Professional Documents
Culture Documents
INGLES
INGLES
Uploaded by
JademOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
INGLES
INGLES
Uploaded by
JademCopyright:
Available Formats
Oficina de Admisión Modalidad virtual CENTRO PREUNIVERSITARIO
CENTRO PREUNIVERSITARIO Modalidad virtual Oficina de Admisión 1
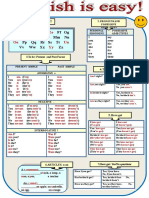
ÍNDICE
INGLÉS
1. SUBJECT PRONOUNS – VERB BE – INDEFINITE ARTICLE 03
A/AN QUESTION WORDS
2. POSSESSIVE ADJECTIVES – POSSESSIVE PRONOUNS 05
– OBJECT PRONOUNS – POSSESSIVE NOUNS – REFLEXIVE PRONOUNS
3. PRESENT SIMPLE – AUXILIARY VERBS “DO / DOES” ADVERBS 09
OF FREQUENCY
4. THERE IS /THERE ARE - DEMOSTRATIVE ADJECTIVES – PLURAL NOUNS. 11
5. PREPOSITIONS OF PLACE AND PREPOSITIONS MOVEMENT 15
6. PRESENT PROGRESSIVE – USE OF QUANTIFIERS (SOME, ANY, MUCH, MANY, 17
A LOT OF , A FEW , FEW , A LITTLE ,LITTLE ) AND “HOW MANY & HOW MUCH”
7. ADJECTIVES – COMPARATIVES – SUPERLATIVES 22
8. PAST BE - PAST PROGRESSIVE PAST SIMPLE 25
(REGULAR VERBS AND IRREGULAR VERBS) AUXILIARY VERB DID
9. MODAL VERBS: “CAN – COULD – MAY – MIGHT – SHOULD – WOULD – MUST” 30
10. FUTURE SIMPLE WITH WILL – GOING TO AND 34
PRESENT CONTINUOUS. TIME EXPRESSIONS FOR THE FUTURE
11. PRESENT PERFECT – ADVERBS (JUST, ALREADY, RECENTLY, 36
EVER, NEVER, YET)
12. PASSIVE VOICE (PRESENT SIMPLE, PRESENT PROGRESSIVE, PAST 40
SIMPLE, PAST PROGRESSIVE, FUTURE, PRESENT PERFECT.
LA ECONOMÍA Y LAS
NECESIDADES, BIENES Y
SERVICIOS
NOCIONES GENERALES DE ECONOMÍA
1. ¿QUÉ ES LA ECONOMÍA?
Economía como administración de la casa es un concepto
antiguo, actualmente precisamos a la economía como la
ciencia de la elección, que parte sus estudios de un
problema económico, esto es: Necesidades ilimitadas VS
Recursos escasos
2 CENTRO PREUNIVERSITARIO Modalidad virtual Oficina de Admisión
Oficina de Admisión Modalidad virtual CENTRO PREUNIVERSITARIO
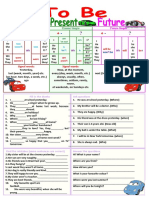
SUBJECT PRONOUNS – VERB BE –
INDEFINITE ARTICLE A/AN
QUESTION WORDS
Positive
I am ( I´m)
He ( He´s)
READING COMPREHENSION She is ( She´s)
it ( It´s)
We ( We´re)
You are ( You ´re)
They ( They´re)
Negative
I am not ( I´m not)
He ( He´s not or he isn´t )
She is not ( She´s not or she isn´t)
it ( It´s not or it isn´t )
We ( We´re not or we aren´t )
You are not ( You ´re not or you
aren´t)
They ( They´re not or they
aren´t )
Question
am I?
he ?
Is She ?
It ?
Answer: we?
1. What’s her name?_______________________ Are you?
they ?
2. How old is she?__________________________
3. Where is she from?______________________
4. Where does she live?_____________________
5. What´s her sister name?_________________
6. What’s her favorite band?_________________
Use the verb be to talk about your country of origin your
occupation and your age.
Form.
I´m Peruvian. I. Write in the correct Verb to be.
You´re a student. 1. Cindy _________my best friend.
She’s Portuguese. 2. Peter and Kate _________ classmates.
They´re journalists. 3. Johnny _______ my brother.
4. You _______ a good student.
5. They __________ in the classroom.
6. It __________an apple.
7. Felicia and I _________ sister.
8. I _______ her teacher.
9. It ________ a book bag.
CENTRO PREUNIVERSITARIO Modalidad virtual Oficina de Admisión 3
10. You _________ a doctor.
II. Order the sentences.
1. The girl / in the room / is
________________________________
2. at / we/ not / are / home
_______________________________
3. is /mother / a/ my / housewife The indefinite articles a and an are used before singular
_____________________________ countable nouns.
We use a before words that begin with a consonant
III. Put forms of be in these sound.
conversations. We use an before words that begin with a vowel
sound.
Steve: This ________ Joan, my sister.
Tom: Hello, Joan ______you a student?
Joan: No, I_______ a dentist. I work in Pasco.
Mike: How are you, Sally?
Sally: I _____fine, thanks.
Mike: _________you hungry? Sally: Yes.
_______There a good restaurant near here? a dog a cow
Mike: Yes. There ______ a good and cheap
restaurant in Proceres Street.
IV. Make sentences about the pictures using the
words in the box. Use He / She / They and the
Present Simple of be.
an elephant an ox
Tired sad thirsty
happy
Hungry bored afraid
cold
We use an before h when it is silent. an hour .
We use a before u when it has consonant
sound . a university
She´s 1. ____ 2. __ 3. _
__ _
4. ____ 5. __ 6. ____ 7. ____
4 CENTRO PREUNIVERSITARIO Modalidad virtual Oficina de Admisión
Oficina de Admisión Modalidad virtual CENTRO PREUNIVERSITARIO
Asking for age.
How old is the baby? He is three years old.
How old is your sister? She´s 27.
A: Hello, María! What are you doing
here? Asking about a procedure or
B: Hi! I'm shopping a book. I thought method.
you were abroad, when did you
arrive? How do you go to school? I go to school by
A: I came back a month ago. car.
B: Why didn't you call me?
A: I have been so busy! By the way, How does it work? I don´t know. It´s new for
how's everything? me.
B: Great! I'm learning french now.
A: Really? And who's your teacher? Asking about an option or choice.
B: My neighbour, Marta.
A: Yes, I know her, and how long have Which car is better? The red one.
you been learning french?
B: Just a pair of months, but I love it! Which is more beautiful, my doll or your doll?
Your doll.
READING COMPREHENSION
Choose the correct question words.
1. 1. _________ is the largest city in the world?
2. 2. _________are they always late?
3. 3. _________ locked the door?
Asking about a thing.
4. 4. _________ did you learn to cook?
5. 5. _________ can I see you again?
What are you doing? Nothing
6.
What is on the table? There is a pencil.
7.
Asking about a time of an event or POSSESSIVE ADJECTIVES – POSSESSIVE
PRONOUNS – OBJECT PRONOUNS –
activity 8. POSSESSIVE NOUNS – REFLEXIVE
PRONOUNS
Where is your book? It is in the bag. 9.
Where do you live? In Lima 10. POSSESSIVE ADJECTIVES
Asking about a time of an event 11.
or activity. READING COMPREHENSION
12.
When is the party? On Friday at 2 o´clock.
When did he arrive? In the afternoon.
Asking for a reason.
Why are you late? Because I missed my bus.
Why did you leave? Because I was tired.
Asking about a person (act as the
subject of the sentence)
Who is that boy? My brother Miguel.
Who are you? I am an English teacher.
CENTRO PREUNIVERSITARIO Modalidad virtual Oficina de Admisión 5
Mark the correct answers We’ve got one sister. ……….. sister is called
1. Who is Ryusei? Lily. he’s got a cat. ………….cat is really big.
a) Her sister.
b) Her father. ………….name is Misty.
c) Her cousin. They are my parents. …………. names are
d) Her brother.
Camila and Peter.
2. What does she like to do in her free time? 2. Circle the correct answer.
a) In her free time, she listens to music. 1. I have a car _________color is red.
b) In her free time, she rides a horse. a. its b. my c. his
2. Alan has a van, ________ Van is very old.
c) In her free time, she rides a bicycle.
a. her b. his c. their
d) In her free time, she dances.
3. Nancy is from England_____ husband is
from Australia.
a. our b. his c. her
POSSESSIVE PRONOUNS
To express who owns (or
‘possesses’) something. A
possessive adjective is used in Sustituye a un nombre
front of a noun (a thing) o sustantivo que
indican posesión, es
decir, a quien
pertenece algo.
My car is in front of the school.
This is Jack and this is his wife, Sue.
1. Complete the text with these words.
-her -his -its -my -my -our
-their
Hello. ……….. name is Willian.
This is………...brother.
……………. name is Michael.
6 CENTRO PREUNIVERSITARIO Modalidad virtual Oficina de Admisión
Oficina de Admisión Modalidad virtual CENTRO PREUNIVERSITARIO
SENTENCE STRUCTURE
Remember that object pronouns always
come after the verb.
verb + object pronouns
Antonio is very nice, I like him.
This jacket is mine. (Antonio es muy amable, me gusta)
Mary loves Peter
Mary loves him
Mary has a dog. The dog is hers.
Object Pronouns can follow a preposition:
She thinks about Peter. She thinks about
him.
1. Julia never eats nuts. She doesn’t like them.
I. Complete the sentences 2. I’m looking for Mathew. Have you seen him?
1. This computer is __________. 3. Lately, I’m missing my sister. I should phone her.
2. The sandwiches are ________.
3. The camera is _____________.
4. All these shoes are _________.
5. These toys are _____________.
6. These pictures are __________.
I. Choose the correct answer.
OBJECT PRONOUNS
a) My homework is difficult. Please
help !
me her it
b) This is a good photo. Do you want to
see ?
them it her
c) I don’t know the new girl. Do you
We don't say: My sister is very friendly. Everyone likes know ?
my sister.
Instead, we say: My sister is very friendly.Everyone
likes her. her him me
d) I don’t eat burgers because I don’t
like .
us you them
CENTRO PREUNIVERSITARIO Modalidad virtual Oficina de Admisión 7
POSSESSIVE NOUNS REFLEXIVE PRONOUNS
We use a reflexive pronoun to
refer back to the subject of the
sentence or clause. Reflexive
pronouns end in "-self"
(singular) or "-selves"
(plural).
