Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Ambe School-Cbse: SECTION-A (20×1 20M)
Uploaded by
Versus Babu0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views2 pagesThis document is the periodic test for 11th grade physics students. It contains a 20 question multiple choice section testing concepts like units, significant figures, kinematics, Newton's laws, work-energy theorem, and momentum conservation. It also contains 2 multi-part conceptual questions involving kinematics and circular motion. The test covers a wide range of fundamental physics topics and is assessing the students' understanding through practical calculations and conceptual questions.
Original Description:
Original Title
4077186_1631932592
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document is the periodic test for 11th grade physics students. It contains a 20 question multiple choice section testing concepts like units, significant figures, kinematics, Newton's laws, work-energy theorem, and momentum conservation. It also contains 2 multi-part conceptual questions involving kinematics and circular motion. The test covers a wide range of fundamental physics topics and is assessing the students' understanding through practical calculations and conceptual questions.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views2 pagesAmbe School-Cbse: SECTION-A (20×1 20M)
Uploaded by
Versus BabuThis document is the periodic test for 11th grade physics students. It contains a 20 question multiple choice section testing concepts like units, significant figures, kinematics, Newton's laws, work-energy theorem, and momentum conservation. It also contains 2 multi-part conceptual questions involving kinematics and circular motion. The test covers a wide range of fundamental physics topics and is assessing the students' understanding through practical calculations and conceptual questions.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
AMBE SCHOOL-CBSE
Manjalpur, Vadodara -11.
Periodic Test-II Year: 2021-22
Subject : Physics
Grade: XI Science Max. Marks: 40
Day & Date: Saturday, 18th September’21 Duration: 1 ½ Hours
Name of the Student: ____________________________________________________________ Section: ________ Seat No. ________
SECTION-A (20×1=20M)
1. The SI unit of universal gravitational constant G:
(a) Nmkg-2 (b) Nm2kg-2 (c) Nm2kg-1 (d)Nmkg-1
2. The number of significant figures in the distance of one light year , 9.4605×1015 m
(a) one (b) three (c)five (d)seven
3. A boy starts from a point A, travels to a point B at a distance of 3 km from A and returns to A. If he
takes two hours to do so, his speed is
(a) 3 km/h (b) zero (c) 2 km/h (d) 1.5 km/h
4. Distance-time graph of a body at rest is
(a) parallel to time axis
(b) parallel to distance axis
(c) inclined to time axis
(d) perpendicular to both axis
5. A body is projected horizontally with a velocity of 4m/s. The velocity of the body after 0.7 s is
nearly (take g=10m/s2)
(a) 10m/s (b) 8m/s (c) 19.2 m/s (d) 11m/s
6. When a body P moves on a circular path, the centripetal acceleration is
(a) directed inwards from P, to the centre of the circle
(b) directed tangential to the circumference of the circle, at P
(c) directed perpendicular to the plane of the circle, at P
(d) directed outward, perpendicular to the circumference of the circle
7. A passenger in a moving bus is thrown forward when the bus is suddenly stopped. This is
explained
(a) by Newton's first law
(b) by Newton's second law
(c) by Newton's third law
(d) by the principle of conservation of momentum
8. A body is sliding down a rough inclined plane which makes an angle of 30 degree with the
horizontal. If the coefficient of friction is 0.26, the acceleration in m/s² is
(a) 1.95 (b) 2.78 (c) 3.47 (d) 4.6
9. According to Work-Energy theorem, the work done by the net force on a particle is equal to the
change in its
(a) kinetic energy (b) angular momentum
(c) linear momentum (d) potential energy
10. A body of mass 20kg falls vertically through a height of 10m. Its loss of potential energy is
(a) 300 J (b) 4000 J (c) 1000 J (d) 1960 J
11. The acceleration of a moving body can be found from
(a) area under velocity – time graph (b) area under distance -time graph
(c) slope of the velocity- time graph (d) slope of distance-time graph
12. Percentage errors in the measurement of mass and speed are 2% and 3% respectively. The error
in the estimate of kinetic energy obtained by measuring mass and speed will be
(a) 8 % (b) 2 % (c) 12% (d) 10%
In the following questions, a statement of assertion(A) is followed by a statement of reason (R).
Mark the correct choice as :
(a) If both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
(b) If both assertion and reason are true and reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
(c) If assertion is true but reason is false.
(d) If both assertion and reason are false.
13. Assertion: In javelin throw, the athlete throws the projectile at an angle slightly more than 450.
Reason: The maximum range does not depend upon angle of projection.
14. Assertion: On a banked curved track, vertical component of normal reaction provides the
necessary centripetal force.
