Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Balingan Pcal Act1lab
Uploaded by
Sophia MarieOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Balingan Pcal Act1lab
Uploaded by
Sophia MarieCopyright:
Available Formats
DAVAO DOCTORS COLLEGE
Pharmacy Department
Gen. Malvar St., Davao City
Name: Queen Iris Valerie Balingan Date: October 28,2020
Group Name: Year/Section: 1st year
V1A
Learning Activity no. 1
Laboratory Equipment
and Apparatus
OBJECTIVES:
At the end of the laboratory class, the student is expected to:
1. Identify the common, simple laboratory equipment and apparatus.
2. Describe the use common, simple laboratory equipment and apparatus.
INTRODUCTION:
Laboratory is a room where research, expirements and etc happened it also manufactured drugs.
Knowing the uses of the equipment being used inside the laboratory and the things to be don before
and after the laboratory session.
PHARMACEUTICAL CALCULATIONS AND TECHNIQUES
3
A. Illustrate and describe the use of common laboratory equipment and apparatus.
Laboratory Equipment Illustration Use
and Apparatus
Safety goggles Safety goggles are
intended to shield the
wearer's eyes from
impact hazards such as
flying fragments,
objects, large chips,
and
particles. Goggles fit
the face immediately
surrounding the eyes
and form
a protective seal
around the eyes.
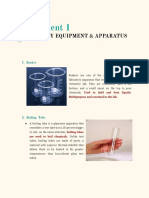
Beakers A beaker is a
cylindrical
container used to
store, mix and heat
liquids in laboratories.
Most are made of
glass, but other non-
corrosive materials,
such as metal and
heat-resistant plastic,
are
also used. Beakers us
ually have a flat
bottoms and a lip
around the top.
Beaker Tongs Use beaker tongs to
handle hot beakers.
These nickel-plated
steel tongs are 25 cm
(10") long and have
plastic coated jaws that
open up to 11 cm
(4.5"). They can
hold beakers ranging
from 100 ml up to 1000
ml.
Erlenmeyer flasks The Erlenmeyer
flask has
diverse uses such as
holding and measuring
chemical liquid
samples, but can also
be used to mix, heat
and boil chemicals.
PHARMACEUTICAL CALCULATIONS AND TECHNIQUES
4
Florence flasks A Florence
Flask/Boiling Flask is a
type of flask used as
an item of laboratory
glassware. It is used as
a container to hold
liquids. A Florence
flask has a round
body, a long neck, and
often a flat bottom.
Test tubes Test tubes are
widely used by
chemists to handle
chemicals, especially
for qualitative
experiments and
assays. ... Test
tubes are convenient
containers for heating
small amounts of
liquids or solids with a
Bunsen burner or
alcohol burner.
The tube is usually
held by its neck with a
clamp or tongs.
Test tubes rack Test tube racks are
laboratory equipment
used to hold upright
multiple test tubes at
the same time. They
are most commonly
used when various
different solutions are
needed to work with
simultaneously, for
safety reasons, for
safe storage of test
tubes, and to ease
the transport of
multiple tubes.
Test Tube Clamp A test tube holder is
used to hold test tubes.
It is used for holding a
test tube in place when
the tube is hot or
should not be touched.
PHARMACEUTICAL CALCULATIONS AND TECHNIQUES
5
Test tube brush Test tubes are
widely used
by chemists to handle
chemicals, especially
for qualitative
experiments and
assays.
Watch glasses A watch glass is a
round, concave glass
dish used for
evaporation in
chemistry. It can also
be employed for
weighing solids and as
a lid for flasks
and beakers.
Crucibles crucibles may be
small laboratory
utensils for conducting
high-temperature
chemical reactions and
analyses or large
industrial vessels for
melting and calcining ...
Crucible tongs Laboratory tongs are
large pincers for
grasping and lifting
vessels of heat-
resistant
material used in high
temperature chemical
reactions.
Funnels A funnel is a tube or
pipe that is wide at the
top and narrow at the
bottom, used for
guiding liquid or
powder into a small
opening.
PHARMACEUTICAL CALCULATIONS AND TECHNIQUES
6
Graduated cylinders used to precisely
measure the volume of
liquids.
Conical graduate used to precisely
measure the volume of
liquids.
