Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Microwaves
Uploaded by
TerkCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Microwaves
Uploaded by
TerkCopyright:
Available Formats
What is a microwave?
Electromagnetic radiations having frequencies between 300 MHz and 300 GHz are referred to be
microwaves. Since frequency and wavelength have an inverse relationship , in terms of wavelength,
microwave ranges from a millimeter to around 1 meter. Microwaves fall between infrared radiation and
radio waves in the electromagnetic spectrum. A few of the properties of microwaves are as follows:
Metal surfaces reflect microwaves. Microwaves with a certain wavelength pass through the
earth’s atmosphere and can be useful in transmitting information to and from satellites in orbit.
Hence, the satellite dishes are made of metal as they reflect microwaves well.
Microwaves of certain frequencies are absorbed by water. This property of microwaves is useful
n cooking. Water in the food absorbs microwaves, which causes the water to heat up, therefore
cooking the food.
Microwave transmission is affected by wave effects such as refraction, reflection, interference,
and diffraction.
Microwaves can pass through glass and plastic. This is the reason why we use a plastic or glass
container in a microwave oven and not metal containers, as metal reflects microwaves.
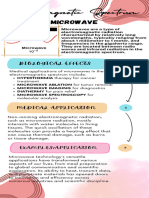
Characteristics of a microwave:
Wavelength: between 1 mm and 1 m
Frequency: range from 300 GHz to 300 MHz
Energy per photon: 0.0000012407053 eV to 0.0012407053 eV (formula: E=hf)
Health Risk:
Because the radiation from microwaves is non-ionizing, it can only cause molecules to move and all talks
about microwave radiation causing cancers or DNA alteration are all rumors. Despite microwaves being
non-ionizing, microwave radiation has the ability to heat body tissue in the same way that it heats food.
Microwaves at high levels can cause a painful burn. The eyes and the testicles are particularly vulnerable
to RF heating because there is little blood flow in them to carry away excess heat. Furthermore, the lens
of the eye is particularly sensitive to extreme heat, and prolonged exposure to high levels of microwaves
can result in cataracts. However, these types of injuries – burns and cataracts – can only be caused by
excessive microwave radiation exposure.
How does a microwave oven uses microwaves to quickly heat food?
Inside the oven, an electron tube known as a magnetron generates microwaves. Microwaves are
reflected within the oven's metal interior, where they are absorbed by food. Microwaves cause the
water molecules in food to vibrate, causing heat to be produced that cooks the food. As a result, foods
with a high water content, such as fresh vegetables, can be cooked faster than other foods. As
microwave energy is absorbed by food, it converts to heat and does not render food "radioactive" or
"contaminated."
You might also like
- Electromagnetic Waves ProjectDocument13 pagesElectromagnetic Waves ProjectDiya Kumar79% (53)
- Microwave Oven ClassDocument33 pagesMicrowave Oven ClassDr. Lenin SBNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic WaveDocument48 pagesElectromagnetic Wavemrs azizi100% (2)
- Electromagnetic Spectrum Microwave 2Document17 pagesElectromagnetic Spectrum Microwave 2janus.gatpandanNo ratings yet
- What Are Microwaves12Document2 pagesWhat Are Microwaves12Joshua SalazarNo ratings yet
- Waves and Wave Properties Physical Science Quiz Presentation Yellow Aqua An - 20231117 - 073039 - 0000Document15 pagesWaves and Wave Properties Physical Science Quiz Presentation Yellow Aqua An - 20231117 - 073039 - 0000Kathleen LeizNo ratings yet