I. Complete each of the sentences below.
a) My brother likes to practice his English by
I. Join the sentences below by using possessive talking to ____________
forms. Study the boxes above.
b) James wasn’t careful and he cut
________________ with a knife.
a) The student has a pen. The pen is on the table.
_____________________________________ c) My sister and I looked at
________________ in the mirror.
b) The man has a car. The car is in the garage.
_____________________________________
d) The repair shop was closed, so I fixed the
c) My friends had a party. The party was fun. car ______________________.
_____________________________________
e) Did you enjoy___________________ at the
d) The women have kids. The kids are playing. party last night?
_____________________________________
f) Cats can get clean by licking ____________
e) India has a population. The population is very
large.
_____________________________________
8 CENTRO PREUNIVERSITARIO Modalidad virtual Oficina de Admisión
Oficina de Admisión Modalidad virtual CENTRO PREUNIVERSITARIO
Answer the question about the
PRESENT SIMPLE – AUXILIARY conversation.
VERBS “DO / DOES”
ADVERBS OF FREQUENCY 1. Does Josh get up late in the morning?
___________________________________
2. Where does he have an online class?
___________________________________
3. When does he go to work?
___________________________________
4. Does he work and study at the same time?
___________________________________
5. What does he sometimes do after work?
___________________________________
We use to talk
about habits
and routines.
We add - s. Verbs ending in a
Run - runs vowel ( a,e,I,o,u )
eat - eats +Y
Add- es when the Play - plays say-
verb ends in –o – says
ss-sh-ch-x. But verb ending in
Fix- fixes go – a consonant
goes (b,c,d,f…) + y
The flowers smell good Study - studies
Mimi sings well.
Affirmative Negative
I I
You work You don´t (do not) work
We We
They They
Liz: Good morning, Josh. Good to have you with us.
How are you today? He He
Josh: I’m good, Thanks. How about you? She She doesn´t work
Liz: I’m wonderful, Thank you. Tell us about your day. works It
Josh: I always get up early in the morning and then It
have a big breakfast.
After that, I sometimes work out or go jogging.
Liz: I heard that you are working and studying at the Questions Short answer
same time.
Josh: Yes. I usually have an online class in the Do I work? Yes, you do. / No, you don’t.
morning at home and I go to work in the afternoon. Do you work? Yes, I do. / No, I don’t.
Liz: That’s interesting! So, what do you do after work? Do we work? Yes, you do. / No, you don’t.
Do they work ? Yes, they do. / No, they don’t.
Josh: I go hanging out with my friends sometimes.
Does he work? Yes, he does. / No, he doesn’t.
Does she work? Yes, she does. / No,she doesn’t.
Does it work? Yes, it does. / No, it doesn’t.
CENTRO PREUNIVERSITARIO Modalidad virtual Oficina de Admisión 9
Monday Once
Tuesday Twice
1. Complete the sentences. Use the
Wednesday Three times
words.
On
Thursday Four times a week
Every Friday Six times
Boil close cost cost like like
meet open speak teach wash Saturday Seven times
Sunday Eight times
1. María ______four languages.
2. The shop in the city centre usually ______at 9
o´clock in the morning. - I have English on Monday.
3. The City Museum _________at 5 o´clock in the - He goes to the market twice a week.
evening. - We go shopping once a week.
4. Tina is a teacher. She _______mathematics to - They play tennis three times a week.
young children.
5. My job is very interesting. I ________a lot of
people.
6. Peter´s car is always dirty. He never ________it.
7. Food is expensive. It ______ a lot of money.
8. Shoes are expensive. They _____a lot of money.
9. Water _____ at 100 degrees Celsius.
10. Julia and I are good friends. I ______ her and she 100% ALWAYS You are always late.
_____me.
90% USUALLY We usually wash our car.
2. Write the negative.
70% OFTEN He often cooks pasta
1. Jane plays the piano very well.
_______________________________ 50% SOMETIME We sometimes play soccer.
S
2. They know my phone number.
10 HARDLY
She hardly ever smiles.
_________________________________ % EVER
RARELY
3. We work very hard. 0% NEVER They are never sad.
_________________________________
4. He has a bath every day. 1. Write sentences from these words.
_______________________________________
a) (always / early / Yanina / arrive)
___________________________________
3. Choose DO or DOES b) (to the cinema / never / I / go)
__________________________________
1. ……… you listen to hip hop? c) (work / Martina / hard / always)
2. ………. you often call your friends? __________________________________
3. ……. Sarah sleep well at night? d) (like / chocolate / children / usually)
4. ……… your parents work a lot?
__________________________________
5. ……… you get up early in the morning.
e) (Edith / parties / enjoy / always)
__________________________________
f) (often / people´s names / I forget)
10 CENTRO PREUNIVERSITARIO Modalidad virtual Oficina de Admisión
Oficina de Admisión Modalidad virtual CENTRO PREUNIVERSITARIO
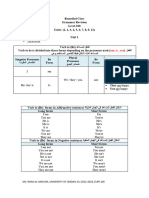
THERE IS /THERE ARE -
DEMOSTRATIVE ADJECTIVES –
PLURAL NOUNS.
READING COMPREHENSION Ambas expresiones significan HAY
Read the text below and answer the questions: en español. La diferencia es:
THERE IS
Se usa con complemento
SINGULAR (una cosa, persona,
lugar, etc.)
THERE ARE
Se usa con complemento PLURAL
(2 0 más cosas, personas, lugares,
etc.)
POSITIVE
AT THE SHOPPING CENTER
This is a shopping center. Its name is “Aventura
Plaza”. There are three floors in this shopping
IS a table.
center. 123th Avenue is behind it and beside it THERE ARE two desks.
there is a parking lot. The shopping center is
between 66th and 67th street. There is policeman
on the corner of 122th Avenue and 66th street. On
the first floors, there are three restaurants. In front
of the main entrance there are two banks and two
cafeteries. A software store is beside restaurant There is a fly on the window.
#1. There’s a post office, between restaurant #3 There are four bedrooms.
and bank. There’s a tree among the benches and
beside it there’s a family. In front of this tree there
is restaurant #2. On the second floor, there are NEGATIVE
clothing stores, grocery stores, shoe stores, and
music stores #2 and #3. There is a grocery store IS NOT a table.
in front of the shoe store #2. On the third floor ARE / two desks.
there is a beautiful cinema and big night club. THERE
N´T.
There is a video game room between fast food #1
and #2. There is a beauty parlor beside the
cinema. The stairs are among the stores.
There isn’t a fly on the window
There are not four bedrooms
Answer the questions:
a) How many floors are there in the shopping center? INTERROGATIVE
_______________________________
_______________________________ .
IS a
b) How many restaurants are on the first floor?
_______________________________ THERE table.
?
_______________________________ ARE two
c) On what floor are the clothing stores? desks.
_______________________________
_______________________________
CENTRO PREUNIVERSITARIO Modalidad virtual Oficina de Admisión 11
II. Write the sentences in the
affirmative (/), negative (x) or as a
question (?).
Is there a fly on the window?
Are there four bedrooms? a) Is there a cinema?
________________________________________
________________✓
b) There isn’t a bike.
__________________________________________
__________________✓
c) There are two schools.
__________________________________________
________________X
d) There isn’t a car.
__________________________________________
__________________?
DEMOSTRATIVE ADJECTIVES
I. Circle the correct option. We use the demostratives
a) There aren’t _____book stores. to indicate some objects in
any / some / a lot of singular or plural and they
b) There are____ parks in this city. There are 20! are near or far.
any / some / a lot of
c) There are ____ people at the gym.
any / some / a lot of
d) There are ____ cars in the petrol station. Only 3.
any / some / a lot of
II. Complete with there is / there are.
SINGULAR PLURAL
NEAR THIS THESE
FAR THAT THOSE
a) _____________a t-shirt on the bed.
b) _____________two books on the floor.
c)_____________four pictures on the wall.
d)_____________many books on the shelves.
12 CENTRO PREUNIVERSITARIO Modalidad virtual Oficina de Admisión
Oficina de Admisión Modalidad virtual CENTRO PREUNIVERSITARIO
IV.Correct the mistakes:
a. Those car is beautiful.
____________________
This is a book That is a book. b. That bags are expensive.
____________________
c. Take this keys.
_________________
d. Go to that shelf and bring these books.
These books are big Those are good books. _______________________
PLURAL OF NOUNS
Reading Comprehension
AMERICANS AND WHERE THEY
LIVE
There are over 300 million
people in the United States.
The average family has 3.19
I. Put in this or these people. 6% of children live in
a) ____________chairs e)_________men households run by one or
b) ____________key f)__________school both grandparents. 68% of
c) ____________boys g)__________man children live with two
d) ____________stores h)__________place parents. 16% of males 25–34 live at home with one
or both parents. 9% of females 25–34 live at home
with one or both parents. 27% of Americans live
II. Put in that or those alone. (Compare this figure to the percentage in
a) ____________house e)_________pants 1940—8%.) 39% of households have a dog. 31% of
b) ____________pupil f)_________woman households have a cat. Homes: 67% of American
c) ____________people g)________picture families own their homes. 25% of homeowners are
d) ____________dog h)__________shoes over 65 years old. The price of homes depends on
the city where you live. Some cities, such as San
Francisco, Boston, San Diego, Honolulu, and New
III.Change the following sentences York, have very expensive homes. The average
from singular to plural. American moves a lot. In a five-year period, 46% of
Americans change their address. Renters move more
than owners. Young people move more than older
a. This book is good. people.
