Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Note Hhhi02-Jul-2022
Uploaded by
nishantOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Note Hhhi02-Jul-2022
Uploaded by
nishantCopyright:
Available Formats
Basics of jammer
• A jammer is a device that blocks transmission or reception of signals, usually by generating more
powerful signal, creating some form of interference at the same frequency ranges that is used by the
device to be blocked.
• A jammers can block the system by jamming the various kinds of incoming signals like Bluetooth, or
signals used for cell phones, GPS signals, etc.
• Types of jammers
◦Portable jammers- These are phone-sized and low-powered devices. They can block data
delivery at a distance up to 15 meters without barriers.
◦Stationary jammers- These are more expensive and powerful. They usually have a larger
jamming radius and wider frequency band. Strong jammers can require additional cooling as they
can overheat. Stationary jammers usually have a range of 100 meters .
• Uses of jammers
◦Military uses - To deal with terrorists and anti social elements.
◦Examination centers to prevent malpractices.
◦In jails
◦In forest areas and deserted areas, where there exists an antisocial activity group etc.
◦Jamming at private place- movie theaters, hospitals and shopping malls where we can use the
jammers to avoid disturbances.
◦The mobile jammers are used in temples, churches, etc.
◦It is used in the seminar halls and meeting rooms to avoid disturbances
• Block diagram of jammer
————————————————————————
Radio Over Internet Protocol (RoIP)
• Radio over Internet Protocol (RoIP) is a technology for transmitting radio communication signals using
the Internet Protocol (IP) standard.
• Radio over Internet Protocol' (Radio Over I.P.) is a process of transmitting and receiving digital voice
packets (eg- audio, data) through the existing Internet Protocol infrastructure.
RoIP bene ts
• Lower cost- Integration with existing IP infrastructure (either LAN, WAN or VPN): Removing the need
for additional installation and maintenance of the network architecture.
• Better coverage: since the Internet is everywhere ,it has large coverage area.
• Reliability - RoIP is more reliable than traditional radio system.
• Communication disruption because of geographical barrier can be easily overcome by this.
• Internet Protocols are a set of rules that governs the communication and exchange of data over the
internet. Both the sender and receiver should follow the same protocols in order to communicate the
data
Drone Technology
• The term “drone” usually refers to any unpiloted aircraft. Sometimes referred to as “Unmanned Aerial
Vehicles" (UAVs), these crafts can carry out an impressive range of tasks, ranging from military
operations to package delivery.
• Drone Categories in India (Registration is required for all but the Nano category)
◦Nano: Less than or equal to 250 grams
◦Micro: From 250 grams to 2kg
◦Small: From 2kg to 25kg
◦Medium: From 25kg to 150kg
◦Large: Greater than 150kg
• Signi cance of Drones:
◦Use of drones in commercial, safety, law and order, disaster management and surveillance
operations reduce manpower requirement and costs.
◦Drones o er low-cost, safe and quick aerial surveys for data collection and are useful for
industries such as power, mining, realty and oil and gas exploration.
Internet of Things (IoT)
• The Internet of Things, or IoT, refers to the billions of physical devices around the world that are now
connected to the internet, all collecting and sharing data.
• A lightbulb that can be switched on using a smartphone app is an IoT device.
• IoT makes once "dumb" devices "smarter" by giving them the ability to send data over the internet,
allowing the device to communicate with people and other IoT-enabled things.
• IoT works in the following way:
◦Devices have hardware like sensors, for example, that collect data.
◦The data collected by the sensors is then shared via the cloud and integrated with software.
◦The software then analyzes and transmits the data to users via an app or website
◦Devices have hardware like sensors, for example, that collect data.
◦The data collected by the sensors is then shared via the cloud and integrated with software.
◦The software then analyzes and transmits the data to users via an app or website.
• Application of IoT
◦Smart Homes
◦Smart City
◦Self-driven Cars
◦IoT Retail Shops
◦Farming
◦Wearables
◦Smart Grids
◦Industrial Internet
◦Telehealth
◦Smart Supply-chain Management
◦Tra c management
◦Water and Waste management
Software-de ned radio (SDR)
• A Software De ned Radio (SDR) is a radio communication system that employs recon gurable
software-based components for processing and conversion of digital signals.
• The basic concept of the SDR software radio is that the radio can be totally con gured or de ned by
the software.
• Unlike traditional radio communication systems, these radio devices are highly exible and versatile.