- University of Engineering and Technology, LahoreDocument14 pagesUniversity of Engineering and Technology, LahoreOsamaFaisalNo ratings yet
- 8.2. EMW-source, Frequency Range, UsesDocument3 pages8.2. EMW-source, Frequency Range, UsesRamananNo ratings yet
- Microwave OvenDocument12 pagesMicrowave OvenAnamul HasanNo ratings yet
- Microwaves and Sound WavesDocument16 pagesMicrowaves and Sound WavesAlexaNo ratings yet
- 12 Bab IIDocument18 pages12 Bab IIsartonyNo ratings yet
- E G2 Campos-Saubon MicrowavesDocument14 pagesE G2 Campos-Saubon MicrowavesGeio Nicolai CatreNo ratings yet
- How A Microwave Oven Works?: By: Emmy MakDocument12 pagesHow A Microwave Oven Works?: By: Emmy MakAkash NiwalNo ratings yet
- How A Microwave Oven Works?: By: Emmy MakDocument12 pagesHow A Microwave Oven Works?: By: Emmy MakVishal MadanNo ratings yet
- Activity 8 - MicrowaveDocument4 pagesActivity 8 - MicrowaveJohn EnricoNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Waves For CookingDocument10 pagesElectromagnetic Waves For CookingUditha MuthumalaNo ratings yet
- Elektrotehnika MikroTalasna SharpDocument10 pagesElektrotehnika MikroTalasna SharpJovica PetrovićNo ratings yet
- Beige White Aesthetic Vintage Scrapbook Group Project PresentationDocument13 pagesBeige White Aesthetic Vintage Scrapbook Group Project Presentationmgxrkc4nsyNo ratings yet
- Beige White Aesthetic Vintage Scrapbook Group Project PresentationDocument13 pagesBeige White Aesthetic Vintage Scrapbook Group Project Presentationmgxrkc4nsyNo ratings yet
- Radiation 4Document128 pagesRadiation 4Argha TalukderNo ratings yet
- NTFPP-Module 3 Microwave Processing of Foods - AjitKSinghDocument12 pagesNTFPP-Module 3 Microwave Processing of Foods - AjitKSinghKeshav RajputNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2 Physics Terminal PDFDocument4 pagesAssignment 2 Physics Terminal PDFFatima chaudharyNo ratings yet
- Microwave Ovens: How Does The Microwave Oven Actually Cook Our Food?Document6 pagesMicrowave Ovens: How Does The Microwave Oven Actually Cook Our Food?knt124No ratings yet
- Electromagnetic SpectrumDocument9 pagesElectromagnetic SpectrumAk R71No ratings yet
- Microwave For YouDocument3 pagesMicrowave For YouTrishdale LeonaNo ratings yet
- Microwave ProcessingDocument5 pagesMicrowave ProcessingPrashanta PokhrelNo ratings yet
- Uses of Electromagnetic WavesDocument4 pagesUses of Electromagnetic WavesMarlou PrincesaNo ratings yet
- Physics Microwaves KS3Document8 pagesPhysics Microwaves KS3Lydia HoNo ratings yet
- Real Life Example of Electromagnetic WaveDocument26 pagesReal Life Example of Electromagnetic WaveAditya KumarNo ratings yet
- Heat TransferDocument2 pagesHeat TransferEmmanueNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer GME221 Eight LectureDocument36 pagesHeat Transfer GME221 Eight Lecturej.a smartNo ratings yet
- Microwave DiathermyDocument9 pagesMicrowave Diathermyinrmpt770% (1)
- Electromagnetic WavesDocument27 pagesElectromagnetic WavesKatrinaNo ratings yet
- Homework Javier SanjurDocument3 pagesHomework Javier SanjurMelanie CerrudNo ratings yet
- Properties of Electromagnetic WavesDocument3 pagesProperties of Electromagnetic WavesAayan AhmadNo ratings yet
- Microwave: Group Members: Gavin Chew Ivan Tiong Adrian Wong Bryan TangDocument4 pagesMicrowave: Group Members: Gavin Chew Ivan Tiong Adrian Wong Bryan TangIVAN TIONG WEI JUN MoeNo ratings yet
