Professional Documents
Culture Documents
L1 - Intro To WW Collection
Uploaded by
Jamie RapajonOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
L1 - Intro To WW Collection
Uploaded by
Jamie RapajonCopyright:
Available Formats
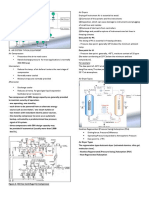
INTRO TO WW COLLECTION 1) Pump base drain
Drainage system – collects of wastewater from source and 2) Sample point drain
conveys it to treatment facilities 3) Equipment maintenance drain
TYPES: 4) Lube oil drains
1. Open sewer system – offsite scope, Chemical Sewer
drainage network open to the atmosphere 1) Laboratory sink drain
2. Close sewer system – process scope, fully
contained drains where toxic and DRAINAGE SYSTEM:
hazardous fluid from equipment are
drained for recovery or safe disposal 1) Non contaminated – open ditches to (retention
OBJECTIVES OF OPEN SEWER: pond/basin) to discharge to environment
1. To avoid flooding 2) Accidentally contaminated – catch basin in curb
2. To collect, convey and segregate effluent stream area to underground pipes to overflow diversion
3. To ensure that discharge meet environmental device to collection pits
requirements 3) Continuously contaminated – open funnel to
underground pipe to collection pit
COMMON DRAINAGE FACILITIES: 4) Laboratory sink drains- drains to pipe to
1. Open channel/ ditches – transfer water to atmospheric tank with internal coating
receiving water body or facility 5) Sanitary sewer – underground pipe to collection
2. Catch basin- a small reservoir for collecting pits
surface run-off 6) Cryogenic spills - ???
3. Open funnel- used in collecting small amount of
drains
4. Manhole- allows inspection and cleaning
especially at sewer line interconnection
5. Underground pipes- used to transport
sewerage
6. Pit/ basin/ pond – a underground concrete
structure used to retain liquid
EFFLUENT SOURCE AND CLASSIFICATION:
1. Non-Contaminated Sewer
2. Accidentally-Contaminated Sewer
3. Continuously-Contaminated Sewer
4. Chemical sewer
5. Sanitary sewer – wastewater from toilet, sink and
kitchen
6. Cryogenic spill – spill from cryogenic handling
equipment
Non-contaminated sewer sources:
1. Surface run-off from road, building and non-
process area
2. Non-contaminated surface run-off from storage
tank bunked area
3. Cooling water or boiler blowdown
4. Demineralized unit effluent
Accidentally-Contaminated Sewer
1. Oil/contaminated water due to accidental leak
2. Surface run-off that is potentially contaminated
Continuously-Contaminated Sewer
1. Water draw off from oil storage tank
2. Surface run off from maintenance workshop area
3. Process water
4. Oily drip/drains
You might also like
- Design of Septic Tank: Engineering Utilities 2Document23 pagesDesign of Septic Tank: Engineering Utilities 2Jovy AndoNo ratings yet
- Basic Principles of Sanitary DesignDocument16 pagesBasic Principles of Sanitary DesignDeniell Kahlil Kyro Gabon100% (2)
- Systematic Methods of Water Quality Parameters Analysis: Analytical MethodsFrom EverandSystematic Methods of Water Quality Parameters Analysis: Analytical MethodsNo ratings yet
- 6.sewage and Sewerage System PDFDocument19 pages6.sewage and Sewerage System PDFIgnacio Jr. PaguyoNo ratings yet
- Sedimentation CalculationDocument10 pagesSedimentation CalculationAmit Christian100% (1)
- Salient Features of Republic Act No 9003Document54 pagesSalient Features of Republic Act No 9003Rhuanne SakuraNo ratings yet
- Design of STPDocument21 pagesDesign of STPMinTzHoNo ratings yet
