Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Concept Map Sample
Uploaded by
Jet MaravillaCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Concept Map Sample
Uploaded by
Jet MaravillaCopyright:
Available Formats
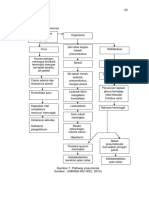
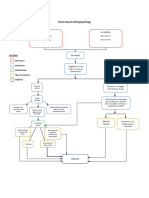
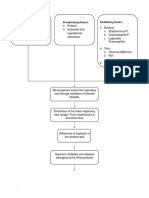
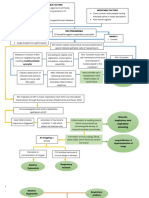
Legend
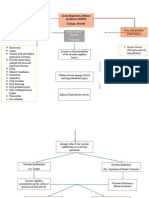
Final Diagnosis
Mode of Transmission
Diagnostic Tests
Pathophysiology
Signs
Symptoms
- Fecal-oral route
- Respiratory
SARS-
Nursing Diagnosis droplets COV- 2
Interventions
Medication
Serious conditions
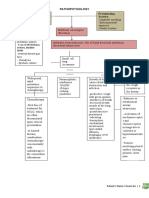
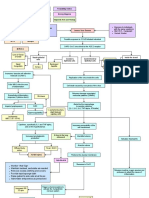
Virus gets in Inflammation of lung Systemic
respiratory system may lead to pneumonia inflammatory
and ARDS response syndrome
Attacks the alveoli Decrease BP
Attach to type II Decrease blood
pneumocyte volume
Damages type II Decrease perfusion
pneumocyte
Process
Process
Type II Multisystem
Process
pneumocytes Mediators go into
Attracts neutrophils organ failure
the bloodstream
Process
and try to destroy release specific
causing endothelial
Process
virus in alveolus inflammatory
Process mediators cells to dilate
Process
Process
Consolidation
Hypoxemia leading to alter gas
exchange
Process
Travels to CNS and Vasodilation and
increase capillary
Process
triggers
hypothalamus permeability
Stimulates
chemoreceptors
Productive
Alveolar edema Increase work of
cough Release Difficulty in
and alveolar breathing due to
prostaglandins to breathing
RT-PCR collapse fluid accumulation
increase body
Increase Triggers reflex Test
temperature
causing SNS to be
RR Scared to
stimulated
infect family
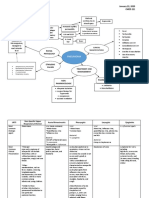
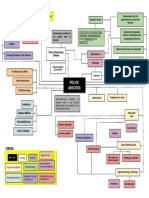
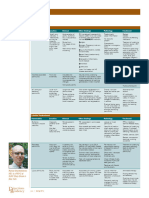
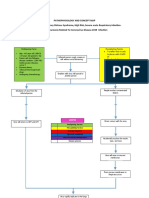
Altered Independent
Raised body
Fever thermoregulation - Monitor the axillary body temperature of the
Increase temperature
Tiredness (38.3 C) related to disease person with concern.
HR condition - Adjust and monitor environmental factors like
Anxiety related to
room temperature and bed linens as
exposure to disease
indicated.
- Encourage to extra clothing.
- Crescent Pharma
Fatigue related to Paracetamol- 500
- Keep person with concern hydrated.
poor physical mg
- Ready oxygen therapy for extreme cases.
condition due to
exposure to disease Independent - Reassess the body temperature.
- Evaluate client and significant other level of Dependent
understanding of diagnosis - Administer antipyretics as prescribed.
Pain - Educate person with concern and family
- Acknowledge the reality of the client's fears and
Independent members about the signs and symptoms of
concerns and encourage expression of feelings.
- Restrict environmental stimuli, especially during planned times hyperthermia and help in identifying factors
- Provide opportunities for questions and answer
for rest and sleep. related to occurrence of fever .
them honestly.
- Encourage the person with concern to maintain a 24-hour
- Be sure that client and care providers have the Inactivity
fatigue or activity log for at least 1 week.
same understanding of terms used causing to
- Help the person with concern with developing a schedule for
- Accept, but avoid reinforcing, the client's denial increase body
daily activity and rest.
of the situation. weight Independent
- Emphasize the importance of frequent rest periods.
- Note comments and behaviors indicative of - Have the person with concern describe himself and identify what he considers as his negative and
- Assist the person with setting priorities for preferred activities
beginning acceptance or use of effective positive traits
and role responsibilities.
strategies to deal with situations. - Discuss the meaning of change to the person with concern and how this would impact his life or
- Teach energy conservation methods.
Collaborative Disturbed body image well-being
- Encourage an exercise conditioning program as appropriate.
