Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Cell Cycle & Meiosis Guide
Uploaded by
Abegail DacayoOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Cell Cycle & Meiosis Guide
Uploaded by
Abegail DacayoCopyright:
Available Formats
CELL CYCLE
➢ Growth
◊ Permanent increase in size and accompanied by cell division and
differentiation to form tissues and organs.
➢ Cell Cycle
◊ is the process a cell undertakes to replicate all of its material
and divide into two identical cells.
◊ It includes interphase, mitosis, and cytokinesis.
◊ It is important because
○ make it possible for organisms
○ to replace cells that are old or damaged
○ to produce new cells
➢ Chromosomes
◊ Are made up of deoxyribonucleic acid or (DNA)
➢ DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid)
◊ It carries or stores our genetic material.
◊ A double Helix
➢ Cancer
◊ It is caused by uncontrolled division of cells.
➢ Nucleosomes
◊ DNA wrapped in protein
➢ Chromatin
◊ is a thread like strand it will be looped or condensed until it
made a bundle which will be chromosomes.
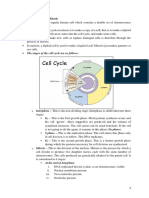
2 MAIN PHASES IN CELL CYCLE
◊ Interphase
◊ Mitotic
➢ Interphase
◊ Resting stage or non-dividing stage.
◊ It absorbs nutrients and building up protoplasm.
◊ Chromosomes appear as long thin threads called chromatin.
◊ Chromatin threads cannot be distinguished individually at this
stage.
◊ Centrioles divide during interphase in ANIMAL CELL.
GEN BIO Page 1
CELL CYCLE /INTERPHASE
STAGES OF INTERPHASE
◊ G1 Phase
◊ rapid growth and replication of organelles.
◊ results in the growth of the cell due to active protein
synthesis and imbibition of materials. Cell organelles are
duplicated, and centrioles are replicated.
◊ Organelles replicate because they can be worn out.
◊ S Phase
◊ is characterized by chromosome duplication as a result of
DNA replication. Each of the 46 chromosomes (23 pairs) is
replicated by the cell
◊ G2 Phase
◊ the cell continues to grow, and asters, spindle fibers, and
other materials needed for cell division are formed.
◊ Replication of centrioles is also completed.
◊ During this stage, the cell double-checks the duplicated
chromosomes for any error so it can make the needed
repair before the actual cell division.
➢ Mitotic Phase
◊ a cell reproduces
◊ each pair is called a duplicated chromosomes
STAGES OF MITOTIC PHASE
◊ Mitosis
◊ Cytokinesis
➢ Mitosis
◊ Somatic cells
◊ A form of nuclear division that produces daughter nuclei
containing the same number of chromosomes as the parent
nucleus.
◊ Daughter nuclei are genetically identical
GEN BIO Page 2
CELL CYCLE/ MITOSIS
STAGES OF MITOSIS
◊ Prophase
○ Formation of chromosome ; condensing of chromatin to
become chromosomes. ; coiling and condensing of chromatin
to become chromosomes.
○ Each chromosome consists of two sister chromatids
attached at the centromere.
○ DNA is distinguishable in this stage since it is chromatin.
○ Chromosomes are now visible under a microscope.
○ Asters form around the centrioles in an animal cell.
○ Asters are made up of microtubules.
○ Spindle forms with spindle fibers extending from one pole of
the cell to the other.
□ Early Prophase
The mitotic spindle starts to form, the
chromosomes start to condense, and the nucleolus
disappears.
In early prophase, the cell starts to break down
some structures and build others up, setting the
stage for division of the chromosomes.
centrioles will move at the opposite poles of nucleus
aster: short strand of microtubules
spindle fiber: elongated made up of microtubules
nucleus will start to breakdown
□ Late Prophase
The nuclear envelope breaks down and the
chromosomes are fully condensed.
In late prophase sometimes also called
prometaphase
The mitotic spindle begins to capture and organize
the chromosomes. The chromosomes become even
more condensed, so they are very compact.
◊ Metaphase
○ Chromosomes line up in single file at the middle of the cell.
○ Centromere is the region that has protein where spindle
fiber will connect.
○ Animal cell has centriole in the metaphase. Plant doesn't
have.
GEN BIO Page 3
CELL CYCLE/MITOSIS
◊ Anaphase
○ sister chromatids separate.
○ spindle fiber is the cause while sister chromatids separate
because spindle fibers begin to shorten.
○ the cell begins to lengthen.
◊ Telophase
○ a nuclear membrane forms around the chromatin
○ the chromosome begin to unwind.