Reason: Centripetal force is not always required for turning.
15. Assertion: In an elastic collision between two bodies, the energy of each body is conserved.
Reason: The total energy of an isolated system is conserved.
CASE ST TUDY BA ASED QUE ESTIONS S: (Questiions 16 tot 20)
PARAGR RAPH: C Consider an isolateed system m of n interacting pparticles.. The muttual forcees betweeen
pairs off particless in the sy
ystem cau
use changges in momenta off the indiv vidual parrticles. By
y third law
w,
the muttual forces betweeen any paair of partticles are equal and oppositte. By seccond law, The chan nge in
momentta for anyy pair of particles
p aare Ft and F t . Thus tthe momentum ch hanges caancel in paairs
and totaal momen ntum of th he system
m remainss constan nt. This leads to a fundamen
f ntal princciple of phhysics
called thhe law of conservaation of linear mom mentum. This law states th hat the tottal linear momentum of
an isolated systeem of inteeracting pparticles is conservved. The rrecoil of a gun on ffiring, exp
plosion of
o a
bomb in nto differeent fragm ments duee to intern
nal forcess, the worrking of rockets
r an
nd jet planes, etc; can
c
be explaained on tthe basis of momeentum con nservatioon.
16. A gu un fires a bullet of mass 50 g with a velocity v o 30m/s.. Becausee of this, th
of he gun is pushed backb
with a velocity
v off 1m/s. The
T mass of the gun n is
(a) 5.5 kg
k (b) 3.5kg
3 (c)
( 1.5kg ((d)0.5kg
17. A bo ody of maass M mov ving with h velocity V explod des into twwo equal parts. If o one comees to rest and
the other
o bod dy moves with velo ocity v, what
w woulld be the value of v? v
V
(a) V (b) (c)
( 4V ((d) 2V
2
18. A bo ody of masss 0.25kg is i projecteed with mu uzzle velo ocity 100m
m/s from thet tank off mass 100 0kg. Calcu
ulate
the recoils
r velo
ocity of th
he tank.
(a) 5m/s
5 (b) 25m/s
2 (c)0.5m/s
( ((d)0.25m//s
19. A bu ullet is fired
d from a rifle.
r If the rifle recoiils freely th
hen the kiinetic enerrgy of the rifle will be
b
(a) less than tthat of bu ullet (b)
( more than thatt of bullett
(c) same
s as thhat of bulllet (d)
( equal to or lesss than thaat of bulleet
20. A bo ody of masss m stand ds on end o of a wooden plank of o length L and mass M. The p plank is flooating on water.
w
If thee body waalks from one o end off the plank k to the otther end att a constan nt speed, tthe resultiing
displlacement of the plan nk is givenn by :
m
mL ML mL L
mL
(a) (b) (c)
( ((d)
M m M m M m
SECCTION-B (2×2=4M M)
21. If x=
=2at-5bt2, where x is in metters and t in seconnds, find tthe dimen
nsions of a and b.
22. A cyyclist movves along a circular path of radius 700 m. If he completees one roound in 111 s, calcullate
i) total
t lengtth of path
h ii) magnituude of thee displaceement iii) aaverage speed
s
SECCTION-C (3×2=6M
( M)
23. Statee and pro
ove Work k-Energy ttheorem.
24. A maan of masss 70 kg staands on a w weighing scale in a lift which is movingg.
a) Up
pwards wwith a unifoorm speed d of 10 mss−1.
b) Do
ownward ds with a uniform
u accceleration
n of 5 ms−22.
c) Up
pwards wwith a unifoorm acceleeration of 5 ms−2.
Whaat would bbe the readding on thee scale in each
e case??
Whaat would bbe the readding if the lift mechaanism faileed and it h
hurtled do
own freelyy under graavity?
SECTTION-D (5×2=10M
( M)
25. Statee triangle llaw of vecctor addition. Give analytical
a t
treatment t to find th
he magnituude and diirection off a
resultant vecto or by usinng this law
w.
ORR
A prrojectile iss projecteed horizo ontally wiith a velocity u. Show that its trajecttory is parrabolic. And A
obtaain expresssions forr:
(a) Time
T of flight (b) Hoorizontal range (c) vvelocity ata any insttant t.
26. (a) State
S the llaws of limiting friction.
(b) Find
F the aacceleratiion of a body slidin ng down a rough iinclined plane.
p
ORR
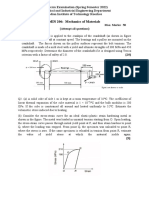
The figure
f shoows the po osition-tim
me graph of
o a body ofo mass 0.0 04 kg. Sugggest a suiitable physical conteext for
this motion.
m W
What is thee time betwween two consecutiive impulsses received by the body? Wh hat is the
magn nitude of eeach impu ulse?