- Collaborate and consult with health care related to inactivity - Evaluate if the person with concerns' level of acceptance of the situation
- Provide comfort such as massage and cool showers.
providers especially cardiologists through online - Consider the person?s ethnicity and community as this can affect how the person views themselves.
- Offer diversional activities that are soothing.
meetings/check ups. - Acknowledge and accept the person?s feelings towards change and confront the person in a
- Help the person develop habits to promote effective rest/sleep
non-judgemental attitude
patterns.
Dependent - Ask the person what he plans to do about his situation
- Ask the person if he has already made some changes and assess adaptation to the situation and
- Advise family to support and provide nutritional needs of the
person with concern. the person?s progress
- Promote sufficient nutritional intake through supplements - The person has verbalized that he was eating healthy during his quarantine period however, he
was not able to perform strenuous activities due to his body pain and fatigue.
prescribed.
Collaborative - Discuss with the person about his response to the changes and if the changes made him feel better
- Collaborate with occupational therapists as needed. or have affected him negatively (ex: diet is too restrictive, does not enjoy physical exercise routine)
- Identify the person?s coping strategies and their effectiveness
- Assist and discuss with the person regarding his next goal for the future
Dependent
- Holland & Barrett Vitamin - The person should be able to maintain his good diet and incorporate light exercises as part of his
C- 500 mg daily routine
- Holland & Barrett Omega-3 Collaborative
Fish Oil- 1200 mg - Collaborate with a personal trainer/coach that can have online meetings
- Holland & Barrett Vitamin
- If the person is exhibiting signs of mental illness, talk with the person if they would be comfortable
D3- 25 ug
with having a psychologist to talk to or if they prefer talking with the nurse about their progress
You might also like
- Functions of A Student Head NurseDocument6 pagesFunctions of A Student Head NurseJan Ayenlieh Balandra Bertumen100% (1)
- Pathophysiology Sa CobidDocument7 pagesPathophysiology Sa Cobidkuro hanabusa100% (2)
- COPD PathoDocument1 pageCOPD PathoGlenn_Ancheta_2074100% (1)
- Pathway pneumoniaDocument1 pagePathway pneumoniaNur Kholis ArswendoNo ratings yet
- Cleaning Standards For WashroomsDocument24 pagesCleaning Standards For WashroomsAalok PandeyNo ratings yet
- Principles of Public Health Nursing Practice - PPT LectureDocument22 pagesPrinciples of Public Health Nursing Practice - PPT LectureManasseh Mvula100% (3)
- Patho ArdsDocument1 pagePatho ArdsJohanisa SultanNo ratings yet
- International Task Force For Prevention of Coronary Heart DiseaseDocument22 pagesInternational Task Force For Prevention of Coronary Heart DiseasealNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology PneumoniaDocument2 pagesPathophysiology PneumoniaSheila Mae Escalante67% (3)
- SARS PathophysioDocument2 pagesSARS PathophysioLouise BravoNo ratings yet
- Neonatal Pneumonia PathophysiologyDocument5 pagesNeonatal Pneumonia PathophysiologyRoderick EstrellaNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of PneumoniaDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of PneumoniaMaria Cristina100% (1)
- MANATAD, Dione Kirk D. January 22, 2020 MD-2035638 CMED 221 Concept Map: PneumoniaDocument4 pagesMANATAD, Dione Kirk D. January 22, 2020 MD-2035638 CMED 221 Concept Map: PneumoniaDK ManatadNo ratings yet
- PATHOPHYSIOLOGYDocument2 pagesPATHOPHYSIOLOGYmadelaine_espiritu0% (1)
- Path o PhysiologyDocument2 pagesPath o PhysiologyJerome Lazaro LumanogNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System by AeyfkerDocument17 pagesRespiratory System by AeyfkerAfkar IshakNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of PneumoniaDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of PneumoniaJesselle LasernaNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of PneumoniaDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of PneumoniaAzria John DemetriNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of COPDDocument1 pagePathophysiology of COPDDimpal ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Client Based Pathophysiology AsthmaDocument1 pageClient Based Pathophysiology AsthmaJoelyn DulayNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology: Patient B's Age: 28 Years OldDocument7 pagesPathophysiology: Patient B's Age: 28 Years Oldkuro hanabusaNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of PneumoniaDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of PneumoniaJeffrey Ramos100% (1)
- Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome by Mr. Ashish RoyDocument45 pagesAcute Respiratory Distress Syndrome by Mr. Ashish RoySyedzulqurnainhussainshah ZulqurnainNo ratings yet
- Covid and Ebola MsDocument7 pagesCovid and Ebola MsAimee Rochelle MaesaNo ratings yet
- Pneumococcal PneumoniaDocument1 pagePneumococcal PneumoniaKierzteen Brianna TaromaNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of PneumoniaDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of PneumoniaJuneNo ratings yet
- Empyema Care GuidelineDocument2 pagesEmpyema Care GuidelineshindyclaudyaNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology Plueral Effusion Secondary To Pneumonia: GreenDocument7 pagesPathophysiology Plueral Effusion Secondary To Pneumonia: Greenkuro hanabusaNo ratings yet
- Non-Modifiable Risk Factor Modifiable Risk Factors: Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS) (Lungs Alveoli)Document3 pagesNon-Modifiable Risk Factor Modifiable Risk Factors: Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS) (Lungs Alveoli)joyrena ochondraNo ratings yet
- Pelvic Abscess Concept MapDocument1 pagePelvic Abscess Concept Mapaijiel talisikNo ratings yet
- Objectives: Table 1. Selected Etiologies of Sore ThroatDocument12 pagesObjectives: Table 1. Selected Etiologies of Sore ThroatRANINo ratings yet
- Objectives: Table 1. Selected Etiologies of Sore ThroatDocument12 pagesObjectives: Table 1. Selected Etiologies of Sore ThroatRiadi riadiNo ratings yet
- Table 25Document2 pagesTable 25Aji Setia UtamaNo ratings yet
- DHFDocument14 pagesDHFSyifa Nur RahmahNo ratings yet
- Abas, Pathophysiology of CapDocument1 pageAbas, Pathophysiology of Capalexander abasNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology Precipitating Factors: Predisposing FactorsDocument2 pagesPathophysiology Precipitating Factors: Predisposing FactorsChristine Pialan SalimbagatNo ratings yet
- Predisposing Factors: Precipitating Factors: Contributing FactorsDocument6 pagesPredisposing Factors: Precipitating Factors: Contributing FactorsKen SimonNo ratings yet
- Pcap PathophysiologyDocument3 pagesPcap PathophysiologyZandra Lyn AlundayNo ratings yet
- Predisposing Factors Disease Precipitating Factors: LegendDocument3 pagesPredisposing Factors Disease Precipitating Factors: LegendSOPHIA LOISE TEJANO FULACHENo ratings yet
- Pcap Pathophysiology PDFDocument3 pagesPcap Pathophysiology PDFMikaela RamosNo ratings yet
- Covid-19 PathophysiologyDocument1 pageCovid-19 PathophysiologyPortia Dulce Patatag ToqueroNo ratings yet
- PneumoniaSystem DisorderDocument1 pagePneumoniaSystem DisorderAA DDNo ratings yet
- Medical Concept: Pericardial Effusion and Cardiac TamponadeDocument1 pageMedical Concept: Pericardial Effusion and Cardiac TamponadeCecil-An DalanonNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument2 pagesDrug Studyjennelyn losantaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan for Pneumonia PatientDocument1 pageNursing Care Plan for Pneumonia PatientvonNo ratings yet
- San Gabriel, GMA, Cavite College of Nursing: Iv. Pathophysiology by The BookDocument2 pagesSan Gabriel, GMA, Cavite College of Nursing: Iv. Pathophysiology by The BookSTEPHANIE LIBO-ONNo ratings yet
- CeftriaxoneDocument2 pagesCeftriaxoneunkown userNo ratings yet
- ICC AUDIT TOOL AND TRIAGE ALGORHYTHM DGMC - WPS PDF Convert PDFDocument40 pagesICC AUDIT TOOL AND TRIAGE ALGORHYTHM DGMC - WPS PDF Convert PDFWendy Dela PenaNo ratings yet
- NCP HemoDocument2 pagesNCP HemoJigs HechNo ratings yet
- Cavitary Oulmonary NoduleDocument5 pagesCavitary Oulmonary NoduleZest IanNo ratings yet
- CeftriaxoneDocument2 pagesCeftriaxoneunkown userNo ratings yet
- AAD-BF-PanniculitisDocument2 pagesAAD-BF-Panniculitiskahkashanahmed065No ratings yet
- Local Factors Systemic Factors: Factor Affecting Wound HealingDocument1 pageLocal Factors Systemic Factors: Factor Affecting Wound HealingMuhd ArifNo ratings yet
- Diseases of Lab AnimalsDocument45 pagesDiseases of Lab AnimalsvetpathforumNo ratings yet
