Professional Documents
Culture Documents
CLASS X BIO SPIRAL Student Notebook LIFE PROCESSES
Uploaded by
Pravind KumarOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
CLASS X BIO SPIRAL Student Notebook LIFE PROCESSES
Uploaded by
Pravind KumarCopyright:
Available Formats
BIOLOGY
CHAPTER 6: LIFE PROCESSES
1. What are the differences between autotrophic and heterotrophic nutrition.
AUTROPHIC HETROTROPHIC
NUTRITION NUTRITION
. Here the organisms prepare their own food In this nutrition organisms are depended
using raw material from outside source like indirectly or directly on other organisms
water and carbon dioxide
This is of two types – 1) chemoautotrophic It is of four typ 1) saprophyti2) parasitic 3)
and 2) photoautotrophic 3)symbiotic 4) holozoic
2. How does amoeba obtain nutrition? Explain with the help of diagram.
When amoeba comes near to the food particle, it extends its finger like
projection called pseudopodia and engulfs the food. This is how food vacuole is
formed. The process of digestion takes place inside the food vacuole. The food
which is not digested is egested out via the cell surface
3. What function is served by the following:
(i) Gastric sphincter (ii) Anal sphincter
Gastric Sphincter-Exit of food from the stomach is regulated by gastric
sphincter.
Anal Sphincter- Exit of undigested food from the body is regulated by large
intestine via the anal sphincter
4. Write down the functions of digestive enzyme.
Organ Enzyme/Secretion Function
Mouth Salivary amylase( Digestion of starch
Saliva)
Stomach Pepsin( Gastric Digestion of Protein
juice)
Copyright@DPSG X-SCIENCE Page | 1
Pancreas Trypsin( Pancreatic Digestion of Protein
juice)
Pancreas Lipase(Pancreatic Digestion of Fats
juice)
5. Draw a neat and well labelled diagram of human digestive system
Ans NCERT Diagram
6.Why is diffusion being not enough to meet the oxygen requirements of all the
cells in multicellular organisms?
AnsSince all the body cells are not in direct contact with the environment
Q7 What are the different ways in which glucose is oxidized to provide energy in
various organisms?
Ans:There are three pathways by which glucose is broken down in the living
organisms:
1. In the first pathway ,glucose is broken down in presence of oxygen. The
end products are carbon-dioxide, water and energy. It takes place in the
mitochondria
2. In the second pathway, glucose breaks down in limited supply of
oxygen. The end products are lactic acid. It takes place inside the
muscle cell.
3. In the third pathway, glucose breaks down in the absence of oxygen.
The end products are carbon dioxide and ethanol. It takes place inside
yeast.
Q8 How is oxygen and carbon dioxide transported in human beings?
Ans :Haemoglobin transports oxygen molecule to all the body cells for cellular
respiration. The haemoglobin pigment present in the blood gets attached to O2
molecules that are obtained from breathing and the blood becomes oxygenated.
This oxygenated blood is then distributed to all the body cells by the heart. After
giving awayO2 to the body cells, blood takes away CO2 which is the end product
of cellular respiration. Now the blood becomes de-oxygenated. Since
haemoglobin pigment has less affinity for CO2is mainly transported in the
dissolved form. This de-oxygenated blood gives CO2 to lung alveoli and takes O2
in return.
Q 9 . Draw a neat and labelled diagram of human respiratory system
Ans NCERT Diagram
Copyright@DPSG X-SCIENCE Page | 2
Q10: Draw a neat and labelled diagram of human heart
Ans NCERT Diagram
Q11 “Lymph is another type of fluid involved in transportation.” Justify this
statement by explaining the process
There is another type of fluid also involved in transportation. This is called
lymph or tissue fluid. Through the pores present in the walls of capillaries some
amount of plasma, proteins and blood cells escape into intercellular spaces in
the tissues to form the tissue fluid or lymph.. Lymph carries digested and
absorbed fat from intestine and drains excess fluid from extra cellular space
back into the blood.Lymph contains lymphocytes so it also fights against
infection
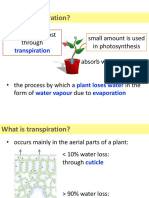
Q12 Which mechanism plays an important role in transportation of water in plants?
