Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Leadership: A Senior Employee Who Sponsors and Supports A Less-Experienced Employee
Leadership: A Senior Employee Who Sponsors and Supports A Less-Experienced Employee
Uploaded by
ProxyYtOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Leadership: A Senior Employee Who Sponsors and Supports A Less-Experienced Employee
Leadership: A Senior Employee Who Sponsors and Supports A Less-Experienced Employee
Uploaded by
ProxyYtCopyright:
Available Formats
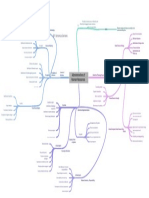
Model self-leadership
Implement the vision and strategy
Encourage employees to create self-set provided by leaders
goals
Promote stability
Encourage the use of self-rewards to
strengthen and increase desirable Self-Leadership(or Self- Coordinate staff and handle day-to-day
behaviours Management) problems
Managers
Create positive thought patterns
A senior employee who sponsors and
supports a less-experienced employee Leaders Press for change
Mentoring
Innovates for the entire organization
Remove Obstacles
Creates vision and meaning for the
Build commitment and Confidence Effective team leaders Contemporary Leadership Roles organization
Team Leadership Are Managers and Leaders the Same?
Create opportunities
Roles of Team Leaders
Liaisons with outsiders
Extroversion
Troubleshooters
Online Leadership Conscientiousness
Conflict Managers
Openness
Coaches
Emotional Intelligence
Benefits Leadership without Authority
Latitude for creative deviance Leadership Traits
Issue Focus
Front-line Information
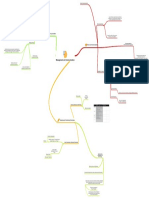
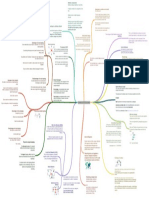
Theories that consider personal qualities
and characteristics that differentiate
Leaders who know who they are, know leaders from non leaders
what they believe in and value, and act on
these values and beliefs openly and
candidly. (ethical people) Trait Theories: Are Leaders Different from
Authentic Leadership Others?
Leadership that conveys values that are
Socialized Charismatic
Leadership The extent to which a leader is likely to
define and structure his or her role and
other-centered versus self-centered by those of employees in order to attain goals
Leadership
leaders who model ethical conduct
Moral Leadership Contemporary Issues in Leadership The Ohio State Studies Initiating Structure
Cornerstones to a "Moral Foundation of The extent to which a leader is likely to
Truth Telling
Leadership" have job relationships characterized by
Consideration
Promise Keeping Leadership as Supervision mutual trust, respect for employees' ideas
and regard for their feelings
Fairness
Gender: Do Men and Women Lead Theories which propose that particular
Respect for the individual Differently? behaviours make for better leaders
Women
Behavioural Theories: Do Leaders Behave
Enhance follower's self-worth in Particular Ways?
Democratic Leadership Men
Lead through inclusion
A leader who emphasizes interpersonal
Employee-oriented leaders
Share leadership and encourage relations
participation Directive Command-and-Control Style
The Michigan Studies
Rely on charisma, expertise, contact, and A leader who emphasizes the technical or
interpersonal skills to influence Production-oriented leaders
Leaders who inspire followers to task aspect of the job
Leadership that critically examines the
transcend their self-interests for the good
status quo with the view to developing and
of the organization
articulating future strategic goals or vision
for the organization The degree of confidence, trust, and
Be more self-confident respect members have for their leaders
Transformational vs. Charismatic Leader-member relations
Inspirational Leadership Substitutes for Leadership