○ spindle fibers begin to break down.
○ two identical nuclei form.
➢ Cytokinesis
◊ division of cytoplasm
○ IN ANIMAL: this forms a crease called furrow in the
middle of the cell.
○ IN PLANT: cell plate will be formed.
○ Cell plate is made up from vesicles join together
*OTHER INFO:
◊ Counting of chromosomes: 1 chromosomes consist of 2 sister
chromatids
◊ If there are 10 chromosomes , the daughter chromosomes will
be 10 as well.
◊ Daughter chromosomes are the chromatids that are separated
during anaphase.
◊ Daughter cell are the genetically identical cells formed when a
cell undergoes cell division or mitosis.
◊ Centrioles are absent in plant cell.
◊ Neurons don't undergo cell division when it's mature.
◊ DNA need to be replicated because 2 cells should have same
copy of material.
GEN BIO Page 4
REPRODUCTION
➢ Reproduction
◊ Production of new organisms
➢ Fertilization
◊ Occurs when the nucleus of the male gamete fuses with nucleus of
the female gamete to form a zygote.
➢ Zygote
◊ It is the fertilized egg.
➢ Embryo
◊ It is formed when the zygote divides by mitosis to form an
embryo.
➢ Gametes
◊ Are reproductive cells that contain half the number of
chromosomes as the normal body cells.
➢ n
◊ Represents the number of set of chromosomes.
➢ Diploid number
◊ Number of chromosomes in the normal body cell.
◊ Complete set of chromosomes.
◊ Represented by 2n
➢ Haploid number
◊ Half diploid.
◊ Half set of chromosomes.
◊ Represented by n
*Humans have 46 DNA molecules therefore humans have 46 chromosomes,
therefore 2n=46 and n=23.
➢ Paternal
◊ Father's chromosomes.
➢ Maternal
◊ Mother's chromosomes.
2 TYPES OF CELLS
◊ Somatic cells (Diploid cells)
○ Undergo mitosis
○ cells in the body
◊ Sex cells (Haploid cells)
○ Undergo Meiosis
○ Gametes
GEN BIO Page 5
MEIOSIS/ MEIOSIS I
➢ Meiosis
◊ Is a form of nuclear division that produces daughter nuclei
containing half the number of chromosomes as the parent
nucleus.
◊ Also known as reduction division.
◊ This is called reduction division because each of the daughter
cells produced contains half the number of chromosomes as the
parent cell.
◊ A production that produces reproductive cells.
◊ A genetic recombination.
◊ Produces 4 daughter cells wherein all daughter cells are unique
and not identical with the parent cell.
◊ It always starts with diploid cell
➢ Male sex chromosome: XY
➢ Female sex chromosome: XX
➢ Homologous Chromosomes
◊ Couple chromosomes/pair chromosome
◊ Pair of maternal and paternal chromosomes.
◊ Chromosomes will pair if:
Has the same length, genes, gene position, location of
centromere.
➢ Synapsis
◊ It is the fusion of homologous chromosomes.
2 DIVISION OF MEIOSIS
◊ Meiosis I
◊ Meiosis II
STAGES OF MEIOSIS I
◊ Interphase I
○ Chromatin threads replicate, producing two identical sister
chromatids attached at the centromere. It is not visible
under the microscope.
○ The pair of centrioles divides.
GEN BIO Page 6
MEIOSIS I/ MEIOSIS II
◊ Prophase I
○ Chromatin threads condense, coil and shorten to become
chromosomes.
○ Chromosomes are now visible under the light microscope.
○ The homologous chromosomes condense and pair up, forming a
tetrad.
○ Crossing over or synapsis can occur during the latter part of this
stage.
○ Chromatids of homologous chromosomes may cross and twist
around one another in chiasma (plural: chiasmata).
○ Crossing over or exchange of genetic material. It produces new
combination of alleles along the chromosomes.
◊ Metaphase I
○ homologous chromosomes align at the equatorial plate, and spindle
fibers attach to the kinetochore of their centromeres.
◊ Anaphase I
○ Homologous pairs separate with sister chromatids.
○ Spindle fibers shorten
○ Each chromosome here is still made up of two chromatids
◊ Telophase I
○ two daughter haploid cells are formed
◊ Cytokinesis I
○ divides the cell into two, each containing half the chromosome
number of the parent cell.
○ Each haploid cell then undergoes another series of divisions
in Meiosis II.
STAGES IN MEIOSIS II
◊ Prophase II
○ The chromosomes condense, and centrioles replicate and
move to opposite poles.
