Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Mixtures of Solids With Liquids
Uploaded by
Pradeep JoshiOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Mixtures of Solids With Liquids
Uploaded by
Pradeep JoshiCopyright:
Available Formats
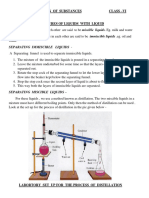
CHAPTER - SEPARATION OF SUBSTANCES CLASS – VI
MIXTURES OF SOLIDS WITH LIQUIDS – can be of two types –
a) Solids which dissolve in liquids
b) Solids which do not dissolve in liquids
SEPARATING SOLIDS THAT DISSOLVE IN LIQUIDS – It is done by two
methods – 1. EVAPORATION
2. CRYSTALLISATION
1.Evaporation – The process of changing liquid into its vapour form on heating is known as
Evaporation. This method is generally used to obtain common salt from sea water.
{ Refer activity 2 on pg – 56 and draw its diagram }
2. Crystallisation is a process which separates a pure solid in the form of its crystals from a
saturated solution.
STEPS FOR CRYSTALLISATION –
1. Prepare a saturated solution of the solid to be separated.
2. Put the saturated solution into a china dish and heat it on a burner.
3. Stir the solution occasionally with a glass rod.
4. Stop heating the solution when small crystals appear on the glass rod.
5. Allow the solution to cool without disturbing it.
6. After some time crystals of pure solid will appear in the china dish.
( Draw a well labelled diagram given on Pg – 57)
This method is used for purification of common salt obtained from sea. It is also used
to obtain crystals of alum and blue vitrol.
SEPARATING SOLIDS THAT DO NOT DISSOLVE IN LIQUIDS –
For this following methods are used –
a) Sedimentation and Decantation
b) Loading
c) Filtration
d) Centrifugation
SEDIMENTATION & DECANTATION –
The process by which heavier insoluble materials in a mixture settle on their own , when left
undisturbed for some time is known as Sedimentation.
The process of pouring clear water above the sediment , into another beaker using a glass rod
without disturbing the sediment is known as Decantation.
These methods are used in water treatment plants that supply drinking water to our homes.
It is also used in washing pulses and rice in our kitchens.
[ DRAW A WELL LABELLED DIAGRAM OF SEDIMENTATION & DECANTATION
from Pg No. 58 of the textbook.]
LOADING –
The process of speeding up sedimentation by adding suitable chemicals so that the light
suspended particles become heavier and settle down is known as loading.
Alum ( phitkari ) is used for this phenomenon.
{ DRAW THE DIAGRAM FROM PG – 59)
FILTRATION –
The process of separating insoluble material from a liquid using filter paper or a fine
porous material ( filter) is known as filtration.
The clean water collected after filtration is known as filtrate.
The solid impurities collected on the top of the filter paper or filter is called as residue.
{ Draw the diagram of filtration from Pg -60}
Filters ( other than filter paper )commonly used are Muslin cloth , cotton wool , charcoal and
fine sand. The choice of filter depends upon the size of particles to be removed.
This method is used to separate tea leaves from tea.
CENTRIFUGATION –
The method used to separate the fine particles suspended in a liquid by rotating the mixture
at high speed is known as Centrifugation. In this method the lighter particles stay at the top
whereas the heavier particles tend to settle at the bottom of the container.
It is done with a machine called as Centrifuge. Eg. Separating cream from milk is done by
centrifugation. Even at homes butter is churned out from cream using a mixer . Butter being
lighter floats at the top. The traditional long handed wooden churner is still used in some
households to separate butter from cream.
