Professional Documents
Culture Documents
ME421 - ch2 - Isentropic Flow - Printing
Uploaded by
Abdullah AkishOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
ME421 - ch2 - Isentropic Flow - Printing
Uploaded by
Abdullah AkishCopyright:
Available Formats
Gas Dynamics (ME 421) Chapter 2: Isentropic Flow with Area Changes
CHAPTER
Isentropic Flow with Area
Changes
Learning Outcomes
16:48
By the end of this chapter, you should:
Ch2: Flow with Area Changes
Explain flow through nozzles and diffusers.
Define choked flow.
Illustrate effect of back flow on nozzles and
diffusers.
Calculate flow properties through nozzles and
diffusers.
Dr. Bagabir
Dr. Ahmed Bagabir 1
Gas Dynamics (ME 421) Chapter 2: Isentropic Flow with Area Changes
Applications
16:48
nozzles and diffusers are found in many engineering
Ch2: Flow with Area Changes
applications including:
Steam turbines,
Gas turbines,
Aircrafts, and
Space crafts.
Dr. Bagabir
2D & 1D Flow
16:48
Ch2: Flow with Area Changes
Two-dimensional flow One-dimensional flow
Dr. Bagabir
𝝆 𝒙 𝒖 𝒙 𝑨 𝒙 = 𝒎 = 𝒄𝒐𝒏𝒔𝒕𝒂𝒏𝒕
4
Dr. Ahmed Bagabir 2
Gas Dynamics (ME 421) Chapter 2: Isentropic Flow with Area Changes
Nozzle & Diffuser
16:48
𝒅𝑨 𝑨 𝒅𝑨 𝑨
= − 𝟏 − 𝑴𝟐 = 𝟏 − 𝑴𝟐
Ch2: Flow with Area Changes
𝒅𝒖 𝒖 𝒅𝒑 𝝆𝒖𝟐
𝒅𝑨 < 𝟎 𝒅𝒖 > 𝟎, 𝒅𝒑 < 𝟎 𝒅𝒖 < 𝟎, 𝒅𝒑 > 𝟎
Dr. Bagabir 𝒅𝑨 > 𝟎 𝒅𝒖 < 𝟎, 𝒅𝒑 > 𝟎 𝒅𝒖 > 𝟎, 𝒅𝒑 < 𝟎
Nozzle & Diffuser
16:48
Ch2: Flow with Area Changes
Dr. Bagabir
Dr. Ahmed Bagabir 3
Gas Dynamics (ME 421) Chapter 2: Isentropic Flow with Area Changes
Converging–Diverging Duct
16:48
It used to accelerate gases from subsonic to
Ch2: Flow with Area Changes
supersonic speed.
M=1
Dr. Bagabir
Mach number is unity at the location of smallest flow
7 area (throat).
Flow through Throat
16:48
Ch2: Flow with Area Changes
Dr. Bagabir
Dr. Ahmed Bagabir 4
Gas Dynamics (ME 421) Chapter 2: Isentropic Flow with Area Changes
Extending Converging Nozzle
16:48
Ch2: Flow with Area Changes
Highest velocity is
sonic velocity at
nozzle exit.
Even if the nozzle
is extended.
Dr. Bagabir
Stagnation Relations
16:48
Ch2: Flow with Area Changes
𝑻𝟎 𝒌−𝟏
=𝟏+ 𝑴𝟐
𝑻 𝟐
𝒌⁄ 𝒌 𝟏
𝑷𝟎 𝒌−𝟏
= 𝟏+ 𝑴𝟐
𝑷 𝟐
𝟏⁄ 𝒌 𝟏
𝝆𝟎 𝒌−𝟏
= 𝟏+ 𝑴𝟐
𝝆 𝟐
Dr. Bagabir
10
Dr. Ahmed Bagabir 5
Gas Dynamics (ME 421) Chapter 2: Isentropic Flow with Area Changes
Exercise #1
16:48
Carbon dioxide flows through a varying-area duct
as shown. The gas enters the duct and expands to
Ch2: Flow with Area Changes
an exit pressure of 200 kPa. Find , u, A, and M at
each 400 kPa and throat (i.e. fill the table).