Leadership
Be assertive and more dominant in Definition
Transformational Leadership The degree of influence a leader has over
behaviour Contingency Theories: Does the Situation
Vision and articulation Matter? power variables such as hiring, firing,
Charismatic Leadership Position power
discipline, promotions, and salary
Rely on their formal position power How Transformational Leadership Works increases
Personal risk
Characteristics Fiedler Contingency Model
Unconventional Behaviour Theories which propose that the situation
has an effect on leaders The degree to which the job assignments
Idealized Influence Task Structure
are procedurized
Sensitivity to followers' needs
Inspirational Motivation The Dark Side of Charismatic Leadership Hersey and Blanchard's Situational
leadership
A paternal model
Intellectual Stimulation
Transactional Leaders A model that focuses on follower
Individualized Consideration The develop an inability to listen to others readiness
Full Range of Leadership Model
Contingent Reward
Because of their overwhelming self- An intuitive model
Leaders who guide or motivate their confidence they may become ego-driven The directive leader lets followers know Path-Goal Theory
Management by Exception followers in the direction of established what is expected of them
goals by clarifying role and task
They hold an unjustifiable belief in their
requirements Determine the outcomes subordinates
rightness on issues The supportive leader is friendly and Leadership Behaviours Effective Leaders
want
Laissez-Faire shows concern for the needs of followers
Employees follow their lead
unquestioningly Reward individuals with their desired
The participative leader consults with outcomes
followers and uses their suggestions
before making a decision
Let individuals know what they need to do
to receive rewards
The achievement-oriented leader sets
challenging goals and expects followers to
perform at their highest level
You might also like
- Public Relations Cases 9th Edition Ebook PDFDocument61 pagesPublic Relations Cases 9th Edition Ebook PDFcarol.canale172100% (42)
- EHQMS Process MatrixDocument2 pagesEHQMS Process MatrixAbdullahKhan100% (6)
- One On One Meeting TemplateDocument2 pagesOne On One Meeting Templatemaria100% (1)
- 20.operational Work Plan Template PDFDocument2 pages20.operational Work Plan Template PDFPeter GathagaNo ratings yet
- Nets For Administrators 2002Document1 pageNets For Administrators 2002Maria MashorNo ratings yet
- Spiritual Centre - ReportDocument4 pagesSpiritual Centre - Reportlavanya thangavelNo ratings yet
- Nature & Significance of ManagementDocument5 pagesNature & Significance of ManagementRahul NairNo ratings yet
- Top Achievement Chart 2021 For ReportingDocument9 pagesTop Achievement Chart 2021 For ReportingKaJong JaclaNo ratings yet
- s1 17 Fbe MMM Guide FinalDocument2 pagess1 17 Fbe MMM Guide FinalJoy HsiehNo ratings yet
- HowtoMotivatePeople MindmapDocument1 pageHowtoMotivatePeople MindmapKris100% (1)
- Martin 2018 Developing An Editorial Team Tools For Sustained SuccessDocument1 pageMartin 2018 Developing An Editorial Team Tools For Sustained SuccessAZIZ EL ABDELLAOUINo ratings yet
- 10 Questions Guide To Make The Most of MentoringDocument9 pages10 Questions Guide To Make The Most of MentoringTatiana Helena EspositoNo ratings yet
- Chap 8Document1 pageChap 8Phu Nguyen NhutNo ratings yet
- Name: Oàn V Hào Student ID: 31201028653 Class: HRM-DH46ISB-01Document1 pageName: Oàn V Hào Student ID: 31201028653 Class: HRM-DH46ISB-01Nguyễn Huỳnh ĐứcNo ratings yet
- Development Plan SampleDocument2 pagesDevelopment Plan Samplemargie faustinoNo ratings yet
- IPM Rubrics MBA 2022-24Document7 pagesIPM Rubrics MBA 2022-24venkatesh sharmaNo ratings yet