*-*-*-**-*-*
You might also like
- Laws of Motion Advanced Level Problems For IIT-JEEDocument5 pagesLaws of Motion Advanced Level Problems For IIT-JEEEr. Vineet Loomba (IIT Roorkee)89% (9)
- 2004 Corolla Electrical Diagram - Engine ControlDocument12 pages2004 Corolla Electrical Diagram - Engine ControlNick Baptiste50% (2)
- Suzuki Xl7 Grand Vitara XL 7 Jc636 2007 2009 en Es InfoDocument68 pagesSuzuki Xl7 Grand Vitara XL 7 Jc636 2007 2009 en Es InfoKandy KnNo ratings yet
- C4.4 - C7.1 A&I LEBH0019-02 EPSA Rev1Document116 pagesC4.4 - C7.1 A&I LEBH0019-02 EPSA Rev1Mohamed ibrahem100% (1)
- Audi A3-A4 Hidden Secret Service MenuDocument4 pagesAudi A3-A4 Hidden Secret Service MenuKakasi HatakeNo ratings yet
- 2 - Properties (Mass Density, Specific Weight, Specific Gravity, Bulk Modulus, Viscosity) PDFDocument13 pages2 - Properties (Mass Density, Specific Weight, Specific Gravity, Bulk Modulus, Viscosity) PDFJojimar JulianNo ratings yet
- Sauer Danfoss 42lDocument68 pagesSauer Danfoss 42ljuan100% (2)
- Geotech Handouts 2013Document138 pagesGeotech Handouts 2013Wong ChingNo ratings yet
- Air Leakage in Vacuum VesselsDocument2 pagesAir Leakage in Vacuum VesselsAccio_thebest100% (3)
- Johnston Sweepers CN and CX200 Operators Guide 50072 MHDocument72 pagesJohnston Sweepers CN and CX200 Operators Guide 50072 MHSimon Cooper0% (1)
- High Temperature Air Combustion Technology (HTAC) (Regenerative Furnace)Document7 pagesHigh Temperature Air Combustion Technology (HTAC) (Regenerative Furnace)Gary LiNo ratings yet
- Periodic TestDocument2 pagesPeriodic TestCR foreverNo ratings yet
- Physics Test Series 1 MaiDocument5 pagesPhysics Test Series 1 MaiSourav MukherjeeNo ratings yet
- Mock 2022-23Document5 pagesMock 2022-23RAJ RUPALINo ratings yet
- Class 11 Pre Annual Physics Set 1 QPDocument8 pagesClass 11 Pre Annual Physics Set 1 QPSanjukta ChandaNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 02 Sept 2023Document6 pagesAdobe Scan 02 Sept 2023Divyesh .RNo ratings yet
- Sample Paper Physics - Grade 11-Model ExaminationDocument12 pagesSample Paper Physics - Grade 11-Model ExaminationSuhaim SahebNo ratings yet
- Physics (Question Paper)Document7 pagesPhysics (Question Paper)Jay Doshi ShashikantNo ratings yet
- Bitsat 99Document14 pagesBitsat 99PRIYANSHU PANJANo ratings yet
- Physics QPDocument6 pagesPhysics QPch22b039No ratings yet
- Pysics 1003endDocument2 pagesPysics 1003endAdewumi AdinoyNo ratings yet
- Fiziks: Institute For NET/JRF, GATE, IIT JAM, M.Sc. Entrance, JEST, TIFR and GRE in Physics D.U. M.Sc. 2017Document10 pagesFiziks: Institute For NET/JRF, GATE, IIT JAM, M.Sc. Entrance, JEST, TIFR and GRE in Physics D.U. M.Sc. 2017most funny videoNo ratings yet
- Assignment & Previous Years' Questions: 2 3 4 X T T TDocument12 pagesAssignment & Previous Years' Questions: 2 3 4 X T T TAshi AggarwalNo ratings yet
- AIIMS Solved Paper 2014Document51 pagesAIIMS Solved Paper 2014Débàshis DashNo ratings yet
- Basara Gnanasaraswathi Campus Kakatiya HillsDocument4 pagesBasara Gnanasaraswathi Campus Kakatiya HillsNitin SharmaNo ratings yet
- Student's Name: Student ID:: A) MCQ Answer Sheet (5 M)Document2 pagesStudent's Name: Student ID:: A) MCQ Answer Sheet (5 M)Nam Anh Nguyễn HữuNo ratings yet
- 11 Phy - Set B Ut-2Document4 pages11 Phy - Set B Ut-2dikshachoud44No ratings yet
- JR Centre of Mass Spp23Document12 pagesJR Centre of Mass Spp23my missionNo ratings yet