You might also like
- Chemistry at Home - A Collection of Experiments and Formulas for the Chemistry EnthusiastFrom EverandChemistry at Home - A Collection of Experiments and Formulas for the Chemistry EnthusiastNo ratings yet
- Separating Substances NotesDocument7 pagesSeparating Substances NotesMohan Reddy KothapetaNo ratings yet
- Class 6 SEPARATION OF SUBSTANCE L-5Document3 pagesClass 6 SEPARATION OF SUBSTANCE L-5Nirali MehtaNo ratings yet
- 9 Chemistry - Is Matter Around Us Pure - Notes & Video LinkDocument8 pages9 Chemistry - Is Matter Around Us Pure - Notes & Video LinkYash TripathiNo ratings yet
- CHE 414 Separation TechniquesDocument12 pagesCHE 414 Separation Techniquesbenjamin bosireNo ratings yet
- Study Material - Separation MethodsDocument7 pagesStudy Material - Separation MethodsSahil NarkhedeNo ratings yet
- Class 6 CH 5 SolvedDocument8 pagesClass 6 CH 5 SolvedsayogitaNo ratings yet
- 6thSci.L5 Separation of substances-TB EXERCISES N KEYWORDSDocument3 pages6thSci.L5 Separation of substances-TB EXERCISES N KEYWORDSʕ ꈍᴥꈍʔNo ratings yet
- 5 Separatopn of Substances: MixtureDocument7 pages5 Separatopn of Substances: MixtureCris CNo ratings yet
- Separation of Substances GR 6 2022-23Document3 pagesSeparation of Substances GR 6 2022-23Prabhu VelNo ratings yet
- 6 (D) Miscellaneous ProcessesDocument59 pages6 (D) Miscellaneous ProcessesYashfa YasinNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry Group 2 Report FinalDocument34 pagesGeneral Chemistry Group 2 Report FinalMara ClaireNo ratings yet
- Report On Sedimentation, Coagulation and Filtration: Name-Section - Semester - Roll NoDocument8 pagesReport On Sedimentation, Coagulation and Filtration: Name-Section - Semester - Roll NoArghyadip SarkarNo ratings yet
- Filtration and Crystallisation by Kudiwa and DhrishaDocument15 pagesFiltration and Crystallisation by Kudiwa and Dhrishadhrisha05No ratings yet
- ChemistryDocument17 pagesChemistryvootlamNo ratings yet
- Physicochemical Processes: Dr. Sana Hanif Assistant ProfessorDocument12 pagesPhysicochemical Processes: Dr. Sana Hanif Assistant ProfessorMohammad ZohaibNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 2 - Separating MixturesDocument7 pagesChemistry 2 - Separating MixturesNaseeb AliNo ratings yet
- 2022 - 3NA - Separation Technique - NotesDocument19 pages2022 - 3NA - Separation Technique - NotesNitin Yadav Praduman (Qss)No ratings yet
- Chemistry - Part 4Document10 pagesChemistry - Part 4BALA GANESHNo ratings yet
- 06 - Sugar Industry (B)Document35 pages06 - Sugar Industry (B)waleed chNo ratings yet
- Separation of Mixtures (Continuation of Notes)Document6 pagesSeparation of Mixtures (Continuation of Notes)mohammed mahdyNo ratings yet
- MSB Class 11 Chemistry-Ch3Document8 pagesMSB Class 11 Chemistry-Ch3zaiddparkar1No ratings yet
- Centrifugation, Desiccation and LevigationDocument16 pagesCentrifugation, Desiccation and Levigationengr587No ratings yet
- Matter & Materials - Term 2: Worksheet 4 - Methods of Physical SeparationDocument8 pagesMatter & Materials - Term 2: Worksheet 4 - Methods of Physical SeparationLyndelle MoyoNo ratings yet
- Separation of Substances: MixtureDocument5 pagesSeparation of Substances: MixtureShivam ZakhmiNo ratings yet
- 8TH Grade Separating MixturesDocument12 pages8TH Grade Separating MixturesKolade Fatai OpeyemiNo ratings yet
- Separating MixturesDocument1 pageSeparating MixturesAlvin Jan CampoNo ratings yet
- Separation Technique How It Separates Description Method Example of Mixture Example of Use in Industry or Daily LifeDocument3 pagesSeparation Technique How It Separates Description Method Example of Mixture Example of Use in Industry or Daily LifeErin TanNo ratings yet
- Advances in Separation Science: Unit 1Document57 pagesAdvances in Separation Science: Unit 1Bhavin SolankiNo ratings yet
