γh -2Cu = 25 x 5 – 2 x 250 = -400kpa (No active pressure is expected at
this level.
Pa at 22m = γh -2Cu = 25 x 22 – 2x250 = 50kpa
The active pressure starts from
H =2 x 250 /25 = 20m
Pa at 20m = 0kpa
1.4. Passive pressure:
Despite embedment of piles below the lowest level of excavation, passive pressure
contribution is neglected and the hence the main resistance is achieved from the
anchors.
2.0 Analysis
The loads considered therefore are as follows;
Since the pile spacing is 2.0m, all loads in kpa are multiplied by 2m to be converted
to kN/m load on pile
Piles are considered vertically restrained at the base.
Piles are horizontally restrained at anchor points.
Calculation for protection works Page 4
+
surcharge load (KN/m) lateral pressure (KN/m)
Fig: Loads on piles
Calculation for protection works Page 5
Pile and anchor locations Anchor forces (KN)
Fig: Horizontal reactions at anchors from analysis
Calculation for protection works Page 6
BMD from analysis, (KNm) SFD from analysis (KN)
Fig: bending moment and shear force diagrams
Calculation for protection works Page 7
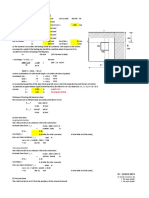
3. Reinforcements in the piles
Flexural reinforcements (mm2) Shear reinforcements (mm2)
Flexural reinforcements
N = 3,745/314 = 11.92
It is important to consider some reinforcements in the piles may be cut during
placing of anchors.
Therefore, at minimum place 14∅20 reinforcements in the piles
Calculation for protection works Page 8
Shear reinforcements
The analysis/design shows the concrete capacity is adequate to resist the shear in
the piles. Therefore minimum tie provisions are adequate.
Anchors, strands and reinforcements
From the previous analysis, it was shown that the maximum horizontal force is
280KN,
With the 250 inclination in the anchor placement, the anchor force has to be
F= 280 / cos 25 = 309KN
Therefore, the required number of strands is
N = F/(fyd x A)
Strand anchor strength is 1770 Mpa
A= Π x (0.6x25.4)2 / 4 = 182.4mm2
N= 309 x 1000 / (1539 x 182.4) = 1.1
2 strands are adequate nonetheless 3 strands are used.
Alternatively reinforcements can be used in place of strands.
Whenever the length of reinforcements should exceed 12m, lapped bars have to be
welded by a professional.
N = F/(fyd x A)
Reinforcement strength is 400 Mpa
Calculation for protection works Page 9
A= Π x (24)2 / 4 = 452mm2
N= 309 x 1000 / (347 x 452) = 1.97
3∅24 reinforcements are adequate.
Anchorage length:
The diameter of grouted anchor is estimated as 0.10m from previous experiences,
Anchorage length is estimated as follows;
L = F / (Π x d x (2/3) x (Cu))
L = 309 x 1000 / (Π x 0.10 x (2/3) x (250))
L= 5,852mm
Considering an additional 1000mm slip length beyond the angle of repose,
L=7000mm is adequate.
