Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter 1
Uploaded by
Millence Myr0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views3 pagesThis document outlines different types of microorganisms including their defining characteristics. It describes prokaryotic cells as lacking a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles, while eukaryotic cells have these structures. Bacteria are introduced as unicellular organisms that reproduce through binary fission. Fungi, protozoa, algae, viruses, and multicellular animal parasites are also summarized based on whether they are prokaryotic or eukaryotic, their nutrition sources, structures like flagella and nuclei, and whether they are unicellular or multicellular.
Original Description:
none
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document outlines different types of microorganisms including their defining characteristics. It describes prokaryotic cells as lacking a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles, while eukaryotic cells have these structures. Bacteria are introduced as unicellular organisms that reproduce through binary fission. Fungi, protozoa, algae, viruses, and multicellular animal parasites are also summarized based on whether they are prokaryotic or eukaryotic, their nutrition sources, structures like flagella and nuclei, and whether they are unicellular or multicellular.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views3 pagesChapter 1
Uploaded by
Millence MyrThis document outlines different types of microorganisms including their defining characteristics. It describes prokaryotic cells as lacking a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles, while eukaryotic cells have these structures. Bacteria are introduced as unicellular organisms that reproduce through binary fission. Fungi, protozoa, algae, viruses, and multicellular animal parasites are also summarized based on whether they are prokaryotic or eukaryotic, their nutrition sources, structures like flagella and nuclei, and whether they are unicellular or multicellular.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
Chapter 1.
KINDS OF MICROORGANISM AND THEIR GENERAL PROPERTIES (Week 3)
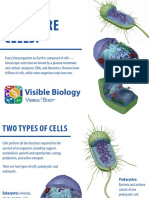
Prokaryotic VS Eukaryotic cells
- Prokaryotic : cell that have no nucleus or other membrane bound organelles
- Organells: Double layered
- Kingdom Archaebacteria: Lack peptidoglycan
- Kingdom Eubacteria: Peptidoglycan cell walls.
SHAPES:
- Bacilli: ROD LIKE. (SING.BACILUS)
- Cocci
EUKARYOTIC CELLS NUCLEUS
- Opposite
- Have nucleus and membrane and bound organelles
DIVERSITY OF MICROORGANISM
1. BACTERIA : (Sing.Bacterium)
- Small single cells (unicellular) organism
- Divide by binary fission (not mitosis)
- SOURCE OF NUTRIENTS VARIES:
HETETROTROPHS: Consume organic chemical
- Autotrophs: Make their own food
- Motility: Many can swim
- Cilia: small hair like structures
- Flagella: Large whip like structures
- Distinguish between motility and BROWNIAN MOTION
PROCARYOTES: Organism that lack the following structures”:
- Nuclear membrane around DNA
- Membrane bound organelles
Mitochondria
Chloroplast
Golgi apparatus
ER, LYSOSOMES
FUNGI: (Sing fungus)
- Eukaryotes “ True nucleus”
DNA is surrounded by nuclear membrane
Cells have MEMBRANE BOUND ORGANELSS: Mitochondria, ER, Etc.
Cells are larger than those of procaryotes
- SOURCE OF NUTRIETS VARIES:
Saprotrophs: Decomposers that fees on dead and decaying matter
PARACITES: Obtain nourishment by parasitizing live animals and plants.
Cell wall made by chitin
May reproduce sexually or asexually
PROTOZOA ( Sing.Protozoan) “ eukaryotic”
- Some are colonial
- Eukaryotes “True nucleus”
- DNA is surrounded by nuclear membrane
- Cells are larger than those of procaryotes
UNICELLULAR
KINGDOM PROTISTA
SEXUAL OR ASEXUAL REPRODUCTION
- FLAGELLA : LONG WHIPN LIKE APPENDAGES
EX: TRICHOMONAS VAGINALIS, CAUSES TRICHOMONIASIS, Asexually transmitted
disease
- CILIA: Small hair like appendages
- NONMOTILE: do not move in their mature forms
Example: Plasmodium
ALGAE (Sing.Alga)
- Eukaryotes “True nucleus”
- Photosynthetic: Important part of food chain because it can produce
VIRUSES: “Not organism”
- Acellular infectious agents not considered living because they lack cells.