- Miscellaneous ProcessesDocument103 pagesMiscellaneous ProcessesAhmed Imran75% (4)
- CrystallizationDocument17 pagesCrystallizationvspandey27No ratings yet
- Miscellaneous Physical Pharmacy ProcessesDocument18 pagesMiscellaneous Physical Pharmacy ProcessesDr. Mussadiq Latif80% (10)
- Methods of Separating Components of MixturesDocument27 pagesMethods of Separating Components of MixturesSrynnENo ratings yet
- Ways of Separating MixturesDocument5 pagesWays of Separating MixturesMay Anne AlmarioNo ratings yet
- The Chemical Earth: Chemistry Half Yearly Exam StudyDocument96 pagesThe Chemical Earth: Chemistry Half Yearly Exam StudykhoocumberNo ratings yet
- Determination of Structure of Organic CompoundsDocument15 pagesDetermination of Structure of Organic Compoundssiyanbolasurprise9No ratings yet
- HARAM SIDDIQUI - Exercise No. 1 - Demonstration Sessions For Various Purification Techniques Such As Filtration, Decantation, Crystallization, Distillation and Chromatography.Document7 pagesHARAM SIDDIQUI - Exercise No. 1 - Demonstration Sessions For Various Purification Techniques Such As Filtration, Decantation, Crystallization, Distillation and Chromatography.Arya SayedNo ratings yet
- Soluble and Insoluble Impurities in WaterDocument14 pagesSoluble and Insoluble Impurities in WaterShameer Majeed. ANo ratings yet
- E - Module of Grade-6. Separation of SubstancesDocument27 pagesE - Module of Grade-6. Separation of Substanceshree1202No ratings yet
- 1.3 Separating Mixtures - OdpDocument2 pages1.3 Separating Mixtures - OdpZaynab ShaikhNo ratings yet
- MSP Unit-1Document117 pagesMSP Unit-1Jeya BharathiNo ratings yet
- Ch07 Separation TechniquesDocument13 pagesCh07 Separation TechniquesFauzan AkbarNo ratings yet
- PURIFICATION of Organic Compounds: 2. SublimationDocument1 pagePURIFICATION of Organic Compounds: 2. SublimationchinnagandiNo ratings yet
- Separation of Liquids (Miscible & Immiscible)Document2 pagesSeparation of Liquids (Miscible & Immiscible)Pradeep JoshiNo ratings yet
- What Is CrystallizationDocument6 pagesWhat Is CrystallizationJhoanna BocalingNo ratings yet
- The Refining ProcessDocument2 pagesThe Refining ProcessbabeNo ratings yet
- Filtration and CrystallizationDocument12 pagesFiltration and CrystallizationDamani RobertsNo ratings yet
- Recrystallization TechniqueDocument3 pagesRecrystallization TechniqueJason BalthisNo ratings yet
- (W) .ch.6 STD 6 ScienceDocument8 pages(W) .ch.6 STD 6 ScienceSmit JayaniNo ratings yet
- Coagulation, Flocculation and ClarificationDocument18 pagesCoagulation, Flocculation and ClarificationMitaPermataSariNo ratings yet
- Vaal University of Technology: Faculty of Engineering and Technology Department of Metallurgical EngineeringDocument18 pagesVaal University of Technology: Faculty of Engineering and Technology Department of Metallurgical EngineeringjamesNo ratings yet
- Site VisitDocument13 pagesSite VisitrasanghafarNo ratings yet
- Different Processes in Separating and Purifying Substances and MixturesDocument3 pagesDifferent Processes in Separating and Purifying Substances and MixturesLarry MarNo ratings yet
- DHW - Lecture 3 - Gravimetric Analysis - 260916Document77 pagesDHW - Lecture 3 - Gravimetric Analysis - 260916Sadiq AlmubarakNo ratings yet
- Level: Class: Teacher: Lecture # 11 Middle VI Ms. Sobia Muzammil Week: 18Document25 pagesLevel: Class: Teacher: Lecture # 11 Middle VI Ms. Sobia Muzammil Week: 18Abdul SamadNo ratings yet
- Decatation MethodDocument20 pagesDecatation MethodTuongVNguyenNo ratings yet
- Year: I Semester: Ii Course Facilitator: Dr.V.Sathish KumarDocument16 pagesYear: I Semester: Ii Course Facilitator: Dr.V.Sathish Kumarsathish_prakash_1No ratings yet
- Separation of Substances Notes Grade 6Document5 pagesSeparation of Substances Notes Grade 6Sanaya SinghNo ratings yet
- Chemistry ProjectDocument15 pagesChemistry Projectarjunv_1458% (31)
