Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Cecilia Martínez, A01197738: Leadership and Management
Cecilia Martínez, A01197738: Leadership and Management
Uploaded by
ProxyYt0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views1 pageManagers must balance individual and community interests by setting strategic objectives, organizing resources, and motivating staff. Effective leadership considers cultural norms and adapts styles to tasks. Ethical leaders treat people well, encourage feedback, and prioritize integrity over personal gain.
Original Description:
Original Title
Leadership_and_Management
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentManagers must balance individual and community interests by setting strategic objectives, organizing resources, and motivating staff. Effective leadership considers cultural norms and adapts styles to tasks. Ethical leaders treat people well, encourage feedback, and prioritize integrity over personal gain.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views1 pageCecilia Martínez, A01197738: Leadership and Management
Cecilia Martínez, A01197738: Leadership and Management
Uploaded by
ProxyYtManagers must balance individual and community interests by setting strategic objectives, organizing resources, and motivating staff. Effective leadership considers cultural norms and adapts styles to tasks. Ethical leaders treat people well, encourage feedback, and prioritize integrity over personal gain.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
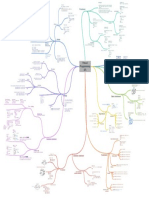
collectivists: act to help community
Cecilia Martínez, 1. Setting objectives & planning
individualists: strong, self-motivated
A01197738 establish general strategic objectives translate to tactical
objectives
managers; max. personal gain 2. Organizing resources to preplan & prepare necesarry resources
manager: person responsible meet the objectives
leadership traits result from cultural
norms & needs of task of setting objectives,
NOT only give instructions
organizing resources &
leaders in diferent countries are admired for motivating staff ensure structure to allow division of tasks
diferent qualitites each section organized to achieve objectives
3. Directing & motivating staff
understand importance of their role & exercisit carefully guiding, leading & overseeing employees
Cultural
make ethical issues discussion part of the business culture
encouragement of leadership in others
Considerations & motivate staff to develop abilities at work
Leadership Functions of business size increases need of coordination between parts
willingness to encourage & consider feedback & opinions
Management increase deal with & motivate
ability to ignore personal interests 4. Coordinating activities weld together all divisions' objectives to achieve sense of
staff at all levels
the ways they treat people purpose Figurehead: symbolic leader
indicators of ethical management by objectives allows to establish targets for all
their attitudes to people & situations leadership Leader: motivate subordinates/
groups
the ways they motivate 5. Controlling & measuring select & train staff
appraise performance against targets 1. Interpersonal roles
the direction in which they lead performance against targets Liaison: link with managers &
take action if underperformance occurs leader of other divisions
act as source, receiver &
etichal leaders must lead ethically components transmitter of info.
ethical leaders must act ethically
Ethical Consideration & Monitor (receiver): collect relevant data to
Leadership Styles managers undertake many roles
operations
degree of responsibility employees
common roles 2. Informational roles Disseminator: send collected info. from
are prepared to take on
ext. & int. sources to relevant people
training & experience of workforce
ethical leadership: leading by Mintzberg's Spokesperson: communicate info. to