- 12 PSPO - APAC - MayDocument1 page12 PSPO - APAC - Maychellappan29No ratings yet
- A Factory of OneDocument1 pageA Factory of OneFranquNo ratings yet
- Crash ProcrastinationDocument1 pageCrash ProcrastinationEric NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Recruitment To Hand-Off Process MapDocument1 pageRecruitment To Hand-Off Process MapMelchNo ratings yet
- 11 Progress Chart FBS NC IIDocument5 pages11 Progress Chart FBS NC IIHerminio T Villaco JrNo ratings yet
- Administracin - de - Recursos - Humanos - PDF Mapa Concptual#2 Final - Es.enDocument1 pageAdministracin - de - Recursos - Humanos - PDF Mapa Concptual#2 Final - Es.enVeronica SerranoNo ratings yet
- PADocument3 pagesPAaashika shresthaNo ratings yet
- Mind MapDocument1 pageMind Mapapi-552131457No ratings yet
- DirectingDocument1 pageDirectingValeriaNo ratings yet
- Internationalization Strategies Advisory ServiceDocument6 pagesInternationalization Strategies Advisory ServiceSir TemplarNo ratings yet
- Data 11052022Document1 pageData 11052022aljarrahcs2431No ratings yet
- Key Management ModelsDocument233 pagesKey Management ModelsJack HarlowNo ratings yet
- Human Resource Manager Security Officer Assistant Administrator Head Procurement Head Production Head Business DevelopmentDocument2 pagesHuman Resource Manager Security Officer Assistant Administrator Head Procurement Head Production Head Business Developmentshazeb aliNo ratings yet
- Presentation 2 JRuff Components of Succession Plan 1-5-17Document37 pagesPresentation 2 JRuff Components of Succession Plan 1-5-17Ambika PhalkeNo ratings yet
- Abdul Haseeb - 8 YOEDocument4 pagesAbdul Haseeb - 8 YOEShahwal KhanNo ratings yet
- UP College of Business Administration: Discussion PapersDocument17 pagesUP College of Business Administration: Discussion PapersReyna ClaveriaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - What Is StrategyDocument59 pagesChapter 1 - What Is StrategyAlex RossiNo ratings yet
- Guide To Writing A Winning ResumeDocument45 pagesGuide To Writing A Winning ResumeMurid PerempuanNo ratings yet
- AT Vs AE Vs ASDocument1 pageAT Vs AE Vs ASCelena.2017gmail.com CelenaNo ratings yet
- LeanIX Poster EA Vs SA Vs TA enDocument1 pageLeanIX Poster EA Vs SA Vs TA enNomadNikNo ratings yet
- Teacher Evaluation Measure T1Document2 pagesTeacher Evaluation Measure T1shehnaz khanNo ratings yet
- Highere Ducation Business Reference ModelDocument2 pagesHighere Ducation Business Reference ModelGabrielGarciaOrjuelaNo ratings yet
- Struktur Organisasi Manulife IndonesiaDocument1 pageStruktur Organisasi Manulife Indonesiabayu unoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9: Strategic ManagementDocument3 pagesChapter 9: Strategic ManagementAnay Gloriana100% (1)
- Management CH 1 Part 1 - Ahmed Yehia - ' Cairo University FCES (Cairo & Zayed) MKTBT NouR - Studocu 2Document1 pageManagement CH 1 Part 1 - Ahmed Yehia - ' Cairo University FCES (Cairo & Zayed) MKTBT NouR - Studocu 2Ahmed FawzyNo ratings yet
- How To Build A Better Lesson by Dr. Jane E. PollockDocument2 pagesHow To Build A Better Lesson by Dr. Jane E. PollockDiana S SanchezNo ratings yet
- Sunita Salariya - ResumeDocument3 pagesSunita Salariya - ResumePraful SinghNo ratings yet
- English Circular Canvas PDFDocument9 pagesEnglish Circular Canvas PDFUyen HoangNo ratings yet
- MS Customer 0107 LoResDocument1 pageMS Customer 0107 LoResragingfire_01No ratings yet
- QMS Process Matrix & ApplicationDocument2 pagesQMS Process Matrix & ApplicationSaravana kumar NagarajanNo ratings yet
- Entrepreneurial Competency PDFDocument12 pagesEntrepreneurial Competency PDFShiela OchoaNo ratings yet
