Professional Documents
Culture Documents
IS 1608: 2005 ISO 6892: 1998: Lower Yield Strength
Uploaded by
SvapneshOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
IS 1608: 2005 ISO 6892: 1998: Lower Yield Strength
Uploaded by
SvapneshCopyright:
Available Formats
IS 1608: 2005
ISO 6892: 1998
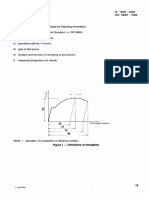
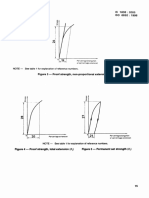
4.9.2.2 lower yield strength (ReL ) : Lowest value of stress during plastic yielding, ignoring any initial
transient effects (see .figure 2).
4.9.3 proof strength, non-proportional extension (/\fJ): Stress at which a non-proportional extension
is equal to a specified percentage of the extensomcter gauge length (/. f ) (see figure 3). The symbol
used is followed by a suffix giving the prescribed percentage, for example: I~po.~~.
4.9.4 proof strength, total extension (Rt ) : Stress at which total extension (elastic extension plus
plastic extension) is equal to a specified percentage of the cxtensorneter gauge length (/. c ) (see figure
4). The symbol used is followed by a suffix giving the prescribed percentage for example: /\to.s.
4.9.5 permanent set strength (/~r): Stress at which, after rernoval of force, a specified permanent
elongation or extension expressed respectively as a percentage of the original gauge length (/"0) or
extensometer gauge length (l"e) has not been exceeded (see figure 5).
The symbol used is followed by a suffix giving the specified percentage of the original gauge length (/"0)
or of the extensometer gauge length (te ), for example: J~rO.2'
5 Symbols and designations
Symbols and corresponding designations are given in table 1.
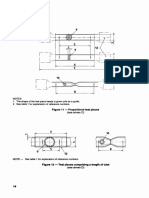
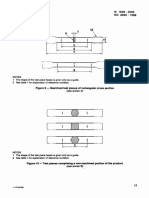
6 Test piece
6.1 Shape and dimensions
6.1.1 General
The shape and dimensions of the test pieces depend on the shape and dimensions of the metallic
product from which the test pieces are taken.
The test piece is usually obtained by machining a sample from the product or a pressed blank or
casting. However products of constant cross-section (sections, bars, wires, etc.) and also as-cast test
pieces (i.e. cast irons and non-ferrous alloys) may be tested without being machined.
The cross-section of the test pieces may be circular, square, rectangular, annular or, in special cases, of
some other shape.
Test pieces, the original gauge length of which is related to the original cross-sectional area by the
equation lJo k ~ are called proportional test pieces. The internationally adopted value for k is 5,65.
=
The original gauge length shall be not less than 20 mm. When the cross-sectional area of the test piece
is too small for this requirement to be met with the coefficient k value of 5,65, a higher value (preferably
11.3) or a non-proportional test piece may be used.
In the case of non-proportional test pieces, the original gauge tength (1.10) is taken independently of the
original cross-sectional area (So).
The dimensional tolerances of the test pieces shall be in accordance with the appropriate annexes
(see 6.2).