L = 8000mm is provided
Calculation for protection works Page 10
You might also like
- Mathcad - MWD056g - Glass Wall With Feature1Document36 pagesMathcad - MWD056g - Glass Wall With Feature1MichaeluiMichaeluiNo ratings yet
- Cylindrical Compression Helix Springs For Suspension SystemsFrom EverandCylindrical Compression Helix Springs For Suspension SystemsNo ratings yet
- Example of Design of A Deep Beam Using Strut Tie ModelDocument34 pagesExample of Design of A Deep Beam Using Strut Tie Modeldaniel workuNo ratings yet
- Strength of Materials and Structures: An Introduction to the Mechanics of Solids and StructuresFrom EverandStrength of Materials and Structures: An Introduction to the Mechanics of Solids and StructuresRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Scaffolding Formwork Design CalculationsDocument17 pagesScaffolding Formwork Design Calculationsbhadrakmishra100% (3)
- Advanced Opensees Algorithms, Volume 1: Probability Analysis Of High Pier Cable-Stayed Bridge Under Multiple-Support Excitations, And LiquefactionFrom EverandAdvanced Opensees Algorithms, Volume 1: Probability Analysis Of High Pier Cable-Stayed Bridge Under Multiple-Support Excitations, And LiquefactionNo ratings yet
- Isolated Footing Design ProblemDocument5 pagesIsolated Footing Design ProblemthabisNo ratings yet
- Structural Design of Raft Foundation Based On Geotechnical AnalysisDocument6 pagesStructural Design of Raft Foundation Based On Geotechnical AnalysisNaresh KumarNo ratings yet
- DESIGN CALCULATIONS - GL-03 2509 - 4.0mDocument17 pagesDESIGN CALCULATIONS - GL-03 2509 - 4.0mmsiddiq1No ratings yet
- 1994 Composite Beam Design ExampleDocument10 pages1994 Composite Beam Design Examplebalamurali031100% (2)
- Reinforced Concrete Beam Deflection and Minimum ThicknessDocument7 pagesReinforced Concrete Beam Deflection and Minimum ThicknessLester John PrecillasNo ratings yet
- Preliminary Structural Design PDFDocument8 pagesPreliminary Structural Design PDFKenny Manuel VettoorNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5 Year 2-1Document28 pagesLecture 5 Year 2-1Saurabh ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Moment of ResistanceDocument10 pagesMoment of ResistanceBabaYakeNo ratings yet
- Design Calculations For Aluminium Profile 13794Document14 pagesDesign Calculations For Aluminium Profile 13794Wilson PesantezNo ratings yet
- Composite Slab For Proposed Residential House-1Document7 pagesComposite Slab For Proposed Residential House-1JosephNo ratings yet
- New Example 14 Simple FrameDocument6 pagesNew Example 14 Simple FrameminnNo ratings yet
- Design of LiningDocument20 pagesDesign of LiningVikas ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Transverse-Design771 TriDocument17 pagesTransverse-Design771 TriBasava SowmyaNo ratings yet
- One-way and Two-way Slab DesignDocument5 pagesOne-way and Two-way Slab DesignMark Kim BadiangNo ratings yet
- Mathcad - PART II Ceiling (ICU) 20200602 (Update) - 2Document418 pagesMathcad - PART II Ceiling (ICU) 20200602 (Update) - 2BQ HeNo ratings yet
- Design of Bridge Superstructure ElementsDocument9 pagesDesign of Bridge Superstructure ElementsPrakash Singh Rawal100% (1)
- Sky Light - 1Document32 pagesSky Light - 1Nazar Bazaraa100% (1)
- Design of Ground Supported Fiber Reinforced Slab Based On AciDocument12 pagesDesign of Ground Supported Fiber Reinforced Slab Based On AciJhon Guzman CALIDADNo ratings yet
- Abutment Design Example To BD 30Document16 pagesAbutment Design Example To BD 30Hermann PankowNo ratings yet
- Design Calculations For Aluminium CW ProfileDocument5 pagesDesign Calculations For Aluminium CW Profilemsiddiq1100% (1)