Dr. Bagabir
11
Exercise #1
16:48
Assume the flow is isentropic, steady, adiabatic, 1D,
and an ideal gas with constant specific heats.
Ch2: Flow with Area Changes
P (kPa) T (K) U (m/s) (kg/m3) c (m/s) A (cm2) M
1400 473 0 0
1000
600
Dr. Bagabir 200
12
Dr. Ahmed Bagabir 6
Gas Dynamics (ME 421) Chapter 2: Isentropic Flow with Area Changes
Flow through Throat
16:48
Ch2: Flow with Area Changes
Dr. Bagabir
13 At M=1 the state is called critical state (*)
Critical Relations (M=1)
16:48
Ch2: Flow with Area Changes
𝑻∗ 𝟐
=
𝑻𝟎 𝒌 + 𝟏
𝒌⁄ 𝒌 𝟏
𝑷∗ 𝟐
=
𝑷𝟎 𝒌+𝟏
𝟏⁄ 𝒌 𝟏
𝝆∗ 𝟐
=
Dr. Bagabir
𝝆𝟎 𝒌+𝟏
14
Dr. Ahmed Bagabir 7
Gas Dynamics (ME 421) Chapter 2: Isentropic Flow with Area Changes
Relations
16:48
Ch2: Flow with Area Changes
For k=1.4:
Dr. Bagabir
15
Exercise #2
16:48
Calculate the critical pressure and temperature for
Ch2: Flow with Area Changes
the flow conditions described in Exercise #1.
Dr. Bagabir
16
Dr. Ahmed Bagabir 8
Gas Dynamics (ME 421) Chapter 2: Isentropic Flow with Area Changes
Back Pressure - Nozzle
16:48
Ch2: Flow with Area Changes
Dr. Bagabir
17
Back Pressure - Nozzle
16:48
1. If the back pressure Pb is equal to P0, there is no
Ch2: Flow with Area Changes
flow and the pressure distribution is uniform
along the nozzle.
2. When the back pressure is reduced (> P*), this
causes the pressure along the nozzle to decrease
in the flow direction.
3. When the back pressure is reduced to P* (M=1),
mass flow reaches a maximum value and the flow
is said to be CHOKED.
4. Further reduction of the back pressure (<P*) does
not result in additional changes in the pressure
Dr. Bagabir
distribution along the nozzle length.
18
Dr. Ahmed Bagabir 9
Gas Dynamics (ME 421) Chapter 2: Isentropic Flow with Area Changes
Back Pressure - Nozzle
16:48
Ch2: Flow with Area Changes
Use equations T and P:
𝒌⁄ 𝒌 𝟏
𝑻𝟎 𝒌−𝟏 𝑷𝟎 𝒌−𝟏
=𝟏+ 𝑴𝟐 = 𝟏+ 𝑴𝟐
𝑻 𝟐 𝑷 𝟐
Dr. Bagabir
19
Converging nozzle can be used as a flowmeter.
Back Pressure - Nozzle
16:48
By differentiating mass equation with respect to M
Ch2: Flow with Area Changes
and setting the result equal to zero. It yields mass
flow rate is a maximum when M=1 at the throat.
Dr. Bagabir
20
Dr. Ahmed Bagabir 10
Gas Dynamics (ME 421) Chapter 2: Isentropic Flow with Area Changes
Back Pressure - Nozzle
16:48
Variation of flow area A through the nozzle relative to
Ch2: Flow with Area Changes
throat area A* can be given by:
𝑨 𝝆 𝒖
=
𝑨∗ 𝝆 ∗ 𝒖 ∗
Dr. Bagabir
21
Back Pressure - Nozzle
16:48
M* is the ratio of the local velocity to the speed of
Ch2: Flow with Area Changes
sound at the throat:
𝒖
𝑴∗ = ∗
= 𝑴 𝑻⁄ 𝑻 ∗
𝒄
∗
𝒌+𝟏
𝑴 =𝑴
𝟐 + 𝒌 − 𝟏 𝑴𝟐
Dr. Bagabir
22
Dr. Ahmed Bagabir 11
Gas Dynamics (ME 421) Chapter 2: Isentropic Flow with Area Changes
Back Pressure - Nozzle
16:48
Various property ratios for isentropic flow through
Ch2: Flow with Area Changes
nozzles and diffusers are listed in table 2-1:
Dr. Bagabir
23
Exercise #3
16:48
Air at 1 MPa and 600°C enters a converging nozzle,
Ch2: Flow with Area Changes
with a velocity of 150 m/s. Determine the mass flow
rate through the nozzle for a throat area of 50 cm2
when the back pressure is:
(a) 0.7 MPa and (b) 0.4 MPa.