○ Nuclear envelope disappears.
○ Spindle fibers appear.
◊ Metaphase II
○ chromosomes align at the equatorial plate.
GEN BIO Page 7
MEIOSIS II
◊ Anaphase II
○ The centromeres divide.
○ Sister chromatids separate to become daughter
chromosomes.
◊ Telophase II
○ Spindle fibers disappear.
○ Nuclear envelopes form around the two daughter
chromosomes at each pole.
○ A nucleolus reforms.
◊ Cytokinesis II
○ Cleavage of cytoplasm results in four daughter cells being
produced, each with half the number of chromosomes as the
parent cell.
GEN BIO Page 8
You might also like
- Biology Class 10 Icse Boards!Document10 pagesBiology Class 10 Icse Boards!nark.jf4No ratings yet
- Unit 3 - First HalfDocument10 pagesUnit 3 - First HalfjohnNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6Document10 pagesChapter 6missmirachannel1No ratings yet
- MitosisDocument16 pagesMitosisAnahita SuriNo ratings yet
- Please Review The Following Concepts:: Page - 1Document36 pagesPlease Review The Following Concepts:: Page - 1newfie848No ratings yet
- Cell DivisionDocument10 pagesCell DivisionGale SatsatinNo ratings yet
- 3.2 Mitosis and MeiosisDocument46 pages3.2 Mitosis and MeiosisAhmed AimanNo ratings yet
- Biology Mitosis Notes (O Level)Document9 pagesBiology Mitosis Notes (O Level)ojilongNo ratings yet
- Cell CycleDocument36 pagesCell Cyclejetes67387No ratings yet
- TEXT READINGS Chapter - 16Document6 pagesTEXT READINGS Chapter - 16tanusehdev17No ratings yet
- Cell DivisionDocument48 pagesCell DivisionMichaelNo ratings yet
- 3.1 Cell Reproduction BiologyDocument53 pages3.1 Cell Reproduction BiologySean CatapangNo ratings yet
- Sexual ReproductionDocument25 pagesSexual Reproductioncxmic19No ratings yet
- Cell Cycle w4Document49 pagesCell Cycle w4Janika RelenteNo ratings yet
- Bio SummaryDocument9 pagesBio SummarySophia BUcarieNo ratings yet
- Cellular Reproduction: Science 8 4 Quarter Lesson 2Document45 pagesCellular Reproduction: Science 8 4 Quarter Lesson 2Cynthia RectoNo ratings yet
- The Cell CycleDocument58 pagesThe Cell Cyclemahigdave2007No ratings yet
- Meiosis in Grasshopper TestisDocument7 pagesMeiosis in Grasshopper TestisRonisa100% (3)
- Unit 3: Genetic Processes 4.1 Cell Division and Genetic MaterialDocument40 pagesUnit 3: Genetic Processes 4.1 Cell Division and Genetic MaterialThatsKindaWackNo ratings yet
- Mitosis and MeiosisDocument42 pagesMitosis and MeiosisNidhi SinghNo ratings yet
- Unit 8 Introduction To Cell DivisionDocument27 pagesUnit 8 Introduction To Cell DivisionTeo PhiriNo ratings yet
- Cell DivisionDocument23 pagesCell DivisionLeonita SwandjajaNo ratings yet
- BIOL223-Lab 7Document40 pagesBIOL223-Lab 7chicken fries100% (2)
- Cell DivisionDocument10 pagesCell DivisionVardan ShrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Early March, Meiosis - Mitosis Study Guide (3.3)Document9 pagesEarly March, Meiosis - Mitosis Study Guide (3.3)ChanelleNo ratings yet
- Class Notes: Cell CycleDocument9 pagesClass Notes: Cell CycleWhyNo ratings yet
- Mitosis and Cell Cycle PowerpointDocument29 pagesMitosis and Cell Cycle PowerpointMutmainnah BurhanuddinNo ratings yet
- Cor 007 Day 16Document23 pagesCor 007 Day 16Rain VicenteNo ratings yet
- Chapter Four.. 2022-10-12 11 - 31 - 55Document34 pagesChapter Four.. 2022-10-12 11 - 31 - 55Altaf Hussain KhanNo ratings yet
- Cell DivisionDocument12 pagesCell DivisionRaýeęś AhmêðNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Unit 3.1Document31 pagesChapter 1 Unit 3.1harshit khareNo ratings yet
