Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Physical Science: General Directions: Your Answer Should Be Written Only in This Paper
Uploaded by
Jeclyn FilipinasOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Physical Science: General Directions: Your Answer Should Be Written Only in This Paper
Uploaded by
Jeclyn FilipinasCopyright:
Available Formats
PHYSICAL SCIENCE
Name: _______________________________________________ Grade & Strand #: ____________________
2 SEMESTER- QUARTER 3, LAS 2
ND
Topic: Polarity of Molecules
Relationship of Polarity of Molecules to its Properties
TEACHER: SHAHANIE JOY S. CASEL
GENERAL DIRECTIONS: YOUR ANSWER SHOULD BE WRITTEN ONLY IN THIS PAPER.
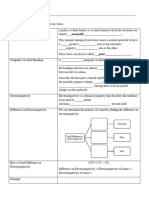
ACTIVITY 1. MATCHING TYPE. MATCH COLUMN A WITH COLUMN B. WRITE THE CHOSEN
LETTER ON THE SPACE PROVIDED.
COLUMN A COLUMN B
______1. Chemical Bond A. It is a measure of how strongly atoms attract bonding electrons to themselves.
______2. Covalent Bond B. It is consists of a chemical symbol surrounded by one to eight dots representing valence electrons.
______3. Electronegativity C. These are forces that hold atoms together in a compound.
______4. Lewis Dot Structure D. It states that atoms gain stability by having eight valence electrons.
______5. Octet Rule E. It is a bond that exists between both non-metals.
ACTIVITY 2. COMPLETION TYPE.
Directions: Complete the table below.
Element Atomic Number Number of Protons Number of Number of Mass Number
Electrons Neutrons
Neon 10 10
Bromine 35 35
Argon 18 22
Radon 88 222
Silicon 14 28
ACTIVITY 2. IDENTIFY ME!
Directions: Choose the term from the box that best describes the statement below. Write your answer on a separate sheet of paper.
Valence Electron Polar Molecule Lewis Structure
Electronegativity Nonpolar Molecule VSEPR Theory
________________________1. It has an electronegativity difference of less than 0.5.
________________________2. It measures the relative tendency of an atom to attract electrons to itself when chemically combined
with another atom.
________________________3. It consists of a chemical symbol surrounded by one to eight dots representing valence
electronegativity difference is less than 0.5.
________________________4. It’s an electronegativity difference is greater than 0.5.
________________________5. It refers to the outermost electrons
________________________6. It is a model used to predict the geometry of individual molecules from the number of electron pairs
surrounding their central atom.
ACTIVITY 3. IDENTIFY WHETHER THE PAIR OF SUBSTANCES ARE SOLUBLE, INSOLUBLE,
MISCIBLE OR IMMISCIBLE.
ACTIVITY 4. LET’S TEST YOUR UNDERSTANDING OF THE LESSON. COMPLETE THE
PARAGRAPH BELOW. WRITE YOUR ANSWER ON THE SPACE PROVIDED.
