Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Advantages and Disadvantages of Series and Parallel Connection
Uploaded by
Mitch Laraquel0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
125 views9 pagesAdvantages and Disadvantages of Series and Parallel Connection
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentAdvantages and Disadvantages of Series and Parallel Connection
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
125 views9 pagesAdvantages and Disadvantages of Series and Parallel Connection
Uploaded by
Mitch LaraquelAdvantages and Disadvantages of Series and Parallel Connection
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 9
Advantages and Disadvantages of Series and
Parallel Connection
A series circuit is a circuit in which resistors or
loads are connected end to end so that the
circuit will have only one path through which
electric current flows. Thus, when a number
of resistors are connected in series, the
effective resistance (total resistance in the
circuit) is gotten by adding the individual
resistance algebraically.
In series connections, the same current flows
across all the branches of the circuits, but
different voltage across it thus making the
resistors to have different voltage across
them. Each resistor or load will experience a
voltage drop. The applied voltage is equal to
the sum of the voltage drop across the
different parts of the circuit. Voltage drop is
proportional to the resistance current being
the same throughout the circuit. When loads
are connected in series, the loads will tend to
have a common switch. This kind of
connection is employed in school halls, street
lights. The problem with this kind of
connection is that when a load develops a
problem, the other connected system will fail.
It’s an all or none type of circuit connection.
Till a load gets energy before it delivers it to
the other and the one to deliver fails, there
will be a black out.
Ohm’s Law in Series Circuits
V
Vtotal = ItotalRtotal
V
VR1 = IR1R 1
VR1 = (0.5A)(3 Ω)= 1.5-v
Rtotal = 3Ω + 10 Ω + 5 Ω VR2 = IR2R 2
Itotal = 9-V
Rtotal = 18 Ω 18 Ω VR2 = (0.5A)(10 Ω)= 5-v
VR3 = IR3R 3
Itotal = 0.5 A
VR3 = (0.5A)(5 Ω)= 2.5-v
Vtotal = VR1 + VR2 + VR3
Vtotal = 1.5V + 5V + 2.5V = 9V
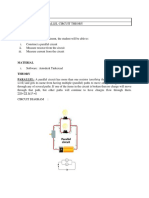
Resistors, loads are said to be connected in
parallel when the end of each of the resistors
or loads have a common point or junction and
the other ends are also connected to a
common point or junction. Such circuits are
known as parallel circuits. Unlike the series
circuit connection, when finding the total
(effective) resistance in a parallel circuit, the
reciprocal of the individual resistance is
taken. Thus, when a number of resistances
are connected in parallel, the reciprocal of the
effective resistance is given by the arithmetic
or algebraic sum of the reciprocal of the
individual resistance.
Parallel circuit connection is very common in
use. Various lamps and electrical appliances
in our homes are connected in parallel so that
each of the lamps or bobs and appliances
can be operated independently. For us to
have control over the individual lamps or
loads, they have to be wired in parallel.
Ohm’s Law in Parallel Circuits
IR1 = VR1 = 9-V =0.9A
R1 10 Ω Itotal = 0.9A + 4.5A +9A = 14.4A Rtotal = = 9-V =0.625 Ω
IR2 = VR2 = 9-V =4.5A
R2 2 Ω 14.4A
IR3 = VR3 = 9-V =9A
R3 1 Ω
Safety Devices at Home
Electricity has two hazards. A thermal hazard
occurs when there is electrical overheating. A
shock hazard occurs when electric current
passes through a person. There are safety
devices that will prevent these hazards.
Read the concepts about these safety
devices.
Circuit breakers: It functions to break the
circuit when the current in the circuit exceeds
the maximum value, and is no longer
considered safe. To do this there is an
electromagnet that will physically break the
circuit when it detects that the current has
exceeded its maximum.
Fuses: Fuses are like circuit breakers in that
they will break a circuit when it detects that it
is too dangerous to operate. Fuses use a
resistance wire with a low melting point
instead of an electromagnet, and when the
current is too great the wire melts and the
circuit will is broken.
Earthing: There are three wires that supply
power to households. These are the active,
neutral and earth wires. Earth wires are put in
so that electric shocks can be avoided when
people come into contact with an active wire
that is in contact with the casing of any
connected appliances. If there was no earth
wire a person would complete the circuit
between the appliances and the ground, and
would receive an electric shock. To reduce
the chance of this happening, the earth wire
provides a better conductive path for the
current. If the current comes into contact with
the casing of an appliance, the earth wire will
create a conductive path from the appliance
to the earth, and a large current will flow to
the earth through this connection.
Double insulation: Insulation is installed so
that wiring and electric appliances are
covered so that the current will only go
through its intended path. The insulation is
made out of an extremely poor conductor in
order to create a safe path for the current to
flow through.