- BS8110 SpreadsheetDocument30 pagesBS8110 SpreadsheetPcEng100% (2)
- 13UJ BeamsDocument82 pages13UJ BeamsthembalethuNo ratings yet
- Jutpani SS20Document23 pagesJutpani SS20Suman NakarmiNo ratings yet
- Calculation B7Document5 pagesCalculation B7gayan jayasingheNo ratings yet
- RC2009 University of HongKong Reinforced Concrete DesignDocument29 pagesRC2009 University of HongKong Reinforced Concrete DesignApril IngramNo ratings yet
- CVX7640 32Document14 pagesCVX7640 32malingauomNo ratings yet
- Continuous BeamDocument24 pagesContinuous Beamdixn__100% (1)
- Doubly Reinforced Beam Design MethodologyDocument12 pagesDoubly Reinforced Beam Design MethodologyZayyan RomjonNo ratings yet
- Purlin and Roof DesignDocument4 pagesPurlin and Roof DesignIndaLastariee100% (1)
- Purlin and Roof DesignDocument4 pagesPurlin and Roof DesignRayan MahgoubNo ratings yet
- Purlin and Roof Design PDFDocument4 pagesPurlin and Roof Design PDFAlthara BaldagoNo ratings yet
- Purlin PDFDocument4 pagesPurlin PDFHassan AlaskaNo ratings yet
- Roof Truss Design and Purlin AnalysisDocument8 pagesRoof Truss Design and Purlin AnalysisJohn Lancer FabobNo ratings yet
- Purlin and Roof Design Terminology of Truss: Rafter (Top Chord)Document4 pagesPurlin and Roof Design Terminology of Truss: Rafter (Top Chord)david karasilaNo ratings yet
- Purlin and Roof DesignDocument4 pagesPurlin and Roof DesignKshitiz JoshiNo ratings yet
- Purlin and Roof Design PDFDocument4 pagesPurlin and Roof Design PDFHassan AlaskaNo ratings yet
- Purlin and Roof DesignDocument4 pagesPurlin and Roof DesignKhairul JaggerNo ratings yet
- Purlin and Roof DesignDocument4 pagesPurlin and Roof DesignErald PeriaNo ratings yet
- PURLIN AND ROOF TRUSS DESIGNDocument4 pagesPURLIN AND ROOF TRUSS DESIGNAnonymous GamerNo ratings yet
- Design of intermediate diaphragm for Bahria Town bridgeDocument14 pagesDesign of intermediate diaphragm for Bahria Town bridgeFAIZAN AHMEDNo ratings yet
- Reinforced Concrete I: Lecture-6Document58 pagesReinforced Concrete I: Lecture-6yihienewNo ratings yet
- Design of One Way SlabDocument31 pagesDesign of One Way SlabRam Ingalkar90% (10)
- Design Analysis 1Document13 pagesDesign Analysis 1Katy PerryNo ratings yet
- Lecture 9 - Concrete Beam ReinforcementDocument21 pagesLecture 9 - Concrete Beam ReinforcementKhaled AlregebNo ratings yet
- Eccentric Footing DesignDocument12 pagesEccentric Footing Designsaubhagya majhiNo ratings yet
- Design of Cantilever Retaining WallDocument23 pagesDesign of Cantilever Retaining WallD.V.Srinivasa RaoNo ratings yet
- CAUSON Assignment 1MDocument5 pagesCAUSON Assignment 1MEmmanuel CausonNo ratings yet
- MBW Truss - Report PDFDocument11 pagesMBW Truss - Report PDFsolebNo ratings yet
- Circular Slab Design PDFDocument15 pagesCircular Slab Design PDFSubrata BiswasNo ratings yet
- Advaita Dictionary in QuotationsDocument4 pagesAdvaita Dictionary in Quotationsmal_sri6798No ratings yet
- Beams Reinforced For Tension OnlyDocument47 pagesBeams Reinforced For Tension OnlyArkie TectureNo ratings yet
- Prestressed Beam Girder Floor Made of High Strength ConcreteDocument18 pagesPrestressed Beam Girder Floor Made of High Strength ConcreteSebastian GusetuNo ratings yet
- Calculation Sheet: Esign Xample Xially Loaded Column in FireDocument8 pagesCalculation Sheet: Esign Xample Xially Loaded Column in FireVDCNo ratings yet
- Measures of Central Tendency and DispersionDocument19 pagesMeasures of Central Tendency and Dispersionkidi mollaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Overview of ResearchDocument24 pagesChapter 1 Overview of Researchkidi mollaNo ratings yet