Volumetric flasks A volumetric flask is
lab glass or
plasticware used to
prepare a solution. It
is used to make up a
solution to a known
volume. Volumetric
flasks are used to
measure volumes
much more precisely
than beakers or
Erlenmeyer flasks.
PHARMACEUTICAL CALCULATIONS AND TECHNIQUES
7
Droppers An eye dropper, also
known as a Pasteur
pipette, or dropper, is
a device used to
transfer small
quantities of liquids. ...
They are used in the
laboratory and also to
dispense small
amounts of liquid
medicines.
Pipettes Pipettes are an
essential laboratory to
ol used to dispense
measured volumes of
liquids.
Pipette bulb Bulb pipettes are used
for dispensing a known
volume of aqueous
liquid. Pipettes are
calibrated with distilled
water.
Burets used for titration in
volumetric analysis.
Compared to pipettes,
the handling
of burettes is different
during
practical use and
calibration.
PHARMACEUTICAL CALCULATIONS AND TECHNIQUES
8
Ring stands, rings, it helps to use devices
and clamps that allow you to
suspend something
over the source of heat
if you need to heat
something.
Tongs and forceps used when fingers are
too large to grasp small
objects or when many
objects need to be held
at one time while the
hands are used to
perform a task. ...
Outside medicine,
people usually refer
to forceps as
tweezers, tongs, pliers,
clips or clamps.
Spatulas and Scoopula is a brand
Scoopula name of a spatula-like
scoop
utensil used primarily
in chemistry lab
settings to transfer
solids: to a weigh paper
for weighing, to a cover
slip to measure melting
point, or a graduated
cylinder, or to a watch
glass from a flask or
beaker through
scraping.
Thermometers used for measuring
temperatures other
than the human body
temperature. It ranges
from -10˚C to
110˚C. Laboratory
thermometers are
designed
for lab purposes such
as checking boiling
point, freezing point, or
temperature of other
substances.
PHARMACEUTICAL CALCULATIONS AND TECHNIQUES
9
Bunsen Burners used to provide a
single, continuous
flame by mixing gas
with air in a controlled
fashion.
Triple Beam Balance used to measure mass
very precisely.
Analytical balance Analytical
balances are highly
sensitive lab
instruments designed
to accurately measure
mass.
Stirring Rod One of their
main uses is to
“scratch” the side of
glassware (such as an
Erlenmeyer Flask) to
start the crystallization
process in many
experiments.
Clay Triangle used to support a
crucible while it is
heated over a Bunsen
burner.
PHARMACEUTICAL CALCULATIONS AND TECHNIQUES
10
Evaporating Dish used for
the evaporation of
solutions and
supernatant liquids,
and sometimes to their
melting point.
Mortar and pestle used to grind up solid
chemicals into fine
powder and crush
solids into smaller
pieces.
Wire gauze used for uniform
distribution of flame
heat in base of a
heated body. It is made
of a iron wire strands
with or without ceramic
interior cores.
Wash bottle used to rinse various
pieces
of laboratory glasswar
e, such as test tubes
and round bottom
flasks.
PHARMACEUTICAL CALCULATIONS AND TECHNIQUES
11
Water bath It is used to incubate
samples in water at a
constant temperature
over a long period of
time.
Alcohol lamp An alcohol lamp is
used for heating,
sterilization, and
combustion in a
laboratory. The alcohol
lamp uses ethyl
alcohol or spirit as
a fuel.
Hot plate used to heat glassware
or its contents.
Some hot plates also
contain a magnetic
stirrer, allowing
the heated liquid to be
stirred automatically.
B. RELATED QUESTIONS TO ANSWER:
1. What are the personal protective equipment (PPE)? Why is it necessary wear
to personal protective equipment in the laboratory?
- Clothing, helments, goggles and etc. PPE is necessary to wear during laboratory to protect
chemical exposures and other things that might happened.
2. Why must you always wash your hands before and after working in a laboratory?
- It is important because of the dirt or chemical that came from the gloves that you are using and it
might affect your health.