__________________________________________________________________
PARENTS NAME AND SIGNATURE
You might also like
- CHEMICAL BONDING-workbokDocument9 pagesCHEMICAL BONDING-workbokJenny Rose BatalonNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 Lewis Electron Dot StructureDocument22 pagesLesson 2 Lewis Electron Dot StructureAngel CapinpinNo ratings yet
- 03 GRADE 12 PASAY Physical Science S2 Q3 W2 PDFDocument20 pages03 GRADE 12 PASAY Physical Science S2 Q3 W2 PDFRemar Jhon PaineNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2: Atomic Structure & Interatomic Bonding: Issues To Address..Document23 pagesChapter 2: Atomic Structure & Interatomic Bonding: Issues To Address..Minh-Hoang NguyenNo ratings yet
- Chem Bondunit 03 Handouts To PrintDocument7 pagesChem Bondunit 03 Handouts To PrintFern HofileñaNo ratings yet
- Britton High School: Chemistry Chapter 12: BondingDocument85 pagesBritton High School: Chemistry Chapter 12: BondingMatthew GraceNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument9 pagesUntitledrona grace ulzoronNo ratings yet
- Name: - Grade: - DateDocument3 pagesName: - Grade: - DateCesarioVillaMartinLabajoJr.No ratings yet
- Chem.g12 q2w7 Module3 PamplonaDocument16 pagesChem.g12 q2w7 Module3 PamplonaRaymalyn MalynNo ratings yet
- Gen Chem 1 Q2 Module 3Document14 pagesGen Chem 1 Q2 Module 3lkNo ratings yet
- LONGTEST Science 9 (AutoRecovered)Document2 pagesLONGTEST Science 9 (AutoRecovered)jerome CarpioNo ratings yet
- Electronegativitiy Worksheet - WELCHDocument5 pagesElectronegativitiy Worksheet - WELCHkamrynwelch1No ratings yet
- Q2W2 - 1 - Chemical Bonding and Lewis StructureDocument25 pagesQ2W2 - 1 - Chemical Bonding and Lewis StructureEl Jie Ancheta Estela100% (1)
- Science 9 Q2 Week 3Document8 pagesScience 9 Q2 Week 3harley_quinn11No ratings yet
- Chemical Bonds Worksheet - AsynchrDocument2 pagesChemical Bonds Worksheet - AsynchrDonna May YbascoNo ratings yet
- Module 2 - Physical Science PDFDocument11 pagesModule 2 - Physical Science PDFDarry Blancia100% (2)
- Chemical Bonding and Molecular StructureDocument47 pagesChemical Bonding and Molecular StructureELVIS BoradNo ratings yet
- Ionic Covalent Bonds PractDocument2 pagesIonic Covalent Bonds PractRina NoviantiNo ratings yet
- Octet Rule and The Formation of Compounds: For General Chemistry 1/ Grade 12 Quarter 2 / Week 2Document12 pagesOctet Rule and The Formation of Compounds: For General Chemistry 1/ Grade 12 Quarter 2 / Week 2ariinnggg onicha100% (1)
- Electron Arrangement and Lewis Dot Symbols - StructuresDocument15 pagesElectron Arrangement and Lewis Dot Symbols - StructuresTanjiroNo ratings yet
- Grade11 Physical Science - Module 3Document5 pagesGrade11 Physical Science - Module 3Erickson SongcalNo ratings yet
- Week 3 - Module 3 (Synchronous)Document33 pagesWeek 3 - Module 3 (Synchronous)Patricia ArandaNo ratings yet
- Science Grade 9: Quarter 2 - Module 2 Chemical BondingDocument16 pagesScience Grade 9: Quarter 2 - Module 2 Chemical BondingElla Suan Tero100% (6)
- Types of Bonds AP ChemistryDocument6 pagesTypes of Bonds AP Chemistry중국이수아No ratings yet
- Physical Science Module 3Document22 pagesPhysical Science Module 3Florence-j Pelayo Tupaz100% (1)
- G9 Q2 W2 Ionic or Covalent CompoundsDocument17 pagesG9 Q2 W2 Ionic or Covalent CompoundsCherrilyn Enverzo33% (3)
- ValenceElectronsandLewisDotStructures 1 PDFDocument8 pagesValenceElectronsandLewisDotStructures 1 PDFStephanie WoodsNo ratings yet
- Supplemental Activities in Science 9 Quarter 2, Week 1Document6 pagesSupplemental Activities in Science 9 Quarter 2, Week 1Rose Ann ChavezNo ratings yet