(I)During daytime (ii)At night
During day time- transpiration pull
At night – root pressure
Q13 What is translocation? How it takes place in plants?
The transport of soluble products of photosynthesis is called translocation and it occurs
in the parts of the vascular tissue known as phloem. The translocation in phloem is
achieved by utilizing energy. Material like sucrose is transferred into phloem tissue
using energy from ATP. This increases the osmotic pressure of the tissue causing water
to move into it. This pressure moves the material in the phloem to tissues which have
less pressure
Q14.What are the differences between the transport of materials in xylem and
phloem?
XYLEM PHLOEM
Here materials like water and minerals Here soluble products of photosynthesis,
are transported amino acids and salts are transported
Transportation takes place through Transpiration takes place due to
forces like transpiration pull and root difference in osmotic pressure utilizing
pressure the energy from ATP molecules
The transpiration in xylem is the passive Transportation in phloem is an active
process. Here the materials are process. Here the material is transported
transported only in upward direction in all direction
Copyright@DPSG X-SCIENCE Page | 3
15 Write any one function of an artificial kidney.
The dialysis machine plays the role of artificial kidney. For patients who suffer from
kidney disease where kidney doesn’t work properly. The hemodialysis machine helps to
filter the waste from the patient’s blood and helps the patient a normal life.
16 Major amount of water is selectively reabsorbed by the tubular part of nephron in
humans. What are the factors on which the amount of water reabsorbed depends?
Some substances in the initial filtrate such as glucose, amino acid, salts and a major
amount of water are selectively re-absorbed as the urine flows along the tube. The
amount of water reabsorbed depends on how much excess water there is in the body
and on how much of dissolved waste there is to be excreted
17.Draw a diagram of an excretory unit of a human kidney and label the following:
Bowman’s capsule, Glomerulus, Collecting Duct, Renal Artery.
Ans NCERT Diagram
18. Draw a neat diagram of human excretory system and label on it : urteter, kidney,
left renal artey and vena cava
Ans NCERT Diagram
19. List the different methods by which plant get rid of excretory waste products.
Ans: Many plants store waste materials in the vacuoles of mesophyll cells and
epidermal cells. When old leaves fall, the waste materials are excreted along with the
leaves.Plants get rid of excess water by the process of transpiration . Plants also excrete
some waste products into the soil around them.
Copyright@DPSG X-SCIENCE Page | 4
Copyright@DPSG X-SCIENCE Page | 5
You might also like
- Life processes and human nutritionDocument25 pagesLife processes and human nutritionTarun Gupta89% (19)
- Ebook PDF Campbell Biology Third 3rd Canadian Edition 2 PDFDocument41 pagesEbook PDF Campbell Biology Third 3rd Canadian Edition 2 PDFmary.martin569100% (31)
- Class 10 Life ProcessDocument11 pagesClass 10 Life ProcessShubham Tiwari100% (2)
- Animal Physiology PDFDocument111 pagesAnimal Physiology PDFShahnawaz MustafaNo ratings yet
- GCSE Biology Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandGCSE Biology Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Transport in Plants and Animals Questions and Answers - Biology Form 2 Topical Revision Transport in Plants - QuestionsDocument10 pagesTransport in Plants and Animals Questions and Answers - Biology Form 2 Topical Revision Transport in Plants - QuestionsOTIENO ELIJAHNo ratings yet