_____________________
b. That girl has dolls. Tell whether the statement is true
_______________________ (T ) or false (F ).
1. Most American children live with their
c. This office is near the bank. grandparents. ________
2. More Americans live alone now than in 1940.
________________________ _______
d. That is my notebook. 3. Most people rent an apartment. ______
4. Americans stay in the same house for their entire
_____________________ lives. ______
5. Cats are more popular than dogs in American
e. This boy is fourteen years old. homes. ________
6. Families in the U.S. are small (fewer than five
________________________
people). ______
f. That dog is black. 7. Most children live with both parents. ____
____________________
CENTRO PREUNIVERSITARIO Modalidad virtual Oficina de Admisión 13
RULES RULE SIX – PLURAL OF
RULE ONE – PLURAL OF NOUNS NOUNS
If the nouns ending in: s, x,o, ch, These things are plural in
sh, add –es. English
Dress / Dresses Watch / Watches Tweezers
Box / Boxes Dish / Dishes Scissors Jeans
Tomato / Match / Matches Glasses Pajamas
Tomatoes Bus / Busses Tongs Shorts
Fox / Foxes Box / Boxes Eyeglasses Binoculars
Potato / Potatoes Pants Piers
Trousers Sunglasses
RULE TWO – PLURAL OF NOUNS Overalls Spectacles
For nouns ending in consonant +
y you drop the –y and add –ies
City / Cities Lady / Ladies
Secretary / Library / Libraries RULE SEVEN – PLURAL OF
Secretaries Country / NOUNS
Baby / Babies Countries Exceptions
Stomach /
RULE THREE – PLURAL OF Stomachs Piano / Pianos
NOUNS Handkerchief / Chief / Chiefs
For nouns ending in –f. or –fe Handkerchiefs Scarf / Scarfs
change for –v then add –es Roof / Roofs Epoch /
Wife / Wives Leaf / Leaves Soprano / Epochs
Wolf / Wolves Knife / Knives Sopranos
RULE FOUR – PLURAL OF There are uncountable nouns and
NOUNS these don’t have plural in English
Some nous are irregular.
Water Bread Coffee Cheese
Man / Men
Rice Juice Tea Paper
Tooth / Teeth Mouse / Mice Sugar Milk Chocolate Glue
Ox / Oxen Person / People Sand Butter Ham Soda
Fish / Fish Goose / Geese hair Flour Jam Ice
Louse / Lice Deer / Deer
Woman / Sheep / Sheep A few nouns of Greek or Latin
Women Child / Children origin retain their original plurals
Foot / Feet
Analysis /
RULE FIVE – PLURAL OF NOUNS Crisis / Crises
Analyses
For nouns which aren’t in the Phenomenon /
Basis / Bases
other rules only add –s to the Phenomena
Memorandum /
nouns. Stimulus / Stimuli
Memoranda
Student / Peruvian /
Students Peruvians
Book / Books Boy / Boys
Apple / Apples Hen / Hens
Marker / Markers Dog / Dogs
14 CENTRO PREUNIVERSITARIO Modalidad virtual Oficina de Admisión
Oficina de Admisión Modalidad virtual CENTRO PREUNIVERSITARIO
Prepositions of place
I. Write the plural form of each noun.
1. dish _____________
2. country __________ We can use prepositions of place to say
3. half _____________ where things are.
4. book ____________ A person lives:
5. boy _____________
6. girl _____________
7. bench __________
8. box ____________ In a country and in a city.
9. shark __________ Rebecca lives in the Peru.
10. stereo ________ She lives in Cerro de Pasco city.
II. Fill in the blanks with the correct plural
form of the noun in parentheses ( ).
1. Most ___________in the U.S. own a
house.(family) On a street, avenue, road, etc.
2. The U.S. has over 300 million ________ . (person) She lives on Pine Street
3. Americans move many __________. (time )
4. Some ________ earn more money than
their________(woman)- (husband)
5. __________are very expensive in
some_________(Home) - (city) At a street address.
6. Divorce is very high in some_______ (country) She lives at 1089 Pine
Street.
Write about Oscar.
PREPOSITIONS OF PLACE AND Oscar lives ______ Canada.
PREPOSITIONS MOVEMENT 2) He lives ______ Toronto.
3) He lives ______ Main Street.
4) He lives ______ 1423 Main Street.
Match the prepositions of place
with their respective images.
Answer the question about the
conversation
1. What is the man´s name?
________________________________
2. What does she need her laptop for?
________________________________
3. Where is the laptop?
________________________________
CENTRO PREUNIVERSITARIO Modalidad virtual Oficina de Admisión 15
Choose the right option. - The tiger is going through the hoop.
The preposition into is used to talk about the
movement that enters a space, usually with a
verb that expresses movement.
- The woman is going into the car.
1. The fridge is between/under the door and the
cupboard.
2. The door is next to/under the shelf.
3. The clock is in/on the wall.
4. The chairs are under/ next to the table
5. The table is under/opposite the cooker.
6. The pot is on/in the cooker.
7. The bin is near/ in front of the drawers.
8. The microwave is next to /under the window
9. The sink is above/under the window.
The preposition over refers to movement at a
higher level than something else. It also can be
used when talking about movement across a
surface.
Prepositions of movement
- The athlete is jumping over the hurdle.
Prepositions of movement or direction are used to
show movement from one place to another. These
prepositions are most often used with verbs of
motion and are found after the verb.
The preposition across is used when talking about
The preposition to is used to indicate a destination movement from one side of something to the other
or direction. which has sides or limits such as a city, road or river.
It is also used to when something touches or
stretches from one side to another.
- The boy is going to school.
- The man is walking across the street.
The preposition through is used when we talk about
movement from one side to another but “in
something”, such as long grass or a forest.
16 CENTRO PREUNIVERSITARIO Modalidad virtual Oficina de Admisión
Oficina de Admisión Modalidad virtual CENTRO PREUNIVERSITARIO
The preposition along is used to show movement
of something in a line that follows the side of
something long.
- They are walking along the street.
The preposition up refers to a higher position
or movement to a higher position.
- The man is driving up the hill.
The preposition from is used to show the place where
someone or something starts.
- The boy is coming from the gym.
Indicates movement to a lower position.
- The boy is going down the stairs.
The preposition around refers to the movement in
circles or in the vicinity of something.
Complete with the prepositions of movement.
- The man is travelling around the world.
1. The boys swam ___________ the lake.
2. Her hair whipped_________ her face in the wind.
3. He jumped __________ the wall.
4. We went for a walk ________ the beach at twilight
5. She doesn’t like riding her bike ____these hills.
PRESENT PROGRESSIVE – USE OF
QUANTIFIERS (SOME, ANY, MUCH, MANY, A
The preposition onto is used to talk about movement LOT OF , A FEW , FEW , A LITTLE ,LITTLE ) AND
to a position on a surface, usually with a verb that “HOW MANY & HOW MUCH”
expresses movement.
- The child is getting onto the bus
We use the present
progressive to
describe something
that is happening now
CENTRO PREUNIVERSITARIO Modalidad virtual Oficina de Admisión 17
Reading Comprehension
RULES
The school's principal is talking to the When the verb ends Example:
teachers. His secretary is sending some mails in one
to the students' parents. The parents are Swim…….swimming
working at the time. And the principal needs a Consonant +vowel + Run ………running
meeting to talk with them about their children. consonant
The children are studying nine asignatures, Double the
and they are wanting to add one more. The consonant
meeting is planed for the next week.
Example:
When the verbs ends
in “Y” add “ing” Study ……..studying
ANSWER
1. What is school's principal doing now? Example:
When the verb ends
___________________________ in “e” add “ing” Dance ….. dancing
Write …….writing
2. What is secretary doing now?
Most verbs only add Example:
____________________________ “ing”
Cook …… cooking
3. Do they like studying nine asignatures? Play …….. playing
____________________________
4. When does the meeting?
____________________________
5. What do the parents doing now?
6. What are they wanting?
____________________________
Remember:
They ´re drinking a cup tea.
She isn´t playing piano.
Is it eating a fish?
Yes,it is. /No it isn´t.
18 CENTRO PREUNIVERSITARIO Modalidad virtual Oficina de Admisión
Oficina de Admisión Modalidad virtual CENTRO PREUNIVERSITARIO
_________________________(?)
I. Choose the correct spelling for the word
underlined in each sentences.
a) Jhon is swimming/swimming in the pool at the
moment.
_________________________(+)
_________________________( - )
b) The girls are putting/putting on their coats. _________________________(?)
c) Hurry up ! We ´re /Wer ´e waiting for you.
d) Look outside! Its/it´s snowing.
e) They are having/having a good time.
_________________________(+)
II. What are they doing? _________________________( - )
_________________________(?)
_________________________(+) _________________________(+)
_________________________( - ) _________________________( - )
_________________________(?) _________________________(?)
_________________________(+)
_________________________( - )
_________________________(?)
_________________________(+)
_________________________( - )
_________________________(?) QUANTIFIERS
We use quantifiers before a
noun, an article or a
determiner to talk about
quantity.
_________________________(+)
_________________________( - )
_________________________(?)
_________________________(+)
_________________________( - )
CENTRO PREUNIVERSITARIO Modalidad virtual Oficina de Admisión 19
Reading Comprehension
SOME
AT THE SUPERMARKET
DIALOGUE
Empleamos some en frases AFIRMATIVAS con
sustantivos INCONTABLES, También usamos
some con sustantivos CONTABLES EN PLURAL.
Some equivale a algo (de), unos o algunos, pero
muchas veces no tiene traducción.
Jhonny: Hey Max, Are you busy?
Walter: Not really, why?
Jhonny: I have to buy some things here
in the supermarket. Can you come with
me?
Walter: Ok, but we have to hurry because There are some tomatoes in the fridge.
I have little time to help you We need some chairs.
Jhonny: First, I need some bread and
I know some of your students.
some eggs
Walter: Do you want some potatoes?
Jhonny: No, I don't want any potatoes.
I'm trying to lose weight ANY
Walter: Oh, come on! Potatoes are
fantastic
Jhonny: Ok, but only a few
Walter: Do you like fish?
Jhonny: Yes, I love fish. Please, get me En frases NEGATIVAS, se emplea con los
some Ocean Perch mismos sustantivos: los INCONTABLES y
Walter: I'm afraid they don't have any CONTABLES EN PLURAL. Any en estos
Ocean Perch. What else do you need? casos equivale a nada (de) o ninguno, pero
Jhonny: I need some Salmon and a little en general no suele tener traducción, sino
sugar que también lo usamos en PREGUNTAS:
There isn't any sand in my shoe.
I didn´t drink any water before going to bed.
Did you drink any water before going to bed?
Do we need any chairs?
MUCH
Solo se emplea much (mucho) con los
sustantivos INCONTABLES en frases
NEGATIVAS y en PREGUNTAS.
I don't smoke much.