amount of time available for participation knowing & doing what's right Leadership and Management Management Roles ext. groups
management culture & business background
main groups take decision & allocating
confidence personality of managers
depends on resources to meet objectives
strenght of character
Effectiveness of
Leadership Styles Entrepreneur: looks for new
importance of the issue opportunities to develop business
take decisions on their own Disturbance handler : respond to changing situations of
set objectives themselves keeps al decision-making at risk/ take responsibility when threatening factors develop
3. Decisional roles
the center of organization Resource allocator: decide allocation of
issue instructions to workers & ensure they
financial, human & other resources
are caried out
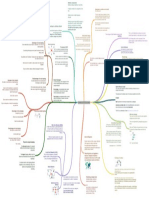
Autocratic Leaders styles Negotiator: represent organizarion in all
workers are dependant & won´t show iniciative important negotiations
low motivation of staff Leadership Styles
one-way communication (NO feedback) Differences Between leadership: act of motivating a group of
leaders are naturally different Management & Leadership people towards common objective
orders issued quickly (ex. police)
from others
in case of crisis desire to succeed & natural
fatherly style used by dominant males where self-confidence that they will
What Makes a
power is used to control & protect employees ability to think beyond the obvious
Good Leader
pay more attention to social aspects of employees creative
concerned with keeping them happy & motivated
encourage others to do the same Leadership Management
decisions with workers interests at heart Paternalistic Leaders
feedback & morale imporvement
multitalented
final decisions taken by management Motivate & inspire others Direct & monior others
higher loyalty & motivation understand wide range of issues Innovators who
encourage others to Problem-solvers
no true participation sense of frustration promotes the active incisive mind; identify heart of issue accept change
participation of rather then unnecessary details Official position of
Cares for personal traits
engage in discution with workers before taking decision workers in decisions responsibility in organization
& qualities
two-way communication
may lead to better final decisions Natural abilities & instincts Skilled & qualified to perform role
workers ofer valuable work experience Democratic Leaders
varies with the task, leaders Believes in the right thing Believes in doing things right
rapid change leads to need to cunsult workers Situational Leaders adapt style to each situation
Respected & trusted by Listened by others because
more acceptable to change when everyone has been involved followers of status
adapt to skills & experience of group
reverse of autocratic style most of decisions left Creates & develops a
to workforce, "hands- Accepts the norms
translates to "let them do it" adapt to task or job culture of change
off" approach
little input from management
effective in research or design teams
experts in the field work better when not tightly supervised Laissez-Faire Leadership
may lead to lack of confidence, poor decisions & poor motivation
may be hard to know if what they are doing is right
You might also like
- Quiz 2 COSC 611Document5 pagesQuiz 2 COSC 611ShalaNo ratings yet
- DEPED Opcrf (Principals, HTS)Document1 pageDEPED Opcrf (Principals, HTS)Carlo Tan-awon100% (12)
- Stakehokders Appraisal On Work ImmersionDocument7 pagesStakehokders Appraisal On Work ImmersionVanessa Marbida Bias100% (1)
- Colour - David HockneyDocument12 pagesColour - David Hockneyapi-24087681250% (2)
- Capsule Research Proposal Format: A. Basic InformationDocument2 pagesCapsule Research Proposal Format: A. Basic InformationCapt Karli67% (3)
- 5f-Management and OperationsDocument17 pages5f-Management and OperationsMak PussNo ratings yet