Residual current devices: RCDs are designed
so that they can stop a current before it
becomes harmful to a person. It does this by
detecting any leakages from the circuit
through a differential current transformer, that
will compare the current flowing through the
live and neutral conductor, and if there is a
differ ence it quickly shuts down the current.
You might also like
- Electrical &electricityDocument11 pagesElectrical &electricityAhmed Jama AdanNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Series, Parallel, Series-Parallel Circuits: Chapter - 3Document71 pagesAnalysis of Series, Parallel, Series-Parallel Circuits: Chapter - 3shimieNo ratings yet
- 2-Masterclass Solar - Electrical Fundamentals Batch 29Document40 pages2-Masterclass Solar - Electrical Fundamentals Batch 29Anthony PoldoNo ratings yet
- Series and Parallel CircuitsDocument16 pagesSeries and Parallel CircuitsAIMNo ratings yet
- Basic Electricity 1Document6 pagesBasic Electricity 1Joanna Fe JaimNo ratings yet
- SSS 1 3RD TermDocument21 pagesSSS 1 3RD TermabiodunokoyaNo ratings yet
- BEE-Module-2 Series and Parallel NetworksDocument36 pagesBEE-Module-2 Series and Parallel NetworksMARK JOHN AL RODAVIANo ratings yet
- Physics MarathonDocument130 pagesPhysics MarathonSantosh TiwariNo ratings yet
- By: Mr. Augosto M. DirectoDocument34 pagesBy: Mr. Augosto M. DirectoArt DollosaNo ratings yet
- Electricity-summaryDocument8 pagesElectricity-summarya kamranNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1-Electrical CircuitDocument67 pagesChapter 1-Electrical CircuitDKM 2ANo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Diode Circuit Analysis and Applications-1Document24 pagesChapter 2 - Diode Circuit Analysis and Applications-1CraigNo ratings yet
- Unit-1 MaterialDocument88 pagesUnit-1 Materialkushalvemula07No ratings yet
- Resistors in CircuitsDocument10 pagesResistors in CircuitsKcirex GarinNo ratings yet
- BEE Module 2 Series and Parallel NetworksDocument36 pagesBEE Module 2 Series and Parallel NetworksHawin ChitNo ratings yet
- Electrostatic and Magnetism ModuleDocument42 pagesElectrostatic and Magnetism ModuleANGELO NINO ALVARADONo ratings yet
- DC CircuitsDocument34 pagesDC CircuitsPeach BubbleNo ratings yet
- Lecture 05Document42 pagesLecture 05amitNo ratings yet
- By: Mr. Augosto M. DirectoDocument34 pagesBy: Mr. Augosto M. DirectoJames RojasNo ratings yet
- Chapter 20 CircuitsDocument9 pagesChapter 20 CircuitsjojonNo ratings yet
- Basic Electro-Mechanical Engineering (EE-170) : Lecture#02Document41 pagesBasic Electro-Mechanical Engineering (EE-170) : Lecture#02Hassnain MassidNo ratings yet
- Electrical Circuits: Topic 1.1A Webinar Presented by - Deepak PaisDocument49 pagesElectrical Circuits: Topic 1.1A Webinar Presented by - Deepak PaisjunaidNo ratings yet
- AC 6 - Basic Electrical Engineering: Course Sem/AY Module No. Lesson Title Week Duration Date Description of The LessonDocument21 pagesAC 6 - Basic Electrical Engineering: Course Sem/AY Module No. Lesson Title Week Duration Date Description of The LessonFerdinand Marcelo AbantoNo ratings yet
- DIRECT CURRENT ReportDocument15 pagesDIRECT CURRENT ReportMary Grace Jerna Artazo Nozal-CuadraNo ratings yet
- Phys 211 14.series and Parallel Circuits 1Document7 pagesPhys 211 14.series and Parallel Circuits 1Regina May Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Electricity: Made By:-Tushar Bhutani X - ADocument36 pagesElectricity: Made By:-Tushar Bhutani X - ATushar BhutaniNo ratings yet
- Currrent Electricity FinalDocument30 pagesCurrrent Electricity FinalSaadullah Shahid100% (1)
- Basic Electricity. B TechDocument14 pagesBasic Electricity. B TechValentine Nwankwo100% (1)