Dr. Bagabir
24
Dr. Ahmed Bagabir 12
Gas Dynamics (ME 421) Chapter 2: Isentropic Flow with Area Changes
Assignment
16:48
Solve problems of the tutorial.
Ch2: Flow with Area Changes
Dr. Bagabir
25
Are all the Outcomes achieved?
16:48
Explain flow through nozzles and diffusers.
Ch2: Flow with Area Changes
Illustrate effect of back flow on nozzles and
diffusers.
Define choked flow.
Calculate flow properties through nozzles and
diffusers.
Dr. Bagabir
26
Dr. Ahmed Bagabir 13
Gas Dynamics (ME 421) Chapter 2: Isentropic Flow with Area Changes
Honest Feedback
16:48
Have you enjoyed it?
Ch2: Flow with Area Changes
Dr. Bagabir
27
Dr. Ahmed Bagabir 14
You might also like
- Instant Download Ebook PDF Aircraft Propulsion 2nd Edition by Saeed Farokhi PDF ScribdDocument41 pagesInstant Download Ebook PDF Aircraft Propulsion 2nd Edition by Saeed Farokhi PDF Scribdcynthia.sutton629100% (44)
- Grade 6 Harmony Course and Exercises PreviewDocument10 pagesGrade 6 Harmony Course and Exercises Previewwenwen16049988% (8)
- Lab Report 4 Colligative PropertiesDocument9 pagesLab Report 4 Colligative Propertiesapi-436054247No ratings yet
- PVV Cal Sheet LabixDocument45 pagesPVV Cal Sheet LabixPranpath Narupantawart50% (2)
- L 31Document12 pagesL 31RadhaAnanthalekshmiNo ratings yet
- 4.3 Motion One DirectionDocument7 pages4.3 Motion One DirectionDonte LymonNo ratings yet
- ME421 - ch2 - Isentropic Flow - Printing - FinalDocument23 pagesME421 - ch2 - Isentropic Flow - Printing - FinalAbdullah AkishNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Fluid StaticsDocument94 pagesChapter 2 Fluid StaticsnazreenNo ratings yet
- Dual Band Bandpass To Bandstop Switchable Filter With Independently Tunable Center Frequency and BandwidthDocument6 pagesDual Band Bandpass To Bandstop Switchable Filter With Independently Tunable Center Frequency and BandwidthShriman NarayanaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Fluid KinematicsDocument84 pagesChapter 3 Fluid KinematicsnazreenNo ratings yet
- Ecoprocesstm SBR Design NotesDocument3 pagesEcoprocesstm SBR Design NotesTrilok ChandraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Fluid PropertiesDocument46 pagesChapter 1 Fluid PropertiesnazreenNo ratings yet
- ME6604-Gas Dynamics and Jet PropulsionDocument19 pagesME6604-Gas Dynamics and Jet PropulsionAnish KumarNo ratings yet
- 2 A Review of Basic Laws - DocDocument17 pages2 A Review of Basic Laws - DocTrường Nguyễn HuyNo ratings yet
- ME6604-Gas Dynamics and Jet Propulsion PDFDocument12 pagesME6604-Gas Dynamics and Jet Propulsion PDFNANCY JUDITHNo ratings yet
- Compressible Flow: Fluid Mechanics: Fundamentals and Application Yunus A. Çengel & John M. Cimbala Chapter 12, Page 612Document12 pagesCompressible Flow: Fluid Mechanics: Fundamentals and Application Yunus A. Çengel & John M. Cimbala Chapter 12, Page 612Petronel MaimelaNo ratings yet
- Power Consumption in Shaking Flasks II Buchs 2000Document8 pagesPower Consumption in Shaking Flasks II Buchs 2000DuvánE.DueñasLópezNo ratings yet
- Flow MeasurementDocument4 pagesFlow MeasurementYong Khar HohNo ratings yet