- Physics ProjektDocument12 pagesPhysics Projektrupendrajain20No ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Radiation: Clasification. CharacterizationDocument24 pagesElectromagnetic Radiation: Clasification. CharacterizationMihai BăiceanuNo ratings yet
- GROUP 2 - General Physics II Microwave RadiationDocument9 pagesGROUP 2 - General Physics II Microwave RadiationRheyven JuanNo ratings yet
- Microondas InglesDocument2 pagesMicroondas InglesVeronica AcostaNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Spectrum Microwave 1Document1 pageElectromagnetic Spectrum Microwave 1FranceLouise DelosReyesNo ratings yet
- Microwaves: Presented By: Hajra Aamir (2017-CH-210) Presented To: Dr. Sikander RafiqDocument17 pagesMicrowaves: Presented By: Hajra Aamir (2017-CH-210) Presented To: Dr. Sikander RafiqSyed Ahmad Ali ShahNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic WavesDocument12 pagesElectromagnetic WavesINSIDIOUSNo ratings yet
- Microwave: Group Members: Gavin Chew Ivan Tiong Adrian Wong Bryan TangDocument4 pagesMicrowave: Group Members: Gavin Chew Ivan Tiong Adrian Wong Bryan TangIVAN TIONG WEI JUN MoeNo ratings yet
- 2023-11-10 11 - 13 - 50.563 - 1Document2 pages2023-11-10 11 - 13 - 50.563 - 1pranitjadhav0407No ratings yet
- Electromagnetic SpectrumDocument16 pagesElectromagnetic SpectrumTanish100% (1)
- Photons and Ionisation: Electromagnetic SpectrumDocument1 pagePhotons and Ionisation: Electromagnetic SpectrumIkhlaas WildNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic WavesDocument23 pagesElectromagnetic WavesNjike ChigbuNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic WaveDocument21 pagesElectromagnetic WaveRadhwan Hameed AsadNo ratings yet
- Microwaves: By:-AksharaDocument3 pagesMicrowaves: By:-AksharaAkshara ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- C14 Electromagnetic SpectrumDocument2 pagesC14 Electromagnetic SpectrumKhaulah HamadNo ratings yet
- Microwaves and AntennaDocument21 pagesMicrowaves and AntennaYousuf KhanNo ratings yet
- C F Ms F: Keywords: Microwaves, IR, Brassica Juncea, EtcDocument1 pageC F Ms F: Keywords: Microwaves, IR, Brassica Juncea, EtcEr Paramjit SinghNo ratings yet
- RF and MWDocument166 pagesRF and MWSOWMIYA S SIT 2020No ratings yet
- (297 304) V9N3PTDocument8 pages(297 304) V9N3PTanweshabehera12No ratings yet
- Elecromagnetic SpectrumDocument11 pagesElecromagnetic SpectrumTIJIN ABE THOMASNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Physics Topic 1 WavesDocument9 pagesIGCSE Physics Topic 1 WavesAbdul RaheemNo ratings yet
- Microwaves: Prepared By: Salman, OvaisDocument7 pagesMicrowaves: Prepared By: Salman, OvaisSalman HabibNo ratings yet
- ELECTROMAGNETIC FIELDS: Exposure is not optional, no one can avoid itFrom EverandELECTROMAGNETIC FIELDS: Exposure is not optional, no one can avoid itNo ratings yet
- Assignment 5Document1 pageAssignment 5TerkNo ratings yet
- ES032 Assignment6Document6 pagesES032 Assignment6TerkNo ratings yet
- EECC2 Thermodynamics ESASDocument2 pagesEECC2 Thermodynamics ESASTerkNo ratings yet
- EECC2 DeformableBodies CC2Document3 pagesEECC2 DeformableBodies CC2TerkNo ratings yet
- Eecc2 Mechanics EsasDocument3 pagesEecc2 Mechanics EsasTerkNo ratings yet
- EECC2 FluidMechanics ESASDocument3 pagesEECC2 FluidMechanics ESASTerkNo ratings yet
- MatSci - Compilation QuizzesDocument11 pagesMatSci - Compilation QuizzesTerkNo ratings yet
- EECC2 Chem ESASDocument3 pagesEECC2 Chem ESASTerkNo ratings yet
- EECC2 Physics ESASDocument2 pagesEECC2 Physics ESASTerkNo ratings yet
- Terms EngeconDocument4 pagesTerms EngeconTerkNo ratings yet
- EECC2 EngMaterials ESASDocument4 pagesEECC2 EngMaterials ESASTerkNo ratings yet