20 CENTRO PREUNIVERSITARIO Modalidad virtual Oficina de Admisión
Oficina de Admisión Modalidad virtual CENTRO PREUNIVERSITARIO
Do you work much?
He didn't spend much money.
Do I have much time? FEW
MANY Con sustantivos CONTABLES EN PLURAL
empleamos few, que equivale a pocos o pocas.
Se emplea Many (muchos) solo con los
sustantivos CONTABLES EN PLURAL,
también en frases NEGATIVAS y en Few studies explore this topic
PREGUNTAS. I've seen very few restaurants in this area
They do wonders with very few resources.
I don't have many students. A - AN
Does she have many clients?
A LOT OF Use it with singular countable nouns in all
types of sentences. Don´t use it with
uncountables.
A lot of (mucho/muchos) es un comodín que
nos sirve tanto para los INCONTABLES como
para los CONTABLES EN PLURAL. ¡Y no
solo eso! También se usa tanto para las frases
afirmativas como para las negativas y las a orange
preguntas. an apple
HOW MUCH
She has a lot of time.
They have a lot of money. Empleamos how much en preguntas como
I have a lot of students equivalente de cuánto o cuánta. Si va seguido
He talks a lot. de un sustantivo, este tiene que ser
INCONTABLE
LITTLE
Little significa poco o poca y se emplea con How much time do we have?
sustantivos INCONTABLES o solo con verbos, How much sauce do you want?
como en el tercer ejemplo. La mayoría de las How much does he know?
veces se emplea very little en lugar de little.
They showed little interest.
There's very little traffic at that time.
I know very little about him.
CENTRO PREUNIVERSITARIO Modalidad virtual Oficina de Admisión 21
c) There are many parties in August.
HOW MANY d) There are many parties in august.
V. Look at the picture and complete the
sentences with the words.
Como te puedes imaginar, how many queda
reservado para cuando hacemos referencia a
sustantivos CONTABLES EN PLURAL. Se
traduce como cuántos o cuántas.
enough / are / any
many / lot of / carton /
much / some.
How many children do you have?
How many tables are there?
How many do you want?
I. Complete these sentences with a word from
the box.
1) We don't have ________ pens. 1. There _________ two carrots.
2) Is there _______ airport in Nottingham? 2. How _________ oranges are there?
3) Is there ________ milk in the fridge? 3: There is one _____________ of milk.
4) I have _________ books I can lend you. 4: There is ____________ meat.
5) She needs _______ money for new clothes. 5: How _____________ butter is there?
6: There are a ____________ eggs.
II. Complete the blanks with 7. There isn’t __________ soda.
much /many / a lot of / a lot 8. There is _____________ bread for the week
1) I have to buy ____ school books.
2) There's not ____ wine left in the bottle.
3) How ____ money do you need?
4) Did I make ____ mistake? ADJECTIVES – COMPARATIVES -
5) Does he smoke ____? SUPERLATIVES
III. Complete.
ADJECTIVES
1. Very ____ shops are open today.
2. Can I have ____ wine, please?
Nouns are people, places,
3. There are a lot of bags in the car. There's very
____ space left. and things, and adjectives
4. I'm not so fast! I need ____ more time. are words that describe
5. The reporter asked me ____ (algunas) nouns. In English words do
questions. NOT have gender but in
Spanish they DO. All nouns
IV.Choose the sentence which is grammatically are either male or female.
correct:
a) There are many partys in August.
b) There are much partys in august.
22 CENTRO PREUNIVERSITARIO Modalidad virtual Oficina de Admisión
Oficina de Admisión Modalidad virtual CENTRO PREUNIVERSITARIO
Reading Comprehension
Mario: Hello, good afternoon.
Computer Technician: How can I help you?
Mario: I'm here because my computer is slowest than
We use: ADJECTIVES + NOUN ever.
Computer Technician: Ok, I'm going to check this out.
Example
Mario: Ok, how is it?
It is a nice day
Computer Technician: It is taking time to turning on, It
Nataly is a very old woman
should be faster.
Do you like Chinese food?
Mario: What do you think about it?
Computer Technician: Yes, it could has the best glitch
ever. Leave me the computer, and I'm going to fix that
glitch. I'm sure that It would be better than before, and
settle a stronger anti virus.
Mario: Thank you.
Computer Technician: Your welcome, see you in two
days
The adjective is before the noun
They live in a modern house (not a
house modern) Write 3 questions with the answer.
a)______________________________
We use the BE + ADJECTIVES _______________________________
The weather is nice today _______________________________
Those shoes are old b)______________________________
The movie wasn´t good. It was boring _______________________________
_______________________________
c)______________________________
The verb: _______________________________
LOOK/ FEEL/ SMELL/ TASTE/ SOUND + ADJECTIVES _______________________________
is
It Smells good COMPARATIVE ADJECTIVES
tastes
is
He Feels tired One way to describe nouns
looks (people, objects, animals, etc.) is
are by comparing them to something
Sad
They Look else. When comparing two things,
sound you’re likely to use adjectives like
smaller, bigger, taller.
I. Traslate in English.
a) bonita _____________
b) alto _______________
c) feo ________________
d) pequeño ___________
e) lindo ______________
CENTRO PREUNIVERSITARIO Modalidad virtual Oficina de Admisión 23
SUPERLATIVE ADJECTIVES
Karina is a better player than Ronaldo.
France is a bigger country than Britain.
Rosamel is two years older than me.
New York is much bigger than Boston. A superlative adjective is used to indicate that one thing
has some feature to a greater or lesser degree than all
others (in a given context)
I. Write the comparative forms
a) Hot ________________
b) Big ________________
c) Expensive ___________
d) Bad ________________
e) Good _______________
f) Thin _________________
II. Make the comparative form. If it's
possible, use 'er'. If not, use 'more'.
a) Russia is far ________ (large) than the UK
b) In the UK, the streets are generally
_________ (narrow) than in the USA.
c) London is__________(busy) than Glasgow.
d) Edith is __________(quiet) than her sister.
III. Make Match the items on the right to the
items on the left.
high farther
far higher
tidy darker
She is the smartest person I know.
Today is the coldest day I can remember.
dark tidier China is the biggest country I have visited.
I. Fill in the spaces using the appropriate
superlative adjective.
1. That building is the __________ (tall) in the
neighborhood.
2. Aunt Janet is the __________ (old).
24 CENTRO PREUNIVERSITARIO Modalidad virtual Oficina de Admisión
Oficina de Admisión Modalidad virtual CENTRO PREUNIVERSITARIO
3. My bicycle is the __________ (nice) thing I
own.
4. The komodo dragon is the __________
(large) lizard in the world.
5. Mt. Denali is the __________ (high) About the conversation
mountain peak in North America. 1. What was the game like yesterday?
____________________________
II. Write two of you own sentences using
superlative adjectives with one syllable. 2. What was the score?
____________________________
1)________________________________
______________________________ 3. Where was Jake?
___________________________
2)________________________________
______________________________ 4. Who was he with?
___________________________
III. Write two of you own sentences using 5. Who was the girl?
superlative adjectives with two syllable. ___________________________
1)________________________________
______________________________________
2)________________________________
______________________________________
PAST BE - PAST PROGRESSIVE PAST
SIMPLE
(REGULAR VERBS AND IRREGULAR
VERBS)
Facts about the past.
AUXILIARY VERB DID
READING ONE Affirmative Negative
FULL FORMS SHORT
FORM
Jake: Hi, Ben! How was the game last
I was I was not I wasn´t
night? You were You were not You weren´t
He was He was not He wasn´t
Ben: Terrific! It was the best game of She was She was not She wasn´t
It was It was not It wasn´t
the season. We were We were not We weren´t
You were You were not You weren´t
Jake: Oh, and I wasn´t there! What was They were They were not They weren´t
the final score?
Questions Short Answers
Ben: 98 to 96 for the Bulls. They were the Was I? Yes, I was. No, I wasn´t.
winners again! Were you? Yes, you were. No, you weren´t.
Was he? Yes, he was. No, he wasn´t.
Where were you? You weren´t at Was she? Yes, she was. No, she wasn´t.
home. Was it? Yes, it was. No, it wasn´t.
Were we? Yes, we were. No, we weren´t.
And your cell phone was off… Were you? Yes, you were. No, you weren´t.
Were they? Yes, they were. No, they weren´t.
Jake: I was at the amusement park …with a girl.
Ben: Ok, that explains it.
Jake: No, you don´t understand. I was taking care of my
little cousin.
CENTRO PREUNIVERSITARIO Modalidad virtual Oficina de Admisión 25
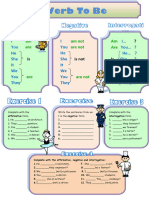
Affirmative I, He, She, It was happy.
We, You, They were late.
Interrogative (When) was I, he, she it happy?
(Why) were we, you, They late? Past Progressive is a form of the verb that
Negative I, He, She It was not (wasn´t) shows the action was in progress at a certain
happy. point, or at some time period in the past.
We, You, They were not ( weren´t)
late
READING TWO
Yesterday, it was raining
and thundering all day.
Ann was playing inside
Use IN: In June – In 1972 – In 2020 the house. She wanted to
Use ON: On June 08th – On April 28th 2009 be outside. She wasn't
The expression of dates: playing outside because it
was raining. She was
1971 = nineteen seventy-one
feeling tired of being trapped inside the house.
2009 = two thousand nine Ann was trying to keep busy inside the house. She
was reading her book until the electricity went out.
Then, she decided to practice her sewing. She was
practicing sewing until
1. Choose the answer! lunchtime. After lunch, she sat
Read the sentence. Circle the correct by the window and watched
the rain
answer.
a. He ________ sick yesterday. While Ann was watching the
were / was / weren’t rain, the phone rang. Her
b. I _____in the school play last year. mother was calling to say she was coming home. She
were / was / is was bringing a new game. Ann and her mother ate
c. _______ you on the bus this afternoon? ice cream and played the game.
Was / Were / Where While they were playing, the rain stopped! But Ann
d. I _________________ late for school didn't even notice. She was having such a good time
today, I was early. with her mom!
wasn’t / weren’t / were
e. They _____ happy with the football score. Answer the following questions. Use the
weren’t / wasn’t / we’re not Past Progressive tense.
f. We ______________tired yesterday. 1. Where was Ann playing yesterday? Why
was / wasn’t / were wasn't she playing outside?