Application of SDR
• Mobile communication- Software de ned radios are very useful in areas such as mobile
communications. By upgrading the software it is possible to apply changes to any standards and even
add new waveforms purely by upgrading the software and without the need for changes to the
hardware
• Research & development: The software de ned radio, SDR is very useful in many research projects.
The radios can be con gured to provide the exact receiver and transmitter requirements for any
application without the need for a total hardware design from scratch.
• Military: The military have made much use of software de ned radio technology enabling them to re-
use hardware and update signal waveforms as needed.
Advantages of SDR technology
• It is possible to achieve very high levels of performance.
• Performance can be changed by updating the software (it will not be possible to update hardware
dependent attributes though).
• It is possible to recon gure radios by updating software
• The same hardware platform can be used for several di erent radios.
Disadvantages of SDR technology
• Analogue to digital converters limit top frequencies that can be used by the digital section.
• For very simple radios the basic platform may be too expensive.
• Development of a software de ned radio requires both hardware and software skills.
CCTV (closed-circuit television)
• CCTV also known as video surveillance, is the use of video cameras to transmit a signal to a speci c
place, on a limited set of monitors.
DVR
• A Digital Video Recorder (DVR) records video to local storage devices, most commonly a hard drive.
• DVR can record analog video sources on-site or capture video from a digital source
• DVRs can be connected to analog cameras via coaxial cables, enabling them to be accessed remotely
DVR vs NVR
• In a DVR system, the camera stream is captured from analog cameras. The recorder processes the
video into a digital format to be stored . In an NVR system, video is captured with digital, or IP (Internet
Protocol) cameras. IP cameras process video directly from the camera itself.
Pros and Cons
• Reliability: Though NVRs are more convenient, DVRs o er a much more reliable connection as they
transmit signal via a wire and not via an internet connection.
• Recording Quality: When NVR systems are functioning properly they provide for much higher quality
footage than a DVR system.
• Installation: Because NVR systems are wireless or Ethernet, installing them is relatively simple. Unlike
a DVR system, which requires a point to point connection to every camera.
• Flexibility: Because the NVR inputs video from a network and not via a cable, it allows for much more
exibility than a DVR system.
• Cost: The biggest di erence between NVR and DVR systems is cost. DVRs are much cheaper than
NVRs
FAX
• Fax (short for facsimile), sometimes called telecopying or telefax (the latter short for telefacsimile), is
the telephonic transmission of scanned printed material (both text and images), normally to a
telephone number connected to a printer or other output device.
• The fax machine or facsimile machine is designed to send and receive an image electrically to another
machine through a telephone line. Basically, it scans printed texts and images from the sender’s
original paper and transmits the exact information to the recipient’s machine. In short, it reproduces
copies of the original documents.
Trunking
• Trunking is a technology for providing network access to multiple clients simultaneously by sharing a
set of circuits, carriers, channels, or frequencies, instead of providing individual circuits or channels for
each client.
• This resembles to the structure of a tree with one trunk and many branches.
• It allows large no. of users to share a channel.
• Trunked radio system - radio system where a large no. of users share a limited pool of channels
Channel allocated on demand & returned to channel pool upon call termination
◦Exploit statistical (random) behaviour of users so that xed no. of channels can accommodate
large no. of users
◦ Trunking theory used by telephone companies to allocate limited # of
◦voice circuits for large no. of telephone lines
◦E cient use of equipment resources - cost savings
◦Disadvantage is that some probability exists that mobile user will be denied access to a channel
EPABX (Electronic Private Automatic Branch Exchange)
• EPABX is an electronic device is a private telephone network used in O ces, Hotels, Industries and
many other places for voice communication.
• It is independent and can work with out any trunk lines
• With the help of this system, businesses aren’t required to run a line from every phone in the building
to the telephone company’s central o ce.
• Advantage-
◦The main advantage of EPABX for large organizations is cutting the cost
◦EPABX system is completely programmable. Hence, companies can modify the setup as per
custom needs.
◦The system has a minimal size & doesn’t occupy much space.
◦The system’s di erent functions like a conference call, call transfer, call waiting, automatic
attendant, auto ring back features help in daily use.