- Excreta DisposalDocument20 pagesExcreta DisposalRahul Netragaonkar75% (4)
- Master Plumber Reviewer: Wastewater TreatmentDocument55 pagesMaster Plumber Reviewer: Wastewater Treatmenthermano balbonNo ratings yet
- Letter To DENR 1Document2 pagesLetter To DENR 1Emily Hohenthaner RadechNo ratings yet
- Sludge in COS TankDocument28 pagesSludge in COS TankJose BijoyNo ratings yet
- 7-Trickling Filter F11Document31 pages7-Trickling Filter F11Jon Bisu Debnath100% (1)
- Septic TankDocument55 pagesSeptic TankAslam Laghari100% (1)
- Anna University Report FormatDocument25 pagesAnna University Report FormatJaya Seelan100% (1)
- Inclined Plate ClarifierDocument2 pagesInclined Plate ClarifierKelvin SiewNo ratings yet
- 2.0 Sewerage NotesDocument11 pages2.0 Sewerage Notesdhevashini narayananNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of Septic Tank Systems in TheDocument57 pagesEvaluation of Septic Tank Systems in TheNesru HamidNo ratings yet
- 0.12siph + 0.16siss + 0.15sian + 0.16sicod + 0.19sibod + 0.22sido WqiDocument34 pages0.12siph + 0.16siss + 0.15sian + 0.16sicod + 0.19sibod + 0.22sido WqiMudin DinNo ratings yet
- Qelia Canal Earth Works Method Statement - Rev 1Document40 pagesQelia Canal Earth Works Method Statement - Rev 1Mohammad Bader Al-Dein67% (6)
- Sewage:: A. Sanitary Sewage B. Industrial Sewage C. Combined SewageDocument19 pagesSewage:: A. Sanitary Sewage B. Industrial Sewage C. Combined SewageCarol TumanengNo ratings yet
- WASTE DISPOSAL TREATMENT and RECYCLINGDocument4 pagesWASTE DISPOSAL TREATMENT and RECYCLINGKimo KenoNo ratings yet
- B. Wastewater TreatmentDocument55 pagesB. Wastewater Treatmentelynah mistiola100% (1)
- Lecture 2. On-Site Wastewater Disposal TechnologiesDocument39 pagesLecture 2. On-Site Wastewater Disposal Technologiesabenezer tesfaye kibretNo ratings yet
- BNR Process BendigoDocument6 pagesBNR Process Bendigobansa79No ratings yet
- Waste Treatment and Disposal For Individual Household and Small Communities-2019Document30 pagesWaste Treatment and Disposal For Individual Household and Small Communities-2019Rotich Vincent100% (1)
- Wastewater and Solid Waste Management NoteDocument403 pagesWastewater and Solid Waste Management NoteAbebawNo ratings yet
- PLUMBING CODE (Summary) : Engr. Jay Naje Monreal, Ree, Rme, RMP, EctDocument18 pagesPLUMBING CODE (Summary) : Engr. Jay Naje Monreal, Ree, Rme, RMP, EctHashirama tobirama100% (2)
- Wastewater CollectionDocument11 pagesWastewater CollectionkaiNo ratings yet
- Sewerage and Drainage EngineeringDocument3 pagesSewerage and Drainage EngineeringRenz PagcaliwaganNo ratings yet
- 39 Reviewer - 3,4,5,8Document7 pages39 Reviewer - 3,4,5,8Gem Melanie SiegaNo ratings yet
- Unit I Sewage Collection Sewerage System Quantity Estimation Hydraulic Design Sanitary EngineeringDocument82 pagesUnit I Sewage Collection Sewerage System Quantity Estimation Hydraulic Design Sanitary EngineeringAditya RajguruNo ratings yet
- Sewage and SanitationDocument27 pagesSewage and SanitationVaibhav KhatingNo ratings yet
- Chapter Four1Document79 pagesChapter Four1Aman KifleNo ratings yet
- COMPLETE NOTES Domestic SewageDocument75 pagesCOMPLETE NOTES Domestic SewageRukaiya ShaikhNo ratings yet
- MODULE 1. Basic Principles of Sanitary DesignDocument5 pagesMODULE 1. Basic Principles of Sanitary DesignKervin SangalangNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Design of Intercepting SewersDocument24 pagesChapter 4 Design of Intercepting SewersAce ThunderNo ratings yet