___________________________________
2. Make it right! ___________________________________
Find the mistake, underline it and write the 2. What was Ann doing before the electricity went
correct word. out? What was she doing until lunchtime?
a. He were here yesterday.
___________________________________
___________________________________
___________________________________
b. I weres asleep at 11 o’clock last night.
3. At the end of the story, the rain stopped. What
___________________________________
c. She were happy with her test result. was Ann doing?
___________________________________ ____________________________________
d. He where in the garden this afternoon. __
______________________________
e. I weren't in the football team last year.
___________________________________
f. They was scared of the dark.
26 CENTRO PREUNIVERSITARIO Modalidad virtual Oficina de Admisión
Oficina de Admisión Modalidad virtual CENTRO PREUNIVERSITARIO
I
We We use the Past Simple to talk about an
He was playing were cooking
You action or situation in the past which is
She
They finished. We often say when it happened
It
(yesterday, last night)
I
We
He
You weren’t crying
She wasn’t running They
It
Chris phoned me yesterday. He wanted to ask me
something.
I lying? Did you enjoy the concert last night?
we going to …?
Was he eating? Were you studying?
she dancing?
it sleeping?
they traveling? READING THREE
Yesterday Noelia went to a fair with her father.
last night / yesterday There were many toys at the fair. She wanted to buy
all the toys. There were
yesterday morning
also many food stalls.
yesterday afternoon As Noelia was hungry,
last Sunday / last year she walked towards
five years ago one of the stalls. But
in nineteen eighty she did not realise that
she had let her father's
hand go. She went to the shop and asked for a
chocolate. The shopkeeper
asked for money. She turned back. But she did not
find her father. She started crying. The kind
shopkeeper gave her a candy. He also told her not
to cry. He took her to a police officer.
The police announced Noelia's name through the
1. A: ___________ they watching TV at midnight? speakers. After some time, her father arrived and
B: No, they ___________. saw Noelia. Noelia ran towards him, hugged him
tightly and cried. Her father bought her many toys.
2. We ___________ eating lunch in the cafeteria at noon. Noelia did not let go of her father's hand ever
again.
3. A: ___________ you talking on the phone a few minutes
ago?
B: No, I __________. Answer these questions.
1. What did Noelia
4. I ___________ walking home when I saw the car
want?______________________
accident.
2. Where did Noelia
go?______________________
5. My classmate and I ___________ studying together at
3. What did she ask for in the
the library.
shop?_____________
4. What did the shopkeeper ask
6. While he ___________ cleaning the house, we
for?_________________________________
___________ cooking.
5. Who announced Noelia's name through the
speakers?
7. A: What ___________ you doing at one o’clock?
______________________________
B: I ___________ sleeping.
6. Whom did Noelia
lug?______________________
CENTRO PREUNIVERSITARIO Modalidad virtual Oficina de Admisión 27
Collect Collected Collected
Create Created Created
Die Died Died
Discover Discovered Discovered
Discuss Discussed Discussed
Divide Divided Divided
Empty Emptied Emptied
AFFIRMATIVE
End Ended Ended
Evaluate Evaluated Evaluated
Finish Finished Finished
Follow Followed Followed
Hire Hired Hired
Identify Indentified Indentified
Improve Improved Improved
Increase Increased Increased
Install Installed Installed
Introduce Introduced Introduced
Invest Invested Invested
NEGATIVE
Investigate Investigated Investigated
Look for Looked for Looked for
Mail Mailed Mailed
Manage Managed Managed
In negative sentences the verb
Modify Modified Modified
doesn´t change.
The base form of the infinitive is Obtain Obtained Obtained
used. Open Opened Opened
Organize Organized Organized
Plan Planned Planned
Practice Practiced Practiced
Prefer Preferred Preferred
QUESTION
Prepare Prepared Prepared
Print Printed Printed
Protect Protected Protected
Realize Realized Realized
Remain Remained Remained
In the interrogative form the verb Return Returned Returned
doesn´t change. Review Reviewed Reviewed
The base form of the infinitive is Save Saved Saved
used.
Share Shared Shared
LIST OF REGULAR VERBS Sign Signed Signed
PRESENT PAST PAST Study Studied Studied
PARTICIPLE Supervise Supervised Supervised
Agree Agreed Agreed Transfer Transferred Transferred
Avoid Avoided Avoided Treat Treated Treated
Borrow Borrowed Borrowed Turn out Turned out Turned out
Call Called Called Talk Talked Talked
Carry Carried Carried Use Used Used
Classify Classified Classified Verify Verified Verified
Close Closed Closed Watch Watched Watched
28 CENTRO PREUNIVERSITARIO Modalidad virtual Oficina de Admisión
Oficina de Admisión Modalidad virtual CENTRO PREUNIVERSITARIO
Work Worked Worked Sweep Swept Swept
IRREGULAR VERBS Swim Swam Swum
Be Take Took Taken
Was, were Been
(am,is,are) Teach Taught Taught
Bear Bore Born
Tell Told Told
Become Became Become
Think Thought Thought
Begin Began Begun
Wear Wore Worn
Bite Bit Bitten
Win Won Won
Break Broke Broken
Write Wrote Written
Bring Brought Brought
Build Built Built
Buy Bought Bought
Catch Caught Caught Complete the sentences in past simple.
Choose Chose Chosen
Come Came Come 1. Susan ___________ (teach) English at
university last year.
Cost Cost Cost
2. John _______________ (not like) studying
Cut Cut Cut English.
Dig Dug Dug 3. My sister ________ (break) my computer.
Do Did Done 4. ________________ (you / know) the answer to
Draw Drew Drew the question?
5. She ________ (be) my favourite singer when I
Drink Drank Drunk
was younger.
Drive Drove Driven 6. George __________ (not be) my best friend.
Eat Ate Eaten
Fall Fell Fallen
Order the words to ask questions and then
match with the appropriate answer.
Get Got Got
Have Had Had 1. park/ where/ your sister/ did?
Hit Hit Hit ________________________________
2. He/ did/ the/ close/window?
Hold Held Held
________________________________
Hurt Hurt Hurt 3. Music/ listen to/ what/ did/ you?
Keep Kept Kept ________________________________
Know Knew Known 4. Film/ you/ did/ the/ like?
Leave Left Left ________________________________
5. Yesterday/ work/ you/ did?
Lose Lost Lost ________________________________
Make Made Made 6. Time/ your friends/ did/ what/ arrive?
Pay Paid Paid ________________________________
Put Put Put 7. They/ the restaurant/ go/ did/ the/ to?
________________________________
Read Read Read 8. Want/ did/ she/ coffee/ a?
Ride Rode Ridden ________________________________
Run Ran Run
Say Said Said a. Yes, I did. It was great.
b. They arrived at nine o´clock.
See Saw Seen c. In the car park.
Sell Sold Sold d. Yes, she did. Coffee and milk.
Send Sent Sent e. Yes, they did.
f. Yes, I did. All day long.
Set up Set up Set up
g. We listened pop music.
Show Showed Shown h. No, he didn’t.
Sing Sang Sung
Sit Sat Sat
Sleep Slept Slept
Speak Spoke Spoken
Steal Stole Stolen
CENTRO PREUNIVERSITARIO Modalidad virtual Oficina de Admisión 29
9. You couldn’t / aren’t allowed to drive without a
licence in the UK.
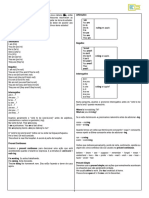
MODAL VERBS:
“CAN – COULD – MAY – MIGHT – 10. Are you hungry? I make / I’ll make something
SHOULD – WOULD – MUST” for you
Reading Comprehension They are Auxiliary verbs
that provide additional
and specific meaning to
the main verb of the
sentence.
Before you start
MURAT: I can’t find the episode of ER
that we recorded yesterday.
RUDITH: It must be there. I saw Max
start the machine.
MURAT: No, it isn’t. He must have
done something wrong.How annoying!
RUDITH: Don’t worry. We can
download it from the Internet.I’ll do it
for you if you like.
MURAT: That’s nice of you. I was
looking forward to watching it tonight.
RUDITH: Well, I won’t be able to do it
until tomorrow – I’ve got to work on that Remenber:
geography project for college. They do not accept conjugation
MURAT: But you don’t have to hand it They do not need other auxiliary verbs
in until Friday. There is no “s” in singular
RUDITH: I know. But I’d better get on There is no “do / does” in the question
with it. You know how There is no “don’t / doesn’t” in the negative.
slow I am! Why don’t I help you fi nish
it?
RUDITH: No, we’re not allowed to get
help from anyone else. It has to be all
our own work.
But thanks for offering.
I. Now read the sentences and choose the
correct words. Subject + Modal Verb + Verb (base
1. Look at my new mobile phone. It must / can form) + Complement.
play movies!
2. What’s your new phone number? I can’t /
mustn’t remember it.
3. Can you change my appointment? I’m busy so I
won’t be able to / don’t have to come at eleven
o’clock tomorrow.
4. Janine can / must be in the offi ce now. I saw Mary could play the piano.
her go in ten minutes ago. We should be grateful.
5. My wallet’s gone! Someone can / must have
stolen it! You should never make it.
6. You’ve got / You’re allowed to show your
driving licence when you rent a car.
7. Take your time. We can’t / don’t have to be
there until six.
8. 8 We’re late. We’d better / We might hurry up.
30 CENTRO PREUNIVERSITARIO Modalidad virtual Oficina de Admisión
Oficina de Admisión Modalidad virtual CENTRO PREUNIVERSITARIO
NEGATIVE It can fly
Subject + Modal Verb + not + Verb
(base form)
Can you speak French?
Mary couldn´t play the piano.
We shouldn´t be grateful.
You shouldn´t never make it.
She can´t drive.
INTERROGATIVE
Modal Verb + Subject + Verb (base
form) + Complement +?
COULD
Could Mary play the piano?
Should we be grateful?
Should you never make it?
Past ability
Past permission
Probability (40%)
CAN Request
We use could for general ability or permission
to do something. We also use could to say that
Ability something is possible now or in the future.
Permission Could is formal.
Probability
I could swim when I was a child.
We can use Can (present) to say that
something is possible or that somebody has
the ability to do something.
CENTRO PREUNIVERSITARIO Modalidad virtual Oficina de Admisión 31
Could you lend me color?
