Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Science Reviewer 2nd Quarter
Uploaded by
redox franciscoOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Science Reviewer 2nd Quarter
Uploaded by
redox franciscoCopyright:
Available Formats
Science Reviewer Atom - The basic unit of matter that makes up an
element.
2nd Quarter
Comes from the Greek word “Atomos”,
Autotrophs – Are organisms capable of synthesizing meaning indivisible.
Contains the subatomic particles we know as
Protons, Electrons and Neutrons.
Was first conceptualized by Democritus between
400-300 BCE.
Democritus’ work - He describes atoms as indivisible
and particularly miniscule.
His work was not known until 1803 during the
time of John Dalton.
nutritive organic molecules from inorganic reagents thru
photosynthesis.
John Dalton (Dalton Atomic Model 1803) – He
proposed his theory of atoms, taking inspiration from the
Photosynthesis - Utilized in the organelle called
work of Democritus.
chloroplasts.
He describes the atoms as solid and
indestructible spheres.
Chlorophyll - Gives plant cells its distinct green color.
JJ Thomson (Plum Pudding Model 1897) – Proposed
atoms contain positive and negatively charged particles.
His work led to the discovery of the proton and
electron.
Ernest Rutherford (Atomic Model 1909) – Conducted
the Gold foil experiment and discovered a more accurate
atomic model
He confirmed the existence of electron at the
surrounding part with the positively charged
proton.
Chloroplast - A cell organelle that is the site of Niels Bohr (Bohr Atomic Model 1913) – Made
Photosynthesis in the plant’s leaf. significant improvements in the model that was first
proposed by Rutherford.
Heterotrophic Organism - Organisms that feed on
autotrophs, or other heterotrophs for sustenance. Erwin Schrodinger (Electron Cloud Model 1926 –
Classified into herbivores, carnivores, and Present) – Proposed the electron cloud which is the
omnivores. currently accepted model until today.
They rely on cellular respiration for energy.
Cellular Respiration – The process by which the
energy of glucose is released in the cell to be used for
biological process.
Takes place in the Mitochondria of the cell.
Occurs in all cells and can take place either with
or without oxygen.
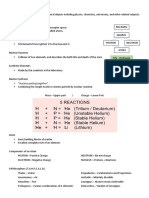
ATP – Adenosine Triphosphate
Negative Ions – Called “anions”
Formed when the atom gains electrons.
Non-metals
Ionic bonds – Formed between metals and non-metals.
Form when electrons are transferred between
atoms.
Covalent bonds - Form when electrons are shared
Element - A pure substance that cannot be separated or between atoms.
broken down into simpler substances by chemical Form between two non-metals.
means.
Ionic compounds – Results in a Neutral Compounds
Atom - The smallest unit of an element that maintains Strong bonds
High melting point
the chemical properties of that element.
Covalent compounds – Results in a Neutral Molecule
Compound - A substance made up of atoms of two or
Weak bonds
more different elements joined by chemical bonds.
Low melting points
Chemical Formula – Sometimes there are subscripts Metallic bonds - Are metal to metal bonds formed by
present. the attraction between positively charged metal ions.
A subscript is a small number that is in a
chemical formula.
Atoms with unfilled valence shells are
considered unstable.
Atoms will try to fill their outer shells by
bonding with other atoms.
Chemical bond - The attractive force that holds atoms
or ions together in a compound.
3 main types of chemical bonds
Covalent
Metallic
Ionic
Covalent bonds form between two non-metals.
Groups 14-17 on the Periodic Table
Atoms - Can share more than one pair of electrons to
create double and triple bonds.
Chlorine Molecule – A single bonding pair so it is
called a single covalent bond. The compound is now
called a molecule.
Ions – Formed when atoms gain or lose electrons.
Positive Ions – Called “cations”
Formed when the atom loses electrons.
