Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Bio Cells
Bio Cells
Uploaded by
Sakinah0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
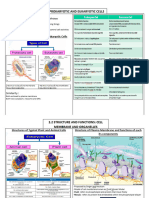
12 views2 pagesThis document summarizes the structure and function of several key organelles in eukaryotic cells. It describes the nucleus, which contains the genetic material DNA and produces ribosomes; mitochondria, which produces ATP through respiration; and the Golgi complex, which packages and transports proteins and lipids. It also outlines lysosomes and phagosomes, which break down waste; ribosomes, which synthesize proteins; chloroplasts, which perform photosynthesis; and vacuoles, which store waste and pigments. The cell wall and endoplasmic reticulum are also summarized as providing structure and transport.
Original Description:
Original Title
bio cells
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document summarizes the structure and function of several key organelles in eukaryotic cells. It describes the nucleus, which contains the genetic material DNA and produces ribosomes; mitochondria, which produces ATP through respiration; and the Golgi complex, which packages and transports proteins and lipids. It also outlines lysosomes and phagosomes, which break down waste; ribosomes, which synthesize proteins; chloroplasts, which perform photosynthesis; and vacuoles, which store waste and pigments. The cell wall and endoplasmic reticulum are also summarized as providing structure and transport.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views2 pagesBio Cells
Bio Cells
Uploaded by
SakinahThis document summarizes the structure and function of several key organelles in eukaryotic cells. It describes the nucleus, which contains the genetic material DNA and produces ribosomes; mitochondria, which produces ATP through respiration; and the Golgi complex, which packages and transports proteins and lipids. It also outlines lysosomes and phagosomes, which break down waste; ribosomes, which synthesize proteins; chloroplasts, which perform photosynthesis; and vacuoles, which store waste and pigments. The cell wall and endoplasmic reticulum are also summarized as providing structure and transport.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
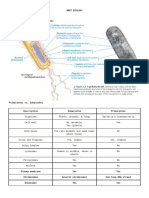
NAME STRUCTURE FUNCTION
NUCLEUS -Nuclear envelope (inner+outer -To separate inner/outer parts of cell
(SPHERICAL, 10-20UM membranes - phosholipids) -Molecule exchange
DIAMETER NORMALLY) -Nuclear pores -DNA + proteins
-Chromatin -Suspension, transport
-Nucleoplasm -Produces ribosomes
-Nucleolus
MITOCHONDRION (1- -Outer membrane -Entry/exit
10UM LENGTH) -Inner membrane (-folded to form: ) -Contains protein, lipids, DNA ->
-Crista (cristae) (-give large surface area makes up remainder
for enzymes in respiration) - Produces energy carrier molecule
-Matrix (-contains some needed ATP (from carbs)
enzymes)
GOLGI COMPLEX -Golgi apparatus -Form lysosomes, secrete
(SIMILAR TO SER) -Stack of membranes – make up carbohydrates (eg in cell walls),
flattened sacs vesicles produce secretory enzymes
-Vesicles – small, round, hollow -‘Labels’ proteins+lipids ->
transported by vesicles (pinched off
ends of cisternae)
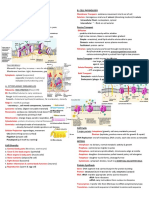
LYSOSOMES/ -Specialised vesicles ^ -Isolate harmful enzymes
PHAGOSOMES -Enzymes (proteases, lypases, -Break down inside phagocytes
(1UM DIAMETER) lysozymes) -Digest worn-out/dead cells
-Found in secretory (epithelial) + -Work with autophagosomes
phagocytic cells (collectors), break down -> release
-Spherical sacs (single membrane) amino acids
-Acidic in comparison to cytoplasm
RIBOSOMES -Large subunit and small subunit -Work with mRNA (during translation)