- Pleural EffusionDocument4 pagesPleural EffusionSidney Bon LuceroNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan for PneumoniaDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan for PneumoniaSergi Lee OrateNo ratings yet
- Communicable Diseases in The PhilippinesDocument3 pagesCommunicable Diseases in The PhilippinesChevelle Valenciano-GaanNo ratings yet
- NCP - Risk For InfectionDocument2 pagesNCP - Risk For InfectionJet Bautista100% (1)
- Periodontal Disease AND Cardiovascular Disease: Dentaid Medical DepartmentDocument17 pagesPeriodontal Disease AND Cardiovascular Disease: Dentaid Medical DepartmentMunteanu DragosNo ratings yet
- Non-Modifiable Factors Modifiable Factors: (Causative Agent: Respiratory Syncytia Virus)Document3 pagesNon-Modifiable Factors Modifiable Factors: (Causative Agent: Respiratory Syncytia Virus)Venice Joy CelociaNo ratings yet
- HodgDocument23 pagesHodgsami ullahNo ratings yet
- Concept Map CovidDocument7 pagesConcept Map CovidMaieca Demecillo100% (3)
- NLE and NCLEX QuestionDocument28 pagesNLE and NCLEX Questionhelenlorenzana042086No ratings yet
- 7 Best Acupressure PointsDocument2 pages7 Best Acupressure Pointskunkuma-balasubramanian-1247No ratings yet
- MSQH 5th Editon Standards - 02 Final GS 17apr 2019Document99 pagesMSQH 5th Editon Standards - 02 Final GS 17apr 2019Aku NieNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Antibacterial Antiinflammatory and Skinwhitening Effect of Centella Asiatica L Urban2018journal of Plant BiotechnologyOpen AccessDocument8 pagesAnalysis of Antibacterial Antiinflammatory and Skinwhitening Effect of Centella Asiatica L Urban2018journal of Plant BiotechnologyOpen AccessRika DestianaNo ratings yet
- Epistaxis: Dr. Wachuka G. Thuku Tutorial Fellow-ENT RegistrarDocument32 pagesEpistaxis: Dr. Wachuka G. Thuku Tutorial Fellow-ENT RegistrarAlexNo ratings yet
- Local - Media2196001544712081207 1 1 2Document60 pagesLocal - Media2196001544712081207 1 1 2jaymar gervacioNo ratings yet
- Lifting and Handling of Casualty HandoutsDocument6 pagesLifting and Handling of Casualty HandoutsIvy Jorene Roman RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Pathology of The Respiratory SystemDocument57 pagesPathology of The Respiratory SystemAngelic khanNo ratings yet
- 2022 - Epidemiologia - Sifilis VIH en Homosexuales HombresDocument25 pages2022 - Epidemiologia - Sifilis VIH en Homosexuales HombresEduardo RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Contoh QuestionnaireDocument15 pagesContoh QuestionnaireRohizan Ya100% (1)
- Febuxostat EMEADocument51 pagesFebuxostat EMEAIndra PaqotzNo ratings yet
- Check your well-being with this situations listDocument2 pagesCheck your well-being with this situations listArlen Mae RayosNo ratings yet
- Heswall Local May 2012Document40 pagesHeswall Local May 2012Talkabout PublishingNo ratings yet
- DG Document Requirements Reference SheetDocument7 pagesDG Document Requirements Reference SheetJosé Larragaña OsunaNo ratings yet
- The Standard - 2014-07-30Document71 pagesThe Standard - 2014-07-30jorina8070% (1)
- OPD JournalDocument2 pagesOPD JournalRalph Elvin MacanlalayNo ratings yet
- DRUG-STUDY (Celecoxib)Document3 pagesDRUG-STUDY (Celecoxib)NicholeGarcesCisnerosNo ratings yet
- ADL-12 (Business Law)Document6 pagesADL-12 (Business Law)samee380No ratings yet
- Essay 3 Acid Rain KraynyayaDocument9 pagesEssay 3 Acid Rain Kraynyayaapi-512016052No ratings yet
- Business Communication: Dabur India LTDDocument30 pagesBusiness Communication: Dabur India LTDshashank nutiNo ratings yet
- 8 Week Powerlifting IntroDocument3 pages8 Week Powerlifting Introlachlan Gill02No ratings yet
- Composition and Regulation of Body FluidsDocument32 pagesComposition and Regulation of Body FluidsAndriKusumaNo ratings yet
- 240-62946386 Vehicle Driver Safety Management Procedure PDFDocument22 pages240-62946386 Vehicle Driver Safety Management Procedure PDFMAdrianRumayar100% (1)
- ASC Catalog MPW10000A Rev 7 Digital 3 1Document27 pagesASC Catalog MPW10000A Rev 7 Digital 3 1RandolphNo ratings yet
- San Pedro Hospital Case Vignette on Pulmonary TBDocument7 pagesSan Pedro Hospital Case Vignette on Pulmonary TBShareen Joyce AgbayaniNo ratings yet
- Woodlands Children's Centre Information and Timetable: September 2013 - March 2014Document12 pagesWoodlands Children's Centre Information and Timetable: September 2013 - March 2014WoodlandsccNo ratings yet
- HEALTH AND NUTRITION: WEIGHT MANAGEMENTDocument29 pagesHEALTH AND NUTRITION: WEIGHT MANAGEMENTJuhany MusaNo ratings yet