PHARMACEUTICAL CALCULATIONS AND TECHNIQUES
12
3. How do you read the volume measurement using graduated cylinders?
4. What is calibration? Why is it necessary to calibrate an instrument?
- It is necessary because it measures the right amount of the product and also the
safety of the using
CONCLUSION:
Knowing the laboratory equipments and its uses also the safety in laboratory.
REFERENCES:
https://www.google.com/search?q=Hot+plate
https://www.google.com/search?q=Alcohol+lamp&tbm
https://www.google.com/search?q=Water+bath&tbm
https://www.google.com/search?q=Mortar+and+pestle&tbm
https://www.google.com/search?q=Evaporating+Dish&tbm
https://www.google.com/search?q=Stirring+Rod&tbm
https://www.google.com/search?q=Clay+Triangle&tbm
https://www.google.com/search?q=Analytical+balance&tbm
https://www.google.com/search?q=Triple+Beam+Balance&tbm
https://www.google.com/search?q=Bunsen+Burners&tbm
PHARMACEUTICAL CALCULATIONS AND TECHNIQUES
https://www.google.com/search?q=Thermometers&tbm 13
https://www.google.com/search?q=Spatulas+and+Scoopulas&tbm
https://www.google.com/search?q=Tongs+and+forceps&sxsrf=
https://www.google.com/search?q=Pipette+bulb&tbm
https://www.google.com/search?q=Pipettes&tbm=
https://www.google.com/search?q=Volumetric+flasks&tbm=
https://www.google.com/search?q=Funnels&tbm=
https://www.google.com/search?q=Watch+glasses&sxsrf=
https://www.google.com/search?q=Crucibles&tbm=
PHARMACEUTICAL CALCULATIONS AND TECHNIQUES
14
You might also like
- Cinema, Pain and Pleasure Consent and The Controlled BodyDocument244 pagesCinema, Pain and Pleasure Consent and The Controlled BodyRadically DarkNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2.3 - Relation and FunctionDocument12 pagesChapter 2.3 - Relation and FunctionPoeil Sergio MoldezNo ratings yet
- Lab Equipment Worksheet: FlameDocument6 pagesLab Equipment Worksheet: FlameSabu LazerNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes in General Chemistry 1Document22 pagesLecture Notes in General Chemistry 1Eeya100% (1)
- Rogue Trader - Necron Character GuideDocument64 pagesRogue Trader - Necron Character GuideTom Johnson100% (2)
- Lab ApparatusDocument29 pagesLab ApparatusEpoditmas SeyerNo ratings yet
- Civil Engineering Multiple Choice Questions and AnswersDocument1 pageCivil Engineering Multiple Choice Questions and Answersengineeringmcqs100% (7)
- Fe Ce 511 Prestressed ConcreteDocument6 pagesFe Ce 511 Prestressed ConcreteJeana Rick GallanoNo ratings yet
- Hambly, Wilfrid D. - The Ovimbundu of Angola (1934)Document370 pagesHambly, Wilfrid D. - The Ovimbundu of Angola (1934)Pedro SoaresNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Lab Mysteries, Fun Laboratory Tools! Chemistry for Kids - Children's Analytic Chemistry BooksFrom EverandChemistry Lab Mysteries, Fun Laboratory Tools! Chemistry for Kids - Children's Analytic Chemistry BooksRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Ce Correl Ports and Harbor (B)Document5 pagesCe Correl Ports and Harbor (B)Glenn Frey Layug0% (1)
- Nano-Glass Ceramics: Processing, Properties and ApplicationsFrom EverandNano-Glass Ceramics: Processing, Properties and ApplicationsNo ratings yet
- CHM019 - Gepulango-Act 1labDocument11 pagesCHM019 - Gepulango-Act 1labKay EstelleNo ratings yet
- Familiarization With Eqipmt and Mats in MicrolabDocument11 pagesFamiliarization With Eqipmt and Mats in MicrolabCristian Kenneth TrillanesNo ratings yet
- Basuel Exercise 1 Lab ApparatusDocument16 pagesBasuel Exercise 1 Lab ApparatusOrdinary GuitaristNo ratings yet