Metals
You might also like
- Chem Lec ReviewerDocument42 pagesChem Lec ReviewerMaryashlyn NableaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Handout #1Document1 pageChemistry Handout #1xanNo ratings yet
- VI - Chemistry (Vol-III) Olympiad Class Work Book: Narayana Group of SchoolsDocument11 pagesVI - Chemistry (Vol-III) Olympiad Class Work Book: Narayana Group of SchoolsRita TripathiNo ratings yet
- LESSON 2 Atoms, Ions and MoleculesDocument14 pagesLESSON 2 Atoms, Ions and MoleculesscientistgenerosoNo ratings yet
- Atomic Model and TheoryDocument36 pagesAtomic Model and TheoryAmber Roanne100% (1)
- General ChemistryDocument7 pagesGeneral ChemistryJeremiah DinioNo ratings yet
- Unit4 - Matter and EenergyDocument21 pagesUnit4 - Matter and EenergyMiguel VintimillaNo ratings yet
- Structure of An Atom and The Periodic TableDocument2 pagesStructure of An Atom and The Periodic TableErika Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Conceptual and Functional Chemistry-Book SummaryDocument8 pagesConceptual and Functional Chemistry-Book SummaryJehan CodanteNo ratings yet
- 2 - The Chemical Basis of LifeDocument6 pages2 - The Chemical Basis of LifeGel Austin PascuaNo ratings yet
- Radiation Production and Characteristics "The Structure of Matter"Document10 pagesRadiation Production and Characteristics "The Structure of Matter"Shara RafisuraNo ratings yet
- Chemistry GhatanaChakraDocument117 pagesChemistry GhatanaChakraBijuNo ratings yet
- Inorg HandoutDocument9 pagesInorg HandoutAlyssa BardillonNo ratings yet
- 新chapter 02auDocument57 pages新chapter 02aurunshiguNo ratings yet
- Unit 2. The AtomDocument26 pagesUnit 2. The Atomgarciaortegajulia5No ratings yet
- Reviewer Sa Chem MidtermsDocument5 pagesReviewer Sa Chem MidtermsKlêïn Arkï Håñ VaulterNo ratings yet
- Physical ScienceDocument5 pagesPhysical ScienceJazz AddNo ratings yet
- Atoms: 1. Atomic StructureDocument7 pagesAtoms: 1. Atomic Structurecherry shane abanesNo ratings yet
- Lesson - Atomic Structure: Scientist DiscoveryDocument4 pagesLesson - Atomic Structure: Scientist DiscoveryKokkilaa ParameswaranNo ratings yet
- Sc.G8.Section 1 (Atom and Bonding) .PresentationDocument56 pagesSc.G8.Section 1 (Atom and Bonding) .Presentationomar badraNo ratings yet
- Chemical ChangesDocument35 pagesChemical ChangesaafaqnasirNo ratings yet
- Psma PrelimsDocument42 pagesPsma PrelimsPrincess Rose GamboaNo ratings yet
- ChemistryDocument6 pagesChemistryJessa Mae AtienzaNo ratings yet
- Atomic TheoryDocument2 pagesAtomic TheoryRodelio ValenzuelaNo ratings yet
- Atoms: NucleusDocument6 pagesAtoms: Nucleusヒルデガルダ HILDEGARDENo ratings yet
- 12Ch2 Atom ModelsDocument31 pages12Ch2 Atom ModelsSarah SaeedNo ratings yet
- AtomicStructure 1Document41 pagesAtomicStructure 1Juned AlamNo ratings yet
- C2-Chemical Basis of LifeDocument2 pagesC2-Chemical Basis of LifeLorrine MagramoNo ratings yet
- Atomicstructurepresentation 170510013215Document16 pagesAtomicstructurepresentation 170510013215Nilimoy Choudhury100% (1)
- Eastern Samar National Comprehensive High School Chemistry 1Document3 pagesEastern Samar National Comprehensive High School Chemistry 1Isaac PiaoNo ratings yet
- The History of AtomDocument13 pagesThe History of AtomKylizzle xxNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Notes For Form 2Document70 pagesChemistry Notes For Form 2Charles OtienoNo ratings yet
- l2.1 Evolution of Atomic ModelDocument33 pagesl2.1 Evolution of Atomic ModelZeke WilliamNo ratings yet
- The Structure of The Atom 5. Electrons in AtomsDocument20 pagesThe Structure of The Atom 5. Electrons in AtomsLore WheelockNo ratings yet
- Chap 4 y 5Document20 pagesChap 4 y 5Lore WheelockNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Gen ChemDocument10 pagesChapter 2 Gen ChemJennifer MalunaoNo ratings yet
- L'évolution Des Modèles Atomiques English Version (Final)Document10 pagesL'évolution Des Modèles Atomiques English Version (Final)Chaymae ER-RAMDANYNo ratings yet