- Chemistry For Engineers Laboratory: CHEM 114Document8 pagesChemistry For Engineers Laboratory: CHEM 114Ivyy Joyce BuanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Notes: The Chemical Context of LifeDocument21 pagesChapter 2 Notes: The Chemical Context of Lifemocha_volfgongNo ratings yet
- 2 Periodical Examination Science 9: Name - Grade & SectionDocument2 pages2 Periodical Examination Science 9: Name - Grade & SectionJanine Ginog FerrerNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding ModuleDocument35 pagesChemical Bonding ModuleMark Paul Lipata Benitez100% (2)
- SCIENCE Grade 9: Quarter 2 - Module 3 Ionic CompoundDocument16 pagesSCIENCE Grade 9: Quarter 2 - Module 3 Ionic CompoundRosalia Busca100% (1)
- SCIENCE Grade 9: Quarter 2 - Module 3 Ionic CompoundDocument16 pagesSCIENCE Grade 9: Quarter 2 - Module 3 Ionic CompoundJaneNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 2013Document18 pagesChemistry 2013taipanpanNo ratings yet
- PS Chemical BondingDocument31 pagesPS Chemical BondingSHEILA MARIE CORTADO - UNDANNo ratings yet
- Lewis StructureDocument38 pagesLewis StructureNicole Joyce Catabay FloresNo ratings yet
- Second Quarterly Summative Test in Science 9Document3 pagesSecond Quarterly Summative Test in Science 9TLGA Emmanuel PotoyNo ratings yet
- Chemical BondingDocument52 pagesChemical BondingzeusdillanpasquinNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry and Cellular Functions: T.A. Blakelock High School Grade 12 University Preparation BiologyDocument16 pagesBiochemistry and Cellular Functions: T.A. Blakelock High School Grade 12 University Preparation Biologyalathena alathenaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 4 Chemistry The Molecular Nature of Matter and Change Silberberg 103 CH 9 Models of Chemical Bonding 7039Document20 pagesChemistry 4 Chemistry The Molecular Nature of Matter and Change Silberberg 103 CH 9 Models of Chemical Bonding 7039John JonesNo ratings yet
- Template ChemDocument5 pagesTemplate ChemKacper JanuszNo ratings yet
- Electrochemistry: Redox Reactions and Standard Reduction PotentialsDocument12 pagesElectrochemistry: Redox Reactions and Standard Reduction PotentialsRaphael NanoNo ratings yet
- Chem f6 PDFDocument7 pagesChem f6 PDFCHONG YUNG FOO MoeNo ratings yet
- IonicBonds LAB 3Document7 pagesIonicBonds LAB 3Yesenia MontanezNo ratings yet
- Subject ChemistryDocument8 pagesSubject ChemistryWinki MansonNo ratings yet
- Activity Sheet Module 3Document3 pagesActivity Sheet Module 3Jessa Mae CasipongNo ratings yet
- Unit 11 - Redox and Electrochem NotesDocument28 pagesUnit 11 - Redox and Electrochem NotesIbsa BekamaNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding NotesDocument9 pagesChemical Bonding NotesLouisiana SollestreNo ratings yet
- Science 9 q2 Mod2Document16 pagesScience 9 q2 Mod2Prince U KennardNo ratings yet
- Electrons Activity SheetDocument8 pagesElectrons Activity SheetTonette ValenzuelaNo ratings yet
- Module 3 Q2 Gen Chem I v.2Document10 pagesModule 3 Q2 Gen Chem I v.2ariinnggg onichaNo ratings yet
- Lewis Structures of Atoms: 1. Identify The Number of Valence Electrons and Draw The Lewis Dot StructureDocument2 pagesLewis Structures of Atoms: 1. Identify The Number of Valence Electrons and Draw The Lewis Dot StructureCarlton GrantNo ratings yet
- Ionic BondingDocument56 pagesIonic BondingAiza TullabangNo ratings yet
- Core & Extension Bonding - Covalent BondingDocument34 pagesCore & Extension Bonding - Covalent BondingMarin PesicNo ratings yet
- Physical Science Module 2Document10 pagesPhysical Science Module 2Mikaela AguilarNo ratings yet