- Human Resources Strategy: Recruiting and Hiring Talented PeopleDocument2 pagesHuman Resources Strategy: Recruiting and Hiring Talented PeopleSimaSenNo ratings yet
- FREE - Alignment - Crosswalk For Conscious Discipline Skills Structures and CLASS IndicatorsDocument2 pagesFREE - Alignment - Crosswalk For Conscious Discipline Skills Structures and CLASS IndicatorsGeisel Hidalgo SalasNo ratings yet
- Employees As CustomersDocument1 pageEmployees As CustomersNoel Saji PaulNo ratings yet
- التمكين الإداري كمدخل لتحسين جودة الخدمة دراسة حالة مؤسسة اتصالات الجزائر بالشلفDocument14 pagesالتمكين الإداري كمدخل لتحسين جودة الخدمة دراسة حالة مؤسسة اتصالات الجزائر بالشلفkymdz2s7vbNo ratings yet
- LD Concept and ConductDocument9 pagesLD Concept and ConductSakshi Singh YaduvanshiNo ratings yet
- Mapping Matrik PenelitianDocument2 pagesMapping Matrik PenelitianKatarina BernardaNo ratings yet
- Intelligent Grading Solution Brochure Ver2Document4 pagesIntelligent Grading Solution Brochure Ver2Welfredo Red Wolf YuLptNo ratings yet
- Acc 07242022Document1 pageAcc 07242022Gaurav PardeshiNo ratings yet
- Organization and ManagementDocument5 pagesOrganization and ManagementElla Q. Engco100% (1)
- 4 Major Contingency Leadership TheoriesDocument1 page4 Major Contingency Leadership TheoriesJordan ChizickNo ratings yet
- Oam Abm 11 OrganizingDocument27 pagesOam Abm 11 OrganizingAllyssa LaquindanumNo ratings yet
- Classical School of Management Taylorism Scientific/strategic ManagementDocument1 pageClassical School of Management Taylorism Scientific/strategic ManagementJohanna HolzerNo ratings yet
- MAPAC Workshop Presentation - Best Practices in Competency ModelingDocument60 pagesMAPAC Workshop Presentation - Best Practices in Competency ModelingAli RazaNo ratings yet
- Handbook of Improving Performance in the Workplace, The Handbook of Selecting and Implementing Performance InterventionsFrom EverandHandbook of Improving Performance in the Workplace, The Handbook of Selecting and Implementing Performance InterventionsNo ratings yet
- Learn Anything - A Collection of Free Structured Resources To Teach Yourself Just About AnythingDocument2 pagesLearn Anything - A Collection of Free Structured Resources To Teach Yourself Just About AnythingProxyYtNo ratings yet
- Solutions-W5 QuizDocument4 pagesSolutions-W5 QuizProxyYtNo ratings yet
- Project ManagementDocument1 pageProject ManagementProxyYtNo ratings yet
- MOTIVATION - 5 FactorsDocument1 pageMOTIVATION - 5 FactorsProxyYtNo ratings yet
- Pascal Programming 101Document1 pagePascal Programming 101ProxyYtNo ratings yet
- Cecilia Martínez, A01197738: Leadership and ManagementDocument1 pageCecilia Martínez, A01197738: Leadership and ManagementProxyYtNo ratings yet
- Decision Making & Strategic Planning: ReviewDocument1 pageDecision Making & Strategic Planning: ReviewProxyYtNo ratings yet
- Math For Machine LearningDocument1 pageMath For Machine LearningProxyYtNo ratings yet
- Creative Problems Solving Methods and Models: Dr. Helena Seli, Clinical Edu ProfDocument1 pageCreative Problems Solving Methods and Models: Dr. Helena Seli, Clinical Edu ProfProxyYtNo ratings yet
- Hot Water With Lemon Is Great: Simple 20-Sec Hug (Your Mom, Dad, Best Friend, Nana, Cousin)Document1 pageHot Water With Lemon Is Great: Simple 20-Sec Hug (Your Mom, Dad, Best Friend, Nana, Cousin)ProxyYtNo ratings yet
- Networks Structure of The InternetDocument1 pageNetworks Structure of The InternetProxyYtNo ratings yet
- Project ProposalDocument4 pagesProject ProposalIsabel Maxine DavidNo ratings yet
- Psychodynamic (Freud, Adler, Jung, Klein, Horney, Erikson & Fromm)Document17 pagesPsychodynamic (Freud, Adler, Jung, Klein, Horney, Erikson & Fromm)Germaine Julia GarridoNo ratings yet