- Cbse 2024 by Neeraj Class 12Document8 pagesCbse 2024 by Neeraj Class 12sciencepedia9No ratings yet
- Physics QPDocument13 pagesPhysics QPAniket DebnathNo ratings yet
- PPPPPPPPDocument102 pagesPPPPPPPPTGX DevilNo ratings yet
- IAS Mains Physics 2004Document9 pagesIAS Mains Physics 2004RATNADEEP BANERJEENo ratings yet
- Namma Kalvi 10th Science Unit Test Question Papers em 220182Document24 pagesNamma Kalvi 10th Science Unit Test Question Papers em 220182sooryasaran1No ratings yet
- 11.01.23 - SR (ALL) - Jee - Main - GTM-5 - QP FINAL (FN)Document22 pages11.01.23 - SR (ALL) - Jee - Main - GTM-5 - QP FINAL (FN)Dinesh BabuNo ratings yet
- Ch-07 Rotational Dynamics Daily: KinematicsDocument4 pagesCh-07 Rotational Dynamics Daily: Kinematicskona14018No ratings yet
- 11 pHYSICS Model Paper-2Document2 pages11 pHYSICS Model Paper-2Venkatesh MNo ratings yet
- 05 - Laws of MotionDocument3 pages05 - Laws of MotionMathan KalyanasundaramNo ratings yet
- Class 11 Assignment 1Document4 pagesClass 11 Assignment 1Darsh TodiNo ratings yet
- Ch-Laws of Motion DPP 03Document5 pagesCh-Laws of Motion DPP 03ROHANNo ratings yet
- Class XI Half Yearly 2019Document3 pagesClass XI Half Yearly 2019Vishal GuptaNo ratings yet
- Physics Past Questions For Sss Senior SecondaryDocument5 pagesPhysics Past Questions For Sss Senior SecondaryJensen MutairuNo ratings yet
- SQP Hy 11 2022 23Document13 pagesSQP Hy 11 2022 23It's all About fitnessNo ratings yet
- Remains Same: Vector Quantities (ch#2) A. Ve BDocument3 pagesRemains Same: Vector Quantities (ch#2) A. Ve BKamran AliNo ratings yet
- Part-1: Physics: (B) 4 S (C) 8 S 500 G 300 G (D) 1 SDocument5 pagesPart-1: Physics: (B) 4 S (C) 8 S 500 G 300 G (D) 1 SSankar UmaNo ratings yet
- University THE 2017:: OF SemesterDocument85 pagesUniversity THE 2017:: OF Semesterمريم صباNo ratings yet
- AIEEE2003Document45 pagesAIEEE2003alabasmNo ratings yet
- Physics M (1st) Dec2019Document2 pagesPhysics M (1st) Dec2019love preetNo ratings yet
- Physics HSSC 1Document5 pagesPhysics HSSC 1Eman AliNo ratings yet
- Diploma Examn, Ation March, II: EngneeringDocument3 pagesDiploma Examn, Ation March, II: EngneeringSudama kumarNo ratings yet
- Class-11 Physics PDFDocument5 pagesClass-11 Physics PDFAlexis Ameen CruzerNo ratings yet
- Sucess Study Circle Monthly Test Sub-Physics (11) F.M-70 Tine 2hrsDocument4 pagesSucess Study Circle Monthly Test Sub-Physics (11) F.M-70 Tine 2hrsAshok PradhanNo ratings yet
- Physics Xi Simple Harmonic Motion Name: - : To Make The Frequency Double of An Oscillator, We Have ToDocument1 pagePhysics Xi Simple Harmonic Motion Name: - : To Make The Frequency Double of An Oscillator, We Have TolohanopiryaNo ratings yet
- 2009 Me - 101 PDFDocument11 pages2009 Me - 101 PDFArka BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- Set A QP Pre Annual XiDocument10 pagesSet A QP Pre Annual Xianish.chandrasekar.bloreNo ratings yet
- JEE ADVANCED-Assignment: Presented by Kailash SharmaDocument6 pagesJEE ADVANCED-Assignment: Presented by Kailash SharmaGulafsha PerweenNo ratings yet
- SQP Class 11th PhysicsDocument41 pagesSQP Class 11th Physicsprecisebusiness23No ratings yet
- Eklavya (NEET) Sample Paper - 1Document58 pagesEklavya (NEET) Sample Paper - 1arja keerthanaNo ratings yet
- Phy 1 RevisionDocument2 pagesPhy 1 RevisionHafsah KhalidNo ratings yet
- Otp - 1 PDFDocument5 pagesOtp - 1 PDFBBA GNo ratings yet