- Chemistry MergedDocument19 pagesChemistry Merged몰라나도No ratings yet
- CH 5.3 Lecture Guide PDFDocument5 pagesCH 5.3 Lecture Guide PDFErica OhNo ratings yet
- Electrons, Atoms, and Molecules in Inorganic Chemistry: A Worked Examples ApproachFrom EverandElectrons, Atoms, and Molecules in Inorganic Chemistry: A Worked Examples ApproachRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (7)
- Barriers in Online Learning and Students' Math PerformanceDocument36 pagesBarriers in Online Learning and Students' Math PerformanceJeclyn FilipinasNo ratings yet
- Name: Jeclyn D. Filipinas First Year (New Curriculum) : EDDK-1A-NEW Professor: DR. JERSON S. CATOTODocument46 pagesName: Jeclyn D. Filipinas First Year (New Curriculum) : EDDK-1A-NEW Professor: DR. JERSON S. CATOTOJeclyn FilipinasNo ratings yet
- Efficacy of Math Video Tutorials On Students' PerformanceDocument33 pagesEfficacy of Math Video Tutorials On Students' PerformanceJeclyn FilipinasNo ratings yet
- Interactive Games Comprehension Development: A Narratology of Students' ChallengesDocument48 pagesInteractive Games Comprehension Development: A Narratology of Students' ChallengesJeclyn FilipinasNo ratings yet
- Applied EconomicsDocument24 pagesApplied EconomicsJeclyn FilipinasNo ratings yet
- LAS Applied EconomicsDocument11 pagesLAS Applied EconomicsJeclyn FilipinasNo ratings yet
- Practical Research 2Document44 pagesPractical Research 2Jeclyn FilipinasNo ratings yet
- Species Richness of Pteridophytes in Mt. Sinaka, Brgy. Datu Ladayon, Arakan, North CotabatoDocument62 pagesSpecies Richness of Pteridophytes in Mt. Sinaka, Brgy. Datu Ladayon, Arakan, North CotabatoJeclyn FilipinasNo ratings yet
- Official List of Students - 11 AristotleDocument2 pagesOfficial List of Students - 11 AristotleJeclyn FilipinasNo ratings yet
- Revealing The Lived Experieces of Students On Modular Learning: A PhenomenologyDocument32 pagesRevealing The Lived Experieces of Students On Modular Learning: A PhenomenologyJeclyn FilipinasNo ratings yet
- The Pains and Gains of Remedial Reading Instruction: A NarratologyDocument49 pagesThe Pains and Gains of Remedial Reading Instruction: A NarratologyJeclyn FilipinasNo ratings yet
- Practical Research 1Document30 pagesPractical Research 1Jeclyn Filipinas100% (1)
- OFFICIAL LIST OF STUDENTS - 10 ArchimedesDocument1 pageOFFICIAL LIST OF STUDENTS - 10 ArchimedesJeclyn FilipinasNo ratings yet
- Tandang SoraDocument2 pagesTandang SoraJeclyn FilipinasNo ratings yet
- Numeracy TestDocument14 pagesNumeracy TestJeclyn FilipinasNo ratings yet
- Grade 9 Class ProgramDocument1 pageGrade 9 Class ProgramJeclyn FilipinasNo ratings yet
- Presidents of The PHDocument2 pagesPresidents of The PHJeclyn FilipinasNo ratings yet
- DLL JECLYN PERDEV 1st-2ndDocument5 pagesDLL JECLYN PERDEV 1st-2ndJeclyn FilipinasNo ratings yet
- SIP New Template BautistaDocument12 pagesSIP New Template BautistaJeclyn FilipinasNo ratings yet
- QuotesDocument3 pagesQuotesJeclyn FilipinasNo ratings yet
- Attendance Sheet Homeroompta MeetingDocument2 pagesAttendance Sheet Homeroompta MeetingJeclyn FilipinasNo ratings yet
- School Form 2 (SF 2)Document3 pagesSchool Form 2 (SF 2)Jeclyn FilipinasNo ratings yet
- BMItemplateDocument2 pagesBMItemplateJeclyn FilipinasNo ratings yet
- Filipinas - Preliminaries Davao1Document14 pagesFilipinas - Preliminaries Davao1Jeclyn FilipinasNo ratings yet
- Attendance SheetDocument6 pagesAttendance SheetJeclyn FilipinasNo ratings yet
- Sum 2, Phy SciDocument2 pagesSum 2, Phy SciJeclyn FilipinasNo ratings yet