- Services-I Notes Unit 2 ADocument65 pagesServices-I Notes Unit 2 A2GI20AT021 Devki HanamshetNo ratings yet
- Environmental Eng. (Sanitaey Eng.)Document12 pagesEnvironmental Eng. (Sanitaey Eng.)عبدالله الحسنيNo ratings yet
- Lecture 18Document47 pagesLecture 18DivyanshNo ratings yet
- Total Hospital Waste Management Collection Treatment & DisposalDocument5 pagesTotal Hospital Waste Management Collection Treatment & DisposalSandeepan ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- Sanitation, Plumbing Design & Installation: B. Wastewater Treatment and Disposal For Building and PremisesDocument47 pagesSanitation, Plumbing Design & Installation: B. Wastewater Treatment and Disposal For Building and Premisesdizonabigailmaereyes100% (1)
- The Plumbing System ReviewerDocument3 pagesThe Plumbing System Reviewerya gurl shainnaNo ratings yet
- Maintainance of SewersDocument6 pagesMaintainance of Sewersgsenv20r09No ratings yet
- WHO WEDC Technical NotesDocument64 pagesWHO WEDC Technical NotesMichaelNo ratings yet
- Water PPT - Copy-1Document43 pagesWater PPT - Copy-1SAQIBPASHANo ratings yet
- 2022 EU 2 Module 2 Designing Building Water Systems Part 3Document60 pages2022 EU 2 Module 2 Designing Building Water Systems Part 3BryanHarold BrooNo ratings yet
- Sewage Disposal SystemDocument5 pagesSewage Disposal SystemSharmaine FalcisNo ratings yet
- Excreta and Sewage DisposalDocument51 pagesExcreta and Sewage DisposalMel Izhra N. MargateNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Sewage Disposal SystemDocument4 pagesChapter 5 Sewage Disposal SystemFernando PascualNo ratings yet
- Trickling Filter (TF)Document30 pagesTrickling Filter (TF)M FahrizalNo ratings yet
- Building Design 2 Drainage NotesDocument2 pagesBuilding Design 2 Drainage NotesLemis Sean VerasNo ratings yet
- Environmental Engineering - 2Document60 pagesEnvironmental Engineering - 2Ubai DullahNo ratings yet
- CONTENTSDocument60 pagesCONTENTSsalmanNo ratings yet
- Unit 4Document92 pagesUnit 4Deepak Narayan PaithankarNo ratings yet
- Sewage - For MidDocument110 pagesSewage - For MidAbuye HDNo ratings yet
- Unit II Sewer Appurtenances Sewer Construction Pumping House Drainage Rainwater Harvesting Sanitary EngineeringDocument58 pagesUnit II Sewer Appurtenances Sewer Construction Pumping House Drainage Rainwater Harvesting Sanitary EngineeringAditya RajguruNo ratings yet
- Group1: Bisda, Mariel Maagtuto, Andrea B. Montilla, Alyssa Mae Oliveria, Rica Leisa M. Ygar, Don KiddieDocument27 pagesGroup1: Bisda, Mariel Maagtuto, Andrea B. Montilla, Alyssa Mae Oliveria, Rica Leisa M. Ygar, Don KiddieAndrea MagtutoNo ratings yet
- Hydrology Final PPTX - GRP.5 PDFDocument55 pagesHydrology Final PPTX - GRP.5 PDFAlvin DeliroNo ratings yet
- Presentation100completed 160315213306Document123 pagesPresentation100completed 160315213306msea100% (1)
- Handout 6 Classification of Sanitray SewerDocument4 pagesHandout 6 Classification of Sanitray SewerMark DaferNo ratings yet
- MODULE 6. Sewage Disposal SystemDocument7 pagesMODULE 6. Sewage Disposal SystemMatt ValenciaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3.1 - CoagulationDocument51 pagesChapter 3.1 - CoagulationHanif NifNo ratings yet
- Privies: Private Sewage Disposal SystemsDocument34 pagesPrivies: Private Sewage Disposal SystemsShaenaBalaodelRosarioNo ratings yet
- Module - 1 IntroductionDocument33 pagesModule - 1 IntroductionIffat SiddiqueNo ratings yet
- Bodog Marinela 2Document5 pagesBodog Marinela 2Sann MyintmgNo ratings yet