- Peran Bidan Daam Promkes MentalDocument141 pagesPeran Bidan Daam Promkes MentalluxNo ratings yet
- Theory Applied To Informatics - Lewin's Change Theory CJNI JournalDocument4 pagesTheory Applied To Informatics - Lewin's Change Theory CJNI Journalالحسن فلاح عبد الحسنNo ratings yet
- The Bonding Patterns: The Dance of The Selves in RelationshipDocument6 pagesThe Bonding Patterns: The Dance of The Selves in RelationshipAna BastanNo ratings yet
- Application Letter BFPDocument2 pagesApplication Letter BFPMaricarDimas100% (1)
- Ethiopian TVET-System: Learning Guide # 3Document4 pagesEthiopian TVET-System: Learning Guide # 3Kefelegn Gulint100% (1)
- Occupational Stressand Its Effectson NursesDocument12 pagesOccupational Stressand Its Effectson NursesTrương Bình TrọngNo ratings yet
- Research Midterm ReviewerDocument22 pagesResearch Midterm ReviewerdonajinegarsulaNo ratings yet
- Econ 600. Seminar Presentation. Aysenur DurakDocument14 pagesEcon 600. Seminar Presentation. Aysenur DurakCHRISTOPHER PHIRINo ratings yet
- A Theoretical Approach - The Worker's Task Stress and Its Association With Job PerformanceDocument13 pagesA Theoretical Approach - The Worker's Task Stress and Its Association With Job PerformanceDwight Jenna de MesaNo ratings yet
- Freedom A Sentence or LiberationDocument7 pagesFreedom A Sentence or Liberationapi-583537917No ratings yet
- Filipino Family HierarchyDocument5 pagesFilipino Family HierarchyNaharia RangirisNo ratings yet
- English Language SBADocument8 pagesEnglish Language SBAShaquan JohnsonNo ratings yet
- Grand Case Presentation GuidelinesDocument10 pagesGrand Case Presentation Guidelinesscribd_lostandfoundNo ratings yet
- Home Visit Record (HVR) #1: Baseline of DataDocument3 pagesHome Visit Record (HVR) #1: Baseline of DataphoebeNo ratings yet
- Chapter One:雅思写作考试的难点所在 (The Main Hurdles in the IELTS Writing Test)Document3 pagesChapter One:雅思写作考试的难点所在 (The Main Hurdles in the IELTS Writing Test)Robert YehNo ratings yet
- Causation in Behavior: Some Fundamental Concepts Regarding Human BehaviorDocument4 pagesCausation in Behavior: Some Fundamental Concepts Regarding Human BehaviorIrtiSam MahinNo ratings yet
- QHSE Internal Meeting Agenda MinutesDocument1 pageQHSE Internal Meeting Agenda MinutesRocky BisNo ratings yet
- Academic Calendar 2023-2024Document1 pageAcademic Calendar 2023-2024joodgazlanNo ratings yet
- Assessment of KidneysDocument1 pageAssessment of KidneysWendy EscalanteNo ratings yet
- Episode 4: Individual Differences and Learner's Interaction: An Observation Guide For The Learner's CharacteristicsDocument7 pagesEpisode 4: Individual Differences and Learner's Interaction: An Observation Guide For The Learner's CharacteristicsHannahclaire Delacruz100% (1)
- Social Media and Mental Health ReflectionDocument2 pagesSocial Media and Mental Health Reflectionapi-373392149No ratings yet
- Guided Art GroupDocument8 pagesGuided Art Groupapi-533603915No ratings yet
- Fakultas Kedokteran Unhas: Syamsu Koordinator Sistem BioetikDocument34 pagesFakultas Kedokteran Unhas: Syamsu Koordinator Sistem BioetikAbduNo ratings yet
- Designing A Nutritional Bar: Name: MYP Year Level: 1 DateDocument10 pagesDesigning A Nutritional Bar: Name: MYP Year Level: 1 DateMonee MnmnNo ratings yet
- Topic 5-Strategic Plan Vision MissionDocument41 pagesTopic 5-Strategic Plan Vision Missionقيصر SllNo ratings yet
- Lindemann, Hilde - Brockmeier, Jens - Hydén, Lars-Christer-Beyond Loss - Dementia, Identity, Personhood-Oxford University Press (2014)Document225 pagesLindemann, Hilde - Brockmeier, Jens - Hydén, Lars-Christer-Beyond Loss - Dementia, Identity, Personhood-Oxford University Press (2014)VASCHOTI TRABANICO100% (1)