You might also like
- Optical Satellite Communication Space Terminal Tec PDFDocument11 pagesOptical Satellite Communication Space Terminal Tec PDFMustafaNo ratings yet
- Physics Form 5 Chapter 1Document39 pagesPhysics Form 5 Chapter 1Leong Laichuo40% (5)
- CATALOG 2020/2021: Antennas & AccessoriesDocument212 pagesCATALOG 2020/2021: Antennas & AccessoriesAnonymous ZlPONGNo ratings yet
- A Seminar ON 5G Wireless Network: - Presented byDocument37 pagesA Seminar ON 5G Wireless Network: - Presented byAbantika MohapatraNo ratings yet
- Wireless Systems Technology OverviewDocument52 pagesWireless Systems Technology OverviewhalpekNo ratings yet
- An Overview of TelecommunicationsDocument14 pagesAn Overview of Telecommunicationsmdude23No ratings yet
- AirScale Micro RRH 4T4R B42 - n78 40 W (AWHQE)Document6 pagesAirScale Micro RRH 4T4R B42 - n78 40 W (AWHQE)fabriciotelecom100% (2)
- It Networking Basic - IiDocument50 pagesIt Networking Basic - IigourimaheshNo ratings yet
- Sensor To CloudDocument15 pagesSensor To CloudMonark MehtaNo ratings yet
- Lecture7 WirelessDocument31 pagesLecture7 WirelessndanghaoNo ratings yet
- Smart Phone Generations and Wireless TechnologiesDocument54 pagesSmart Phone Generations and Wireless TechnologiesSkvkNo ratings yet
- BY Upasana GaikwadDocument30 pagesBY Upasana GaikwadRenu YadavNo ratings yet
- LO1 Plan For Installation of Telecommunications Network EquipmentDocument28 pagesLO1 Plan For Installation of Telecommunications Network EquipmentAnonymous AguLF9963HNo ratings yet
- Intranets and Wireless NetworksDocument28 pagesIntranets and Wireless NetworksseekjpNo ratings yet
- Wireless Tech in Embedded Systems GuideDocument20 pagesWireless Tech in Embedded Systems GuideAradhana MehraNo ratings yet
- Networking:: Group MembersDocument35 pagesNetworking:: Group MemberssameermahajanNo ratings yet
- Presented By: Vishwank Roll-1004252 ETC-4Document18 pagesPresented By: Vishwank Roll-1004252 ETC-4Vishwank SinghNo ratings yet
- Overview of Emerging TechnologiesDocument7 pagesOverview of Emerging TechnologiesInduja TrNo ratings yet
- 5G The NanocoreDocument35 pages5G The NanocoreKhushboo Soni100% (1)
- CSE190 Wireless Communication LectureDocument34 pagesCSE190 Wireless Communication LectureDr PNo ratings yet
- Explaining operations of zigbee, WiFi, infrared and Bluetooth networksDocument9 pagesExplaining operations of zigbee, WiFi, infrared and Bluetooth networksViJay KuMarNo ratings yet
- 5th Unit Pervasive ComputingDocument13 pages5th Unit Pervasive Computingashok2003No ratings yet
- Mobile Computing: PresentationDocument16 pagesMobile Computing: Presentationreach2ghoshNo ratings yet
- 4G Technology: Presented by Varun JayakumarDocument26 pages4G Technology: Presented by Varun JayakumarVarun JayakumarNo ratings yet
- Wireless Communication: Presented byDocument9 pagesWireless Communication: Presented byapi-19799369No ratings yet
- MCDocument159 pagesMCHetul GajjarNo ratings yet
- Mobile Computing: Presenting by P.Shravya 17S41A0573 Cse-BDocument16 pagesMobile Computing: Presenting by P.Shravya 17S41A0573 Cse-BRANGA RAJA VAMSHINo ratings yet
- Trends and Impact of Cloud Computing and Mobile AppsDocument31 pagesTrends and Impact of Cloud Computing and Mobile AppsMarivic AndradaNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Wireless CommunicationDocument18 pagesIntroduction to Wireless CommunicationSachin GdNo ratings yet
- Wireless Devices ExplainedDocument29 pagesWireless Devices ExplainedAnonymous yB5ZHepNo ratings yet
- Chapter One: Overview of Wireless CommunicationDocument24 pagesChapter One: Overview of Wireless CommunicationMehari TemesgenNo ratings yet