- Construction Maintenance of SewersDocument79 pagesConstruction Maintenance of SewersNivedita Godara C-920No ratings yet
- Septic Tank Overview and DesignDocument15 pagesSeptic Tank Overview and DesignJordan Benson PauloNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1:introduction To Sanitary EngineeringDocument29 pagesChapter 1:introduction To Sanitary EngineeringPratik GhimireNo ratings yet
- L1 UtilitiesDocument3 pagesL1 UtilitiesJamie RapajonNo ratings yet
- Basic Depressuring Why 1Document4 pagesBasic Depressuring Why 1Jamie RapajonNo ratings yet
- Blocked OutletDocument1 pageBlocked OutletJamie RapajonNo ratings yet
- Flammable Combustible Liquids - Hazards OSH AnswersDocument5 pagesFlammable Combustible Liquids - Hazards OSH AnswersJamie RapajonNo ratings yet
- L1 - Pumps ReviewerDocument3 pagesL1 - Pumps ReviewerJamie RapajonNo ratings yet
- L1 - Reviewer in WW TreatmentDocument1 pageL1 - Reviewer in WW TreatmentJamie RapajonNo ratings yet
- Reviewer - Control Valves (Concepts - Sizing.Hydraulics)Document30 pagesReviewer - Control Valves (Concepts - Sizing.Hydraulics)Jamie RapajonNo ratings yet
- Unep - Malaysia - Winnie Lyn Suwandi PDFDocument2 pagesUnep - Malaysia - Winnie Lyn Suwandi PDFSirilus YekrianusNo ratings yet
- TS TRT Alt Med WST DispDocument18 pagesTS TRT Alt Med WST DispAl MamunNo ratings yet
- Environmental Impact Assessment Is TheDocument31 pagesEnvironmental Impact Assessment Is TheRamakrishna ReddyNo ratings yet
- Rocker ScientificDocument10 pagesRocker ScientificRody JHNo ratings yet
- Inson 2021Document9 pagesInson 2021Aljane Grantos SimNo ratings yet
- Water - Pollution in IndiaDocument17 pagesWater - Pollution in India398 -Sahifa SayedNo ratings yet
- Đề Thi Thử 02Document5 pagesĐề Thi Thử 029zmjzv5s2vNo ratings yet
- Bioenzyme BrochureDocument1 pageBioenzyme BrochureDayday AbleNo ratings yet
- Solid Waste Management Associated With The Development of 3R Initiatives: Case Study in Major Urban Areas of VietnamDocument9 pagesSolid Waste Management Associated With The Development of 3R Initiatives: Case Study in Major Urban Areas of VietnamMuhammad FahriNo ratings yet
- The Nutrient Cycle: Executive SummaryDocument5 pagesThe Nutrient Cycle: Executive SummaryBenson MwathiNo ratings yet
- MSDS PREMIUM MOTOR OIL API SJ SAE 40 Material Safety Certificate CitrolDocument5 pagesMSDS PREMIUM MOTOR OIL API SJ SAE 40 Material Safety Certificate Citroleliseujh100% (1)
- Automatic Tap Water ControlingDocument38 pagesAutomatic Tap Water ControlingAngel AngalinaNo ratings yet
- Experiment: Depth Filtration:: ObjectiveDocument6 pagesExperiment: Depth Filtration:: ObjectivemansoorNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document41 pagesChapter 4Encik ComotNo ratings yet
- EEESDocument21 pagesEEESHardik kapoorNo ratings yet
- Ec7 Sample PagesDocument8 pagesEc7 Sample PagesSudhin George MathewNo ratings yet
- Most Probable Number (MPN) Test: Principle, Procedure, ResultsDocument4 pagesMost Probable Number (MPN) Test: Principle, Procedure, ResultsHammad KingNo ratings yet
- BS en 16932-1-2018Document36 pagesBS en 16932-1-2018chootymalli9760No ratings yet
- Environmental Damage of MiningDocument3 pagesEnvironmental Damage of Miningnabilowers74No ratings yet
- City Ordinance 314 Solid Waste MGMTDocument8 pagesCity Ordinance 314 Solid Waste MGMTCharina MiclatNo ratings yet
- Aerodredge GreaceremovalDocument4 pagesAerodredge Greaceremovalvirat_daveNo ratings yet
- Eco-Friendly Vacations WordDocument3 pagesEco-Friendly Vacations WordJessica LiNo ratings yet