- Scope Functions Objectives Importance: Educational ManagementDocument1 pageScope Functions Objectives Importance: Educational ManagementNika Andrea N. PalermoNo ratings yet
- What Is Management? The Four Functions of ManagementDocument28 pagesWhat Is Management? The Four Functions of ManagementJoeNo ratings yet
- Chapter One (Managers and You in The Workplace)Document1 pageChapter One (Managers and You in The Workplace)d94n8mfvtgNo ratings yet
- OrgMan 12 NotesDocument18 pagesOrgMan 12 NotesDenine Dela Rosa OrdinalNo ratings yet
- Ch01 - MGT Understanding The Manager's JobDocument38 pagesCh01 - MGT Understanding The Manager's Jobsuonxaochuangot2708No ratings yet
- ABM104 ModuleDocument4 pagesABM104 ModuleKeith BumaatNo ratings yet
- Engineering Management Notes PrelimsDocument6 pagesEngineering Management Notes PrelimsSittie Farhanna MutinNo ratings yet
- Performance Management: People CMM Level 2 Process AreaDocument7 pagesPerformance Management: People CMM Level 2 Process Areaapi-3754364No ratings yet
- Doctor of Philosophy in ManagementDocument4 pagesDoctor of Philosophy in ManagementYan ŸanNo ratings yet
- Skills Skills: Management ManagementDocument7 pagesSkills Skills: Management ManagementAhmed MorsyNo ratings yet
- TranHuongGiang MO A1Document19 pagesTranHuongGiang MO A1Hương GiangNo ratings yet
- Nature and Concepts of ManagementDocument16 pagesNature and Concepts of ManagementPercephone RazonableNo ratings yet
- Erroneous Cues of Leadership Implications For Leadership Emergence and Leadership SelectionDocument20 pagesErroneous Cues of Leadership Implications For Leadership Emergence and Leadership SelectionParon SuksmithNo ratings yet
- Transformational Leadership Through Effective Internal CommunicationDocument30 pagesTransformational Leadership Through Effective Internal Communicationanon_7256579690% (1)
- Management: Science, Theory and PracticeDocument12 pagesManagement: Science, Theory and PracticeAyrton BenavidesNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8Document2 pagesChapter 8Perbielyn BasinilloNo ratings yet
- ENT 103 Opportunity Seeking ReportingDocument9 pagesENT 103 Opportunity Seeking Reportingtianbeds132No ratings yet
- Lecture 9Document19 pagesLecture 9Irish VargasNo ratings yet
- Leadership (CHP 7)Document35 pagesLeadership (CHP 7)Sabbir100% (1)
- # 7 OrganizingDocument18 pages# 7 OrganizingBella TorresNo ratings yet
- Leading (Slide)Document7 pagesLeading (Slide)AldrinNyandangNo ratings yet
- MG 8591 Pom NotesDocument218 pagesMG 8591 Pom NotesSundar 2151No ratings yet
- Activity2 1Document1 pageActivity2 1Bernice Cagbabanua MondingNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Management ReviewerDocument2 pagesFundamentals of Management ReviewerJovzkieNo ratings yet
- Northouse8e PPT 04Document21 pagesNorthouse8e PPT 04ARSLAN MEHMOODNo ratings yet
- Iani Adl Version1Document3 pagesIani Adl Version1Dominican MaSiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Managers & Managing (JG) : Management Efficiency EffectivenessDocument2 pagesChapter 1 - Managers & Managing (JG) : Management Efficiency EffectivenessDiva Tertia AlmiraNo ratings yet
- Organization and Management NotesDocument19 pagesOrganization and Management NotesSchanelle RenoballesNo ratings yet
- Management PemasaranDocument31 pagesManagement PemasaranNita ElianaNo ratings yet
- Principles and Practices of Management Notes - Knec Study Materials, Revision Kits and Past PapersDocument91 pagesPrinciples and Practices of Management Notes - Knec Study Materials, Revision Kits and Past PapersEudius muthoni100% (1)
- Mid Yearn Develoment PlanDocument3 pagesMid Yearn Develoment PlanKristine BaldomaroNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan: (With Inclusion of The Provisions of D.O. No. 8, S. 2015 and D.O. 42, S. 2016)Document6 pagesLesson Plan: (With Inclusion of The Provisions of D.O. No. 8, S. 2015 and D.O. 42, S. 2016)LOU BALDOMARNo ratings yet
