Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Properties of Solids-1
Uploaded by
Debadyuti Sarkar0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views1 pageThis document outlines a procedure to determine the void volume, solid density, and porosity of a catalyst particle. A weighed sample of silica gel is placed in a beaker of water and boiled to displace air from the pores. The increase in weight and decrease in water volume after boiling are used to calculate the pore volume. From the pore volume and weight, the density of the solid material and porosity can be determined. Key measurements include the weight and volume changes before and after boiling the sample.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document outlines a procedure to determine the void volume, solid density, and porosity of a catalyst particle. A weighed sample of silica gel is placed in a beaker of water and boiled to displace air from the pores. The increase in weight and decrease in water volume after boiling are used to calculate the pore volume. From the pore volume and weight, the density of the solid material and porosity can be determined. Key measurements include the weight and volume changes before and after boiling the sample.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views1 pageProperties of Solids-1
Uploaded by
Debadyuti SarkarThis document outlines a procedure to determine the void volume, solid density, and porosity of a catalyst particle. A weighed sample of silica gel is placed in a beaker of water and boiled to displace air from the pores. The increase in weight and decrease in water volume after boiling are used to calculate the pore volume. From the pore volume and weight, the density of the solid material and porosity can be determined. Key measurements include the weight and volume changes before and after boiling the sample.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
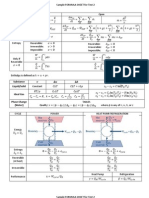
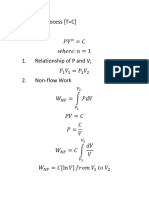
Aim: To determine void volume, solid density and porosity of a catalyst particle.
Apparatus: 100 ml beaker, measuring cylinder, weighing balance.
Theory: The void volume or pore volume of a catalyst particle can be estimated by boiling a
weighed sample immersed in a liquid such as water. After the air in the pores has been
displaced, the sample is superficially dried and weighed. The increase in weight divided by
the density of the liquid gives the pore volume. The volume of water displaced is a measure
of the volume occupied by the solid material. From this volume & weight of the sample, the
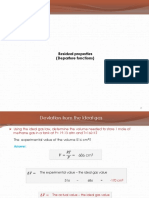
density of the solid can be obtained. Void fraction or porosity of the particle,
Ɛ𝑝 = void volume of the particle⁄total volume of particle
Procedure: Take a measured quantity of silica gel. Put in a 100 ml measuring cylinder, pour
measured volume of water. Wait for 5 min or so to see the change in volume of water. Note
down the change in water volume at steady state. Boil the water & catalyst. Cool it, remove
the catalyst & dry it superficially on filter paper. Take the weight; find the change in the
weight of the catalyst.
Observations:
Weight of the catalyst before boiling in water= 𝑤1 𝑔𝑚 =
Weight of the catalyst after boiling in water= 𝑤2 𝑔𝑚 =
Volume of water before putting catalyst in water= 𝑣1 𝑚𝑙 =
Volume of water after putting catalyst in water = 𝑣2 𝑚𝑙 =
Change in volume of water after putting cat in water = (𝑣2 − 𝑣1 ) = 𝑣 𝑚𝑙 =
Change in weight of cat after boiling = (𝑤2 − 𝑤1 ) = 𝑤 𝑔𝑚 =