- Networks: - Jeslin JojuDocument12 pagesNetworks: - Jeslin Jojujeremy jacobNo ratings yet
- SWICOM: An SDR-Based Wireless Communication Gateway For VehiclesDocument22 pagesSWICOM: An SDR-Based Wireless Communication Gateway For VehiclesBhaskar BossNo ratings yet
- IT Training For StudentsDocument30 pagesIT Training For StudentsSubra maniyam majumderNo ratings yet
- Mobile Computing IntroductionDocument178 pagesMobile Computing Introductiongoraniya reenaNo ratings yet
- Project On Wirelees CommunicationDocument24 pagesProject On Wirelees CommunicationyatinasthaNo ratings yet
- NetworksDocument38 pagesNetworksnigelmudzi2003No ratings yet
- Introduction To Mobile Computing: A Concise OverviewDocument38 pagesIntroduction To Mobile Computing: A Concise Overviewعمار طعمةNo ratings yet
- INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTER NETWORK - FinalDocument26 pagesINTRODUCTION TO COMPUTER NETWORK - Finalcharmanejoy.barrientosNo ratings yet
- Overview of Emerging TechnologiesDocument18 pagesOverview of Emerging TechnologiesInduja TrNo ratings yet
- Wireless Comm PrinciplesDocument95 pagesWireless Comm PrinciplesSenthilathiban ThevarasaNo ratings yet
- Software Defined RadioDocument17 pagesSoftware Defined RadioJyoti BaliNo ratings yet
- Everything You Need to Know About Wi-Fi and Li-Fi TechnologyDocument10 pagesEverything You Need to Know About Wi-Fi and Li-Fi TechnologyMeer Zafarullah Noohani100% (1)
- Introdution To Internet of Things (Iot) : Module-2Document40 pagesIntrodution To Internet of Things (Iot) : Module-2Aanchal VermaNo ratings yet
- Computer Networks 3Document69 pagesComputer Networks 3Anthony Mafuta MayilameneNo ratings yet
- Lecture CellularTechnologies Part2Document78 pagesLecture CellularTechnologies Part2DanishNo ratings yet
- Intro to Data Comms & Computer NetworksDocument52 pagesIntro to Data Comms & Computer NetworksFerlyn Maye Angeles BenavidesNo ratings yet
- Securing IT Systems with Up-to-Date PracticesDocument45 pagesSecuring IT Systems with Up-to-Date PracticesSam DariNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document18 pagesChapter 1PlaY HARDNo ratings yet
- Lecture001 Basic Concepts of Mobile Computing (1) (Autosaved) (Autosaved)Document29 pagesLecture001 Basic Concepts of Mobile Computing (1) (Autosaved) (Autosaved)Joshua SongoroNo ratings yet
- HowTheIoTConnectDevices Y7Document15 pagesHowTheIoTConnectDevices Y7Sobha ANo ratings yet
- COM Network Models. Week 2Document45 pagesCOM Network Models. Week 2tweneannabel120No ratings yet
- IoT LoRaDocument27 pagesIoT LoRaPranjal YadavNo ratings yet
- CSC134 Chapter 8 PDFDocument44 pagesCSC134 Chapter 8 PDFQurratul FatihahNo ratings yet
- Chapter 01 Computer Networks and The InternetDocument90 pagesChapter 01 Computer Networks and The Internetgaucon12007No ratings yet
- Introduction To Wireless TechnologyDocument67 pagesIntroduction To Wireless TechnologyOlasupo OkunaiyaNo ratings yet
- Part I. Fundamental Concepts and DefinitionsDocument73 pagesPart I. Fundamental Concepts and Definitionskiiza ericNo ratings yet
- 3G and 4G: From: R.ROHITH (07S41A0533)Document11 pages3G and 4G: From: R.ROHITH (07S41A0533)Pranay RajNo ratings yet
- Term Paper IT-655Document11 pagesTerm Paper IT-655davidhenry001No ratings yet
- Mimo With Software Defined Radio: Navin KumarDocument38 pagesMimo With Software Defined Radio: Navin Kumarnavinrk100% (2)
- 4G Wireless Technology PresentationDocument26 pages4G Wireless Technology PresentationParag SenNo ratings yet
- Data Transmission: Presented By: Kristina Westin Andy Noll Jen StoeDocument35 pagesData Transmission: Presented By: Kristina Westin Andy Noll Jen StoeMiri ZeynalliNo ratings yet