- Review MODULE - MATHEMATICS (Vectors & Analytic Geometry in Three Dimension)Document1 pageReview MODULE - MATHEMATICS (Vectors & Analytic Geometry in Three Dimension)rhodel cosyeloNo ratings yet
- Physics - Solution Set For Homework Book Chapter - 15 KTG & ThermodynamicsDocument4 pagesPhysics - Solution Set For Homework Book Chapter - 15 KTG & ThermodynamicsKishorNo ratings yet
- Security SystemDocument20 pagesSecurity SystemSee Hari TejaNo ratings yet
- Electromotive Force Magnetic FluxDocument8 pagesElectromotive Force Magnetic FluxJalal Al-SaifNo ratings yet
- Design of Two Wheeled Electrica VehicleDocument76 pagesDesign of Two Wheeled Electrica VehicletoceanduongNo ratings yet
- Learning Activity Sheet: Do The Exercise!Document9 pagesLearning Activity Sheet: Do The Exercise!Najmah Sirad AmpaNo ratings yet
- Viva Bee LabDocument2 pagesViva Bee Labhari mNo ratings yet
- Pilar JembatanDocument37 pagesPilar JembatanMAWAR08100% (4)
- EN 10025 Grade S355J2C Normalized or Normalized Formed (+N)Document3 pagesEN 10025 Grade S355J2C Normalized or Normalized Formed (+N)melvin ekboteNo ratings yet
- Code AsterDocument16 pagesCode AsterStefano MilaniNo ratings yet
- Science8 - q1 - Mod4 - Effect of Temperature To The Speed of Sound - v4Document25 pagesScience8 - q1 - Mod4 - Effect of Temperature To The Speed of Sound - v4Hariette Denisse BarriosNo ratings yet
- MCQ For Module6Document3 pagesMCQ For Module6Ijaz TalibNo ratings yet
- Electronic and Optical Properties of Three Phases of Titanium Dioxide Rutile, Anatase, and Brookite PDFDocument10 pagesElectronic and Optical Properties of Three Phases of Titanium Dioxide Rutile, Anatase, and Brookite PDFRaghav MehraNo ratings yet
- Dino Tego Cera and Rano SetsDocument2 pagesDino Tego Cera and Rano Setsthanh nhan dinhNo ratings yet
- Objectives: Laboratory 1. The Structure of Mechanisms, Fundamentals and ExamplesDocument11 pagesObjectives: Laboratory 1. The Structure of Mechanisms, Fundamentals and ExamplesGabriel IulianNo ratings yet
- Contactor Rollarc SF6Document24 pagesContactor Rollarc SF6Dong BachNo ratings yet
- CMT Capitolul 4 - Transmisii Curele DintateDocument19 pagesCMT Capitolul 4 - Transmisii Curele DintateANANo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document19 pagesChapter 1raghu ramNo ratings yet
- Control Valve HandbookDocument236 pagesControl Valve HandbookTon Blok100% (1)
- Cap 8 Livro PDFDocument36 pagesCap 8 Livro PDFDiogo FonaNo ratings yet
- Pump SelectionDocument112 pagesPump SelectionSIVAPATHASEKARAN100% (6)
- Xray HistoryDocument5 pagesXray Historyapi-3710134No ratings yet
- Energy Bar Graph White-Boarding L: DirectionsDocument2 pagesEnergy Bar Graph White-Boarding L: DirectionssammyNo ratings yet
- Froude-Krylov Force CoefficientDocument20 pagesFroude-Krylov Force CoefficientLazaros NtoanidisNo ratings yet
- Transient Considerations of Flat-Plate Solar CollectorsDocument5 pagesTransient Considerations of Flat-Plate Solar CollectorsmangouarNo ratings yet
- Design Pull RodDocument1 pageDesign Pull RodSACHINNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 12 Physics Semiconductor Devices Important QuestionsDocument1 pageCBSE Class 12 Physics Semiconductor Devices Important QuestionsShashi KiranNo ratings yet
- M1pp Jan13Document99 pagesM1pp Jan13JW1212No ratings yet
- O Syllabus Outline: BS. Applied Geology 2 Professional (Morning)Document13 pagesO Syllabus Outline: BS. Applied Geology 2 Professional (Morning)Pak DesireNo ratings yet
- Difference Between Unearthed CableDocument14 pagesDifference Between Unearthed CableArnab GhoshNo ratings yet