Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Поурочный план 11 класс Free and Forced Electromagnetic waves
Uploaded by
Сымбат Хусайнова0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views7 pagesThis document contains a lesson plan for an 11th grade physics class on electromagnetic oscillations. The lesson plan aims to teach students about free and forced oscillations in LC circuits. Key objectives include sketching LC oscillator circuits and graphs of current and charge over time, and applying relationships between oscillation properties and circuit components like inductance and capacitance. The lesson involves an introduction, discussion of key concepts, examination of energy transfers in LC circuits, and a formative assessment. Differentiation strategies and a reflection on the lesson's effectiveness are also included.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document contains a lesson plan for an 11th grade physics class on electromagnetic oscillations. The lesson plan aims to teach students about free and forced oscillations in LC circuits. Key objectives include sketching LC oscillator circuits and graphs of current and charge over time, and applying relationships between oscillation properties and circuit components like inductance and capacitance. The lesson involves an introduction, discussion of key concepts, examination of energy transfers in LC circuits, and a formative assessment. Differentiation strategies and a reflection on the lesson's effectiveness are also included.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views7 pagesПоурочный план 11 класс Free and Forced Electromagnetic waves
Uploaded by
Сымбат ХусайноваThis document contains a lesson plan for an 11th grade physics class on electromagnetic oscillations. The lesson plan aims to teach students about free and forced oscillations in LC circuits. Key objectives include sketching LC oscillator circuits and graphs of current and charge over time, and applying relationships between oscillation properties and circuit components like inductance and capacitance. The lesson involves an introduction, discussion of key concepts, examination of energy transfers in LC circuits, and a formative assessment. Differentiation strategies and a reflection on the lesson's effectiveness are also included.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 7
Long-term plan unit: School:
IA. Electromagnetic oscillations
Date: Teacher name:
Grade: 11 Number present: Absent:
Theme of the lesson Free and forced electromagnetic oscillations.
Learning objective that
is achieved at this 11.4.2.1 - describe the conditions for the occurrence of free and
lesson(Subject
Programme reference) forced oscillations
Lesson objectives In this lesson, the students should be able to:
1. Sketch an LC oscillator and explain which quantities oscillate and
what constitutes one period of the oscillation.
2. For an LC oscillator, sketch graphs of the potential difference
across the capacitor and the current through the inductor as
functions of time, and indicate the period T on each graph.
3. For an LC oscillator, apply the relationships between the angular
frequency ω (and the related frequency f and period T ) and the
values of the inductance and capacitance.
4. Starting with the energy of a block–spring system, explain the
derivation of the differential equation for charge q in an LC
oscillator and then identify the solution for q(t).
Success criteria Learners achieve this learning objective, if they
Knowledge
Can find the current i(t) in the inductor as a function of time. giving
the charge q(t) on the capacitor in an LC oscillator
Comprehension
Can apply for an LC oscillator the relationship between the charge
amplitude Q, the current amplitude I, and the angular frequency ω.
Application
Can calculate for an LC oscillator the current i in the inductor for
any given time and identify the amplitude I of the current
oscillations
Language objectives The students should be able to answer orally all the questions
within the discussion as well as the questions in the formative
assessment.
Values instilled at the *Independent learning
lesslesson Appreciation for the unique abilities of each learner
Respect for other’s opinion
* Lifelong learning that theories learned from our discussion could
be applied also to practical life and as well as the problems solved
in this lesson might be helpful in taking the Physics SAT, SET and
Cambridge Exams
Cross-curricular links *Visual Literacy Instruction – the students must understand,
appreciate and comprehend what they have seen in the videos
*Utilization of IT in teaching and learning process.