- Ribosomal proteins and ribosomal to create specific sequence of amino
RNA (rRNA) acids – proteins. (Protein synthesis)
CHLOROPLASTS -Double membrane encasing -Used for photosynthesis
-Stroma (– gel-like insides) -Light dependant – Thylakoid
-Thylakoid (-fluid filled sacks) -Light independent - Stroma
-Granum (grana) (-stacked thylakoids)
-Lemella (lamellae) (-thylakoid
membranes that link grana)
VACUOLES -Tonoplast (single membrane) -Support – makes cells turgid
-Cell sap (solution of mineral salts, -Temporary food store
sugars, amino acids, waste & -Pigments may colour petals = attract
sometimes pigments.) insects
CELL WALL -Plants/algae = cellulose -Maintain cell shape – support
-Fungi - chitin -Protection from pathogens
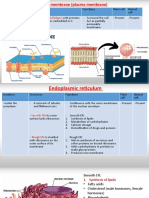
ROUGH -Channel-like structures (cisternae) + -Works with ribosomes to make 3D
ENDOPLASMIC fluid proteins + transport
-Ribosomes on outer surface (large
RETICULUM surface area = lots of protein synthesis)
SMOOTH -Similar to ^, but no ribosomes -Storing, synthesizing, processing
ENDOPLASMIC lipids, phospholipids and cholesterol
RETICULUM
You might also like
- Reviewer in General ZoologyDocument12 pagesReviewer in General ZoologyJasmine Fritz CabreraNo ratings yet
- BBMS1001 NotesDocument41 pagesBBMS1001 NotesHelen WanNo ratings yet
- Biotech Notes SST 2022Document13 pagesBiotech Notes SST 2022yessomegudstuffNo ratings yet
- Cell StructuresDocument5 pagesCell StructuresSTEM 15 - John Benedict SebucaoNo ratings yet
- Biology Summary Important PointsDocument17 pagesBiology Summary Important PointsNguyen TaNo ratings yet
- Dwnload Full Human Physiology From Cells To Systems 8th Edition Lauralee Sherwood Solutions Manual PDFDocument36 pagesDwnload Full Human Physiology From Cells To Systems 8th Edition Lauralee Sherwood Solutions Manual PDFwoodrowbutleroev8100% (9)
- Full Download Human Physiology From Cells To Systems 8th Edition Lauralee Sherwood Solutions ManualDocument36 pagesFull Download Human Physiology From Cells To Systems 8th Edition Lauralee Sherwood Solutions Manualgambolrapinous.ggqcdr100% (40)
- Lecture/Week 2/ Pre-Recorded Lecture BasedDocument6 pagesLecture/Week 2/ Pre-Recorded Lecture Basedmaria apolonia vergaraNo ratings yet
- Human Physiology From Cells To Systems 8th Edition Lauralee Sherwood Solutions ManualDocument25 pagesHuman Physiology From Cells To Systems 8th Edition Lauralee Sherwood Solutions ManualLauraMitchellfgie100% (51)
- Cellular Structures and Processes - Indd - OsmosisDocument21 pagesCellular Structures and Processes - Indd - Osmosisabdul moeez cheema0% (1)
- General Zoology Module 1 Lesson 1-2.5Document5 pagesGeneral Zoology Module 1 Lesson 1-2.5Paul PanizaNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure & Function Cell Theory: Definition of Cell Plant CellDocument6 pagesCell Structure & Function Cell Theory: Definition of Cell Plant Celljean magallonesNo ratings yet
- Cellular Structure & Function: NotesDocument21 pagesCellular Structure & Function: NotesAbu AbdalahNo ratings yet
- Organelle, Descrpition and FunctionDocument2 pagesOrganelle, Descrpition and Functionjahajaha_svensson609No ratings yet
- The CellDocument11 pagesThe Cellxuxi dulNo ratings yet
- Biomolecules PDFDocument5 pagesBiomolecules PDFgabo uyNo ratings yet
- (Zoolone) Animal CellDocument5 pages(Zoolone) Animal CellRenee Margarette GrapilonNo ratings yet
- Cell BIOLOGYDocument4 pagesCell BIOLOGYAria Moon100% (1)
- Anaphy Lab ReviewerDocument6 pagesAnaphy Lab ReviewerJhom Andrei ApolinarNo ratings yet
- General Biology 1Document4 pagesGeneral Biology 1Valerie HermenegildoNo ratings yet
- Bot 1Document16 pagesBot 1Lawrence SarmientoNo ratings yet
- Nmat Biology Cell Biology 1.1 Eukaryotic & Prokaryotic CellsDocument12 pagesNmat Biology Cell Biology 1.1 Eukaryotic & Prokaryotic Cellssavina100% (1)