Probability (35%
or less)
MAY We use might to say that something is a possibility.
Might is formal.
Probability It might be quicker to travel by train.
(50%)
Permission
We use may to say that something is a possibility.
May is informal
She might have bought a new car.
Ronaldo may have taken the bus to
school.
SHOULD
May I come in?
Advice
You can use should to give or to give an opinion.
You should do more exercises.
32 CENTRO PREUNIVERSITARIO Modalidad virtual Oficina de Admisión
Oficina de Admisión Modalidad virtual CENTRO PREUNIVERSITARIO
MUST
Carlos Shouldn´t drink beer.
Prohibition
Probability
(100%)
We use must to express present or future obligation
WOULD that comes from the speaker. It’s internal obligation,
not a rule or a law.
They must give their exams now.
Asking for
permission
Request
Invitation
Preferences Rosa mustn´t smoke in the class
I would play soccer.
I. Write statements and questions, using the
words below and the modal verbs in brackets.
a) Their children / not read or write / yet (can)
____________________________________
____________________________________
b) your old mobile phone / play videos / ? (could)
_______________________________
_______________________________
c) you / hear / that strange noise / ? (can)
I would buy the house. _______________________________
_______________________________
d) After the operation / I / not walk properly / for two
weeks (could)
_______________________________
_______________________________
e) It / be / very hot / in Madrid / in August (can)
_______________________________
_______________________________
CENTRO PREUNIVERSITARIO Modalidad virtual Oficina de Admisión 33
II. Complete the sentences with the correct modal
verb: should / can / mustn’t / could
READING
1 You ______________ smoke in public places.
2 You ______________ eat a healthy diet.
3 You ______________ respect other people’s Dear Andrew,
opinions. I´ve got great news! Next week, Katie and I are
4 She ______________ always sing really well. going to travel to South America. Our flight
5 ______________ you leave us alone now? leaves on Monday. We are going to spend six
weeks there. In Peru, We are going to go on
the Inca trail and we are going to hike through
III. Give two pieces of advice for the the Sacred Valley to Machu picchu. The trip
will probably cost a lot of money and I know it
situations below. Use an appropriate won´t be easy, but We´ve planned everything
modal verb. carefully. We are going to buy strong
backpacks and warm sleeping bags – the
1. Your sister wants to leave school and become nights are very cold there, even in the
a mechanic. summer. We are going to carry a lot of water
with us because we aren´t sure the water
She there will be clean enough to drink. I hope we
_______________________________ won´t get altitude sickness – that can be a
serious problem high up in the Andes
2. Your teacher is working too hard and is Mountains! What are you going to do this
exhausted. summer? Write and tell me!
Jenny
He / She
_______________________________
3. One of your friends is very bossy and nobody
wants to spend time with them.
He / She
_______________________________ FUTURE WITH “WILL”
4. Your friend wants to get married. You think
she’s too young.
You form the future simple with:
She / he
will or won´t + infinitive.
_______________________________
I
IV. Circle the correct option.
You
1. I’m not sure where Azucena is. She could / ´ll (will)
He/She/It
must be at the office. won´t (will not) go by train
We
2. The letter should / couldn’t arrive tomorrow.
They
It was sent by express delivery.
3. You don’t have to / mustn’t smoke at a petrol
When you make a decision at the time of
station. You can’t / could cause an speaking.
explosion. I´ll have a return ticket.
4. That painting is obviously a forgery. It I ´ll pay cash
mustn’t / can’t be by Van Gogh.
5. That doesn’t have to / can’t be right! The To make predictions.
answers must / can be wrong. It´ll be sunny in Cerro de Pasco tomorrow.
(It will be sunny in Cerro de Pasco tomorrow)
It won´t be rainy. (It will not be rainy)
FUTURE SIMPLE WITH WILL – A: Will it be snowy in Cerro de Pasco?
GOING TO AND PRESENT B: Yes, it will.
CONTINUOUS.
A: Will there be rain in Carhuamayo?
TIME EXPRESSIONS FOR THE
FUTURE B: No, there won´t.
To make an offer or promises.
- I will have 20 on my
tests.
- I promise, I will practice more
English
34 CENTRO PREUNIVERSITARIO Modalidad virtual Oficina de Admisión
Oficina de Admisión Modalidad virtual CENTRO PREUNIVERSITARIO
g) It __________________________cold
Affirmative Short Form tomorrow. It’s august. (be)
I will I’ll Make interrogative sentences in future
you will you’ll simple (will)
he will he’ll
(what/ learn/ they) __________________________
she will she’ll
(it/ snow) _________________________________
it will it’ll (he / hard/ study / will)
we will we’ll _________________________________________
they will they’ll (do/ your /will/ homework you)
_________________________________________
Negative Short Form
Form FUTURE WITH “GOING TO”
I will not I won’t. / I’ll not.
You will not You won’t. / You’ll not.
He will not He won’t. / He’ll not.
She will not She won’t. / She’ll not.
It will not It won’t. / It’ll not. The structure of going to is:
We will not We won’t. / We’ll not.
They will not They won’t. / They’ll not.
Subject + be + going + infinitive
Question Short answer
You use going to + infinitive:
Will I ___? Yes, I will / No, I won´t
Will you ___? Yes, I will / No, I won´t I am going to buy a new car.
Will he ___? Yes, he will / No, he won´t
I ‘m going to go swimming
Will she ___? Yes, she will / No, she won´t
Will it ___? Yes, it will / No, it won´t He is not going to take the exam
Will we ___? Yes, we will / No, we won´t It isn’t going to rain
Will they ___? Yes, they will / No, they won´t Are you going to paint the house?
To talk about future intentions or plans.
- I´m going to see my friends more often.
- I´m not going to take work home
Complete the sentences in future simple (will –
won´t) To talk about something which we can see
now is sure to happen in the future.
a) We ___________________________a good time
in the swimming pool. It’s cold. (have) - I´m going to have a baby.
b) I ___________________________as a singer
because I like music very much. (work)
c) My best friend
_____________________________to the park Complete the sentences with going to.
a) I ________________ meet my friends after
because she is ill. (go) class. Would you like to join us?
d) My cousins _____________________________by b) A: _______ your brother ________________
travel next week?
plane. It’s very expensive. (travel)
B: Yes, he _______.
e) They ___________________________their c) Alex ________________ go to work today
exams. They always study a lot. (pass) because he is sick.
d) Bob and Cathy ________________ see a
f) Your brother movie tonight. It starts at seven o’clock.
_____________________________the film. It’s a e) A: _______ you ________________ do
western and she loves them. (like) your homework?
CENTRO PREUNIVERSITARIO Modalidad virtual Oficina de Admisión 35
B: Yes, I _______.
f) We’re too busy, so we ________________ Complete with the present continuous in the
have lunch. future.
a) I (get up) ________________ very early
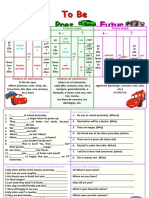
tomorrow morning, at five o’clock.
FUTURE WITH “PRESENT b) A:_____ John (come) ________________
CONTINUOUS” to the party?
B: No, he _____.
c) I (go) ________________ to a shopping
We use to show that something is planned and mall this weekend.
will be done in the near future. d) No, we (go out) ________________ on
It is the most usual way of expressing immediate Friday. We are staying home.
plans. e) Tomorrow is Saturday! I (sleep)
________________ late!
f) I (play) ________________ football
I am
tomorrow afternoon at two-thirty.
You He are
g) Sally, turn off the TV! We (eat)
She is
traveling tomorrow. ________________ dinner soon.
It is
h) No, we (have) ________________ a
We is
meeting today. It’s at three o’clock
They are
tomorrow.
are
I am
You are
He is
She is not traveling
tomorrow.
It is
We are Vocabulary
They are
Time expressions for the future
Tomorrow (mañana)
Are you I am.
Next Monday (el lunes que viene)
Is he he is.
Next week (la próxima semana)
Is she she is. Next month (el próximo mes)
Is it it is. Next year (el año que viene)
Are we traveling? Yes, You In an hour or so (en una hora más o menos)
are.
Are you we
are.
Are they they
are.
Are you I am not. PRESENT PERFECT – ADVERBS
(JUST, ALREADY, RECENTLY,
Is he he isn’t.
EVER, NEVER, YET)
Is she she isn’t.
Is it traveling? No, it isn’t.
Are we you aren’t.
Are you we aren’t.
Are they they aren’t.
36 CENTRO PREUNIVERSITARIO Modalidad virtual Oficina de Admisión
Oficina de Admisión Modalidad virtual CENTRO PREUNIVERSITARIO
Reading Comprehension We form the Present
perfect with have/has + the
past participle. In spoken
English we usually use the
contracted form ’ve/’s
participles. For
example, be – was
adverbs recently
and once, twice, etc.
AFFIRMATIVE
Answer The Questions:
1) Does Jessica like her job? SUBJECT + AUX.VERB HAVE/HAS +
_________________________________
2) How long has she been working there?
VERB PAST PARTICIPLE +
________________________________ COMPLEMENT.
3) What is tiring for her?
_________________________________
Write two questions with the answer. She has stolen all the chocolate!
a) _______________________________ He has studied Latin.
__________________________________
He has hurt his leg
b) _______________________________
__________________________________
NEGATIVE
SUBJECT + AUX.VERB HAVEN´T/HASN´T +
VERB PAST PARTICIPLE + COMPLEMENT.
CENTRO PREUNIVERSITARIO Modalidad virtual Oficina de Admisión 37
. We haven’t lost our tickets.
We haven’t heard that song already.
She has left her phone in a taxi.
INTERROGATIVE ALREADY
(ya)
AUX.VERB HAVE/HAS + SUBJECT +
VERB PAST PARTICIPLE + We use already in affirmative sentences to say
COMPLEMENT? that something happened before now.
I've already drunk three coffees this
morning.
. Has it rained all day? I've already done it.
Have you eaten Thai food before? Have you already written to John?
Have I explained it well? Has she finished her homework already?
USE OF “FOR and SINCE” JUST
(acabo,de)
FOR: (Por, durante) Periodo de
tiempo “for two months, for five days, for
hours, for a week.”
We use just in affirmative sentences to say that
something has happened very recently
Amy has just finished her homework
I have just watched a horror movie.