ICT skills Powerpoint Presentation usage
Previous learning Grade 10 topics
Course of the lesson
Planne Planned activities at the lesson Resources
d
stages
of the
lesson
Beginni 1. Introduction of new topic and its learning objectives.
ng 2. Brief discussion of the glossary or keywords. Previous lesson
3. What do you mean by electromagnetic oscillations?
Middle We have examined simple single-loop circuits containing resistors
and capacitors (RC circuits) or resistors and inductors (RL circuits)
Now we’ll consider simple single-loop circuits containing inductors
and capacitors: LC circuits
We’ll see that LC circuits have currents and voltages that vary
sinusoidally with time, rather than increasing or decreasing
exponentially with time, as in RC and RL circuits
These variations of voltage and current in LC circuits are called
electromagnetic oscillations
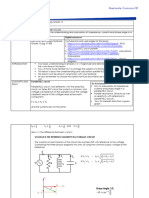
Consider a simple single-loop circuit consisting of an inductor and a
capacitor
The energy stored in the electric field of a capacitor with capacitance
C is given by UE = q2/2C
The energy stored in the magnetic feld of an inductor with inductance
L is given by UB = Li2/2
The charge on the capacitor varies with time
• Max positive to zero to max negative to zero back to max positive
The current in the inductor varies with time
• Zero to max negative to zero to max positive back to zero
The energy in the inductor varies with the square of the current and
the energy in the capacitor varies with the square of the charge
• The energies vary between zero and a maximum value
After reaching its maximum I0, the current i(t) continues to transport
charge between the capacitor plates, thereby recharging the capacitor.
Since the inductor resists a change in current, current continues to
flow, even though the capacitor is discharged. This continued current
causes the capacitor to charge with opposite polarity. The electric
field of the capacitor increases while the magnetic field of the
inductor diminishes, and the overall effect is a transfer of energy from
the inductor back to the capacitor. From the law of energy
conservation, the maximum charge that the capacitor re-acquires is q0.
However, the capacitor plates are charged opposite to what they were
initially.
Formative assessment
End
Differentiation – how do you Assessment – how are Health and safety regulations
plan to give more support? How you planning to check
do you plan to challenge the students’ learning?
more able learners?
Seating plan is used to Formative assessment is
differentiate. By placing students prepared for the students
of different abilities next to each to assess their learning
other where one will be of good for this day.
influence to the other and might The assessment is
explain the task more to his or attached at the end of
her groupmate in doing the this lesson plan.
experiment.
Reflection Use the space below to reflect on your lesson. Answer the most relevant
Were the questions from the box on the left about your lesson.
lesson
objectives/lea
rning
objectives
realistic? Did
all learners
achieve the
LO?
If not, why?
Did my
planned
differentiation
work well?
Did I stick to
timings?
What changes
did I make
from my plan
and why?
Summary evaluation
What two things went really well (consider both teaching and learning)?
1:
2:
What two things would have improved the lesson (consider both teaching and learning)?
1:
2:
What have I learned from this lesson about the class or achievements/difficulties of
individuals that will inform my next lesson?
You might also like
- Iit Jee Fiit Jee Study MaterialDocument21 pagesIit Jee Fiit Jee Study MaterialVishal_9360% (60)