- w5, Phy Sci LASDocument2 pagesw5, Phy Sci LASJeclyn FilipinasNo ratings yet
- w6, Phy Sci LASDocument2 pagesw6, Phy Sci LASJeclyn FilipinasNo ratings yet
- Sum 1, Phy SciDocument3 pagesSum 1, Phy SciJeclyn Filipinas100% (1)
- CasperDocument18 pagesCasperJeclyn FilipinasNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2.7Document25 pagesLesson 2.7Alec BaldwinNo ratings yet
- 3.1 Classification If ElementsDocument19 pages3.1 Classification If ElementsSharon RamaiahNo ratings yet
- Mod-8 WA #8Document6 pagesMod-8 WA #8Lueshen WellingtonNo ratings yet
- Say Chemical Bonding and Molecular StructureDocument13 pagesSay Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structuresivaranjini S.VNo ratings yet
- Sri Chaitanya Iit Academy: Work SheetDocument8 pagesSri Chaitanya Iit Academy: Work SheetLisa ParkerNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Investigatory Project 12 BDocument20 pagesChemistry Investigatory Project 12 Banitta0% (1)
- IntroductionDocument72 pagesIntroductionMichael AdesanyaNo ratings yet
- Band Theory in Solid StateDocument4 pagesBand Theory in Solid StatePaulami Bose100% (1)
- Instrumental Analytical Techniques: An Overview of Chromatography and SpectrosDocument52 pagesInstrumental Analytical Techniques: An Overview of Chromatography and SpectrosK V SATHEESHKUMAR MECHNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes-MoleDocument15 pagesLecture Notes-MoleKotyada ParthivNo ratings yet
- The Quasi-Free Electron and Electron Effective Mass, M: ECE G201Document23 pagesThe Quasi-Free Electron and Electron Effective Mass, M: ECE G201kurniawanNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) FormatDocument2 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan (DLP) FormatJim Alesther Lapina100% (2)
- Atomic+orbital+worksheet 3 & 4Document2 pagesAtomic+orbital+worksheet 3 & 4RYAN SCOTTNo ratings yet
- 4.4 Elements in Group 1Document14 pages4.4 Elements in Group 1Matteau LeeNo ratings yet
- Periodic Table NotesDocument4 pagesPeriodic Table NotesSyuhadah RashidNo ratings yet
- Notes Periodic Classification of ElementsDocument6 pagesNotes Periodic Classification of ElementsKumar AbhishantNo ratings yet
- Jim's A'Level Notes - Inorganic ChemistryDocument86 pagesJim's A'Level Notes - Inorganic Chemistryjimbaker007100% (3)
- Gujarat Technological University: W.E.F. AY 2017-18Document2 pagesGujarat Technological University: W.E.F. AY 2017-18raj royel100% (1)
- Atoms Molecules and IonsDocument78 pagesAtoms Molecules and IonszulqarnainkhaliqNo ratings yet
- CHM 102 PQDocument8 pagesCHM 102 PQkaptainpsalmyNo ratings yet
- Atom McqsDocument13 pagesAtom McqsMrunmayee ManeNo ratings yet
- 3 - Modern Atomic TheoryDocument28 pages3 - Modern Atomic Theorysalvador.xyriesyuan.g7peaceNo ratings yet
- Chem 155 Quiz 3 Review Topics and Questions With AnswersDocument6 pagesChem 155 Quiz 3 Review Topics and Questions With Answersuvir iitmNo ratings yet
- Chemistry-Nuclear Model of An AtomDocument10 pagesChemistry-Nuclear Model of An AtomRosa Mia Paglilingan100% (1)
- The Nature of MoleculesDocument42 pagesThe Nature of Moleculeseasy99No ratings yet
- Daily Lesson Plan in Physical Science 12Document5 pagesDaily Lesson Plan in Physical Science 12joyceNo ratings yet
- Raman Spectroscopy Basic Principle and TechniqueDocument9 pagesRaman Spectroscopy Basic Principle and TechniqueMohd Zulhairi Mohd NoorNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Mot PDFDocument37 pagesChapter 2 Mot PDFfatin harrisNo ratings yet
- Neutron Activation AnalysisDocument20 pagesNeutron Activation AnalysisDesinta PuspitasariNo ratings yet