- Section A 1. The Characteristics of Living Things, Cell Structure, Function and SpecializationDocument12 pagesSection A 1. The Characteristics of Living Things, Cell Structure, Function and SpecializationJerry100% (1)
- GRB Physical Chemistry IIT JEE PDFDocument995 pagesGRB Physical Chemistry IIT JEE PDFsachin gupta75% (12)
- Wood AnatomyDocument16 pagesWood AnatomyDennis GilberoNo ratings yet
- Grapevine Structure and FunctionDocument15 pagesGrapevine Structure and FunctionRudy Tisnado AlejoNo ratings yet
- Life ProcessesDocument53 pagesLife Processessagar100% (1)
- Buku Rujukan Biologi T5 KSSM FullDocument192 pagesBuku Rujukan Biologi T5 KSSM Fullpooh67% (3)
- Life Processes Class 10 Notes Science - MyCBSEguide - CBSE Papers & NCERT SolutionsDocument5 pagesLife Processes Class 10 Notes Science - MyCBSEguide - CBSE Papers & NCERT SolutionsRajiv KabadNo ratings yet
- Life Processes Notes NewDocument10 pagesLife Processes Notes NewIshanNo ratings yet
- Sugggested Questions 2022Document16 pagesSugggested Questions 2022Peter HaobijamNo ratings yet
- Class X Physics NCERT Solution by NTSE GuruDocument6 pagesClass X Physics NCERT Solution by NTSE GuruNTSE GuruNo ratings yet
- Life Processes NotesDocument7 pagesLife Processes NotesTalented ShivaanshNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 - Life ProcessesDocument13 pagesChapter 5 - Life ProcessesAnshika yadavNo ratings yet
- ChopinDocument50 pagesChopinjojemjoeNo ratings yet
- Life ProcesssesDocument37 pagesLife ProcesssesAnanya ShakyaNo ratings yet
- Life ProcessesDocument7 pagesLife ProcesseskrithicktcrNo ratings yet
- Modes of Nutrition: Now The Question Arises How Autotrophic Nutrition Occurs in Plants Using Photosynthesis?Document6 pagesModes of Nutrition: Now The Question Arises How Autotrophic Nutrition Occurs in Plants Using Photosynthesis?Nilkanth Patel100% (1)
- Bio Notes Class XDocument129 pagesBio Notes Class XPhani Kumar AllamrajuNo ratings yet
- Biology Revision Sheet ByjussDocument12 pagesBiology Revision Sheet ByjussTaniya WadhwaniNo ratings yet
- Life Processes-2Document10 pagesLife Processes-2Vipul BullaNo ratings yet
- Life Processes Questions Q1Document15 pagesLife Processes Questions Q1Geeta ReddyNo ratings yet
- Life ProcessesDocument7 pagesLife Processesomkar108140% (1)
- The Kidneys in Human Beings Are A Part of The System For (A) Nutrition. (B) Respiration. (C) Excretion. (D) TransportationDocument17 pagesThe Kidneys in Human Beings Are A Part of The System For (A) Nutrition. (B) Respiration. (C) Excretion. (D) TransportationManj TamtaNo ratings yet
- 10 Science Notes 06 Life Processes 1Document12 pages10 Science Notes 06 Life Processes 1All Rounder HindustanNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter 6 Life Processes NotesDocument12 pagesCBSE Class 10 Science Chapter 6 Life Processes NotesAVIRUP DASNo ratings yet
- Modes of NutritionDocument19 pagesModes of NutritionPC Mad BoyNo ratings yet
- NCERT - Sol - Life ProcessesDocument11 pagesNCERT - Sol - Life ProcessesRagini BaghelNo ratings yet
- 6 LIFE PROCESSESDocument28 pages6 LIFE PROCESSEShaswinthkrishna1511No ratings yet
- 6, Life Processes: NCERT (CBSE) Textbook Exercise QuestionsDocument5 pages6, Life Processes: NCERT (CBSE) Textbook Exercise QuestionsTarique WaliNo ratings yet