You might also like
- Euronorm 2-80Document16 pagesEuronorm 2-80Phung Tuan AnhNo ratings yet
- 2015.12.08 Material Models EN10002Document6 pages2015.12.08 Material Models EN10002Herman AucampNo ratings yet
- 343 3khbDocument35 pages343 3khbshimic32000100% (1)
- Testing of SteelDocument7 pagesTesting of Steelmushroom0320No ratings yet
- Derivation of torsion theory formulaDocument9 pagesDerivation of torsion theory formulasayerzNo ratings yet
- Mechanical testing - Tensile testing overviewDocument45 pagesMechanical testing - Tensile testing overviewshrikantajitNo ratings yet
- Note - The Concept of Parallel Length Is Replaced by The Concept of Distance Between Grips For Non-Machined Test PiecesDocument1 pageNote - The Concept of Parallel Length Is Replaced by The Concept of Distance Between Grips For Non-Machined Test PiecesSvapneshNo ratings yet
- Mapua University School of Mechanical and Manufacturing EngineeringDocument17 pagesMapua University School of Mechanical and Manufacturing EngineeringIsaiah BabilaNo ratings yet
- Tensile TestingDocument2 pagesTensile TestingFsNo ratings yet
- Moment End ConnectionsDocument8 pagesMoment End ConnectionsEfrainz TorresNo ratings yet
- Experiment 2Document2 pagesExperiment 2Ahmetgözde GözdeahmetNo ratings yet
- Lab Report-Strength of MaterialsDocument23 pagesLab Report-Strength of MaterialsArvin ArviniNo ratings yet
- Engineering Tensile Stress Strain DiagramsDocument9 pagesEngineering Tensile Stress Strain DiagramsMaurizio FalconieriNo ratings yet
- Imperfection, Residual Stress and Yield Slenderness Limit of Very High Strength (VHS) Circular Steel Tubes, 2003 (H Jiao, X.-L Zhao)Document17 pagesImperfection, Residual Stress and Yield Slenderness Limit of Very High Strength (VHS) Circular Steel Tubes, 2003 (H Jiao, X.-L Zhao)Phan Đào Hoàng HiệpNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Testing - Tensile Testing, Part 1Document4 pagesMechanical Testing - Tensile Testing, Part 1Mehmet Soysal100% (1)
- Bang So Sanh LinhDocument24 pagesBang So Sanh LinhMinh Vuong TranNo ratings yet
- Reaffirmed 2006Document13 pagesReaffirmed 2006harikri3113No ratings yet
- Twi Tensile TestingDocument10 pagesTwi Tensile TestingchungndtNo ratings yet
- Torsion Test AnalysisDocument19 pagesTorsion Test AnalysisHaziq PazliNo ratings yet
- 09.JiaYiing E.materials100 ReportDocument10 pages09.JiaYiing E.materials100 ReportJack JongNo ratings yet
- Tensile Testing Lab Determines Plastic PropertiesDocument36 pagesTensile Testing Lab Determines Plastic PropertiesalkharfaneNo ratings yet
- Design of Diagonal Cross-Bracings - Part 2 Experimental Study PDFDocument5 pagesDesign of Diagonal Cross-Bracings - Part 2 Experimental Study PDFGonzalo AbarcaNo ratings yet
- Tensile Test of Mild SteelDocument6 pagesTensile Test of Mild SteelAnshuman Dash100% (2)
- 1-Deformed and Plain Billet-Steel Bars For ConcreteDocument4 pages1-Deformed and Plain Billet-Steel Bars For ConcreteMJKHT100% (1)
- Example 8Document17 pagesExample 8Minishree BarkacharyNo ratings yet
- Guide To Physical Weld TestingDocument18 pagesGuide To Physical Weld TestingAMARA N SNo ratings yet
- TCVN 312 - 84Document9 pagesTCVN 312 - 84huytai8613100% (1)
- Uniaxial Tensile Test ExplainedDocument5 pagesUniaxial Tensile Test ExplainedSyed Imtinan AhmedNo ratings yet
- EWEC Copenhagen 2001-FlangeBoltFatigueDocument4 pagesEWEC Copenhagen 2001-FlangeBoltFatigueMarcWorldNo ratings yet