- 14) Structure Guideline August 2017Document40 pages14) Structure Guideline August 2017lwin_oo2435No ratings yet
- Worked Example To Eurocode 2 Vol. 1Document224 pagesWorked Example To Eurocode 2 Vol. 1vbisketi100% (25)
- Standard Specification For Building MaterialsDocument18 pagesStandard Specification For Building Materialskidi mollaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2.1.2018 - Frame - Wind Load PDFDocument56 pagesChapter 2.1.2018 - Frame - Wind Load PDFHawaiiChongNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Hypothesis TestingDocument27 pagesChapter 5 Hypothesis Testingkidi mollaNo ratings yet
- Research Design GuideDocument67 pagesResearch Design Guidekidi mollaNo ratings yet
- Isolated footing design calculationsDocument9 pagesIsolated footing design calculationskidi mollaNo ratings yet
- RC Structural Design Review Checklist: Plot No. Date Location Owner ConsultantDocument2 pagesRC Structural Design Review Checklist: Plot No. Date Location Owner ConsultantyosiboyNo ratings yet
- How To Design R.C. Flat Slabs Using Finite Element AnalysisDocument16 pagesHow To Design R.C. Flat Slabs Using Finite Element Analysisocenkt100% (10)
- B+G+2 Residential Building ST.: Summary of PricesDocument51 pagesB+G+2 Residential Building ST.: Summary of Priceskidi mollaNo ratings yet
- Type Contract Owner Name Here) : Site DiaryDocument3 pagesType Contract Owner Name Here) : Site Diarypawan_aggarwal_22No ratings yet
- Notice To Proceed To Contractor: Appendix 8 Sample Letter 2Document1 pageNotice To Proceed To Contractor: Appendix 8 Sample Letter 2kidi mollaNo ratings yet
- Plastic Analysis of Unbraced Portal Frames of Steel Structures in PDFDocument99 pagesPlastic Analysis of Unbraced Portal Frames of Steel Structures in PDFbiniamNo ratings yet
- 123961-Article Text-338797-1-10-20151015Document20 pages123961-Article Text-338797-1-10-20151015Maria Dasilva MarichoyNo ratings yet
- Approval LetterDocument1 pageApproval Letterkidi mollaNo ratings yet
- Awetu SF1 PDFDocument3 pagesAwetu SF1 PDFkidi mollaNo ratings yet
- Area of SteelDocument4 pagesArea of Steelkidi mollaNo ratings yet
- CH 44 - Subsoil DrainageDocument8 pagesCH 44 - Subsoil DrainageLit Phen TuNo ratings yet
- Footing design analysisDocument3 pagesFooting design analysiskidi mollaNo ratings yet
- Remark Material Quality: Footing DesignDocument1 pageRemark Material Quality: Footing Designkidi mollaNo ratings yet
- Compaction TestDocument1 pageCompaction Testkidi mollaNo ratings yet
- Strap Footing: Material Quality Remark &assumptionsDocument3 pagesStrap Footing: Material Quality Remark &assumptionskidi mollaNo ratings yet
- Askale Worke March 3, 2020Document41 pagesAskale Worke March 3, 2020kidi mollaNo ratings yet
- Strap Footing: Material Quality Remark &assumptionsDocument3 pagesStrap Footing: Material Quality Remark &assumptionskidi mollaNo ratings yet
- 044-Rebar Control SheetDocument1 page044-Rebar Control Sheetkidi mollaNo ratings yet
- Ato Gosaye ReportDocument30 pagesAto Gosaye Reportkidi mollaNo ratings yet
- CRYSTALLIZATION PROCESS OPTIMIZATIONDocument42 pagesCRYSTALLIZATION PROCESS OPTIMIZATIONKTINE0894% (16)
- Wheatstone Bridge-Giant Magnetoresistance (GMR) Sensors Based On Co/Cu Multilayers For Bio-Detection ApplicationsDocument6 pagesWheatstone Bridge-Giant Magnetoresistance (GMR) Sensors Based On Co/Cu Multilayers For Bio-Detection ApplicationsRISKA PRAMESWARI PUTRINo ratings yet