- Introduction to Electromagnetic EngineeringFrom EverandIntroduction to Electromagnetic EngineeringRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- PBL 2022-2023 HandbookDocument11 pagesPBL 2022-2023 HandbookСымбат ХусайноваNo ratings yet
- (Dislocations in Solids 1) F.R.N. Nabarro - Dislocations in Solids - Elastic Theory (1979, North-Holland Publishing Co)Document179 pages(Dislocations in Solids 1) F.R.N. Nabarro - Dislocations in Solids - Elastic Theory (1979, North-Holland Publishing Co)Hariom PrakashNo ratings yet
- How To Make Salvia ExtractDocument37 pagesHow To Make Salvia ExtractTinchenkoNo ratings yet
- Stat & Prob 1 LPDocument22 pagesStat & Prob 1 LPWilber TuryasiimaNo ratings yet
- AP Physc em Inductance Unit Plan 2016-12-06Document3 pagesAP Physc em Inductance Unit Plan 2016-12-06黃吏維No ratings yet
- Course Outline Phy108 Inter 23Document3 pagesCourse Outline Phy108 Inter 23Ahmed Ajmine NehalNo ratings yet
- Series and Parallel CombinationDocument24 pagesSeries and Parallel Combinationalzidi0% (1)
- Topic 5 - Electric Circuits Y11 Scheme of WorkDocument15 pagesTopic 5 - Electric Circuits Y11 Scheme of WorkpaultonkinsonNo ratings yet
- Parallel Circuit Lab Lesson Plan E-Portfolio VersionDocument6 pagesParallel Circuit Lab Lesson Plan E-Portfolio Versionapi-668691050No ratings yet
- Electrical Engineering Lab (2 Year Chemical)Document23 pagesElectrical Engineering Lab (2 Year Chemical)VishalNo ratings yet
- Modified Lesson Plan: I. ContentDocument7 pagesModified Lesson Plan: I. ContentDharyl BallartaNo ratings yet
- Reflect Upon: How Would You Relate The Idea of Kirchhoff's Rule To Your Life As A Student and As Member of YourDocument2 pagesReflect Upon: How Would You Relate The Idea of Kirchhoff's Rule To Your Life As A Student and As Member of YourDesiree TorresNo ratings yet
- EMSAT Phy Syllabus 2021Document24 pagesEMSAT Phy Syllabus 2021Sou Al KazzazNo ratings yet
- ELTR110 Sec2 PDFDocument114 pagesELTR110 Sec2 PDFifeniyiNo ratings yet
- RC Differentiator and IntegratorDocument5 pagesRC Differentiator and IntegratorMd. AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Basic Ee Module 1 Discussion 2 Me2bDocument41 pagesBasic Ee Module 1 Discussion 2 Me2bStephen papaNo ratings yet
- AC6 Module9Document25 pagesAC6 Module9Fred BorjaNo ratings yet
- Course Outline ELEC 1002 Electrical Principles IDocument4 pagesCourse Outline ELEC 1002 Electrical Principles IFiveCent NickelNo ratings yet
- BE STheory Outline Fall2022 20221028Document4 pagesBE STheory Outline Fall2022 20221028Abubakar SajidNo ratings yet
- GeneralPhysics12 Q3 Ver4 Mod3 CapacitanceandCapacitors Ver4Document17 pagesGeneralPhysics12 Q3 Ver4 Mod3 CapacitanceandCapacitors Ver4belloheideliza2No ratings yet
- 1.BBV10503 - Principle Electrical TechnologyDocument4 pages1.BBV10503 - Principle Electrical TechnologyMohd HakimNo ratings yet
- Experiment Name: Introduction To Circuits. Students:: Osama Othman Rodaina Basem Asem DiabDocument8 pagesExperiment Name: Introduction To Circuits. Students:: Osama Othman Rodaina Basem Asem DiabًNo ratings yet
- Step 1 - To Make The Course Recognition: Steps, Phases of The Learning Strategy To DevelopDocument7 pagesStep 1 - To Make The Course Recognition: Steps, Phases of The Learning Strategy To DevelopNano NanoNo ratings yet
- Achieve Physics Public Specification 2020 ENGDocument24 pagesAchieve Physics Public Specification 2020 ENGSou Al KazzazNo ratings yet
- Q1W6Document5 pagesQ1W6Marc Allen CadangNo ratings yet
- Maths Revison List Year 10 All Sets Dec 15Document10 pagesMaths Revison List Year 10 All Sets Dec 15ollie deanNo ratings yet
- XII PhysicsDocument55 pagesXII PhysicsCharu BhanotNo ratings yet
- Achieve Physics Public Test Specifications English 2023Document23 pagesAchieve Physics Public Test Specifications English 2023LohuerNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan: Aims and ObjectivesDocument5 pagesLesson Plan: Aims and ObjectivesNJABULO NGUBANENo ratings yet