- Science-Q2-Notes BanzonDocument3 pagesScience-Q2-Notes BanzonfeytNo ratings yet
- NotesDocument3 pagesNotesClarice TorresNo ratings yet
- 12s080201batomsdevelopment of The Atomic Theory1 171015140731Document21 pages12s080201batomsdevelopment of The Atomic Theory1 171015140731Cristeah AlemaniaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 Atoms, Molecules, & IonsDocument3 pagesLesson 2 Atoms, Molecules, & IonsRachel VillasisNo ratings yet
- As We All KnowDocument6 pagesAs We All KnowOmlean JairusNo ratings yet
- Intellectual Revolutions in The History of ScienceDocument5 pagesIntellectual Revolutions in The History of ScienceJustine Alyssa PardoNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Class 11 (Punjab Board)Document583 pagesChemistry Class 11 (Punjab Board)Ali Abbas GilaniNo ratings yet
- Atoms:: Development of The Atomic TheoryDocument18 pagesAtoms:: Development of The Atomic TheoryJamie BaczewskiNo ratings yet
- Atom 1Document13 pagesAtom 1Julius AlbardaNo ratings yet
- Atoms ReadingDocument3 pagesAtoms Readingdivya raghavNo ratings yet
- Atomic Particles, Atomic Mass and Weight, and Atomic ModelsDocument17 pagesAtomic Particles, Atomic Mass and Weight, and Atomic ModelshhahahahaNo ratings yet
- Atomic Theory of MatterDocument61 pagesAtomic Theory of MattersandeepNo ratings yet
- 2atomic TheoryDocument18 pages2atomic TheoryAnalie SacedonNo ratings yet
- Anaphy Chapter 2Document3 pagesAnaphy Chapter 2BrigitteNo ratings yet
- Handouts in SciDocument5 pagesHandouts in Scistrawberry shortcakeNo ratings yet
- Unit FDocument16 pagesUnit FVenkateswara Rao DoodalaNo ratings yet
- Physical Science ReviewerDocument13 pagesPhysical Science Reviewerjus jusNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document12 pagesChapter 2Erica Lumamba TabiosNo ratings yet
- Atoms, Molecules, and Ions: Jim Geiger Cem 151Document60 pagesAtoms, Molecules, and Ions: Jim Geiger Cem 151Junaid AlamNo ratings yet
- Early Description of MatterDocument24 pagesEarly Description of MatterAllea JeanNo ratings yet
- Sacraments at The Service of CommunionDocument3 pagesSacraments at The Service of Communionredox franciscoNo ratings yet
- ENGLISH 8-Module 2 1 Lecture On Grammatical SignalsDocument27 pagesENGLISH 8-Module 2 1 Lecture On Grammatical Signalsredox franciscoNo ratings yet
- Sacraments at The Service of CommunionDocument3 pagesSacraments at The Service of Communionredox franciscoNo ratings yet
- Sacrament of Marriage and Holy OrderDocument7 pagesSacrament of Marriage and Holy Orderredox franciscoNo ratings yet
- SSC Math 3 SLM Q4 M6 V1.0 CC Released 29jun2021Document24 pagesSSC Math 3 SLM Q4 M6 V1.0 CC Released 29jun2021redox franciscoNo ratings yet
- English 8 Lecture 2 - 2Document1 pageEnglish 8 Lecture 2 - 2redox franciscoNo ratings yet
- Sci9 M 2 3 - Carbon CompoundsDocument35 pagesSci9 M 2 3 - Carbon Compoundsredox franciscoNo ratings yet
- Module 2 1 (AQS)Document30 pagesModule 2 1 (AQS)redox franciscoNo ratings yet
- TLE 8 Module 2 3 Performing Mensuration and CalculationDocument33 pagesTLE 8 Module 2 3 Performing Mensuration and Calculationredox franciscoNo ratings yet
- Module 2 5 - EcosystemDocument39 pagesModule 2 5 - Ecosystemredox franciscoNo ratings yet
- Science 8 - Module 2 3 - Earthquakes - Seismic WavesDocument23 pagesScience 8 - Module 2 3 - Earthquakes - Seismic Wavesredox francisco100% (1)
- English 6 - Lesson 1 5Document17 pagesEnglish 6 - Lesson 1 5redox franciscoNo ratings yet
- Module 2 4 - Lecture - Understanding TyphoonDocument25 pagesModule 2 4 - Lecture - Understanding Typhoonredox francisco100% (1)
- Science 8 - Module 2 2 - How Damaging Can An Earthquake BeDocument39 pagesScience 8 - Module 2 2 - How Damaging Can An Earthquake Beredox franciscoNo ratings yet
- CL ESP Reviewer 2nd QuarterDocument2 pagesCL ESP Reviewer 2nd Quarterredox franciscoNo ratings yet