- Life ProcessesDocument12 pagesLife ProcesseskkNo ratings yet
- HSBDocument12 pagesHSBjemima MillsNo ratings yet
- Life Processes Class 10 Biology Question AnswersDocument3 pagesLife Processes Class 10 Biology Question AnswersshalomNo ratings yet
- Ch 6 Life Processes NCERT Solutions (1)Document11 pagesCh 6 Life Processes NCERT Solutions (1)aalia hasanNo ratings yet
- 03 Life Processes Chapter Wise Important QuestionsDocument17 pages03 Life Processes Chapter Wise Important Questionsmm8871100% (1)
- LIFE PROCESSES NotesDocument6 pagesLIFE PROCESSES Notes9 D 140413 LOHITH KUNAPARAJUNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 10 Life Processes QuestionsDocument5 pagesCBSE Class 10 Life Processes QuestionsDeepakNo ratings yet
- Life Processes Notes Grade 10Document6 pagesLife Processes Notes Grade 10Danny BlessyNo ratings yet
- Solution 1:: Intext Exercise 1Document18 pagesSolution 1:: Intext Exercise 1OjasNo ratings yet
- BiologyDocument37 pagesBiologyThanosithebest12No ratings yet
- Life ProcessesDocument27 pagesLife Processesyogeshjngid41No ratings yet
- Class 10 Science (Bio) Term 1 CH 6 Life Process CWDocument6 pagesClass 10 Science (Bio) Term 1 CH 6 Life Process CWDivyanshi MalavNo ratings yet
- Unit Life Process Cbse 10Document14 pagesUnit Life Process Cbse 10Himanshu NagareNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Solutions Ncert Class 10Document12 pagesChapter 6 Solutions Ncert Class 10senthil2003kasNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 1 Life - ProcessesDocument33 pagesChapter - 1 Life - Processesarya avyukt100% (1)
- Class 10TH Biology Life ProcessDocument6 pagesClass 10TH Biology Life ProcessChirag KashyapNo ratings yet
- Untitled 1Document4 pagesUntitled 1Umang MaheshwariNo ratings yet
- Life ProcessesDocument10 pagesLife ProcessesAishwarya nNo ratings yet
- 23982021080308314123Document12 pages23982021080308314123budesasaiaw.v.re32.90No ratings yet
- 10th Life ProcessDocument10 pages10th Life ProcessSunil SeerviNo ratings yet
- Life Process Text SolutionDocument11 pagesLife Process Text Solutionkamruleslaam_5123739No ratings yet
- Class 10 Ch6 Life ProcessesDocument7 pagesClass 10 Ch6 Life ProcessesNeeyati BhardwajNo ratings yet
- 5 LIFE PROCESSES NotesDocument10 pages5 LIFE PROCESSES Notesprintcopyxerox printcopyxeroxNo ratings yet
- IFE RocessesDocument12 pagesIFE RocessesPravat TiadiNo ratings yet
- Life Processes GuideDocument9 pagesLife Processes GuideBhaskar SharmaNo ratings yet
- LIFE PROCESSESDocument6 pagesLIFE PROCESSESRakesh KumarNo ratings yet
- LIFE PROCESSES CLASS X BIOLOGYDocument34 pagesLIFE PROCESSES CLASS X BIOLOGYVipul GuptaNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan Sep 05, 2021iytzitst88txdDocument8 pagesAdobe Scan Sep 05, 2021iytzitst88txdKumari KNo ratings yet
- Lifes Internal Secrets VDocument23 pagesLifes Internal Secrets VYash PatelNo ratings yet
- Class - XI Physics Practical Year-2020-21Document33 pagesClass - XI Physics Practical Year-2020-21RiyaNo ratings yet
- Pair of Linear Equations in Two VariablesDocument26 pagesPair of Linear Equations in Two VariablesPravind KumarNo ratings yet
- Citizenship Activity Azadi Ki Amrit KahaniyanDocument1 pageCitizenship Activity Azadi Ki Amrit KahaniyanPravind KumarNo ratings yet
- Quadratic Equations: Factorisation MethodDocument12 pagesQuadratic Equations: Factorisation MethodPravind KumarNo ratings yet
- BibliographyDocument1 pageBibliographyPravind KumarNo ratings yet