- 8 Chapter 7a Mass Transfer Coefficients For Various GeometriesDocument31 pages8 Chapter 7a Mass Transfer Coefficients For Various GeometriesMathaneshan RajagopalNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7a Mass Transfer Coefficients For Various GeometriesDocument26 pagesChapter 7a Mass Transfer Coefficients For Various GeometriesrushdiNo ratings yet
- Nomenclature For Gpsa Engineering Data Book, 12 Ed - Section 9, Heat ExchangersDocument8 pagesNomenclature For Gpsa Engineering Data Book, 12 Ed - Section 9, Heat ExchangerstizeskiNo ratings yet
- 02 - ConvectionDocument64 pages02 - ConvectionSimon PechoNo ratings yet
- One-Dimensional Compressible Flow: Thermodynamics and Fluid Mechanics SeriesFrom EverandOne-Dimensional Compressible Flow: Thermodynamics and Fluid Mechanics SeriesNo ratings yet
- Fluid Module 2 For MeDocument18 pagesFluid Module 2 For Memeow meowNo ratings yet
- Fan LawsDocument39 pagesFan LawsbhatrkNo ratings yet
- Institute of Technology and Management: Second Internal Assessment Test, September 2020 - 21Document3 pagesInstitute of Technology and Management: Second Internal Assessment Test, September 2020 - 21wahqhanhasanNo ratings yet
- Two Phase Flow Measurement and CFD Analysis in An Air Lift LoopDocument6 pagesTwo Phase Flow Measurement and CFD Analysis in An Air Lift LooperpublicationNo ratings yet
- Eat 231: Thermodynamics: Mass and Energy Analysis of Control VolumesDocument36 pagesEat 231: Thermodynamics: Mass and Energy Analysis of Control VolumesYazid NazriNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Analysis of Pipeline FlowsDocument43 pagesChapter 5 Analysis of Pipeline FlowsnazreenNo ratings yet
- PROCESS FAB PACKAGE 390 SubDocument4 pagesPROCESS FAB PACKAGE 390 SubSandeep VaishnavNo ratings yet
- Journal Pre-Proof: Computers and Chemical EngineeringDocument44 pagesJournal Pre-Proof: Computers and Chemical EngineeringMarcin ChęcińskiNo ratings yet
- Fluid FlowDocument15 pagesFluid FlowRahul TaleNo ratings yet
- Fluid FlowDocument15 pagesFluid Flowdekra abdoNo ratings yet
- Spreadsheet To Calculate # of Tanks in Series According To Tank Geometry, Flow and AerationDocument7 pagesSpreadsheet To Calculate # of Tanks in Series According To Tank Geometry, Flow and Aerationnguyen anNo ratings yet
- Spreadsheet To Calculate # of Tanks in Series According To Tank Geometry, Flow and AerationDocument7 pagesSpreadsheet To Calculate # of Tanks in Series According To Tank Geometry, Flow and Aerationnguyen anNo ratings yet
- Spreadsheet To Calculate # of Tanks in Series According To Tank Geometry, Flow and AerationDocument7 pagesSpreadsheet To Calculate # of Tanks in Series According To Tank Geometry, Flow and Aerationnguyen anNo ratings yet
- Chapter - II - Fundamental of 1-D Compressible FlowDocument92 pagesChapter - II - Fundamental of 1-D Compressible FlowshmyeNo ratings yet
- Mixed Bed Deionisers - Anion Regeneration Parameters CalculationDocument1 pageMixed Bed Deionisers - Anion Regeneration Parameters CalculationZi Wei LeongNo ratings yet
- Experiment 2Document7 pagesExperiment 2Edyazuan ChannelNo ratings yet
- Effect of Hole Cleaning On Drilling Rate and PerformanceDocument7 pagesEffect of Hole Cleaning On Drilling Rate and PerformanceazeazeazeNo ratings yet