- OBLIGATE INTACELLULAR PARASITES:
Mulcellular Animal Parasites:
- Eukaryotes “True nucleus”
- Multicellular animals usually are visible to our naked eye
- Microscopic during some stages of life cycle
- Spend part of all of their lives inside an animal host
HELMINTHS
- FLATWORM (Platyhelminths) E.G TAPEWORM
- ROUNDWORMS (NEMATODES) E.G ASCARIS, PINWORM
You might also like
- The Completely Different World of Protists - Biology Book for Kids | Children's Biology BooksFrom EverandThe Completely Different World of Protists - Biology Book for Kids | Children's Biology BooksNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Prokaryotic and EukaryoticDocument13 pagesChapter 2 Prokaryotic and EukaryoticMark Francis S. RajasNo ratings yet
- MP ReportDocument14 pagesMP ReportMark Francis S. RajasNo ratings yet
- Cellular Structure and Taxonomy HandoutDocument11 pagesCellular Structure and Taxonomy Handoutkjdobdin23No ratings yet
- The Cell As The Fundamental Unit of Life: The Structure and Function of Cellular OrganellesDocument39 pagesThe Cell As The Fundamental Unit of Life: The Structure and Function of Cellular OrganellesMANASI SAWANTNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure P N eDocument46 pagesCell Structure P N eSaqib CHNo ratings yet
- Life Science StudyGuideDocument113 pagesLife Science StudyGuideNthabeleng RamotseoaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 Cell Parts and FunctionDocument60 pagesLecture 3 Cell Parts and FunctionEsther Suan-LancitaNo ratings yet
- The Cell As The Fundamental Unit of Life: The Structure and Function of Cellular OrganellesDocument39 pagesThe Cell As The Fundamental Unit of Life: The Structure and Function of Cellular OrganellesAngelica Muñoz DamirezNo ratings yet
- Mrs. Anamika Sahu GulbakeDocument40 pagesMrs. Anamika Sahu GulbakeAnamika SahuNo ratings yet
- Chapter-2-Prokaryotes-and-Eukaryotes-MICROBIOLOGY AND PARAASITOLOGYDocument2 pagesChapter-2-Prokaryotes-and-Eukaryotes-MICROBIOLOGY AND PARAASITOLOGYIsaiah PascuaNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsDocument7 pagesProkaryotic and Eukaryotic Cellsjodeoiraluis josonNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellDocument19 pagesProkaryotic and Eukaryotic CellReanne MeregildoNo ratings yet
- General Biology 1Document7 pagesGeneral Biology 1Charmaine PamesaNo ratings yet
- Quarter 1 - Module 1: Cells: The Building Blocks of LifeDocument7 pagesQuarter 1 - Module 1: Cells: The Building Blocks of LifeCharmaine PamesaNo ratings yet
- Cell Biology - Unit - 1Document19 pagesCell Biology - Unit - 1shivangipurohitNo ratings yet
- Els NotesDocument2 pagesEls Notesramosinducil05No ratings yet
- BIOLOGYDocument103 pagesBIOLOGYKamesh RamamoorthyNo ratings yet
- The CellDocument3 pagesThe CellMary Ann FriasNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotes & Eukaryotes: Justin Abasula & Sofia Isabelle AbayDocument17 pagesProkaryotes & Eukaryotes: Justin Abasula & Sofia Isabelle AbayjasminedevesaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1-Introduction To The CellDocument18 pagesLecture 1-Introduction To The CellThuto SmithNo ratings yet
- Taxonomy 2Document16 pagesTaxonomy 2johanndarasin777No ratings yet
- The Cell and Its OrganellesDocument7 pagesThe Cell and Its OrganellesJanine JoverNo ratings yet
- Genbio1 ReviewerDocument15 pagesGenbio1 ReviewerMichelle VillafuerteNo ratings yet
- Archaea Yeast-Are Mold-Is A Protozoa - Are Algal Cells Since Viruses Are A Cellular - TheyDocument5 pagesArchaea Yeast-Are Mold-Is A Protozoa - Are Algal Cells Since Viruses Are A Cellular - TheyJemima Kesia ApallaNo ratings yet
- 1st Summative Exam - General BiologyDocument12 pages1st Summative Exam - General BiologyAgatha AquinoNo ratings yet
- Invertebrate: Second Stage 2020-2021Document37 pagesInvertebrate: Second Stage 2020-2021Shaker MahmoodNo ratings yet