- Cell Cycle, Mitosis and MeiosisDocument6 pagesCell Cycle, Mitosis and Meiosislil taniaNo ratings yet
- Mitosis: Cell Division: Meiosis and MitosisDocument21 pagesMitosis: Cell Division: Meiosis and Mitosisaybs solamoNo ratings yet
- Cell Division Guide by Dr. SANYAOLU ARINOLADocument21 pagesCell Division Guide by Dr. SANYAOLU ARINOLAOlogunja PaulNo ratings yet
- Cell Cycle and Cell DivisionDocument5 pagesCell Cycle and Cell DivisionParth GoyalNo ratings yet
- L4 - Sexual ReproductionDocument58 pagesL4 - Sexual ReproductionTiffany LimNo ratings yet
- Cell DivisionDocument31 pagesCell DivisionShin Thant Ko B10 June SectionNo ratings yet
- Cell CycleDocument11 pagesCell Cycleashley cagadasNo ratings yet
- Biology ExamDocument17 pagesBiology ExamSai Adrienne RealubitNo ratings yet
- Compressed Notes Chapter 3: Cell Division Sb015Document10 pagesCompressed Notes Chapter 3: Cell Division Sb015SYAZWAN BIN MUSTAFA MoeNo ratings yet
- MODULE-2Document37 pagesMODULE-2nutssdeez944No ratings yet
- Mitotic Cell Division - Exercise 7: ObjectivesDocument56 pagesMitotic Cell Division - Exercise 7: ObjectivesANnur RAshidNo ratings yet
- G8 Science Q4 Week 2 Cell Division Mitosis MeiosisDocument52 pagesG8 Science Q4 Week 2 Cell Division Mitosis MeiosisLeyannNo ratings yet
- Cell DivisionDocument86 pagesCell DivisionaliNo ratings yet
- AP Cell Cycle Mitosis and MeiosisDocument33 pagesAP Cell Cycle Mitosis and MeiosisAlexa Feliz De PedroNo ratings yet
- Mitotic Cell Division - Exercise 7: ObjectivesDocument56 pagesMitotic Cell Division - Exercise 7: Objectiveskaran79No ratings yet
- Cell DivisionDocument55 pagesCell DivisionjohnpenielmontalesNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2Document58 pagesLecture 2shaheenNo ratings yet
- General Embryology Part A-1Document46 pagesGeneral Embryology Part A-1Uti SolomonNo ratings yet
- Agric QuizDocument3 pagesAgric QuizKelsy SalazarNo ratings yet
- How Bacteria and Eukaryotes Divide CellsDocument69 pagesHow Bacteria and Eukaryotes Divide CellsAhmed MohamadNo ratings yet
- Cell Division and Meiosis Chapter SummaryDocument12 pagesCell Division and Meiosis Chapter SummaryNoor Hidayah SambliNo ratings yet
- BBC1-K11-13 Cell ReplicationDocument81 pagesBBC1-K11-13 Cell Replicationirvan tpNo ratings yet
- Micro TeachingDocument12 pagesMicro TeachingIke MasNo ratings yet
- G8 Science Q4- Week 2 Cell-Division-Mitosis-Meiosis-PptDocument52 pagesG8 Science Q4- Week 2 Cell-Division-Mitosis-Meiosis-PptrebeccaNo ratings yet
- Bio F4 Chap 6Document53 pagesBio F4 Chap 6Vinieysha LoganathanNo ratings yet
- Structure of Chromosomes, Cell Cycle, Cell DivisionDocument35 pagesStructure of Chromosomes, Cell Cycle, Cell DivisionXyzNo ratings yet
- Cellular Reproduction AND GeneticsDocument103 pagesCellular Reproduction AND GeneticsJanrex Karl FaelagmaoNo ratings yet
- Human Chromosomes: An Illustrated Introduction to Human CytogeneticsFrom EverandHuman Chromosomes: An Illustrated Introduction to Human CytogeneticsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Etech 2ND Quarter (Lesson 6-12)Document18 pagesEtech 2ND Quarter (Lesson 6-12)Abegail DacayoNo ratings yet
- Oral Communication Second QuarterDocument15 pagesOral Communication Second QuarterAbegail DacayoNo ratings yet
- Etech 2ND Quarter (Lesson 6-8)Document5 pagesEtech 2ND Quarter (Lesson 6-8)Abegail DacayoNo ratings yet
- Cpar Gamaba ArtistsDocument9 pagesCpar Gamaba ArtistsAbegail DacayoNo ratings yet
- CCT Module 3 001 PDFDocument35 pagesCCT Module 3 001 PDFIecjs BwgiNo ratings yet