- 2 Marks With AnswersDocument9 pages2 Marks With AnswersAeronaughtycs HamdanNo ratings yet
- Week 9 Lecture Material - Watermark PDFDocument52 pagesWeek 9 Lecture Material - Watermark PDFايهاب عبدالعظيمNo ratings yet
- Second Internal Assessment Test, September 2020 - 21Document2 pagesSecond Internal Assessment Test, September 2020 - 21wahqhanhasanNo ratings yet
- MBBR Pack - GB - 1.0 - 06-10-2015Document8 pagesMBBR Pack - GB - 1.0 - 06-10-2015SvetlanaNo ratings yet
- A C M V: PsychrometryDocument31 pagesA C M V: PsychrometryMessi CakeNo ratings yet
- Lecture 17-18: Illustrations - 1: Nozzles, Diffusers, Turbines, CompressorsDocument24 pagesLecture 17-18: Illustrations - 1: Nozzles, Diffusers, Turbines, Compressorsmanish_aspiringNo ratings yet
- Institute of Aeronautical Engineering: (Autonomous) (Dundigal - 500 043, Hyderabad)Document5 pagesInstitute of Aeronautical Engineering: (Autonomous) (Dundigal - 500 043, Hyderabad)MARUTHU PANDIYANNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 Psychrometric ChartDocument10 pagesLecture 3 Psychrometric ChartAlifd0% (1)
- MAE 306 Exp 2 Air Speed Measurement UpdatedDocument19 pagesMAE 306 Exp 2 Air Speed Measurement UpdatedEvan YoungbergNo ratings yet
- Topic 2 - Molecular Transport Part 1Document35 pagesTopic 2 - Molecular Transport Part 1NUR HIJANAH BINTI MOHAMAD ZAHIDNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics FormulasDocument3 pagesFluid Mechanics FormulasDeo WarrenNo ratings yet
- Lecture 16Document16 pagesLecture 16yash sononeNo ratings yet
- Noise Reduction For Centrifugal Fan With Non-Isometric Forward-Swept Blade ImpellerDocument5 pagesNoise Reduction For Centrifugal Fan With Non-Isometric Forward-Swept Blade ImpellerVitthal KhandagaleNo ratings yet
- Full ThesisDocument107 pagesFull ThesisRaghavaNo ratings yet
- Lee 1994Document4 pagesLee 1994ninocfjrNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer by ConvectionDocument61 pagesHeat Transfer by ConvectionJason Yap Han YuenNo ratings yet
- Me 6604 GDJP 2 Marks With AnswersDocument16 pagesMe 6604 GDJP 2 Marks With AnswersKanagarajNo ratings yet
- Nomenclature For Gpsa Engineering Data Book, 12 ED. Section 9, Heat ExchangersDocument8 pagesNomenclature For Gpsa Engineering Data Book, 12 ED. Section 9, Heat ExchangersshikerNo ratings yet
- Nomenclature For Gpsa Engineering Data Book, 12 ED. Section 9, Heat ExchangersDocument8 pagesNomenclature For Gpsa Engineering Data Book, 12 ED. Section 9, Heat ExchangersRajesh PanchalNo ratings yet
- ME6604 GDJP - by Civildatas - Com 1Document151 pagesME6604 GDJP - by Civildatas - Com 1JamesNo ratings yet
- Specs of Voltage TransformersDocument11 pagesSpecs of Voltage TransformersSatya VasuNo ratings yet
- 4 - Momentum EquationDocument10 pages4 - Momentum EquationAbdullah AkishNo ratings yet
- 3 - Fluid Kinematics and DynamicsDocument35 pages3 - Fluid Kinematics and DynamicsAbdullah AkishNo ratings yet
- 2 - Fluid - StaticsDocument30 pages2 - Fluid - StaticsAbdullah AkishNo ratings yet
- Science 101 PhysDocument1 pageScience 101 PhysAbdullah AkishNo ratings yet
- ME421 - ch3 - Shock Wave - PrintingDocument24 pagesME421 - ch3 - Shock Wave - PrintingAbdullah AkishNo ratings yet