- Experiment No. 1 Familiarization With Laboratory Apparatus in General Chemistry ObjectiveDocument7 pagesExperiment No. 1 Familiarization With Laboratory Apparatus in General Chemistry ObjectiveCrisha GutierrezNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1: Laboratory Equipment & ApparatusDocument12 pagesAssignment 1: Laboratory Equipment & ApparatusJAN MIKYLLA TABAMONo ratings yet
- Pia - Team 3 ..Document38 pagesPia - Team 3 ..anaNo ratings yet
- BEA, Emil Andrew-CPE211Document3 pagesBEA, Emil Andrew-CPE211Na-yeon ImNo ratings yet
- Reflective EssayDocument14 pagesReflective EssayDIONISIO, Mariah Sofia F.No ratings yet
- AnaChemLab 1stDocument6 pagesAnaChemLab 1stPhranxies Jean BlayaNo ratings yet
- Barecuatro - BSN1-11L - Preliminary ActivitiesDocument19 pagesBarecuatro - BSN1-11L - Preliminary ActivitiesAngelica Claire BarecuatroNo ratings yet
- Test Tubes Are Used byDocument3 pagesTest Tubes Are Used byGray MacGardenNo ratings yet
- DUCHA - Activity 1Document5 pagesDUCHA - Activity 1FRANCHESKA DUCHANo ratings yet
- Notes To Convert ChemDocument2 pagesNotes To Convert ChemAdelaide Fleona Marie TrinidadNo ratings yet
- CASTRO LaboratoryApparatusDocument7 pagesCASTRO LaboratoryApparatusIrene Grace A. CastroNo ratings yet
- CHM 1103 Lab #1 - Student ReportDocument3 pagesCHM 1103 Lab #1 - Student ReportBeyonce SkekelNo ratings yet
- Assignment: Inorganic and Organic Chemistry CHM101Document3 pagesAssignment: Inorganic and Organic Chemistry CHM101Cj DelfinNo ratings yet
- Genchem La 1 SantanDocument10 pagesGenchem La 1 SantanDece Andrea SantanNo ratings yet
- 10 Laboratory ApparatusDocument2 pages10 Laboratory ApparatusTaki TachibanaNo ratings yet
- 01 Activity 1 ChemDocument3 pages01 Activity 1 ChemDeocades DexinNo ratings yet
- Pictures Description UsesDocument4 pagesPictures Description UsesRanice Krizelle LomibaoNo ratings yet
- Experiment 1 - Data SheetDocument4 pagesExperiment 1 - Data SheetApple PinpinNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Activity No. 1 - Common Laboratory ApparatusesDocument11 pagesLaboratory Activity No. 1 - Common Laboratory ApparatusesJuliane JaynNo ratings yet
- Syahruddin MaulanaDocument12 pagesSyahruddin MaulanaMaulNo ratings yet
- Topic 1 Introductory To Laboratory Safety and ApparatusDocument6 pagesTopic 1 Introductory To Laboratory Safety and ApparatusChuan Ning LeNo ratings yet
- Form 1 Bio PDFDocument77 pagesForm 1 Bio PDFJoel Herrera ChirwaNo ratings yet
- Pre Laboratory ActivityDocument9 pagesPre Laboratory ActivityKerstien ValdezNo ratings yet
- CHEM2212 - ESTANOCO - SAMUEL.M. - Activity 1 LABORATORY EQUIPMENTDocument6 pagesCHEM2212 - ESTANOCO - SAMUEL.M. - Activity 1 LABORATORY EQUIPMENTSam EstanocoNo ratings yet
- Act 3 LabDocument7 pagesAct 3 LabNadzrata KipliNo ratings yet
- Basique Lab TechniquezDocument4 pagesBasique Lab TechniquezfrancisckrizylleNo ratings yet
- Laboratory EquipmentsDocument5 pagesLaboratory EquipmentsMyca Katrina CantaneroNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Apparatus and Its UsesDocument27 pagesLaboratory Apparatus and Its UsesJonaRose PeroyNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Form One & TwoDocument61 pagesChemistry Form One & Twothomaspodo76No ratings yet
- Gen Bio Lab ManualDocument18 pagesGen Bio Lab ManualVALERIE JOY CATUDIONo ratings yet
- Activity 1 Basic Tools in MicrobiologyDocument9 pagesActivity 1 Basic Tools in MicrobiologyRAYYAN ENIL ABDURAHAMNo ratings yet