Density of water 𝜌𝑤 gm/cc
Calculations:
𝑤 𝑚𝑙⁄
Pore volume, 𝑣𝑔 = = 𝑔𝑚
𝑤1 𝜌𝑤
Void fraction or porosity of the particle,
𝑤1 𝑣𝑔
Ɛ𝑝 =
𝑤1 𝑣𝑔 + 𝑤1 /𝜌𝑠
𝑣𝑔 𝜌𝑠
=
𝑣𝑔 𝜌𝑠 + 1
Where the true density of solid catalyst is 𝜌𝑠 ,
𝑤1
𝜌𝑠 = ; 𝑎𝑛𝑑 𝑣𝑔′ = 𝑤1 𝑣𝑔
(𝑣 − 𝑣𝑔′ )
Result: Pore volume 𝑣𝑔 = ; True density of solid 𝜌𝑠 = Porosity of solid Ɛp =
You might also like
- Module 3 - Weight-Volume RelationshipDocument31 pagesModule 3 - Weight-Volume RelationshipkaicaNo ratings yet
- Design of DecanterDocument8 pagesDesign of DecanterChristian PatiñoNo ratings yet
- Mid Term Cheat SheetDocument1 pageMid Term Cheat Sheethalide90No ratings yet
- Problem On Steam Nozzle 04Document46 pagesProblem On Steam Nozzle 04Dr. BIBIN CHIDAMBARANATHANNo ratings yet
- Problem: ON Steam NozzleDocument43 pagesProblem: ON Steam NozzleDr. BIBIN CHIDAMBARANATHANNo ratings yet
- Bathroom Science: 70 Fun and Wacky Science ExperimentsFrom EverandBathroom Science: 70 Fun and Wacky Science ExperimentsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Sample Formula Sheet For ThermodynamicsDocument2 pagesSample Formula Sheet For Thermodynamicsmicrop_aras100% (3)
- Lecture 11 Thermal Ii (14 .07.2020)Document26 pagesLecture 11 Thermal Ii (14 .07.2020)Dr. BIBIN CHIDAMBARANATHANNo ratings yet
- Chen 3009 - Tutorial 6 2020Document22 pagesChen 3009 - Tutorial 6 2020Rosario QFNo ratings yet
- Unit-Iii Properties of Pure Substances, Ideal Gases and SteamDocument55 pagesUnit-Iii Properties of Pure Substances, Ideal Gases and SteamSurya KrishnanNo ratings yet
- Lec 4Document14 pagesLec 4أمير حامدNo ratings yet
- Lec 2 1st LawDocument20 pagesLec 2 1st LawPei Shuang Ch'ngNo ratings yet
- Other Properties of FluidsDocument19 pagesOther Properties of Fluidsmicklier baduriaNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Report No. 1Document3 pagesLaboratory Report No. 1Sana NgaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Propeller TheoryDocument37 pagesChapter 3 Propeller TheorytvkbhanuprakashNo ratings yet
- Demetillo Hydraulics-FormulaDocument1 pageDemetillo Hydraulics-FormulaFrancis John DemetilloNo ratings yet
- Chap 1 Lecture 3 and Chap 2 IntroDocument12 pagesChap 1 Lecture 3 and Chap 2 IntroJHONALYN NOGUERANo ratings yet
- Lecture 10 Thermal Ii (09.07.2020)Document30 pagesLecture 10 Thermal Ii (09.07.2020)Dr. BIBIN CHIDAMBARANATHANNo ratings yet
- FormulrioDocument2 pagesFormulrioJHOEL GONZALO GALINDO FABIANNo ratings yet
- Problem Session 3Document20 pagesProblem Session 3İkigül Aşçıevladı KirlitaşNo ratings yet
- Pipe NetworkDocument9 pagesPipe NetworkSilverlandNo ratings yet
- Mixed CapacitorDocument10 pagesMixed CapacitorMr SonuNo ratings yet
- Capture D'écran . 2024-03-23 À 11.19.38 PMDocument6 pagesCapture D'écran . 2024-03-23 À 11.19.38 PMbouarabidris8No ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Solutions: Mole fraction (ϰ)Document11 pagesChapter 1 Solutions: Mole fraction (ϰ)Jinal VadodariyaNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamic Web HandoutDocument2 pagesThermodynamic Web HandoutYaren ErelNo ratings yet
- ThermodynamicsDocument13 pagesThermodynamicsKira ToNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 - ApplicationDocument54 pagesChapter 10 - ApplicationAmeer SabryNo ratings yet
- Soil Mechanics 3.0 For PDFDocument18 pagesSoil Mechanics 3.0 For PDFomay12No ratings yet
- Problem Session-2Document32 pagesProblem Session-2İkigül Aşçıevladı KirlitaşNo ratings yet
- GASES-CHM130 by DELZYDocument15 pagesGASES-CHM130 by DELZYmisakisuki7No ratings yet
- Hydrogeology Physical PropertiesDocument28 pagesHydrogeology Physical PropertieslendlNo ratings yet