RECENTLY
(recientemente)
SINCE: (Desde). Momento
concreto / Inicio de acción. “since last year,
since 1945” I have been very busy recently
Recently I have felt really tired
NEVER
(nunca)
I have never visited Berlin
I have never been to Italy.
USE OF THE YET
ADVERBS (aun,todavia,ya)
38 CENTRO PREUNIVERSITARIO Modalidad virtual Oficina de Admisión
Oficina de Admisión Modalidad virtual CENTRO PREUNIVERSITARIO
2 A (How many times/Jill/move/house)
We use yet in questions to ask about something that __________________________?
we expect to happen. We use (not…) yet in negative B Five times!
3 A (ever/ sing/ a solo)
sentences to say that something we expected to
__________________________?
happened hasn’t happened. B Once at primary school, when I was five.
4 A (be/ cold/ recently)
__________________________?
Have you met Judy yet? B No it hasn’t. The weather’s been lovely.
I haven't visited the Tate Gallery yet III. Put the adverbs in the correct place in the
Has he arrived yet? sentences or questions. Write in yourexercise
They haven't eaten yet book.
1 Have you had dinner? (yet)
Have you had dinner yet?
EVER 2 This letter has arrived for you. (just)
(alguna,vez) ____________________________
3 I’ve seen this film. (already)
_____________________________
4 We haven’t met the new boss. (yet)
_____________________________
5 Mary’s told me she’s getting married! (just)
Have you ever been to England? _____________________________
Has she ever met the Prime Minister?
IV Read the text:
LATELY
(ultimanente)
Who are they? What have they
done?
What has happened?
Generalmente se ubican al final de la oración o Roger and Melinda have owned their
sailboat for 10 years. During that
inicio. Se usan en oraciones afirmativas, negativas e
time, they have sailed together many
interrogativas. times. They have sailed to lots of
places.
They have sailed on the Pacific
I have been very busy lately Ocean. They have also sailed on the
Tommy has played a lot of videogames Atlantic Ocean. They have even
lately. sailed around the Gulf of Mexico
twice. However, they have never
I. Complete the second sentence so that it has a sailed on the Arctic Ocean or Indian
similar meaning to the first sentence. Use the Ocean.
Present perfect of the verb in brackets. In the last year, Roger and Melinda
have sailed around the Hawaiian
1 I can’t find my purse. (lose) Islands and across the Hudson Bay.
I ’ve lost my purse. Roger and Melinda love to travel in
2 Gerry can’t remember the time of the interview. their sailboat!
(forget)
Gerry ________________________
3 Amy is on her way to school. (go)
Amy________________________ 1.Rewrite the following sentences as positive or
4 I don’t know that man. (never/meet) negative sentences, yes/no questions, WH-
I ____________________________ questions (using the underlined word or phrase)
5 There’s something wrong with my dad’s leg. and tag questions.
(break) Examples for the sentence
My dad ______________________
“Nick has broken the glass.”
II. Write the questions for the answers usingthe Negative: Nick has not broken the glass.
words in brackets. Yes/No Question: Has Nick broken the glass?
1. A (ever/ see/ a snake)
WH-Question: Who has broken the glass?
Have you ever seen a snake?
B No I haven’t – only on TV. Tag Question: Nick has broken the glass, hasn't he?
CENTRO PREUNIVERSITARIO Modalidad virtual Oficina de Admisión 39
a. Roger and Melinda have owned their sailboat PASSIVE VOICE
for 10 years. (PRESENT SIMPLE, PRESENT
PROGRESSIVE, PAST SIMPLE, PAST
PROGRESSIVE, FUTURE, PRESENT
PERFECT.)
NEGATIVE:
___________________________________
___________________________________
Yes/ No Question:
Reading
__________________________________
__________________________________
WH-QUESTION:
This is a can.
Over two billion of them are thrown
__________________________________
away every year in Britain alone. But
__________________________________
these cans are destroying the tropical
forests. How?
Tag Question: The cans are made from aluminium.
__________________________________ Aluminium is extracted from bauxite.
__________________________________ Bauxite isn´t found deep in the ground
like other metals, but in the soil. Most
b) They have sailed on the Pacific Ocean. bauxite can be removed large areas of
forest have to be cut down. Then a
NEGATIVE: power station have to be built to
provide the electricity so that the
___________________________________ aluminium can be extracted from the
___________________________________ bauxite. Then roads are needed to
transport that aluminium. So some
Yes/No Question: trees must be destroyed.
__________________________________ However, the forest needn´t be
__________________________________ destroyed. Aluminium can be recycled
easily and cheaply. But at the moment
WH-QUESTION: most cans are buried in the ground
again. This waste should be stopped.
__________________________________ In Sweden and some states in the
__________________________________ USA, 95% of cans are recycled. Cans
are taken back to supermarkets and
Tag Question: are exchanged for money.
This should be done everywhere. The
__________________________________
tropical forest mustn´t be destroyed
__________________________________ just for drink cans.
La voz pasiva se utiliza para mostrar interés por
la persona o cosa que es objeto de una acción,
en lugar de la persona o cosa que realiza dicha
acción.
Passive Voice is used when the focus is on
the action. It is not importan to know who or
what is performing the action.
Sometimes a statement in passive is more
polite than active voice.
40 CENTRO PREUNIVERSITARIO Modalidad virtual Oficina de Admisión
Oficina de Admisión Modalidad virtual CENTRO PREUNIVERSITARIO
ACTIVE PASSIVE
I write a letter A letter is written
A letter is being
I am writing a letter
A passive voice consist of: written
I wrote a letter A letter was written
The subject.
I was writing a A letter was being
The verb BE in the correct tense. letter written
The past participle of the verb needed. I have written a A letter has been
Sometimes the agent and / or other letter written
complements. A letter had been
I had written a letter
written
A letter will be
ACTIVE VOICE I will write a letter
written
I am going to write A letter is going to
a letter be written
A letter must be
I must write a letter
written
I should have A letter should have
written a letter been written
SUBJECT + VERB “BE” + PAST PARTICPLE.
PASSIVE VOICE
Our house was designed by a famous
TENSE PASSIVE architect.
PRESENT Our car was stolen last night.
AM, IS, ARE + PARTICIPLE This tree was planted by my grandfather.
SIMPLE
PRESENT AM, IS, ARE + BEING + This book was written by Agatha Christie.
PROGRESSIVE PARTICIPLE The omelette was made with eggs, cheese
and peppers
PRESENT HAVE / HAS BEEN +
PERFECT PARTICIPLE
PAST
WAS, WERE + PARTICIPLE
SIMPLE
PAST WAS, WERE + BEING +
PROGRESSIVE PARTICIPLE Rewrite these sentences in the passive
PAST voice.
HAD BEEN + PARTICIPLE
PERFECT
a. Someone built this house 200 years ago.
FUTURE __________________________________________
WILL BE + PARTICIPLE
WILL b. A thief stole my purse.
FUTURE BE AM, IS, ARE GOING TO BE + __________________________________________
GOING TO PARTICIPLE c. The police will arrest the robbers.
__________________________________________
MUST, SHOULD, … + BE +
MODAL d. They produce cars in this factory.
PARTICIPLE __________________________________________
MODAL MUST / SHOULD, … + HAVE e. They serve breakfast at eight o’clock every day.
PERFECT BEEN + PARTICIPLE __________________________________________
f. People throw away tones of rubbish every day.
__________________________________________
g. They make coffee in Brazil.