- Bunsen BurnerDocument17 pagesBunsen BurnerMaiza TiborNo ratings yet
- Part 1-3 (Chem For Engineers) Mora, Hanilav C. Bsce 1aDocument8 pagesPart 1-3 (Chem For Engineers) Mora, Hanilav C. Bsce 1aHanilavMoraNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Experiment 1 Common Laboratory Apparatus and GlasswaresDocument5 pagesLaboratory Experiment 1 Common Laboratory Apparatus and GlasswaresJohn Carl DomingoNo ratings yet
- 20 Common Laboratory ApparatusDocument11 pages20 Common Laboratory ApparatusJINGKY HUMAMOY100% (1)
- Tasks Ped4 Word - FRANGRUESODocument7 pagesTasks Ped4 Word - FRANGRUESOFran Grueso CerezoNo ratings yet
- Activity No. 1 Comon Laboratory ApparatusDocument9 pagesActivity No. 1 Comon Laboratory ApparatusJoaquin Angelo CortesNo ratings yet
- Laboratory EquipmentsDocument16 pagesLaboratory EquipmentsedomanpcNo ratings yet
- Activity 1 Basic Tools in MicrobiologyDocument9 pagesActivity 1 Basic Tools in MicrobiologyRAYYAN ENIL ABDURAHAMNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Activity 1Document8 pagesLaboratory Activity 1PERJES, Sigrid Maial A.No ratings yet
- Chemistry For EngineersDocument18 pagesChemistry For EngineersEunice AlonzoNo ratings yet
- Chemistry For Engineers (NS 111) : SafetyDocument11 pagesChemistry For Engineers (NS 111) : SafetyMark Angelo Belza SotoNo ratings yet
- Laboratory EquipmentsDocument12 pagesLaboratory EquipmentsJohnmar FortesNo ratings yet
- CHEM181 Act.-1Document8 pagesCHEM181 Act.-1villanuevazachderamaNo ratings yet
- GENERAL CHEMIST-WPS OfficeDocument4 pagesGENERAL CHEMIST-WPS OfficeYra kyranNo ratings yet
- List of Basic Chemistry Apparatus: 1. Safety Goggles, Lab Gown, Latex Gloves and Surgical MaskDocument2 pagesList of Basic Chemistry Apparatus: 1. Safety Goggles, Lab Gown, Latex Gloves and Surgical MaskDen Angelica DungoNo ratings yet
- Activity 2 Glasswares 2Document5 pagesActivity 2 Glasswares 2EDCEL PEDRONo ratings yet
- Chemestry Laboratory PracticesDocument84 pagesChemestry Laboratory PracticesSadjo Florez sandovalNo ratings yet
- INTRODUCTIONDocument48 pagesINTRODUCTIONJed Nicole AngonNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Safety: Prep By: JM Lapasaran CEU, Department of Physical Science and MathematicsDocument36 pagesLaboratory Safety: Prep By: JM Lapasaran CEU, Department of Physical Science and MathematicsSharlene MelchorNo ratings yet
- Activity 2 - Common Laboratory Apparatus and OperationsDocument9 pagesActivity 2 - Common Laboratory Apparatus and OperationsBARRY EPHRAIM PELICANONo ratings yet
- Bio-Glasses: An IntroductionFrom EverandBio-Glasses: An IntroductionJulian JonesNo ratings yet
- Pcal Act2labDocument5 pagesPcal Act2labSophia MarieNo ratings yet
- Davao Doctors College Pharmacy Department Gen. Malvar ST., Davao CityDocument6 pagesDavao Doctors College Pharmacy Department Gen. Malvar ST., Davao CitySophia MarieNo ratings yet
- Davao Doctors College Pharmacy Department Gen. Malvar ST., Davao CityDocument12 pagesDavao Doctors College Pharmacy Department Gen. Malvar ST., Davao CitySophia MarieNo ratings yet
- AGAR PREPARATION MidtermDocument12 pagesAGAR PREPARATION MidtermSophia MarieNo ratings yet
- Group-3 Ddslab9 ScriptDocument6 pagesGroup-3 Ddslab9 ScriptSophia MarieNo ratings yet
- Group 7 Determine Alcohol by Specific GravityDocument4 pagesGroup 7 Determine Alcohol by Specific GravitySophia MarieNo ratings yet