- Plant Tissue Culture Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument55 pagesPlant Tissue Culture Multiple Choice QuestionsOmprakash Shete100% (1)
- How Does IPTG Induced Gene Expression Work at A Molecular Level - QuoraDocument3 pagesHow Does IPTG Induced Gene Expression Work at A Molecular Level - QuoraDiksha GahlotNo ratings yet
- Science Chapter 3 Form 4Document16 pagesScience Chapter 3 Form 4Muhammad Akmal Kamaluddin100% (1)
- WORKSHEET 5.10 Cell & Mitosis Crossword PuzzleDocument4 pagesWORKSHEET 5.10 Cell & Mitosis Crossword PuzzleNurul Huda IsaNo ratings yet
- Plant BreedingDocument36 pagesPlant BreedingRhene BarcelonNo ratings yet
- STPM Term 3 BiologyDocument9 pagesSTPM Term 3 BiologyYeap Chee BengNo ratings yet
- Chapter 15Document15 pagesChapter 15nfnf otupyooorefnNo ratings yet
- A2 Section B by DR - Nermeen MustafaDocument110 pagesA2 Section B by DR - Nermeen MustafaAdiba AnjumNo ratings yet
- Lac Operon - Genetics-Essentials-Concepts-and-ConnectionsDocument15 pagesLac Operon - Genetics-Essentials-Concepts-and-ConnectionsDiandra AnnisaNo ratings yet
- Bio CHP 2 MCQ QuestionsDocument8 pagesBio CHP 2 MCQ QuestionsSanjanaNo ratings yet
- 1 An Observation - The Krebs CycleDocument33 pages1 An Observation - The Krebs CycleOmbrog JustinNo ratings yet
- Perkembangan Sel-Sel Spermatogenik Dan Kualitas Sperma Pascapemberian Ekstrak Pegagan (Centella Asiatica)Document10 pagesPerkembangan Sel-Sel Spermatogenik Dan Kualitas Sperma Pascapemberian Ekstrak Pegagan (Centella Asiatica)Pradd OattgNo ratings yet
- Asexual Vs Sexual ReproductionDocument9 pagesAsexual Vs Sexual ReproductionEdenNo ratings yet
- VariationDocument39 pagesVariationmarziahNo ratings yet
- Clonal SelectionDocument12 pagesClonal SelectionUmang PatelNo ratings yet
- Summary of Metabolism LectureDocument20 pagesSummary of Metabolism Lectureaquasrk250No ratings yet
- Protien-Synthesis Lesson PlanDocument8 pagesProtien-Synthesis Lesson PlanHAIDEE VASQUEZNo ratings yet
- CellBio30NotesDiagramsDocument47 pagesCellBio30NotesDiagramsuyenNo ratings yet
- Reproduction and Human Development Test For Practice AnswersDocument7 pagesReproduction and Human Development Test For Practice AnswersAngela Joan YedersbergerNo ratings yet
- Karas Ghattas - RNA and Protein Synthesis - Pdf.kamiDocument3 pagesKaras Ghattas - RNA and Protein Synthesis - Pdf.kamiKaras GhattasNo ratings yet
- Characteristics of Living Things Lecture NotesDocument12 pagesCharacteristics of Living Things Lecture NotesErica HartNo ratings yet
- Mutation: - Today? Mutation Refers To Changes That Occur Within GenesDocument18 pagesMutation: - Today? Mutation Refers To Changes That Occur Within Genesapplemango93No ratings yet
- Fasv Xii Biology MS PB 2023-24Document7 pagesFasv Xii Biology MS PB 2023-24BOLDNo ratings yet
- Embryology Lecture Notes - 2 Cleavage and TypesDocument6 pagesEmbryology Lecture Notes - 2 Cleavage and TypestrivikramraoNo ratings yet
- 1 ReproductioninOrganismsDocument22 pages1 ReproductioninOrganismsPriNce KhatriNo ratings yet
- Syllabus Breakup - Class 10 (Biology)Document2 pagesSyllabus Breakup - Class 10 (Biology)AaraNo ratings yet
- How One Scientist Impacted Understanding of Human ReproductionDocument2 pagesHow One Scientist Impacted Understanding of Human ReproductionDanakey CentenoNo ratings yet
- Apoptosis: Dr. Bimal PatelDocument22 pagesApoptosis: Dr. Bimal PatelBimal PatelNo ratings yet
- Molecular and Cellular Mechanisms of BiosignalingDocument86 pagesMolecular and Cellular Mechanisms of BiosignalingJon QNo ratings yet