- VisibleBody Cell ComparisonDocument10 pagesVisibleBody Cell ComparisonAnjarika TripathyNo ratings yet
- General Biology: System Consists of TheDocument3 pagesGeneral Biology: System Consists of ThePhilipp MendozaNo ratings yet
- PPT1.2 Cell Doctrine PDFDocument44 pagesPPT1.2 Cell Doctrine PDFBharath KumarNo ratings yet
- General Biology Reviewer2Document12 pagesGeneral Biology Reviewer2zephyra neithNo ratings yet
- General Biology Reviewer1Document12 pagesGeneral Biology Reviewer1zephyra neithNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 CELL BIO - 2014 FinalDocument17 pagesUnit 4 CELL BIO - 2014 FinalTizita EmanaNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotes vs. EukaryotesDocument6 pagesProkaryotes vs. EukaryotesChennille Ann Bleu GundayaoNo ratings yet
- Micro Chapter 2Document34 pagesMicro Chapter 2Farrah GwynethNo ratings yet
- Botany InformationDocument19 pagesBotany InformationJana Mohamed Mohamed Asaad Ibrahim AwadNo ratings yet
- GenbioDocument11 pagesGenbioLizzeille Anne Amor MacalintalNo ratings yet
- The Microbial World and You: Types of MicrobesDocument23 pagesThe Microbial World and You: Types of MicrobesCatherine Noynay RaagasNo ratings yet
- Anaphy PrelimsDocument20 pagesAnaphy PrelimsEkoy TheRealNo ratings yet
- Brief History Cytology Hierarchy of Structural Organization - Cell Structure - MitosisDocument52 pagesBrief History Cytology Hierarchy of Structural Organization - Cell Structure - MitosisPJ PomarNo ratings yet
- Basic Cell Types, Cell Structure and Function,& Cell ModificationsDocument28 pagesBasic Cell Types, Cell Structure and Function,& Cell ModificationsMary Ann Gonzales Abeñon100% (1)
- Group 3 Prokaryotic Vs Eukaryotic Cells HandoutsDocument4 pagesGroup 3 Prokaryotic Vs Eukaryotic Cells HandoutsClaire Angelie Ruaya100% (1)
- General Biology Cells1Document6 pagesGeneral Biology Cells1Kristine CarvajalNo ratings yet
- Cell Theory Consists of Three PrinciplesDocument8 pagesCell Theory Consists of Three PrinciplesdaddysharkNo ratings yet
- Protists Study Guide - LenaDocument3 pagesProtists Study Guide - LenaLena ReimerNo ratings yet
- LESSON 3 - Prokaryotid Vs Eukaryotic CellsDocument41 pagesLESSON 3 - Prokaryotid Vs Eukaryotic CellsHyacinth RaeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 ReviewDocument6 pagesChapter 1 ReviewDung NguyenNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 - 3Document32 pagesUnit 1 - 3Sunita SharmaNo ratings yet
- Anaphy Prelims 1Document20 pagesAnaphy Prelims 1Ekoy TheRealNo ratings yet
- Week 4 - Plant Structure and FunctionsDocument50 pagesWeek 4 - Plant Structure and FunctionsPrincess De LeonNo ratings yet
- Unit Mahluk Hidup - Penyusun Mahluk HidupDocument21 pagesUnit Mahluk Hidup - Penyusun Mahluk HiduprinaNo ratings yet
- Biology: Classification of CellsDocument28 pagesBiology: Classification of CellskerbieNo ratings yet
- BIOOODocument7 pagesBIOOOGlenn Xavier Olleta SalazarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Biological ClassificationDocument9 pagesChapter 2 Biological ClassificationYashiNo ratings yet
- Lecture 02 - Questions - Summary - S2024Document6 pagesLecture 02 - Questions - Summary - S2024sydneepnNo ratings yet
- Invertebrate: Second Stage 2020-2021Document37 pagesInvertebrate: Second Stage 2020-2021Shaker MahmoodNo ratings yet
- CeluarDocument7 pagesCeluarJef PerezNo ratings yet
- Activity 15-23 SUMMARY UpdatedDocument7 pagesActivity 15-23 SUMMARY UpdatedZoe Kristeun GutierrezNo ratings yet
- The Cell FinalDocument48 pagesThe Cell FinalJuliane Caniele IndiongcoNo ratings yet
- Development Status'Document2 pagesDevelopment Status'Millence MyrNo ratings yet
- NCM 110 LECTURE 06 Internet and Personal Digital AssistantDocument3 pagesNCM 110 LECTURE 06 Internet and Personal Digital AssistantMillence MyrNo ratings yet
- Models & Computer SystemDocument5 pagesModels & Computer SystemMillence MyrNo ratings yet