- Rise of Nationalism in EuropeDocument17 pagesRise of Nationalism in EuropePravind KumarNo ratings yet
- Bus Routes Area Wise Combined 21-22Document3 pagesBus Routes Area Wise Combined 21-22Pravind KumarNo ratings yet
- SA Constitution Advantages and DisadvantagesDocument2 pagesSA Constitution Advantages and DisadvantagesPravind KumarNo ratings yet
- Map RevisionDocument25 pagesMap RevisionPravind KumarNo ratings yet
- Mandela's inspiring vision for a free South AfricaDocument3 pagesMandela's inspiring vision for a free South AfricaPravind KumarNo ratings yet
- NewsletterDocument4 pagesNewsletterPravind KumarNo ratings yet
- Ix Biology Notes (08!07!2021)Document3 pagesIx Biology Notes (08!07!2021)Dilson Babu DonNo ratings yet
- Bio LO.9 Questions M.DiaaDocument40 pagesBio LO.9 Questions M.DiaaRoxanne RoxyNo ratings yet
- Answered CXC Cells QuestionsDocument10 pagesAnswered CXC Cells QuestionsKeelah BennNo ratings yet
- Aimpt 2011 Mains Exam Solved PaperDocument18 pagesAimpt 2011 Mains Exam Solved PaperNavneet YadavNo ratings yet
- Aqa 8464B1H QP Nov21Document28 pagesAqa 8464B1H QP Nov21ShepardNo ratings yet
- Sol: WWW - Cbse.site/sc/fm117: To Purchase Hard Book of From Amazon Click HereDocument19 pagesSol: WWW - Cbse.site/sc/fm117: To Purchase Hard Book of From Amazon Click HereosumNo ratings yet
- Morphological and Anatomical Characters of Piper Betle L. From Madaya Township, Mandalay RegionDocument19 pagesMorphological and Anatomical Characters of Piper Betle L. From Madaya Township, Mandalay RegionAxel PangloliNo ratings yet
- Grade 11 BiologyDocument50 pagesGrade 11 BiologyLax ReignNo ratings yet
- 307 48 ET V1 S1 - File1 PDFDocument22 pages307 48 ET V1 S1 - File1 PDFaaaatniNo ratings yet
- 0610 w19 QP 42 PDFDocument24 pages0610 w19 QP 42 PDFrachitNo ratings yet
- Plant Anatomy An Applied ApproachDocument3 pagesPlant Anatomy An Applied ApproachPallavi ShawNo ratings yet
- 091 51 Final Biologi t5 Dlp-6-26Document21 pages091 51 Final Biologi t5 Dlp-6-26risya mariaNo ratings yet
- Biology 9700 FM23 Paper 2-SolvedDocument20 pagesBiology 9700 FM23 Paper 2-Solvedrayedr602No ratings yet
- Plant Anatomy & PhysiologyDocument2 pagesPlant Anatomy & PhysiologyGwenn PosoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 Transpiration Transport and Support in PlantsDocument119 pagesChapter 11 Transpiration Transport and Support in PlantsVenice LoNo ratings yet
- STM 007 Gen Biology ReviewerDocument12 pagesSTM 007 Gen Biology ReviewerAllessandra AlejandroNo ratings yet
- Sceince Mcqs General FinalDocument32 pagesSceince Mcqs General FinalSyed Atiq TurabiNo ratings yet
- Biology Paper 2Document14 pagesBiology Paper 2Adam K C TiongNo ratings yet
- Practical 2Document6 pagesPractical 2Ah BoonNo ratings yet
- Plant Cell and Animal CellDocument12 pagesPlant Cell and Animal CellKimverheart Dennisse NavalNo ratings yet
- Biology: Organic CompoundsDocument28 pagesBiology: Organic CompoundsMockinjayNo ratings yet
- Plant and Animal Tissues ComparedDocument12 pagesPlant and Animal Tissues Comparedhemlata GautamNo ratings yet
- Plant Tissue and Anatomy NotesDocument15 pagesPlant Tissue and Anatomy Noteskhan kashif100% (1)
- Cambridge Assessment International Education: Biology 9700/22 May/June 2019Document16 pagesCambridge Assessment International Education: Biology 9700/22 May/June 2019hendra pesiwarissaNo ratings yet
- I B.SC Botany - Root Secondary GrowthDocument13 pagesI B.SC Botany - Root Secondary Growthjeline raniNo ratings yet