- Trigo 2021Document6 pagesTrigo 2021Pradeep JoshiNo ratings yet
- Remedial Imp. Questions.Document16 pagesRemedial Imp. Questions.Pradeep JoshiNo ratings yet
- CH - 4 Separation of Mixture of Two SolidsDocument2 pagesCH - 4 Separation of Mixture of Two SolidsPradeep JoshiNo ratings yet
- Separation of Liquids (Miscible & Immiscible)Document2 pagesSeparation of Liquids (Miscible & Immiscible)Pradeep JoshiNo ratings yet
- DistillationDocument15 pagesDistillationSachi DesaiNo ratings yet
- Kromatografi Lapis Tipis-Densitometri Untuk Analisis Residu Pestisida Diazinon Dalam Sawi Hijau (Brassica Juncea L.)Document5 pagesKromatografi Lapis Tipis-Densitometri Untuk Analisis Residu Pestisida Diazinon Dalam Sawi Hijau (Brassica Juncea L.)Yocca AsmaraNo ratings yet
- 3 ChromatographyDocument26 pages3 ChromatographyKhadim Hussain KHNo ratings yet
- Extractive Distillation PDFDocument12 pagesExtractive Distillation PDFROHAN PATILNo ratings yet
- DistillatnDocument149 pagesDistillatnVinayak ThalangeNo ratings yet
- CH# 2 XI (Chem 11 Exam Task)Document3 pagesCH# 2 XI (Chem 11 Exam Task)Zeeshan Haider ChemistNo ratings yet
- Tugas 1 40040117060067 SyadilalutfimDocument6 pagesTugas 1 40040117060067 SyadilalutfimSyadila LutfiNo ratings yet
- Biotech Lab 8 Paper ChromatographyDocument3 pagesBiotech Lab 8 Paper ChromatographyClinton YmbongNo ratings yet
- 2022 Kromatografi (Teori-Handout 2)Document35 pages2022 Kromatografi (Teori-Handout 2)Nabila Putri SabilaNo ratings yet
- How To Convert Batch Into MCSGP KnauerDocument14 pagesHow To Convert Batch Into MCSGP KnauerWalad WirawanNo ratings yet
- Adapalene Gel - British PharmacopoeiaDocument4 pagesAdapalene Gel - British PharmacopoeiaCon Bò Sữa Thất TìnhNo ratings yet
- CatalogSotras 2015 PDFDocument354 pagesCatalogSotras 2015 PDFInfinity PneumaticNo ratings yet
- Distillation Column PipingDocument57 pagesDistillation Column PipingKaran Singh92% (13)
- Distillation Column Design ReportDocument27 pagesDistillation Column Design ReportUsama Akram100% (1)
- Packed Distillation Columns: 1. Determination of The Column HeightDocument7 pagesPacked Distillation Columns: 1. Determination of The Column Heightramsrivatsan1992No ratings yet
- CHE 306 Lab 5Document6 pagesCHE 306 Lab 5Freddy QuijanoNo ratings yet
- Purification Methods FlashcardsDocument35 pagesPurification Methods FlashcardsLejNo ratings yet
- CHE4613LAB7Document6 pagesCHE4613LAB7Huda AlkhouriNo ratings yet
- Fractional Distillation: Organic Lab - AemoodyDocument2 pagesFractional Distillation: Organic Lab - AemoodyJose BelisarNo ratings yet
- Chromatographic Separations PDFDocument90 pagesChromatographic Separations PDFAishah SamNo ratings yet
- Membrane Based BioseparationDocument24 pagesMembrane Based BioseparationFarance 1PrajNo ratings yet
- Binary Column Distillation Internal Stage by Stage BalanceDocument51 pagesBinary Column Distillation Internal Stage by Stage BalanceAbdul QuddusNo ratings yet
- Mixing Chamber - Flocculation - SedimentationDocument6 pagesMixing Chamber - Flocculation - SedimentationOlivia NorrNo ratings yet
- Distillation Column Hydrogen PeroxideDocument6 pagesDistillation Column Hydrogen PeroxideKatiane MesquitaNo ratings yet
- CHM 510Document6 pagesCHM 510aiqalNo ratings yet
- DWCDocument52 pagesDWCTeeranun NakyaiNo ratings yet
- Molecular DistillationDocument5 pagesMolecular DistillationJames KabugoNo ratings yet
- 2019-Mass TransferDocument74 pages2019-Mass TransferFareeha SaeedNo ratings yet
- Methods of Purification of Organic CompoundsDocument9 pagesMethods of Purification of Organic CompoundsTolani AyoNo ratings yet
- High Pressure Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) PDFDocument13 pagesHigh Pressure Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) PDFmitalNo ratings yet