- Bsbwor502 Lead and Manage Team EffectivenessDocument8 pagesBsbwor502 Lead and Manage Team EffectivenessQuynn AnnNo ratings yet
- HBBOODocument20 pagesHBBOOAnne VinuyaNo ratings yet
- The Functions of Management (Final)Document8 pagesThe Functions of Management (Final)adityakalani000oooNo ratings yet
- At&t - Group 3Document9 pagesAt&t - Group 3Juveriah FaruquiNo ratings yet
- What Is CompetencyDocument20 pagesWhat Is CompetencybimoNo ratings yet
- Orma - Chapter 1 Nature and Concepts of ManagementDocument55 pagesOrma - Chapter 1 Nature and Concepts of ManagementAbby Rosales - PerezNo ratings yet
- Organizational Structure TREE22Document37 pagesOrganizational Structure TREE22Reem AmrNo ratings yet
- Rangkuman Uas MPSDMDocument26 pagesRangkuman Uas MPSDMdella salsabilaNo ratings yet
- Human Resources Management in Construction (COTM 5201) (COTM 5201)Document9 pagesHuman Resources Management in Construction (COTM 5201) (COTM 5201)kndhinaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document1 pageChapter 1Aisyah Nabihah Mohd ZakiNo ratings yet
- Class 12 BST CH 7Document3 pagesClass 12 BST CH 7Atishya JainNo ratings yet
- Final Ledearship StylesDocument24 pagesFinal Ledearship StylesUmesh PatilNo ratings yet
- Name: Nashwa Jalil Ahmed Tambe ROLL - NO:43 Class.S.Y Bcom Div: A Subject: Business ManagementDocument6 pagesName: Nashwa Jalil Ahmed Tambe ROLL - NO:43 Class.S.Y Bcom Div: A Subject: Business ManagementNashwa TambeNo ratings yet
- Coaching For Better Result PDFDocument10 pagesCoaching For Better Result PDFsnas2206No ratings yet
- Learning Objectives Learning Objectives: Reflection Question Reflection QuestionDocument6 pagesLearning Objectives Learning Objectives: Reflection Question Reflection QuestionRona TuburanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Tutorial - Managers and Managing - Part 1Document22 pagesChapter 1 Tutorial - Managers and Managing - Part 1Ali SaloNo ratings yet
- Competency Framework: The Business Continuity Enviroment The Organisational Environment Ethics and ValuesDocument25 pagesCompetency Framework: The Business Continuity Enviroment The Organisational Environment Ethics and ValuesAlberto VentoNo ratings yet
- Lab Management - Notes Term 01Document24 pagesLab Management - Notes Term 01Janus FideliNo ratings yet
- Basic Management Functions What Do Managers Do?Document19 pagesBasic Management Functions What Do Managers Do?xintongqiu0No ratings yet
- 5064 Asm 1Document3 pages5064 Asm 1qh11022003No ratings yet
- 18MBA21 Human Resource Management VTUDocument6 pages18MBA21 Human Resource Management VTUVishnu PrasannaNo ratings yet
- OPERATION MANAGEMENT - Alao KyutiiiDocument2 pagesOPERATION MANAGEMENT - Alao KyutiiiJhonares CapiliNo ratings yet
- ? Core CompetenciesDocument23 pages? Core CompetenciesRamy MagdyNo ratings yet
- HM003 - Sahil Kumar - Assignmant 3 - An E-Poster PresentationDocument3 pagesHM003 - Sahil Kumar - Assignmant 3 - An E-Poster PresentationjdncwefdfnNo ratings yet
- An Agile Performance ManagementDocument2 pagesAn Agile Performance ManagementadarshrNo ratings yet
- Strategy-Driven Talent Management: A Leadership ImperativeFrom EverandStrategy-Driven Talent Management: A Leadership ImperativeRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- Solutions-W5 QuizDocument4 pagesSolutions-W5 QuizProxyYtNo ratings yet
- Learn Anything - A Collection of Free Structured Resources To Teach Yourself Just About AnythingDocument2 pagesLearn Anything - A Collection of Free Structured Resources To Teach Yourself Just About AnythingProxyYtNo ratings yet
- MOTIVATION - 5 FactorsDocument1 pageMOTIVATION - 5 FactorsProxyYtNo ratings yet
- Project ManagementDocument1 pageProject ManagementProxyYtNo ratings yet
- Pascal Programming 101Document1 pagePascal Programming 101ProxyYtNo ratings yet
- Math For Machine LearningDocument1 pageMath For Machine LearningProxyYtNo ratings yet