- Mahirap To DzaiDocument15 pagesMahirap To Dzaih ่100% (1)
- RPT Physics Form 5Document12 pagesRPT Physics Form 5SazlinAinaNo ratings yet
- Esees-1-0S Eses: KLS's Gogte Institute of Technology, Udyambag, BelagaviDocument6 pagesEsees-1-0S Eses: KLS's Gogte Institute of Technology, Udyambag, BelagavielmorsyNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan in Science 8Document4 pagesLesson Plan in Science 8mohamed harbNo ratings yet
- PHY319 - Electronics Practical I: ParticularsDocument5 pagesPHY319 - Electronics Practical I: ParticularsEddie Rio CokerNo ratings yet
- Lesson PlanDocument4 pagesLesson PlanEman AliNo ratings yet
- 5 SLK Capacitors FinalDocument19 pages5 SLK Capacitors FinalJansen YarteNo ratings yet
- Electricity Generation B8-SCI-WK6 - 2Document4 pagesElectricity Generation B8-SCI-WK6 - 2Kofi PaaNo ratings yet
- Basic Electrical Engineering Course Layout ContentsDocument5 pagesBasic Electrical Engineering Course Layout ContentsFahad SafiNo ratings yet
- MondayDocument3 pagesMondayKen Ryu LudangcoNo ratings yet
- Ultrasonics PPT1Document12 pagesUltrasonics PPT1twovissionsNo ratings yet
- WorkDocument13 pagesWorkKshama PandeyNo ratings yet
- DR. ISRAEL ETL7129printDocument13 pagesDR. ISRAEL ETL7129printAlfredNo ratings yet
- 2nd Sem - Basic Electrical EngineeringDocument4 pages2nd Sem - Basic Electrical Engineeringamjadali544No ratings yet
- Electronics, John Wiley and Sons, 1994Document3 pagesElectronics, John Wiley and Sons, 1994Fere GodspowerNo ratings yet
- Electrical Technology Grade 12 T1 W4 2021Document7 pagesElectrical Technology Grade 12 T1 W4 2021swshnz25gnNo ratings yet
- Courseoutline BE Spring 2020Document4 pagesCourseoutline BE Spring 2020prince12No ratings yet
- PHY 101 PowerpointDocument233 pagesPHY 101 PowerpointSyed ShahNo ratings yet
- Studymate Solutions To CBSE Board Examination 2013-2014: PHYSICS (Theory)Document19 pagesStudymate Solutions To CBSE Board Examination 2013-2014: PHYSICS (Theory)Vaibhav DubeyNo ratings yet
- Syllabus For ENGR065-01: Circuit Theory: Designation: Catalog DescriptionDocument4 pagesSyllabus For ENGR065-01: Circuit Theory: Designation: Catalog DescriptionErkanNo ratings yet
- Syllabus For Electromagnetic Fields and WavesDocument10 pagesSyllabus For Electromagnetic Fields and WavesHalefom HaileNo ratings yet
- Physics Essential Unit 7 (E07)Document5 pagesPhysics Essential Unit 7 (E07)Jaxon FlameNo ratings yet
- Weekweek 83Document5 pagesWeekweek 83Diana Joy Ancheta CldheiNo ratings yet
- EECE 1311 Electric CircuitsDocument6 pagesEECE 1311 Electric CircuitsMad lolNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1Document53 pagesLecture 1Virat BhangeNo ratings yet
- Achieve Physics Public Test Specifications - Eng - 2022 - JulyDocument25 pagesAchieve Physics Public Test Specifications - Eng - 2022 - JulyMansour AlmuainiNo ratings yet
- Physics Investigatory Project - Safa Azeem Zaina 2Document18 pagesPhysics Investigatory Project - Safa Azeem Zaina 2Reshma Mahjabeen100% (3)
- Phy0300 AnamikaDocument17 pagesPhy0300 Anamikaapi-312287352No ratings yet
- G8 DLL ElectricityDocument4 pagesG8 DLL ElectricityChanieNo ratings yet
- Oscillating-Circuits 0 PDFDocument31 pagesOscillating-Circuits 0 PDFjoseNo ratings yet
- Course Outline (PHY 108) - Summer 2023Document3 pagesCourse Outline (PHY 108) - Summer 2023fiad.sarowarNo ratings yet
- PHYS 10 21 V2 P Center of MassDocument10 pagesPHYS 10 21 V2 P Center of MassСымбат ХусайноваNo ratings yet
- PHYS 10 21 V1 P Center of MassDocument20 pagesPHYS 10 21 V1 P Center of MassСымбат ХусайноваNo ratings yet