- Acoustic Treatment Guidelines - Cinema RoomsDocument16 pagesAcoustic Treatment Guidelines - Cinema RoomsMatia CamporaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 - Stability of SlopesDocument34 pagesChapter 11 - Stability of SlopesAashish regmi0% (1)
- Lecture 27Document36 pagesLecture 27alfredomotaNo ratings yet
- S9Fe-Ivb-36: Relate Impulse and Momentum To Collision of Objects (E.G, Vehicular Collision) (S9Fe-Ivb-36)Document6 pagesS9Fe-Ivb-36: Relate Impulse and Momentum To Collision of Objects (E.G, Vehicular Collision) (S9Fe-Ivb-36)Lorieley EugenioNo ratings yet
- Design, Implementation and Validation of A Motorized Wedge Filter For A Telecobalt Machine (Bhabhatron-II)Document7 pagesDesign, Implementation and Validation of A Motorized Wedge Filter For A Telecobalt Machine (Bhabhatron-II)arakbaeNo ratings yet
- Compressor Part 3Document64 pagesCompressor Part 3ShishajimooNo ratings yet
- Unit 9 (DESIGN OF SHEAR REINFORCEMENT)Document29 pagesUnit 9 (DESIGN OF SHEAR REINFORCEMENT)Zara Nabilah76% (25)
- Brochures ClimaPRO+Document16 pagesBrochures ClimaPRO+Dam Ngoc KienNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 Uniform Circular MotionDocument10 pagesChapter 9 Uniform Circular MotionZhu JiankunNo ratings yet
- Chapter C21 Site-Specific Ground Motion Procedures For Seismic DesignDocument16 pagesChapter C21 Site-Specific Ground Motion Procedures For Seismic DesignsharethefilesNo ratings yet
- Structural Analysis of Aircraft Wing J Nose Panel Using Mono and Multi Core Composite MaterialsDocument6 pagesStructural Analysis of Aircraft Wing J Nose Panel Using Mono and Multi Core Composite MaterialsstaedtlerpNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Fracture Mechanics of Concrete: 1.1 GeneralDocument2 pagesIntroduction To Fracture Mechanics of Concrete: 1.1 GeneralOat GTNo ratings yet
- 9259478Document64 pages9259478Brajesh Kumar100% (1)
- Final Project Design of Five Star Hotel.Document1 pageFinal Project Design of Five Star Hotel.Stephen LeyeNo ratings yet
- Instrumental Analysis ManualDocument71 pagesInstrumental Analysis ManualArmando PerezNo ratings yet
- Blue Strand Wire RopeDocument13 pagesBlue Strand Wire Ropemary joy PanamaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry HHW Competency Based QuestionsDocument4 pagesChemistry HHW Competency Based QuestionsMehjabeen NizamiNo ratings yet
- Unified Formalism For Erbium-Doped Fiber Amplifiers and LasersDocument10 pagesUnified Formalism For Erbium-Doped Fiber Amplifiers and LasersVastavikta SinghNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Semiconductor Detectors: P (T) CT Exp (-E /2kT)Document18 pagesChapter 7 Semiconductor Detectors: P (T) CT Exp (-E /2kT)Phani TejaNo ratings yet
- EML 3500 Online Course GuideDocument10 pagesEML 3500 Online Course GuideAbood M. ShaatNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lessson Plan in Properties of Gases - Boyle's LawDocument5 pagesDetailed Lessson Plan in Properties of Gases - Boyle's Lawjonelllantero032No ratings yet
- Remanit: Stainless, Acid and Heat-Resistant Special Steel Grades À La CarteDocument36 pagesRemanit: Stainless, Acid and Heat-Resistant Special Steel Grades À La Cartepipedown456No ratings yet
- Wilberforce PendulumDocument9 pagesWilberforce PendulumLeo KutsNo ratings yet
- Science 2Document16 pagesScience 2RicalynNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Fluid MechanicsDocument57 pagesChapter 3 Fluid MechanicsYtayew, Gizaw BirhanuNo ratings yet
- SimulationDocument143 pagesSimulationnilesh_erusNo ratings yet
- 01 - 1 - Introduction To Separation Processes - StudentsDocument36 pages01 - 1 - Introduction To Separation Processes - StudentsAdruNo ratings yet