- 1586 C022Document12 pages1586 C022Engr Shahnawaz GhanchiNo ratings yet
- Gusset PlatesDocument12 pagesGusset PlatesJason GarnerNo ratings yet
- Effective Length Factors For Gusset Plate BucklingDocument12 pagesEffective Length Factors For Gusset Plate Bucklingkaranderohan100% (2)
- Experiment 8Document15 pagesExperiment 8Jaya Mae MañagoNo ratings yet
- Bending Test.Document24 pagesBending Test.Suzzo Sherwood0% (1)
- Analysis of Tension MembersDocument7 pagesAnalysis of Tension MembersAekJayNo ratings yet
- Press q3 Ass 2Document5 pagesPress q3 Ass 2Arslan RaoNo ratings yet
- Pengaruh Bentuk Takikan (Notched) Pada Poros Baja Karbon St. 60 Akibat Beban TarikDocument5 pagesPengaruh Bentuk Takikan (Notched) Pada Poros Baja Karbon St. 60 Akibat Beban TarikDelioPradanaNo ratings yet
- Tensile Test On SteelDocument14 pagesTensile Test On SteelDev SoniNo ratings yet
- BS 1881 Part 117 83 Spli Tensile StrengthDocument10 pagesBS 1881 Part 117 83 Spli Tensile Strengthrajeshji_000No ratings yet
- Tensile Test PresentationDocument36 pagesTensile Test Presentationssdivi100% (2)
- Charpy Impact Test For Metallic MaterialsDocument6 pagesCharpy Impact Test For Metallic MaterialsqwertyNo ratings yet
- Sheet Metal FormingDocument7 pagesSheet Metal FormingHussien EbrhimNo ratings yet
- Seminar Report On FEA Analysis of Shear Test Punching, TE ProjectDocument16 pagesSeminar Report On FEA Analysis of Shear Test Punching, TE Projectnishantgaurav48No ratings yet
- 2002 - Shear Lag in Double Angle Truss ConnectionsDocument8 pages2002 - Shear Lag in Double Angle Truss ConnectionsPO AsselinNo ratings yet
- Din en 1320-1996Document18 pagesDin en 1320-1996edcam13No ratings yet
- Tensile TestDocument8 pagesTensile TestChaminduKrishanRupasinghe100% (1)
- Experiment # 2 Tension Testing of MetalsDocument3 pagesExperiment # 2 Tension Testing of MetalsJ. Fabián MenaNo ratings yet
- Tensile TestDocument7 pagesTensile TestDhedhe PrasetyaNo ratings yet
- Connections and Tension Member DesignDocument9 pagesConnections and Tension Member DesignVigneshwari MahamuniNo ratings yet
- 6.1 Direct Design Moments and Flexural ReinforcementDocument14 pages6.1 Direct Design Moments and Flexural ReinforcementAnonymous OnzJpzNo ratings yet
- Ass 05 Tension in Circular RoodsDocument11 pagesAss 05 Tension in Circular RoodsMia HussainNo ratings yet
- Iisrt Raju Be (Civil)Document4 pagesIisrt Raju Be (Civil)IISRTNo ratings yet
- Collapse Arrestors For Deepwater Pipelines Cross-Over MechanismsDocument36 pagesCollapse Arrestors For Deepwater Pipelines Cross-Over MechanismsGovernment MULENo ratings yet
- Tensile Test AnalysisDocument8 pagesTensile Test AnalysisNazmul HasanNo ratings yet
- Engineering Vibroacoustic Analysis: Methods and ApplicationsFrom EverandEngineering Vibroacoustic Analysis: Methods and ApplicationsStephen A. HambricNo ratings yet
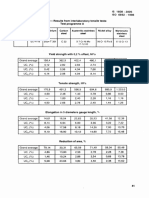
- ISO 6892 and ISO 1608 mechanical property standardsDocument1 pageISO 6892 and ISO 1608 mechanical property standardsSvapneshNo ratings yet
- Table K.1 - Results From Interlaboratory Tensile Tests: Test Programme ADocument1 pageTable K.1 - Results From Interlaboratory Tensile Tests: Test Programme ASvapneshNo ratings yet
- Is 1608 - 2005 - 39Document1 pageIs 1608 - 2005 - 39SvapneshNo ratings yet
- Is 1608 - 2005 - 36Document1 pageIs 1608 - 2005 - 36SvapneshNo ratings yet