- ME421 ch1 Introduction TutorialDocument2 pagesME421 ch1 Introduction TutorialAbdullah AkishNo ratings yet
- ME421 ch1 Introduction PrintingDocument15 pagesME421 ch1 Introduction PrintingAbdullah AkishNo ratings yet
- Name: Teacher: Date: Score:: Converting Between Percents, Decimals, and FractionsDocument2 pagesName: Teacher: Date: Score:: Converting Between Percents, Decimals, and FractionsValentina SidhartaNo ratings yet
- GL SINU840Dsl PDFDocument96 pagesGL SINU840Dsl PDFRMK BrothersNo ratings yet
- Unit One: Introduction To ProgrammingDocument43 pagesUnit One: Introduction To ProgrammingabdiNo ratings yet
- Radar HW1Document2 pagesRadar HW1blue_fire_englandNo ratings yet
- New Microsoft Office Word DocumentDocument1,245 pagesNew Microsoft Office Word DocumentChinmaya nayakNo ratings yet
- Cengage Maths Solutions-Trigonometry Inverse+Trigonometric+FunctionsDocument54 pagesCengage Maths Solutions-Trigonometry Inverse+Trigonometric+Functionskayjayme318No ratings yet
- TDS 400kVA 20kV 400V 50Hz Dyn5 - 5 IndoorDocument2 pagesTDS 400kVA 20kV 400V 50Hz Dyn5 - 5 IndoorAfrizal AntariksaNo ratings yet
- Resource Description Framework (RDF)Document24 pagesResource Description Framework (RDF)Jahir HasanNo ratings yet
- $RE54804Document301 pages$RE54804psmNo ratings yet
- A526365 PDFDocument19 pagesA526365 PDFTimothy ThorntonNo ratings yet
- Math Corrproblems 2019Document4 pagesMath Corrproblems 2019weng paraleNo ratings yet
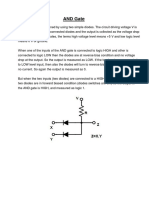
- AND Gate. Project PhysicsDocument6 pagesAND Gate. Project PhysicssumitaNo ratings yet
- ECE468 Computer Organization & Architecture The Design Process & ALU DesignDocument16 pagesECE468 Computer Organization & Architecture The Design Process & ALU DesignchandruuncleNo ratings yet
- Coordination CompoundDocument17 pagesCoordination CompoundRohit Mehta0% (1)
- Bank Tables - ArchitectureDocument5 pagesBank Tables - ArchitectureMathan Anto MarshineNo ratings yet
- MAT214ALecture4 19Document5 pagesMAT214ALecture4 19goflux pwnsNo ratings yet
- Experiment 10 (Chemistry)Document10 pagesExperiment 10 (Chemistry)nikenantha100% (1)
- Activity No. 1.2 Synthesis. Nature's NumberDocument4 pagesActivity No. 1.2 Synthesis. Nature's NumberKenneth Herrera0% (1)
- Measuring Romi Slide DeckDocument51 pagesMeasuring Romi Slide Deckabhishek_sharma_150No ratings yet
- ACSDocument28 pagesACSCristhian JuliánNo ratings yet
- Corrosion - WikipediaDocument16 pagesCorrosion - WikipediaAVINASHRAJNo ratings yet
- Solar Power ScribDocument9 pagesSolar Power ScribJose C. Lita JrNo ratings yet
- Solved Hugo Has A Concave Utility Function of U W w0 5Document1 pageSolved Hugo Has A Concave Utility Function of U W w0 5M Bilal SaleemNo ratings yet
- GTDocument31 pagesGTMD. TasneemNo ratings yet
- Poon 2001Document10 pagesPoon 2001Al CaponeNo ratings yet
- Madanapalle Institute of Technology & Science: Madanapalle (Ugc-Autonomous) WWW - Mits.ac - inDocument41 pagesMadanapalle Institute of Technology & Science: Madanapalle (Ugc-Autonomous) WWW - Mits.ac - inRavikanth NssNo ratings yet
- Chassis, Aerodynamics and FeaDocument25 pagesChassis, Aerodynamics and FeaSivaPrasad Chekri100% (1)