- Health AssestmentDocument3 pagesHealth AssestmentMillence MyrNo ratings yet
- MicrobiologyDocument6 pagesMicrobiologyMillence MyrNo ratings yet
- Tolentino DrugDocument3 pagesTolentino DrugMillence MyrNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Principles of Life 3rd Edition HillisDocument42 pagesTest Bank For Principles of Life 3rd Edition Hillismangcornuntune6o9xNo ratings yet
- Importance of BiodiversityDocument2 pagesImportance of Biodiversityapi-567816601No ratings yet
- Experiment 3 Nucleic AcidsDocument5 pagesExperiment 3 Nucleic AcidsLloyd Patrick D. Gilig83% (6)
- 150 MCQ, Biochemistry, 2nd SemDocument43 pages150 MCQ, Biochemistry, 2nd SemBhavana PalNo ratings yet
- New Species of The Genus Curvularia. Fungal Keratitis 2020Document14 pagesNew Species of The Genus Curvularia. Fungal Keratitis 2020Anonymous argZ1ZNo ratings yet
- Official: Á1046Ñ Cell-Based Advanced Therapies and Tissue-Based ProductsDocument25 pagesOfficial: Á1046Ñ Cell-Based Advanced Therapies and Tissue-Based ProductsDilawar BakhtNo ratings yet
- 03errata 2edn New To Upload Biochemistry Rebecca JamesDocument1 page03errata 2edn New To Upload Biochemistry Rebecca JamesAastha jain0% (1)
- Pim 1Document19 pagesPim 1肖茹雪No ratings yet
- Evolution of Desire PDFDocument2 pagesEvolution of Desire PDFMaria0% (11)
- (BOTAFUN) Life From LightDocument2 pages(BOTAFUN) Life From LightBen Joshua MancileNo ratings yet
- IvIg DoseDocument28 pagesIvIg DoseFransisca Dhani KurniasihNo ratings yet
- Kharghar, Navi Mumbai - 410 210Document1 pageKharghar, Navi Mumbai - 410 210Ankit TiwariNo ratings yet
- General Pathology ReviewDocument52 pagesGeneral Pathology Reviewferranco100% (1)
- EOL Exemplo 01Document7 pagesEOL Exemplo 01Amanda BarbioNo ratings yet
- Brain Aging OriginalDocument21 pagesBrain Aging Originaldocrubes50No ratings yet
- Double Muscling in Farm AnimalsDocument22 pagesDouble Muscling in Farm AnimalsRizaLeighFiguesNo ratings yet
- PEC28 Formaldehyde 153 393Document241 pagesPEC28 Formaldehyde 153 393Nouhaila YahdihNo ratings yet
- Tim Ingold Building, Dwelling, Living: How Animals and People Make Themselves at Home in The World' 2.4Document4 pagesTim Ingold Building, Dwelling, Living: How Animals and People Make Themselves at Home in The World' 2.4Let VeNo ratings yet
- Cell PhysiologyDocument7 pagesCell PhysiologyReslie Joy Serrano100% (1)
- Graduate Aptitude Test-Biotechnology (Gat-B) 2021 Parts / Sections Number of Questions Number of Questions To Be Attempted MarksDocument2 pagesGraduate Aptitude Test-Biotechnology (Gat-B) 2021 Parts / Sections Number of Questions Number of Questions To Be Attempted MarksSamarth SinghNo ratings yet
- Adrenal Glands: Module 11: Endocrine SystemDocument9 pagesAdrenal Glands: Module 11: Endocrine SystemLANCE GILL Tolentino100% (2)
- Topic Outline: APR 14, 2021 Dr. Michelle BuelaDocument5 pagesTopic Outline: APR 14, 2021 Dr. Michelle BuelaSGD5Christine MendozaNo ratings yet
- Sperm Donor Genetic Test Results Donor # 5488 Donor Carrier StatusDocument1 pageSperm Donor Genetic Test Results Donor # 5488 Donor Carrier StatusMaríaJoséEscotoNo ratings yet
- 2019 Haplogroup RDocument713 pages2019 Haplogroup RKlaus MarklNo ratings yet
- Munchkin Cat: Jump To Navigation Jump To SearchDocument6 pagesMunchkin Cat: Jump To Navigation Jump To SearchFullsun LeeNo ratings yet
- Sat Practice Test 1 Answers - CDocument17 pagesSat Practice Test 1 Answers - CAhmed EzzatNo ratings yet
- What Is BiodiversityDocument3 pagesWhat Is BiodiversityJulie marie PalmaNo ratings yet
- Discussion of Agri KnowledgeDocument24 pagesDiscussion of Agri KnowledgerahulNo ratings yet
- Female With Hemofilia - Căutare GoogleDocument1 pageFemale With Hemofilia - Căutare GooglegrigmihNo ratings yet
- 8-Human Health and Disease Ncert SolutionsDocument4 pages8-Human Health and Disease Ncert SolutionsPoonam PathakNo ratings yet