__________________________________________
CENTRO PREUNIVERSITARIO Modalidad virtual Oficina de Admisión 41
You might also like
- Recapitulare Verbul To BE (A Fi)Document1 pageRecapitulare Verbul To BE (A Fi)Chitic FlorentinaNo ratings yet
- Summary IIIDocument2 pagesSummary IIIcristiane olivieraNo ratings yet
- Week 2 Nationalaties - Verb Be StudentsDocument27 pagesWeek 2 Nationalaties - Verb Be StudentsMARIA FERNANDA ÑATO CHAMORRONo ratings yet
- Verbo To Be InglésDocument9 pagesVerbo To Be Ingléslady cary quispeNo ratings yet
- Ingl ES: Apuntes de Un Primer Curso deDocument71 pagesIngl ES: Apuntes de Un Primer Curso deLeonidas Valencia100% (1)
- Lengua Extranjera: Comunidad Y SociedadDocument20 pagesLengua Extranjera: Comunidad Y SociedadEDITH.MARISA6932No ratings yet
- EnglishDocument4 pagesEnglishiagosoaresfluxNo ratings yet
- Week 2 Nationalaties - Verb Be StudentsDocument27 pagesWeek 2 Nationalaties - Verb Be StudentsMARIA FERNANDA ÑATO CHAMORRONo ratings yet
- English Is EasyDocument2 pagesEnglish Is EasyNafirKeyh100% (1)
- Pres SimpleDocument3 pagesPres SimpleHristina DimitrovaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3.: Positive NegativeDocument1 pageLesson 3.: Positive NegativeBudi LaksanaNo ratings yet
- To Be PDFDocument2 pagesTo Be PDFMihaela VerboncuNo ratings yet
- Texto de Aprendizaje: Segundo y Tercer Trimestre 2022Document22 pagesTexto de Aprendizaje: Segundo y Tercer Trimestre 2022Duam AibellNo ratings yet
- AFIRMATIVADocument6 pagesAFIRMATIVAemmNo ratings yet
- Aa Ee Ii Oo Uu Yy: BB CC DD FF GG HH JJ KK LL MM NN PP QQ RR Ss TT VV WW XX ZZDocument2 pagesAa Ee Ii Oo Uu Yy: BB CC DD FF GG HH JJ KK LL MM NN PP QQ RR Ss TT VV WW XX ZZaygulNo ratings yet
- My Your His Her Its Our Your Their: He She It He She It He She ItDocument1 pageMy Your His Her Its Our Your Their: He She It He She It He She ItAriana Ioana RusNo ratings yet
- My Your His Her Its Our Your Their: He She It He She It He She ItDocument1 pageMy Your His Her Its Our Your Their: He She It He She It He She ItAriana Ioana RusNo ratings yet
- Guia Verbo Tu BeDocument5 pagesGuia Verbo Tu Befrancisco cabreraNo ratings yet
- Verbo To Be (Ser/ Estar) : EjemplosDocument5 pagesVerbo To Be (Ser/ Estar) : Ejemplosfrancisco cabreraNo ratings yet
- Simple Present Continous Kelas 6 SDDocument9 pagesSimple Present Continous Kelas 6 SDSumar SonoNo ratings yet
- Verb Be-Verb To BeDocument4 pagesVerb Be-Verb To BeKamil HenriquezNo ratings yet
- Verb To Be Exers ALumno Ivan¡Freddy Garcia GarecaDocument2 pagesVerb To Be Exers ALumno Ivan¡Freddy Garcia GarecaivanNo ratings yet
- Inglês Módulo 04 Cbmerj: Verb To Be (Am/is/are)Document2 pagesInglês Módulo 04 Cbmerj: Verb To Be (Am/is/are)Vitor GreyNo ratings yet
- Present Continuous (Notes)Document1 pagePresent Continuous (Notes)Gyori AnnaNo ratings yet
- To BE-present SimpleDocument1 pageTo BE-present SimpleIoana PopescuNo ratings yet
- Material de Apoyo Preparatoria Abierta M PDFDocument29 pagesMaterial de Apoyo Preparatoria Abierta M PDFmauriciola88No ratings yet
- To Be Verb 2Document70 pagesTo Be Verb 2Chisco80No ratings yet
- Lesson 1Document13 pagesLesson 1Laura Melissa Guzman100% (1)
- ELPR 100 Grammar Revision PDFDocument21 pagesELPR 100 Grammar Revision PDFopportunityroseNo ratings yet
- The Verb To Be': Hello, Ben. Hi! Pam and PeterDocument8 pagesThe Verb To Be': Hello, Ben. Hi! Pam and PeterAndreea BalanNo ratings yet
- English - Present SimpleDocument1 pageEnglish - Present Simplerembodi21No ratings yet
- The verb "to be" Το ρήμα «είμαι» ΚατάφασηDocument2 pagesThe verb "to be" Το ρήμα «είμαι» ΚατάφασηMaria PinakouliaNo ratings yet
- 07 La-Conjugaison-De-Be-Et-HaveDocument3 pages07 La-Conjugaison-De-Be-Et-HaveYves DoumingouNo ratings yet
- Unit 1: 1.1 Some Basic Elements of The Sentence. Personal Pronouns Possessive AdjectivesDocument7 pagesUnit 1: 1.1 Some Basic Elements of The Sentence. Personal Pronouns Possessive Adjectivesmaxiiit0No ratings yet
- Subject / Sujeto Object / Objeto Possessive Adjective / Adjetivo Posesivo ( )Document7 pagesSubject / Sujeto Object / Objeto Possessive Adjective / Adjetivo Posesivo ( )PilarNo ratings yet
- Instituto de Educación Superior Tecnológico Público "Cañete" Unidad Didáctica: Comunicación Empresarial StudentDocument4 pagesInstituto de Educación Superior Tecnológico Público "Cañete" Unidad Didáctica: Comunicación Empresarial StudentLuis Angel Vasquez ReyesNo ratings yet
- Ingles 1Document1 pageIngles 1Valdir VillalobosNo ratings yet
- To Be - AffirmativeDocument11 pagesTo Be - AffirmativeKevin LaymitoNo ratings yet
- Exercises 21 Week 11 English IiiDocument1 pageExercises 21 Week 11 English IiiChristian TrujilloNo ratings yet
- Level A1Document8 pagesLevel A1Jorge GarcíaNo ratings yet
- كورس صيفى معدلDocument33 pagesكورس صيفى معدلSabreen AbdoNo ratings yet
- Pronouns UsageDocument35 pagesPronouns UsageMistyNo ratings yet
- Verb To Be / Verbo Ser O Estar: Affirmative Spanish FullDocument8 pagesVerb To Be / Verbo Ser O Estar: Affirmative Spanish FullDaniel BlascoNo ratings yet
- Modulo de Inglés 2 BeginnerDocument20 pagesModulo de Inglés 2 BeginnerNancy Soraya Ludeña RamírezNo ratings yet
- Personal Pronouns and Verb To BeDocument6 pagesPersonal Pronouns and Verb To BeMaría Jesús Valerio BeltránNo ratings yet
- TO BE - Cls 4-1Document5 pagesTO BE - Cls 4-1mihaela amaricaiNo ratings yet
- Basic Greetings: First PartDocument3 pagesBasic Greetings: First Partvaleria100% (1)
- Demonstrative Pronouns Primary SchoolDocument3 pagesDemonstrative Pronouns Primary SchoolsaidatulnorNo ratings yet
- Signal Words: Signal Words: Signal Words:: Past SimpleDocument1 pageSignal Words: Signal Words: Signal Words:: Past SimpleValdir VillalobosNo ratings yet
- To Be (Past, Present, Future)Document1 pageTo Be (Past, Present, Future)Eduard LisogorNo ratings yet
- Possessive PronounsDocument1 pagePossessive PronounsAbbie WanyiiNo ratings yet
- To Be Acordeon 2 PDFDocument1 pageTo Be Acordeon 2 PDFAngel TapiaNo ratings yet
- Grammar For 1º-2º EsoDocument10 pagesGrammar For 1º-2º Esogaby38No ratings yet
- Apostila Ingles 7Document5 pagesApostila Ingles 7KEISSY SILVANo ratings yet
- G Ing 01 Sem2 22Document4 pagesG Ing 01 Sem2 22Lennin Brayan Diaz HerreraNo ratings yet
- 00 - To BeDocument2 pages00 - To Belagobelisa5771No ratings yet
- Verb To Be MineDocument1 pageVerb To Be MinekelitantunesNo ratings yet
- Grammar Practice - Verb To Be: Subject PronounsDocument2 pagesGrammar Practice - Verb To Be: Subject PronounsAndrea CarvalhoNo ratings yet
- Final Review 7th Grade May 2018 AnswersDocument4 pagesFinal Review 7th Grade May 2018 Answersapi-239697108No ratings yet
- Patterns of Devt in WritingDocument32 pagesPatterns of Devt in WritingCruzille Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Language Cert C1 - ListeningDocument5 pagesLanguage Cert C1 - ListeningZoltán FarkasNo ratings yet
- Offering Help and ServiceDocument9 pagesOffering Help and ServicePratiwi BudiartiNo ratings yet
- Unit 1: CommunicationDocument2 pagesUnit 1: CommunicationJorgen KasmollariNo ratings yet
- Speld Sa Set 6 A Bet-DsDocument20 pagesSpeld Sa Set 6 A Bet-DsCorina SpNo ratings yet
- English: Recognizing Adverbs of MannerDocument13 pagesEnglish: Recognizing Adverbs of MannerJane Bunuan SaludaresNo ratings yet
- Structuralism SummaryDocument3 pagesStructuralism SummaryumamaNo ratings yet
- Clinical and Neuroimaging Characteristics of Primary Progressive AphasiaDocument17 pagesClinical and Neuroimaging Characteristics of Primary Progressive Aphasiamariafernanda portoNo ratings yet
- Article Translation Group 8Document10 pagesArticle Translation Group 8Muh arkan syafNo ratings yet
- New Market Leader Pre-Intermediate U4 Great IdeasDocument4 pagesNew Market Leader Pre-Intermediate U4 Great IdeasjonsnowNo ratings yet
- Authors PurposeDocument11 pagesAuthors PurposeKebeen blind as a batNo ratings yet
- Conjugation of Japanese Verb Lesson 1-25 of MNN 1Document306 pagesConjugation of Japanese Verb Lesson 1-25 of MNN 1Esohr100% (2)
- Local Media214770771995948410Document16 pagesLocal Media214770771995948410Mykhaela Louize GumbanNo ratings yet
- Active Voice Vs Passive Voice - RyanDocument4 pagesActive Voice Vs Passive Voice - RyanJor VBNo ratings yet
- Ene Oana Maria - Gr.915 - Essay Why Am I A Good ListenerDocument1 pageEne Oana Maria - Gr.915 - Essay Why Am I A Good ListenerOana Maria EneNo ratings yet
- Welcome To Online Learning With: Mrs ShahidDocument24 pagesWelcome To Online Learning With: Mrs ShahidsNo ratings yet
- AdvEngInUse Test U2Document14 pagesAdvEngInUse Test U2enkarniNo ratings yet
- Mixed Verb Tenses 12904Document2 pagesMixed Verb Tenses 129041319O27 - Tannya Erika MayastetaNo ratings yet
- Teaching AdultsDocument63 pagesTeaching AdultsAnNgôNo ratings yet
- 5 Nov 2020 Regular and Irregular Verbs: There Are Mainly Three Types of Irregular VerbsDocument20 pages5 Nov 2020 Regular and Irregular Verbs: There Are Mainly Three Types of Irregular Verbskaziba stephenNo ratings yet
- Patria Sable Corpus College: Student'S Speech Acts in Facebook StatusDocument46 pagesPatria Sable Corpus College: Student'S Speech Acts in Facebook StatusJee En BeeNo ratings yet
- Worksheets - INB PagesDocument47 pagesWorksheets - INB PagesYadira GuillenNo ratings yet
- Arabic Language - Seasons, Vocabulary & Its Vocabulary Construction of WordsDocument5 pagesArabic Language - Seasons, Vocabulary & Its Vocabulary Construction of WordsBianca Grace TorinoNo ratings yet
- Mixed Tenses - 7th GradeDocument1 pageMixed Tenses - 7th GradeiulianaNo ratings yet
- Metonymy and Word-Formation - Cambridge Scholars Publishing (2017)Document260 pagesMetonymy and Word-Formation - Cambridge Scholars Publishing (2017)Luka Smiljanic100% (1)
- E-Syllabus - Intensive French - Oral SkillsDocument7 pagesE-Syllabus - Intensive French - Oral Skillsghada.shushariNo ratings yet
- Present Perfect WorksheetDocument3 pagesPresent Perfect WorksheetFrancisco LuceroNo ratings yet
- 52 (Sanskrit)Document16 pages52 (Sanskrit)deeptir79No ratings yet
- English: Quarter 3 - Module 2: HomographsDocument19 pagesEnglish: Quarter 3 - Module 2: HomographsVenus Marie Real-CatubayNo ratings yet
- The Essay: Thesis Statements IntroductionsDocument9 pagesThe Essay: Thesis Statements IntroductionsŞevval TemizNo ratings yet