- 6 PPT V2 Physics 11 Electromagnetic Oscillations. Free and Forced OscillationsDocument8 pages6 PPT V2 Physics 11 Electromagnetic Oscillations. Free and Forced OscillationsСымбат ХусайноваNo ratings yet
- 5 PPT V2 Physics 11 Electromagnetic Oscillations. Free and Forced OscillationsDocument8 pages5 PPT V2 Physics 11 Electromagnetic Oscillations. Free and Forced OscillationsСымбат ХусайноваNo ratings yet
- 4 PPT V2 Physics 11 Electromagnetic Oscillations. Free and Forced OscillationsDocument19 pages4 PPT V2 Physics 11 Electromagnetic Oscillations. Free and Forced OscillationsСымбат ХусайноваNo ratings yet
- Geometry, Topology and Physics - M.nakaharaDocument509 pagesGeometry, Topology and Physics - M.nakaharaNing Bao100% (4)
- B. Eng (Hons) Chemical Engineering: Course OutlineDocument9 pagesB. Eng (Hons) Chemical Engineering: Course OutlinemarkNo ratings yet
- Crossflow Turbine - A DIY Design ManualDocument6 pagesCrossflow Turbine - A DIY Design ManualAbhiroop89% (9)
- Kallam Haranadhareddy Institute of Technology: Department of Mechanical EngineeringDocument2 pagesKallam Haranadhareddy Institute of Technology: Department of Mechanical EngineeringsuswagatNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13 - GiancoliDocument4 pagesChapter 13 - GiancoliHectorCabzNo ratings yet
- A126 PDFDocument3 pagesA126 PDFProduction DepartmentNo ratings yet
- TUM CV2 SummaryDocument24 pagesTUM CV2 SummaryAbdullah Al SefatNo ratings yet
- WMA12 01 Que 20220119Document36 pagesWMA12 01 Que 20220119Mysterio OfficiallyNo ratings yet
- TFM Lajara CamachoDocument190 pagesTFM Lajara CamachorigobertoguerragNo ratings yet
- Std. 12 SCIENCE MATHS (050) (GSHSEB) : Year 2020 - 21 Deleted Portion & Non Deleted PortionDocument3 pagesStd. 12 SCIENCE MATHS (050) (GSHSEB) : Year 2020 - 21 Deleted Portion & Non Deleted PortionTwisha ParmarNo ratings yet
- Table of Design Properties For Metric Steel Bolts M5 To M39 - Eurocode 3Document8 pagesTable of Design Properties For Metric Steel Bolts M5 To M39 - Eurocode 3balamuruganNo ratings yet
- 01 Soil FormationDocument52 pages01 Soil FormationJonelNo ratings yet
- TPS65131-Q1 Positive-And Negative-Output DC-DC Converter: 1 Features 3 DescriptionDocument35 pagesTPS65131-Q1 Positive-And Negative-Output DC-DC Converter: 1 Features 3 DescriptionsachinNo ratings yet
- ChE 101.01 Physical and Thermal PropertiesDocument49 pagesChE 101.01 Physical and Thermal Propertieshamz786No ratings yet
- Welded ConnectionsDocument8 pagesWelded ConnectionsNitesh SinghNo ratings yet
- List of Rationalised Content in Textbooks For Class IXDocument32 pagesList of Rationalised Content in Textbooks For Class IXGaurang JhaNo ratings yet
- MA2111 MI Jan 2010 QP PDFDocument3 pagesMA2111 MI Jan 2010 QP PDFwhyfiveNo ratings yet
- Velocity and Acceleration PowerPointDocument22 pagesVelocity and Acceleration PowerPointSheila Marie100% (1)
- Vibration LabDocument15 pagesVibration LabAngarajSharmaNo ratings yet
- Chen 3009 - Tutorial 7 2020Document22 pagesChen 3009 - Tutorial 7 2020Rosario QFNo ratings yet
- 04 TimberDocument30 pages04 TimberolgaNo ratings yet
- Physical Quantities and Measurement STD 7 Physics NotesDocument6 pagesPhysical Quantities and Measurement STD 7 Physics NotesMyScribd_ieltsNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4-2 Sheet Metal FormingDocument19 pagesChapter 4-2 Sheet Metal FormingIhsan SamohNo ratings yet
- Standardization of Sodium Thiosulphate NDocument2 pagesStandardization of Sodium Thiosulphate NJoshua NathanaelNo ratings yet
- Calculation of Expected Sliding Distance of CaissonDocument36 pagesCalculation of Expected Sliding Distance of CaissonDinar IstiyantoNo ratings yet
- Organic ChemistryDocument2,476 pagesOrganic Chemistrytilakmirle75% (4)
- UtilityDocument39 pagesUtilityAsif AzizNo ratings yet
- Pinoy Ree - EeDocument138 pagesPinoy Ree - EeChilvin ChipmunkNo ratings yet