- 2 Guia Del Proyecto Ene 2018Document1 page2 Guia Del Proyecto Ene 2018Ariel NazdaNo ratings yet
- Biomentors Classes Online, MumbaiDocument3 pagesBiomentors Classes Online, MumbaiSmit PatelNo ratings yet
- Thermal Properties 1Document8 pagesThermal Properties 1Sidhiprada PradhanNo ratings yet
- Fuels & CombustionDocument3 pagesFuels & Combustionkadimisetti sakethNo ratings yet
- Entropy and The Second Law of ThermodynamicsDocument6 pagesEntropy and The Second Law of Thermodynamicskhandaker raiyanNo ratings yet
- Tablas W Q Du DH DSDocument3 pagesTablas W Q Du DH DSMarisol CarrilloNo ratings yet
- CE 108 - Lecture 1 - Introducton To FluidsDocument18 pagesCE 108 - Lecture 1 - Introducton To FluidsJeric GeronaNo ratings yet
- 4th Sem Core T9 (Unit 3) (Class-4)Document3 pages4th Sem Core T9 (Unit 3) (Class-4)Beat SpNo ratings yet
- 3D Heat Conduction Equation DriverationDocument3 pages3D Heat Conduction Equation Driverationルウィンコ オーNo ratings yet
- Formulario Tercer Parcial 2021Document2 pagesFormulario Tercer Parcial 2021Michael OlivaresNo ratings yet
- Ore Geomorph Remote SensingDocument4 pagesOre Geomorph Remote SensingPrayas DuttaNo ratings yet
- MT 21006 TP Unit 4 Lec 4 30 Oct 2023Document10 pagesMT 21006 TP Unit 4 Lec 4 30 Oct 2023Aditya GajbhiyeNo ratings yet
- Fluids PDFDocument2 pagesFluids PDFRenzo AlvizNo ratings yet
- EntropyDocument57 pagesEntropyShihabudheenNo ratings yet
- Flu Mech ExDocument18 pagesFlu Mech ExLeonardo RedNo ratings yet
- Hydraulics - Lecture 4 - BuoyancyDocument18 pagesHydraulics - Lecture 4 - Buoyancymeh mehNo ratings yet
- Internal Combustion Engines - MidtermsDocument29 pagesInternal Combustion Engines - Midtermsfoj90532No ratings yet
- H°P° - Ejercicio 1 (Diseño de Vigas Pretensadas)Document8 pagesH°P° - Ejercicio 1 (Diseño de Vigas Pretensadas)Ronald Alcides Mirones ColqueNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Fluid Power: Fluid Mechanics, Hydraulics & PneumaticsDocument25 pagesIntroduction To Fluid Power: Fluid Mechanics, Hydraulics & Pneumaticsshahzaibkhan ccpNo ratings yet
- HE Lecture 11Document8 pagesHE Lecture 11presidentisc nit-rourkelaNo ratings yet
- Integral Transform (Class-5)Document8 pagesIntegral Transform (Class-5)Beat SpNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics FigaciddDocument31 pagesThermodynamics FigaciddMohammad Mubeen Ahsan Abrar Hussain100% (1)
- Mosfet-4: Basic FET AmplifiersDocument18 pagesMosfet-4: Basic FET AmplifiersKomay Abo ShakraNo ratings yet
- المحاضرة الثانيةDocument18 pagesالمحاضرة الثانيةbeiguiiuirrNo ratings yet
- Ecuación de AntoineDocument2 pagesEcuación de AntoineValentina MenesesNo ratings yet
- Packed Bed Absorber - Without Chemical ReactionDocument13 pagesPacked Bed Absorber - Without Chemical ReactionAhmadSatrioNo ratings yet
- Gtx106 - Differential Calculus IV - 2023 - CDocument6 pagesGtx106 - Differential Calculus IV - 2023 - Claila qistinaNo ratings yet
- Methods and Instruments Used in Brewing Control - Selected QuestionsFrom EverandMethods and Instruments Used in Brewing Control - Selected QuestionsNo ratings yet
- GMAT Idiomatic ExpressionsDocument90 pagesGMAT Idiomatic ExpressionsDebadyuti SarkarNo ratings yet
- Mba FT 2023-25Document31 pagesMba FT 2023-25Debadyuti SarkarNo ratings yet
- Adsorption of Oxalic AcidDocument2 pagesAdsorption of Oxalic AcidDebadyuti SarkarNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 1Document11 pagesChapter - 1Debadyuti SarkarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6Document3 pagesChapter 6Debadyuti SarkarNo ratings yet