- ElectricityDocument49 pagesElectricityShubham RoutNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes-Basic Electrical and Electronics Engineering Notes PDFDocument30 pagesLecture Notes-Basic Electrical and Electronics Engineering Notes PDFMDR PRAPHU100% (1)
- LP - Akomah Seth8GMATH NYU-POLY LESSON B1Document9 pagesLP - Akomah Seth8GMATH NYU-POLY LESSON B1Jay SeaNo ratings yet
- TOPIC-2 3 4 ModuleDocument67 pagesTOPIC-2 3 4 ModuleGhabriel Javier SembranoNo ratings yet
- PHYSICAL SCIENCE TERM 3 E Cape 1 - 1680Document160 pagesPHYSICAL SCIENCE TERM 3 E Cape 1 - 1680Shudufhadzo PrettyNo ratings yet
- Voltage, Current and Resistance ExplainedDocument34 pagesVoltage, Current and Resistance ExplainedPaul Senen DiduloNo ratings yet
- Lab Report 8 PDFDocument8 pagesLab Report 8 PDFRajput JanjuaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document11 pagesChapter 2Sam BelloNo ratings yet
- ElectricityDocument15 pagesElectricityapi-246793885No ratings yet
- Electrical Engineering IntroductoryDocument78 pagesElectrical Engineering Introductoryandi lisnaini ramadhaniNo ratings yet
- ElectricityDocument6 pagesElectricityDarshita GolechhaNo ratings yet
- Series Parallel Circuit Notes PDFDocument6 pagesSeries Parallel Circuit Notes PDFClaireDiscipuloNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 DC Analysis AllDocument32 pagesChapter 2 DC Analysis Allyibelta abebeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5AnalysisofSeriesParallelSeries ParallelCircuitsDocument54 pagesChapter 5AnalysisofSeriesParallelSeries ParallelCircuitsLyssa ChoiNo ratings yet
- WEEK 7 Module - CircuitsDocument6 pagesWEEK 7 Module - CircuitsSatsuki MomoiNo ratings yet
- Electricity Notes For CBSE Class 10 PhysicsDocument5 pagesElectricity Notes For CBSE Class 10 Physicssadiyaarchive22No ratings yet
- Electrical Drives and ControlDocument224 pagesElectrical Drives and ControlvanthiyadevnNo ratings yet
- Recap On CH - 10 of G - 11 With TGDocument7 pagesRecap On CH - 10 of G - 11 With TGKhin Khin ThanNo ratings yet
- Report Elec Lab 3Document7 pagesReport Elec Lab 3HARITH IZHAMNo ratings yet
- Electricity & Magnetism Chapters 17, 19-21Document51 pagesElectricity & Magnetism Chapters 17, 19-21Miranti UrbaningrumNo ratings yet
- Lesson 8 Series and Parallel CircuitsDocument18 pagesLesson 8 Series and Parallel Circuits23 ZACH Benjamin Isaac IV LabayenNo ratings yet
- Current ElectricityDocument10 pagesCurrent ElectricityClemence TafitiNo ratings yet
- Topic 2 - Basic LawsDocument5 pagesTopic 2 - Basic LawsUmakandan MuniandyNo ratings yet
- Electrical LabDocument17 pagesElectrical LabBlack HeartNo ratings yet
- 4.3 Electric CircuitsDocument19 pages4.3 Electric CircuitsMuhammad Amin SuhaimiNo ratings yet
- Elements of Electrical and Electronics Engineering (2EE101) : SESSION - 2020 - 21Document137 pagesElements of Electrical and Electronics Engineering (2EE101) : SESSION - 2020 - 21Pratham GolwalaNo ratings yet
- Electric CircuitsDocument13 pagesElectric CircuitsDanica A. MirandaNo ratings yet
- Resistive Circuit PracticeDocument11 pagesResistive Circuit PracticeBrandon BarndtNo ratings yet
- Cells in Series and Parallel2Document33 pagesCells in Series and Parallel2Maduamaka IhejiamatuNo ratings yet
- Electric Circuits Analysis 1 - With Page NumbersDocument15 pagesElectric Circuits Analysis 1 - With Page Numberskenneth1195No ratings yet
- Heat Vs Temperature VisualsDocument3 pagesHeat Vs Temperature VisualsMitch LaraquelNo ratings yet
- 1Document1 page1Mitch LaraquelNo ratings yet
- Why Is The Philippines Prone To TyphoonsDocument2 pagesWhy Is The Philippines Prone To TyphoonsMitch LaraquelNo ratings yet
- Typhoon FormDocument4 pagesTyphoon FormMitch LaraquelNo ratings yet
- Tan Delta For Beginners - PresentationDocument52 pagesTan Delta For Beginners - PresentationlrpatraNo ratings yet
- Omron 3g3mvDocument310 pagesOmron 3g3mvJermaine StrachanNo ratings yet