- ANNUAL-11th PHYSICS-SAMPLEDocument8 pagesANNUAL-11th PHYSICS-SAMPLEsyed ayaaanNo ratings yet
- Zq-Mult Choice Test 3 CSBDocument8 pagesZq-Mult Choice Test 3 CSBdimensiondmcNo ratings yet
- SAMPLE PAPER 3 QuestionDocument21 pagesSAMPLE PAPER 3 QuestionmuthuNo ratings yet
- JEE 2024 PAPERS - CompressedDocument413 pagesJEE 2024 PAPERS - CompressedPranavi MuthusamyNo ratings yet
- XII PhysicsDocument60 pagesXII PhysicsBhavana ShindeNo ratings yet
- +1 Physics: Adayar - Adambakkam - East Tambaram - Pallavaram - PammalDocument18 pages+1 Physics: Adayar - Adambakkam - East Tambaram - Pallavaram - Pammalvsivaraman94No ratings yet
- JEE Paper 10 Solutions - UnlockedDocument27 pagesJEE Paper 10 Solutions - UnlockedDhanalakshmi ThiyagarajanNo ratings yet
- Physics: (Mock Test-3) 1Document7 pagesPhysics: (Mock Test-3) 1Piyush khadatkarNo ratings yet
- List of Registered StudentsDocument19 pagesList of Registered StudentsNilanjan SarkarNo ratings yet
- Project File LawsDocument5 pagesProject File LawsSonaNo ratings yet
- RCD 2 (Neu)Document9 pagesRCD 2 (Neu)Paul RoqueNo ratings yet
- MidTermExamination MIN206Document2 pagesMidTermExamination MIN206keshavmandowraNo ratings yet
- Computational Fluid Dynamics Simulation of Microfluidic Droplet Formation Using The Two-Phase Level Set MethodDocument13 pagesComputational Fluid Dynamics Simulation of Microfluidic Droplet Formation Using The Two-Phase Level Set MethodApurva PatelNo ratings yet
- TURBINEDocument10 pagesTURBINEi AnuRagNo ratings yet
- L-4 COC Knowlge Exam 2013Document6 pagesL-4 COC Knowlge Exam 2013Abdulkerim Sebre100% (1)
- James Zarrinpour, M.S, EIT Forterra Pipe & Precast: ACPA 2018 Pipe School - Murfreesboro, TennesseeDocument36 pagesJames Zarrinpour, M.S, EIT Forterra Pipe & Precast: ACPA 2018 Pipe School - Murfreesboro, TennesseeTete Lunarejo AguilarNo ratings yet
- Massey Ferguson MF 3645 TRACTOR Service Parts Catalogue Manual (Part Number 1637213)Document15 pagesMassey Ferguson MF 3645 TRACTOR Service Parts Catalogue Manual (Part Number 1637213)qlb898316No ratings yet
- Mohd Fazlee - CV - Cert Updated Oct 20201Document12 pagesMohd Fazlee - CV - Cert Updated Oct 20201yousab creator2No ratings yet
- Amercron - Your Partner in Solution SourceDocument2 pagesAmercron - Your Partner in Solution SourceAbigail Panlilio0% (1)
- Chapter 4 PDFDocument20 pagesChapter 4 PDFSiti Arbaiyah AhmadNo ratings yet
- Jindal MLC Order Calculation - RatesDocument14 pagesJindal MLC Order Calculation - Ratesbewithkiran0% (1)
- Problem Description: Design of Chain Drive For Power Transmission in Conveyor Belt of Cement FactoryDocument2 pagesProblem Description: Design of Chain Drive For Power Transmission in Conveyor Belt of Cement FactoryAvinash Ajit SinghNo ratings yet
- Shaft Design (Mini Project 2) Machine Design ProjectDocument26 pagesShaft Design (Mini Project 2) Machine Design ProjectMohammad Tahir100% (5)
- Ad 0747336Document354 pagesAd 0747336droessaert_stijnNo ratings yet
- Aluminium Motors PDFDocument8 pagesAluminium Motors PDFelrajilNo ratings yet
- Fundamentos Del Codigo ASME, Secciones I y VIII Div. 1Document50 pagesFundamentos Del Codigo ASME, Secciones I y VIII Div. 1white9013No ratings yet
- SKF Xtra Power BeltsDocument24 pagesSKF Xtra Power BeltsCarlos A. Marroquin CordovaNo ratings yet
- IMU Mock 2Document35 pagesIMU Mock 2Himanshu VasisthaNo ratings yet