- GROUP 6 SCRIPT Learning Activity 9 Optical ActivityDocument5 pagesGROUP 6 SCRIPT Learning Activity 9 Optical ActivitySophia MarieNo ratings yet
- Physics Full Book TestDocument3 pagesPhysics Full Book TestLearnEnglish WithAriNo ratings yet
- Indirect taxation-GDDocument31 pagesIndirect taxation-GD19BCO543 Rubalakshmi BNo ratings yet
- Soal B. Inggris Kelas X Semester 2Document5 pagesSoal B. Inggris Kelas X Semester 2Aliyah Al-IhsaniyahNo ratings yet
- Construction Material TestingDocument2 pagesConstruction Material TestingHassan MajeedNo ratings yet
- Certificate of Analysis: Scrooby'S Laboratory Service CCDocument1 pageCertificate of Analysis: Scrooby'S Laboratory Service CCmusaNo ratings yet
- Image-Based On-Line Measurement of Crepe Structure: White PaperDocument12 pagesImage-Based On-Line Measurement of Crepe Structure: White PaperAhmed AsforaNo ratings yet
- Outline Impact of A TeacherDocument3 pagesOutline Impact of A TeacherShakirah SariNo ratings yet
- Rapid Load Testing On Piles Interpretation GuideliDocument19 pagesRapid Load Testing On Piles Interpretation GuidelifabulosofigueroaNo ratings yet
- Irrigation Engineering 2015 2019Document12 pagesIrrigation Engineering 2015 2019SIDDHARTHA MAITYNo ratings yet
- AQLI 2021 Report - EnglishglobalDocument15 pagesAQLI 2021 Report - EnglishglobalEcopresa.mdNo ratings yet
- Prejudice Towards Sex Workers Depends On The Sexual Activity and Autonomy of Their Work, Hobbies and Daily ActivitiesDocument18 pagesPrejudice Towards Sex Workers Depends On The Sexual Activity and Autonomy of Their Work, Hobbies and Daily ActivitiessergiforteasanchezNo ratings yet
- How The World WorksDocument9 pagesHow The World Worksapi-346324074No ratings yet
- Exercise 4.9 Review Questions: Understanding and FluencyDocument3 pagesExercise 4.9 Review Questions: Understanding and FluencySGillespieNo ratings yet
- English NotesDocument2 pagesEnglish NotessachaNo ratings yet
- Analytical Method Development and Validation of Stability Indicating RP-HPLC Method For Estimation of Lercanidipine Hydrochloride and Enalapril Maleate in CombinationDocument8 pagesAnalytical Method Development and Validation of Stability Indicating RP-HPLC Method For Estimation of Lercanidipine Hydrochloride and Enalapril Maleate in CombinationBaru Chandrasekhar RaoNo ratings yet
- Spin Your Self Talk: A Guide To Breaking Out of A Self-Talk RutDocument11 pagesSpin Your Self Talk: A Guide To Breaking Out of A Self-Talk RutAmelia HandayaniNo ratings yet
- Internship Report 1Document27 pagesInternship Report 1Saarthak AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Swintec 401DPs Adding Machine Operations ManualDocument14 pagesSwintec 401DPs Adding Machine Operations ManualDaniel & Jennifer DenigNo ratings yet
- Question Text: FeedbackDocument12 pagesQuestion Text: FeedbackANGELU RANE BAGARES INTOLNo ratings yet
- Solution Manual For Quantitative Analysis For Management 12Th Edition Render Stair Hanna Hale 0133507335 978013350733 Full Chapter PDFDocument36 pagesSolution Manual For Quantitative Analysis For Management 12Th Edition Render Stair Hanna Hale 0133507335 978013350733 Full Chapter PDFdouglas.schrandt250100% (13)
- Vinyl Wallpaper With Non-Woven BackingDocument9 pagesVinyl Wallpaper With Non-Woven BackingSantosh AiholeNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 P.E.E.L Paragraph RubricDocument1 pageUnit 2 P.E.E.L Paragraph RubricbenjaminsnitkerNo ratings yet
- 8601 Assignmnt 1Document24 pages8601 Assignmnt 1saimasheikh869No ratings yet