- Microtubules Which Occur On Exposed Membrane SurfacesDocument3 pagesMicrotubules Which Occur On Exposed Membrane Surfacesprettyfriends 05No ratings yet
- Human Physiology From Cells To Systems 9th Edition Sherwood Solutions ManualDocument36 pagesHuman Physiology From Cells To Systems 9th Edition Sherwood Solutions Manualsanjaktouchbox1wfw100% (27)
- 02 PlantAnatomyDocument50 pages02 PlantAnatomyPoonam RanieNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure Function Review PresentationDocument8 pagesCell Structure Function Review PresentationCharles IppolitoNo ratings yet
- Biology: Cell StructureDocument3 pagesBiology: Cell StructureFernanda AntonialliNo ratings yet
- Cell Biology: Komal SaparaDocument72 pagesCell Biology: Komal SaparaKomalNo ratings yet
- Biomedi Sem3 149306NOLDocument102 pagesBiomedi Sem3 149306NOLDennis Ebenezer DhanarajNo ratings yet
- Histology EpitheliumsDocument4 pagesHistology EpitheliumsNORHANA PHARINo ratings yet
- BIO C2 @notastpm04Document35 pagesBIO C2 @notastpm04Aprillia ChanNo ratings yet
- Lec1 - CytologyDocument3 pagesLec1 - CytologyEloisa Trina GenerosoNo ratings yet
- Cells: B. Cell PhysiologyDocument29 pagesCells: B. Cell PhysiologyShyenNo ratings yet
- MBIO Quiz 1 Reviewer AeschylusDocument7 pagesMBIO Quiz 1 Reviewer AeschylusIra Jamila Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Cells, Tissues, Glands and Membranes HODocument116 pagesCells, Tissues, Glands and Membranes HOᜀᜎ᜔ᜎᜒᜈ᜔ ᜃᜓᜇᜒᜀᜋᜆ᜔No ratings yet
- Y3 Bio Notes Unit 1Document24 pagesY3 Bio Notes Unit 1SANJAY SHIVANINo ratings yet
- Cellular PhysiologyDocument32 pagesCellular Physiologyانس ابوهيبة0% (1)
- The CellDocument17 pagesThe CelluissojohnyzNo ratings yet
- Cell Structures 2Document10 pagesCell Structures 2STEM 15 - John Benedict SebucaoNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure & Function: Endoplasmic Reticulum ERDocument2 pagesCell Structure & Function: Endoplasmic Reticulum ERLiling CassiopeiaNo ratings yet
- BY Arif Mohiddin Mds 1 Year Dept of Oral PathologyDocument40 pagesBY Arif Mohiddin Mds 1 Year Dept of Oral PathologyArif MohiddinNo ratings yet
- General Biology Notes For Grade 11 (1st Semester)Document37 pagesGeneral Biology Notes For Grade 11 (1st Semester)shieeesh.aNo ratings yet
- Genbio NotesDocument10 pagesGenbio NotesD-B02 Ancheta IanNo ratings yet
- Basic HistologyDocument2 pagesBasic HistologyAngel DumalagNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure WrittenDocument3 pagesCell Structure WrittenKhuat Ngan HaNo ratings yet
- Genetics Lab Dent 1Document6 pagesGenetics Lab Dent 1FRANCHEZKA ANGELICA TANIEGRANo ratings yet
- Biology Quiz1 NotesDocument3 pagesBiology Quiz1 NotesJayden DagsaNo ratings yet
- Plant Anatomy PDFDocument54 pagesPlant Anatomy PDFSung Min Lee100% (1)
- Parts of The CellDocument3 pagesParts of The CellMa Claire TumboconNo ratings yet
- Animal CellDocument11 pagesAnimal CellKella OrtegaNo ratings yet
- Notes 2Document4 pagesNotes 2Anamari KolakNo ratings yet
- محاضرة 2Document41 pagesمحاضرة 2AbdulNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure and Cell OrganisationDocument106 pagesCell Structure and Cell Organisationwienna1987No ratings yet
- Chromosomes: Nucleus Cytoplasm SurfaceDocument4 pagesChromosomes: Nucleus Cytoplasm SurfaceRameesha RanaNo ratings yet
- Cell 3Document10 pagesCell 3OscarNo ratings yet
- ANAPHY - CellsDocument17 pagesANAPHY - CellsRenalin ArauneNo ratings yet
- Cell/Plasma MembraneDocument4 pagesCell/Plasma MembraneKrizsharei Cerrado CerradoNo ratings yet
- Biology Cells Microscopy 1Document14 pagesBiology Cells Microscopy 1Andrea Trish NicolasNo ratings yet