- Science 8 - Module 2 1 - Faults and EarthquakesDocument36 pagesScience 8 - Module 2 1 - Faults and Earthquakesredox franciscoNo ratings yet
- English 6 - Lesson 1 3 FDocument21 pagesEnglish 6 - Lesson 1 3 Fredox franciscoNo ratings yet
- Module 12 Tle 10Document13 pagesModule 12 Tle 10redox franciscoNo ratings yet
- English 6 Lesson 1 2Document15 pagesEnglish 6 Lesson 1 2redox franciscoNo ratings yet
- Module 34 Tle 10Document13 pagesModule 34 Tle 10redox franciscoNo ratings yet
- Leadership Styles-Mckinsey EdDocument14 pagesLeadership Styles-Mckinsey EdcrimsengreenNo ratings yet
- Lieh TzuDocument203 pagesLieh TzuBrent Cullen100% (2)
- CV Augusto Brasil Ocampo MedinaDocument4 pagesCV Augusto Brasil Ocampo MedinaAugusto Brasil Ocampo MedinaNo ratings yet
- KsDocument5 pagesKsnurlatifahNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument216 pagesUntitledMONICA SIERRA VICENTENo ratings yet
- IEC TC 56 Dependability PDFDocument8 pagesIEC TC 56 Dependability PDFsaospieNo ratings yet
- 1 in 8.5 60KG PSC Sleepers TurnoutDocument9 pages1 in 8.5 60KG PSC Sleepers Turnoutrailway maintenanceNo ratings yet
- Sandstorm Absorbent SkyscraperDocument4 pagesSandstorm Absorbent SkyscraperPardisNo ratings yet
- Quarter 1-Week 2 - Day 2.revisedDocument4 pagesQuarter 1-Week 2 - Day 2.revisedJigz FamulaganNo ratings yet
- Chapter - I Introduction and Design of The StudyDocument72 pagesChapter - I Introduction and Design of The StudyramNo ratings yet
- ELEVATOR DOOR - pdf1Document10 pagesELEVATOR DOOR - pdf1vigneshNo ratings yet
- Cummin C1100 Fuel System Flow DiagramDocument8 pagesCummin C1100 Fuel System Flow DiagramDaniel KrismantoroNo ratings yet
- Clockwork Dragon's Expanded ArmoryDocument13 pagesClockwork Dragon's Expanded Armoryabel chabanNo ratings yet
- Z-Purlins: Technical DocumentationDocument11 pagesZ-Purlins: Technical Documentationardit bedhiaNo ratings yet
- Sample Resume For Supply Chain Logistics PersonDocument2 pagesSample Resume For Supply Chain Logistics PersonAmmar AbbasNo ratings yet
- Final Project Strategic ManagementDocument2 pagesFinal Project Strategic ManagementMahrukh RasheedNo ratings yet
- PMP Assesment TestDocument17 pagesPMP Assesment Testwilliam collinsNo ratings yet
- Radon-222 Exhalation From Danish Building Material PDFDocument63 pagesRadon-222 Exhalation From Danish Building Material PDFdanpalaciosNo ratings yet
- Book 1518450482Document14 pagesBook 1518450482rajer13No ratings yet
- PC Model Answer Paper Winter 2016Document27 pagesPC Model Answer Paper Winter 2016Deepak VermaNo ratings yet
- Sample Monologues PDFDocument5 pagesSample Monologues PDFChristina Cannilla100% (1)
- SLA in PEGA How To Configue Service Level Agreement - HKRDocument7 pagesSLA in PEGA How To Configue Service Level Agreement - HKRsridhar varmaNo ratings yet
- Wholesale Terminal Markets - Relocation and RedevelopmentDocument30 pagesWholesale Terminal Markets - Relocation and RedevelopmentNeha Bhusri100% (1)
- Lesson 3 - ReviewerDocument6 pagesLesson 3 - ReviewerAdrian MarananNo ratings yet
- Canoe Matlab 001Document58 pagesCanoe Matlab 001Coolboy RoadsterNo ratings yet
- Advanced Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics (Cheg6121) : Review of Basic ThermodynamicsDocument74 pagesAdvanced Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics (Cheg6121) : Review of Basic ThermodynamicsetayhailuNo ratings yet
- Science 4 Diagnostic/Achievement TestDocument5 pagesScience 4 Diagnostic/Achievement TestGe PebresNo ratings yet
- DeliciousDoughnuts Eguide PDFDocument35 pagesDeliciousDoughnuts Eguide PDFSofi Cherny83% (6)
- Meno's Paradox of Inquiry and Socrates' Theory of RecollectionDocument10 pagesMeno's Paradox of Inquiry and Socrates' Theory of RecollectionPhilip DarbyNo ratings yet
- Clark SM 616 Service ManualDocument20 pagesClark SM 616 Service Manualenid100% (55)