- Leadership: A Senior Employee Who Sponsors and Supports A Less-Experienced EmployeeDocument1 pageLeadership: A Senior Employee Who Sponsors and Supports A Less-Experienced EmployeeProxyYtNo ratings yet
- Networks Structure of The InternetDocument1 pageNetworks Structure of The InternetProxyYtNo ratings yet
- Decision Making & Strategic Planning: ReviewDocument1 pageDecision Making & Strategic Planning: ReviewProxyYtNo ratings yet
- Creative Problems Solving Methods and Models: Dr. Helena Seli, Clinical Edu ProfDocument1 pageCreative Problems Solving Methods and Models: Dr. Helena Seli, Clinical Edu ProfProxyYtNo ratings yet
- Hot Water With Lemon Is Great: Simple 20-Sec Hug (Your Mom, Dad, Best Friend, Nana, Cousin)Document1 pageHot Water With Lemon Is Great: Simple 20-Sec Hug (Your Mom, Dad, Best Friend, Nana, Cousin)ProxyYtNo ratings yet
- HRM Question BankDocument14 pagesHRM Question BankNeelam senNo ratings yet
- Listening RPHDocument3 pagesListening RPHSharkirin NazianNo ratings yet
- Love COT First QuarterDocument4 pagesLove COT First QuarterLovella Caputilla100% (1)
- The Roadmap For Innovating Sarawak Educational LandscapeDocument5 pagesThe Roadmap For Innovating Sarawak Educational Landscapebrenda nyapusNo ratings yet
- How To Be Goal Oriented - Definition & ExamplesDocument3 pagesHow To Be Goal Oriented - Definition & Examples1105195794No ratings yet
- Effects of Family Functioning and Family Hardiness On Self-Efficacy Among College StudentsDocument9 pagesEffects of Family Functioning and Family Hardiness On Self-Efficacy Among College StudentsSunway UniversityNo ratings yet
- Low and High Prep Differentiation StrategiesDocument4 pagesLow and High Prep Differentiation StrategiesMaureen WallNo ratings yet
- 11 PDFDocument233 pages11 PDFHatsune MikuNo ratings yet
- Human Error in Accidents-Ug-1Document10 pagesHuman Error in Accidents-Ug-1Aman GautamNo ratings yet
- Che Lesson PlanDocument4 pagesChe Lesson PlanmhehannNo ratings yet
- Assesment 2Document5 pagesAssesment 2Jose LopezNo ratings yet
- Iss Clark Kozma DebateDocument8 pagesIss Clark Kozma Debateapi-357361009100% (1)
- Insight: DR Ashish Debsikdar Resident-PsychiatryDocument73 pagesInsight: DR Ashish Debsikdar Resident-PsychiatrysprimalNo ratings yet
- ADB QualificationsDocument10 pagesADB QualificationsMark MedinaNo ratings yet
- Methods of TrainingDocument6 pagesMethods of TrainingMarian PamfilNo ratings yet
- Suspended Judgement and Six Thinking HatsDocument43 pagesSuspended Judgement and Six Thinking HatsPooja SheoranNo ratings yet
- 5.teori Personaliti TEORI AARON BECKDocument35 pages5.teori Personaliti TEORI AARON BECKJinn Ting TanNo ratings yet
- Solomon TekaDocument91 pagesSolomon TekaMeseret AbebeNo ratings yet
- Cyril Pottor College of Education Pv2B Home Economics (Major) Svetlana Dowding Pedagogy 2 Assignment #2 Essay On Micro TeachingDocument3 pagesCyril Pottor College of Education Pv2B Home Economics (Major) Svetlana Dowding Pedagogy 2 Assignment #2 Essay On Micro TeachingDaniel DowdingNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 - Using ICT in Developing 21st Century Skills Part 1Document11 pagesUnit 1 - Using ICT in Developing 21st Century Skills Part 1Jenica Mariel Gabaisen100% (2)
- Republic of The Philippines Department of EducationDocument3 pagesRepublic of The Philippines Department of EducationYvetteNo ratings yet
- Carl Rogers Person-Centered TheoryDocument7 pagesCarl Rogers Person-Centered TheoryElayiee33% (3)
- KSSR Assignment Role of Teacher Task 1Document14 pagesKSSR Assignment Role of Teacher Task 1YanHongNo ratings yet
- Ledermann Bodenmann Et Al. (2010) - Psychometrics of The Dyadic Coping Inventory in Three Language GroupsDocument12 pagesLedermann Bodenmann Et Al. (2010) - Psychometrics of The Dyadic Coping Inventory in Three Language GroupsRalukusha_No ratings yet
- Thesis TopicDocument1 pageThesis TopicshawnratulNo ratings yet