- IS 1608: 2005 ISO 6892: 1998: 2,5 D From The GripDocument1 pageIS 1608: 2005 ISO 6892: 1998: 2,5 D From The GripSvapneshNo ratings yet
- Is 1608 - 2005 - 27Document1 pageIs 1608 - 2005 - 27SvapneshNo ratings yet
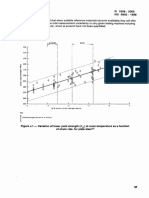
- Measurement Uncertainty Calculation for Room Temperature Tensile TestingDocument1 pageMeasurement Uncertainty Calculation for Room Temperature Tensile TestingSvapneshNo ratings yet
- ISO 6892: 1998 Annex K: Related To Material. TestDocument1 pageISO 6892: 1998 Annex K: Related To Material. TestSvapneshNo ratings yet
- Is 1608 - 2005 - 25Document1 pageIs 1608 - 2005 - 25SvapneshNo ratings yet
- Is 1608 - 2005 - 34Document1 pageIs 1608 - 2005 - 34SvapneshNo ratings yet
- IS 1608: 2005 ISO 6892: 1998: C.2.3Original Gauge Length C.2.3.1 Proportional Test PiecesDocument1 pageIS 1608: 2005 ISO 6892: 1998: C.2.3Original Gauge Length C.2.3.1 Proportional Test PiecesSvapneshNo ratings yet
- MM MM: A.2 Dimensions of The TestDocument1 pageMM MM: A.2 Dimensions of The TestSvapneshNo ratings yet
- (Ijo) N: Is 1608: 2005 Iso 6892: 1998Document1 page(Ijo) N: Is 1608: 2005 Iso 6892: 1998SvapneshNo ratings yet
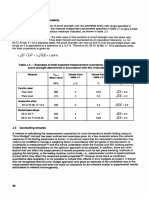
- ISO 6892:1998 and IS 1608:2005 tensile test data uncertaintyDocument1 pageISO 6892:1998 and IS 1608:2005 tensile test data uncertaintySvapneshNo ratings yet
- Is 1608 - 2005 - 30Document1 pageIs 1608 - 2005 - 30SvapneshNo ratings yet
- Is 1608 - 2005 - 31Document1 pageIs 1608 - 2005 - 31SvapneshNo ratings yet
- IS 1608: 2005 ISO 6892: 1998: Width Original Gauge Lengtn Original Cross - Sec - Ronal Area Thickness MMDocument1 pageIS 1608: 2005 ISO 6892: 1998: Width Original Gauge Lengtn Original Cross - Sec - Ronal Area Thickness MMSvapnesh100% (1)
- Is 1608 - 2005 - 23Document1 pageIs 1608 - 2005 - 23SvapneshNo ratings yet
- Figure 13 - Test Piece Cut From A TubeDocument1 pageFigure 13 - Test Piece Cut From A TubeSvapneshNo ratings yet
- Is 1608 - 2005 - 29Document1 pageIs 1608 - 2005 - 29SvapneshNo ratings yet
- ISO 6892 test report requirementsDocument1 pageISO 6892 test report requirementsSvapneshNo ratings yet
- Is 1608 - 2005 - 20Document1 pageIs 1608 - 2005 - 20SvapneshNo ratings yet
- Is 1608 - 2005 - 24Document1 pageIs 1608 - 2005 - 24SvapneshNo ratings yet
- ISO tube test standardsDocument1 pageISO tube test standardsSvapneshNo ratings yet
- IS 1608: 2005 ISO 6892: 1998: Figure 3 - Proof Strength, Non-Proportional ExtensionDocument1 pageIS 1608: 2005 ISO 6892: 1998: Figure 3 - Proof Strength, Non-Proportional ExtensionSvapneshNo ratings yet
- Figure 9 - Machined Test Pieces of Rectangular Cross SectionDocument1 pageFigure 9 - Machined Test Pieces of Rectangular Cross SectionSvapneshNo ratings yet
- 11 Determination of Percentage Elongation After FractureDocument1 page11 Determination of Percentage Elongation After FractureSvapneshNo ratings yet
- Is 1608 - 2005 - 10Document1 pageIs 1608 - 2005 - 10SvapneshNo ratings yet
- IS 1608: 2005 ISO 6892: 1998: III IIIDocument1 pageIS 1608: 2005 ISO 6892: 1998: III IIISvapneshNo ratings yet
- Is 1608 - 2005 - 18Document1 pageIs 1608 - 2005 - 18SvapneshNo ratings yet
- Solid Mechanics Question BankDocument2 pagesSolid Mechanics Question BankSIVANESANNo ratings yet