- Build a radiant battery charger using negative energyDocument9 pagesBuild a radiant battery charger using negative energysuso73100% (2)
- 8921a ManualDocument601 pages8921a ManualПетер СмирновNo ratings yet
- 900-0662 Onan SYNC 1320 Master Synchronizer Controller Owners Manual (11-2010)Document48 pages900-0662 Onan SYNC 1320 Master Synchronizer Controller Owners Manual (11-2010)Artemio Garcia BarrientosNo ratings yet
- 67393D 12 17 OJ DV Instr - GB PDFDocument29 pages67393D 12 17 OJ DV Instr - GB PDFvvukmirovic_2No ratings yet
- 02 IRIS2 - NV - Controller-ENDocument36 pages02 IRIS2 - NV - Controller-ENAhmedNo ratings yet
- MFL71946442 04 S 230512Document32 pagesMFL71946442 04 S 230512hiems19No ratings yet
- CT 32D11Document54 pagesCT 32D11Paul StofkoNo ratings yet
- ALCOMA Microwave AL17F ManualDocument50 pagesALCOMA Microwave AL17F ManualDiHLoS100% (1)
- Setup and Installation Requirements for 10,000 Watt FM Broadcast TransmitterDocument17 pagesSetup and Installation Requirements for 10,000 Watt FM Broadcast TransmitterTran Thanh HungNo ratings yet
- AN2731Document26 pagesAN2731WayneNo ratings yet
- Smart PumpDocument78 pagesSmart PumpRavi RanjanNo ratings yet
- CT Unidrive SP Elevator Solution Software User Guide - Issue 3 PDFDocument222 pagesCT Unidrive SP Elevator Solution Software User Guide - Issue 3 PDFjayb1984No ratings yet
- User Manual Kullanim Kilavuzu: Rs 350 M Pro - Rs 350 MW Pro Rs 450 M Pro - Rs 450 MW Pro Rs 550 M Pro - Rs 550 MW ProDocument88 pagesUser Manual Kullanim Kilavuzu: Rs 350 M Pro - Rs 350 MW Pro Rs 450 M Pro - Rs 450 MW Pro Rs 550 M Pro - Rs 550 MW ProSerhan AysanNo ratings yet
- Zeme India Earthing BroucherDocument8 pagesZeme India Earthing BrouchervipinNo ratings yet
- Dual Full-Bridge MOSFET Driver With Microstepping TranslatorDocument16 pagesDual Full-Bridge MOSFET Driver With Microstepping TranslatorВладимир ЯткевичNo ratings yet
- 4.2V To 18V, 3A 1ch Synchronous Buck Converter With Integrated FETDocument22 pages4.2V To 18V, 3A 1ch Synchronous Buck Converter With Integrated FETDouglas BeltránNo ratings yet
- Calculation Size of Neutral Earthing Transformer (NET) : Generator DetailsDocument6 pagesCalculation Size of Neutral Earthing Transformer (NET) : Generator DetailsBramNo ratings yet
- High Voltage Safe Working ProcedureDocument10 pagesHigh Voltage Safe Working ProcedureYhon Tyang NdusunNo ratings yet
- Most Common Errors in Service Entrance and Load Side Installations Prior to Final DU InspectionDocument193 pagesMost Common Errors in Service Entrance and Load Side Installations Prior to Final DU InspectionJoel RemegioNo ratings yet
- 9441 Panasonic SA-AK270PL GCP Sistema Audio CD Multidisco MP3-Casette Manual de ServicioDocument121 pages9441 Panasonic SA-AK270PL GCP Sistema Audio CD Multidisco MP3-Casette Manual de Serviciowilmerk_159990No ratings yet
- Kac 748Document11 pagesKac 748Marcelo G HNo ratings yet
- Installation and Operating Instructions Intelligent Paperless Recorder DS 500Document109 pagesInstallation and Operating Instructions Intelligent Paperless Recorder DS 500jonathanxmakerNo ratings yet
- Sharp CD-C422, 2800Document56 pagesSharp CD-C422, 2800Mario Lozano SNo ratings yet
- Obed Internship Knust CSIR ReportDocument22 pagesObed Internship Knust CSIR ReportKelvin LokkoNo ratings yet
- 2 - 181108 EKX-4 Introduction EN - ExtendedDocument134 pages2 - 181108 EKX-4 Introduction EN - ExtendedFrank Almenares Urzola100% (1)
- MR-J4 - B - RJ020 MR-J4-T20: General-Purpose AC ServoDocument314 pagesMR-J4 - B - RJ020 MR-J4-T20: General-Purpose AC Servoid autopartNo ratings yet
- Installation Guide For Product Link PL121SR and PL321 ACTUAL 2015 PDFDocument98 pagesInstallation Guide For Product Link PL121SR and PL321 ACTUAL 2015 PDFSimon VasquezNo ratings yet
- W2252TQ Service ManualDocument23 pagesW2252TQ Service Manualnelutuanv0% (1)