- The Basics of Cell Life with Max Axiom, Super Scientist: 4D An Augmented Reading Science ExperienceFrom EverandThe Basics of Cell Life with Max Axiom, Super Scientist: 4D An Augmented Reading Science ExperienceNo ratings yet
- Microbiology: a QuickStudy Laminated 6-Page Reference GuideFrom EverandMicrobiology: a QuickStudy Laminated 6-Page Reference GuideNo ratings yet
- Functions Polyfit (MATLAB®)Document3 pagesFunctions Polyfit (MATLAB®)zhee_pirateNo ratings yet
- Safety Talks Index: English SpanishDocument6 pagesSafety Talks Index: English SpanishYous_80No ratings yet
- Scheduling Guide For Program ManagersDocument96 pagesScheduling Guide For Program Managersapi-27145250100% (3)
- Salary OCTOBER2023Document1 pageSalary OCTOBER2023depiha5135No ratings yet
- Digital Marketing Strategic Planning IntegrationDocument61 pagesDigital Marketing Strategic Planning Integrationruby.nicholson732100% (54)
- Preventive Migraine TreatmentDocument20 pagesPreventive Migraine TreatmentNatalia BahamonNo ratings yet
- Sir - Tds.taishanc - csm.EB 450GDocument1 pageSir - Tds.taishanc - csm.EB 450GAbdullah SahlyNo ratings yet
- TASK 4 - Self Reflection - Communicating Insights and AnalysisDocument2 pagesTASK 4 - Self Reflection - Communicating Insights and Analysis20T3136 Nainika TrivediNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 PhotosynthesisDocument10 pagesChapter 10 PhotosynthesisMicky BanderaNo ratings yet
- Quantitative Techniques in BusinessDocument20 pagesQuantitative Techniques in BusinessHarold Dela FuenteNo ratings yet
- Lab 1 Direct Shear Lab 1 Direct Shear TestTestDocument9 pagesLab 1 Direct Shear Lab 1 Direct Shear TestTest7e1a8821100% (1)
- Curtain Wall ShadingDocument8 pagesCurtain Wall ShadingNajeela BanuNo ratings yet
- EUT-04-Komoditi Kakao PTPN XII V1Document19 pagesEUT-04-Komoditi Kakao PTPN XII V1sumantriNo ratings yet
- S10 - Q2 - Summative Test 1Document5 pagesS10 - Q2 - Summative Test 1Letsirk Saluta Ramos100% (1)
- A Micro-Project Report On ": Metal Detector Circuit"Document34 pagesA Micro-Project Report On ": Metal Detector Circuit"Om PawarNo ratings yet
- Datasheet - PRISM INtegratorDocument2 pagesDatasheet - PRISM INtegratorjpgironNo ratings yet
- CP Output 2Document2 pagesCP Output 2EllaineNo ratings yet
- 1061 - Disinfectant Fluid Phenolic TypeDocument15 pages1061 - Disinfectant Fluid Phenolic TypeKaushik SenguptaNo ratings yet
- Grammar and Vocabulary 6Document6 pagesGrammar and Vocabulary 6ishaanNo ratings yet
- Quality Assurance Kits C7000 - TP12-2Document11 pagesQuality Assurance Kits C7000 - TP12-2Willian S.No ratings yet
- Pes Institute of Technology & Management, ,: Prerana Educational & Social Trust (R), ShivamoggaDocument2 pagesPes Institute of Technology & Management, ,: Prerana Educational & Social Trust (R), ShivamoggaarjuninformationNo ratings yet
- Al-Qadir Jinnah Science Academy Mallian Kalan: Near Govt. H/S Mallian Kalan Sheikhupura, Cell # 03024741124Document1 pageAl-Qadir Jinnah Science Academy Mallian Kalan: Near Govt. H/S Mallian Kalan Sheikhupura, Cell # 03024741124Qadir RafiqueNo ratings yet
- Thesis Statement To Kill A MockingbirdDocument6 pagesThesis Statement To Kill A MockingbirdINeedHelpWritingAPaperSiouxFalls100% (2)
- NewItem 158 MSIHC-REPORTDocument77 pagesNewItem 158 MSIHC-REPORTANKUSHNo ratings yet
- Annexure I Change Control FormDocument4 pagesAnnexure I Change Control FormSÜMME AÇIKGÖZNo ratings yet
- Q2.6 Seafloor SpreadingDocument18 pagesQ2.6 Seafloor SpreadingJhon KyleNo ratings yet
- Gujarat Technological UniversityDocument1 pageGujarat Technological UniversityJainam JoshiNo ratings yet
- CookiesDocument14 pagesCookiescodigocarnetNo ratings yet
- Heep 118Document6 pagesHeep 118dkclarkNo ratings yet
- Report On Saras DairyDocument91 pagesReport On Saras DairyAjay Singh Rathore100% (9)