- Taste: Surprising Stories and Science About Why Food Tastes GoodFrom EverandTaste: Surprising Stories and Science About Why Food Tastes GoodRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (20)
- AP® Chemistry Crash Course, For the 2020 Exam, Book + Online: Get a Higher Score in Less TimeFrom EverandAP® Chemistry Crash Course, For the 2020 Exam, Book + Online: Get a Higher Score in Less TimeRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- The Nature of Drugs Vol. 1: History, Pharmacology, and Social ImpactFrom EverandThe Nature of Drugs Vol. 1: History, Pharmacology, and Social ImpactRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- Periodic Tales: A Cultural History of the Elements, from Arsenic to ZincFrom EverandPeriodic Tales: A Cultural History of the Elements, from Arsenic to ZincRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (137)
- It's Elemental: The Hidden Chemistry in EverythingFrom EverandIt's Elemental: The Hidden Chemistry in EverythingRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (10)
- Is That a Fact?: Frauds, Quacks, and the Real Science of Everyday LifeFrom EverandIs That a Fact?: Frauds, Quacks, and the Real Science of Everyday LifeRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (4)
- Chemistry for Breakfast: The Amazing Science of Everyday LifeFrom EverandChemistry for Breakfast: The Amazing Science of Everyday LifeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (14)
- Chemistry for Breakfast: The Amazing Science of Everyday LifeFrom EverandChemistry for Breakfast: The Amazing Science of Everyday LifeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (90)
- Tribology: Friction and Wear of Engineering MaterialsFrom EverandTribology: Friction and Wear of Engineering MaterialsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- AP Chemistry Flashcards, Fourth Edition: Up-to-Date Review and PracticeFrom EverandAP Chemistry Flashcards, Fourth Edition: Up-to-Date Review and PracticeNo ratings yet
- Guidelines for Defining Process Safety Competency RequirementsFrom EverandGuidelines for Defining Process Safety Competency RequirementsRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- The Periodic Table: A Very Short IntroductionFrom EverandThe Periodic Table: A Very Short IntroductionRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Monkeys, Myths, and Molecules: Separating Fact from Fiction, and the Science of Everyday LifeFrom EverandMonkeys, Myths, and Molecules: Separating Fact from Fiction, and the Science of Everyday LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Handbook of Formulating Dermal Applications: A Definitive Practical GuideFrom EverandHandbook of Formulating Dermal Applications: A Definitive Practical GuideNo ratings yet
- The Disappearing Spoon: And Other True Tales of Madness, Love, and the History of the World from the Periodic Table of the ElementsFrom EverandThe Disappearing Spoon: And Other True Tales of Madness, Love, and the History of the World from the Periodic Table of the ElementsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (146)
- Formulating, Packaging, and Marketing of Natural Cosmetic ProductsFrom EverandFormulating, Packaging, and Marketing of Natural Cosmetic ProductsNo ratings yet
- Ingredients: A Visual Exploration of 75 Additives & 25 Food ProductsFrom EverandIngredients: A Visual Exploration of 75 Additives & 25 Food ProductsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Chemistry: a QuickStudy Laminated Reference GuideFrom EverandChemistry: a QuickStudy Laminated Reference GuideRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Phase Equilibria in Chemical EngineeringFrom EverandPhase Equilibria in Chemical EngineeringRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (11)
- Organic Chemistry for Schools: Advanced Level and Senior High SchoolFrom EverandOrganic Chemistry for Schools: Advanced Level and Senior High SchoolNo ratings yet