- The Investigation of Heat Transfer by Background Oriented Shlieren MethodDocument11 pagesThe Investigation of Heat Transfer by Background Oriented Shlieren MethodjulurusandeepNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan ME-102 Thermodynamics (EE)Document3 pagesLesson Plan ME-102 Thermodynamics (EE)fida khanNo ratings yet
- Regine Choe PDFDocument248 pagesRegine Choe PDFdavoodibrahimNo ratings yet
- Corrosion in Flexible Burner HosesDocument88 pagesCorrosion in Flexible Burner Hosesmviteazu100% (1)
- Ams03 GBDocument27 pagesAms03 GBmurtaliNo ratings yet
- Arun Jose Tom, Module 3, Bme PDFDocument120 pagesArun Jose Tom, Module 3, Bme PDFAswith ShenoyNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A 362 (1995) 487-498Document12 pagesNuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A 362 (1995) 487-498AresshioNo ratings yet
- Interaction With Earth Surface (Remote Sensing)Document33 pagesInteraction With Earth Surface (Remote Sensing)Sadia Sheikh100% (1)
- CPDA The Specification Design and Construction of Drainage and Sewerage Systems Using Vitrified Clay PipesDocument55 pagesCPDA The Specification Design and Construction of Drainage and Sewerage Systems Using Vitrified Clay PipesfaisaltmNo ratings yet
- 2018 Physics (1) (Sample Past Paper) PDFDocument19 pages2018 Physics (1) (Sample Past Paper) PDFAkuNo ratings yet
- Skirt Design PDFDocument8 pagesSkirt Design PDFTemesgen100% (1)
- C7-1 ADocument79 pagesC7-1 AAnonymous 24lnhhNo ratings yet
- Physical transformations of pure substances exercisesDocument1 pagePhysical transformations of pure substances exercisesAmirali MasoumiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3-Random - VariablesDocument66 pagesChapter 3-Random - VariablesBonsa HailuNo ratings yet
- 6 BMGT 220 Normal Approximation To B.d-P.d.Document2 pages6 BMGT 220 Normal Approximation To B.d-P.d.Pamela ChimwaniNo ratings yet
- Negros Academy: Learning Module IN Mathematics 9 2nd QuarterDocument16 pagesNegros Academy: Learning Module IN Mathematics 9 2nd QuarterLourdes de JesusNo ratings yet
- TLE - Shielded Metal Arc Welding 10 ThirdDocument4 pagesTLE - Shielded Metal Arc Welding 10 ThirdFlorinda GagasaNo ratings yet
- Design and Fabrication of a Hydraulic Floor CraneDocument29 pagesDesign and Fabrication of a Hydraulic Floor CraneVignesh DeepNo ratings yet
- Laboratory EquipmentsDocument3 pagesLaboratory EquipmentsDipaloy DattaNo ratings yet
- Bhaskara II: Casey GregoryDocument16 pagesBhaskara II: Casey GregoryVinayakaNo ratings yet
- Engineering Mathematics by Mohammad Abdul HalimDocument249 pagesEngineering Mathematics by Mohammad Abdul HalimArnobNo ratings yet
- E545-99 Neutron Image QualityDocument4 pagesE545-99 Neutron Image QualityaboutdestinyNo ratings yet
- Experiment No.12 PDFDocument5 pagesExperiment No.12 PDFAlisha AkterNo ratings yet
- Bom Grundfox Pump HSDocument80 pagesBom Grundfox Pump HSHai DoNo ratings yet
- Lapp Pro210738enDocument3 pagesLapp Pro210738enRatchakorn SartsermNo ratings yet
- Chemical Engineering in Practice Second Edition - SamplerDocument99 pagesChemical Engineering in Practice Second Edition - SampleraseethepalliNo ratings yet
- 7 3 A Tolerances ModifiedDocument4 pages7 3 A Tolerances Modifiedapi-30880110360% (5)
- Beam Design As Per BNBC 2020 and ACI 318-08Document1 pageBeam Design As Per BNBC 2020 and ACI 318-08আসিফ মাহমুদNo ratings yet
- Neuroimaging - Methods PDFDocument372 pagesNeuroimaging - Methods PDFliliana lilianaNo ratings yet