- Program-Electronics and Telecommunication Engg: Unit 3-Physical LayerDocument42 pagesProgram-Electronics and Telecommunication Engg: Unit 3-Physical LayerANIKET BABARNo ratings yet
- Celestion Ckt-S-Tf1530EDocument6 pagesCelestion Ckt-S-Tf1530EGiovanni VirdisNo ratings yet
- Redline-LTE Glossary of Terms - 2021-Master-V1.2Document17 pagesRedline-LTE Glossary of Terms - 2021-Master-V1.2Tommy AsselinNo ratings yet
- Temporary Authority Ship Radio License CAPE BYRON 08 SEP 2023 11-31-59Document1 pageTemporary Authority Ship Radio License CAPE BYRON 08 SEP 2023 11-31-59GeorgeNo ratings yet
- Introduction To The Ran14.0 Fe Ature Dynamic Target Rot Adju StmentDocument19 pagesIntroduction To The Ran14.0 Fe Ature Dynamic Target Rot Adju StmentEric KouamoNo ratings yet
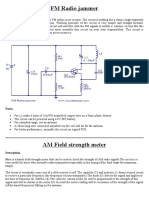
- FM Radio Jammer: DescriptionDocument4 pagesFM Radio Jammer: DescriptionnickususNo ratings yet
- Topic 1: Introduction To Next Generation Network (NGN)Document57 pagesTopic 1: Introduction To Next Generation Network (NGN)Shabil MuhammadNo ratings yet
- NE845 User ManualDocument5 pagesNE845 User ManualExartis GeorgeNo ratings yet
- WTH100 User Manual: QSZACCWTH100UM0100Document7 pagesWTH100 User Manual: QSZACCWTH100UM0100pepitoNo ratings yet
- Subiecte - Navigatie II (Si)Document6 pagesSubiecte - Navigatie II (Si)MariusNo ratings yet
- Evolution 2000 Package Product SheetDocument2 pagesEvolution 2000 Package Product SheetPetr PolakNo ratings yet
- EE 614 Solid State Microwave Devices AssignmentDocument1 pageEE 614 Solid State Microwave Devices Assignmentajay meenaNo ratings yet
- High Voltage Testing Measurement Equipment CatalogDocument46 pagesHigh Voltage Testing Measurement Equipment CatalogHari HidayatNo ratings yet
- Automatic Speed Control Based On Zones: Project Members 921711112023 921711112041 921711112049 Guided by (AP/ICE)Document17 pagesAutomatic Speed Control Based On Zones: Project Members 921711112023 921711112041 921711112049 Guided by (AP/ICE)Acu Healer Rasa KumarNo ratings yet
- Ir 2030Document101 pagesIr 2030Dmitry BlokhinNo ratings yet
- 2023-06 High Voltage Test Laboratory Concept Data-Engenharia V1.0Document384 pages2023-06 High Voltage Test Laboratory Concept Data-Engenharia V1.0Smart BoxNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Behavior of Composite Laminates With Electromagnetic High Impedance SurfacesDocument10 pagesMechanical Behavior of Composite Laminates With Electromagnetic High Impedance SurfacesSebastian AndreoliNo ratings yet
- Manual Prog P030Document22 pagesManual Prog P030Dennis Garces ZaldivarNo ratings yet
- TBL50100 - 1 - LISN Manual - V1 - 0 - 20230415Document11 pagesTBL50100 - 1 - LISN Manual - V1 - 0 - 20230415Michael MayerhoferNo ratings yet
- Tailoring MIL-STD-464A and MIL-STD-461F Requirements For Space Systems ApplicationsDocument4 pagesTailoring MIL-STD-464A and MIL-STD-461F Requirements For Space Systems ApplicationsnazmiNo ratings yet
- IIIT Nagpur Digital Signal Processing Exam Paper During Covid-19 2020 Pandemic.Document1 pageIIIT Nagpur Digital Signal Processing Exam Paper During Covid-19 2020 Pandemic.ANKIT BHURANENo ratings yet
- Presentation On ZXC10 BTSDocument19 pagesPresentation On ZXC10 BTSAli TahirNo ratings yet
- A Comparative Study of Different Types of Mixer ToDocument6 pagesA Comparative Study of Different Types of Mixer ToJosué DZUDIENo ratings yet
- Radar SystemsDocument22 pagesRadar SystemsAman BansalNo ratings yet
- A Novel Equivalent Circuit For Eshaped Slot Patch Antenna PDFDocument4 pagesA Novel Equivalent Circuit For Eshaped Slot Patch Antenna PDFbhawnaNo ratings yet
- Conti Session ProposalDocument8 pagesConti Session ProposalMynee TVNo ratings yet